Unintended Effects of the Intended Herbicides on Transgenic Herbicide-Resistant Crops
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Glyphosate-Resistant Crops
2.1. Phytotoxicity
2.2. Mineral Nutrition
2.3. Secondary Metabolites
2.4. Crop Disease
2.5. Nodulation and Nitrogen Fixation
2.6. Effects on the Crop Through Effects on Insects
2.7. Hormesis
2.8. Glyphosate Accumulation in Harvested Food Products
3. Glufosinate-Resistant Crops
4. Dicamba-Resistant Crops
5. 2,4-D-Resistant Crops
6. HPPD Inhibitor-Resistant Crops
7. Summary
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| HR | herbicide-resistant |
| GR | glyphosate-resistant |
| HPPD | the enzyme hydroxyphenylpyruvate dioxygenase |
| GluR | glufosinate-resistant |
| AMPA | aminomethylphosphonic acid |
| GOX | the enzyme glyphosate oxidoreductase |
| EPSPS | the enzyme 5-enolpyruvylshikimate-3-phosphate synthase |
| MRL | maximum residue level |
| GS | glutamine synthetase |
| DR | dicamba-resistant |
| 2,4-DR | 2,4-D-resistant |
| HPPDR | HPPD herbicide-resistant |
References
- Duke, S.O.; Powles, S.B. Glyphosate: A once in a century herbicide. Pest Manag. Sci. 2008, 64, 319–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Padgette, S.R.; Taylor, N.B.; Nida, D.L.; Bailey, M.R.; MacDonald, J.; Holden, L.R.; Fuchs, R.L. The composition of glyphosate-tolerant soybean seeds is equivalent to that of conventional soybeans. J. Nutr. 1996, 126, 702–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taylor, M.; Bickel, A.; Mannion, R.; Bell, E.; Harrigan, G.C. Dicamba-resistant soybeans (Glycine max L.) MON 87708 and MON 87708 x MON 89788 are compositionally equivalent to conventional soybean. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2017, 65, 8037–8045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, N.B.; Fuchs, R.L.; MacDonald, J.; Shariff, A.R.; Padgette, S.R. Compositional analysis of glyphosate-tolerant soybeans treated with glyphosate. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1999, 47, 4469–4473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCann, M.C.; Liu, K.; Trujillo, W.A.; Dobert, R.C. Glyphosate-tolerant soybeans remain compositionally equivalent to conventional soybeans (Glycine max L.) during three years of field testing. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2005, 53, 5331–5335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCann, M.C.; Rogan, G.J.; Fitzpatrick, S.; Trujillo, W.A.; Sorbet, R.; Hartnell, G.F.; Riodan, S.G.; Nemeth, M.A. Glyphosate-tolerant alfalfa is compositionally equivalent to conventional alfalfa (Medicago sativa L.). J. Agric. Food Chem. 2006, 54, 7187–7192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duke, S.O.; Rimando, A.M.; Pace, P.F.; Reddy, K.N.; Smeda, R.J. Isoflavone, glyphosate, and aminomethylphosphonic acid levels in seeds of glyphosate-treated, glyphosate-resistant soybean. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2003, 51, 340–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bøhn, T.; Cuhra, M.; Traavik, T.; Sanden, M.; Fagan, J.; Primicerio, R. Compositional differences in soybeans on the market: Glyphosate accumulates in Roundup Ready GM soybeans. Food Chem. 2014, 153, 207–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duke, S.O. (Ed.) Herbicide-Resistant Crops; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Duke, S.O. Biotechnology: Herbicide-Resistant Crops. In Encyclopedia of Agriculture and Food Systems; Alfen, V.N., Ed.; Elsevier: San Diego, CA, USA, 2014; Volume 2, pp. 94–116. [Google Scholar]
- Duke, S.O. Perspectives on transgenic, herbicide-resistant crops in the USA almost 20 years after introduction. Pest Manag. Sci. 2015, 71, 652–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Green, J.M. Current state of herbicides in herbicide-resistant crops. Pest Manag. Sci. 2014, 70, 1351–1357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Green, J.M.; Siehl, D.L. History and outlook for glyphosate-resistant crops. Rev. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2021, 255, 67–91. [Google Scholar]
- Duke, S.O.; Lydon, J.; Koskinen, W.C.; Moorman, T.B.; Chaney, R.L.; Hammerschmidt, R. Glyphosate effects on plant mineral nutrition, crop rhizophere microbiota, and plant disease in glyphosate-resistant crops. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2012, 60, 10375–10397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duke, S.O. Glyphosate: Uses other than in glyphosate-resistant crops, mode of action, degradation in plants, and effects on non-target plants and agricultural microbes. Rev. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2021, 255, 1–65. [Google Scholar]
