Abstract
The need to intensify agriculture to meet increasing nutritional needs, in combination with the evolution of unmanned autonomous systems has led to the development of a series of “smart” farming technologies that are expected to replace or complement conventional machinery and human labor. This paper proposes a preliminary methodology for the economic analysis of the employment of robotic systems in arable farming. This methodology is based on the basic processes for estimating the use cost for agricultural machinery. However, for the case of robotic systems, no average norms for the majority of the operational parameters are available. Here, we propose a novel estimation process for these parameters in the case of robotic systems. As a case study, the operation of light cultivation has been selected due the technological readiness for this type of operation.
1. Introduction
The evolution of technology and the transition to the digitalized world of automation has driven momentum for the introduction and use of autonomous robotic systems. As a result, multiple processes across industrial production and associated service domains are being robotized [1]. The paradigm shift towards robotization is evident in the agricultural sector. The need for increased efficiency of agricultural practices with reduced environmental burden [2] drives the evolution of technology towards integrated “smart” farming systems that replace conventional farming practices [3,4]. Knowledge-based agriculture management systems that employ autonomous systems have been introduced that aim to reduce inputs by considering site-specific and time-specific crop conditions and needs [5,6]. However, feasibility studies examining the costs and benefits arising from the implementation of agricultural robotic systems, as a newly introduced technology, are essential to support wider adoption by users in the sector [7,8]. The cost elements relate to the development of the robotic system, the investment, the maintenance, set-up, and use. Benefits relate to the saving of labor replaced by robotic systems and the higher quality/efficiency of the operations performed. In addition, many of the human activities augmented by robotics might be harmful, dangerous, and performed under difficult, all-weather conditions.
A first approach for the comparison between conventional and autonomous systems, in terms of their economic feasibility, was presented by Sørensen et al. (2005) [9]. In their work, an evaluation of the impact of the implementation of innovative technologies (robotic weeding and an integrated system for band steaming) in organic farming was presented. Based on their results, labor demand could be reduced up to 85% in a sugar beet production case study and c. 60% for carrot production. A second work on the system analysis and feasibility assessment of robotic systems in agriculture was presented by Pedersen et al. (2006) [10]. In their work, three applications of robotics implementation in agricultural operations executed conventionally by human-labor were examined, namely: field scouting (cereals), weeding (sugar beet), and grass cutting (golf courses). Reductions of operating costs of up to 24% were reported. However, the relative literature is still poor with no detailed cost analysis of the impact of labor replacement by robotic systems, and especially comparisons where robotic systems replace or augment conventional agricultural machinery. Furthermore, for a holistic evaluation of an robotic agricultural operation system, hidden cost elements have to be quantified, such as changes in soil fertility due to less compaction of a lighter operating system, the potential for optimized execution of operations [11,12], the reduced environmental impact [13], the increased precision of the executed operations, the workability extension due to the reduced field readiness requirements, and the added value of specialized operations where robots are replacing limited human skills in executed tasks.
This paper proposes a preliminary methodology for the economic analysis of the employment of robotic systems in arable farming. This methodology is based on the basic processes for estimating the use cost for agricultural machinery. However, for the case of robotic systems, no average norms are available for the majority of the critical operational parameters. Therefore, we propose an estimation process to quantify these parameters. Due its technological readiness, light cultivation has been selected as a case study.
In the following sections, a conventional and a robotic system are described and examined in two scenario cases, namely: a small-scale farm and a large-scale farm, followed by a break-down of all costs. The work focuses on the economic feasibility of replacing conventional practices with a respective robotized alternative. Even though it is a theoretical approach, an indicative case study is presented to facilitate discussion and considers the sensitivity of predetermined indicators for the introduction of these new technologies.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Field Efficiency of Agricultural Machinery
Robotic agricultural systems developed until now are characterized by a considerably lower capacity compared to conventional agricultural machinery. Consequently, to perform the same amount of work in a defined area within a specific time window (due to workability and timeliness constraints) could require robotic machines.
The available (workable—in agronomic terms) time for performing a task in a field area , can be expressed as:
where —“d” stands for “days”—is the working period, w (dimensionless) is the workability coefficient and working hours per day [14]. The area capacity (Area capacity of an agricultural machine expresses the worked area per time unit) [15] of the machinery should comply with the following condition:
Considering the above constraint, the number of units n required for the completion of an agricultural task is given by:
The efficiency of conventional machinery has been modelled using international operational standards, such as those provided by American Society of Agricultural and Biological Engineers (ASABE). These provide data on likely operational speed and width to calculate capacity . However, these standards do not necessarily apply for robotic agricultural systems, even though they can be acknowledged as agricultural machinery. In general, field efficiency of an agricultural machinery system (undependably of its conventional or robotic nature) is defined by:
where is the total operation time needed to perform the task and is the net operational time, namely the time needed for the machine to complete the task without any idle time under optimum conditions, as presented below:
where denotes the optimum (in terms of agronomic requirements) operating speed and the named operating width of the machinery.
An important issue arising is the estimation of the idle times in the operation of the robotic agricultural system. For the purposes of the present study, these times include: (i) the recharging time for electric battery-operated systems, (ii) the time needed for the machine to reach the recharging station (ii) the time needed to mount and unmount the implement, and (iv) the idle time during turning points in the field headlands:
where presents the types of different idle times that can be observed during the execution of agricultural operations.
2.2. Costs Estimation Model
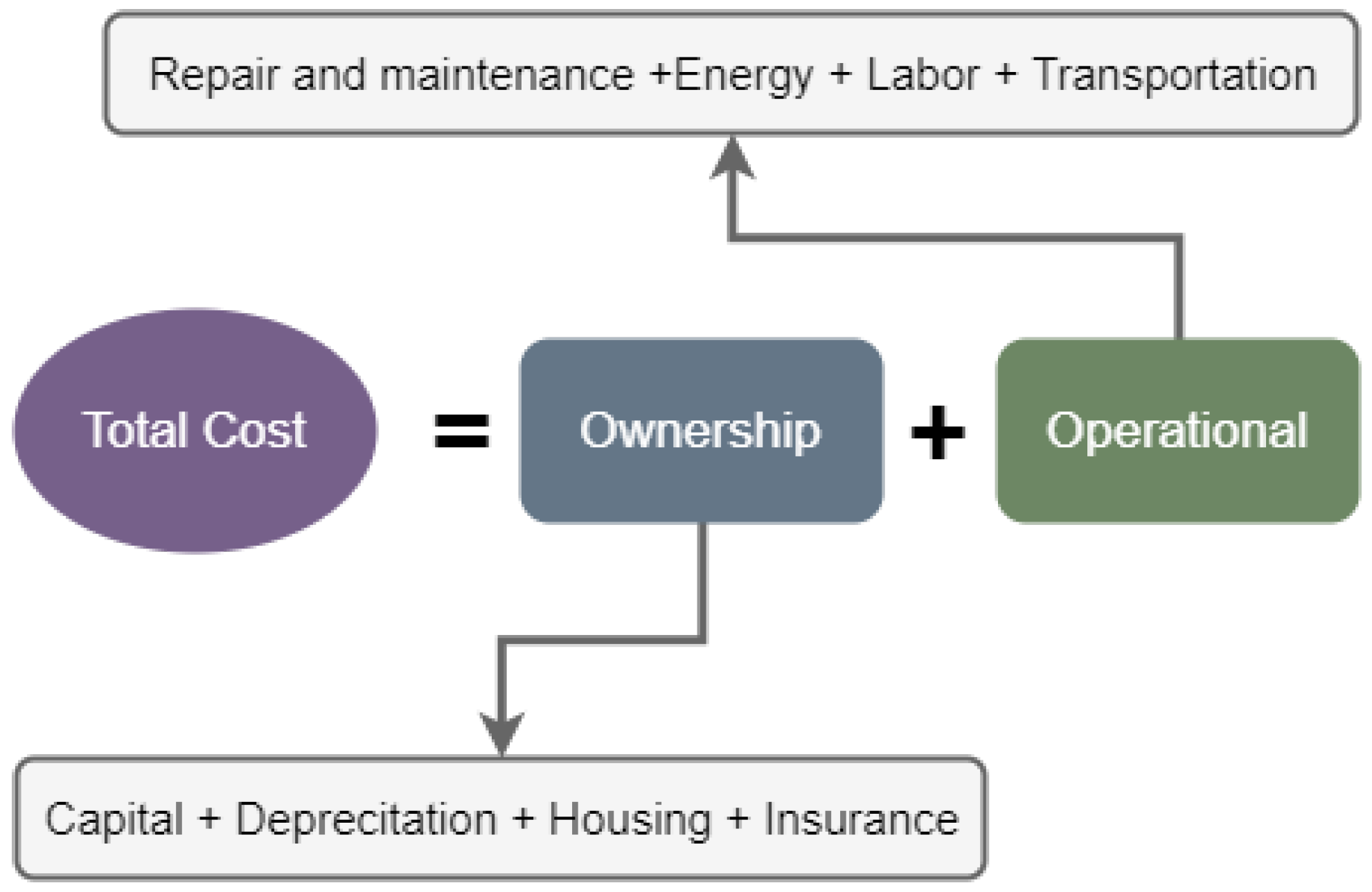
For economic assessment, the operational processes (e.g., crop and soil treatments) within a production system remain identical for both conventional and robotic systems. A schematic presentation of the individual cost elements considered in the determination of the economic model is demonstrated in Figure 1. This cost assessment model applied both for conventional equipment and robotic systems.
