Comprehensive Evaluation of Nanhaia speciosa Germplasm Resources Using Agronomic Traits, Molecular Markers, and Metabolomics
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Reagents and Plant Materials
2.1.1. Chemical Reagents
2.1.2. Plant Materials
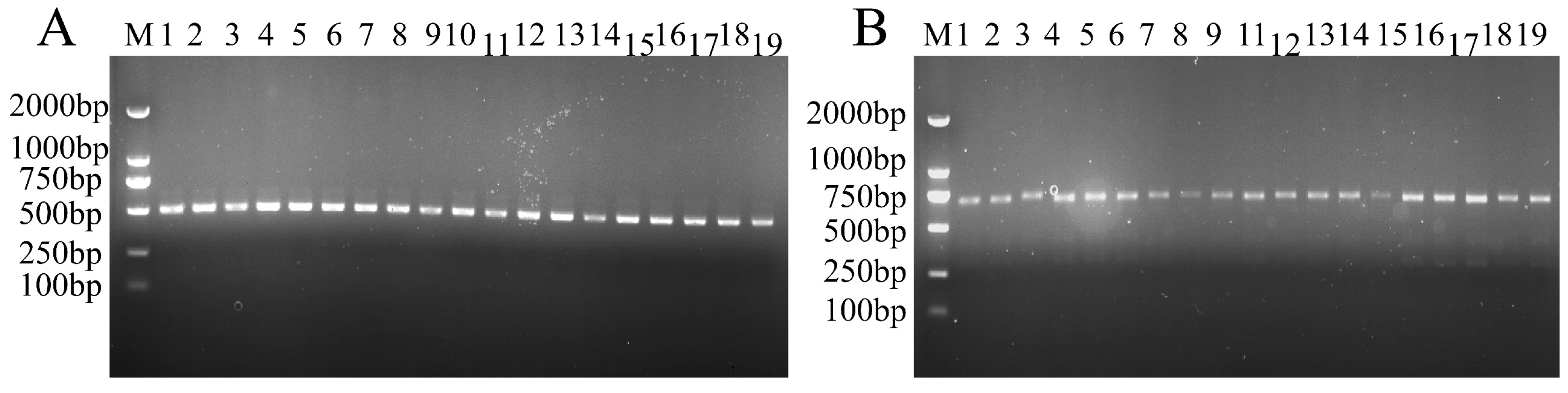
2.2. Genome DNA Extraction, PCR Amplification, and Sequence Analysis
2.2.1. Genomic DNA Extraction and Quality Control
2.2.2. PCR Amplification and Optimization
2.2.3. Sequencing and Bioinformatics
2.3. Genetic Diversity Analysis of Agronomic Traits
2.4. Preparation of MS Samples
2.5. UPLC-Q-Orbitrap/MS Analysis
2.6. Multicriteria Evaluation System for Germplasm Performance
3. Results
3.1. Molecular Characterization of Chloroplast Barcodes
3.2. Molecular Divergence Assessment and Barcode Gap Evaluation
3.3. Phylogenetic Analysis
3.4. Analysis of Variance in Agronomic Phenotypic Traits and Biochemical Characteristics
3.5. Diversity Analysis of Agronomic and Biochemical Traits in N. speciosa Germplasms
3.6. Multivariate Analysis of Agronomic and Biochemical Traits in N. speciosa Germplasms
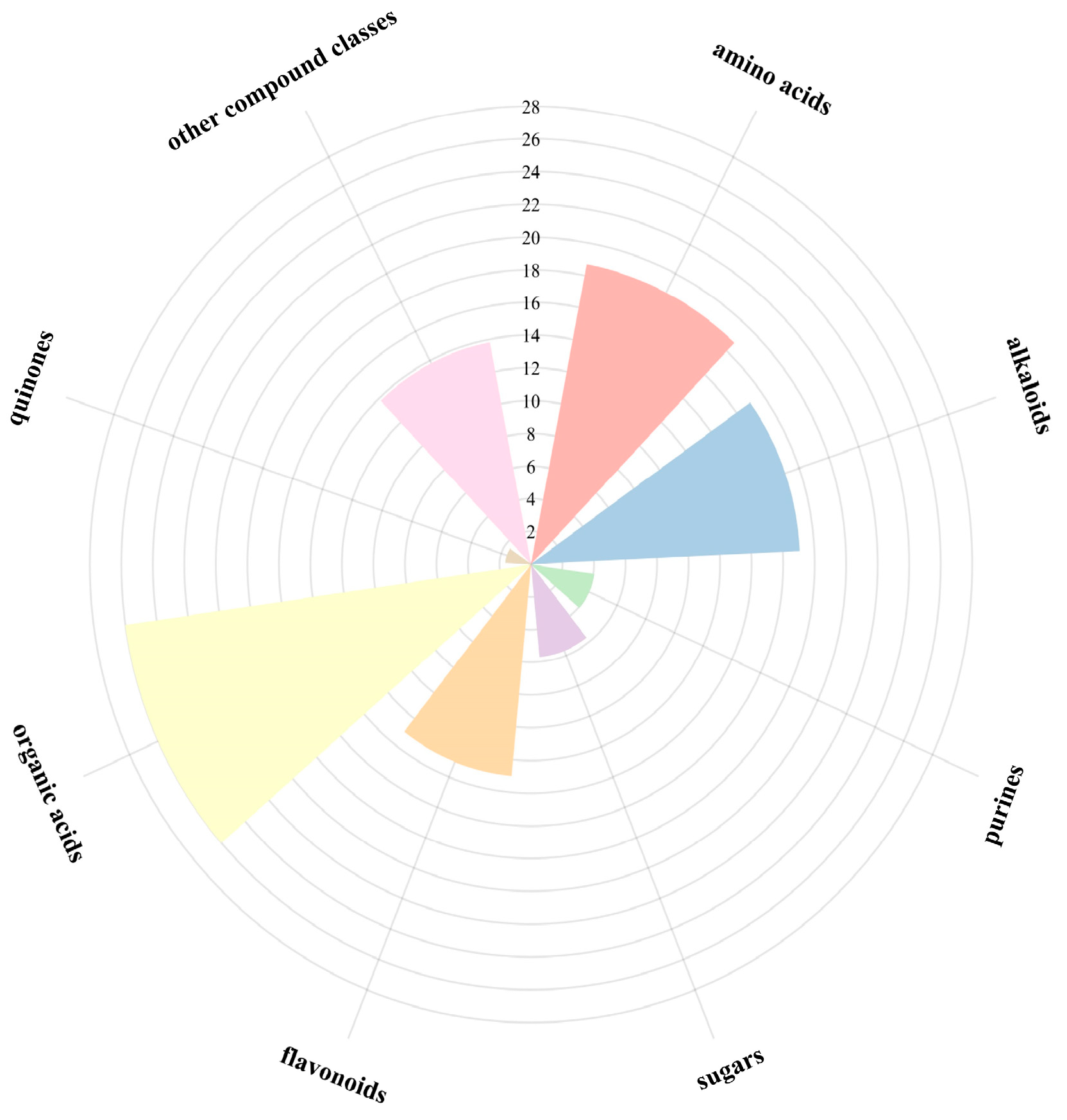
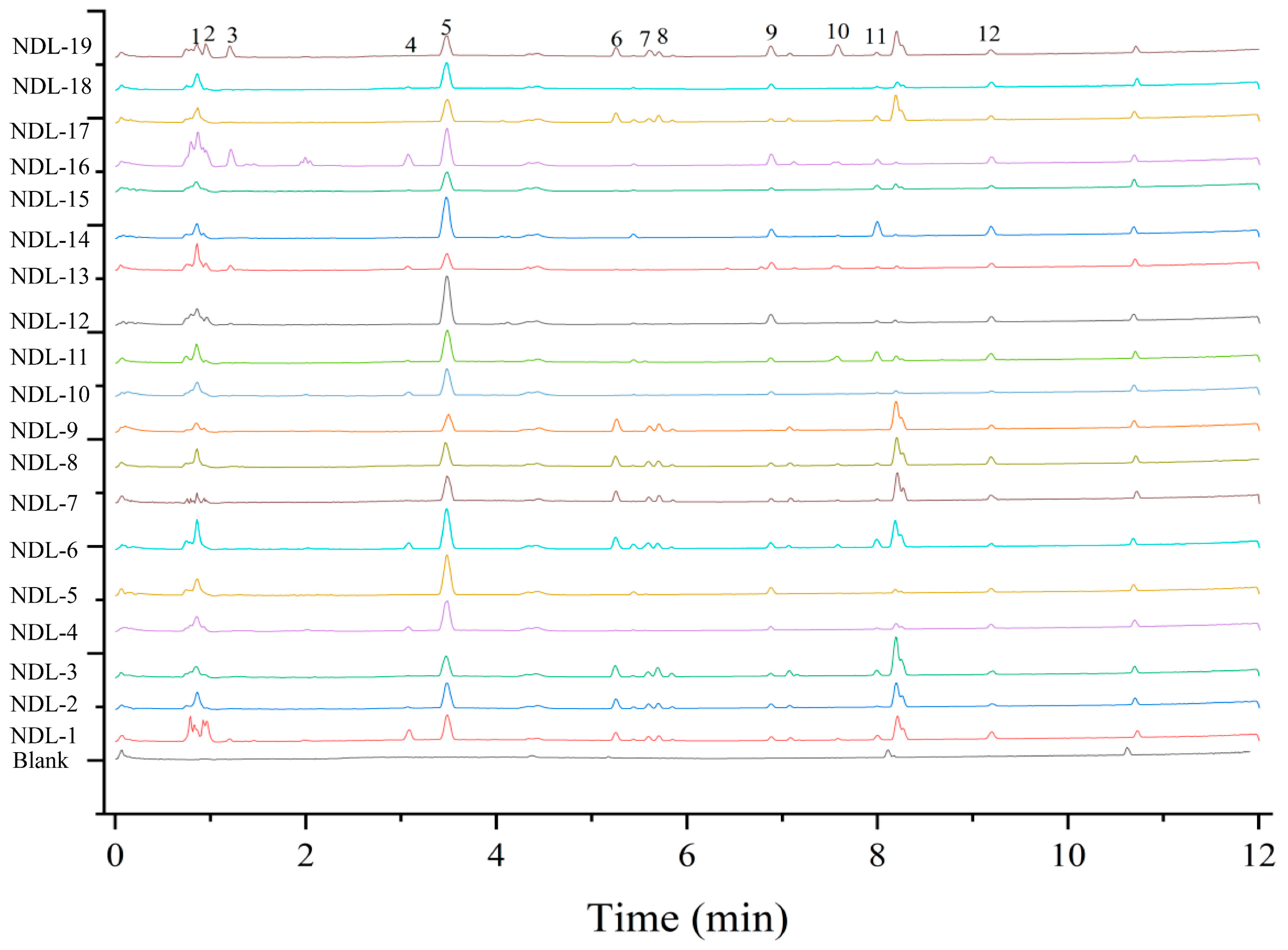
3.7. Metabolomic Differences Analysis of Different Germplasms of N. speciosa
3.7.1. UPLC-Q-Orbitrap/MS Was Employed for the Qualitative Analysis of Samples
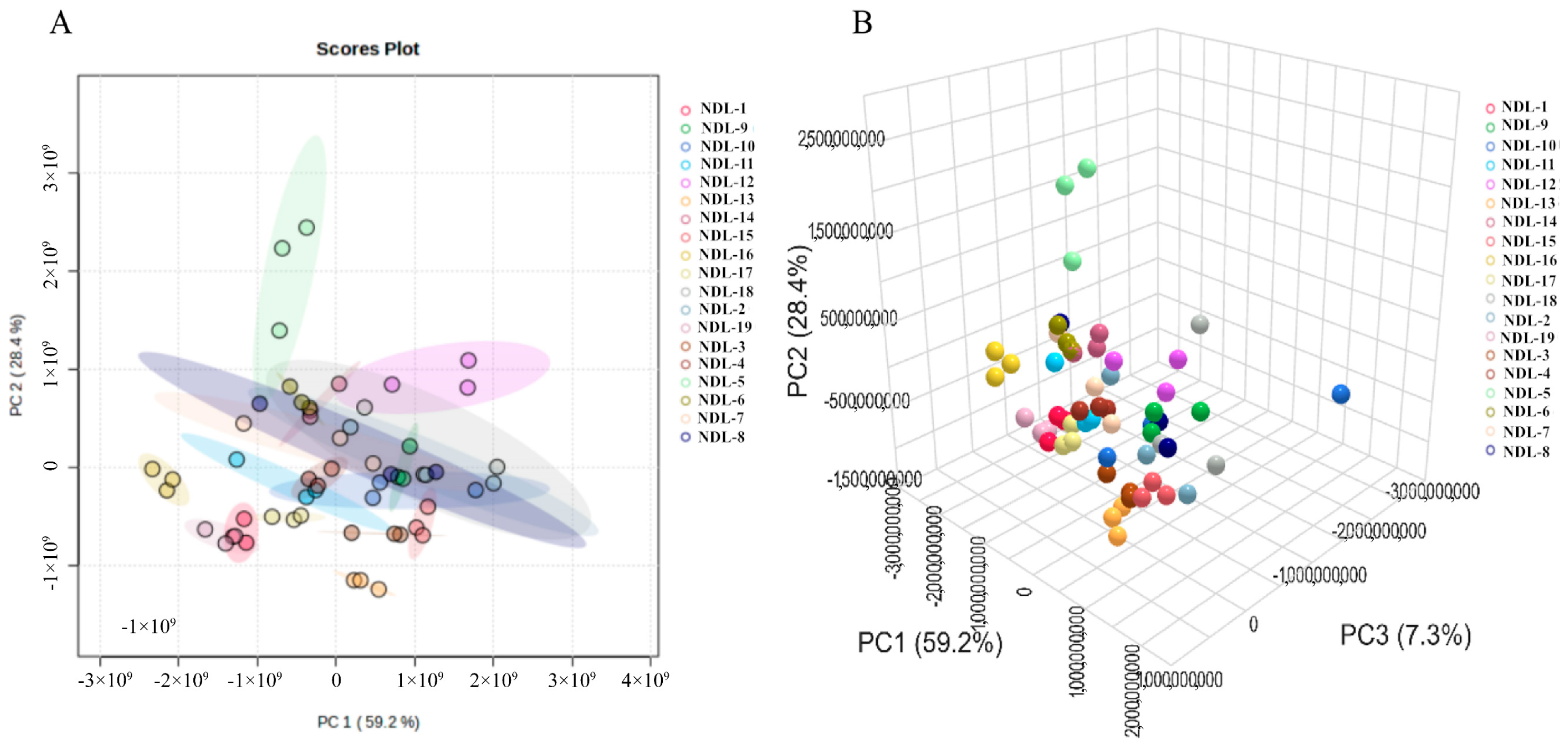
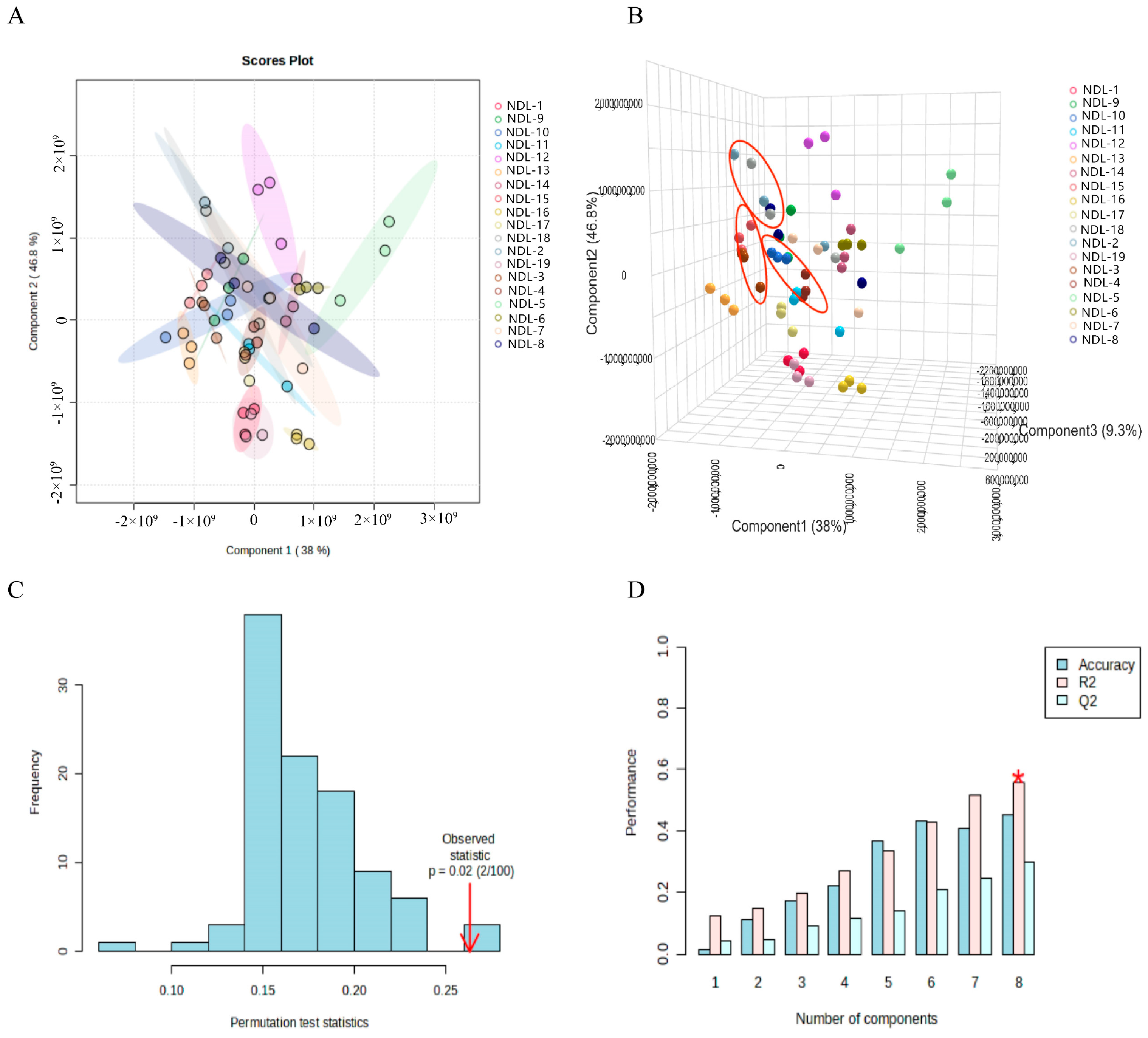
3.7.2. Principal Component Analysis (PCA) and Partial Least Squares Discriminant Analysis (PLS-DA)
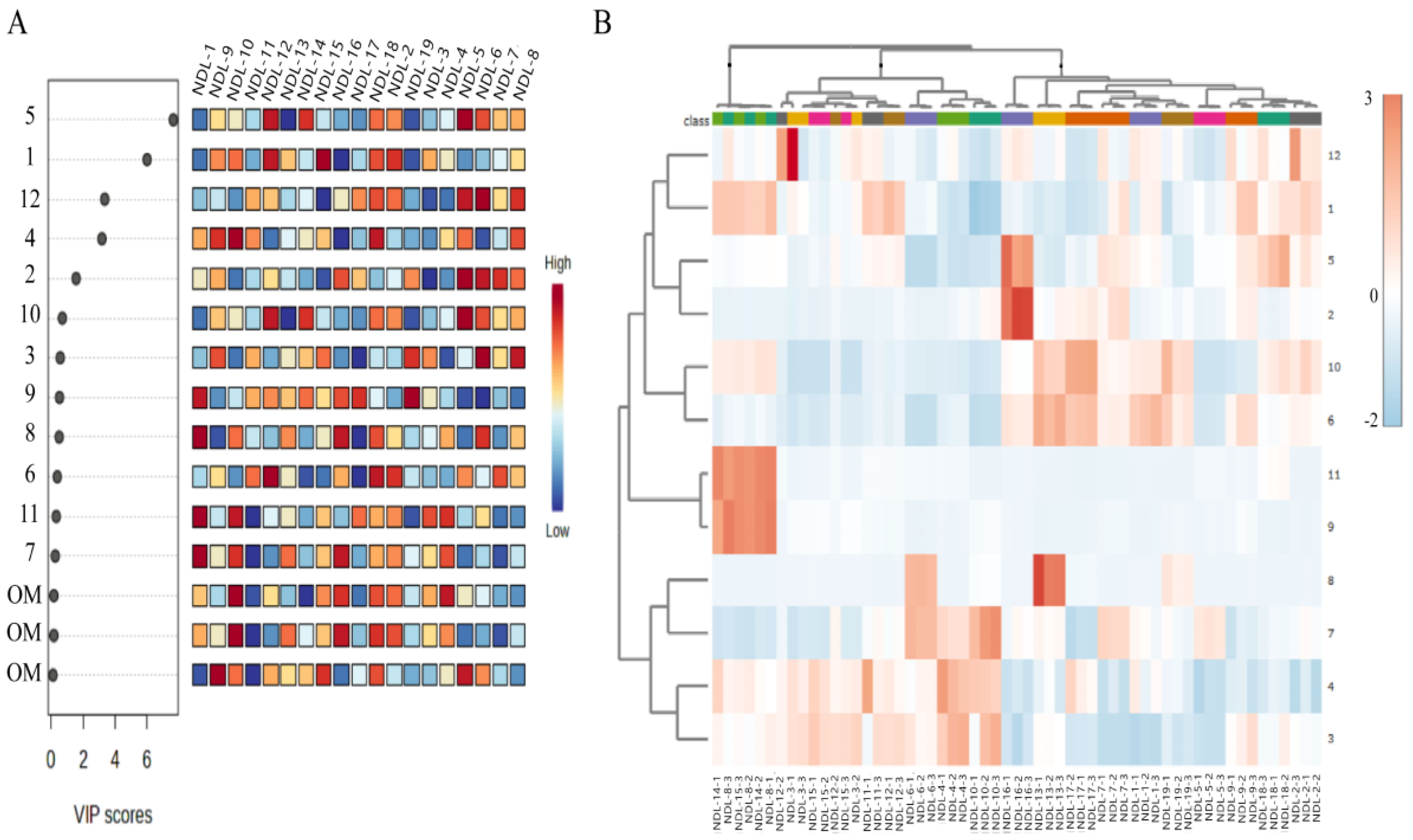
3.7.3. Determination of Key Metabolites and Assessment of Their Differential Abundance Through Heat Map Analysis in Professional Plant Metabolomics
3.8. Comprehensive Performance Evaluation and Analysis of Different Germplasms of N. speciosa
4. Discussion
4.1. DNA Barcoding: Potential and Limitations
4.2. Multi-Omics Integration Enhances Germplasm Evaluation
4.3. Reconciling Molecular and Metabolic Classification Differences
4.4. Implications for Breeding and Conservation
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| N. speciosa | Nanhaia speciosa |
References
- Su, Y.X.; He, C.M.; Wang, C. Research progress on cultivation and application of Nanhaia speciosa. Trop. For. 2019, 47, 26–29. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Wan, X.; Zhang, L. Global new species of vascular plants published in 2020. Biodivers. Sci. 2021, 29, 1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mo, Y.; Zheng, H.; Huang, Y.; Li, P.; Cai, G.; Zeng, Q. Herbal Textual Research and Character Identification of Southern Medicine Nanhaia speciosa. Lishizhen Med. Mater. Med. Res. 2018, 29, 1361–1362. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zu, B.; Jiang, J.; Long, L.; Liang, Y.; Tan, Z.; Lai, K. Research Overview of Edible Nanhaia speciosa Root Soup Products. Chin. Seas. 2020, 45, 133–136. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Niu, P.; Meng, Q.; He, X.; Wang, S.; Yi, Y.J.; Zhang, Y.J. Study on ultrasonic-assisted extraction process and antioxidant activity of total alkaloids from Millettia speciosa Champ. Food Sci. Technol. 2023, 48, 216–222. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Y.R.; Peng, L.S.; Xiao, J. Research progress on main chemical constituents and pharmacological effects of Millettia speciosa Champ. J. Hunan Univ. Chin. Med. 2020, 40, 503–506. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, C.; Mo, Y.Y.; Feng, S.S.; Meng, M.W.; Chen, S.Y.; Huang, H.M.; Ling, X.; Song, H.; Liang, Y.H.; Ou, S.F.; et al. Urinary metabonomics study of anti-depressive mechanisms of Millettia speciosa Champ on rats with chronic unpredictable mild stress-induced depression. