Uncertainty of CERES-Maize Calibration under Different Irrigation Strategies Using PEST Optimization Algorithm
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Filed Experimental Treatments
2.2. RZWQM2 Calibrations with PEST
2.3. Unicertainty Analysis of Crop Parameters and Model Predictions
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Uncertainty in Model Calibration among Sub-Datasets
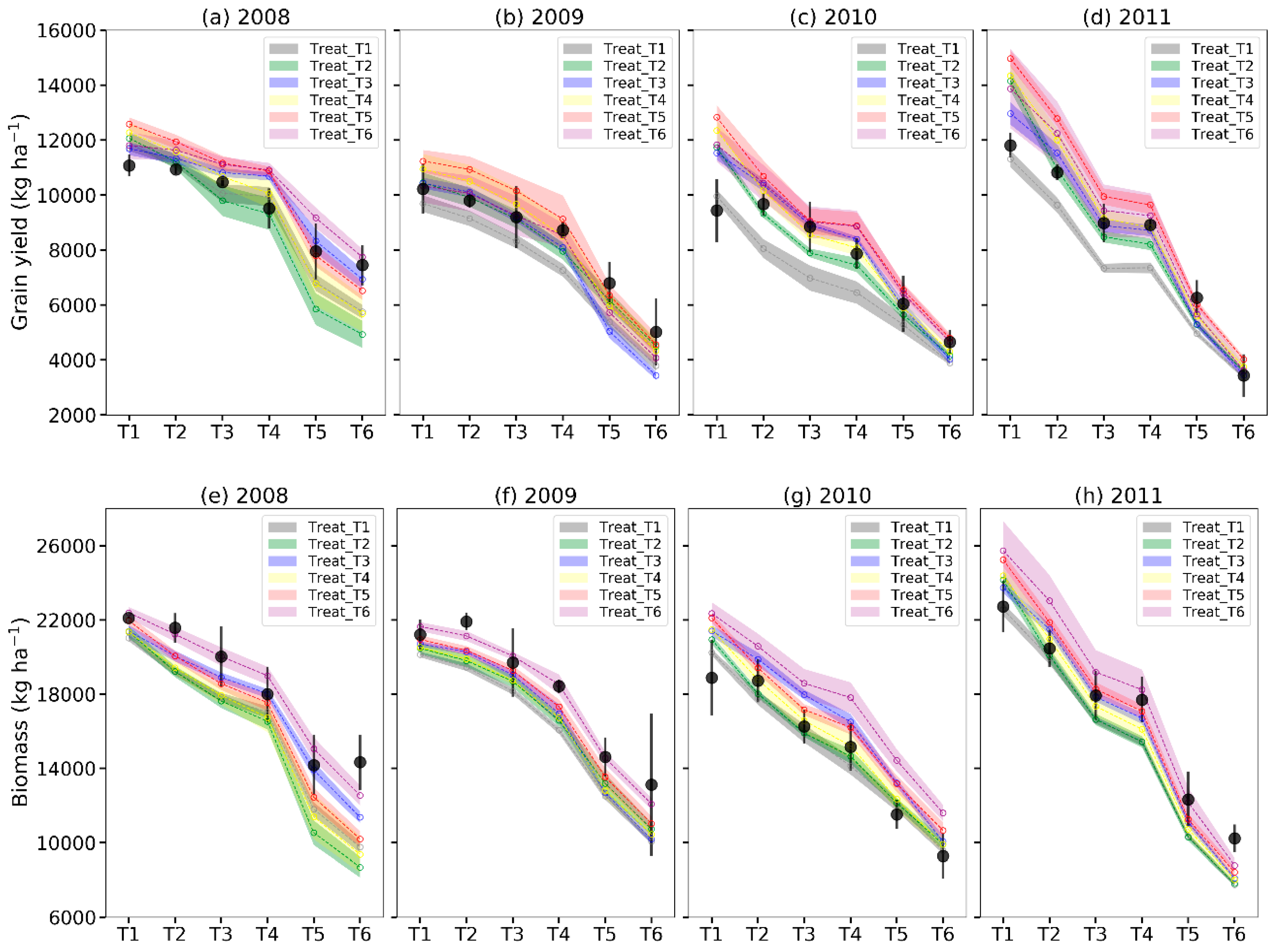
3.2. Uncertainty in Model Predicitions Based on Calibration-By-Year Method
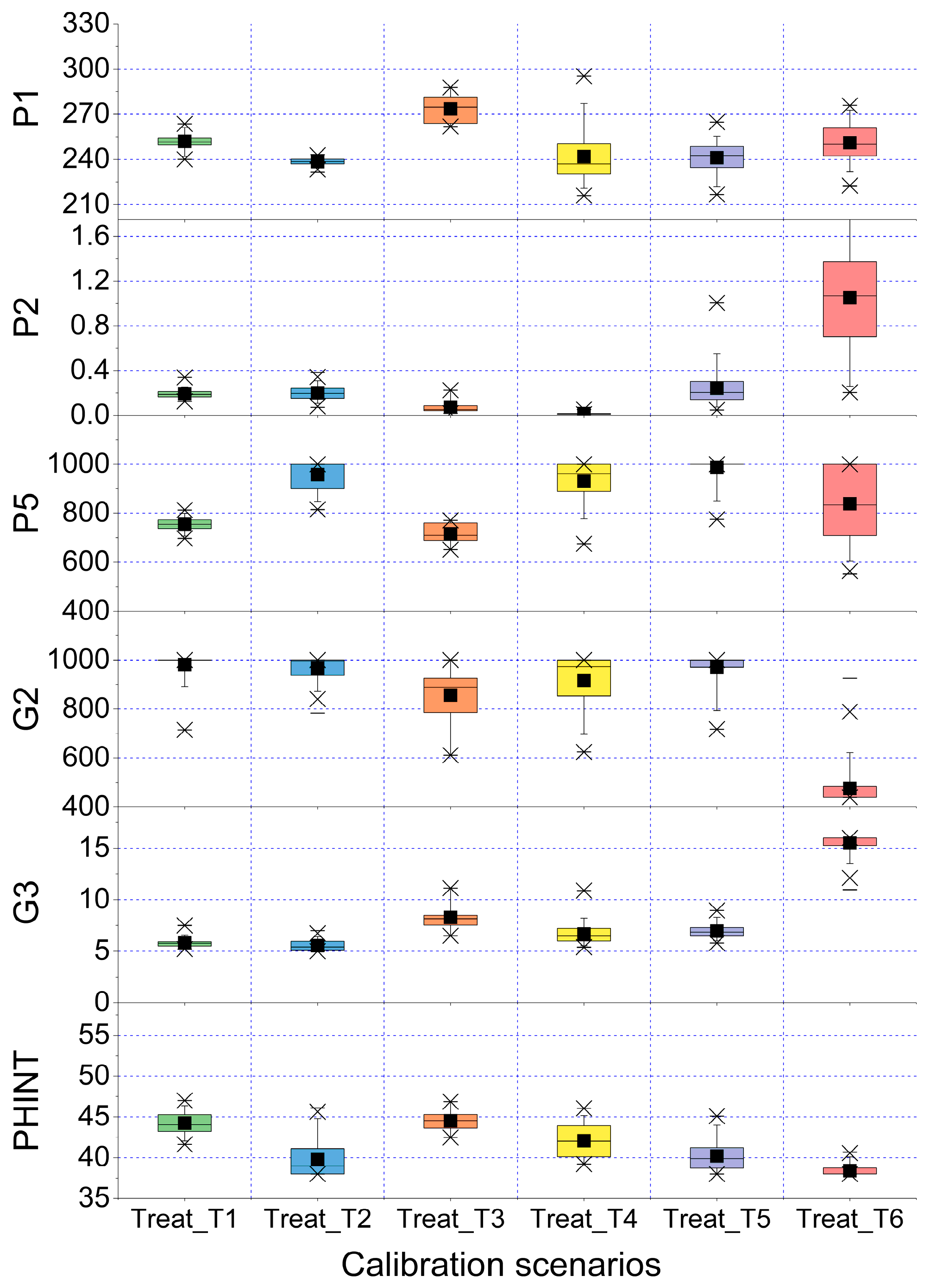
3.3. Uncertainty in Model Predicitons Based on Calibration-by-Treatment Method
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ahuja, L.R.; Ma, L. Parameterization of agricultural system models: Current approaches and future needs. In Agricultural System Models in Field Research and Technology Transfer; Ahuja, L.R., Ma, L., Howell, T.A., Eds.; Lewis Publishers: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2002; pp. 273–316. [Google Scholar]
- Madsen, H. Parameter estimation in distributed hydrological catchment modelling using automatic calibration with multiple objectives. Adv. Water Resour. 2003, 26, 205–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beven, K.; Binley, A. The future of distributed models: Model calibration and uncertainty prediction. Hydrol. Process. 1992, 6, 279–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeJonge, K.C.; Ascough, J.C.; Ahmadi, M.; Andales, A.A.; Arabi, M. Global sensitivity and uncertainty analysis of a dynamic agroecosystem model under different irrigation treatments. Ecol. Model. 2012, 231, 113–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, Q.X.; Green, T.R.; Ma, L.; Erskine, R.H.; Malone, R.W.; Ahuja, L.R. Optimizing soil hydraulic parameters in RZWQM2 under fallow conditions. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2010, 74, 1897–1913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.; Trout, T.J.; Ahuja, L.R.; Bausch, W.C.; Saseendran, S.A.; Malone, R.W.; Nielsen, D.C. Calibrating RZWQM2 model for maize responses to deficit irrigation. Agric. Water Manage. 2012, 103, 140–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.; Ahuja, L.R.; Saseendran, S.A.; Malone, R.W.; Green, T.R.; Nolan, B.T.; Bartling, P.N.S.; Flerchinger, G.N.; Boote, K.J.; Hoogenboom, G.A. Protocol for parameterization and calibration of RZWQM2 in field research. In Methods of Introducing System Models into Agricultural Research; Ahuja, L.R., Ma, L., Eds.; SSSA book series; American Society of Agronomy, Inc.; Crop Science Society of America, Inc.; Soil Science Society of America, Inc.: Madison, WI, USA, 2011; pp. 1–64. [Google Scholar]
