Incorporation of Manure into Ridge and Furrow Planting System Boosts Yields of Maize by Optimizing Soil Moisture and Improving Photosynthesis
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Site Description
2.2. Experimental Treatments and Design
2.3. Data Collection and Measurements
2.3.1. Precipitation and Air Temperature
2.3.2. Soil Water Storage
2.3.3. Dry Matter Accumulation and Grain Yield
2.3.4. Relevant Photosynthetic Parameters
2.3.5. Evapotranspiration and Water Use Efficiency
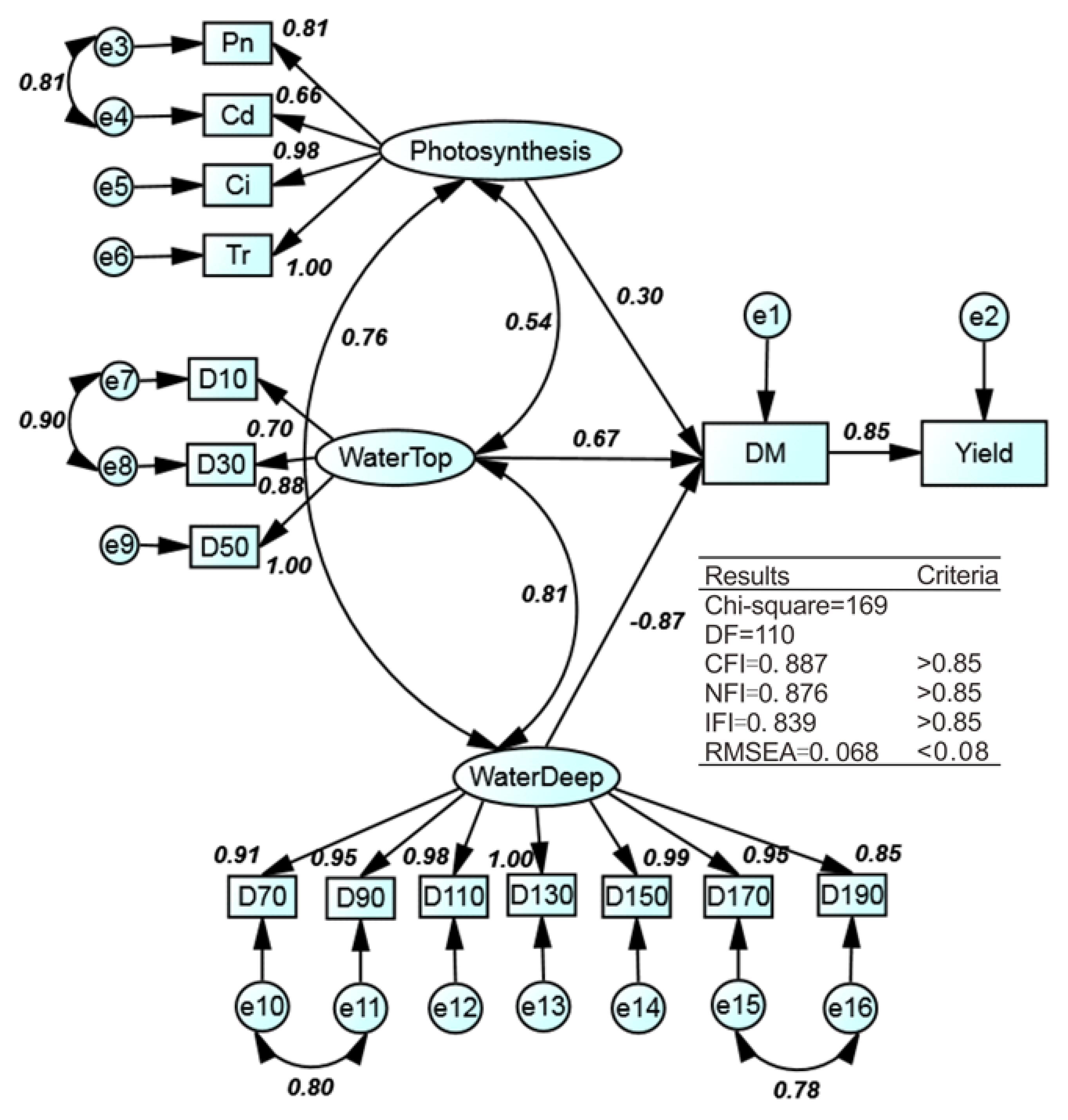
2.3.6. Structural Equation Model
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Rainfall and Air Temperature at the Experimental Site
3.2. Photosynthetic Parameters
3.3. Dry Matter Accumulation
3.4. Soil Moisture Dynamics
3.5. Yield, Evapotranspiration, and Water Use Efficiency
3.6. Model Development
4. Discussion
4.1. Soil Moisture Conservation of Ridge and Furrow Planting with Manure Amendment
4.2. Yields Boosting Effect of Ridge and Furrow Planting with Manure Amendment
4.3. Advantage of Structural Equation Modeling
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ren, X.; Chen, X.; Jia, Z. Effect of rainfall collecting with ridge and furrow on soil moisture and root growth of corn in semiarid northwest China. J. Agron. Crop Sci. 2010, 196, 109–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, S.; Jan, A.; Zhang, P.; Khan, M.N.; Cai, T.; Wei, T.; Ren, X.; Jia, Q.; Han, Q.; Jia, Z. Effects of ridge-covering mulches on soil water storage and maize production under simulated rainfall in semiarid regions of China. Agric. Water Manag. 2016, 178, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Zhang, X.; Yu, X.; Hou, H.; Fang, Y.; Ma, Y. Maize-faba bean rotation under double ridge and furrows with plastic mulching alleviates soil water depletion. Agric. Water Manag. 2018, 207, 59–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Hou, X.; Jia, Z.; Han, Q.; Ren, X.; Yang, B. Effects on soil temperature, moisture, and maize yield of cultivation with ridge and furrow mulching in the rainfed area of the Loess Plateau, China. Agric. Water Manag. 2013, 116, 101–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gan, Y.T.; Siddique, K.H.M.; Turner, N.C.; Li, X.G.; Niu, J.; Yang, C.; Liu, L. Ridge-furrow mulching systems—An innovative technique for boosting crop productivity in semiarid rain-fed environments—Chapter seven. Adv. Agron. 2013, 118, 429–476. [Google Scholar]