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2021, 205, 114338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Wang, J.; Wang, Y.; Chen, M.; Shi, X.; Zhou, X.; Zhang, Z. Phytochemistry and antioxidant activities of the rhizome and radix of Millettia speciosa based on UHPLC-Q-Exactive Orbitrap-MS. Molecules 2022, 27, 7398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Sun, W.; Xu, B.; Wu, E.; Cui, Y.; Hao, K.; Zhang, G.; Zhou, C.; Xu, Y.; Li, J.; et al. Polysaccharides from the roots of millettia speciosa champ modulate gut health and ameliorate cyclophosphamide-induced intestinal injury and immunosuppression. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 766296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, M.; Zhang, M.; Yang, Q.; Wang, Q.; Ma, B.; Li, Z.; Cheng, W.; Tang, H.; Feng, S.; Wang, Z. Metabolomic profiling of M. speciosa champ at different growth stages. Food Chem. 2022, 376, 131941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.Y.; Ma, W.Y.; Wang, Q.L.; Yang, Q.; Yan, X.X.; Tang, H.; Li, Z.Y.; Li, Y.Y.; Feng, S.X.; Wang, Z.N. Flavonoid-enriched extract from Millettia speciosa Champ prevents obesity by regulating thermogenesis and lipid metabolism in high-fat diet–induced obese C57BL/6 mice. Food Sci. Nutr. 2022, 10, 445–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Liu, P.; Lou, N.; He, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Li, A. Overview of research on the consumption of Nanhaia speciosa. Food Res. Dev. 2016, 47, 168–172. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Yang, D.; Liu, X.; Fan, P.; Wu, Y. Traditional usage of wild edible plants reflecting the dietary habits and the awareness of health care of LI minority in Baoting and Lingshui, Hainan Island, China: An ethnobotanical approach. Bangladesh J. Bot. 2019, 48, 279–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hang, Y.; Gong, L.; Dong, X.; Xue, D. Research Progress on Development and Utilization of Nanyao Nanhaia speciosa. Spec. Wild Econ. Anim. Plant Res. 2023, 1, 1–13. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Feng, Y.M.; Huang, C.Y.; Lin, Z.; Li, J.; Zhao, B. Research progress on cultivation of Millettia speciosa in Lingnan area. For. Sci. Technol. 2022, 6, 51–54. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, W.; Jiang, Z.T.; Mo, Y.L.; Jiang, X.J.; Wei, X.; Shi, Y.C. Effects of different cultivation measures on yield of Nanhaia speciosa. J. Guangxi Acad. Sci. 2023, 39, 71–77. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Boczkowska, M.; Łapiński, B.; Kordulasińska, I.; Dostatny, D.F.; Czembor, J.H. Promoting the use of common oat genetic resources through diversity analysis and core collection construction. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, 0167855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fallahi, F.; Abdossi, V.; Bagheri, M.; Ghanbari Jahromi, M.; Mozafari, H. Genetic diversity analysis of Eggplant Germplasm from Iran: Assessments by morphological and SSR markers. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2022, 49, 11705–11714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, W.; Lu, M.; Peng, J.; Lv, H.; Shi, J.; Zhang, S.; Liu, Z.; Duan, J.; Chen, D.; Dai, W.; et al. Nontargeted and targeted metabolomics analysis provides novel insight into nonvolatile metabolites in Jianghua Kucha tea germplasm (Camellia sinensis var. assamica cv. Jianghua). Food Chem. X 2022, 13, 100270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chapepa, B.; Mapuranga, R.; Manjeru, P. Characterisation of upland cotton grown in Zimbabwe using agronomical and morphological markers for Verticillium wilt tolerance. Cogent. Food Agric. 2020, 6, 1766734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hebert, P.D.; Cywinska, A.; Ball, S.L.; DeWaard, J.R. Biological identifications through DNA barcodes. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. B Biol. Sci. 2003, 270, 313–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hajibabaei, M.; Singer, G.A.; Hebert, P.D.; Hickey, D.A. DNA barcoding: How it complements taxonomy, molecular phylogenetics and population genetics. Trends Genet. 2007, 23, 167–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, L.; Li, Y.; Mao, X.; Wang, Y. Metabolomics applications for plant-based foods origin tracing, cultivars identification and processing: Feasibility and future aspects. Food Chem. 2024, 449, 139227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nkhoma, N.; Shimelis, H.; Laing, M.D.; Shayanowako, A.; Mathew, I. Assessing the genetic diversity of cowpea [Vigna unguiculata (L.) Walp.] germplasm collections using phenotypic traits and SNP markers. BMC Genet. 2020, 21, 110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kress, W.J.; Erickson, D.L.; Swenson, N.G.; Thompson, J.; Uriarte, M.; Zimmerman, J.K. DNA barcoding of invasive species in the flora of Ontario, Canada. Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2011, 11, 1012–1021. [Google Scholar]
- Arus, P.; Ortan, T.J. Inheritance patterns and linkage relationships of eight genes of celery. J. Hered. 1984, 75, 11–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Zhao, Z.; Li, Z.; Zeng, R.; Li, W. Distinguishing features of Prunus humilis, P. japonica, P. pedunculata seeds and their adulterant based on DNA barcoding, morphological characterization, and chemical profiles. Fitoterapia 2024, 175, 105942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oliveira, M.M.; Cruz-Tirado, J.P.; Barbin, D.F. Nontargeted analytical methods as a powerful tool for the authentication of spices and herbs: A review. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2019, 18, 670–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, S.; Yang, Y.; Wang, J.; Chen, X.; Liu, T.; Zhuo, Q. Analysis of differences between unifloral honeys from different botanical origins based on non-targeted metabolomics by ultra-high performance liquid chromatography-quadrupole time-of-flight mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. 2021, 39, 291–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Esteki, M.; Shahsavari, Z.; Simal-Gandara, J. Gas chromatographic fingerprinting coupled to chemometrics for food authentication. Food Rev. Int. 2020, 36, 384–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.Y.; Zhou, Q.; Yang, J.; Hong, D.Y.; Zhang, D.Q. DNA barcoding of Paeonia (Paeoniaceae) using psbk-psbl and atpF-atpH spacer regions. PLoS ONE. 2012, 7, e41870. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, P. Research on Quality Standards of Nanhaia speciosa Medicinal Material. Master’s Thesis, Guangzhou University of Chinese Medicine, Guangzhou, China, 2019. (In Chinese). [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, S.; Sharma, V.; Chaudhary, S.; Tyagi, A.; Mishra, P.; Priyadarshini, A.; Singh, G.P. Evaluation of phenotypic and metabolic diversity in wheat genotypes under drought stress. Front. Plant Sci. 2020, 11, 553. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, M.J.; Moon, Y.; Tou, J.C.; Mou, B.; Waterland, N.L. Nutritional and phytochemical variability in lettuce cultivars: Implications for breeding and consumer health. Food Chem. 2016, 205, 375–383. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, J.; Wu, X.I.; Liu, C.; Newmaster, S.; Ragupathy, S.; Kress, W.J. Progress in the use of DNA barcodes in the identification and classification of medicinal plants. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2021, 208, 111691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blaxter, M.L. The promise of a DNA taxonomy. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. B. Biol. Sci. 2004, 359, 669–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sucher, N.J.; Carles, M.C. DNA barcoding of medicinal plant species for authentication and quality control. Planta Med. 2014, 80, 288–294. [Google Scholar]