- He, J.; Jones, J.W.; Graham, W.D.; Dukes, M.D. Influence of likelihood function choice for estimating crop model parameters using the generalized likelihood uncertainty estimation method. Agric. Syst. 2010, 103, 256–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harmel, R.D.; Smith, P.K. Consideration of measurement uncertainty in the evaluation of goodness-of-fit in hydrologic and water quality modeling. J. Hydrol. 2007, 337, 326–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yen, H.; Wang, X.; Fontane, D.G.; Harmel, R.D.; Arabi, M. A framework for propagation of uncertainty contributed by parameterization, input data, model structure, and calibration/validation data in watershed modeling. Environ. Modell. Softw. 2014, 54, 211–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shan, S.; Wang, G.G. Survey of modeling and optimization strategies to solve high-dimensional design problems with computationally-expensive black-box functions. Struct. Multidiscip. Optim. 2010, 41, 219–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, Q.Y.; Sorooshian, S.; Gupta, V. Effective and Efficient Global Optimization for Conceptual Rainfall-Runoff Models. Water Resour. Res. 1992, 28, 1015–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Reichert, P.; Abbaspour, K.C.; Xia, J.; Yang, H. Comparing uncertainty analysis techniques for a SWAT application to the Chaohe Basin in China. J. Hydrol. 2008, 358, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- PESThomePage.org-HOME PAGE; Doherty, J. PEST: Model-Independent Parameter Estimation. Available online: http://www.pesthomepage.org/ (accessed on 8 May 2019).
- Iizumi, T.; Yokozawa, M.; Nishimori, M. Parameter estimation and uncertainty analysis of a large-scale crop model for paddy rice: Application of a Bayesian approach. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2009, 149, 333–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skahill, B.E.; Doherty, J. Efficient accommodation of local minima in watershed model calibration. J. Hydrol. 2006, 329, 122–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fang, Q. Optimizing and uncertainty evaluation of soil and crop parameters in root zone water quality model. Trans. CSAE 2012, 28, 118–123, (in Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Ma, L.; Ahuja, L.R.; Nolan, B.T.; Malone, R.W.; Trout, T.J.; Qi, Z. Root Zone Water Quality Model (RZWQM2): Model use, calibration, and validation. Trans. ASABE 2012, 55, 1425–1446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.J. The genetic algorithm and its application to calibrating conceptual rainfall-runoff models. Water Resour. Res. 1991, 27, 2467–2471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sumner, N.R.; Fleming, P.M.; Bates, B.C. Calibration of a modified SFB model for twenty-five Australian catchments using simulated annealing. J. Hydrol. 