Abstract
Biological nitrogen fixation and plant hormone synthesis promoted by Azospirillum spp. bacteria play a role in enhancing crop productivity and reducing losses. This may constitute a strategy to enhance crop productivity and reducing losses, thereby increasing nitrogen fertilization efficiency. This research aimed to evaluate the effects of Azospirillum brasilense Ab-V5 and Ab-V6 strain inoculation and nitrogen fertilization on the agronomic characteristics and productivity of two maize hybrids (Zea mays L.) AS 1572 and AG 9030. Experiments were carried out at Santa Maria, RS, Brazil in the 2013/2014 and 2014/2015 growing seasons using a 2 × 2 × 5 factorial arrangement to distribute two maize hybrids, inoculated, or not, with Azospirillum brasilense, and five nitrogen doses (0, 60, 120, 240, and 480 kg ha−1). Kernel yield, mass, and dimensions, as well as kernel number on the cobs, stalk diameter, plant height, ear insertion height, prolificacy, nitrogen use efficiency (NUE), and their correlations were measured. Compared to uninoculated plants, higher kernel yield (p < 0.05) was observed for AS 1572 hybrid when inoculated with A. brasilense, with an increase of 0.978 Mg ha−1 or 10.95%. This effect was primarily due to the higher NUE rate and the increase (p < 0.05) in the number of kernels per cob. The AG 9030 hybrid showed no response to inoculation. A. brasilense inoculation increased the NUE rate of the AS 1572 hybrid in the condition N zero dose at N 60 kg ha−1 dose. Nitrogen fertilization increased crop productivity, notably by raising kernel mass and other productivity components, but reduced the NUE rate. The maximum technical efficiency obtained for the AS 1572 hybrid was of 10.705 Mg ha−1 with a N dose of 342 kg ha−1, whereas the AG 9030 hybrid produced a maximum grain yield of 10.089 Mg ha−1 with a dose of 350 kg ha−1 of N. We conclude that the inoculation with A. brasilense increases NUE, maize grain yield, and agronomic characteristic in the AS 1572 hybrid.
1. Introduction
Growing maize (Zea mays) is a socially and economically important activity for Brazilian farmers. Due to maize’s genetic variability, and its adaptability to the most varied environmental conditions [1], this cereal is cultivated in all regions of Brazil, from the far north to the far south, and in low to high altitudes. In the last twenty years, the cultivated area for maize has increased by 31%, and production by 167% [2]. Productivity gains are attributed to the use of more advanced technology, such as high yield potential seeds, pest-resistant and/or disease-tolerant varieties, and localized and directed fertilization according to soil analysis and plant demand.
In order to improve crop productivity, the proper supply of nutrients to plants is essential, especially nitrogen, which is one of the most limiting and necessary nutrients for maize [3]. Insufficient N supply adversely affects grain yield, reducing the number of eggs which continue to develop while the maize ear is forming, and the number of ears per plant [4]. However, the amount of nitrogen available per unit time through readily soluble sources, such as urea, characterizes a problem when the bioavailability of the nutrient does not match the plants’ capacity to assimilate. Moreover, industrial N sources, besides being imported products obtained through the burning of fossil fuels, are susceptible to high losses due to volatilization and/or lixiviation when applied during tillage [5,6]. Thus, lower recovery of nitrogen in the form of production is expected, representing a high risk of surface and underground water contamination.
It was discovered that some microorganisms, especially Azospirillum spp., can associate with the gramineous rhizosphere and provide assimilable N from N2 [7]. Since then, strategies such as the employment of diazotrophic bacteria including Azospirillum spp., which fix biological nitrogen and synthesize hormones that promote plant growth [8,9,10,11,12,13], have been studied extensively. Inoculation of these bacteria has been shown to improve root development and radical surface, water and nutrient absorption, and plant tolerance to stress conditions such as salinity and water deficit, among others [8,12,14,15]. These effects have significant potential to increase crop productivity and reduce losses by increasing the efficiency of nutrient usage [16,17]. A. brasilense Ab-V5 and Ab-V6 strains were isolated and selected from maize in Brazil, and provided an average yield increase of 823 and 785 kg ha−1, respectively [11]. As these strains were isolated from specific regional situations, studies are needed to test their effects in different environmental conditions in order to attest the agricultural applications of such commercial inoculants.
To that end, this research aims to assess the agronomic characteristics and the grain yield of maize kernels inoculated with Azospirillum brasilense Ab-V5 and Ab-V6 strains and fertilized with nitrogen doses.