- Benbrook, C.M. Trends in glyphosate use in the United States and globally. Environ. Sci. Eur. 2016, 28, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Richmond, M.E. Glyphosate: A review of its global use, environmental impact, and potential health effects on humans and other species. J. Environ. Stud. Sci. 2018, 8, 416–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elmore, R.W.; Roeth, F.W.; Klein, R.N.; Knezevic, S.Z.; Martin, A.; Nelson, L.A.; Shapiro, C.A. Glyphosate-resistant soybean cultivar response to glyphosate. Agron. J. 2001, 93, 404–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nandula, V.K.; Reddy, K.N.; Rimando, A.M.; Duke, S.O.; Poston, D.H. Glyphosate-resistant and -susceptible soybean (Glycine fmax) and canola (Brassica napus) dose response and metabolism relationships with glyphosate. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2007, 55, 3540–3545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hetherington, P.R.; Reynolds, T.L.; Marshall, G.; Kirkwood, R.C. The absorption, translocation and distribution of the herbicide glyphosate in maize expressing the CP-4 transgene. J. Exp. Bot. 1999, 50, 1567–1576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duke, S.O. Metabolic degradation of glyphosate in soil microbes, endophytes, crops, and weeds. In Resistance in Weeds from Herbicide Metabolism; Nandula, V.K., Beffa, R., Eds.; John Wiley & Son, Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2025; pp. 41–80. [Google Scholar]
- Hoagland, R.E. Effects of glyphosate on metabolism of phenolic compounds. VII. Effects of glyphosine and glyphosate metabolites on phenylalanine ammonia-lyase activity, growth, and protein, chlorophyll, and anthocyanin levels in soybean (Glycine max) seedlings. Weed Sci. 1980, 28, 496–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, K.N.; Rimando, A.M.; Duke, S.O. Aminomethylphosponic acid, a metabolite of glyphosate, causes injury in glyphosate-treated, glyphosate-resistant soybean. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2004, 52, 5139–5143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebelhar, S.A.; Varsa, E.C.; Hart, C.D. Soil pH and manganese effects on yield of Roundup Ready® soybeans. In III Illinois Fertilizer Conference Proceedings; Illinois Fertilizer and Chemical Association: Bloomington, IL, USA, 2006; pp. 54–65. [Google Scholar]
- Corrêa, E.L.; Dayan, F.E.; Owen, D.K.; Rimando, A.M.; Duke, S.O. Glyphosate-resistant and conventional canola (Brassica napus L.) responses to glyphosate and aminomethylphosponic acid (AMPA) treatment. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2016, 64, 3508–3513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McClinchey, S.; Gillespie, J.B.; Fisher, T.L.; Taylor, K.; Challender, M.; Schmidt, D.H. Quality characteristics of glyphosate-tolerant canola containing a glyphosate acetyltransferase transgene (Event DP- Ø7073496-4). Crop Sci. 2016, 56, 1736–1746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siehl, D.L.; Castle, L.A.; Gorton, R.; Keenan, R.J. The molecular basis of glyphosate resistance by an optimized microbial acetyltranferase. J. Biol. Chem. 2007, 282, 11446–11455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bidóia, V.S.; Costa, Y.K.S.; Gratão, P.L.; Carbonari, C.A.; Duke, S.O.; Carvalho, L.B. Effects of glyphosate on glyphosate-resistant maize growth and metabolic parameters in the greenhouse and field. Crop Forage Turfgrass Manag. 2024, 10, e20308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Araújo, G.B.; Albrecht, A.J.P.; Albrecht, L.P.; Carvalho, H.W.P.; Migliavacca, R.A.; Silva, A.F.M. Effect of glyphosate and glufosinate on nutritional content and agronomic performance of maize possessing cp4epsps and pat transgenes. Aust. J. Crop Sci. 2021, 15, 773–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruns, H.A.; Abbas, H.K. Comparisons of herbicide treated and cultivated herbicide-resistant corn. Int. J. Agron. 2010, 1, 798127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, M.A.; Snipes, C.E. Tolerance of transgenic cotton to topical applications of glyphosate. J. Cotton Sci. 1999, 3, 19–26. [Google Scholar]
- Pline, W.A.; Wilcut, J.W.; Duke, S.O.; Edmisten, K.L.; Wells, R. Tolerance and accumulation of shikimic acid in response to glyphosate applications in glyphosate-resistant and conventional cotton (Gossypium hirsutum L.). J. Agric. Food Chem. 2002, 50, 506–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cerny, R.E.; Bookout, J.T.; Cajacob, C.A.; Groat, J.R.; Hart, J.L.; Heck, G.R.; Huber, S.A.; Listello, J.; Martens, A.B.; Oppenhuizen, M.E.; et al. Development and characterization of a cotton (Gossypium hirsutum L.) event with enhanced reproductive resistance to glyphosate. Crop Sci. 2010, 50, 1375–1384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabachnik, M.I.; Medved, T.Y.; Dyatlova, N.M.; Rudomino, M.V. Organophosphorus complexones. Russ. Chem. Rev. 1974, 43, 733–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duke, S.O. Glyphosate. In Herbicides-Chemistry, Degradation and Mode of Action Volume III; Kearney, P.C., Kaufman, D.D., Eds.; Marcel Dekker, Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 1988; pp. 1–70. [Google Scholar]
