Abstract
A major challenge of the Sustainable Development Goals linked to Agriculture, Food Security, and Nutrition, under the current global crop production paradigm, is that increasing crop yields often have negative environmental impacts. It is therefore urgent to develop and adopt optimal soil-improving cropping systems (SICS) that can allow us to decouple these system parameters. Soil salinization is a major environmental hazard that limits agricultural potential and is closely linked to agricultural mismanagement and water resources overexploitation, especially in arid climates. Here we review literature seeking to ameliorate the negative effect of soil salinization on crop productivity and conduct a global meta-analysis of 128 paired soil quality and yield observations from 30 studies. In this regard, we compared the effectivity of different SICS that aim to cope with soil salinization across 11 countries, in order to reveal those that are the most promising. The analysis shows that besides case-specific optimization of irrigation and drainage management, combinations of soil amendments, conditioners, and residue management can contribute to significant reductions of soil salinity while significantly increasing crop yields. These results highlight that conservation agriculture can also achieve the higher yields required for upscaling and sustaining crop production.
1. Introduction
Global crop production faces the challenge of decoupling higher yields from associated environmental impact in order to achieve some of the most ambitious goals of the 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development [1,2]. This constitutes a major shift from the current paradigms of many agricultural systems [3], where productivity losses due to declining soil quality are either offset by increasing agricultural inputs, labor, or technology [4,5]. However, such increased use of agricultural inputs may reduce farmers’ profits due to the disproportionate costs, while also having new negative impacts on the environment, due to the unsustainable use of energy and resources in producing inputs [6] and as a consequence of their application. The results are often subtle and exhibit gradual, physical, chemical, and biological degradation [7,8,9,10]. On the other hand, conservation agriculture faces severe limitations when it comes to upscaling and sustaining crop yield [11]. Since, on average, irrigation doubles the yield per unit area, it is unlikely that the amount of irrigated land will diminish in the future given the increasing global needs for food and forage.
Secondary soil salinization, typically referring to the accumulation of water-soluble salts in the soil owing to human activities, results into a deterioration or loss of one or more of the functions of soil [12,13]. Together with its natural or primary form, soil salinization emerges as a major environmental constrain impeding soil productivity, agricultural sustainability, and food security, particularly in arid and semi-arid regions of the world [14,15,16]. Currently, saline soils occur in at least 100 countries [17], in total covering 932.2 Mha [18], with hotspots in Pakistan, China, United States, India, Argentina, Sudan, and many countries in Central and Western Asia [19,20], as well as in the Mediterranean coastline [12]. Salinization has a large impact on global production of food and forage. Qadir et al. [21] calculated the annual losses of the agricultural sector as 27.3 million US dollars, either due to progressively reduced productivity of salinized lands or their abandonment because of it. Bridges and Oldeman [22] estimate that, at a global scale, every minute an area of 3 ha of arable land becomes unproductive due to secondary salinization, therefore driving between 10 and 20 million hectares of irrigated land to zero productivity every year. Thus, soil salinization will remain as one of the key challenges for food production and to meeting the needs of the world population, now expected to reach 9 billion people by 2050 [23].
Secondary soil salinization it typically caused by an imbalance between transpiration and water inputs from rainfall and irrigation. This imbalance comes in combination with soil characteristics that impede or difficult leaching [24,25,26,27]. This combination of factors is of particular interest in dryland irrigated cropping systems due to feedback effects that cause a negative spiral of soil degradation that can lead to desertification. Wrong irrigation practices (e.g., waterlogging) and misplanning (e.g., temporal overirrigation) are major drivers of soil salinization [21,27]. Other factors include the use of unlined canals and reservoirs and vegetation clearing, in combination with inadequate drainage that filters salts into the groundwaters [28], from where the dissolved salts can be remobilized to the upper layers of the soil by means of upward water flows during dry periods [29,30]. The quality of the irrigation water is also very important. Nevertheless, when appropriate agricultural and irrigation strategies are followed, moderately saline water may be used for irrigating tolerant crops and may, in some cases, prove beneficial to fruit quality and less often to yield [31,32].
Based on the above, secondary soil salinization is closely linked to the use of inefficient cropping systems (i.e., choices of crop, crop rotation, tillage practice, irrigation, and nutrient and pest management applied on a particular field over a particular period). Soil improvement is then necessary to break the negative spiral of degradation, increased inputs, increased costs, and damage to the environment, seeking at the same time to make farming systems sustainable and profitable [33]. For this to be possible, soil-improving cropping systems (SICS) need to emerge or be devised to result in a durable increased ability of the soil to fulfill its functions, including food and biomass production, buffering and filtering capacity, and provision of other ecosystem services. In order for these SICS to be adopted in their full potential and not be abandoned (e.g., Lahmar [34]), they need to also favor higher yields or provide some other competitive added value, thus influencing the profitability as well as sustainability of crop production systems [35,36,37].
In this context, we review literature pertaining SICS that aim to prevent, mitigate, or remediate the negative impacts of soil salinization and ameliorate the associated soil functions and ecosystem services relevant to agricultural production, aiming not to describe the problem, but looking for solutions. Based on this, we conduct a meta-analysis of a total of 128 cases from 30 publications spanning among 11 countries (Australia, China, India, Pakistan, Uzbekistan, Niger, Oman, Tunisia, Egypt, Spain, and Italy) that simultaneously report on soil quality and yield with respect to tested SICS. This review covers agronomical practices intending to halt and, when possible, reverse secondary salinization, focusing on amelioration measures.