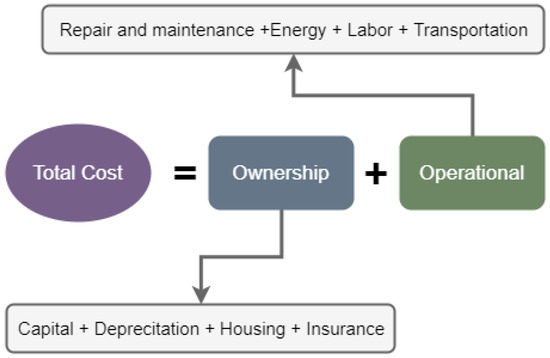
Figure 1.
Cost elements considered in the economic assessment.
The total cost of an agricultural machine is the summation of two main elements, namely the ownership cost () and the operational cost (). The investment in an agricultural robotic system requires capital for the purchase and the ownership of the machinery. The ownership cost represents the summation of the capital (), the depreciation (), the housing (), and the insurance cost (). The capital cost represents the interest charge, or the interest cost of the money used in the investment of the operating system. It is composed of the net investment cost over the machine’s lifetime:
where is the purchase price, is the book value, and represents the real interest rate calculated by:
with representing the interest, and the inflation rate. As depreciation cost is defined the reduction of the initial value of the machinery resulting from its exploitation [16]. The most common and simple method for estimating the depuration cost is the “fixed depreciation method” which equivalently allocates the value loss from the machinery use within the years of the investment:
where is the salvage value of the machinery at the end of its economic life . Regarding the storing and the safeguarding of the machinery, housing and insurance cost are also considered. These cost elements can be significant in the case of a robotic system due to specific requirements that have to be met. Housing and insurance costs are estimated on a purchase value basis, by considering appropriate coefficients. Thus, housing cost is given by: , where is the housing cost coefficient, while the insurance cost is given by: , where represents the insurance coefficient.
The operational cost of a system is the summation of the repair and maintenance cost (), the energy cost (i.e., fuel consumption or electric energy), (), the labor cost, (), and the farm to field transportation cost, (). For the calculation of the repair and maintenance cost for the conventional machinery system (i.e., for the tractor and the implement), the ASABE standards estimation process is utilized [17].
where and are the repair and maintenance factors and , expressed in hours, stands for the accumulated working hours of the machinery. For estimation of the repair and maintenance cost for robotic system, for the purposes of the present paper, it is considered as a percentage of the respective conventional system’s repair and maintenance cost in accordance to Bubeck et al. (2016) [18] approach, accordingly an electric engine presents lower repair and maintenance requirements compared to a conventional one. For the case of conventional machinery, the prediction of the energy cost, that is the engine fuel consumption during the operation, was based on the specific volumetric fuel consumption approach as it is described in ASAE D497.5 (2006) [19]. For the case of the robotic system, the energy cost is calculated by: , where M (kW) is the machine power, , the operation process duration, and is the cost of energy.
Regarding the labor cost in the case of the robotic system, although the system performs autonomously, man labor may be needed for the so-called ‘residual’ tasks, such as system advancements and reconfigurations, potential safety monitoring, and recharging. For the specific study, the total duration of the performed labor-task coincidences with the total duration of the operation although the worker(s) is not completely occupied. However, due to the potential given for the execution of other parallel tasks, only a part of the hourly wage is allocated of the labor cost of the robotic system. Finally, the transportation cost regards the cost for the transportation of the machinery between the farm and the field and between different fields. The transportation of the robotic system usually requires the use of a wagon, especially if the distance between fields is significant.
2.3. Case Study Description
To demonstrate the proposed methodological approach, a case study is presented. The aim of the study is to compare the cost of performing a specific agricultural task with the use of a robotic system and the use of conventional system. To assess the effect of the field area to the resulting cost of using robotic or conventional systems, two area scenarios have been selected to be investigated, namely, a small-scale (10 ha farm) and a large-scale (100 ha farm) scenario. The task chosen for the demonstration of the methodology is that of light cultivation for weed removal in row cropping systems, representing a singular field operation and not a coupled and more complex one. The cost elements regarding conventional machinery are calculated with the use of the ASABE standards [19,20].
In terms of the conventional machinery, the task is performed using a mechanical row crop cultivator (C-shank). In the case of the small-scale scenario (10-ha farm), a tractor of 40 kW was considered, while in the case of the larger scale scenario (100 ha farm) a tractor of 80 kW was selected, based on the agricultural machinery selection and sizing principles. The selected robotic platform regards the typical closed framed, four-wheel electrical driving, and four-wheel active steering system [21]. The robotic system carries a mechanical row crop cultivator (C-shank) of an operating width of 1.2 m, operating in a speed of 4 km h−1. Table 1 presents the parameters considered for the calculation of the total use cost for both the robotic system and the conventional agricultural system as a basic scenario.

Table 1.
Input parameters for the economic model (RS—Robotic System; CS—Conventional System; SCS—small-scale scenario; LSS—Large-scale scenario).
The assessment is performed in the end of the first year of the investment with respect to the calculation of the book value and the repair and maintenance cost of the equipment. The salvage value set at 10% of the purchase value for the conventional system. For the robotic system, the salvage values were considered to be 9% increased, compared to the conventional system which uses internal combustion engines [22].
For the sake of comparison, the following assumptions are made. The robotic system can operate autonomously at full power for approximately 4 h before recharging. The recharging duration is 3 h and it takes place on field side (no transportation is needed). The time needed for mounting and unmounting the implement in the robot was considered as 2 h, in total. Additionally, given the robot’s holonomic kinematics and size, it was assumed that it takes approximately 5 s for a headland turn to the adjacent row.
The housing and insurance coefficients are considered as three times the respective conventional ones since this type of machinery needs advanced storage conditions (higher security, weather protection, accompanying IT equipment, etc.). The repair and maintenance cost of the electric robotic system is considered a 75% of the respective conventional one [18]. For the case of the implement, the repair and maintenance factors are the same for both robotic and conventional systems [20]. For the estimation of the repair and maintenance cost, it is assumed that the conventional machinery works approximately 1066 h year−1 [19] given a 15-year lifespan and 16,000 h total working hours. The robotic system is assumed to be working for approximately 2000 h year−1 [16]. Lastly, regarding the conventional machinery, the specific fuel consumption was estimated at 0.478 l KWh−1 [19] and the average diesel cost for agricultural use was set to 1.038 € L−1 [23]. Additionally, the lubricant cost was considered as 10% of the fuel cost [15]. Finally, in the case of the robotic system, the half wage was considered (7.5 € h−1) to be allocated to the tasks of monitoring the robotic system, the implement mounting and unmounting, and the recharging set-up tasks.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Total Cost
Table 2 presents the input parameters and the resulting cost elements for the selected case study. With the implementation of the proposed economic model, the cost of performing light soil cultivation deploying the robotic system is approximately 2.7 times higher than the one deploying the conventional system in the case of the small-scale farm scenario and 1.9 times higher in the case of the large-scale farm scenario. This is mainly attributed to the significantly lower efficiency of the robotic system, which, for the specific case study examined, was calculated at 50%, approximately. This low efficiency caused by the assumption made that the robots return to the recharging station and spend 3 h idle time to recharge before resuming operation.

Table 2.
Calculated parameters and costs (RS—Robotic System; CS—Conventional System; SCS—small-scale scenario; LSS—Large-scale scenario).
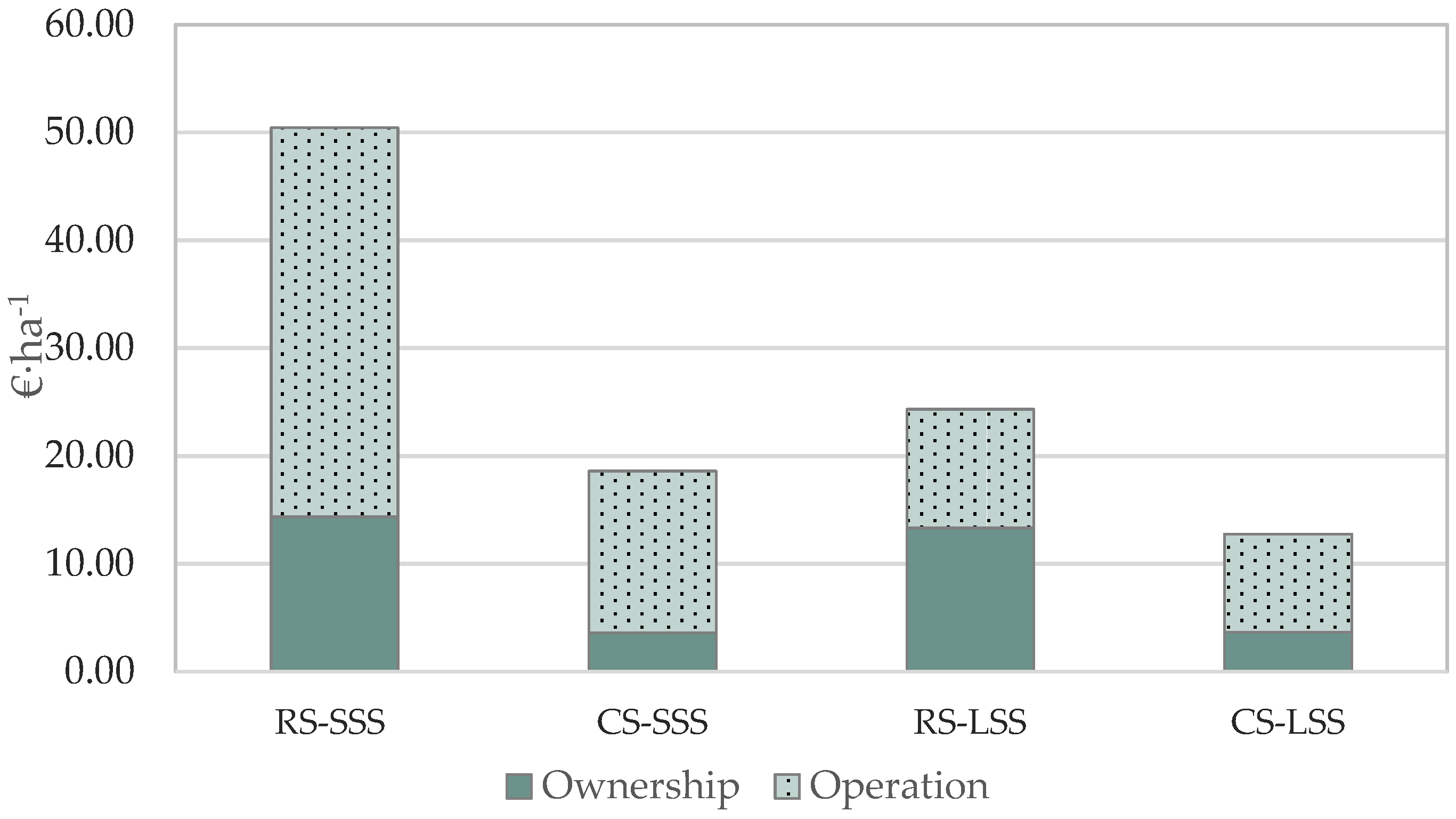
Figure 2 presents the total cost per unit area for both robotic and conventional systems in the case study examined. The ownership cost in the case of the robotic system counts for approximately 54.8% of the total cost in the large-scale farm scenario, and this fact is attributed to the deployment of a system of four robots to cope with the time constraints for the allocated task completion. The respective percentage for the small-scale scenario is 28.4%. In contrast, the corresponding percentages for the conventional system are considerably lower, namely, 19.3% and 28.9% for the large-scale and small-scale scenarios, respectively, due to the lower purchase cost of the system.