2. Materials and Methods
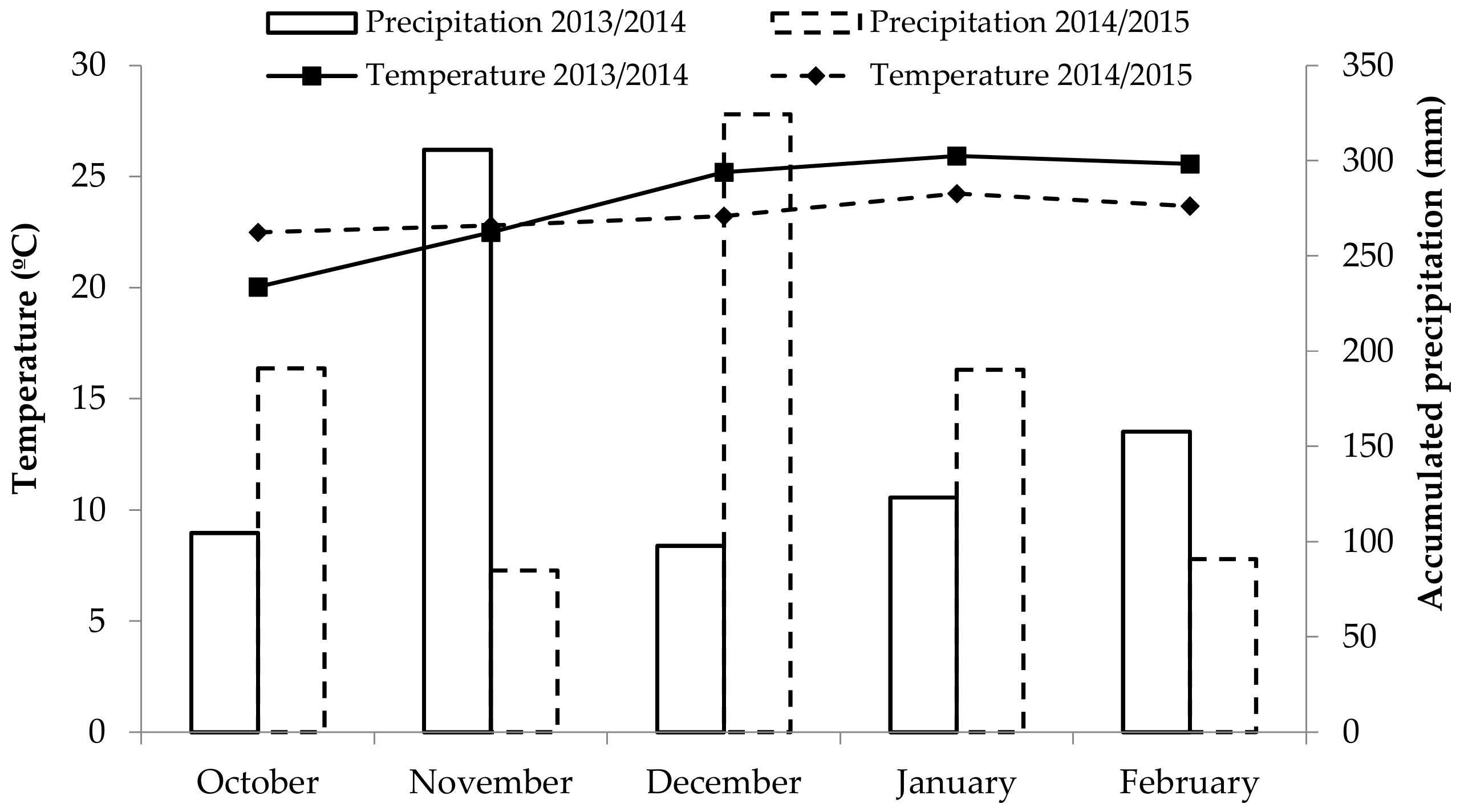
The research was laid out in a randomized complete block design with a 2 × 2 × 5 factorial arrangement to evaluate two maize hybrids, inoculated or not, with Azospirillum brasilense, and five nitrogen doses (0 kg ha−1, 60 kg ha−1, 120 kg ha−1, 240 kg ha−1, and 480 kg ha−1). Twenty treatments with four repetitions each were tested. The field experiment (non-irrigated) was conducted in Santa Maria, which is 95 m above sea level, located in the central region of the Brazilian state of Rio Grande do Sul at latitude 29.71′80″ south, longitude 53.73′31″ west. The soil is classified as red dystrophic oxisol with clay texture [18] and the climate is humid subtropical (Cfa) type according to the Köppen classification [19]. Average daily precipitation and temperature data were obtained at a meteorological station of the Brazilian National Institute of Meteorology (INMET), located at the Federal University of Santa Maria (Figure 1).
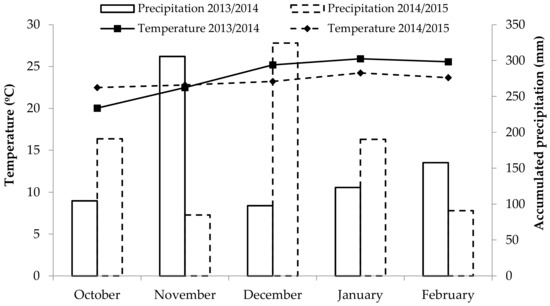
Figure 1.
Accumulated rainfall and mean air temperature during the experiment in Santa Maria-RS, in 2013/2014 and 2014/2015.
Areas were cultivated with black oat (Avena strigosa L.) prior to the experiment to produce straw for the no-tillage system. Soil samples were collected at 0 to 20 cm depth for chemical analysis, and the recommended fertilizer protocol (see below) was carried out in May before maize seeding. The values found corresponding to the soil analyses for the harvests of 2013/2014 and 2014/2015 were, respectively: clay, 23.0% and 24.0%; pH in water, 5.0 and 5.2; CEC, 7.5 and 9.9 cmolc/dm3; Al, 0.7 and 0.6 cmolc/dm3; Ca, 4.5 and 6.2 cmolc/dm3; Mg, 2.1 and 2.8 cmolc/dm3; P, 17.5 and 12.6 mg/dm3; K, 84 and 108 mg/dm3; organic matter, 2.2% and 2.4%; and saturation by bases, 47.8% and 67.5%.