- Little, D.P.; Stevenson, D.W. A comparison of algorithms for the identification of specimens using DNA barcodes: Examples from gymnosperms. Cladistics 2007, 23, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meier, R.; Shiyang, K.; Vaidya, G.; Ng, P.K. DNA barcoding and taxonomy in Diptera: A tale of high intraspecific variability and low identification success. Syst. Biol. 2006, 55, 715–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moritz, C.; Cicero, C. DNA barcoding: Promise and pitfalls. PLoS Biol. 2004, 2, 354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Will, K.W.; Rubinoff, D. Myth of the molecule: DNA barcodes for species cannot replace morphology for identification and classification. Cladistics 2004, 20, 47–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Will, K.W.; Mishler, B.D.; Wheeler, Q.D. The perils of DNA barcoding and the need for integrative taxonomy. Syst. Biol. 2005, 54, 844–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rose, J.P.; Toledo, C.A.; Lemmon, E.M.; Lemmon, A.R.; Sytsma, K.J. Out of sight, out of mind: Widespread nuclear and plastid-nuclear discordance in the flowering plant genus Polemonium (Polemoniaceae) suggests widespread historical gene flow despite limited nuclear signal. Syst. Biol. 2021, 70, 162–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hollingsworth, P.M.; Forrest, L.L.; Spouge, J.L.; Hajibabaei, M.; Ratnasingham, S.; van der Bank, M.; Chase, M.W.; Cowan, R.S.; Erickson, D.L.; Fazekas, A.J. Selecting barcoding loci for plants: Evaluation of seven candidate loci with species-level sampling in three divergent groups of land plants. Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2009, 9, 439–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, W.; Gao, Y.; Xie, W.; Gong, L.; Lu, K.; Wang, W.; Li, Y.; Liu, X.; Zhang, H.; Dong, H. Multi-omics revolution in crop improvement: From data integration to predictive breeding. Trends Plant Sci. 2022, 27, 844–856. [Google Scholar]
- Hörandl, E.; Emadzade, K. Evolutionary classification: A case study on the diverse plant genus Ranunculus L.(Ranunculaceae). Perspect. Plant Ecol. Evol. Syst. 2012, 14, 310–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drisya Ravi, R.S.; Nair, B.R.; Siril, E.A. Morphological diversity, phenotypic and genotypic variance and heritability estimates in Moringa oleifera Lam: A less used vegetable with substantial nutritional value. Genet. Resour. Crop Evol. 2021, 68, 3241–3256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, T.; Lu, J.; Zhang, W.; Wang, W.; Wan, Y.; Pei, Y.; Mao, F.; Wang, L.; Li, J. Evaluation of genetic variation of morphological and clubroot-resistance traits of radish and metabonomic analysis of clubroot-resistant cultivar. Sci. Hortic. 2023, 321, 112272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Yan, J.; Jiang, S.; Li, X.; Min, H.; Wang, X.; Hao, D. Resequencing 250 soybean accessions: New insights into genes associated with agronomic traits and genetic networks. Geno. Prot. Bioinform. 2022, 20, 29–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lasky, J.R.; Des Marais, D.L.; McKay, J.K.; Richards, J.H.; Juenger, T.E.; Keitt, T.H. Characterizing genomic variation of Arabidopsis thaliana: The roles of geography and climate. Mol. Ecol. 2012, 21, 5512–5529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jacob, F.; Vernaldi, S.; Maekawa, T. The evolutionary origin of complex features in metabolites and enzymes. Nat Commun. 2022, 13, 7141. [Google Scholar]