1997, 197, 166–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marshall, L.; Nott, D.; Sharma, A. A comparative study of Markov chain Monte Carlo methods for conceptual rainfall-runoff modeling. Water Resour. Res. 2004, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ritter, A.; Muñoz-Carpena, R. Performance evaluation of hydrological models: Statistical significance for reducing subjectivity in goodness-of-fit assessments. J. Hydrol. 2013, 480, 33–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sima, N.Q.; Harmel, R.D.; Fang, Q.X.; Ma, L.; Andales, A.A. A modified F-test for evaluating model performance by including both experimental and simulation uncertainties. Environ. Modell. Softw. 2018, 104, 236–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thorp, K.R.; Batchelor, W.D.; Paz, J.O.; Kaleita, A.L.; DeJonge, K.C. Using cross-validation to evaluate CERES-Maize yield simulations within a decision support system for precision agriculture. Trans. ASABE 2007, 50, 1467–1479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fensterseifer, C.A.; Streck, N.A.; Baigorria, G.A.; Timilsina, A.P.; Zanon, A.J.; Cera, J.C.; Rocha, T.S. On the number of experiments required to calibrate a cultivar in a crop model: The case of CROPGRO-soybean. Field Crop. Res. 2017, 204, 146–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKay, M.D.; Beckman, R.J.; Conover, W.J. A comparison of three methods for selecting values of input variables in the analysis of output from a computer code. Technometrics 1979, 21, 239–245. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, L.; Ascough, J.C., Jr.; Ahuja, L.R.; Shaffer, M.J.; Hanson, J.D.; Rojas, K.W. Root zone water quality model sensitivity analysis using the monte carlo simulation. Trans. ASAE 2000, 43, 883–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moriasi, D.N.; Arnold, J.G.; van Liew, M.W.; Bingner, R.L.; Harmel, R.D.; Veith, T.L. Model evaluation guidelines for systematic quantification of accuracy in watershed simulations. Trans. ASABE 2007, 50, 885–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trout, T.J.; Bausch, W.C. USDA-ARS Colorado maize water productivity data set. Irrig. Sci. 2017, 35, 241–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, R.G.; Pereira, L.S.; Raes, D.; Smith, M. Crop Evapotranspiration-Guidelines for Computing Crop Water Requirements-FAO Irrigation and Drainage Paper 56; FAO: Rome, Italy, 1998; Volume 300, p. D05109. [Google Scholar]