2. SICS Strategies for Soil Salinization
From a farmer’s point of view, the ideal situation is the availability of irrigation water of good quality at an affordable price. If these conditions are not favorable and farmers have to deal with a problem of salinization, they adopt different cropping systems in order to minimize the economic impact of salinization on crops. Once the problem of salinization is well-established after several years of exploitation, they either abandon land [38,39] or try to implement measures to minimize the negative impacts. In this last group of measures, biotechnology and engineering can be of help.
The management of soil salinization may involve approaches addressed to improve either recharge or discharge management. Managing recharge involves minimizing salinity by reducing net recharge to groundwater. On the other hand, managing discharge design solutions to reduce salt entering into water reservoirs or assuming soil salinity and adapting scenarios such as planting salt-tolerant crops [40].
Four strategies have been proposed by Qadir et al. [41], each one composed of different measures, as a remedy to halt secondary salinization of agricultural lands. The first strategy combines different agronomic techniques and aims at minimizing the negative impact of salinity on yield and fruit quality. The second strategy pursues the use of irrigation water of better quality and the prevention of further salinization by an improvement of drainage. The third strategy is the planting of salt-tolerant plants in order to extract salts from the system. Finally, the fourth strategy is the mechanical removing of salts from the soils.
The best solution to dealing with the dual threat of salinity and water saturation is the drainage of a net flux of salt away from the root zone, thus controlling the water table height. Irrigation with an adequate quantity of water of good quality as leaching fraction and installing a suitable drainage network are then proposed as the most sustainable and affordable solutions to prevent salinization when sources of water of good quality are available [42]. The use of desalinized water is an effective solution, but the costs (often above 0.50 € m−3) are too high for many farmers. Requests to reduce price by taxation exemptions or state subsidies increased in South-East Spain as water quality deteriorates and farmers have to rely more and more on desalinized water. Mixing water of different sources (desalinized and well water) could be a partial solution for moderately tolerant crops.
Once the problem of salinization is well-established, farmers may adopt different management decisions to minimize the impact of salinization. Among them, the management of irrigation and fertilization appears to be among the most crucial techniques for halting further degradation of soils. The selection of crops tolerant to moderate levels of salts can be considered as far as the cash obtained by their cultivation does not lessen their acceptance by farmers. Biosaline agriculture seems, so far, the last resort when the soil accumulates in the root zone large amounts of salts. Although there is a growing interest in developing crops able to tolerate high levels of salinity, very few of these crops can be considered cash crops of high interest for growers. As we show below, in the near future we may expect some help from biotechnology for reclaiming salinized lands. Screening germplasm of halophytes plants could be of interest for recovering lands heavily affected by the problem of salinization. The use of salt-tolerant rootstocks and varieties is very likely to increase in the years to come. Transgenic crops have also been proposed as a solution to deal with salinized soils. Significant progress is also developing from classical breeding, using new approaches for screening tolerant genotypes [43,44,45].
Three groups of SICS approach can be distinguished: (1) preventing or halting secondary salinization, (2) coping with salinization, and (3) reversing salinization. These SICS are discussed below.
2.1. Preventing or Halting Secondary Salinization
The basic concept for preventing secondary salinization in an irrigated area is to maintain a balance between the salt introduced by irrigation and the salt in drainage water [39]. For keeping such a balance, efficient and sustainable procedures for draining the salts applied by irrigation are required, while efficient methods are equally needed for diminishing the amount of fertilizer salts applied. Effective procedures and suitable methods are reviewed below.
2.1.1. Leaching
Farmers can mitigate the negative effect of salinity on yield by managing the level of salt in the soil through leaching [46]. Leaching refers to the practice of applying an extra amount of water of reasonable quality beyond crop requirements to prevent salts from building up in the soil. Leaching is considered one of the main tools for controlling salinity [29,42]. Leaching can contribute to reduce soil water salinity by discharging salts from the upper horizons to the lower soil layers. The concept is to maintain the salts dissolved and to flush them below the root zone. For obtaining better results, it is important to bear in mind the hydraulic characteristics of the soil, especially in heterogeneous soils where soil texture stratification determines water mobility and salt dynamics [47]. The amount of water needed to achieve the desired salt balance is referred to as the leaching requirement or the leaching fraction. However, excess irrigation also increases the leaching of nutrients and other agrochemicals applied to the soils [48], and thus often degrades the quality of the water bodies receiving them [49,50]. In addition, leaching reduces water and nutrient use efficiency because increases the amount of irrigation water applied and diminishes the availability of fertilizers in the root zone [51].
Under limited water supply of suboptimal quality, the farmer has to compromise between allocating all irrigation water to plant the maximum area possible without applying a leaching fraction, thus assuming some reduction in crop yield per unit area or alternatively reducing the cultivation area but allocating some water for leaching, thus eventually increasing crop yield per unit area [52]. Modeling suggests that leaching of the excess salt from the soil once salinity levels exceed the crop’s salinity threshold is more profitable [52].