- Li, M.; Liu, M.; Wang, B.; Shi, L. Metabolomics analysis of stem extracts from Dalbergia sissoo. Molecules 2022, 27, 1982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alami, M.M.; Ouyang, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Shu, S.; Yang, G.; Mei, Z.; Wang, X. The current developments in medicinal plant genomics enabled the diversification of secondary metabolites’ biosynthesis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 15932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pichersky, E.; Lewinsohn, E. Convergent evolution in plant specialized metabolism. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 2011, 62, 549–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hacquard, S.; Spaepen, S.; Garrido-Oter, R.; Schulze-Lefert, P. Interplay between innate immunity and the plant microbiota. Annu. Rev. Phytopathol. 2017, 55, 565–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strauss, J.; Reyes-Dominguez, Y. Regulation of secondary metabolism by chromatin structure and epigenetic codes. Fungal Genet. Biol. 2011, 48, 62–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bose, U.; Juhász, A.; Broadbent, J.A.; Komatsu, S.; Colgrave, M.L. Multi-omics strategies for decoding smoke-assisted germination pathways and seed vigour. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 7512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolfender, J.L.; Marti, G.; Thomas, A.; Bertrand, S. Plant metabolomics: From holistic data to relevant biomarkers. Curr. Med. Chem. 2019, 26, 1925–1946. [Google Scholar]
- Crossa, J.; Pérez-Rodríguez, P.; Cuevas, J.; Montesinos-López, O.; Jarquín, D.; Campos, G.; Burgueño, J.; González-Camacho, J.M.; Pérez-Elizalde, S.; Beyene, Y. Genomic selection in plant breeding: Methods, models, and perspectives. Trends Plant Sci. 2017, 22, 961–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| Naming | Source (Town, City, Province) | GPS Positioning (North Latitude, East Longitude) |
|---|---|---|
| NDL-1 | Fulin, Yunfu, Guangdong | 22.6830161, 111.9125324 |
| NDL-2 | 22.6939529, 111.9153171 | |
| NDL-3 | Xingping, Yangshuo, Guangxi | 24.9220809, 110.5309201 |
| NDL-4 | 24.9396041, 110.5366816 | |
| NDL-5 | Yao Gu, Yunfu, Guangdong | 22.8870317, 112.2879645 |
| NDL-6 | 22.8872130, 112.2874863 | |
| NDL-7 | 22.8504033, 112.3070249 | |
| NDL-8 | 22.8504489, 112.3072114 | |
| NDL-9 | 22.8485882, 112.3068318 | |
| NDL-10 | 22.8469868, 112.3067984 | |
| NDL-11 | Gaoliang, Deqing, Guangdong | 23.1771246, 111.9555338 |
| NDL-12 | 23.2899006, 111.9535036 | |
| NDL-13 | 23.2899567, 111.9535581 | |
| NDL-14 | Bolao, Lingshan, Guangxi | 22.1199661, 109.1271791 |
| NDL-15 | 22.1071753, 109.1192201 | |
| NDL-16 | 22.1215900, 109.1172618 | |
| NDL-17 | Heshe, Danzhou, Hainan | 19.5938770, 109.7374584 |
| NDL-18 | Heqing, Danzhou, Hainan | 19.5279646, 109.6673995 |
| NDL-19 | 19.5355961, 109.6783948 |
| DNA Barcode | Forward and Reverse Primers | Primer Sequences (5′–3′) | PCR Reaction Program |
|---|---|---|---|
| psbk-psbl | psbk-psbl-F | TTAGCATTTGTTTGGCAAG | 95 °C, 3 min; 95 °C, 15 s, 49.6 °C, 15 s, and 72 °C, 90 s, 35×; 72 °C, 5 min |
| psbk-psbl-R | AAAGTTTGAGAGTAAGCTA | ||
| atpF-atpH | atpF-atpH-F | ACTCGCACACACTCCCTTTCC | 95 °C, 3 min; 95 °C, 15 s, 56.1 °C, 15 s, and 72 °C, 90 s, 35×; 72 °C, 5 min |
| atpF-atpH-R | GCTTTTATGGAAGCTTTAACAAT |
| Level | Observed Value |
|---|---|
| 1 | X1 ≤ X − 2σ |
| 2 | X − 2σ < X2 ≤ X − σ |
| 3 | X − σ < X3 ≤ X |
| 4 | X < X4 ≤ X + σ |
| 5 | X + σ < X5 ≤ X + 2σ |
| 6 | X6 > X + 2σ |
| Level | Observed Value | Leaflet Length | Leaflet Width | Root Diameter | Vitamin B3 | Protein | Total Sugars |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | X1 ≤ X − 2σ | 0.5 | 0.5 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 |
| 2 | X − 2σ < X2 ≤ X − σ | 1.0 | 1.0 | 2.0 | 2.0 | 2.0 | 2.0 |
| 3 | X − σ < X3 ≤ X | 1.5 | 1.5 | 3.0 | 3.0 | 3.0 | 3.0 |
| 4 | X < X4 ≤ X + σ | 2.0 | 2.0 | 4.0 | 4.0 | 4.0 | 4.0 |