Pre-planting fertilization was carried out according to the recommendations of the RS/SC [20] for a potential grain yield of 10 Mg ha−1 by applying the dose equivalent of 39.28 kg ha−1 of P and 41.51 kg ha−1 of K. The base-dressing nitrogen fertilization was performed by applying the dose equivalent of 30 kg ha−1 in the planting furrow. Top-dressing fertilization was performed at phenological stages V4 and V8 (four and eight developed leaves respectively). At each of these two stages, urea (containing 45% N by weight) was distributed at the different levels of N that composed the treatments (top-dressing doses equivalent to 60 kg ha−1, 120 kg ha−1, 240 kg ha−1, and 480 kg ha−1). For the plots without nitrogen (controls), base and top-dressing nitrogen applications were not performed.
The sowing dates were 16 October, 2013 and 28 October, 2014 for the 2013/2014 and 2014/2015 growing seasons, respectively. The seed was planted by seeder with 0.5 m between rows and 0.34 m between plants in the row, in 6.0 m by 2.5 m plots with five rows each. Genotypes AS 1572® (Monsanto®, São Paulo, Brazil), an early growth cycle hybrid, and AG 9030® (Monsanto®, São Paulo, Brazil), a super-early growth cycle hybrid, were used, and both were genetically modified to resist Diatraea saccharalis Fabricius and Helicoverpa zea Boddie. In each plot, the edge rows (rows 1 and 5 of the experimental units) were disregarded from the assessments, and seeder regulation aimed to obtain an approximate population of 60,000 plants per hectare.
Seeds were inoculated with strains Ab-V5 and Ab-V6 of the bacterium Azospirillum brasilense at concentrations of 2.0 × 108 CFU mL−1 and 6.6 × 106 CFU per seed, using 200 mL ha−1 of inoculant Azototal® (Total Biotecnologia® Indústria e Comércio S.A, Curitiba, Brazil). No-inoculation plots were seeded first, followed by those for inoculated seed. Atrazine and simazine herbicides were used for weed control at the appearance of the first developed maize leaf. To control milhã (Digitaria horizontalis L. Scop) and papuã (Brachiaria plantaginea Link) grasses, a systemic selective herbicide was used, between V4 and V6 stages.
The kernel harvests were performed manually on one of the central rows of each plot, after the physiological maturation stage, on 20 March 2014 and 26 March 2015, for the 2013/2014 and 2014/2015 growing seasons respectively. We randomly chose five plants from each plot and measured the stalk diameter with a digital pachymeter, and plant height (from the soil to the flag leaf) and ear insertion height with a graduated measuring tape. For the maize ears, we measured the length using a ruler graduated in mm and the diameter using a digital pachymeter. We also counted the number of kernel rows per cob and the number of kernels per row, from which we obtained the number of kernels per cob. Plant prolificacy was assessed through the ratio between the number of ears and the number of plants in the cultivation row.
To assess the productivity of kernels per hectare, we threshed the ears harvested from the middle row of each plot in a stationary thresher, weighed the kernels and, finally, determined the moisture level by heating until a constant weight was obtained. The mass of the grains was obtained by manually counting one thousand kernels, weighing them, and subsequently adjusting for 13% moisture. Nitrogen use efficiency (NUE) (kg kg−1) was calculated as the ratio of GY/Nt, where GY indicates grain yield (kg) and Nt indicates the total N (kg). Total N was estimated by the N dose applied + soil total N content as described by [21]. The soil total N was estimated based on soil organic matter content at a depth of 20 cm (2000 m3).
The data, which were normally distributed, were analyzed by a mixed procedure (proc mixed). Collected data were analyzed for interactions between inoculation and hybrids (I × H), inoculation and nitrogen doses (I × N), hybrids and nitrogen doses (H × N), and inoculation, hybrids and nitrogen doses (I × H × N). Significant interactions were merged according to the treatments and then subjected to the means were compared by the GLM procedure (proc Generalized Linear Model). The SAS Academic Program® (Cary, NC, USA) [22] was used to perform the analyses, with the year of harvest included as a random variable in the model because of the lack of an experimental control and the inability to repeat the environmental conditions of the experiment. For the characteristics evaluating function of the A. brasilense inoculation or maize hybrids, we used a comparison of means through the F test at a 5% significance level, while regression equations estimated the variables assessed as a function of the different N doses. The statistical regression models were chosen according to the significance of the highest degree (third, second, and first, respectively). Pearson’s correlation test was conducted between the evaluated variables.
3. Results
The hybrids tested have distinct agronomic characteristics, which may in themselves have contributed to the statistically significant differences found for most of the variables evaluated. AG 9030 is super-early with hard grains, producing high yields of large kernels. AS 1572 has an early cycle, and produces jagged kernels, found on typically longer and larger-diameter cobs; this is likely to be related to its comparatively longer period at stages V12 to V17, during which kernel number and ear size are determined [23]. Thus, kernel productivity for the two hybrids is comparable, but achieved by different means. Such agronomic differences allowed the same kernel productivity for the hybrids tested (Table 1).