Seasonal analyses of groundwater salinity have revealed that the highest electrical conductivity value is commonly observed in summer [53], when rainfall is lower and evapotranspiration increases. In relevance to cropping systems, this could mean that early summer crops and/or picking fruits from only the first few nodes of the stem and then stopping cultivation, or alternatively winter cultivations (in the open air or under plastic) may be more beneficial. The first conclusion is also reached by Daliakopoulos et al. [54] for a tomato (Solanum lycopersicum L.) crop.
Soil salinity can be diminished by preseason salt leaching using high amounts of water, an action typically referred to as salt flushing. However, an appropriate leaching fraction must be maintained along the season to prevent subsequent resalinization of the topsoil layer. In this sense, Forkutsa et al. [55] observed that preseason leaching did not entirely remove salts from the soil profile at two out of three experimental plots, but rather shifted the salts from the upper (0–0.8 m) to the lower (0.8–2 m) soil layer. Even worse, in their experiments, strong groundwater contribution to evapotranspiration triggered secondary resalinization of topsoil during the next season. Consequently, complementary techniques to preseason leaching have to be put in practice in order to efficiently remove salts beyond root zone.
The use of rainwater to leach salts from soil has been proposed as a win–win strategy to control soil salinization in protected cultivation as well as in cultivation in the open field. Ashraf and Saeed [56] described the use the monsoon rainwater to leach the excess of soil salts after a maize (Zea mays L.)–wheat (Triticum aestivum L.)– dhaincha (Sesbania bispinosa W.Wight) crop rotation. Panagea et al. [57] surveyed protected cultivation farmers’ opinion to know which remedial measures for salinization are more easily to be adopted. Rainwater harvesting from greenhouse roofs was clearly the best strategy for farmers, in part because of their willingness to adopt this measure and its reduced cost. Harvested rainwater can be used for irrigation purposes, either on its own or mixed with water of poorer quality, or alternatively employed for leaching. When two different qualities of irrigation water exist, cyclic irrigation with intermittent leaching fractions can be performed to keep salinity under levels not affecting crop productivity. Crescimanno and Garofalo [58] suggest that this strategy is more effective for leaching salts than imposing a leaching fraction at each irrigation event.
2.1.2. Drainage
Where leaching is practiced, drainage must be enhanced to carry away the excess of (salty) drainage water, therefore preventing or reducing the upward flow of salts. For leaching to be more effective, an adequate drainage network is then needed. Improving drainage efficiency to lower groundwater table, while considering environmental and water availability considerations, may be more effective than leaching salts from the root zone [58]. Since the drainage and salinity control of an irrigated area by open drain systems poses limitations, the installation of subsurface drainage is recommended for supplementing open drain systems, even at policy-level [59]. To this end, Kitamura et al. [39] suggest installing subsurface tile drainage and minimizing the subsequent environmental degradation caused by saline drainage downstream by controlling the effluent quantity and quality with retention ponds at the end of the drainage system. This measure allows monitoring of the evolution of groundwater quality. Konukcu et al. [60] alternatively proposed “dry drainage”, i.e., setting aside part of the available land for evaporation of the water in excess and having the concurrent salt transported as a partial solution for groundwater salinization. The idea is that if water inflow (rainwater excess, field application losses, watercourse, and/or canal seepage losses) within a given area balances the water outflow (supply to crops from water table, evaporation from uncropped areas, artificial, and/or natural drainage sinks), then the water table will be stable. Then, if the area left without crops is large enough and the evaporation from this area is fast enough, necessary balance can be achieved without artificial tile drainage. Given that many farmers partly rely on groundwater for irrigation, improving drainage without improving irrigation scheduling seems not advisable [55].
“Biodrainage” involves growing certain types of plants that cover their main water demand directly from the canal seepage water or the capillary fringe immediately above it [61,62]. This consumption may help maintaining a safe aquifer level, thereby preventing saturation of the top 2 m of soil. It is doubtful, however, if biodrainage can reduce salinity to such an extent that crops can be grown profitably [63,64]. The success of biodrainage depends on soil texture and on ground water electrical conductivity. Planting poplars (Populus spp.) and tamarisks (Tamarix gallica L.) is applicable in many cases [30,64], but this technology should be combined with conventional engineering-based measures [65]. Some authors question the efficiency of biodrainage due to its limited effects [66,67].
2.1.3. Water Table Management
The prevention of the upward flow of salt is also achieved by lowering water tables. Percolation control methods, such as puddling and subsoil compaction [68,69], have been proposed as measures to prevent the upward flux of dissolved salts.
Lowering water tables may also bring about some decrease in surface soil salinity. Different strategies can be put in practice with this goal in mind. Revegetation with deep-rooted salt-tolerant species can produce a partial and short-term rehabilitation of salt-affected land. The problem is that after the initial decrease in the water table, the hydraulic gradient towards the root zone increases and so does the intrusion of groundwater. Wet (sub)soils impair the efficiency of roots to elude salts, so that there is an increased transport of sodium and chloride to the aerial parts (shoots and leaves). Eventually, salt concentrations in the root zone reach levels that substantially decrease the availability of water to the plants. Consequently, there is a reduction in leaf area index, and in consequence, a decrease in transpiration causing the water table to rise back, often to its initial levels. One undesirable effect that needs to be considered is the long-term accumulation of salt in the root zone of perennial plants that use groundwater. Fully understanding this process is fundamental to the development of sustainable agricultural systems and the management of saline land [70].
