Comparing the Grain Yields of Direct-Seeded and Transplanted Rice: A Meta-Analysis
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Data Collection
2.2. Data Analysis
2.3. Publication Bias
3. Results
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Khush, G.S. Strategies for increasing the yield potential of cereals: Case of rice as an example. Plant Breed. 2013, 132, 433–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avnery, S.; Mauzerall, D.L.; Fiore, A.M. Increasing global agricultural production by reducing ozone damages via methane emission controls and ozone-resistant cultivar selection. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2013, 19, 1285–1299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, S.; Tang, Q.; Zou, Y. Current status and challenges of rice production in China. Plant Prod. Sci. 2009, 12, 3–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakraborty, D.; Ladha, J.K.; Rana, D.S.; Jat, M.L.; Gathala, M.K.; Yadav, S.; Rao, A.N.; Ramesha, M.S.; Raman, A. A global analysis of alternative tillage and crop establishment practices for economically and environmentally efficient rice production. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 9342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tuong, T.P.; Castillo, E.G.; Cabangon, R.C.; Boling, A.; Singh, U. The drought response of lowland rice to crop establishment practices and N-fertilizer sources. Field Crops Res. 2002, 74, 243–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, S.; Nie, L.; Wang, F.; Huang, J.; Peng, S. Agronomic performance of inbred and hybrid rice cultivars under simplified and reduced-input practices. Field Crops Res. 2017, 210, 129–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, S.; Velasco, L.; Toriyama, K.; Heong, K.L.; Hardy, B. Trends in crop establishment methods in Asia and research issues. In Rice is Life: Scientific Perspectives for the 21st Century; International Rice Research Institute: Los Baños, Philippines, 2005; pp. 178–181. [Google Scholar]
- Tuong, T.; Bouman, B. Rice production in water scarce environments. In Water Productivity in Agriculture: Limits and Opportunities for Improvement; Kijne, J., Barker, R., Molden, D., Eds.; CABI Publishing: Wallingford, UK, 2003; pp. 53–67. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, V.; Ladha, J.K. Direct Seeding of Rice: Recent Developments and Future Research Needs. Adv. Agron. 2011, 111, 297–413. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, L.; Hussain, S.; Liu, H.; Peng, S.; Huang, J.; Cui, K.; Nie, L. Implications of low sowing rate for hybrid rice varieties under dry direct-seeded rice system in central China. Field Crops Res. 2015, 175, 87–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farooq, M.; Siddique, K.H.M.; Rehman, H.; Aziz, T.; Lee, D.J.; Wahid, A. Rice direct seeding: Experiences, challenges and opportunities. Soil Tillage Res. 2011, 111, 87–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, S.; Velasco, L. Economics of Direct Seeding in Asia: Patterns of Adoption and Research Priorities; International Rice Research Institute: Los Banos, Philippines, 2002; pp. 6–7. [Google Scholar]