- Qin, S.; Zhang, J.; Dai, H.; Wang, D.; Li, D. Effect of ridge-furrow and plastic-mulching planting patterns on yield formation and water movement of potato in a semi-arid area. Agric. Water Manag. 2014, 131, 87–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Wei, L.; Wang, H.; Ma, S.; Ma, B. Responses of rainwater conservation, precipitation–use efficiency and grain yield of summer maize to a furrow-planting and straw-mulching system in northern China. Field Crops Res. 2011, 124, 223–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Wang, R.; Ma, B.; Xiong, Y.; Qiang, S.; Wang, C.; Liu, C.; Li, F. Ridge-furrow with full plastic film mulching improves water use efficiency and tuber yields of potato in a semiarid rainfed ecosystem. Field Crops Res. 2014, 161, 137–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, J.; Liu, X.; Song, L.; Lin, X.; Zhang, H.; Shen, C.; Chu, H. Nitrogen fertilization directly affects soil bacterial diversity and indirectly affects bacterial community composition. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2016, 92, 41–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iqbal, S.; Arif, M.; Thierfelder, C.; Yasmeen, T.; Li, T. Reducing nitrogen losses and increasing maize productivity in organic manures-amended soils by increasing the ridge to furrow proportion. Exp. Agric. 2019, 55, 428–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-Báscones, M.; Antolín-Rodríguez, J.M.; Bravo-Sánchez, C.T.; Martín-Gil, J.; Martín-Ramos, P. Dried pig manure from a cogeneration plant as a fertilizer for nitrate vulnerable zones. Agronomy 2019, 9, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Amusan, A.O.; Adetunji, M.T.; Azeez, J.O.; Bodunde, J.G. Effect of the integrated use of legume residue, poultry manure and inorganic fertilizers on maize yield, nutrient uptake and soil properties. Nutr. Cycl. Agroecosyst. 2011, 90, 321–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tétard–Jones, C.; Edwards, M.G.; Rempelos, L.; Gatehouse, A.M.; Eyre, M.; Wilcockson, S.J.; Leifert, C. Effects of previous crop management, fertilization regime and water supply on potato tuber proteome and yield. Agronomy 2013, 3, 59–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gosal, S.K.; Gill, G.K.; Sharma, S.; Walia, S.S. Soil nutrient status and yield of rice as affected by long-term integrated use of organic and inorganic fertilizers. J. Plant Nutr. 2018, 41, 539–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cisse, A.; Arshad, A.; Wang, X.; Yattara, F.; Hu, Y. Contrasting Impacts of long-term application of biofertilizers and organic manure on grain yield of winter wheat in North China Plain. Agronomy 2019, 9, 312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bayu, W.; Rethman, N.F.G.; Hammes, P.S.; Alemu, G. Effects of farmyard manure and inorganic fertilizers on sorghum growth, yield, and nitrogen use in a semi-arid area of Ethiopia. J. Plant Nutr. 2006, 29, 391–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adediran, J.A.; Taiwo, L.B.; Akande, M.O.; Sobulo, R.A.; Idowu, O.J. Application of organic and inorganic