In this respect, Australia has an extensive salinity problem caused by the replacement of the native vegetation composed of deep-rooted perennials with shallow-rooted annual species. Connors [71] explains that the replacement of native perennial evergreen vegetation by winter–spring active, annual crops, and pastures, and by inactive fallows, changes the hydrological balance increasing the drainage through the soil profile. Salt is then leached deeply in the profile causing water tables to gradually rise, bringing salt to the surface of the lower parts of the land. The conclusion is that modifying the original vegetation causes changes difficult to predict because they occur in the long term, but the final effect is bare, erosion-prone land, and salinized streams [71]. This can be seen also in the pampas of Argentina [72]. One solution to this secondary salinity relies on the reintegration of perennial crops back into the agricultural systems with the aim of returning the hydrological function to one that fits better with the original landscape [70]. Revegetation can also reduce soil salinity by the direct uptake of salt if the proper species is chosen.
2.2. Coping with Salinization
A second approach to deal with the already established secondary salinization of agricultural lands is to improve field management including irrigation, fertilization, tillage, and crop selection. Minimizing the impact of salinization on crop yield and fruit quality often lies in the hands of the manager. Therefore, upgrading farmers’ skills to deal with salinization is required. Methods of accomplishing better farm management regarding salinization follow.
2.2.1. Irrigation Management
Water management is a key element to deal with salinization. Even the use of water with moderated salt content can lead to an increase of the salt content of the soil under semi-arid conditions, especially on soils with low saturated hydraulic conductivity [73]. Therefore, more efficient irrigation through modification of watering schedules and a decrease of watering consumption must be accomplished to halt the process of soil degradation.
Given the role of over-optimal irrigation in aggravating the problem of salinization, it is necessary to correct farmers’ attitude toward the value of water. Irrigation water is still cheap in many countries, which does not encourage water conservation by farmers [74]. Some progress has been made in water pricing, especially in some arid and semi-arid areas where water is very scarce and a valuable resource [75]. English et al. [76] argued that in light of the limited water availability and dubious quality, economically efficient irrigation will develop into the new paradigm of irrigation management. Matthews et al. [52] explained how farmers’ willingness to pay more for water increases as water availability and quality decrease. They also suggest that under limited supply of irrigation water, it is more profitable to reduce cultivation area in order to allocate enough water for leaching. Economic efficiency requires decision-makers to explicitly consider costs, revenues, and the opportunity cost of water in their decisions. Different procedures linked to the system, timing and dose of irrigation are available.
Regarding the irrigation system, flood irrigation is a common cause of water table rising, especially in clay and loamy soils, where deep drainage is impeded, making salts present in groundwater to ascend to the upper soil layers [21,30]. Under conditions of aridity, these soils might drive a process of salinization even using water of good quality for irrigation. Hence, flood irrigation should be forbidden in these cases.
Micro-irrigation has several advantages when the irrigation water is saline. Except for low growing crops, irrigation with micro-sprinklers or sprayers avoids wetting of the leaves with saline water, wetting that causes extensive damages to the green tissues of the plant. Because micro-irrigation is normally applied more frequently than conventional irrigation, continuous leaching of the soil volume from which the plant extracts the water is achieved. Leaching can also be provided intermittently, between growing seasons, and by seasonal rainfall, when soil salinity in the root zone is maintained below detrimental levels [77]. When compared to flood irrigation, drip irrigation might increase the risk of salinization of upper soil horizons but prevents salt leaching to groundwater [78]. However, Hanson et al. [79] demonstrated that for a given amount of applied water, the wetting pattern around emitters results in a higher leaching fraction and lower salinity levels than in other irrigation systems. On the other hand, drip irrigation commonly uses lower irrigation volumes and allows heavier yields, reaching then higher water use efficiency. Subsurface drip irrigation has been proposed as additional measure since it reduces evaporation from the soil [79] and permits better moisture distribution compared to conventional drip irrigation [31]. More efficient irrigation schemes must be tuned on the limit of deficit irrigation (see below) and plant salt tolerance, because lower leaching may increase soil salinity.
Deficit irrigation (DI) involves the application of water below full crop water requirements, so that a mild crop water stress is allowed with bearable effects on yield. The three most common deficit irrigation strategies are (1) regulated deficit irrigation (RDI), where water deficit is applied at certain developmental stages; (2) partial root-zone drying (PRD), where alternatively half of the root system is fully wetted while the other half is allowed to dry; and (3) sustained deficit irrigation (SDI), where water deficit is uniformly distributed over the whole crop cycle [80,81].
Cuevas et al. [81] demonstrated that even severe levels of water stress in selected phenological stages (RDI) can bring economic benefits to loquat (Eriobotrya japonica Lindl., a subtropical fruit tree sensitive to salinization) producers, not only by reducing irrigation costs, but also by increasing the value of the crop. The application of postharvest regulated deficit irrigation for more than 10 years in the same loquat orchard confirms the sustainability of such an irrigation strategy [82]. Limited water resources in semi-arid areas of the Mediterranean coast suggest the adoption of this strategy. In this regard, fruit crops and vines (Vitis vinifera L.) are frequently subjected to regulated deficit irrigation with water of poor quality, allowing higher profits if appropriately selected phenological phases are targeted [83,84]. It is important to consider, however, that RDI with saline water imposes an additional stress on the plants.