- Peng, S. Reflection on China’s rice production strategies during the transition period. Sci. Sin. Vitae 2014, 44, 845–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhushan, L.; Ladha, J.K.; Gupta, R.K.; Singh, S.; Tirolpadre, A.; Saharawat, Y.S.; Gathalaa, M.; Pathaka, H. Saving of water and labor in a rice–wheat system with no-tillage and direct seeding technologies. Agron. J. 2007, 99, 1288–1296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Hussain, S.; Zheng, M.; Peng, S.; Huang, J.; Cui, K.; Nie, L. Dry direct-seeded rice as an alternative to transplanted-flooded rice in central China. Agron. Sustain. Dev. 2015, 35, 285–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Ge, Q.; Chu, G.; Xu, C.; Yan, J.; Zhang, X.; Wang, D. Seasonal differences in the rice grain yield and nitrogen use efficiency response to seedling establishment methods in the middle and lower reaches of the Yangtze River in China. Field Crops Res. 2017, 205, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DerSimonian, R.; Laird, N. Meta-analysis in clinical trials. Control. Clin. Trials. 1986, 7, 177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furukawa, T.A.; Barbui, C.; Cipriani, A.; Brambilla, P.; Watanabe, N. Imputing missing standard deviations in meta-analyses can provide accurate results. J. Clin. Epidemiol. 2006, 59, 7–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gurevitch, J.; Hedges, L.V. Statistical Issues in Ecological Meta-Analyses. Ecology 1999, 80, 1142–1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kallenbach, C.; Grandy, A.S. Controls over soil microbial biomass responses to carbon amendments in agricultural systems: A meta-analysis. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2011, 144, 241–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kline, R.B. Data preparation and screening. In Principles and Practice of Structural Equation Modeling; The Guilford Press: New York, NY, USA, 1998; pp. 67–94. [Google Scholar]