| 5 | X + σ < X5 ≤ X + 2σ | 2.5 | 2.5 | 5.0 | 5.0 | 5.0 | 5.0 |
| 6 | X6 > X + 2σ | 3.0 | 3.0 | 6.0 | 6.0 | 6.0 | 6.0 |
| Level | Observed Value | Vitamin B3 | Total Sugars | Total Flavonoids | VIP Score | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| α,α- Trehalose | Hypaphorine | |||||
| 1 | X1 ≤ X − 2σ | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 |
| 2 | X − 2σ < X2 ≤ X − σ | 2.0 | 2.0 | 2.0 | 2.0 | 2.0 |
| 3 | X − σ < X3 ≤ X | 3.0 | 3.0 | 3.0 | 3.0 | 3.0 |
| 4 | X < X4 ≤ X + σ | 4.0 | 4.0 | 4.0 | 4.0 | 4.0 |
| 5 | X + σ < X5 ≤ X + 2σ | 5.0 | 5.0 | 5.0 | 5.0 | 5.0 |
| 6 | X6 > X + 2σ | 6.0 | 6.0 | 6.0 | 6.0 | 6.0 |
| Sequence | Alignment Length (bp) | GC Content (%) | Conserved Site | Conservation Index (%) | Variability Index (%) | Variable Sites | Parsimony Informative Sites |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| psbk-psbl | 444 | 28.05 | 426 | 95.9 | 4.1 | 18 | 10 |
| atpF-atpH | 599 | 25.04 | 547 | 91.3 | 8.7 | 52 | 33 |
| Sequence | Intraspecific Genetic Distance | Interspecific Genetic Distance | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Minimum | Maximum | Mean | Minimum | Maximum | Mean | |
| psbk-psbl | 0 | 0.0027 | 0.0021 | 0.0017 | 0.0568 | 0.0360 |
| atpF-atpH | 0 | 0.0786 | 0.0644 | 0.1743 | 1.2937 | 0.7431 |
| Sample | Leaf Length (cm) | Leaflet Length (cm) | Leaflet Width (cm) | Root Diameter (cm) | Vitamin B3 Content (μg/g) | Protein Content (mg/g) | Total Sugars Content (mg/g) | Total Flavonoids Content (mg/g) | Hypaphorine Content (mg/g) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NDL-1 | 19.7 ± 2.06 A | 8.97 ± 4.25 AB | 2.83 ± 1.30 BD | 0.70 ± 0.15 C | 29.25 ± 1.01 A | 0.89 ± 0.11 I | 43.00 ± 0.33 | 0.89 ± 0.07 | 1.94 ± 0.18 B |
| NDL-2 | 15.77 ± 1.72 ABC | 8.56 ± 2.20 ABC | 4.77 ± 1.45 A | 1.10 ± 0.36 ABC | 39.60 ± 0.50 C | 1.09 ± 0.14 J | 128.87 ± 0.81 A | 1.00 ± 0.02 E | 1.63 ± 0.09 A |
| NDL-3 | 12.26 ± 2.10 CD | 4.47 ± 0.38 E | 2.53 ± 0.45 C | 0.92 ± 0.22 ABC | 42.69 ± 0.75 D | 1.06 ± 0.07 J | 80.96 ± 1.94 D | 1.00 ± 0.03 F | 1.62 ± 0.11 A |
| NDL-4 | 7.77 ± 2.55 EF | 4.93 ± 0.45 DE | 1.70 ± 0.46 C | 1.17 ± 0.20 ABC | 43.51 ± 0.55 D | 0.36 ± 0.06 BC | 121.01 ± 0.23 E | 0.72 ± 0.08 A | 1.63 ± 0.14 A |
| NDL-5 | 12.70 ± 1.45 CD | 10.20 ± 1.97 A | 5.07 ± 1.45 A | 1.18 ± 0.36 ABC | 23.01 ± 0.48 | 0.62 ± 0.04 EF | 123.24 ± 0.27 | 0.86 ± 0.07 D | 1.93 ± 0.21 B |
| NDL-6 | 15.23 ± 2.00 BC | 6.06 ± 1.75 BCDE | 2.27 ± 0.45 C | 0.83 ± 0.35 BC | 36.50 ± 1.00 B | 0.59 ± 0.08 EF | 113.21 ± 0.48 | 0.80 ± 0.10 BC | 1.66 ± 0.54 |
| NDL-7 | 12.63 ± 1.65 CD | 4.81 ± 0.48 E | 4.88 ± 0.16 A | 1.13 ± 0.24 ABC | 60.69 ± 0.77 | 0.51 ± 0.04 DE | 109.21 ± 0.19 | 0.79 ± 0.08 B | 1.78 ± 0.38 |
| NDL-8 | 9.93 ± 1.08 DE | 8.93 ± 1.84 ABC | 1.60 ± 0.20 C | 1.52 ± 0.11 A | 11.57 ± 0.53 | 0.52 ± 0.03 DE | 122.58 ± 0.32 | 0.85 ± 0.01 | 1.91 ± 0.25 B |
| NDL-9 | 15.37 ± 1.35 BC | 6.08 ± 0.75 E | 1.81 ± 0.18 C | 0.73 ± 0.37 C | 43.83 ± 0.46 D | 0.84 ± 0.07 HI | 112.69 ± 0.57 | 0.83 ± 0.05 | 1.58 ± 0.13 |
| NDL-10 | 7.68 ± 2.38 EF | 4.98 ± 0.58 DE | 1.75 ± 0.52 C | 1.21 ± 0.17 ABC | 45.10 ± 0.64 E | 0.54 ± 0.03 DE | 122.21 ± 0.13 E | 0.73 ± 0.06 A | 1.53 ± 0.28 |
| NDL-11 | 4.83 ± 1.45 FG | 6.50 ± 2.10 BCDE | 4.97 ± 1.56 A | 1.31 ± 0.32 BC | 51.74 ± 0.62 | 0.37 ± 0.02 BC | 117.26 ± 0.36 B | 0.92 ± 0.10 E | 2.07 ± 0.33 C |
| NDL-12 | 9.73 ± 1.27 DE | 5.37 ± 1.90 CDE | 2.67 ± 0.65 C | 0.99 ± 0.31 ABC | 29.72 ± 0.50 A | 0.44 ± 0.02 CD | 109.42 ± 0.24 C | 1.04 ± 0.10 F | 1.96 ± 0.16 B |
| NDL-13 | 12.53 ± 2.09 CD | 4.37 ± 1.20 DE | 1.60 ± 0.20 C | 0.97 ± 0.20 ABC | 29.92 ± 0.61 A | 0.67 ± 0.03 FG | 95.93 ± 0.25 | 0.91 ± 0.06 | 0.94 ± 0.11 |
| NDL-14 | 3.78 ± 0.61 G | 7.73 ± 1.46 ABCD | 4.37 ± 1.42 AB | 1.42 ± 0.21 A | 47.78 ± 0.72 | 0.19 ± 0.05 A | 116.86 ± 0.66 B | 1.16 ± 0.09 F | 2.08 ± 0.34 C |