Table 1.
Productivity and plant agronomic characteristics of inoculated corn hybrids with Azospirillum brasilense and submitted to nitrogen rates in the 2013/2014 and 2014/2015 harvests.
In isolation, inoculating with A. brasilense increased the number of kernels per cob (Table 1). For the remaining response variables, the effect of inoculation with A. brasilense depended on the maize hybrid (Table 1). Hybrid AS 1572 showed a strong response to inoculation with the strains tested, as demonstrated by an increase in productivity. This hybrid, inoculated with A. brasilense, showed an increase of 0.978 Mg ha−1 or 10.95% compared to the same hybrid without inoculation (Table 2). Inoculation of hybrid AS 1572 increased the NUE rate (+10.64%), number of kernels per row (+5.54%), the number of grains per cob (+5.19%) and ear diameter (+1.24%). Such variables contributed to the equivalent kernel productivity increment described for inoculated hybrid AS 1572. Alterations of this kind, in productivity and agronomic characteristics, were not observed for hybrid AG 9030 (Table 2).

Table 2.
Interaction between inoculation with Azospirillum brasilense and corn hybrids on the grain yield and plant agronomic characteristics associated.
Nitrogen fertilization affected kernel productivity and most components of maize yield (Table 1). Nitrogen dose fertilization and NUE have an inverse and linear relationship (Table 1) (y = 184.75 – 37.267x; r2 = 0.8415). The soil total N content was 48 kg ha−1, which was estimated by the soil organic matter contents; the remaining nitrogen was derived from the N dose treatments. NUE reduction due to increasing N doses was expected, because the more available nitrogen per unit time, the lower is the assimilation efficiency due to an increase in leaching, nitrification, and/or volatilization losses among other reasons.
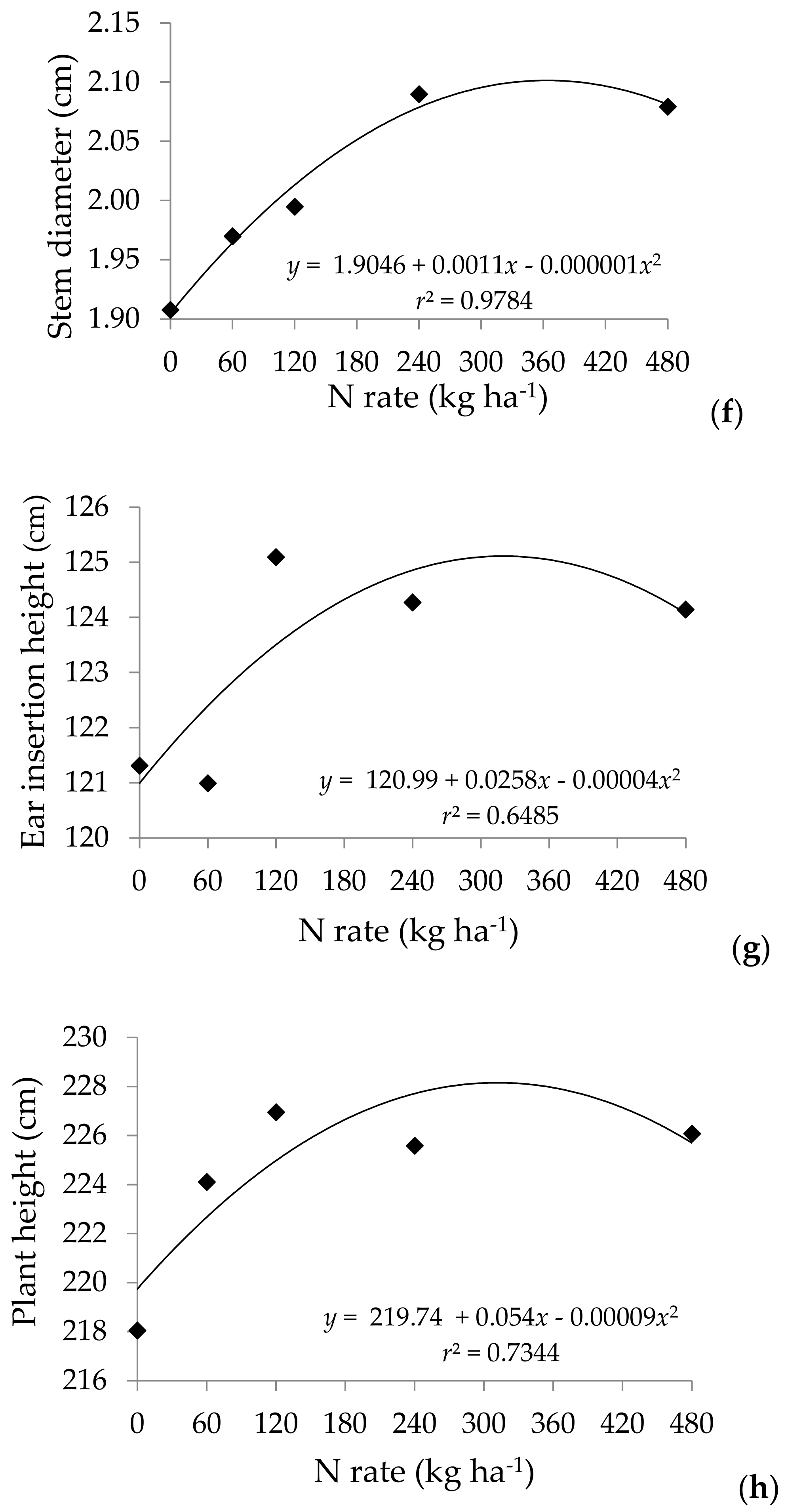
There was an interaction between maize hybrids and nitrogen doses in respect to the productivity and the number of kernels per cob (Figure 2). The maximum technical efficiency obtained for hybrid AS 1572 was of 10.705 Mg ha−1 with a dose of 342 kg ha−1 of N (y = 7.2036 + 0.0205x − 0.00003x2), while hybrid AG 9030 had a maximum productivity of 10.089 Mg ha−1 with a dose of 350 kg ha−1 of N (y = 8.8642 + 0.0070x – 0.00001x2). The tested hybrids reached the yield potential with similar nitrogen rates.