- Rosenthal, R. The file drawer problem and tolerance for null results. Psychol. Bull. 1979, 86, 638–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duval, S.; Tweedie, R. Trim and fill: A simple funnel-plot–based method of testing and adjusting for publication bias in meta-analysis. Biometrics 2000, 56, 455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, D.; Ling, X.; Huang, J.; Peng, S. Meta-analysis and dose-response analysis of high temperature effects on rice yield and quality. Environ. Exp. Bot. 2017, 141, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshida, S. Fundamentals of Rice Crop Science; International Rice Research Institute: Los Baños, Philippines, 1981; pp. 238–239. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, V.P.; Dhyani, V.C.; Singh, S.P.; Kumar, A.; Manalil, S.; Chauhan, B.S. Effect of herbicides on weed management in dry-seeded rice sown under different tillage systems. Crop Prot. 2016, 80, 118–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, A.N.; Johnson, D.E.; Sivaprasad, B.; Ladha, J.K.; Mortimer, A.M. Weed management in direct-seeded rice. Adv. Agron. 2007, 93, 153–255. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, H.; Pratley, J.; Lemerle, D.; Haig, T. Crop cultivars with allelopathic capability. Weed Res. 1999, 39, 171–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narwal, S.S. Weed management in rice: Wheat rotation by allelopathy. Crit. Rev. Plant Sci. 2000, 19, 249–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sudianto, E.; Beng-Kah, S.; Ting-Xiang, N.; Saldain, N.E.; Scott, R.C.; Burgos, N.R. Clearfield rice: Its development, success, and key challenges on a global perspective. Crop Prot. 2013, 49, 40–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teosdale, J.R.; Beste, C.E.; Potts, W.E. Response of weeds to tillage and cover crop residues. Weed Sci. 1991, 39, 195–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zimdahl, R.L. Fundamentals of Weed Science; Academic Press Inc.: San Diego, CA, USA, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Sudhir-Yadav Gill, G.; Humphreys, E.; Kukal, S.S.; Walia, U.S. Effect of water management on dry seeded and puddled transplanted rice. Part 1: Crop performance. Field Crops Res. 2011, 120, 112–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Timsina, J.; Singh, U.; Badaruddin, M.; Meisner, C.; Amin, M.R. Cultivar, nitrogen, and water effects on productivity, and nitrogen-use efficiency and balance for rice-wheat sequences of Bangladesh. Field Crops Res. 2001, 72, 143–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, S.; Humphreys, E.; Salim, M.; Chauhan, B.S. Optimizing sowing management for short duration dry seeded aman rice on the High Ganges River Floodplain of Bangladesh. Field Crops Res. 2014, 169, 77–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villegas, A.N.; Zandstra, H.G. Identification of soil moisture requirement for germination and emergence of dry seeded rice. Philipp. J. Crop Sci. 1979, 4, 142–145. [Google Scholar]