fertilizer for sustainable maize and cowpea yields in Nigeria. J. Plant Nutr. 2005, 27, 1163–1181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alpha, J.; Chen, J.; Zhang, G. Effect of nitrogen fertilizer forms on growth, photosynthesis, and yield of rice under Cadmium stress. J. Plant Nutr. 2009, 32, 306–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Song, H.; Zhou, L.; Xu, Z.; Zhou, G. Vertical distributions of chlorophyll and nitrogen and their associations with photosynthesis under drought and rewatering regimes in a maize field. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2019, 272, 40–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schiavon, M.; Ertani, A.; Francioso, O.; Nardi, S. Manure fertilization gives high-quality earthworm coprolites with positive effects on plant growth and N metabolism. Agronomy 2019, 9, 659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Arhonditsis, G.B.; Stow, C.A.; Steinberg, L.J.; Kenney, M.A.; Lathrop, R.C.; McBride, S.J.; Reckhow, K.H. Exploring ecological patterns with structural equation modeling and Bayesian analysis. Ecol. Model. 2006, 192, 385–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pollman, C.D. Mercury cycling in aquatic ecosystems and trophic state-related variables—Implications from structural equation modeling. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 499, 62–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chinese Soil Taxonomy Cooperative Research Group. Chinese Soil Taxonomy (Revised Proposal); Institute of Soil Science/Chinese Agricultural Science and Technology Press, Academic Sinica: Beijing, China, 1995; pp. 42–59. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, X.; Li, C.; Zhang, M.; Wang, R.; Chen, B. Controlled release urea improved the nitrogen use efficiency, yield and quality of potato (Solanum tuberosum L.) on silt loamy soil. Field Crops Res. 2015, 181, 60–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stevens, R.D.; Tello, J.S. A latitudinal gradient in dimensionality of biodiversity. Ecography 2018, 41, 2016–2026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhou, L.; Jin, S.; Liu, C.; Xiong, Y.; Si, J.; Li, X.; Gan, Y.; Li, F. Ridge-furrow and plastic-mulching tillage enhances maize-soil interactions: Opportunities and challenges in a semiarid agroecosystem. Field Crops Res. 2012, 126, 181–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, X.; Zhang, P.; Chen, X.; Guo, J.; Jia, Z. Effect of different mulches under rainfall concentration system on corn production in the semi-arid areas of the Loess Plateau. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 19019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhou, L.; Li, F.; Jin, S.; Song, Y. How two ridges and the furrow mulched with plastic film affect soil water, soil temperature and yield of maize on the semiarid Loess Plateau of China. Field Crops Res. 2009, 113, 41–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hengsdijk, H.; Meijerinkb, G.W.; Mosuguc, M.E. Modeling the effect of three soil and water conservation practices in Tigray, Ethiopia. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2005, 105, 29–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saha, S.; Prakash, V.; Kundu, S.; Kumar, N.; Mina, B.L. Soil enzymatic activity as affected by long term application of farm yard manure and mineral fertilizer under a rainfed soybean-wheat system in N–W Himalaya. Eur. J. Soil Biol. 2008, 44, 309–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boitt, G.; Simpson, Z.P.; Tian, J.; Black, A.; Wakelin, S.A.; Condron, L.M. Plant biomass management impacts on short–term soil phosphorus dynamics in a temperate grassland. Biol. Fertil. Soils 2018, 54, 397–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, A.; Patel, D.; Kumar, M.; Ramkrushna, G.; Mukherjee, A.; Layek, J.; Ngachan, S.; Buragohain, J. Impact of seven years of organic farming on soil and produce quality and crop yields in eastern Himalayas, India. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2017, 236, 142–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, G.; Sun, B. Nitrogen leaching under corn cultivation stabilized after four years application of pig manure to red soil in subtropical China. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2012, 146, 73–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maji, D.; Misra, P.; Singh, S.; Kalra, A. Humic acid rich vermicompost promotes plant growth by improving microbial community structure of soil as well as root nodulation and mycorrhizal colonization in the roots of Pisum sativum. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2017, 110, 97–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melero-Vara, J.M.; López-Herrera, C.J.; Prados-Ligero, A.M.; Vela-Delgado, M.D.; Navas-Becerra, J.A.; Basallote-Ureba, M.J. Effects of soil amendment with poultry manure on carnation Fusarium wilt in greenhouses in southwest Spain. Crop Prot. 2011, 30, 970–976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dambreville, C.; Hallet, S.; Nguyen, C.; Morvan, T.; Germon, J.C.; Philippot, L. Structure and activity of the denitrifying community in a maize-cropped field fertilized with composted pig manure or ammonium nitrate. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2006, 56, 119–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iqbal, A.; He, L.; Khan, A.; Wei, S.; Akhtar, K.; Ali, I.; Ullah, S.; Munsif, F.; Zhao, Q.; Jiang, L. Organic manure coupled with inorganic fertilizer: An approach for the sustainable production of rice by improving soil properties and nitrogen use efficiency. Agronomy 2019, 9, 651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dubey, R.; Dubey, P.; Abhilash, P. Sustainable soil amendments for improving the soil quality, yield and nutrient content of Brassica juncea (L.) grown in different agroecological zones of eastern Uttar Pradesh, India. Soil Tillage Res. 2019, 195, 104418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, S.; Upadhyaya, A. A survey of soils for aggregate stability and glomalin, a glycoprotein produced by hyphae of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi. Plant Soil 1998, 198, 97–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xin, X.; Qin, S.; Zhang, J.; Zhu, A.; Yang, W.; Zhang, X. Yield, phosphorus use efficiency and balance response to substituting long-term chemical fertilizer use with organic manure in a wheat-maize system. Field Crop. Res. 2017, 208, 27–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Mi, W.; Su, L.; Shan, Y.; Wu, L. Controlled-release fertilizer enhances rice grain yield and N recovery efficiency in continuous non-flooding plastic film mulching cultivation system. Field Crop. Res. 2019, 231, 122–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Ren, Y.; Zhang, S.; Chen, Y.; Wang, N. Applications of organic manure increased maize (Zea mays L.) yield and water productivity in a semi-arid region. Agric. Water Manag. 2017, 187, 88–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daszkowska-Golec, A.; Szarejko, I. Open or close the gate—Stomata action under the control of phytohormones in drought stress conditions. Front. Plant Sci. 2013, 4, 138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhang, D.; Jiao, X.; Du, Q.; Song, X.; Li, J. Reducing the excessive evaporative demand improved photosynthesis capacity at low costs of irrigation via regulating water driving force and moderating plant water stress of two tomato cultivars. Agric. Water Manag. 2018, 199, 22–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raich, J.W.; Mora, G. Estimating root plus rhizosphere contributions to soil respiration in annual croplands. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2005, 69, 634–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Qin, A.; Ning, D.; Liu, Z.; Sun, B.; Zhao, B.; Xiao, J.; Duan, A. Insentek sensor: An alternative to estimate daily crop evapotranspiration for maize plants. Water 2019, 11, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Qin, A.; Ning, D.; Liu, Z.; Sun, B.; Zhao, B.; Xiao, J.; Duan, A. Structural equation modeling of soil moisture effects on evapotranspiration of maize in the North China Plain. Natl. Acad. Sci. Lett. 2019, 42, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, J.; Cheng, J.; Sun, L.