- Allen, R.G.; Pereira, L.S.; Smith, M.; Raes, D.; Wright, J.L. FAO-56 dual crop coefficient method for estimating evaporation from soil and application extensions. J. Irrig. Drainage Eng.-ASCE 2005, 131, 2–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahuja, L.R.; Rojas, K.W.; Hanson, J.D.; Shaffer, M.J.; Ma, L. The Root Zone Water Quality Model; Water Resources Publication: Highlands Ranch, CO, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Brooks, R.; Corey, T. Hydraulic Properties of Porous Media. Hydrol. Pap. Colorado State Univ. 1964, 3, 1–27. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, L.; Hoogenboom, G.; Ahuja, L.R.; Ascough, J.C.; Saseendran, S.A. Evaluation of the RZWQM-CERES-Maize hybrid model for maize production. Agric. Syst. 2006, 87, 274–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.; Ahuja, L.R.; Trout, T.J.; Nolan, B.T.; Malone, R.W. Simulating maize yield and biomass with spatial variability of soil field capacity. Agron. J. 2016, 108, 171–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boote, K.J. Concepts for calibrating crop growth models. In 1999 DSSAT Version 3; Hoogenboom, G., Wilkens, P.W., Tsuji, G.Y., Eds.; University of Hawaii: Honolulu, HI, USA, 1999; Volume 4, pp. 179–199. [Google Scholar]
- Fang, Q.; Ma, L.; Qi, Z.; Shen, Y.; He, L.; Xu, S.; Kisekka, I.; Sima, M.; Malone, R.W.; Yu, Q. Optimizing Et-Based Irrigation Scheduling for Wheat and Maize with Water Constraints. Trans. ASABE 2017, 60, 2053–2065. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- Marek, G.W.; Marek, T.H.; Xue, Q.; Gowda, P.H.; Evett, S.R.; Brauer, D.K. Simulating evapotranspiration and yield response of selected corn varieties under full and limited irrigation in the Texas High Plains using DSSAT-CERES maize. Trans. ASABE 2017, 60, 837–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Qi, Z.; Gu, Z.; Gui, D.; Zeng, F. Optimizing irrigation rates for cotton production in an extremely arid area using RZWQM2-simulated water stress. Trans. ASABE 2017, 60, 2041–2052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Crop Parameter | Parameter Sensitivity Analysis | Parameter Calibration | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SWC | LAI | Grain Yield | Biomass | Range | Initial | |
| P1 | 0.004 | 0.23 | 3.43 | 5.38 | 100–450 | 250 |
| P2 | 0.000 | 0.00 | 0.02 | 0.03 | 0–2 | 0.2 |
| P5 | 0.003 | 0.06 | 2.80 | 2.38 | 500–1000 | 600 |
| G2 | 0.001 | 0.02 | 2.54 | 1.77 | 440–1000 | 900 |
| G3 | 0.001 | 0.03 | 2.90 | 2.06 | 5–16 | 6 |
| PHINT | 0.004 | 0.16 | 1.46 | 2.03 | 38–55 | 50 |
| Soil Depth (cm) | Soil Bulk Density (g cm−3) | Saturated Soil Water Content (cm3 cm−3) | Field Capacity (cm3 cm−3) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0–15 | 1.492 | 0.437 | 0.231 |