- Steinrücken, H.C.; Amrhein, N. The herbicide glyphosate is a potent inhibitor of 5-enolpyruvylshikimic acid-3-phosphate synthase. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1980, 94, 1207–1212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duke, S.O.; Wauchope, R.D.; Hoagland, R.E.; Wills, G.D. Influence of glyphosate on uptake and translocation of calcium ion in soybean seedlings. Weed Res. 1983, 23, 133–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duke, S.O.; Vaughn, K.C.; Wauchope, R.D. Effects of glyphosate on uptake, translocation, and intracellular localization of metal cations in soybean (Glycine max) seedlings. Pestic. Biochem. Physiol. 1985, 24, 384–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bott, S.; Tesfamariam, T.; Candan, H.; Cakmak, I.; Römheld, V.; Newmann, G. Glyphosate-induced impairment of plant growth and micronutrient status in glyphosate-resistant soybean (Glycine max L.). Plant Soil 2008, 312, 185–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zobiole, L.H.S.; Kremer, R.J.; Oliveira, R.S., Jr.; Constantin, J. Glyphosate affects chlorophyll, nodulation and nutrient accumulation of “second generation” glyphosate-resistant soybean (Glycine max L.). Pestic. Biochem. Physiol. 2011, 99, 53–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zobiole, L.H.S.; Kremer, R.J.; Oliveira, R.S., Jr.; Constantin, J. Glyphosate effects on photosynthesis, nutrient accumulation, and nodulation in glyphosate-resistant soybean. J. Plant Nutrit. Soil Sci. 2012, 175, 319–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonçalves, C.G.; Dos Reis, M.R.; Dos Santos, G.R.; Matuo, E.; Reis, R.M.; Souza, M.F. Glyphosate formulations on nutritional condition and productivity of Roundup Ready soybean. Commun. Soil Sci. Plant Anal. 2017, 48, 2119–2125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petter, F.A.; Zuffo, A.M.; Netom, F.A.; Pacheco, L.P.; Almeida, F.A.; Andrade, R.; Junior, J.M.Z. Effect of glyphosate and water stress on plant morphology and nutrient accumulation in soybean. Aust. J. Crop Sci. 2016, 10, 251–257. [Google Scholar]
- Johal, G.S.; Huber, D.M. Glyphosate effects on diseases of plants. Eur. J. Agron. 2009, 32, 144–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez, D.A.; Loening, U.E.; Graham, M.C. Impacts of glyphosate-based herbicides on disease resistance and health of crops: A review. Environ. Sci. Eur. 2018, 30, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duke, S.O.; Reddy, K.N.; Bu, K.; Cizdziel, J.V. Effects of glyphosate on mineral content of glyphosate-resistant soybeans (Glycine max). J. Agric. Food. Chem. 2012, 60, 6764–6771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duke, S.O.; Rimando, A.M.; Reddy, K.N.; Cizdziel, J.V.; Bellaloui, N.; Shaw, D.R.; Williams, M.M.; Maul, J.E. Lack of transgene and glyphosate effects on yield and mineral and amino acid content of glyphosate-resistant soybean. Pest Manag. Sci. 2018, 74, 1166–1173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kandel, Y.R.; Bradley, C.A.; Wise, K.A.; Chilvers, M.I.; Tenuta, A.U.; Davis, V.M.; Esker, P.D.; Smith, D.L.; Licht, M.A.; Mueller, D.S. Effect of glyphosate application on sudden death syndrome of glyphosate-resistant soybean under field conditions. Plant Dis. 2015, 99, 347–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, F.R.; Rech, R.; Duke, S.O.; Carvalho, L.B. Lack of effects of glyphosate and glufosinate on growth, mineral content, and yield on glyphosate- and glufosinate-resistant maize. GM Crops Food 2018, 9, 180–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reddy, K.N.; Cizdziel, J.V.; Williams, M.M.; Maul, J.E.; Rimando, A.M.; Duke, S.O. Glyphosate resistance technology has minimal effect on maize mineral nutrition and yield. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2018, 66, 10139–10146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bidóia, V.S.; Santos Neto, J.C.; Maciel, C.D.G.; Tropaldi, L.; Carbonari, C.A.; Duke, S.O.; Carvalho, L.B. Lack of significant effects of glyphosate on glyphosate-resistant maize in different field locations. Agronomy 2023, 13, 1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, W.R.; Sammons, R.D.; Grabiak, R.C.; Mehrsheikh, A.; Bleeke, M.S. Computer simulation of the interactions of glyphosate with metal ions in phloem. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2012, 60, 6077–6087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huber, S.C.; Li, K.; Nelson, R.; Ulanov, A.; DeMuro, C.M.; Baxter, I. Canopy position has a profound effect on soybean seed composition. PeerJ 2016, 4, e2452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaner, D.L.; Hadler-Hassar, T.; Henry, W.G.; Koger, W.B. A rapid in vivo shikimate accumulation assay with excised leaf discs. Weed Sci. 2005, 53, 769–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lappé, M.A.; Bailey, E.B.; Chlidress, C.; Setchell, K.D.R. Alterations in clinically important phytoestrogens in genetically modified, herbicide-tolerant soybeans. J. Med. Foods 1999, 1, 241–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bohm, G.M.B.; Rombaldi, C.V.; Genovese, M.I.; Castilhos, C.; Alves, B.J.R.; Rumjanek, N.G. Glyphosate effects on yield, nitrogen fixation, and seed quality in glyphosate-resistant soybean. Crop Sci. 2014, 54, 1737–1743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bohm, G.M.B.; Amarante, L.; Bohm, E.M.; Rombaldi, C.V.; Genovese, M.I. Glyphosate influence the soil microorganism sensibility, physiological parameters of the plant, isoflavones and residues in seeds and soil. J. Agric. Ecol. Res. 2015, 5, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schafer, J.R.; Hallett, S.G.; Johnson, W.G. Response of giant ragweed (Ambrosia trifida), horseweed (Conyza canadensis), and common lambsquarters (Chenopodium album) biotypes to glyphosate in the presence of absence of soil microorganisms. Weed Sci. 2012, 60, 641–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, M.M.; Bradley, C.A.; Duke, S.O.; Maul, J.E.; Reddy, K.M. Goss’s wilt incidence in sweet corn is independent of transgenic traits and glyphosate. HortScience 2015, 50, 1791–1794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnett, K.A.; Sprague, C.L.; Kirk, W.W.; Hanson, L.E. Influence of glyphosate on Rhizoctonia crown and root rot (Rhizoctonia solani) in glyphosate-resistant sugar beet. Weed Sci. 2012, 60, 113–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baird, R.; Batson, W.; Watson, C.; Hightower, P. Evaluation of transgenic cotton varieties and a glyphosate application of seedling disease incidence. Mycopathol. 2004, 158, 363–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baley, G.J.; Campbell, K.G.; Yenish, J.; Kidwell, K.K.; Paulitz, T.C. Influence of glyphosate, crop volunteer and root pathogens on glyphosate-resistant wheat under controlled environmental conditions. Pest Manag. Sci. 2009, 65, 288–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Powell, J.R.; Swanton, C.J. A critique of studies evaluating glyphosate effects on diseases associated with Fusarium spp. Weed Res. 2008, 48, 307–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammerschmidt, R. How glyphosate affects plant disease development: It is more than enhanced susceptibility. Pest Manag. Sci. 2018, 74, 1054–1063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duke, S.O.; Pan, Z.; Bajsa-Hirschel, J.; Tamang, P.; Hammerschmidt, R.; Lorsbach, B.A.; Sparks, T.C. Molecular targets of herbicides and fungicides—Are there useful overlaps for fungicide discovery? J. Agric. Food Chem. 2023, 71, 20532–20548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samac, D.; Foster-Hartnett, D. Effect of glyphosate application on foliar diseases of glyphosate-tolerant alfalfa. Plant Dis. 2012, 96, 1104–1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, P.C.C.; Baley, G.J.; Clinton, W.P.; Bunkers, G.J.; Alibhai, M.F.; Paulitz, T.; Kidwell, K.K. Glyphosate inhibits rust diseases in glyphosate-resistant wheat and soybean. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 17290–17295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, P.C.C.; Clark, C.; Andrade, G.; Balbi, M.C.; Caldwell, P. The control of Asian rust by glyphosate in glyphosate-resistant soybeans. Pest Manag. Sci. 2008, 64, 353–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Einhardt, A.M.; Oliviera, L.M.; Ferreira, S.; Araújo, W.L.; Mederios, D.B.; Fernie, A.R.; Rodrigues, F.A. Defense responses and oxidative metabolism of glyphosate-resistant soybean plants infected by Phakopsora pachyrhizi modulated by glyphosate and nickel. Physiol. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2022, 118, 101817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Claus, A.; Roncatto, E.; Barroso, A.A.M.; De Milo, L.L.M. Herbicides reduce the severity and sporulation of Phakopsora pachyrhizi in soybean with triple herbicide resistance. Pest Manag. Sci. 2023, 79, 3749–3756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anderson, J.A.; Kolmer, J.A. Rust control in glyphosate tolerant wheat following application of the herbicide glyphosate. Plant Dis. 2005, 89, 1136–1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pankey, J.H.; Griffin, J.L.; Colyer, P.D.; Schneider, R.W.; Miller, D.K. Preemergence herbicide and glyphosate effect on seedling disease in glyphosate-resistant cotton. Weed Technol. 