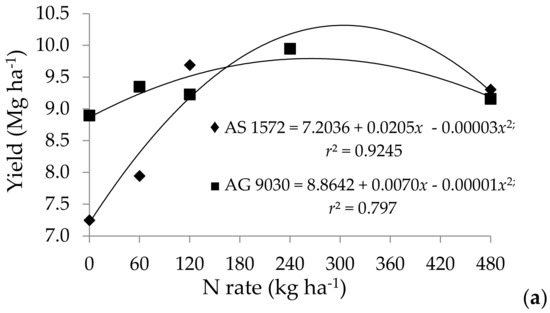
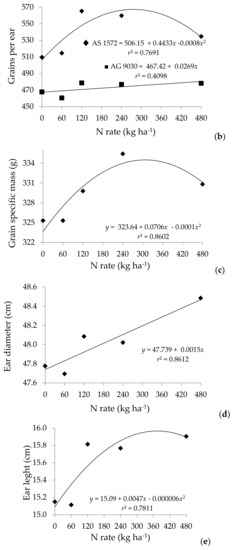
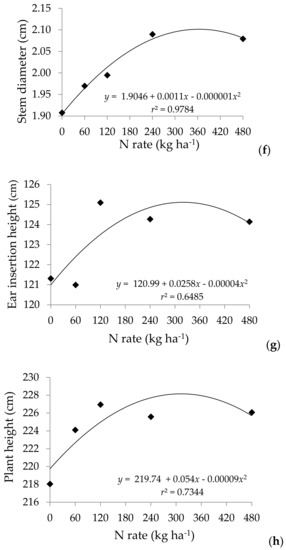
Figure 2.
Grain yield (a) and plant agronomic characteristics (b–h) of corn hybrids as a function of nitrogen rates.
There was no interaction between the levels of nitrogen fertilization and inoculation with A. brasilense for grain yield and agronomic characteristics. However, a triple interaction (I × H × N) was observed for NUE (Table 1). A. brasilense inoculation increases the NUE rate of the AS 1572 hybrid (y = 206.73 − 1.0603x + 0.0013x2; r2 = 0.8742) in the condition of N zero dose (183.27 kg kg−1) and at the N dose of 60 kg ha−1 (76.09 kg kg−1) compared to the same hybrid without inoculation (y = 172.32 − 0.841x + 0.0011x2; r2 = 0.9118) at the N zero dose (150.55 kg kg−1) and at the N dose of 60 kg ha−1 (71.07 kg kg−1). These results corroborate the advantages described above for the AS 1572 hybrid inoculated with A. brasilense.
4. Discussion
Several authors reported productivity gains attributed to inoculation with A. brasilense in different cultures [8,9,11,14,15,16,24,25,26,27]. All these studies attribute the success of inoculation to biologically fixed nitrogen through the action of the nitrogenase complex [14] and/or the production of phytohormones. Phytohormones exert an effect over the development of the pollen grain and the formation of the pollen tube, increase plant fertility and kernel specific weight, augment nutrient absorption and foliar area index through the more extensive radical surface and, lastly, maximize the capture of solar power for the development of the plants and grains [28].
In this study Hybrid AS 1572 showed a strong response to inoculation with the strains tested, as demonstrated by an increase of NUE and productivity. These increments may be related to the assumptions described above. Increasing the NUE is essential for sustainable agricultural development, and the evidence indicates that A. brasilense inoculation can reduce losses by increasing the efficiency of nutrients usage and thus increase crop productivity. [11] verified that the macro and micronutrient levels in leaves and grains were increased upon inoculation with A. brasilense. The results obtained allowed recommendation of strains Ab-V4, Ab-V5, Ab-V6, and Ab-V7 for maize crops. Results with these strains did not differ from those without inoculation treatments and with an N dose of 80 kg ha−1.