Deficit irrigation strategies save water, but also have the potential to improve the management of soil salinity by a better control of rising water tables and by a reduction in the ingress of salts by irrigation water. Nonetheless, deficit irrigation does not provide the same degree of leaching as full irrigation, so it may enhance soil salinization when agricultural plots are irrigated with low-water quality [85,86]. Although deficit irrigation in combination with drip irrigation technologies could leach salts away from the root zone in a very efficient way [78], a potential risk for increasing the salinization of upper soil layers emerges during the periods when irrigation is diminished (or completely interrupted), because the leaching fraction could then be insufficient to displace the salts from the active root zone of the crops [87]. Nonetheless, increasing irrigation efficiency would help sustaining present crop production levels, while reducing leaching demands [55]. However, contrary results have been reported on cantaloupe melon (Cucumis melo L.) in arid zones of Iran [88].
Given the central role of irrigation in secondary salinization, a more drastic alternative is the conversion of irrigated land to rain-fed production systems. This conversion reduces yield and fruit quality (especially fruit size), and limits farmers profits, so it is likely to be adopted only when other strategies for fighting salinization have failed. It often requires changing the crops and selecting drought-tolerant ones. Once this decision is adopted, measures can be taken to maximize the effectiveness of rainwater through adopting different tillage practices to reduce water losses and crop demands.
2.2.2. Nutrient Management
One obvious approach to deal with salinization is limiting the amount of fertilizer salts applied. This implies optimized fertilization programs, with fertilizers and doses correctly chosen and adjusted. Many authors have emphasized the importance of reducing fertilizer applications to prevent further salinization of groundwaters [26]. Diminishing the amounts of fertilizers applied as well as implementing fractional fertilization programs may contribute to halting the process of secondary salinization [89]. Improving irrigation and fertilization management and increasing their efficiency through fertigation is key for sustainable agriculture in arid and semi-arid areas [38]. In summary, carefully limited fertigation allows water-savings, a reduction of pollution caused by the fertilizers, a reduction in production costs, and provides higher net return for the farmer. Considering also that excessive fertilization, of nitrogen in particular, may be detrimental for fruit quality at harvest and especially during storage [90].
The choice of fertilizers is another key factor for limiting salinization. The results of many experiments located in areas prone to secondary salinization show the negative effect of potassium chloride on yield through an accumulation of salts in the soil, while potassium sulfate has less impact on soils [77]. Properly choosing the type of fertilizers can substantially reduce the risk of salt leaching to groundwater.
Several reports indicate that supplemental Ca may alleviate the negative effects caused by NaCl salinity on plant growth [91]. Grattan and Grieve [92] explain how an adequate supply of Ca2+ maintains the integrity of the cell membrane and its selectivity, thereby reducing Na+ and Cl− toxicity. The addition of several organic acids (humic, fulvic, carboxylic, maleic, etc.) [93] seems to enhance plant response. Similarly, an improvement in salinity tolerance is achieved with the application of salicylic acid, a molecule implicated in plant signaling defense that also helps coping with salinity [94,95]. Several mechanisms operate to enhance plant growth under salt stress after the application of salicylic acid, among them is decreasing K+ efflux and H+ influx from the mature root zone that occurs in response to NaCl and activating the expression of salt tolerance genes under moderate, but not under severe, salt stress [96,97]. On the other hand, salinity interferes with P translocation. This can be corrected by either Ca fertilization or by foliar application of P [91].
2.2.3. Soil Management
Soil management includes practices adopted to reduce the amount of irrigation required for soil water conservation and used by crops and weeds. It includes tillage, mulching, and direct drilling.
Different studies have revealed that reducing soil evaporation by allowing the persistence of a residue layer in the surface of the soil would notably decrease secondary soil salinization [55]. In this regard, straw mulching is a promising option for farmers to control soil salinity, as it decreases soil water evaporation and regulates soil water and salt movement [98,99,100,101,102,103,104,105]. Pang et al. [32] found a significant decrease in salt content in the upper 40 cm soil depth when straw mulching was implemented. Less clear results were found in deeper soil layers. Straw mulching seems to decrease the salt content of the surface of the soil through regulating the salt vertical distribution, which could reduce the salt damage to the crops, enhance their yields, and reduce the risk of soil salinization and erosion.