| NDL-15 | 12.53 ± 1.70 CD | 4.20 ± 1.05 E | 2.53 ± 0.45 C | 0.91 ± 0.24 ABC | 28.84 ± 0.65 A | 0.19 ± 0.06 A | 81.34 ± 0.23 D | 0.81 ± 0.06 C | 1.02 ± 0.23 |
| NDL-16 | 17.07 ± 2.42 AB | 3.83 ± 0.35 E | 1.67 ± 0.21 C | 0.81 ± 0.20 BC | 49.66 ± 0.61 | 0.27 ± 0.03 AB | 137.76 ± 0.26 | 0.92 ± 0.11 E | 1.61 ± 0.14 A |
| NDL-17 | 5.67 ± 2.50 FG | 4.30 ± 0.95 DE | 1.50 ± 0.20 C | 0.96 ± 0.46 ABC | 45.00 ± 0.78 E | 0.29 ± 0.07 AB | 108.61 ± 0.36 C | 0.87 ± 0.09 D | 1.35 ± 0.25 |
| NDL-18 | 15.83 ± 1.67 ABC | 8.59 ± 2.21 ABC | 4.81 ± 1.47 A | 1.12 ± 0.37 ABC | 38.96 ± 0.77 C | 0.38 ± 0.05 BC | 129.42 ± 1.58 A | 1.23 ± 0.10 | 1.71 ± 0.26 |
| NDL-19 | 7.77 ± 2.45 EF | 5.93 ± 0.65 E | 2.00 ± 0.10 C | 0.69 ± 0.27 C | 37.44 ± 0.44 B | 0.75 ± 0.06 GH | 88.91 ± 0.26 | 0.91 ± 0.07 E | 1.16 ± 0.13 |
| Traits | Mean ± SD | Range | CV (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Morphological | |||
| Leaf length/cm | 11.51 ± 4.22 | 3.78–19.70 | 36.66 |
| Leaflet length/cm | 6.25 ± 1.87 | 3.83–10.20 | 29.92 |
| Leaflet width/cm | 2.92 ± 1.31 | 1.50–5.07 | 44.86 |
| Root diameter/cm | 1.03 ± 0.22 | 0.69–1.52 | 21.36 |
| Biochemical | |||
| Vitamin B3 content μg/g | 38.67 ± 11.09 | 11.57–60.69 | 28.68 |
| Protein content mg/g | 0.56 ± 0.26 | 0.19–1.09 | 48.43 |
| Total sugar content mg/g | 108.55 ± 1.75 | 43.00–137.76 | 20.04 |
| Total flavonoids content mg/g | 0.91 ± 0.13 | 0.72–1.23 | 14.29 |
| Hypaphorine content mg/g | 1.64 ± 0.32 | 1.02–2.08 | 19.51 |
| Traits and Biochemical Characteristics | Distribution Frequency | H′ | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | ||
| Leaf length | 0.000 | 0.291 | 0.351 | 0.368 | 0.328 | 0.000 | 1.338 |
| Leaflet length | 0.000 | 0.328 | 0.364 | 0.237 | 0.328 | 0.155 | 1.412 |
| Leaflet width | 0.000 | 0.291 | 0.354 | 0.155 | 0.364 | 0.000 | 1.167 |
| Root diameter | 0.000 | 0.328 | 0.364 | 0.364 | 0.237 | 0.155 | 1.211 |
| Vitamin B3 content | 0.155 | 0.155 | 0.351 | 0.364 | 0.237 | 0.155 | 1.417 |
| Protein content | 0.000 | 0.328 | 0.368 | 0.328 | 0.291 | 0.155 | 1.470 |
| Total sugar content | 0.155 | 0.237 | 0.291 | 0.316 | 0.237 | 0.000 | 1.236 |
| Total flavonoids content | 0.000 | 0.237 | 0.316 | 0.328 | 0.237 | 0.000 | 1.118 |
| Hypaphorine content | 0.155 | 0.237 | 0.368 | 0.368 | 0.237 | 0.000 | 1.365 |
| Traits and Biochemical Characteristics | PCA | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| PC1 | PC2 | PC3 | |
| Vitamin B3 content | 0.057 | −0.483 | 0.822 |
| Protein content | −0.266 | 0.712 | 0.139 |
| Total sugars content | 0.532 | −0.427 | 0.011 |
| Total flavonoids content | 0.497 | 0.269 | 0.327 |
| Hypaphorine content | 0.767 | −0.310 | 0.362 |
| Eigenvalue (λ) | 2.862 | 2.151 | 1.225 |
| Contribution rate (%) | 31.804 | 23.895 | 13.614 |
| Cumulative contribution rate (%) | 31.804 | 55.699 | 69.313 |
| Leaf length | −0.308 | 0.708 | 0.226 |
| Leaflet length | 0.626 | 0.667 | −0.269 |
| Leaflet width | 0.743 | 0.270 | 0.406 |
| Root diameter | 0.794 | −0.310 | −0.362 |
| Number | Key Metabolite Markers | Molecular Formula | Molecular Weight | Retention Time (min) | VIP Score |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | α,α-Trehalose | C12H22O11 | 342.1159 | 0.881 | 6.5543 |
| 2 | Citric acid | C6H8O7 | 192.0269 | 1.204 | 2.6019 |
| 3 | 2-Hydroxycinnamic acid | C9H8O3 | 164.0474 | 1.221 | 0.7748 |
| 4 | trans-3-Indoleacrylic acid | C11H9NO2 | 187.0633 | 3.075 | 3.6106 |
| 5 | Hypaphorine | C14H18N2O2 | 246.1367 | 3.496 | 7.6284 |
| 6 | 4′,6-Dimethoxyisoflavone-7-O-β-D-glucopyranoside | C23H24O10 | 460.1373 | 5.766 | 0.1194 |
| 7 | 3-Hydroxybenzoic acid | C7H6O3 | 138.0316 | 5.767 | 0.1050 |
| 8 | 1-Octen-3-yl-6-O-[(2R,3R,4R)-3,4-dihydroxy-4-(hydroxymethyl)tetrahydro-2-furanyl]-β-D-glucopyranoside | C19H34O10 | 422.2151 | 5.82 | 0.3250 |
| 9 | 6-Methoxyflavanone | C16H14O3 | 254.0943 | 6.953 | 0.6759 |