- Wmw, W.; Mmp, M.; Bandara, C.; Rao, A.N.; Bhandari, D.C.; Ladha, J.K. Direct-seeded rice culture in Sri Lanka: Lessons from farmers. Field Crops Res. 2011, 121, 53–63. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, M.; Tao, Y.; Hussain, S.; Jiang, Q.; Peng, S.; Huang, J.; Cui, K.; Nie, L. Seed priming in dry direct-seeded rice: Consequences for emergence, seedling growth and associated metabolic events under drought stress. Plant Growth Regul. 2016, 78, 167–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, D.B.; Yadav, A.; Malik, R.K.; Gurjeet, G. Efficacy of PIH 2023, penoxsulam and azimsulfuron for post-emergence weed control in wet direct seeded rice. In Proceedings of the Biennial Conference, Indian Society of Weed Science, Hisar, India, 2–3 November 2007; Department of Agronomy, CCS Haryana Agricultural University: Hisar, India, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Gopal, R.; Jat, R.K.; Malik, R.K.; Kumar, V.; Alam, M.M.; Jat, M.L.; Mazid, M.A.; Saharawat, Y.S.; McDonald, A.; Gupta, R. Direct Dry Seeded Rice Production Technology and Weed Management in Rice Based Systems; Technical Bulletin; International Maize and Wheat Improvement Center: New Delhi, India, 2010; p. 28. [Google Scholar]
- Miro, B.; Ismail, A.M. Tolerance of anaerobic conditions caused by flooding during germination and early growth in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Front. Plant Sci. 2013, 4, 269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, L.; Zhan, X.; Yu, T.; Nie, L.; Huang, J.; Cui, K.; Wang, F.; Li, Y.; Peng, S. Yield performance of direct-seeded, double-season rice using varieties with short growth durations in central China. Field Crops Res. 2018, 227, 49–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schnier, H.F.; Dingkuhn, M.; De Datta, S.K.; Mengel, K.; Faronilo, J.E. Nitrogen fertilization of direct-seeded flooded vs. transplanted rice: I. nitrogen uptake, photosynthesis, growth, and yield. Crop Sci. 1990, 30, 1276–1284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, B. Effects of Soil Organic Matter on Functional Soil Properties—Review of the Literature and Underlying Data; Department of the Environment: Canberra, Australia, 2014.
- Yao, S.H.; Zhang, B.; Hu, F. Soil biophysical controls over rice straw decomposition and sequestration in soil: The effects of drying intensity and frequency of drying and wetting cycles. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2011, 43, 590–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suriyagoda, L.; Costa, W.A.J.M.D.; Lambers, H. Growth and phosphorus nutrition of rice when inorganic fertiliser application is partly replaced by straw under varying moisture availability in sandy and clay soils. Plant Soil 2014, 384, 53–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saleque, M.A.; Kirk, G.J.D. Root-induced solubilization of phosphate in the rhizosphere of lowland rice. New Phytol. 