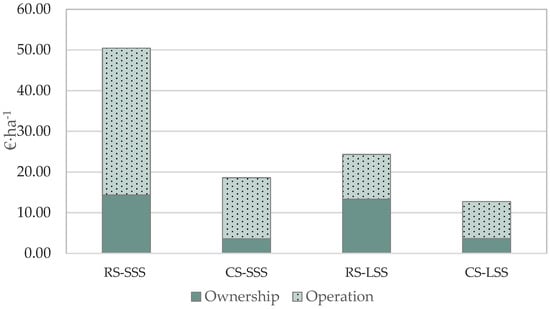
Figure 2.
Ownership cost and operation cost contribution to total cost (RS—Robotic System; CS—Conventional System; SSS—Small-Scale Scenario; LSS—Large-Scale Scenario).
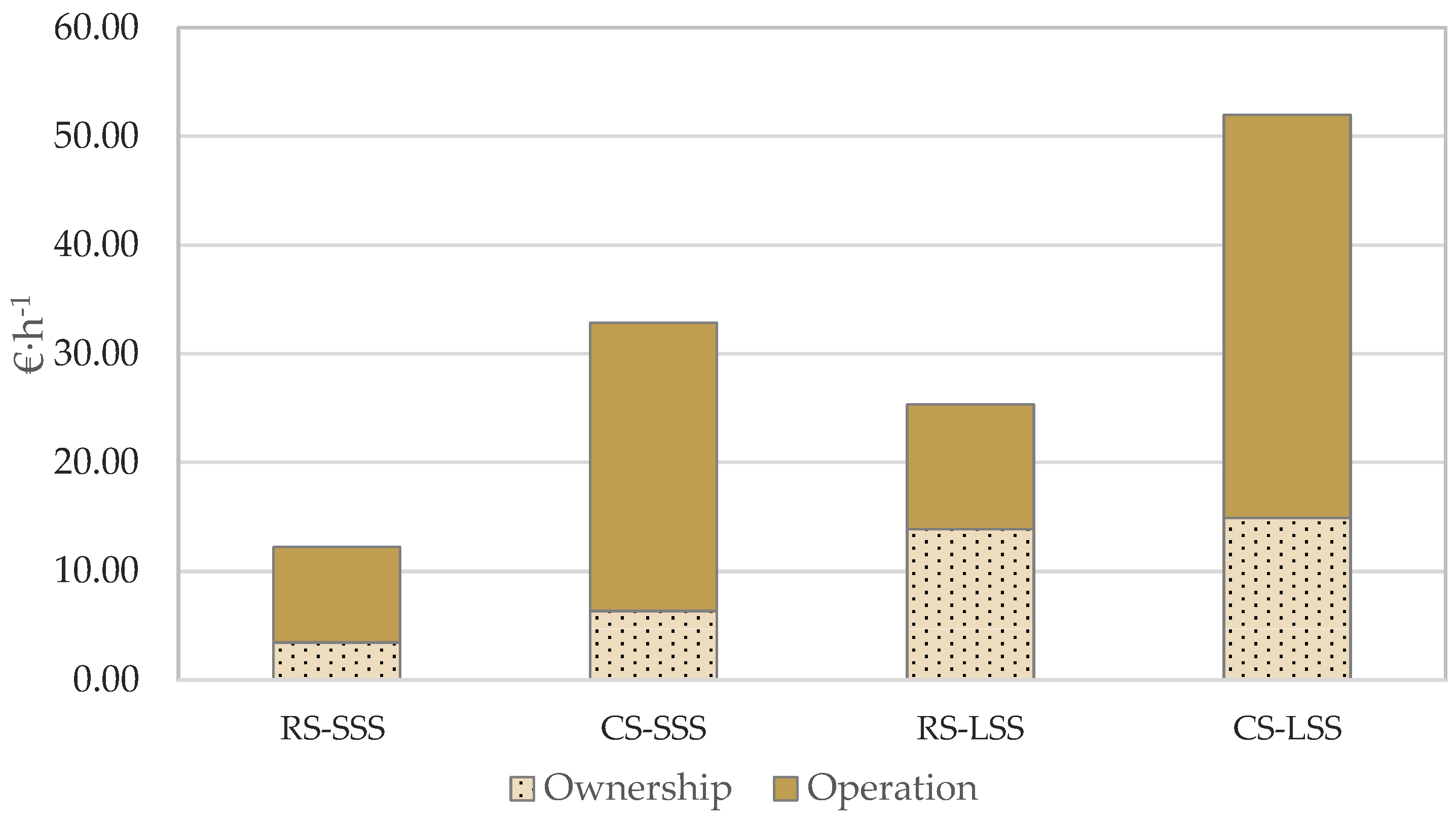
Figure 3 presents the total cost per unit time for both robotic and conventional systems in the case study examined. In the case of the robotic system, the operation cost contributes 45.2% and 71.6% of the total cost per unit time for the large-scale scenario and the small-scale scenario, respectively. The comparable percentages for the conventional system are 71.4% for the large-scale scenario and 80.7% for the small-scale scenario.
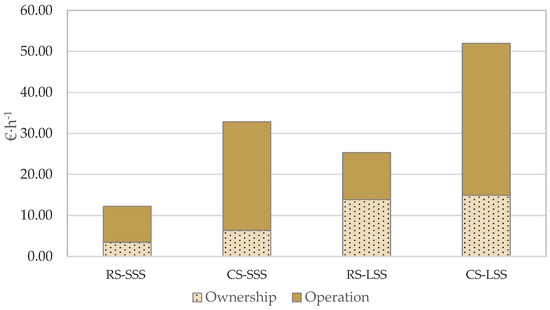
Figure 3.
Ownership cost and operation cost contribution to hourly cost (RS—Robotic System; CS—Conventional System; SSS—Small-Scale Scenario; LSS—Large-Scale Scenario).