2005, 19, 312–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murtza, T.; You, M.P.; Barbetti, M.J. Application timing of herbicide, glyphosate and atrazine sway respective epidemics of foliar pathogens in herbicide-tolerant rapeseed. Plant Pathol. 2022, 71, 507–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mengistu, A.; Reddy, K.N.; Bellaloui, N.; Walker, E.R.; Kelly, H.M. Effect of glyphosate on Macrophomina phaseolina in vitro and its effect on disease severity of soybean in the field. Crop Prot. 2013, 54, 23–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehta, S.; Kumar, A.; Achary, V.M.M.; Ganesan, P.; Rathi, N.; Singh, A.; Sahu, K.P.; Lal, S.K.; Das, T.K.; Reddy, M.K. Antifungal activity of glyphosate against fungal blast disease on glyphosate tolerant OsmEPSPS transgenic rice. Plant Sci. 2021, 311, 111009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reddy, K.N.; Abbas, H.K.; Zablotowicz, R.M.; Abel, C.A.; Kroger, C.H. Mycotoxin occurrence and Aspergillus flavus soil propagules in a corn and cotton glyphosate-resistant cropping systems. Food Addit. Contam. 2007, 24, 1367–1373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rheeder, J.P.; van der Westhuizen, L. Fusarium and fumonisin in GM maize grown by small-scale farmers in KwaZulu-Natal, South Africa. S. Afr. J. Sci. 2024, 120, 15905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ai, Y.; You, M.P.; Barbetti, M.J. Glyphosate application affects white leaf spot (Neopseudocercosporella capsellae) development on glyphosate-tolerant canola. Plant Pathol. 2025, 74, 786–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ai, Y.; You, M.P.; Barbetti, M.J. Insights into how glyphosate constrains conidial germination but stimulates morphological transformation of the white leaf spot pathogen Neopseudocercosporella capsellae in glyphosate-tolerant rapeseed (Bassica napus). Plant Pathol. 2025; Early View. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moorman, T.B.; Becerril, J.M.; Lydon, J.; Duke, S.O. Production of hydroxybenzoic acids by Bradyrhizobium japanicum strains after treatment with glyphosate. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1992, 40, 289–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, K.N.; Hoagland, R.E.; Zablotowicz, R.M. Effect of glyphosate on growth, chlorophyll, and nodulation in glyphosate-resistant and susceptible soybean (Glycine max) varieties. J. New Seeds 2001, 2, 37–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- King, C.A.; Purcell, L.C.; Vories, E.D. Plant growth and nitrogenase activity of glyphosate tolerant soybean in response to foliar glyphosate applications. Agron. J. 2001, 93, 179–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, K.N.; Zablotowicz, R.M. Glyphosate-resistant soybean response to various salts of glyphosate and glyphosate accumulation in soybean nodules. Weed Sci. 2003, 51, 496–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zablotowicz, R.M.; Reddy, K.N. Nitrogenase activity, nitrogen content, and yield responses to glyphosate in glyphosate-resistant soybean. Crop Protect. 2007, 26, 370–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quesada, W.A.; Santos-Amaya, O.F.; Garica-Souza, E.; Silva, A.P.N.; Haddi, K. Glyphosate-induced lethal and stimulatory responses in two key lepidopteran pests of corn and soybean: Spodoptera frugiperda and Chrysodeixis includens. Crop Protect. 2025, 197, 107357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duke, S.O.; Belz, R.G.; Carbonari, C.A.; Velini, E.D. Understanding herbicide hormesis: Evaluating its positive and negative aspects with emphasis on glyphosate. Adv. Weed Sci. 2025, 43, e020250104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belz, R.G.; Duke, S.O. Stepping beyond hormesis modeling and sub-NOAEL predictions in plant biology. Curr. Opin. Environ. Sci. Health 2022, 28, 100366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erofeeva, E.A. Environmental hormesis: From cell to ecosystem. Curr. Opin. Environ. Sci. Health 2022, 29, 100378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
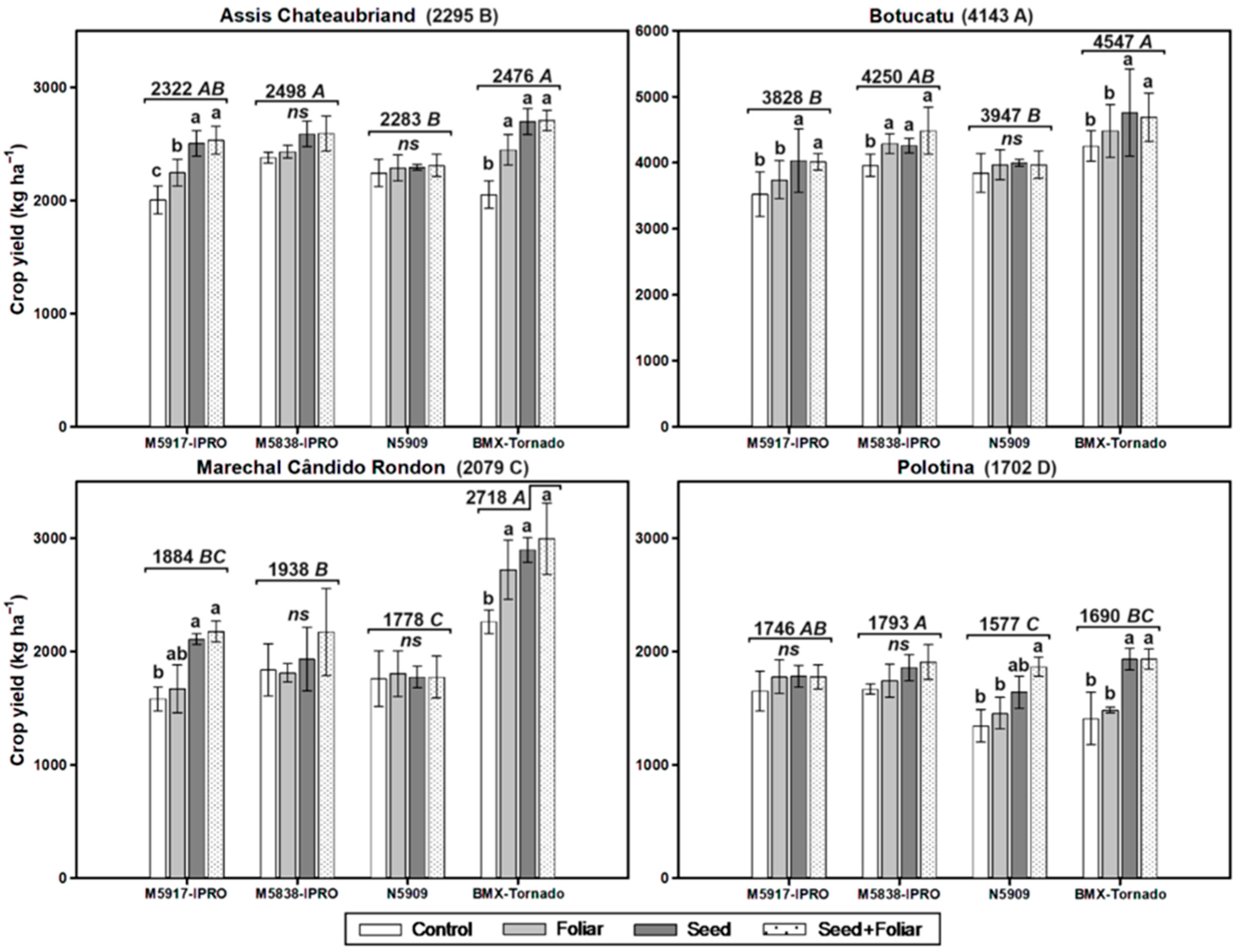