However, inoculation benefits were obtained only for the AS 1572 hybrid. In experiments carried out in two harvests in the municipality of Erechim, RS, Brazil, [29] had already recorded the association of A. brasilense strains Ab-V5 and Ab-V6 with the Defender hybrid for silage. The authors also reported there were differences between the studied harvests and that, in the 2012/2013 harvest, positive effects were also obtained for the AS 1572 hybrid, as used in the present study. [30] reported that the response to inoculation depends on the specific relationship between cultivar and strain, with variety BRS 296 responding to the inoculation with diazotrophic bacteria, among which was Azospirillum brasilense strain Sp245, while cultivar BRS 276 was not responsive to inoculation, in two years of evaluation. [16,31] established, both in field and greenhouse conditions, the existence of an affinity of A. brasilense strain Sp245 for wheat and of A. irakense strain KBC1 for maize, exposing the differences between plant species.
Possibly, the association between bacteria and plants is linked to the types of radicular exudates which, in turn, alter according to the specific edaphoclimatic conditions. This is because the microorganisms direct themselves towards the roots using chemical recognition, being attracted by the gradients of carbon sources that exist between the soil and the rhizosphere [32,33,34]. We consider the study of such relationships between strains of A. brasilense and cultivars important, encompassing the effects of different edaphoclimatic conditions and how these can maximize positive responses from inoculation, and improve decision-making regarding hybrid selection, associated with the inoculation technology for diazotrophic bacteria.
Therefore, the different responses of the hybrids to inoculation may also be related to their development cycles. Hybrid AS 1572, characterized as early, demands more days to reach physiological maturity, and this means that the edaphoclimatic condition must be kept stable (ideal) for longer compared to hybrid AG 9030, with its super-early cycle. This problem becomes more evident when it is taken into account that the lack of water and nutrients at the stages of floral initiation (V12 to V17) and grain filling (R1 to R6), when the fertilization of egg cells occurs, affects the number of kernels per ear and, consequently, the productivity of the culture [23]. Transitory conditions of water stress, for example, even if they occurred discretely, act to favor the production of radical exudates, especially with hybrid AS 1572, promoting bacterial growth in the rhizosphere and the synthesis of phytohormones.
Some researchers such as [12,35,36] observed that the benefits conferred by Azospirillum spp., such as the growth of roots and improved nutrient (NPK) absorption, result from the interaction between cultivars and environmental conditions, with the benefits being more evident in water stress conditions. According to [35] the production of abscisic acid is closely related to water stress in plants; the higher the concentration of the phytohormone, the lower the transpiration rate of the plants through the closing of the stomas, and the more substantial the development of roots. In this case, diazotrophic bacteria may induce or mediate mechanisms of tolerance to situations of stress such as salinity, drought, very high or low temperatures, and mineral deficiencies [35].
Although we did not observe an interaction between levels of nitrogen fertilization and inoculation with A. brasilense, for grain yield and agronomic characteristics, A. brasilense inoculation increased the NUE rate of the AS 1572 hybrid in the condition of N zero dose at N 60 kg ha−1 dose. These results indicate that the inoculation benefits are associated with the use of low N doses. Other studies determined there was an interaction between N dose and inoculation with Azospirillum spp. [16,17,27,29]. These authors determined that positive responses to inoculation depend on the use of low or average doses of N in cover, increasing the efficiency of nitrogen fertilization in such conditions. This is explained by the fact that high N doses regulate the expression of BNF activity due to the high energy costs of N2 reduction [37].
5. Conclusions
The inoculation of maize seeds with Azospirillum brasilense Ab-V5 and Ab-V6 strains increased the NUE rate (+10.64%), corn yield (+978 kg ha−1), the number of grains per row (+1.83 grains), the number of grains per cob (+28.78 grains), and the ear diameter (+0.61 cm) of the AS 1572 hybrid.
A. brasilense inoculation increases the NUE rate of the AS 1572 hybrid in the condition N zero dose at N 60 kg ha−1. This suggests that inoculation benefits are associated with low N soil contents, although we did not detect any interactions for the other variables studied.
A. brasilense inoculation possibly had beneficial effects on the hybrid AS 1572 between stages V12 and V17, the period in which the number of eggs and the ears size, and therefore the grain yield, are defined. This period is especially critical for water stress, but A. brasilense use may mitigate this negative effect.
Field experiments present enormous complexities regarding interactions between edaphoclimatic conditions and survival of diazotrophic bacteria; however, inoculants containing A. brasilense Ab-V5 and Ab-V6 strains may be adopted by farmers due to their low cost and ease of use.
The NUE decreases due to increasing N doses. The maximum technical efficiency of the culture was obtained with doses of 342 kg ha−1 and 350 kg ha−1 of nitrogen for hybrids AS 1572 and AG 9030, respectively.