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, H. Effect of antecedent soil water on preferential flow in four soybean plots in southwestern China. Soil Sci. 2017, 182, 83–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garrigues, S.; Boone, A.; Decharme, B.; Olioso, A.; Albergel, C.; Calvet, J.; Moulin, S.; Buis, S.; Martin, E. Impacts of the soil water transfer parameterization on the simulation of evapotranspiration over a 14-year Mediterranean crop succession. J. Hydrometeorol. 2018, 19, 3–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
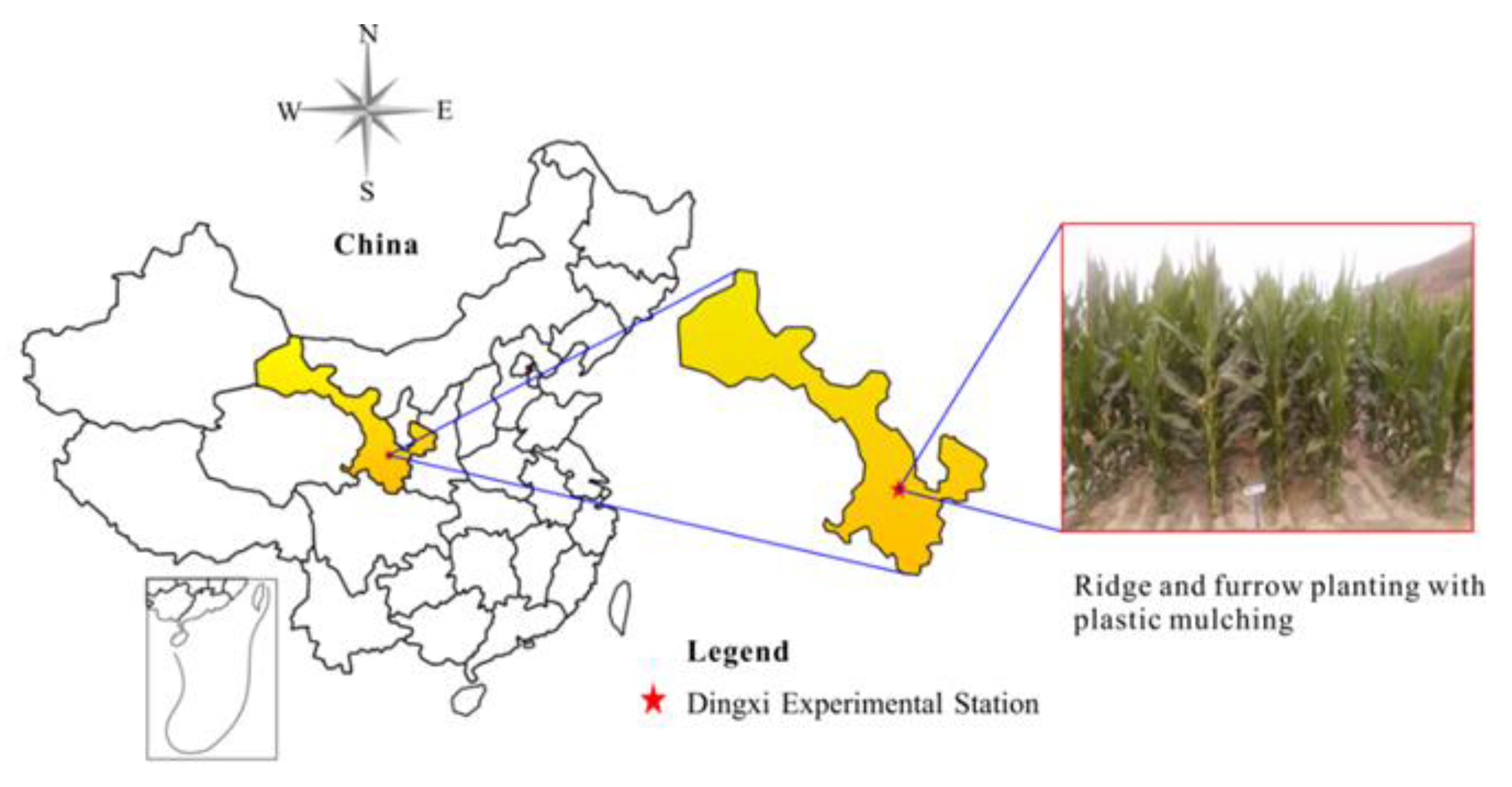




| Soil Depth | Bulk Density | Wilting Point | Holding Capacity | Organic Matter Content | Total Nitrogen | Total Phosphorus | Available Potassium |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| cm | g cm−3 | cm3 cm−3 | g kg−1 | mg kg−1 | |||
| 0–20 | 1.18 | 8.64 | 22.9 | 11.9 | 1.16 | 1.26 | 378.5 |
| 20–40 | 1.22 | 8.85 | 23.3 | 11.7 | 1.19 | 1.34 | 358.6 |
| 40–60 | 1.14 | 9.40 | 23.5 | 11.4 | 1.06 | 1.27 | 278.4 |
| 60–80 | 1.06 | 9.30 | 23.5 | 10.9 | 1.03 | 1.18 | 196.3 |
| 80–100 | 1.16 | 9.60 | 23.7 | 11.2 | 1.12 | 1.21 | 152.4 |
| 100–120 | 1.13 | 9.65 | 23.7 | 10.7 | 1.13 | 1.12 | 115.7 |
| 120–140 | 1.15 | 9.70 | 23.8 | 10.9 | 1.08 | 1.03 | 116.9 |
| 140–160 | 1.18 | 9.60 | 23.7 | 10.7 | 1.02 | 0.89 | 113.2 |
| 160–180 | 1.15 | 9.90 | 23.9 | 10.1 | 0.99 | 0.85 | 110.2 |
| 180–200 | 1.16 | 10.0 | 23.9 | 10.2 | 0.83 | 0.79 | 111.3 |
| Fertilizer Types | Percentage Composition (%) | Application Rates (kg ha−1) | Equivalent NPK Rates (kg ha–1) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N | P2O5 | K2O | ||||
| Chemical fertilizer | Urea | N: 46 | 490 | 225 | – | – |
| Calcium superphosphate | P2O5: 16 | 560 | – | 90 | – | |
| Potassium chloride | K2O: 60 | 120 | – | – | 72 | |
| Control-released fertilizer | N-P2O5-K2O: 25-10-8 | 900 | 216 | 90 | 72 | |
| Manure fertilizer | Sheep manure | N-P2O5-K2O: 1.85-1.50-1.25 | 6000 | 110 | 90 | 74 |
| 50% urea | N: 46 | 245 | 112 | – | – | |
| Property | pH | EC (dS m−1) | Moisture Content (%) | Orgainc C (g kg−1) | Water Soluble Organic C (g kg−1) | Total N (g kg−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Manure | 8.1 | 4.87 | 58.6 | 204.2 | 13.7 | 18.5 |
| Property | Available N (mg kg−1) | Total P (g kg−1) | Available P (mg kg−1) | Total K (g kg−1) | Available K (mg kg−1) | Decomposition Rate (%) |
| Manure | 74.1 | 15.2 | 152.4 | 12.1 | 128.6 | 68.3 |
| Treatments | DMmax | B | K | Vmax | DASmax | R2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| g plant−1 | g plant−1 day−1 | day | ||||
| 2017 | ||||||
| CK | 339 c | 546 | 0.062 | 5.26 c | 102 a | 0.996 ** |
| RFC | 382 b | 403 | 0.059 | 5.64 b | 102 a | 0.994 ** |
| RFR | 382 b | 497 | 0.062 | 5.92 b | 100 ab | 0.995 ** |