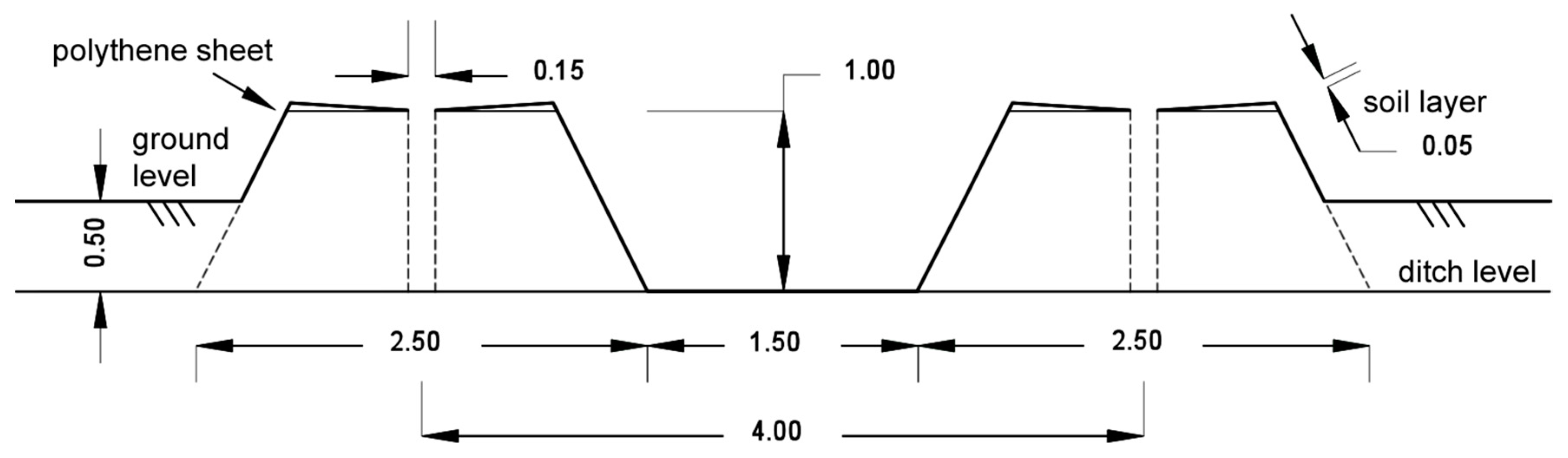
Hira and Thind [106] proposed a plantation technique for Eucalyptus trees in salt-affected, non-irrigated plots, using mound and ridge covered with polyethylene sheet and covered on turn with 5–6 cm of soil layer (Figure 1). In this technique, the plantation is done on a hole made in the center of the sheet in a way that rainwater can move radially and deep into the soil profile. This method improves the establishment and growth of the trees in comparison with flat plantations and mound and ridge not covered with polyethylene and at the same time reduces soil salinity.
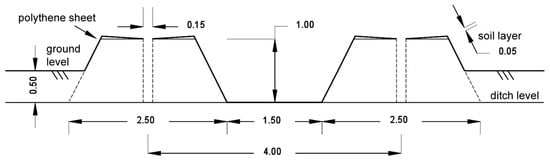
Figure 1.
Diagram showing the construction of ridge and hole and application of polyethylene sheet [106].
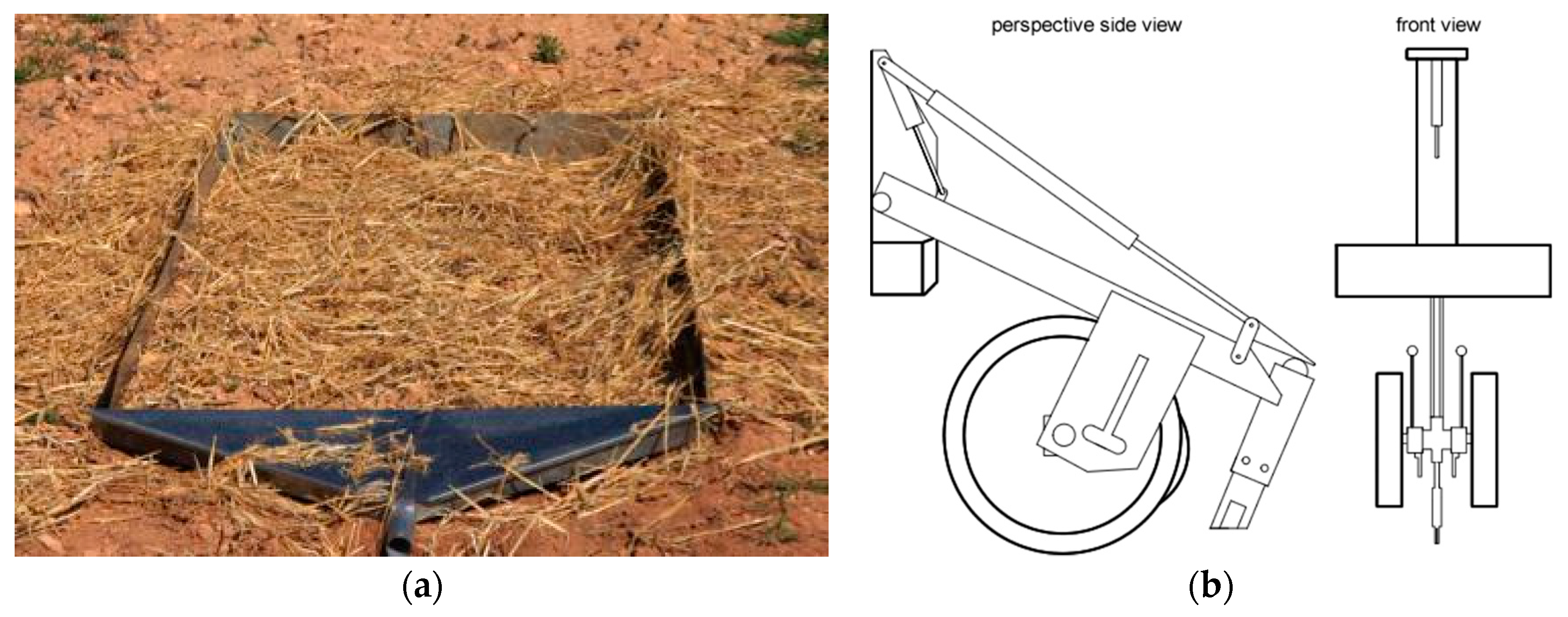
Combining direct drilling (Figure 2b) and mulching (Figure 2a) improves rainwater infiltration and reduces moisture evaporation from the soil, thus diminishing the accumulation of salt in the upper soil layers during summer and improving leaching during winter. Mendes and Carvalho [72] suggest direct drilling and cover crops in soils with low values of hydraulic conductivity of semi-arid zones, even when using irrigation water with moderate salinity.