- Krenchinski, F.H.; Pereira, V.G.C.; Giovannelli, B.F.; Cesco, V.J.S.; Alcantara de la Cruz, R.; Velini, E.D.; Carbonari, C.A. Glyphosate hormesis improves agronomic characteristics and yield of glyphosate-resistant soybean under field conditions. Agronomy 2024, 14, 1559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brants, I.O.; Graham, W. Use of N-(Phosphonomethyl) Glycine and Derivatives Thereof. U.S. Patent 6,083,878, 4 July 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Cuhra, M. Review of GMO safety assessment studies: Glyphosate residues in Roundup Ready crops is an ignored issue. Environ. Sci. Eur. 2015, 27, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agostini, L.P.; Dettagni, R.S.; dos Reis, R.S.; Stur, E.; dos Santos, E.V.W.; Ventorim, D.P.; Garcia, F.M.; Cardoso, R.C.; Graceli, J.B.; Laura, I.D. Effects of glyphosate exposure on human health: Insights from epidemiological and in vitro studies. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 705, 135808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vicini, J.L.; Jensen, P.K.; Young, B.M.; Swarthout, J.T. Residues of glyphosate in food and dietary exposure. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2021, 20, 5226–5257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bou-Mitri, C.; Dagher, S.; Makkawi, A.; Khreyss, Z.; Hassan, H.F. Glyphosate in food: A narrative review. J. Agric. Food Res. 2025, 19, 101643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solomon, K.R. Measured exposures to glyphosate in applicators and the general populations: An updated review of the scientific literature since 2020. Pest Manag. Sci. 2025, 81, 4947–4961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barker, A.L.; Dayan, F.E. Fate of glyphosate during processing of glyphosate-resistant sugar beet (Beta vulgaris). J. Agric. Food Chem. 2019, 67, 2061–2065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghanizadeh, H.; Harrington, K.C. Perspective: Root exudation of herbicides as a novel mode of herbicide resistance in weeds. Pest Manag. Sci. 2020, 76, 2543–2547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Combs, D.K.; Hartnell, G.F. Alfalfa containing the glyphosate-tolerant trait has no effect on feed intake, milk composition, or milk production of dairy cattle. J. Dairy Sci. 2008, 91, 673–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takano, H.K.; Dayan, F.E. Glufosinate-ammonium: A review of the current state of knowledge. Pest Manag. Sci. 2020, 76, 3911–3925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takano, H.K.; Beffa, R.; Preston, C.; Westra, P.; Dayan, F.E. Physiological factors affecting uptake and translocation of glufosinate. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2020, 68, 3026–3032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, S.; Evans, R.; Singh, B. Herbicidal inhibitors of amino acid biosynthesis and herbicide-tolerant crops. Amino Acids 2006, 30, 195–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stewart, S.D.; Steckel, L.E.; Steckel, S. Evaluation of WideStrike® cotton (Gossypium hirsutum L.) injury from early season herbicide and insecticide tank mixes. J. Cotton Sci. 2013, 17, 219–226. [Google Scholar]
- Carbonari, C.A.; Latorre, D.O.; Gomes, G.L.G.C.; Velini, E.D.; Owens, D.K.; Pan, Z.; Dayan, F.E. Resistance to glufosinate is proportional to phosphinothricin acetyltransferase expression and activity in LibertyLink® and WideStrike® cotton. Planta 2016, 243, 925–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krenchinski, F.H.; Carbonari, C.A.; Cesco, V.J.S.; Albrecht, A.J.P.; Arcuri, M.L.C.; Maia, I.G.; Velini, E.D. Glufosinate resistance level is proportional to phosphinothricin acetyltransferase gene expression in glufosinate-resistant maize. J. Agric. Food. Chem. 2018, 66, 12641–12650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rojano-Delgado, A.; Priego-Capote, F.; Barro, F.; de Castro, M.D.L.; de Prado, R. Liquid chromatography-diode array detection to study the metabolism of glufosinate in Triticum aestivum T-590 and influence of the genetic modification on its resistance. Phytochemistry 2013, 96, 116–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lanclos, D.Y.; Webster, E.P.; Zhang, W.; Linscombe, S.D. Response of glufosinate-resistant rice (Oryza sativa) to glufosinate application timings. Weed Technol. 2003, 17, 157–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, K.N.; Zablotowicz, R.M.; Bellaloui, N.; Ding, W. Glufosinate effects on nitrogen nutrition, growth, yield, and seed composition in glufosinate-resistant and glufosinate-sensitive soybean. Inter. J. Agron. 2011, 2011, 109280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mundt, T.T.; Albrecht, L.P.; Albrecht, A.J.P.; Krenchinski, H.; Pereira, V.G.C.; Wagner, G.; Silva, A.F.M.; Carbonari, C.A. Growth and development of soybean plants with the Pat gene under different glufosinate rates. Intl. J. Agric. Biol. 2021, 26, 217–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krenchinski, F.H.; Albrecht, A.J.P.; Cesco, V.J.S.; Rodrigues, D.M.; Pereira, V.G.C.; Albrecht, L.P.; Carbonari, C.A.; Filho, R.V. Post-emergent applications of isolated and combined herbicides on corn culture with cp4-epsps and pat genes. Crop Protect. 