Author Contributions
F.R.S. (conception and design of study, acquisition of data, analysis and/or interpretation of data, and drafting the manuscript); J.V. (conception and design of study); T.N.M. (conception and design of study, and critical review); C.C.A.M. (acquisition of data and analysis); S.N. (acquisition of data and analysis); T.J.T. (acquisition of data, analysis and interpretation of data); L.R.D. (acquisition of data and analysis); G.R.M. (critical review)
Funding
Coordenação de Aperfeiçoamento de Pessoal de Nível Superior (CAPES) and Conselho Nacional de Desenvolvimento Científico e Tecnológico (CNPq).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Teixeira, F.F.; Andrade, R.V.; Oliveira, A.C.; Ferreira, A.d.S.; Santos, M.X. Diversidade no germoplasma de milho coletado na região Nordeste do Brasil. Rev. Bras. Milho Sorgo 2002, 1, 59–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Companhia Nacional de Abastecimento (CONABI). Acompanhamento da Safra Brasileira: Grãos. In Safra 2017/2018. Décimo Segundo Levantamento, Setembro de 2018; Conab: Brasília, Brazil, 2018; p. 148. [Google Scholar]
- Alcantara, R.M.C.M.; Sousa, S.R.; Xavier, G.R.; Rocha, M.M.; Rumjanek, N.G. Mecanismos Bioquímicos, Fisiológicos e Moleculares Relacionados Com a Eficiência de uso de Nitrogênio em Leguminosas e Gramíneas; Embrapa Meio Norte: Brasilia, Brazil, 2009; p. 39. [Google Scholar]
- Duete, R.R.C.; Muraoka, T.; Silva da, E.C.; Trivelin, P.C.O.; Ambrosano, E.J. Manejo da adubação nitrogenada e utilização do nitrogênio (15N) pelo milho em Latossolo Vermelho. Rev. Bras. Ciênc. Solo 2008, 32, 161–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da Ros, C.O.; Aita, C.; Giacomini, S.J. Volatilização de amônia com aplicação de uréia na superfície do solo, no sistema plantio direto. Cienc. Rural 2005, 35, 799–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorensini, F.; Cereta, C.A.; Girotto, E.; Cerini, J.B.; Lourenzi, C.R.; Conti, L.; Trindade, M.M.; Melo, G.W.; Brunetto, G. Lixiviação e volatilização de nitrogênio em um Argissolo cultivado com videira submetida à adubação nitrogenada. Cienc. Rural 2012, 42, 1173–1179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bulow, J.F.W.; Von Döbereiner, J. Potential for nitrogen fixation in maize genotypes in Brazil. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1975, 72, 2389–2393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cassán, F.; Perrig, D.; Sgroy, V.; Masciarelli, O.; Penna, C.; Luna, V. Azospirillumbrasilense Az39 and Bradyrhizobiumjaponicum E109, inoculated singly or in combination, promote seed germination and early seedling growth in corn (Zea mays L.) and soybean (Glycine max L.). Eur. J. Soil Biol. 2009, 45, 28–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montañez, A.; Abreu, C.; Gill, P.R.; Hardarson, G.; Sicardi, M. Biological nitrogen fixation in maize (Zea mays L.) by 15N isotope dilution and identification of associated culturable diazotrophs. Biol. Fertil. Soils 2009, 45, 253–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bashan, Y.; Bashan, L.E. How the plant growth-promoting bacterium Azospirillum promotes plant growth a critical assessment. Adv. Agron. 2010, 108, 77–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hungria, M.; Campo, R.J.; Souza, E.M.; Pedrosa, F.O. Inoculation with selected strains of Azospirillum brasilense and A. Lipoferum improves yields of maize and wheat in Brazil. Plant Soil 2010, 331, 413–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moutia, J.F.Y.; Saumtally, S.; Spaepen, S.; Vanderleydejn, J. Plant growth promotion by Azospirillumsp in sugarcane is influenced by genotype and drought stress. Plant Soil 2010, 337, 233–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Videira, S.S.; Oliveira, D.M.; Moraes, R.F.; Borges, W.L.; Baldani, V.L.D.; Baldani, J.I. Genetic diversity and plant growth promoting traits of diazotrophic bacteria isolated from two Pennisetum purpureum Schum. Genotypes grown in the field. Plant Soil 2012, 356, 51–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steenhoudt, O.; Vanderleyden, J. Azospirillum, a free-living nitrogen-fixing bacterium closely associated with grasses: Genetic, biochemical and ecological aspects. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2000, 24, 487–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bashan, Y.; Holguin, G.; Bashan, L.E. Azospirillum plant relations physiological, molecular, agricultural, and environmental advances. Can. J. Microbiol. 2004, 50, 521–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dobbelaere, S.; Croonenborgghs, A.; Thys, A.; Ptacek, D.; Okon, Y.; Vanderleyden, J. Effect of inoculation with wild type Azospirillum brasilense and A. Irakenses trains on development and nitrogen uptake of spring wheat and grain maize. Biol. Fert. Soils 2002, 36, 284–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araújo, E.O.; Martins, M.R.; Vitorino, A.C.T.; Mercante, F.M.; Urquiaga, S.S. Effect of nitrogen fertilization associated with diazotrophic bacteria inoculation on nitrogen use efficiency and its biological fixation by corn determined using 15 N. Afr. J. Microbiol. Res. 2015, 9, 643–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Empresa Brasileira De Pesquisa Agropecuária—EMBRAPA; Centro Nacional de Pesquisas de Solos. Sistema Brasileiro de Classificação de Solos, 3rd ed.; Embrapa: Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, 2013; p. 353. [Google Scholar]