Figure 2.
(a) Details of straw mulch application on an experimental erosion plot, Canals, Valencia (Photo: A. Cerdá). (b) Direct drill stump jump seeder adapted from patent EP0506661B1 filed in 1990.
2.2.4. Crop Rotation
It is well-established that cropping systems that rely on long fallowing for soil moisture conservation are suboptimal because this method favors the raising of water tables. Therefore, in the evolution of cropping systems seeking to halt salinization, a significant shift takes place towards the substitution of long fallowing by crop rotation. One option in this context is to include summer active perennials in the cropping systems. The major herbaceous option is lucerne (Medicago sativa L.) species that fits well into a wheat–sheep system, providing valuable summer fodder as well as additional transpiration [71]. Greiner [107] recommends increasing cropping frequency as it raises farm income and reduces recharge to groundwater.
For economic reasons, tree planting is not a favored option, unless trees have commercial value as tree fruit crops. Nonetheless, the need to use more perennials in the different cropping systems is clear. Several genera are likely of value in this respect, although few are as widely adapted as lucerne. Cocks [27] suggests targeting plant genera growing in dry Mediterranean areas. These may include perennial species of the family Fabaceae such as Astragalus, Hedysarum, Lotus, Onobrychis, Psoralea, and Trifolium that can match the water-use and nitrogen-fixing capacities of lucerne.
Gabriel et al. [48] analyzed the impact of replacing long fallow by barley (Hordeum vulgare L.) and vetch (Vicia villosa Roth) as cover crops, on water, nitrogen, and salinity dynamics of a maize cropping system. The results show that replacing fallow with cover crops can be effective in reducing nitrate leaching and in maintaining or reducing top layer soil salinity. The reduction of salinity in the experimental plots using cover crops allows lowering irrigation volumes for leaching, as well as reducing the risks of deep-water contamination by nitrates. Continuous cropping systems, incorporating legumes into the rotation, could make thus a significant contribution to the restoration of salt and water balances and prevent or even reverse salinization.
Weaver et al. [108] analyzed drainage water quality in the subsoil of sodic and non-sodic Vertisols under selected crop rotations including cotton, for instance in continuous cotton (Gossypium hirsutum L.), cotton–dolichos (Lablab purpureus Sweet), and cotton–wheat cropping systems. Their result show that in all cases the salinity of the drainage water was many times higher than the water used for irrigation. Salinization of shallow groundwaters under irrigated cotton in Vertisol soils is, therefore, a clear possibility. Salinization of the root zone may occur in cotton-based rotations in soils of poor structure and limited drainage even when irrigated with water of reasonable quality. To underline the importance of rotations, Cao et al. [109] emphasize that soil salt content more than doubled where a paddy rice (Oryza sativa L.)–wheat (or oilseed rape) cropping system was converted into intensive cultivation of vegetable crops. In addition to the induced secondary salinization, the continuous growing of the same vegetables in the same soil can result in the accumulation of autotoxins [109].
Sustaining the productivity of rice fields in the Liverpool Plains in Australia depends to a great extent on reducing the recharge to the groundwater system by changing land use practices [107]. The first approach applies to maintaining the total water balance by growing deep-rooted crops over an area capable to consume the recharge of the area of the rice field. The second approach involves achieving a whole farm water balance for average and for wet climatic conditions to find out optimum cropping patterns to minimize the recharge from rice field. The results from the second approach reveal that it is possible to control net recharge under above-average rainfall using a suitable cropping mix [110].
A completely different option is the use of mixed systems composed of herbaceous annuals and woody perennials, preferably fruit trees, to take advantage of their distinct root characteristics and seasonal dynamics that offer a range of competitive and complementary interactions. Deep-rooted, summer active perennials may reach deep profiles of dry soil, thus providing a horizontally discontinuous high capacity storage buffer [111].