| RFM | 406 a | 637 | 0.067 | 6.80 a | 96 b | 0.992 ** |
| 2018 | ||||||
| CK | 352 c | 375 | 0.058 | 5.11 c | 102 a | 0.996 ** |
| RFC | 379 b,c | 424 | 0.061 | 5.78 b | 99 b | 0.994 ** |
| RFR | 399 b | 555 | 0.064 | 6.39 a | 99 b | 0.995 ** |
| RFM | 440 a | 378 | 0.060 | 6.59 a | 99 b | 0.992 ** |
| Year/Treatments | Pre (mm) | SWS (mm) | ETc (mm) | GY (kg ha–1) | WUE (kg ha–1 mm–1) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Before Sowing | After Harvest | |||||
| 2017 | ||||||
| CK | 324 | 272 b | 283 b | 313 b,c | 7797 b | 24.9 b |
| RFC | 324 | 284 a | 256 c | 352 a | 7949 b | 22.6 c |
| RFR | 324 | 279 ab | 279 b | 324 b | 7698 b | 23.8 bc |
| RFM | 324 | 271 b | 297 a | 298 c | 9242 a | 31.0 a |
| 2018 | ||||||
| CK | 425 | 270 b | 310 c | 385 b | 9593 c | 24.9 c |
| RFC | 425 | 286 a | 312 c | 399 a | 9929 b | 24.9 c |
| RFR | 425 | 292 a | 364 a | 353 c | 9756 b,c | 27.6 b |
| RFM | 425 | 269 b | 351 b | 343 c | 11,102 a | 32.4 a |
| Latent Variables | Correlation Coefficients | Direct Effects on DM | Indirect Effects on Yield | Contribution to DM | Contribution to Yields | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Photosynthesis | WaterTop | WaterDeep | |||||
| Photosynthesis | 1 | 0.54 * | 0.76 ** | 0.30 * | 0.26 * | 0.09 | 0.07 |
| WaterTop | — | 1 | 0.81 ** | 0.67 ** | 0.57 * | 0.45 * | 0.32 * |
| WaterDeep | — | — | 1 | –0.87 ** | –0.74 ** | 0.76 ** | 0.55 * |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Qin, A.; Fang, Y.; Ning, D.; Liu, Z.; Zhao, B.; Xiao, J.; Duan, A.; Yong, B. Incorporation of Manure into Ridge and Furrow Planting System Boosts Yields of Maize by Optimizing Soil Moisture and Improving Photosynthesis. Agronomy 2019, 9, 865. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy9120865
Qin A, Fang Y, Ning D, Liu Z, Zhao B, Xiao J, Duan A, Yong B. Incorporation of Manure into Ridge and Furrow Planting System Boosts Yields of Maize by Optimizing Soil Moisture and Improving Photosynthesis. Agronomy. 2019; 9(12):865. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy9120865
Chicago/Turabian StyleQin, Anzhen, Yanjie Fang, Dongfeng Ning, Zhandong Liu, Ben Zhao, Junfu Xiao, Aiwang Duan, and Beibei Yong. 2019. "Incorporation of Manure into Ridge and Furrow Planting System Boosts Yields of Maize by Optimizing Soil Moisture and Improving Photosynthesis" Agronomy 9, no. 12: 865. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy9120865
APA StyleQin, A., Fang, Y., Ning, D., Liu, Z., Zhao, B., Xiao, J., Duan, A., & Yong, B. (2019). Incorporation of Manure into Ridge and Furrow Planting System Boosts Yields of Maize by Optimizing Soil Moisture and Improving Photosynthesis. Agronomy, 9(12), 865. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy9120865