3.2. Cost Analysis
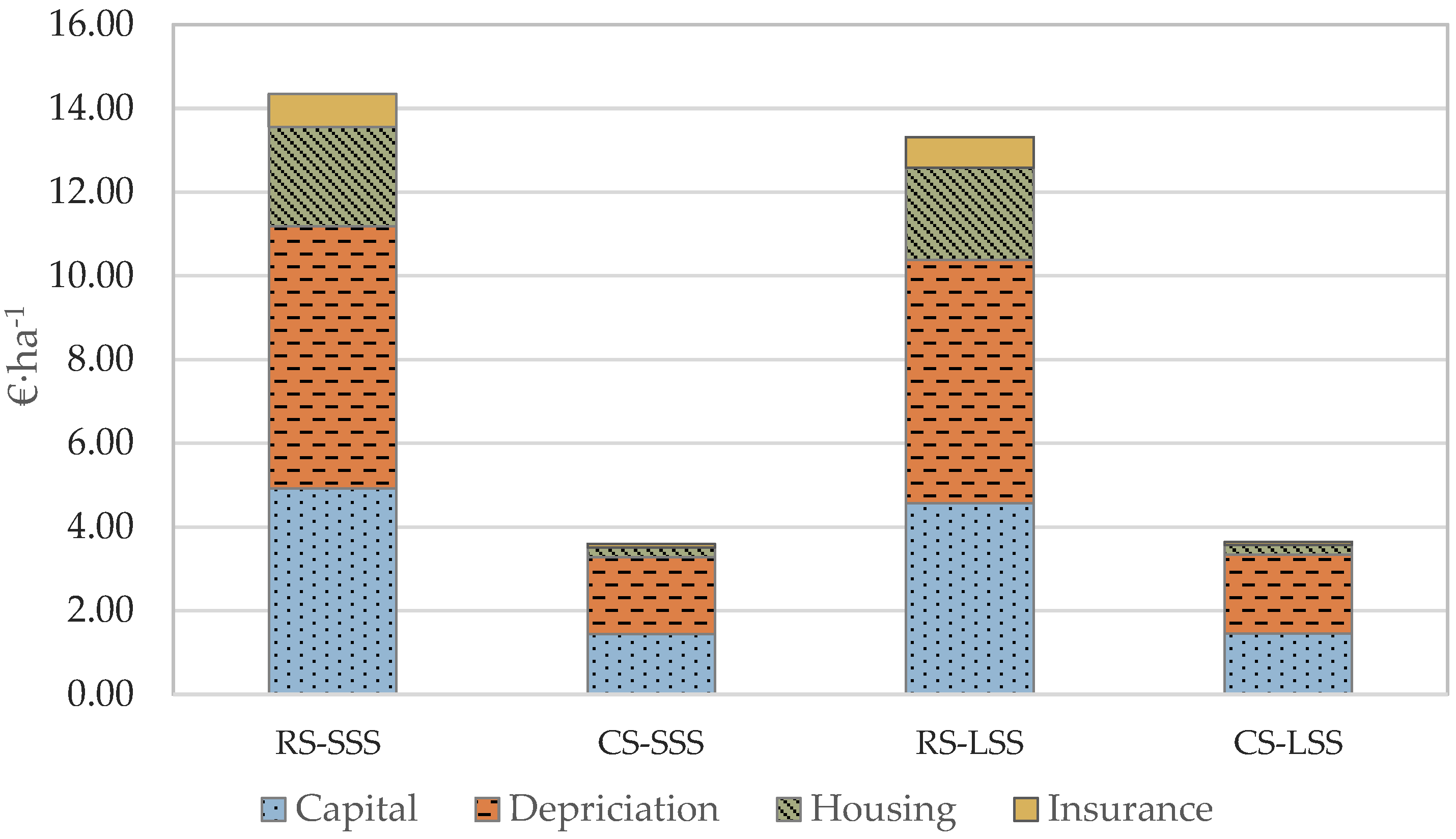
Figures 5–8 present the analysis of the individual ownership and operation cost both per unit area and unit time for the specific operation. As it can be seen in Figure 4, with respect to the unit area cost, the capital and the depreciation cost are the most significant ownership cost elements compared to housing and insurance cost. More specifically, the capital and depreciation cost contribute 78% of the total ownership cost in the case of the robotic system (both in the small and large-scale scenarios). The comparable percentage for the conventional machinery is 91%. This difference is caused by the fact that in the case of the robotic system, the housing and insurance coefficients were assumed to be three times higher compared to the respective conventional ones.
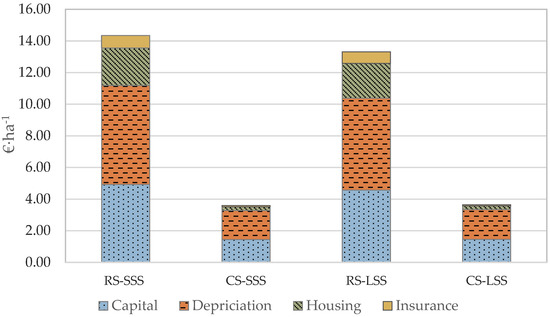
Figure 4.
Ownership cost per unit area analysis (RS—Robotic System; CS—Conventional System; SSS—Small-Scale Scenario; LSS—Large-Scale Scenario).
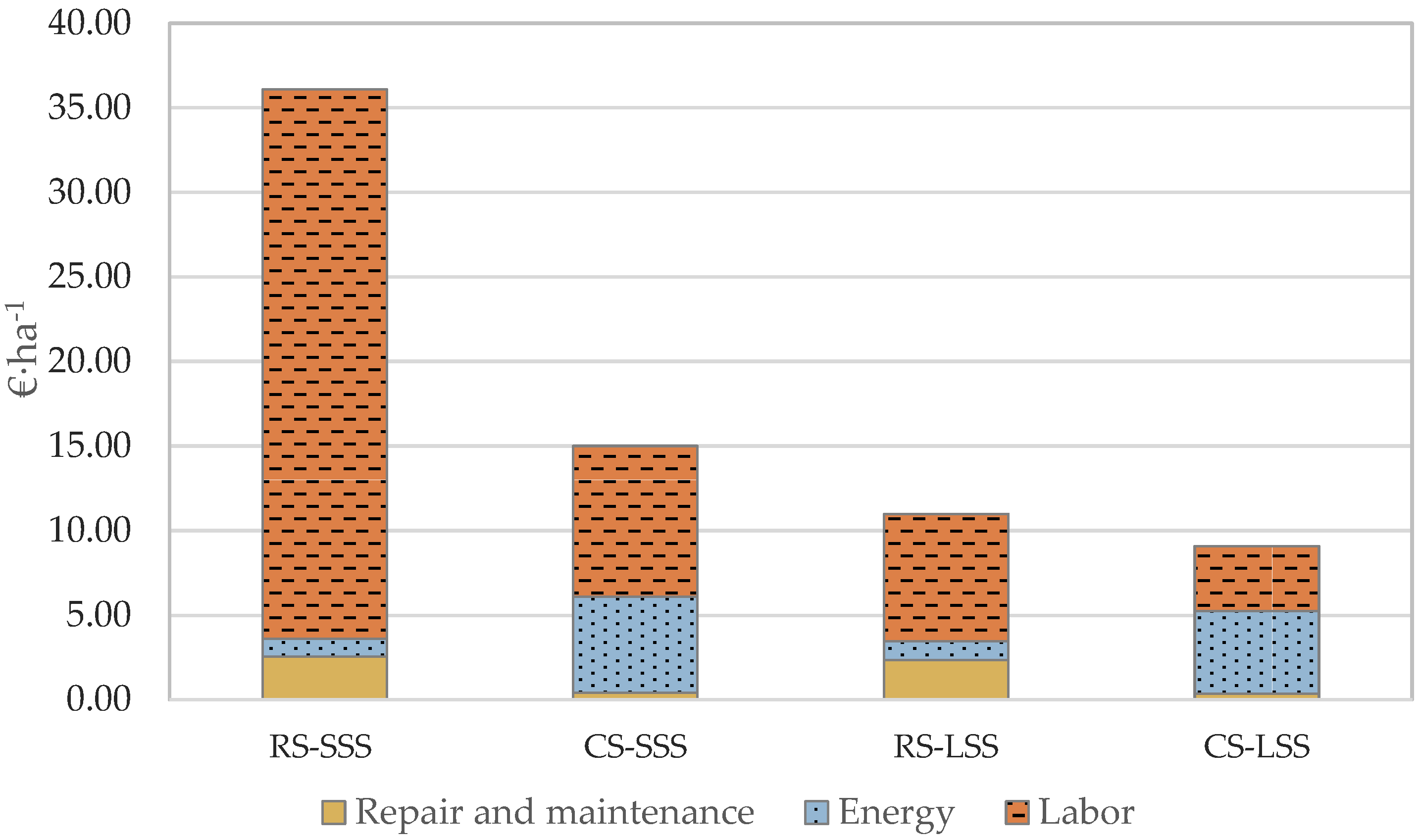
As demonstrated in Figure 5, in the case of the small-scale robotic system, the labor cost contributes 64.4% of the total cost and 90% of the operation cost. The comparable percentages in the case of the conventional system are 47.8% and 59.3%, respectively, even though the hourly wage of the worker (15 € h−1) is double the robotic system’s operator (7.5 € h−1). Additionally, for the conventional systems (small-scale) the labor cost is the most significant cost per unit area contributing towards 59.3% of the total operating cost. On the other hand, in the large-scale scenario, the energy cost of the machinery is 53.5% of the operation cost.
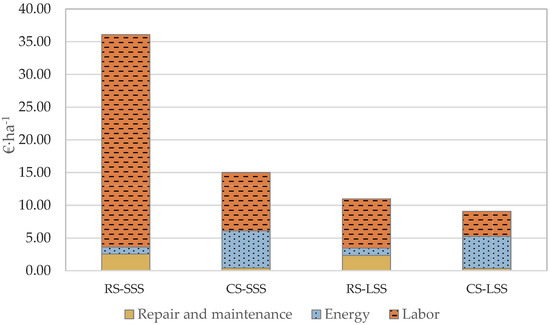
Figure 5.
Operation cost per unit area analysis (RS—Robotic System; CS—Conventional System; SSS—Small-Scale Scenario; LSS—Large-Scale Scenario).
The repair and maintenance cost, in the case of the robotic system (small and large-scale application), contribute significantly towards the total operation cost compared to the conventional system due to the increased annual use hours assumed. The contribution of the repair and maintenance cost is more significant in the case of the large-scale farm (21.5% of the total operation cost) compared to the small-scale 10-ha farm (approximately 7.1% of the total operation cost).