2018, 106, 156–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albrecht, A.J.P.; Silva, A.F.M.; Krenchinski, F.H.; Albrecht, L.P.; Giovanelli, B.F.; Wobeto, K.S.; Pereira, V.G.C.; Victoria Filho, R. Growth, development, and chlorophyll indexes of glyphosate and glufosinate-tolerant maize under herbicide application. Agron. Colomb. 2022, 40, 41–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albrecht, M.; Kortekamp, A. The in vitro effect of the herbicide Basta® (glufosinate ammonium) on potential fungal grapevine pathogens. Eur. J. Hort. Sci. 2009, 74, 112–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tada, T.; Kanzaki, H.; Norita, E.; Uchiyama, H.; Nakamura, I. Decreased symptoms of rice blast disease on leaves of bar-expressing transgenic rice plants following treatment with bialaphos. Mol. Plant Microbe Interact. 1996, 9, 762–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, I.P. Glufosinate-ammonium-induced pathogen inhibition and defense responses culminate in disease and defense responses culminate in disease protection in bar-transgenic rice. Plant Physiol. 2008, 146, 213–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uchimiya, H.; Fujii, S.; Huang, J.; Fushimi, T.; Nishioka, M.; Kim, K.M.; Yamada, M.K.; Kurusu, T.; Kuchitsu, K.; Tagawa, M. Transgenic rice plants conferring increased tolerance to rice blast and multiple environmental stresses. Mol. Breed. 2002, 9, 25–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Browning, M.; Ruemmele, B.A.; Chandlee, J.M.; Kausch, J.M.; Kausch, A.P.; Jackson, N. Glufosinate reduces fungal diseases in transgenic glufosinate-resistant bentgrasses (Agrostis spp.). Weed Sci. 2003, 51, 130–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tubajika, K.M.; Damann, K.E. Glufosinate-ammonium reduces growth and aflatoxin B1 production by Aspergillus flavus. J. Food Protect. 2002, 65, 1483–1487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruns, H.A.; Abbas, H.K. Effects of glufosinate–ammonium and urea on aflatoxin and fumonisin levels in corn. Plant Health Prog. 2006, 7, 1–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Novais, C.B.; Giovannetti, M.; Faria, S.M.; Sbrana, C. Two herbicides, two fungicides and spore-associated bacteria affect Funneliformis mosseae extraradical mycelium structural traits and viability. Mycorrhiza 2019, 29, 341–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dragićcević, M.; Platiša, J.; Nikolić, R.; Todorović, S.; Bogdanović, M.; Mitić, N.; Simonović, A. Herbicide phosphinothricin causes direct stimulation hormesis. Dose–Response 2013, 11, 344–360. [Google Scholar]
- Donn, G. Method of Increasing the Yield of Herbicide Resistant CROP Plants. U.S. Patent 5,739,082, 14 April 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Garcia, J.R.; Vargas, A.A.M.; Perboni, L.T.; Souza, E.A.; Tessaro, D.; Lucio, F.R.; Agostinetto, D. Physiological attributes of Enlist E3™ soybean seed submitted to herbicides application. Planta Daninha 2020, 38, e020220418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia, N.S.; Dayan, F.E.; Camargo, E.R.; Ceolin, B.C.; Deuner, S.; Avila, L.A. Auxin-mimic herbicides dilemma: Their benefits and limitations. Pest Manag. Sci. 2025, 81, 4973–4992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mortensen, D.A.; Ryan, M.R.; Smith, R.G. Another step on the transgene-facilitated herbicide treadmill. Pest Manag. Sci. 2024, 80, 4145–4149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Russell, K.R.; Dotray, P.A.; Ritchie, G.L.; Kelly, B.R. Effects of 2,4-D choline on fruiting in sensitive cotton. Weed Technol. 2023, 37, 352–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russell, K.R.; Dotray, P.A.; Pabuayon, L.B.; Richie, G.L. Dicamba effects on fruiting in sensitive cotton. Weed Technol. 2021, 35, 43–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCown, S.; Barber, T.; Norsworthy, J.K. Response of non-dicamba-resistant soybean to dicamba as influenced by growth stage and herbicide rate. Weed Technol. 2018, 32, 513–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soltani, N.; Brown, L.; Sikkema, P.H. Response of dicamba-resistant soybean to glyphosate/dicamba application rate and timing. Amer. J. Plant Sci. 2019, 10, 1022–1029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaccaro, M.L.M.; Norsworthy, J.K.; Brabham, C.B. Dicamba translocation in soybean and accumulation in seed. Weed Sci. 2020, 68, 333–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henry, J.L.; Lin, C.-H.; Weirich, J.W.; Smeda, R.J. Persistence of dicamba residue in harvested soybeans. Agrosys. Geosci. Environ. 2024, 7, e20564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kniss, A.R. Soybean response to dicamba: A meta-analysis. Weed Technol. 