- Peel, M.C.; Finlayson, B.L.; Mcmahon, T.A. Updated world map of the Köppen-Geiger climate classification. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2016, 11, 1633–1644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Comissão De Fertilidade Do Solo RS/SC. Manual de Adubação e Calagem Para os Estados do Rio Grande do Sul e Santa Catarina, 10th ed.; Núcleo Regional Sul-Sociedade Brasileira de Ciência do SoloSegunda reimpressãoCapa: Porto Alegre, Brazil, 2004; p. 400. [Google Scholar]
- Moll, R.; Kamprath, E.; Jackson, W. Analysis and interpretation of factors which contribute to efficiency of nitrogen utilization. Agron. J. 1982, 74, 562–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- SAS. SAS/STAT 9.3 User’s Guide; SAS Institute Inc.: Cary, NC, USA, 2011; p. 8621. [Google Scholar]
- Bergamaschi, H.; Matzenauer, R. Cultivos temporários: Milho. In Agrometeorologia dos Cultivos: O Fator Meteorológico na Produção Agrícola, 1st ed.; Monteiro, J.E.B.A., Ed.; Instituto Nacional de Meteorologia: Brasília, Brazil, 2009; 530p. [Google Scholar]
- Lana, M.C.; Dartora, J.; Mairini, D.; Hann, J.E. Inoculation with Azospirillum, associated with nitrogen fertilization in maize. Rev. Ceres 2012, 59, 399–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morais, R.F.; Quesada, D.M.; Reis, V.M.; Urquiaga, S.; Alves, B.J.; Boddey, R.M. Contribution of biological nitrogen fixation to elephant grass (Pennisetum purpureum Schum.). Plant Soil 2012, 356, 23–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dartora, J.G.; Guimarães, V.F.; Marini, D.; Sander, G. Adubação nitrogenada associada à inoculação com Azospirillum brasilense e Herbaspirillum seropedicae na cultura do milho. Rev. Bras. Eng. Agríc. Ambient. 2013, 17, 1023–1029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galindo, F.S.; Teixeira Filho, M.C.M.; Buzetti, S.; Santini, J.M.K.; Alves, C.J.; Nogueira, L.M.; Ludkiewicz, M.G.Z.; Andreotti, M.; Bellotte, J.L.M. Corn Yield and Foliar Diagnosis Affected by Nitrogen Fertilization and Inoculation with Azospirillum brasilense. Rev. Bras. Ciênc. Solo 2016, 40, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barassi, C.A.; Sueldo, R.J.; Creus, C.M.; Carrozzi, L.; Casanovas, E.M.; Pereyra, M.A. Potencialidad de Azospirillum en Optimizar el Crecimiento Vegetal Bajo Condiciones Adversas. In Azospirillum Sp.: Cell Physiology, Plant Interactions and Agronomic Research in Argentina; Cassán, F.D., Garcia De Salamone, I., Eds.; Asociación Argentina de Microbiologia: Buenos Aires, Argentina, 2008; pp. 49–59. [Google Scholar]
- Skonieski, F.R.; Viégas, J.; Martin, T.N.; Nörnberg, J.L.; Meinerz, G.R.; Tonin, T.J.; Bernhard, P.; Frata, M.T. Effect of seed inoculation with Azospirillum brasilense and nitrogen fertilization rates on maize plant yield and silage quality. Rev. Bras. Zootec. 2017, 46, 722–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, J.S.; Moreira, L.Q.; Giori, F.G.; Reis, V.M. Avaliação de Duas Cultivares de Trigo Inoculadas Com Bactérias Diazotróficas em Condições de Casa de Vegetação; Boletim de Pesquisa e Desenvolvimento, Ed.; Embrapa Agrobiologia: Seropédica, Brazil, 2010; p. 20. [Google Scholar]
- Dobbelaere, S.; Croonenborgghs, A.; Thys, A.; Ptacek, D.; Vandereyden, J.; Dutto, P.; Labandera-Gonzalez, C.; Caballero-mellado, J.; Aguirre, J.F.; Kapulnik, Y.; et al. Responses of agronomically important crops to inoculation with Azospirillum. Aust. J. Plant. Physiol. 2001, 28, 871–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badri, D.V.; Weir, T.L.; Van Der Lelie, D.; Vivanco, J.M. Rhizosphere chemical dialogues: Plant-microbe interactions. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2009, 20, 642–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blanco, R.B.; Sicardi, M.; Frioni, L. Plant genotype and nitrogen fertilization effects on abundance and diversity of diazotrophic bacteria associated with maize (Zea mays L.). Biol. Fertil. Soils 2015, 51, 391–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merino, C.; Nannipieri, P.; Matus, F. Soil carbon controlled by plant, microorganism and mineralogy interactions. J. Soil Sci. Plant 2015, 15, 321–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimkpa, C.; Weinand, T.; Asch, F. Plant–rhizobacteria interactions alleviate abiotic stress conditions. Plant Cell Environ. 2009, 32, 1682–1694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilyas, N.; Bano, A. Azospirillum strains isolated from roots and rhizosphere soil of wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) grown under different soil moisture conditions. Biol. Fertil. Soils 2010, 46, 393–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reis, V.M.; Teixeira, K.R.S. Fixação Biológica de Nitrogênio–Estado da arte. In Processos Biológicos No Sistema Solo-Planta: Ferramentas Para Uma Agricultura Sustentável; Aquino, A.M., Assis, R.L., Eds.; Embrapa Informação Tecnológica: Brasília, Brazil, 2005; pp. 151–180. [Google Scholar]
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).