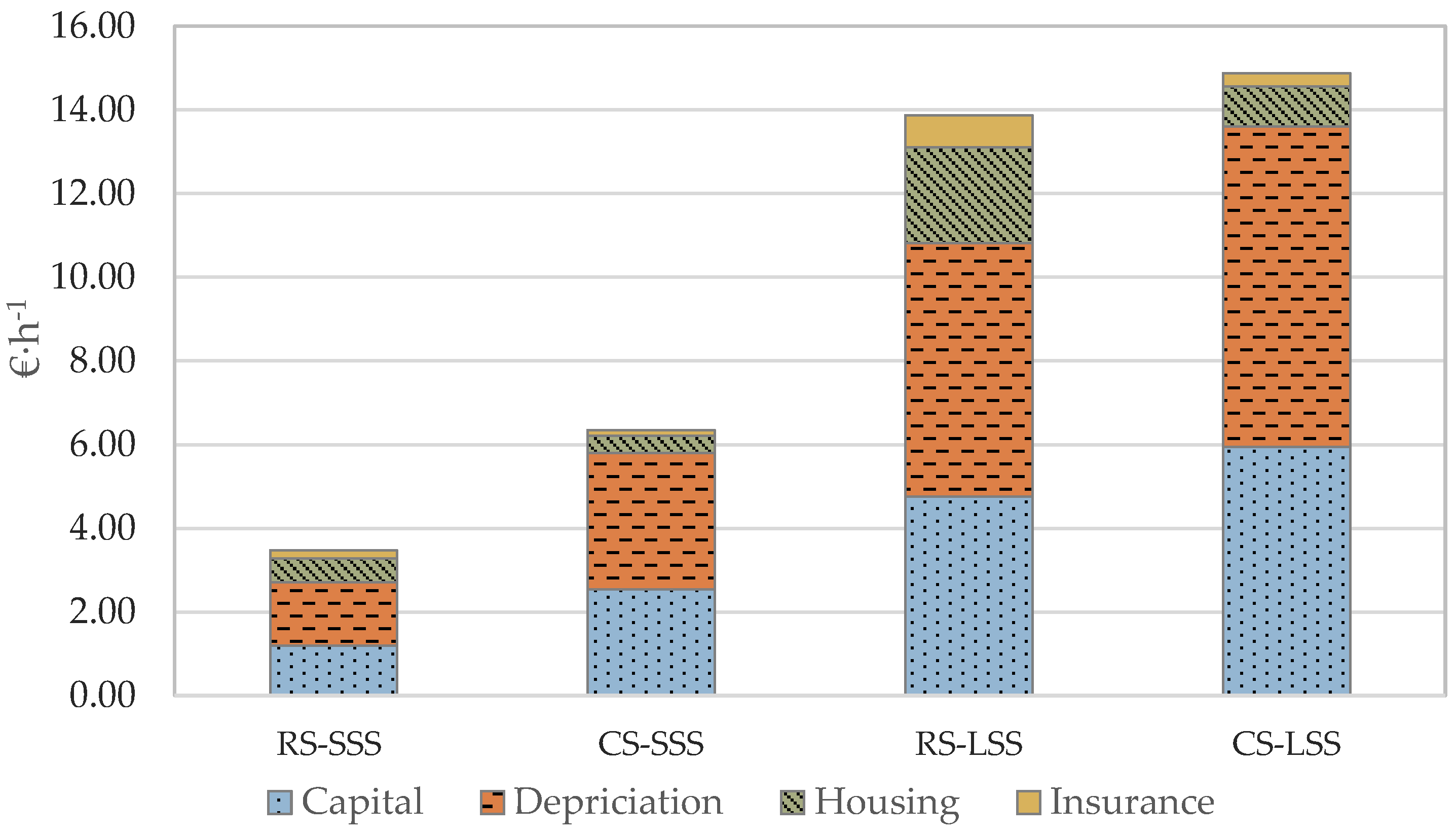
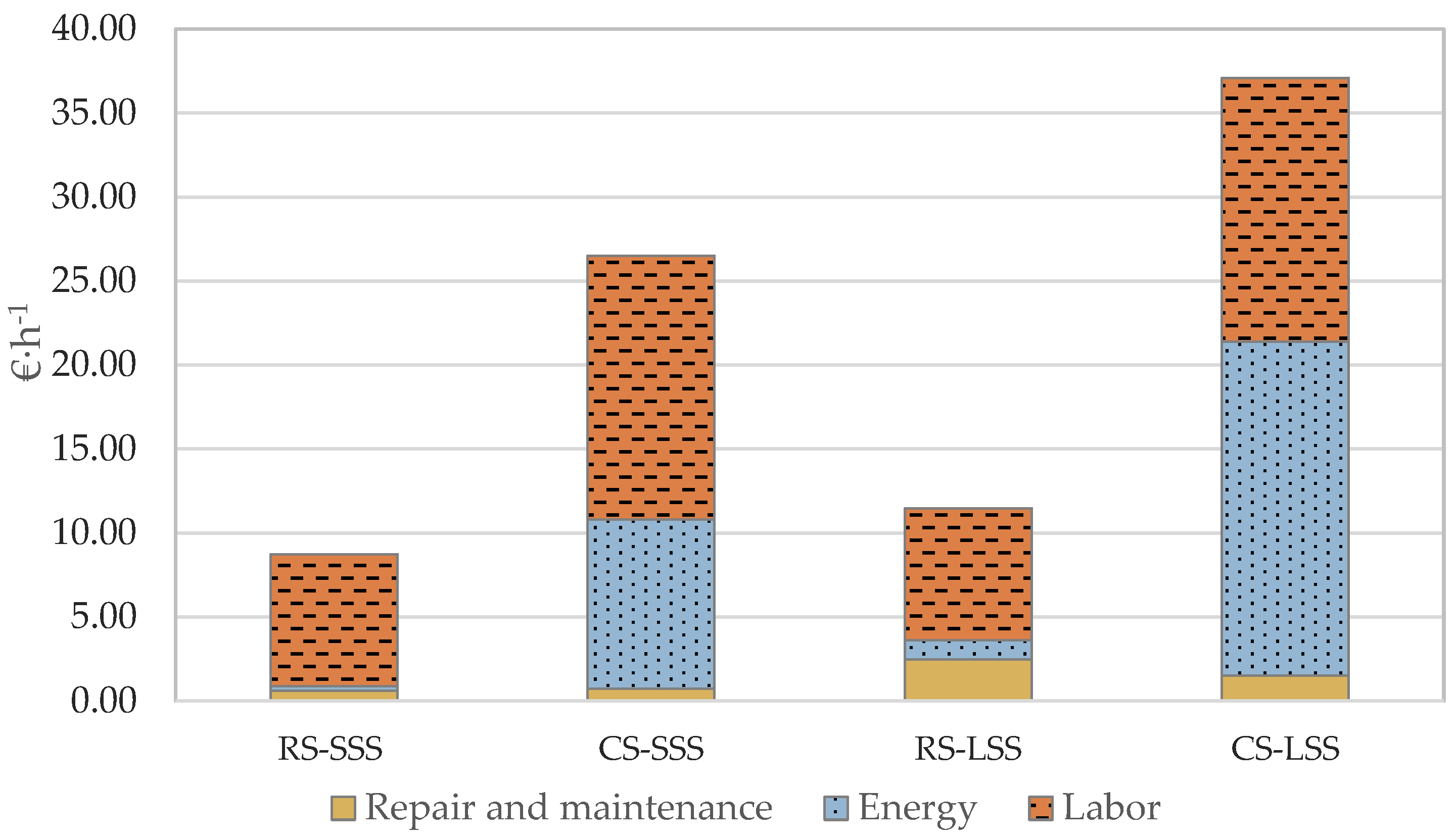
As depicted in Figure 6, the ownership cost per unit time is significantly higher in the large-scale scenario compared to the small-scale scenario, for both the robotic and the conventional systems. Additionally, the robotic systems, as presented in Figure 7, have lower operational cost per unit time, compared to the conventional systems, mainly due to the higher labor and energy cost of the latter. In fact, the energy cost per unit time in the case of the large-scale conventional system is the most significant factor in determining operating cost. In the case of the large-scale farm, the energy cost contributes 53.5% of the total operation cost, while in the small-scale farm, the comparable percentage is 38%. For the small-scale farm in the case of the robotic system, the most important contributing factor is the labor cost, accounting for 90% of the operation cost. Nevertheless, in the case of the large-scale farm, the respective percentage of labor cost is 68.5%, while repair and maintenance cost contribute 21.5% of the total operation cost.
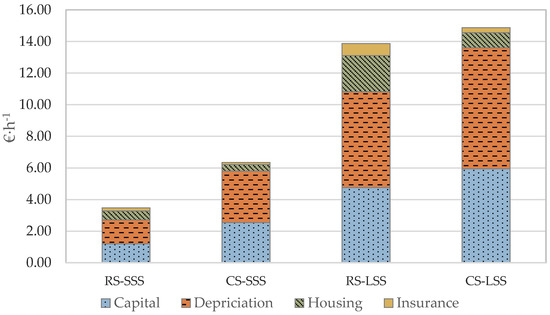
Figure 6.
Ownership cost per unit time analysis (RS—Robotic System; CS—Conventional System; SSS—Small-Scale Scenario; LSS—Large-Scale Scenario).
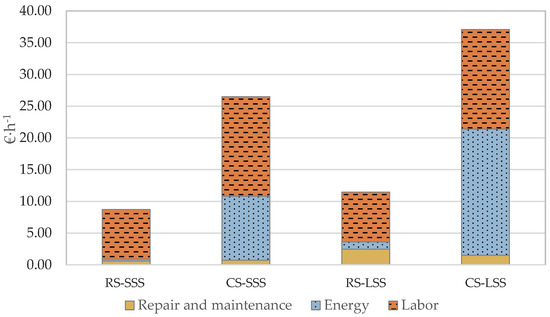
Figure 7.
Operation cost per unit time analysis (RS—Robotic System; CS—Conventional System; SSS—Small-Scale Scenario; LSS—Large-Scale Scenario).
3.3. Sensitivity Analysis
This section presents a sensitivity analysis on the input–output parameters of the basis case study previously presented. This analysis is essential for the case of the robotic system as a newly introduced technology characterized by a number of parameters known, at the moment, under a high level of uncertainty. The total cost output has been tested in terms of its sensitivity against changes in the hourly wage of the workers, the field efficiency, the purchase price, and the annual use of the machinery.
