Soil Nitrification Potential Influences the Performance of Nitrification Inhibitors DCD and DMPP in Cropped and Non-Cropped Soils
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Soil Sampling
2.2. Soil Incubation and Nitrification Potential Measurement
2.3. Data Analysis
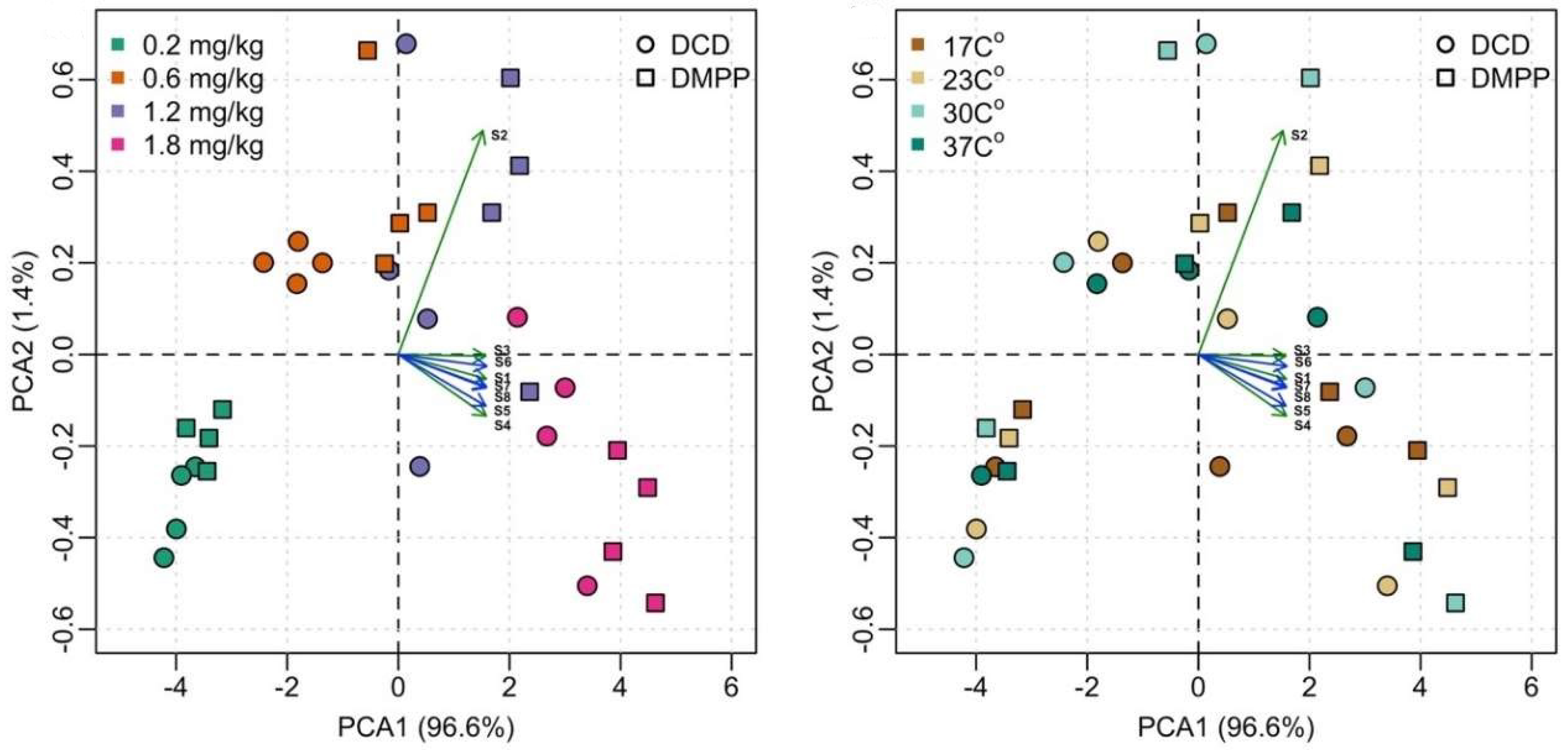
3. Results
3.1. Nitrification Potential Among Land-Use Type and Temperatures
3.2. Effect of Soil NP Rates on NI Effectiveness
3.2.1. Variation Among NI Application Rates and Temperature
3.2.2. Variation among NI types
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Coskun, D.; Britto, D.T.; Shi, W.; Kronzucker, H.J. Nitrogen transformations in modern agriculture and the role of biological nitrification inhibition. Nat. Plants 2017, 3, 17074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taylor, A.E.; Myrold, D.D.; Bottomley, P.J. Temperature affects the kinetics of nitrite oxidation and nitrification coupling in four agricultural soils. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2019, 107523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, A.E.; Giguere, A.T.; Zoebelein, C.M.; Myrold, D.D.; Bottomley, P.J. Modeling of soil nitrification responses to temperature reveals thermodynamic differences between ammonia-oxidizing activity of archaea and bacteria. ISME J. 2017, 11, 896–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shaw, L.J.; Nicol, G.W.; Smith, Z.; Fear, J.; Prosser, J.I.; Baggs, E.M. Nitrosospira spp. can produce nitrous oxide via a nitrifier denitrification pathway. Environ. Microbiol. 2006, 8, 214–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Firestone, M.K.; Davidson, E.A. Microbiological basis of NO and N2O production and consumption in soil. Exch. Trace Gases Terr. Ecosyst. Atmos. 1989, 47, 7–21. [Google Scholar]
- Font-Palma, C. Methods for the Treatment of Cattle Manure—A Review. C J. Carbon Res. 2019, 5, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilsanz, C.; Báez, D.; Misselbrook, T.H.; Dhanoa, M.S.; Cárdenas, L.M. Development of emission factors and efficiency of two nitrification inhibitors, DCD and DMPP. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2016, 216, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lam, S.K.; Suter, H.; Mosier, A.R.; Chen, D. Using nitrification inhibitors to mitigate agricultural N2O emission: A double-edged sword? Glob. Chang. Biol. 2017, 23, 485–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Friedl, J.; Scheer, C.; Rowlings, D.W.; Mumford, M.T.; Grace, P.R. The nitrification inhibitor DMPP (3, 4-dimethylpyrazole phosphate) reduces N2 emissions from intensively managed pastures in subtropical Australia. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2017, 108, 55–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rose, T.J.; Wood, R.H.; Rose, M.T.; Van Zwieten, L. A re-evaluation of the agronomic effectiveness of the nitrification inhibitors DCD and DMPP and the urease inhibitor NBPT. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2018, 252, 69–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, Y.; Di, H.J.; Cameron, K.C.; He, J.Z. Effects of nitrogen application rate and a nitrification inhibitor dicyandiamide on ammonia oxidizers and N2O emissions in a grazed pasture soil. Sci. Total Environ. 2013, 465, 125–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, J.; Saggar, S.; Giltrap, D.L.; Bolan, N.S. Decomposition of dicyandiamide (DCD) in three contrasting soils and its effect on nitrous oxide emission, soil respiratory activity, and microbial biomass—An incubation study. Soil Res. 2008, 46, 517–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaman, M.; Blennerhassett, J.D. Effects of the different rates of urease and nitrification inhibitors on gaseous emissions of ammonia and nitrous oxide, nitrate leaching and pasture production from urine patches in an intensive grazed pasture system. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2010, 136, 236–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keener, W.K.; Arp, D.J. Kinetic studies of ammonia monooxygenase inhibition in Nitrosomonas europaea by hydrocarbons and halogenated hydrocarbons in an optimized whole-cell assay. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1993, 59, 2501–2510. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, S.N.; Verma, A. Environmental review: The potential of nitrification inhibitors to manage the pollution effect of nitrogen fertilizers in agricultural and other soils: A review. Environ. Pract. 2007, 9, 266–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di, H.J.; Cameron, K.C. Inhibition of ammonium oxidation by a liquid formulation of 3, 4-Dimethylpyrazole phosphate (DMPP) compared with a dicyandiamide (DCD) solution in six New Zealand grazed grassland soils. J. Soils Sediments 2011, 11, 1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, X.; Duan, Y.; Schramm, A.; Eriksen, J.; Petersen, S.O. 3, 4-Dimethylpyrazole phosphate (DMPP) reduces activity of ammonia oxidizers without adverse effects on non-target soil microorganisms and functions. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2016, 105, 67–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menéndez, S.; Barrena, I.; Setien, I.; González-Murua, C.; Estavillo, J.M. Efficiency of nitrification inhibitor DMPP to reduce nitrous oxide emissions under different temperature and moisture conditions. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2012, 53, 82–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Irigoyen, I.; Muro, J.; Azpilikueta, M.; Aparicio-Tejo, P.; Lamsfus, C. Ammonium oxidation kinetics in the presence of nitrification inhibitors DCD and DMPP at various temperatures. Soil Res. 2003, 41, 1177–1183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, T.; Suter, H.; Liu, R.; Yuan, S.; Chen, D. Effects of nitrification inhibitors on gross N nitrification rate, ammonia oxidizers, and N2O production under different temperatures in two pasture soils. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 28344–28354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Qi, L.; Bi, Q.; Dai, P.; Sun, D.; Sun, C.; Liu, W.; Lu, L.; Ni, W.; Lin, X. Comparative effects of 3, 4-dimethylpyrazole phosphate (DMPP) and dicyandiamide (DCD) on ammonia-oxidizing bacteria and archaea in a vegetable soil. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2015, 99, 477–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, X.X.; Zhang, L.L.; Wu, Z.J.; Li, D.P.; Shang, Z.C.; Gong, P. Effects of the nitrification inhibitor DMPP on soil bacterial community in a Cambisol in northeast China. J. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 2013, 13, 580–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di, H.J.; Cameron, K.C. Nitrous oxide emissions from two dairy pasture soils as affected by different rates of a fine particle suspension nitrification inhibitor, dicyandiamide. Biol. Fertil. Soils 2006, 42, 472–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruser, R.; Schulz, R. The effect of nitrification inhibitors on the nitrous oxide (N2O) release from agricultural soils—A review. J. Plant Nutr. Soil Sci. 2015, 178, 171–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vitale, L.; Tedeschi, A.; Polimeno, F.; Ottaiano, L.; Maglione, G.; Arena, C.; De Marco, A.; Magliulo, V. Water regime affects soil N2O emission and tomato yield grown under different types of fertilisers. Ital. J. Agron. 2018, 74–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vitale, L.; Ottaiano, L.; Polimeno, F.; Maglione, G.; Amato, U.; Arena, C.; Di Tommasi, P.; Mori, M.; Magliulo, V. Effects of 3, 4-dimethylphyrazole phosphate-added nitrogen fertilizers on crop growth and N2O emissions in Southern Italy. Plant Soil Environ. 2013, 59, 517–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akiyama, H.; Yan, X.; Yagi, K. Evaluation of effectiveness of enhanced-efficiency fertilizers as mitigation options for N2O and NO emissions from agricultural soils: Meta-analysis. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2010, 16, 1837–1846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barth, G.; Von Tucher, S.; Schmidhalter, U. Effectiveness of 3, 4-dimethylpyrazole phosphate as nitriflcation inhibitor in soil as influenced by inhibitor concentration, application form, and soil matric potential. Pedosphere 2008, 18, 378–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guardia, G.; Marsden, K.A.; Vallejo, A.; Jones, D.L.; Chadwick, D.R. Determining the influence of environmental and edaphic factors on the fate of the nitrification inhibitors DCD and DMPP in soil. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 624, 1202–1212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McGeough, K.L.; Watson, C.J.; Müller, C.; Laughlin, R.J.; Chadwick, D.R. Evidence that the efficacy of the nitrification inhibitor dicyandiamide (DCD) is affected by soil properties in UK soils. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2016, 94, 222–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelliher, F.M.; Clough, T.J.; Clark, H.; Rys, G.; Sedcole, J.R. The temperature dependence of dicyandiamide (DCD) degradation in soils: A data synthesis. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2008, 40, 1878–1882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaves, B.; Opoku, A.; De Neve, S.; Boeckx, P.; Van Cleemput, O.; Hofman, G. Influence of DCD and DMPP on soil N dynamics after incorporation of vegetable crop residues. Biol. Fertil. Soils 2006, 43, 62–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marsden, K.A.; Marín-Martínez, A.J.; Vallejo, A.; Hill, P.W.; Jones, D.L.; Chadwick, D.R. The mobility of nitrification inhibitors under simulated ruminant urine deposition and rainfall: A comparison between DCD and DMPP. Biol. Fertil. Soils 2016, 52, 491–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, P.; Zhang, L.; Wu, Z.; Shang, Z.; Li, D. Does the nitrification inhibitor dicyandiamide affect the abundance of ammonia-oxidizing bacteria and archaea in a Hap-Udic Luvisol? J. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 2013, 13, 35–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gong, P.; Zhang, L.L.; WU, Z.J.; Chen, Z.H.; Chen, L.J. Responses of ammonia-oxidizing bacteria and archaea in two agricultural soils to nitrification inhibitors DCD and DMPP: A pot experiment. Pedosphere 2013, 23, 729–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stempfhuber, B.; Engel, M.; Fischer, D.; Neskovic-Prit, G.; Wubet, T.; Schöning, I.; Gubry-Rangin, C.; Kublik, S.; Schloter-Hai, B.; Rattei, T. pH as a driver for ammonia-oxidizing archaea in forest soils. Microb. Ecol. 2015, 69, 879–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouskill, N.J.; Eveillard, D.; Chien, D.; Jayakumar, A.; Ward, B.B. Environmental factors determining ammonia-oxidizing organism distribution and diversity in marine environments. Environ. Microbiol. 2012, 14, 714–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erguder, T.H.; Boon, N.; Wittebolle, L.; Marzorati, M.; Verstraete, W. Environmental factors shaping the ecological niches of ammonia-oxidizing archaea. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2009, 33, 855–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mukhtar, H.; Lin, Y.P.; Anthony, J. Ammonia Oxidizing Archaea and Bacteria in East Asian Paddy Soils—A Mini Review. Environments 2017, 4, 84. [Google Scholar]
- Duan, P.; Wu, Z.; Zhang, Q.; Fan, C.; Xiong, Z. Thermodynamic responses of ammonia-oxidizing archaea and bacteria explain N2O production from greenhouse vegetable soils. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2018, 120, 37–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukhtar, H.; Lin, Y.P.; Lin, C.M.; Petway, J.R. Assessing Thermodynamic Parameter Sensitivity for Simulating Temperature Response of Soil Nitrification. Environ. Sci. Process. Impacts 2019, 21, 1596–1608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suter, H.; Chen, D.; Li, H.; Edis, R.; Walker, C. Comparison of the ability of the nitrification inhibitors DCD and DMPP to reduce nitrification and N2O emissions from nitrogen fertilisers. In Proceedings of the 19th World Congress of Soils Science, Brisbane, Australia, 1–6 August 2010; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Torralbo, F.; Menéndez, S.; Barrena, I.; Estavillo, J.M.; Marino, D.; González-Murua, C. Dimethyl pyrazol-based nitrification inhibitors effect on nitrifying and denitrifying bacteria to mitigate N2O emission. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 13810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barth, G.; Von Tucher, S.; Schmidhalter, U. Influence of soil parameters on the effect of 3, 4-dimethylpyrazole-phosphate as a nitrification inhibitor. Biol. Fertil. Soils 2001, 34, 98–102. [Google Scholar]
- Tourna, M.; Stieglmeier, M.; Spang, A.; Könneke, M.; Schintlmeister, A.; Urich, T.; Engel, M.; Schloter, M.; Wagner, M.; Richter, A. Nitrososphaera viennensis, an ammonia oxidizing archaeon from soil. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 8420–8425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lehtovirta-Morley, L.E.; Ge, C.; Ross, J.; Yao, H.; Nicol, G.W.; Prosser, J.I. Characterisation of terrestrial acidophilic archaeal ammonia oxidisers and their inhibition and stimulation by organic compounds. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2014, 89, 542–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehtovirta-Morley, L.E.; Ross, J.; Hink, L.; Weber, E.B.; Gubry-Rangin, C.; Thion, C.; Prosser, J.I.; Nicol, G.W. Isolation of ‘Candidatus Nitrosocosmicus franklandus’, a novel ureolytic soil archaeal ammonia oxidiser with tolerance to high ammonia concentration. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2016, 92, fiw057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Q.Q.; Bakken, L.R. Comparison of Nitrosospira strains isolated from terrestrial environments. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 1999, 30, 171–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, R.D.; Morita, R.Y. Low-temperature growth and whole-cell kinetics of a marine ammonium oxidizer. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 1985, 21, 239–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zerulla, W.; Barth, T.; Dressel, J.; Erhardt, K.; von Locquenghien, K.H.; Pasda, G.; Rädle, M.; Wissemeier, A. 3, 4-Dimethylpyrazole phosphate (DMPP)—A new nitrification inhibitor for agriculture and horticulture. Biol. Fertil. Soils 2001, 34, 79–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benckiser, G.; Christ, E.; Herbert, T.; Weiske, A.; Blome, J.; Hardt, M. The nitrification inhibitor 3, 4-dimethylpyrazole-phosphat (DMPP)-quantification and effects on soil metabolism. Plant Soil 2013, 371, 257–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiske, A.; Benckiser, G.; Ottow, J.C.G. Effect of the new nitrification inhibitor DMPP in comparison to DCD on nitrous oxide (N2O) emissions and methane (CH4) oxidation during 3 years of repeated applications in field experiments. Nutr. Cycl. Agroecosyst. 2001, 60, 57–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mukhtar, H.; Lin, Y.-P. Soil Nitrification Potential Influences the Performance of Nitrification Inhibitors DCD and DMPP in Cropped and Non-Cropped Soils. Agronomy 2019, 9, 599. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy9100599
Mukhtar H, Lin Y-P. Soil Nitrification Potential Influences the Performance of Nitrification Inhibitors DCD and DMPP in Cropped and Non-Cropped Soils. Agronomy. 2019; 9(10):599. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy9100599
Chicago/Turabian StyleMukhtar, Hussnain, and Yu-Pin Lin. 2019. "Soil Nitrification Potential Influences the Performance of Nitrification Inhibitors DCD and DMPP in Cropped and Non-Cropped Soils" Agronomy 9, no. 10: 599. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy9100599
APA StyleMukhtar, H., & Lin, Y. -P. (2019). Soil Nitrification Potential Influences the Performance of Nitrification Inhibitors DCD and DMPP in Cropped and Non-Cropped Soils. Agronomy, 9(10), 599. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy9100599