| 10 | Formononetin | C16H12O4 | 268.0736 | 7.484 | 1.7185 |
| 11 | (−)-Maackiain | C16H12O5 | 284.0687 | 7.886 | 0.1110 |
| 12 | 1,3:2,4-Bis(3,4-dimethylobenzylideno) sorbitol | C24H30O6 | 414.2045 | 9.195 | 4.7971 |
| Germplasm | Leaflet Length | Leaflet Width | Root Diameter | Vitamin B3 | Protein | Total Sugars | Total Score |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NDL-1 | 2.5 | 1.5 | 2.0 | 1.0 | 5.0 | 1.0 | 13.0 |
| NDL-2 | 2.5 | 2.5 | 4.0 | 4.0 | 6.0 | 4.0 | 23.0 |
| NDL-3 | 1.5 | 1.5 | 3.0 | 4.0 | 5.0 | 2.0 | 17.0 |
| NDL-4 | 1.5 | 1.5 | 4.0 | 4.0 | 3.0 | 4.0 | 18.0 |
| NDL-5 | 2.5 | 2.5 | 4.0 | 2.0 | 4.0 | 4.0 | 19.0 |
| NDL-6 | 1.5 | 1.5 | 3.0 | 3.0 | 4.0 | 4.0 | 17.0 |
| NDL-7 | 1.5 | 2.5 | 4.0 | 5.0 | 3.0 | 4.0 | 20.0 |
| NDL-8 | 2.5 | 1.5 | 6.0 | 1.0 | 3.0 | 4.0 | 18.0 |
| NDL-9 | 1.5 | 1.5 | 2.0 | 4.0 | 5.0 | 4.0 | 18.0 |
| NDL-10 | 1.5 | 1.5 | 4.0 | 4.0 | 3.0 | 4.0 | 18.0 |
| NDL-11 | 2.0 | 2.5 | 5.0 | 5.0 | 3.0 | 4.0 | 21.5 |
| NDL-12 | 1.5 | 1.5 | 3.0 | 3.0 | 3.0 | 4.0 | 16.0 |
| NDL-13 | 1.5 | 1.5 | 3.0 | 3.0 | 4.0 | 3.0 | 16.0 |
| NDL-14 | 2.0 | 2.5 | 5.0 | 4.0 | 2.0 | 4.0 | 19.5 |
| NDL-15 | 1.0 | 1.5 | 3.0 | 3.0 | 2.0 | 2.0 | 12.5 |
| NDL-16 | 1.0 | 1.5 | 2.0 | 5.0 | 2.0 | 5.0 | 16.5 |
| NDL-17 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 3.0 | 4.0 | 2.0 | 4.0 | 15.0 |
| NDL-18 | 2.5 | 2.5 | 4.0 | 4.0 | 3.0 | 4.0 | 20.0 |
| NDL-19 | 1.5 | 1.5 | 2.0 | 3.0 | 4.0 | 3.0 | 15.0 |
| Germplasm | Vitamin B3 | Total Sugars | Total Flavonoids | VIP Score | Total Score | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| α,α- Trehalose | Hypaphorine | |||||
| NDL-1 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 3.0 | 2.0 | 4.0 | 11.0 |
| NDL-2 | 4.0 | 4.0 | 4.0 | 6.0 | 3.0 | 21.0 |
| NDL-3 | 4.0 | 2.0 | 4.0 | 4.0 | 3.0 | 17.0 |
| NDL-4 | 4.0 | 4.0 | 2.0 | 3.0 | 3.0 | 16.0 |
| NDL-5 | 2.0 | 4.0 | 3.0 | 2.0 | 4.0 | 15.0 |
| NDL-6 | 3.0 | 4.0 | 3.0 | 2.0 | 4.0 | 16.0 |
| NDL-7 | 5.0 | 4.0 | 3.0 | 2.0 | 4.0 | 18.0 |
| NDL-8 | 1.0 | 4.0 | 3.0 | 3.0 | 4.0 | 15.0 |
| NDL-9 | 4.0 | 4.0 | 3.0 | 4.0 | 3.0 | 18.0 |
| NDL-10 | 4.0 | 4.0 | 2.0 | 4.0 | 3.0 | 17.0 |
| NDL-11 | 5.0 | 4.0 | 4.0 | 2.0 | 5.0 | 20.0 |
| NDL-12 | 3.0 | 4.0 | 5.0 | 6.0 | 5.0 | 23.0 |
| NDL-13 | 3.0 | 3.0 | 4.0 | 3.0 | 1.0 | 14.0 |
| NDL-14 | 4.0 | 4.0 | 5.0 | 2.0 | 5.0 | 20.0 |
| NDL-15 | 3.0 | 2.0 | 3.0 | 6.0 | 2.0 | 16.0 |
| NDL-16 | 5.0 | 5.0 | 4.0 | 1.0 | 3.0 | 18.0 |
| NDL-17 | 4.0 | 4.0 | 3.0 | 2.0 | 3.0 | 16.0 |
| NDL-18 | 4.0 | 4.0 | 6.0 | 5.0 | 5.0 | 24.0 |
| NDL-19 | 3.0 | 3.0 | 3.0 | 1.0 | 2.0 | 12.0 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yang, J.; Lai, N.; Zheng, Y.; Ji, R.; Wang, P.; Dai, W.; Cheng, G.; He, X. Comprehensive Evaluation of Nanhaia speciosa Germplasm Resources Using Agronomic Traits, Molecular Markers, and Metabolomics. Agronomy 2025, 15, 508. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15030508
Yang J, Lai N, Zheng Y, Ji R, Wang P, Dai W, Cheng G, He X. Comprehensive Evaluation of Nanhaia speciosa Germplasm Resources Using Agronomic Traits, Molecular Markers, and Metabolomics. Agronomy. 2025; 15(3):508. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15030508
Chicago/Turabian StyleYang, Jing, Nanchen Lai, Yiqin Zheng, Ruifeng Ji, Ping Wang, Wei Dai, Gantao Cheng, and Xin He. 2025. "Comprehensive Evaluation of Nanhaia speciosa Germplasm Resources Using Agronomic Traits, Molecular Markers, and Metabolomics" Agronomy 15, no. 3: 508. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15030508
APA StyleYang, J., Lai, N., Zheng, Y., Ji, R., Wang, P., Dai, W., Cheng, G., & He, X. (2025). Comprehensive Evaluation of Nanhaia speciosa Germplasm Resources Using Agronomic Traits, Molecular Markers, and Metabolomics. Agronomy, 15(3), 508. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15030508