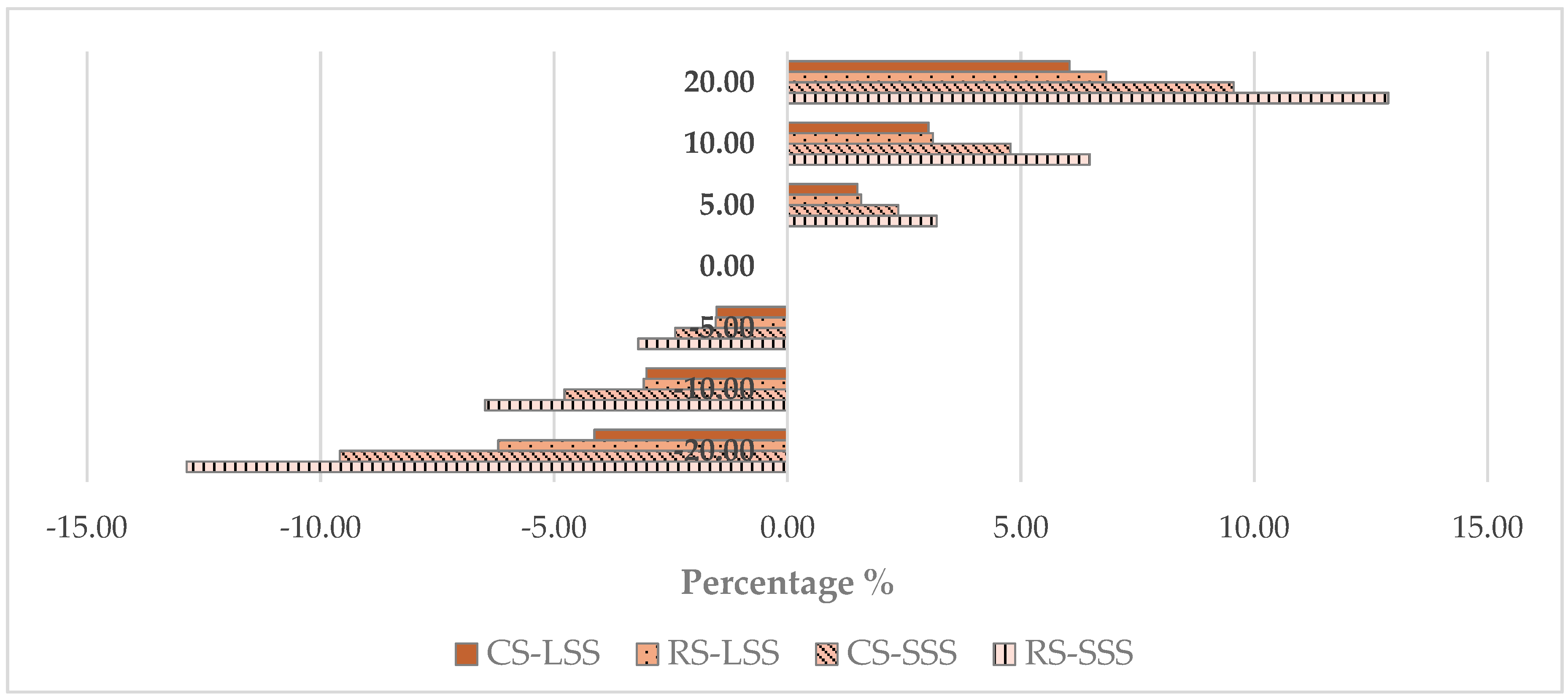
Figure 8 presents the sensitivity of the total cost as a function of the hourly wage of the workers. According to Figure 8, the change in the total cost is more significant in the small-scale scenario compared to the large-scale one, both for the conventional and the robotic systems. Indicatively, an increase of 20% in hourly wage in the case of the small-scale robotic system leads to an increase in the total cost of approximately 12%, while in the case of the large-scale scenario, the change in the total cost is limited to approximately 6%. Considering, a 20% increase in the hourly wage the cost of the small-scale robotic system turns to be 2.8 times higher than the respective conventional. Additionally, with a 20% decrease, the cost of the small-scale robotic system is 2.6 times higher than the respective conventional. In the large-scale scenario, the robot cost remains consistently 1.9 times higher than the conventional.
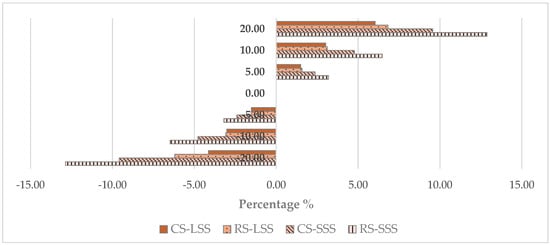
Figure 8.
Sensitivity analysis—total cost vs. hourly wage (RS—Robotic System; CS—Conventional System; SSS—Small-Scale Scenario; LSS—Large-Scale Scenario).
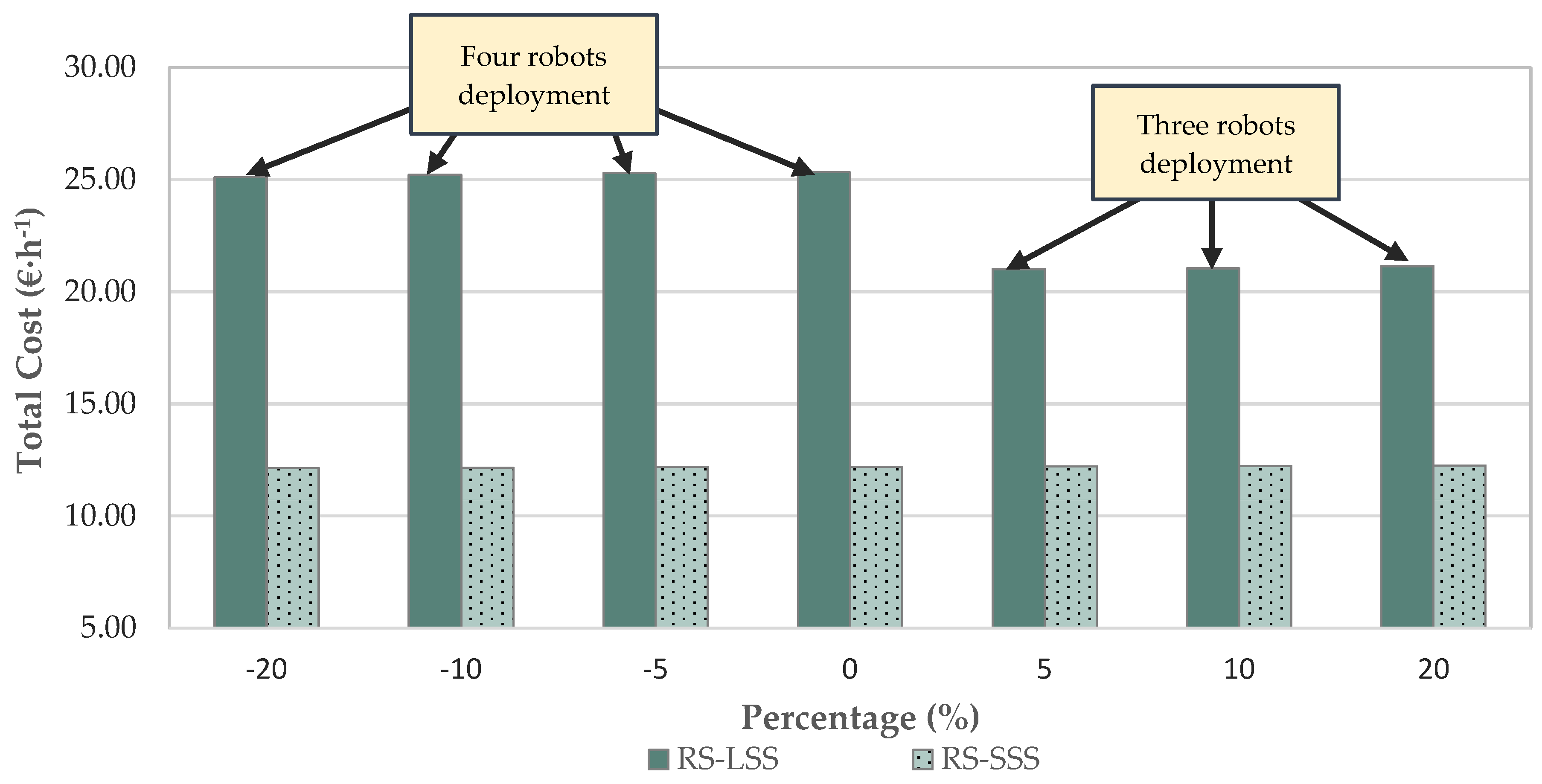
In the case of multiple-robotic systems, such as in the large-scale scenario, increasing the field efficiency of the units leads to the reduction of the number of units required to complete the operation within a specific time window. However, the reduction in the number of units does not always lead to reduction of the total cost. For example, an increase in the field efficiency of the robots of 5% results to a reduction of 17% of the total cost per unit time (namely from 25.34 € h−1 for the case of the basis scenario to 21.02 € h−1) and a reduction to the required number of units from four to three (Figure 9). Considering, however, the total completion time for the cases of four and three robots, which is 96 h and 121 h, respectively, the total cost is higher in the case that three robots are implemented, although the increased efficiency. For higher increases in the field efficiency of the robots, however, the system of three robots becomes more economic. With a 20% increase in the efficiency, the small-scale robotic system cost becomes 2.27 times higher than the conventional one (2.9 times higher in the basis scenario), and the large-scale robotic system cost becomes 1.77 times higher than the conventional one (1.9 times higher in the basis scenario).