2018, 32, 507–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castner, M.C.; Norsworthy, J.K.; Barber, T.; Gbur, E.; Roberts, T. Does dicamba exposure elicit a hormetic response in sensitive soybean? Crop Forage Turfgrass Manag. 2021, 7, e20121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milosevic, L.; Osipitan, O.A.; Scott, J.E.; Knezevic, S.Z. Soybean tolerance to ultra-low does of dicamba: Hormesis or not. Crop Prot. 2023, 173, 106356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sperry, B.P.; Scholtes, A.B.; Golus, J.A.; Viera, B.C.; Reynolds, D.B.; Kruger, G.R.; Irby, J.T.; Eubank, T.W.; Barber, L.T.; Dodds, D.M. Soybean dose-response to 2,4-D and dicamba at vegetative and reproductive growth stages. Pest Manag. Sci. 2022, 78, 2759–2766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bohnenblust, E.; Egan, J.F.; Mortentsen, D.; Tooker, J. Direct and indirect effects of the synthetic-auxin herbicide dicamba on two lepidopteran species. Environ. Entomol. 2013, 42, 586–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freydier, L.; Lundgren, J.G. Unintended effects of the herbicides 2,4-Dand dicamba on lady beetles. Ecotoxicology 2016, 25, 1270–1277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kataria, H.R.; Gisi, U. Interactions of fungicide-herbicide combinations against plant pathogens and weeds. Crop Protect. 1990, 9, 403–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torra, J.; Alcántara de la Cruz, R.; de Figueiredo, M.R.A.; Gaines, T.A.; Jugulam, M.; Merotto, A., Jr.; Palma-Bautista, C.; Rojano-Delgado, A.M.; Riechers, D.E. Metabolism of 2,4-D in plants: Comparative analysis of metabolic detoxification pathways in tolerant crops and resistant weeds. Pest Manag. Sci. 2024, 80, 6041–6052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, T.R.; Shan, G.; Walsh, T.A.; Lira, J.M.; Cui, C.; Song, P.; Zhuang, M.; Arnold, N.L.; Lin, G.; Yau, K.; et al. Robust crop resistance to broadleaf and grass herbicides provided by aryloxyalkanoate dioxygenase transgenes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 20240–20245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Rotondaro, S.L.; Ma, M.; Rosser, S.W.; Olberding, E.L.; Wendelburg, B.M.; Addelfinskaya, Y.A.; Balcer, J.L.; Blewett, T.C.; Clements, B. Metabolism and residues of 2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid in DAS-40278-9 maize (Zea mays) transformed with aryloxyalkanoate dioxygenas-1 gene. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2016, 64, 7438–7444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Charles, G.W.; Constable, G.A.; Llewellyn, D.J.; Hickman, M.A. Tolerance of cotton expressing a 2,4-D detoxification gene to 2,4-D applied in the field. Aust. J. Agric. Res. 2007, 58, 780–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marques, R.F.; Marchi, S.R.; Pinheiro, G.H.R.; Souza, R.M.; Assunção, H.F.; Lúcio, F.R. Hormesis of 2,4-D choline salt in biometric aspects of cotton. J. Agric. Sci. 2019, 11, 283–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lurquin, P.F. Production of a toxic metabolite in 2,4-D-resistant GM crop plants. Biotech 2016, 6, 82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duke, S.O.; Dayan, F.E. New herbicide modes of action for new commercial herbicides—Searching for the “Holy Grail”. Pest Manag. Sci. 2022, 78, 1303–1313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schultz, J.L.; Weber, M.; Allen, J.; Bradley, K.W. Evaluation of weed management programs and response of FG72 soybean to HPPD-inhibiting herbicides. Weed Technol. 2015, 29, 653–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singletary, M.M.; Dotray, P.A.; Baldwin, G.; Pabuayon, I.L.B.; Asher, S.; Hixson, A.C. Axant™ Flex cotton response to topramezone applied early-or mid-postemergence. Weed Technol. 2025, 39, e49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Duke, S.O.; Carvalho, L.B. Unintended Effects of the Intended Herbicides on Transgenic Herbicide-Resistant Crops. Agronomy 2025, 15, 2448. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15112448
Duke SO, Carvalho LB. Unintended Effects of the Intended Herbicides on Transgenic Herbicide-Resistant Crops. Agronomy. 2025; 15(11):2448. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15112448
Chicago/Turabian StyleDuke, Stephen O., and Leonardo B. Carvalho. 2025. "Unintended Effects of the Intended Herbicides on Transgenic Herbicide-Resistant Crops" Agronomy 15, no. 11: 2448. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15112448
APA StyleDuke, S. O., & Carvalho, L. B. (2025). Unintended Effects of the Intended Herbicides on Transgenic Herbicide-Resistant Crops. Agronomy, 15(11), 2448. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15112448