| 15–45 | 1.492 | 0.437 | 0.242 |
| 45–75 | 1.492 | 0.437 | 0.230 |
| 75–105 | 1.568 | 0.408 | 0.206 |
| 105–135 | 1.568 | 0.408 | 0.205 |
| 130–165 | 1.617 | 0.390 | 0.263 |
| 160–190 | 1.617 | 0.390 | 0.310 |
| Calibration Methods | Calibration Scenarios | Calibrated Parameter Values with PEST * | Averaged Parameter Values from the Selected Φ Cases within 10% of Calibrated Φ Values and Their CV Values (in Parentheses, %) ** | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| P1 | P2 | P5 | G2 | G3 | PHINT | Case Numbers | P1 | P2 | P5 | G2 | G3 | PHINT | ||
| All treatments in one year (Calibration-by-Year) | Year_08 | 283.3 | 0.76 | 1000 | 450 | 16.0 | 47.6 | 44 | 287.2 (6.6) | 0.8 (35.6) | 904 (15.3) | 458 (6.2) | 15.1 (6.9) | 43.6 (5.6) |
| Year_09 | 244.5 | 0.06 | 617 | 659 | 8.5 | 38.0 | 50 | 241.9 (2.7) | 0.1 (35.0) | 669 (11.8) | 623 (26.4) | 9.0 (19.8) | 38.1 (0.9) | |
| Year_10 | 255.9 | 0.20 | 555 | 911 | 9.6 | 53.6 | 74 | 248.4 (4.7) | 0.2 (37.1) | 544 (3.5) | 792 (22.5) | 12.2 (21.0) | 53.1 (2.5) | |
| Year_11 | 264.1 | 0.22 | 633 | 967 | 8.2 | 50.3 | 151 | 254.4 (5.5) | 0.2 (57.5) | 667 (3.9) | 838 (16.6) | 9.9 (22.0) | 49.8 (2.0) | |
| Average | 259.6 | 0.29 | 681 | 777 | 9.7 | 47.9 | 258.0 (4.9) | 0.3 (41.3) | 696 (8.6) | 678 (17.9) | 11.6 (17.4) | 46.2 (2.7) | ||
| CV *** | 5.8 | 94.8 | 26.5 | 28.1 | 39.0 | 12.4 | 7.8 | 99.5 | 21.6 | 26 | 23.3 | 14.4 | ||
| One treatment for all years (Calibration-by-Treatment) | Treat_T1 | 258.4 | 0.19 | 757 | 997 | 5.7 | 44.9 | 77 | 252. (2.1) | 0.2 (20.6) | 755 (3.5) | 981 (5.0) | 5.8 (7.3) | 44.2 (3.0) |
| Treat_T2 | 239.9 | 0.21 | 889 | 1000 | 5.6 | 43.2 | 140 | 238.5 (0.9) | 0.2 (31.3) | 958 (6.1) | 966 (4.8) | 5.5 (9.1) | 39.8 (5.4) | |
| Treat_T3 | 279.3 | 0.06 | 687 | 893 | 8.3 | 45.3 | 11 | 273.5 (3.5) | 0.1 (79.5) | 716 (5.4) | 856 (14.6) | 8.3 (17.6) | 44.5 (3.1) | |
| Treat_T4 | 237.3 | 0.01 | 936 | 951 | 6.8 | 43.5 | 45 | 241.8 (7.3) | 0.02 (58.4) | 931 (8.8) | 916 (12.3) | 6.7 (14.8) | 42.1 (4.8) | |
| Treat_T5 | 249.9 | 0.20 | 825 | 1000 | 7.0 | 43.8 | 99 | 241.1 (4.2) | 0.2 (62.8) | 986 (4.3) | 970 (6.4) | 7.0 (9.7) | 40.2 (4.5) | |
| Treat_T6 | 266.9 | 1.03 | 1000 | 441 | 16.0 | 39.8 | 164 | 251.1 (4.9) | 1.0 (43.5) | 839 (17.9) | 476 (14.9) | 15.5 (5.9) | 38.4 (1.9) | |
| Average | 256.5 | 0.27 | 831 | 879 | 8.1 | 43.8 | 249.7 (3.8) | 0.3 (49.3) | 864 (7.6) | 861 (9.7) | 8.1 (10.7) | 41.5 (3.8) | ||
| CV *** | 5.9 | 124.8 | 14 | 22.8 | 44.5 | 4.7 | 5.2 | 128.1 | 13.0 | 22.6 | 46.0 | 6.0 | ||