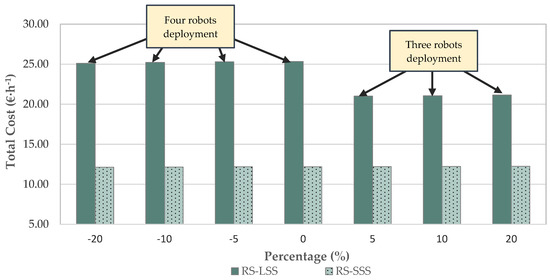
Figure 9.
Sensitivity analysis—hourly cost vs. efficiency (RS—Robotic System; CS—Conventional System; SSS—Small-Scale Scenario; LSS—Large-Scale Scenario).
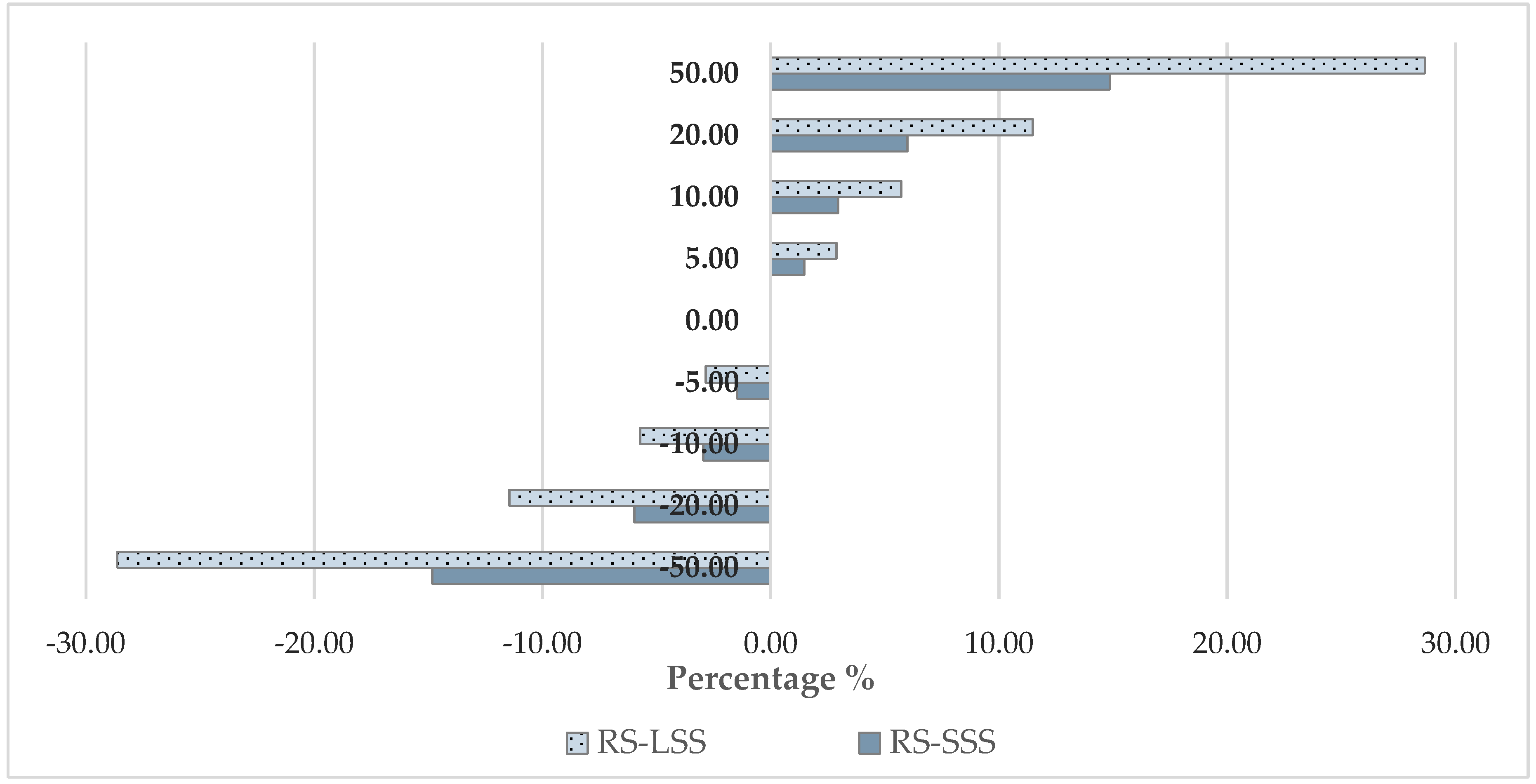
Considering that the ownership cost is a significant cost element in the case of the robotic system, a reduction in the number of robots will have a direct high impact in the total cost. The importance of the total machinery investment cost in the case of the robotic system is also highlighted in Figure 10 where the sensitivity of the total hourly cost in relation to purchase price changes is presented. For the small-scale scenario, considering a 50% increase in the purchase price of the robotic system, the total operation cost increases by 14.8%, increasing the ratio between the robotic system cost and the conventional system cost up to 3.1, while considering a 50% reduction in the purchase price of the robotic system the total operation cost the ratio between the robotic system cost and the conventional system cost is reduced to 2.3. The corresponding ratios for the case of large-scale scenario and a change in the purchase price of 50% and −50%, are 2.5 and 1.36, respectively.
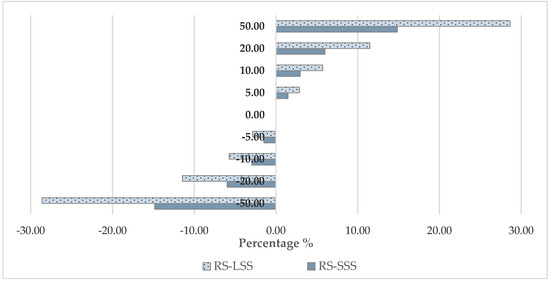
Figure 10.
Sensitivity analysis—total cost vs. purchase price (RS—Robotic System; SSS—Small-Scale Scenario; LSS—Large-Scale Scenario).
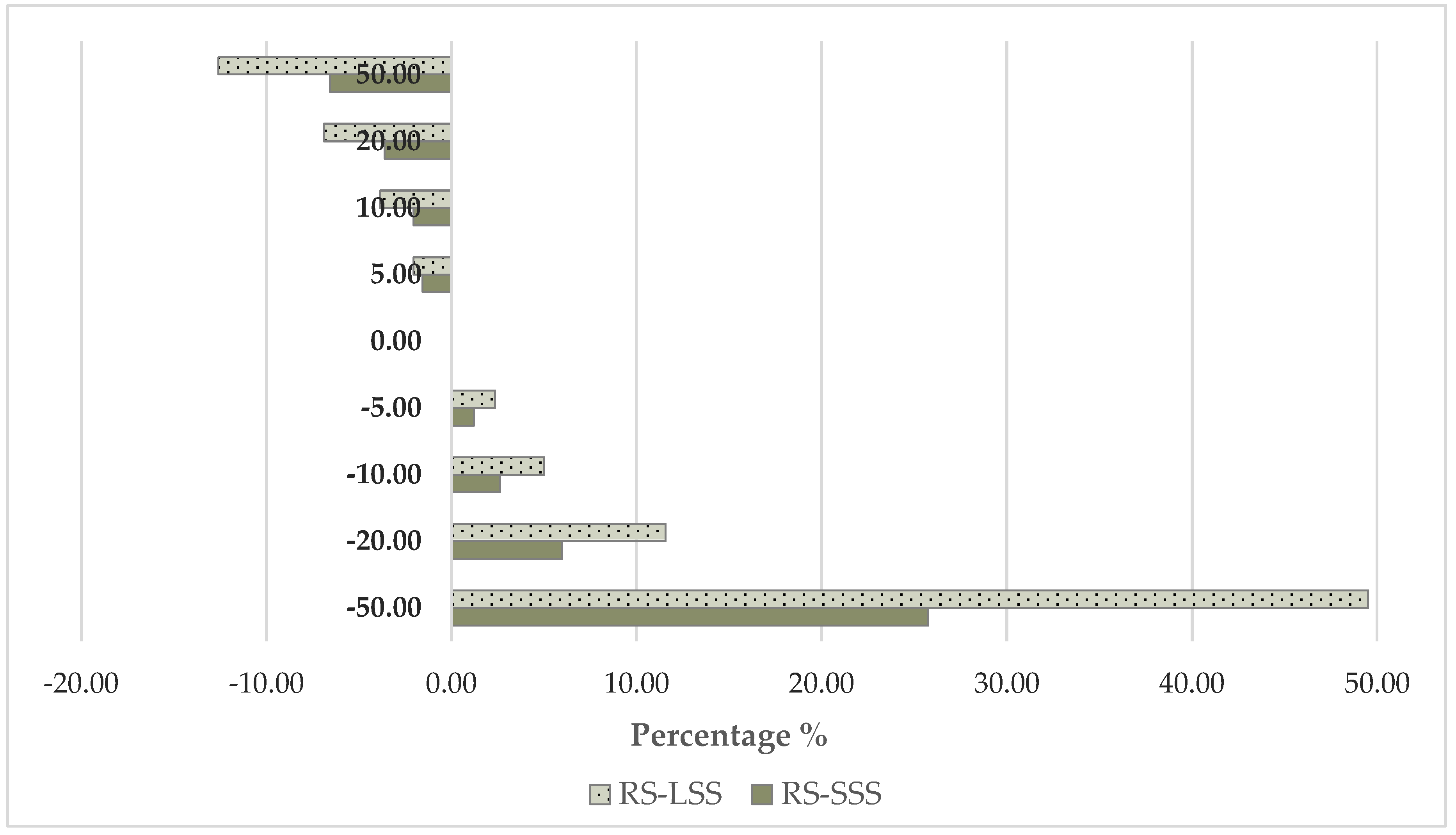
The total cost of an operation is inversely proportional to the annual use of the machinery. As it is depicted in Figure 11, when the annual use increases gradually up to 50%, the rate of cost reduction is smaller than the growth rate of the cost observed with the corresponding percentage reduction. In the case of the robotic system, the autonomous operation feature contributes to a potential increase in the workability of the system which can operate in various weather conditions due to lower risk of soil compaction. With a 20% increase in the annual use, the small-scale robotic system cost becomes 2.62 times higher than the cost of the conventional one, and 2.88 times higher with a 20% decrease. In the large-scale scenario, a 20% increase leads to 2.2 times higher robotic costs compared to the cost of the conventional system, while a 20% decrease results to a corresponding ratio of 2.64.