1995, 129, 325–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, S.; Cassman, K.G.; Virmani, S.S.; Sheehy, J.; Khush, G.S. Yield potential trends of tropical rice since the release of ir8 and the challenge of increasing rice yield potential. Crop Sci. 1999, 39, 1552–1559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, Y.; Tang, Q.; Zou, Y.; Li, D.; Qin, J.; Yang, S.; Chen, L.; Xia, B.; Peng, S. Yield potential and radiation use efficiency of “super” hybrid rice grown under subtropical conditions. Field Crops Res. 2009, 114, 91–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FAOSTAT. FAO Statistical Databases; Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) of the United Nations: Rome, Italy, 2019; Available online: www.fao.org/faostat/en/#data (accessed on 24 October 2019).




| Region | Observation Number | Proportion (%) |
|---|---|---|
| India | 167 | 38 |
| China | 111 | 25 |
| Philippines | 79 | 18 |
| Pakistan | 22 | 5 |
| Cambodia | 12 | 3 |
| Iran | 12 | 3 |
| Sri Lanka | 12 | 3 |
| Korea | 8 | 2 |
| Bangladesh | 4 | 1 |
| Nepal | 4 | 1 |
| Thailand | 3 | 1 |
| Ivory Coast | 3 | 1 |
| Malaysia | 2 | <1 |
| Japan | 1 | <1 |
| Total | 440 | 100 |
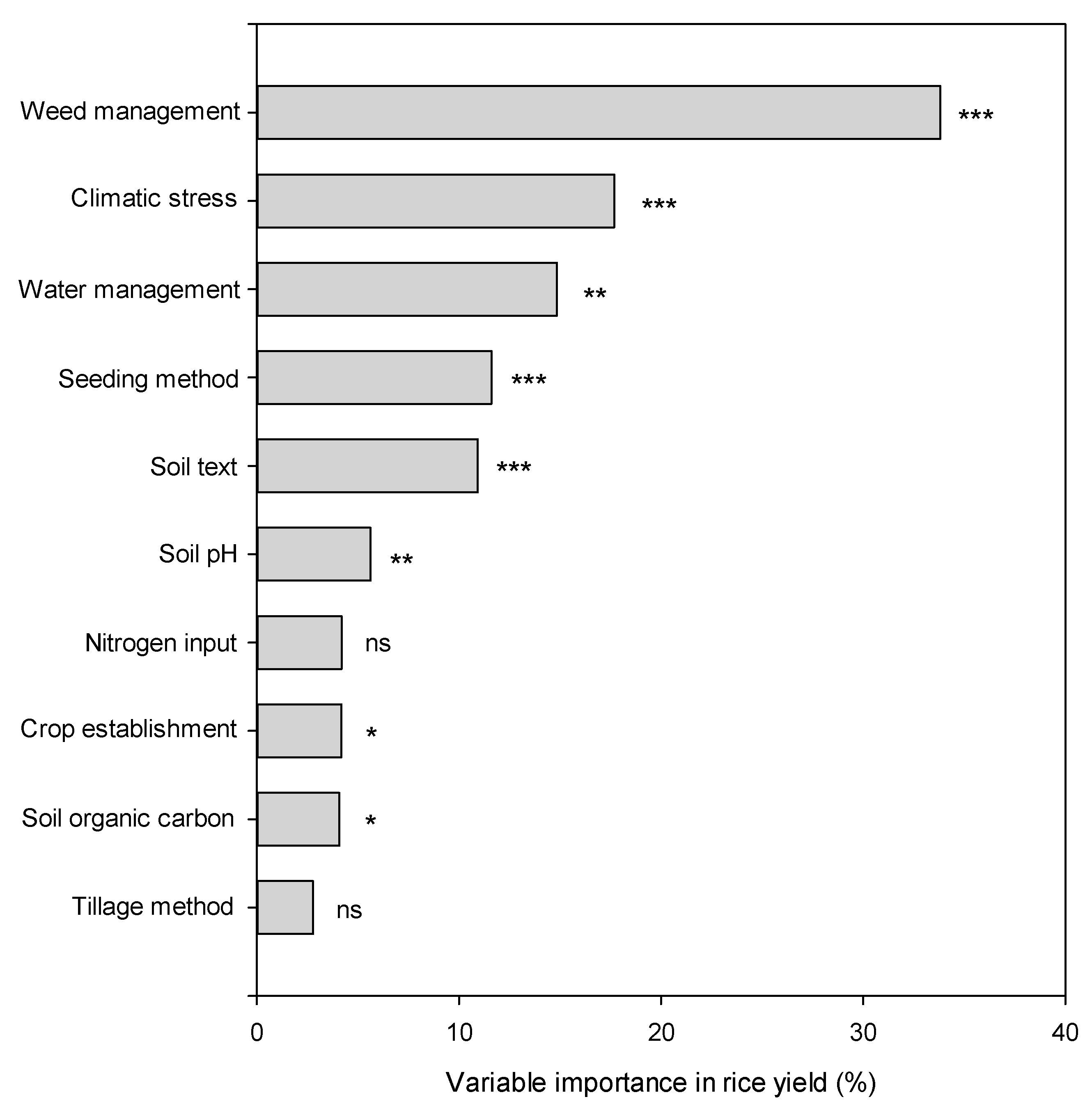
| Variable | QB | df | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Crop establishment | 5.85 | 1 | 0.016 |
| Seeding method | 24.73 | 2 | 0.000 |
| Tillage method | 1.11 | 2 | 0.573 |
| Weed control | 221.41 | 2 | 0.000 |
| Water management | 11.50 | 2 | 0.003 |
| Nitrogen input | 4.60 | 2 | 0.100 |
| Soil organic carbon | 5.07 | 1 | 0.024 |
| Soil texture | 18.88 | 1 | 0.000 |
| Soil pH | 8.80 | 1 | 0.003 |
| Climatic stress | 63.82 | 1 | 0.000 |
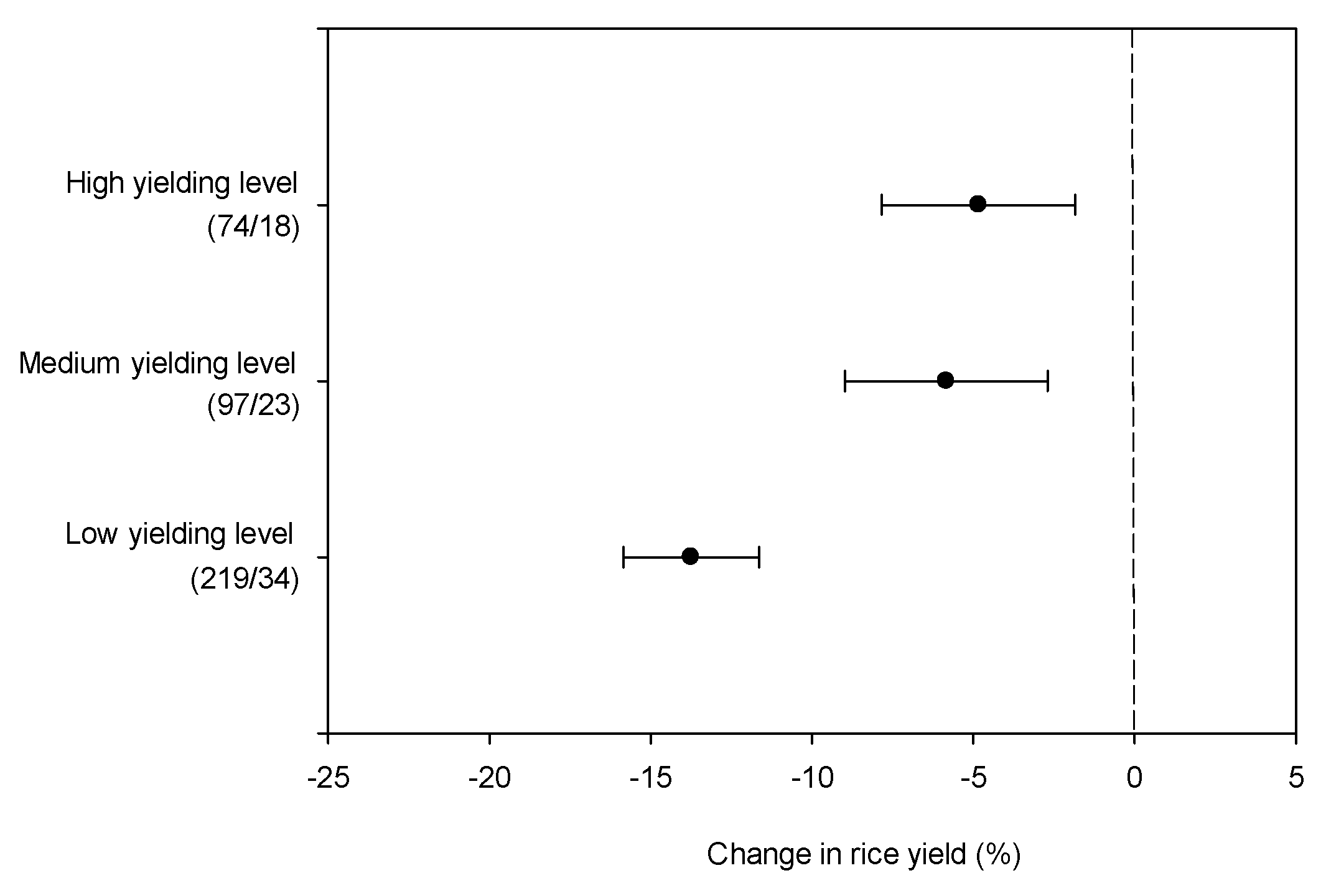
| Yielding level | 27.01 | 2 | 0.000 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xu, L.; Li, X.; Wang, X.; Xiong, D.; Wang, F. Comparing the Grain Yields of Direct-Seeded and Transplanted Rice: A Meta-Analysis. Agronomy 2019, 9, 767. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy9110767
Xu L, Li X, Wang X, Xiong D, Wang F. Comparing the Grain Yields of Direct-Seeded and Transplanted Rice: A Meta-Analysis. Agronomy. 2019; 9(11):767. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy9110767
Chicago/Turabian StyleXu, Le, Xiaoxiao Li, Xinyu Wang, Dongliang Xiong, and Fei Wang. 2019. "Comparing the Grain Yields of Direct-Seeded and Transplanted Rice: A Meta-Analysis" Agronomy 9, no. 11: 767. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy9110767
APA StyleXu, L., Li, X., Wang, X., Xiong, D., & Wang, F. (2019). Comparing the Grain Yields of Direct-Seeded and Transplanted Rice: A Meta-Analysis. Agronomy, 9(11), 767. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy9110767