| Calibration Methods | Calibration Scenarios with PEST | Yield and Biomass Predictions by PEST Optimized Parameters | Selected Case Numbers | Yield and Biomass Predictions with the Optimized Parameters from the Selected Cases within 10% of Calibrated Φ Values | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Yield | Biomass | Yield | Biomass | |||||||||
| RMSE * | RRMSE * | RMSE * | RRMSE * | RMSE ** | RRMSE ** | CV *** | RMSE ** | RRMSE ** | CV *** | |||
| All data | Initial | 2964 | 35 | 3403 | 20 | |||||||
| Calibration-by-Year; All treatments (T1–T6) in one year | Year_08 | 1366 | 16 | 1817 | 11 | 44 | 1350 | 16 | 11 | 1770 | 10 | 9 |
| Year_09 | 2560 | 30 | 2819 | 16 | 50 | 2337 | 28 | 47 | 2607 | 15 | 19 | |
| Year_10 | 1232 | 15 | 2408 | 14 | 74 | 1256 | 15 | 15 | 2610 | 15 | 9 | |
| Year_11 | 1624 | 19 | 1995 | 12 | 151 | 984 | 12 | 11 | 1804 | 11 | 4 | |
| Average | 1695 | 20 | 2260 | 13 | 1482 | 17 | 21 | 2198 | 13 | 10 | ||
| Calibration-by-Treatment; One treatment for all years (2008–2011) | Treat_T1 | 1078 | 13 | 1882 | 11 | 77 | 1139 | 13 | 10 | 1945 | 11 | 6 |
| Treat_T2 | 984 | 12 | 2068 | 12 | 140 | 1117 | 13 | 9 | 2074 | 12 | 9 | |
| Treat_T3 | 876 | 10 | 1568 | 9 | 11 | 865 | 10 | 7 | 1552 | 9 | 6 | |
| Treat_T4 | 1194 | 14 | 1813 | 11 | 45 | 1134 | 13 | 9 | 1929 | 11 | 11 | |
| Treat_T5 | 1108 | 13 | 1542 | 9 | 99 | 1332 | 16 | 15 | 1679 | 10 | 6 | |
| Treat_T6 | 1158 | 13 | 1823 | 11 | 164 | 1121 | 13 | 14 | 1806 | 11 | 19 | |
| Average | 1066 | 12 | 1783 | 11 | 1118 | 13 | 11 | 1831 | 11 | 10 | ||
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fang, Q.; Ma, L.; Harmel, R.D.; Yu, Q.; Sima, M.W.; Bartling, P.N.S.; Malone, R.W.; Nolan, B.T.; Doherty, J. Uncertainty of CERES-Maize Calibration under Different Irrigation Strategies Using PEST Optimization Algorithm. Agronomy 2019, 9, 241. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy9050241
Fang Q, Ma L, Harmel RD, Yu Q, Sima MW, Bartling PNS, Malone RW, Nolan BT, Doherty J. Uncertainty of CERES-Maize Calibration under Different Irrigation Strategies Using PEST Optimization Algorithm. Agronomy. 2019; 9(5):241. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy9050241
Chicago/Turabian StyleFang, Quanxiao, L. Ma, R. D. Harmel, Q. Yu, M. W. Sima, P. N. S. Bartling, R. W. Malone, B. T. Nolan, and J. Doherty. 2019. "Uncertainty of CERES-Maize Calibration under Different Irrigation Strategies Using PEST Optimization Algorithm" Agronomy 9, no. 5: 241. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy9050241
APA StyleFang, Q., Ma, L., Harmel, R. D., Yu, Q., Sima, M. W., Bartling, P. N. S., Malone, R. W., Nolan, B. T., & Doherty, J. (2019). Uncertainty of CERES-Maize Calibration under Different Irrigation Strategies Using PEST Optimization Algorithm. Agronomy, 9(5), 241. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy9050241