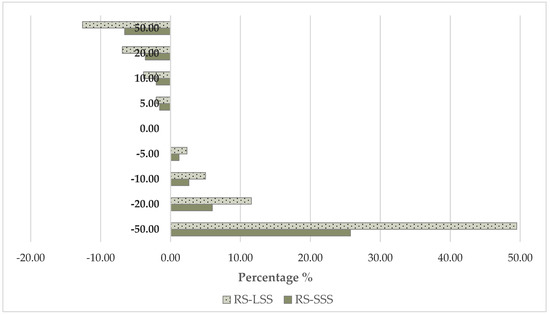
Figure 11.
Sensitivity analysis—total cost vs. annual use (RS—Robotic System; SSS—Small-Scale Scenario; LSS—Large-Scale Scenario).
4. Conclusions
In this paper, we present a preliminary economic analysis of the introduction of agricultural robotic systems, providing all individual cost elements and corresponding models for their estimation. Additionally, a case study of a robotic system performing light soil cultivation was presented and the calculated cost was compared to the cost of the respective conventional system. Based on the case study results and the sensitivity analysis, the ratio between the cost of the operation executed by a robotic system and cost of the operation executed by a conventional agricultural machinery system ranged between 2.27 and 3.1 for the case of the small-farm scenario, and between 1.36 and 1.9 for the case of the large-scale scenario, always in favor of the conventional system. The main reason for the higher cost of the robotic system is the higher operating time due to the lower field efficiency of the system attributed mainly to the recharging process. For the case study, a recharging time of 3 h was considered. Reducing this time to 2 h, the cost ratio between the two systems is modified to 2.32 and 1.82 for the small-scale (from 2.7 in the basis case study) and the large scale scenario (from 1.9 in the basis case study), respectively, while by reducing the recharging time to 1 h, the cost ratio between the two systems is modified to 1.94 and 1.54, for the small-scale (from 2.7 in the basis case study) and the large scale scenario (from 1.9 in the basis case study).
Furthermore, the labor cost, although reduced compared to the conventional system, highly affects the cost of the robotic system due to the longest duration of the operations. When completely removing human workers out of the robotic system, ceteris paribus, the ratio between the cost of the robotic system and the cost conventional system is reduced to 0.96 for the small-case scenario, meaning that the robotic system becomes more economic, and to 1.31 for the large-scale scenario. However, completely removing human from the loop is not currently possible.
The calculated cost represents estimations of the total cost in the case of robotic systems since a number of parameters are known under high uncertainty and various assumptions have to be employed. Hence, there are parameters of which the values can be accurately determined, such as the investment cost, the workers’ wages, and the cost of energy, while on the other hand, various parameters need to be determined through new experimental measurements or estimations. Such parameters include the repair and maintenance factors or the salvage value since this type of machinery is not widespread and the relevant operation and maintenance parameters have not been quantified yet.
The question on the economic feasibility of replacing conventional agricultural machinery systems with robotic systems remains. At the moment, due to the lack of scientific approaches on the cost estimation of robotic systems in agriculture, it is highly questionable to speculate in a general view that production cost is reduced by the implementation of agricultural robotics. Furthermore, manned agricultural machinery systems have been evolved with many continuous adaptions and, during the last period, with advanced embedded information systems and automations, providing a very well established and efficient system which is a strong competitor for upcoming agricultural robotic systems. However, a clear answer on the comparison of the efficiency of the two systems requires a more comprehensive break-down analysis of the corresponding processes, accurate consideration of the complementary tasks executed by human labor in agricultural robotic systems, and a holistic approach that considers the added value of the latter system in terms of soil compaction prevention, accurate execution of tasks, and replacement of limited human skills in specialized field tasks, among others. These considerations are considered as future research questions.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, D.B. and V.M.; methodology, D.K., M.G.L. and G.V.; software, D.K. and M.G.L.; validation, G.V. and A.B.; formal analysis, S.P. and C.G.S.; data curation, D.K. and G.V..; writing—original draft preparation, D.K., M.G.L., G.V., V.M., and A.B.; writing—review and editing, D.B., C.G.S., and S.P.; visualization, D.K. and M.G.L.; supervision, D.B.
Funding
The work was supported by the project “Research Synergy to address major challenges in the nexus: energy-environment-agricultural production (Food, Water, Materials)”—NEXUS, funded by the Greek Secretariat for Research and Technology (GSRT)—Pr. No. MIS 5002496.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Qureshi, M.O.; Syed, R.S. The impact of robotics on employment and motivation of employees in the service sector, with special reference to health care. Saf. Health Work 2014, 5, 198–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toledo, O.M.; Steward, B.L.; Gai, J.; Tang, L. Techno-economic analysis of future precision field robots. In Proceedings of the American Society of Agricultural and Biological Engineers Annual International Meeting 2014, Montreal, QC, Canada, 13–15 July 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Hyde, J.; Engel, P. Investing in a Robotic Milking System: A Monte Carlo Simulation Analysis. J. Dairy Sci. 2002, 85, 2207–2214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bochtis, D.D.; Sørensen, C.G.C.; Busato, P. Advances in agricultural machinery management: A review. Biosyst. Eng. 2014, 126, 69–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bongiovanni, R.; Lowenberg-Deboer, J. Precision agriculture and sustainability. Precis. Agric. 2004, 5, 359–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liakos, K.G.; Busato, P.; Moshou, D.; Pearson, S.; Bochtis, D. Machine learning in agriculture: A review. Sensors 2018, 18, 2674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moradi, M.; Moradi, M.; Bayat, F. On robot acceptance and adoption: A case study. In Proceedings of the 2018 Artificial Intelligence and Robotics (IRANOPEN): the 8th Conference on Artificial Intelligence and Robotics, Qazvin, Iran, 8 April 2018; pp. 21–25. [Google Scholar]
- Mottaleb, K.A. Technology in Society Perception and adoption of a new agricultural technology: Evidence from a developing country. Technol. Soc. 2018, 55, 126–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sørensen, C.G.; Nielsen, V. Operational analyses and model comparison of machinery systems for reduced tillage. Biosyst. Eng. 2005, 92, 143–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedersen, S.M.; Fountas, S.; Have, H.; Blackmore, B.S. Agricultural robots - System analysis and economic feasibility. Precis. Agric. 2006, 7, 295–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bochtis, D.D.; Sørensen, C.G.; Busato, P.; Berruto, R. Benefits from optimal route planning based on B-patterns. Biosyst. Eng. 2013, 115, 389–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jensen, M.F.; Bochtis, D.; Sørensen, C.G. Coverage planning for capacitated field operations, part II: Optimisation. Biosyst. Eng. 2015, 39, 149–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodias, E.; Berruto, R.; Busato, P.; Bochtis, D.; Sørensen, C.G.; Zhou, K. Energy savings from optimised in-field route planning for agricultural machinery. Sustainability 2017, 9, 1956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Busato, P.; Berruto, R. Minimising manpower in rice harvesting and transportation operations. Biosyst. Eng. 2016, 151, 435–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsatsarelis, C. Agricultural Machinery Management, 1st ed.; Giachoudi Publications: Thessaloniki, Greece, 2006; ISBN 960-7425-86-3. [Google Scholar]
- Bochtis, D.; Sorensen, C.G.; Kateris, D. Operations Management in Agriculture, 1st ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2018; ISBN 9780128097168. [Google Scholar]
- American Society of Agricultural and Biological Engineers (ASABE). Agricultural Machinery Management—ASAE EP496.3 FEB2006 (R2015); ASABE: St. Joseph, MI, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Bubeck, S.; Tomaschek, J.; Fahl, U. Perspectives of electric mobility: Total cost of ownership of electric vehicles in Germany. Transp. Policy 2016, 50, 63–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- American Society of Agricultural and Biological Engineers (ASABE). Agricultural Machinery Management Data—ASAE D497.5 FEB2006; ASABE: St. Joseph, MI, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- American Society of Agricultural and Biological Engineers (ASABE). Agricultural Machinery Management Data— ASAE D497.7 MAR2011 (R2015); ASABE: St. Joseph, MI, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Grimstad, L.; From, P. The Thorvald II Agricultural Robotic System. Robotics 2017, 6, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Propfe, B.; Redelbach, M.; Santini, D.J.; Friedrich, H.; Characteristics, V.; Sh, M.; Mercedes, S. Cost Analysis of Plug-in Hybrid Electric Vehicles including Maintenance & Repair Costs and Resale Values Implementing Agreement on Hybrid and Electric Vehicles. Proc. 26th Int. Batter. Hybrid Fuel Cell Electr. Veh. Symp. 2012, 5, 6862. [Google Scholar]
- Ministry of Development and Competitiveness Liqid Fuel Prices Observatory. Available online: http://www.fuelprices.gr/PriceStats?prodclass=1&nofdays=7&order_by=9 (accessed on 17 December 2018).
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).