2.2.5. Salinity Tolerant Crops and Rootstocks
In many areas where irrigation is necessary for crop production, salinization of soil seems unavoidable. Therefore, to guarantee food production in such areas, growing crops with yield reduction thresholds well above the salinity of the irrigation water is required. Recent trends and future projections suggest that the need to produce more food and fiber for the expanding population will lead to an increase in the use of salt-prone water and lands making the use of salt-tolerant crops more urgent every day [112,113]. A distinction is made between plants able to tolerate low levels of salinity (glycophytes) and those really adapted to saline soils (halophytes). Here, we may include the cultivation of tolerant crops for reclaiming salinized soils. However, most crops are glycophytes and are able to withstand only moderate levels of salinity. Only a few crops can be considered real halophytes. Among herbaceous crops, Tanji and Kielen [114] cite rye (Secale cereal L.), oilseed rape, guar (Cyamopsis tetragonoloba Taub.), wheat, kenaf (Hibiscus cannabinus L.), barley, and cotton. Among vegetables, it is worth citing purslane (Portulaca oleracea L.) and artichoke (Cynara scolymus L.), and among fruit trees, guava (Psidium guajava L.), guayule (Parthenium argentatum A. Gray), and different genera of palms. Recent studies in subtropical areas of South Europe have shown that pomegranate (Punica granatum L.), olive (Olea europaea L.), grape (Vitis vinifera), and mango (Mangifera indica L.) can also be considered as moderately salt-tolerant [115,116,117]. Some adaptability in salt tolerance may be expected depending on soil properties, types of rhizobacteria found there, phenological growth stage, and on agronomical practices including here the use of salt-resistant rootstocks [118,119]. Therefore, the investigation of soil improving cropping systems and the selection of salt-tolerant crops, salt-tolerant rootstocks, and symbiotic biological agents are currently considered to reduce the losses in yield under saline conditions [120,121,122].
Some examples of plant diversification for the optimal utilization of salt-affected soils and saline-sodic waters emerge thank to the different salt tolerance exhibited by crops. The plant species that have shown potential utility under such harsh environments are often divided into five groups: (1) fiber, grain, and special crops; (2) forage grass and shrub species; (3) medicinal and aromatic plant species; (4) biofuel crops; and (5) fruit trees [123]. The selection must be based on the ability of the plant to withstand elevated levels of soil salinity while providing a marketable product or one that can be used on-farm [124]. Whatever the products contemplated, viz. timber, cellulose, biomass, fruit, essential oils, etc., they will have to compete with products obtained elsewhere, commonly in more favorable conditions. Connor [71] addressed an interesting question: “what opportunities exist to include olive as a component of cropping systems including at present eucalypt in Australia?” Similar to eucalypts, olive is evergreen, summer active, and drought-resistant, but contrary to eucalypts, olive has the advantage of producing very valuable edible oil. More details can be found in the studies of Qadir et al. [125].
A variety of practices, including grafting, microbial agent application and plant modification, have been used to improve soil quality and enhance crop growth in protected cultivation of vegetables [126]. The utility of rootstocks to combat biotic and abiotic stresses in fruit crop production is well-known since the antiquity, probably starting about the beginning of the first millennium [127]. Actually, Plinius the Elder documented its use in ancient Greece in his Natural History. In Mediterranean fruit crops tolerant to salinity such as olive, pomegranate or fig (Ficus carica L.), the use of rootstocks is still negligible; however, in temperate-zone and subtropical fruit trees, rootstocks tolerant to salt represent an excellent tool for their cultivation in degraded soils. More recently, there is interest in using the same approach for vegetable production in salty soils or for vegetables irrigated with poor quality water, especially in the families Cucurbitaceae and Solanaceae. Given the success obtained in fruit crops and the promissory results obtained so far [128], a growing use of grafting in vegetable production is largely expected.
Independently of the chosen crop species, there are varieties better adapted to salinization because their phenology allows them to avoid critical periods of the year like summer, when evaporation from the soil increases bringing up salts to the upper soil layers. It is thus essential to develop varieties that are phenologically capable of sustaining excess salt throughout its life span and still produce high yields [129]. The use of microorganisms (Trichoderma harzianum isolate T78 and Pseudomonas stutzeri) has been proposed also as a mean to enhance soil microbiological diversity and mitigate salinity effects on plant growth [54,130,131].
A controversial solution may come from transgenic modified plants. Previous work has suggested the capacity to enhance salt tolerance of staple food crops by inserting transgenes in them. Abebe et al. [132] showed already that ectopic expression of the mtlD gene from Escherichia coli implicated in the biosynthesis of mannitol improves wheat tolerance to water stress and salinity. This same gene is effective in poplar trees [133]. It has been shown that plant growth increases in a higher extent in transgenic potato plants (Solanum tuberosum L.) grown under NaCl and polyethylene glycol stresses compared with control potato plants when betaine aldehyde dehydrogenase gene from spinach (Spinacia oleracea L.) was introduced in them. These results indicate that transgenic potato plants tolerate salinity better [134].
Less controversial is the use of wild relatives for enhancing salt tolerance in crops and the utilization of their ability by conventional breeding. There is considerable variability in salt tolerance between and within crops that can be exploited. Furthermore, close relatives to main staple crops such as wheat and barley offer an opportunity to improve yield by producing new hybrids with enhanced tolerance to salinity. The use of wild relatives to wheat and barley has been addressed by Munns et al. [42]. Colmer et al. [135] analyzed the underlying mechanisms of salt tolerance of several halophyte genera of the tribe Triticeae and the possibility of using wild species to hybridize them with durum and bread wheat. Similar approaches are suggested for wheat and the more salt-tolerant barley, searching into the germplasm of Triticum dicoccoides Schweinf. and Hordeum spontaneum Thell. the progenitors of cultivated wheat and barley [136].
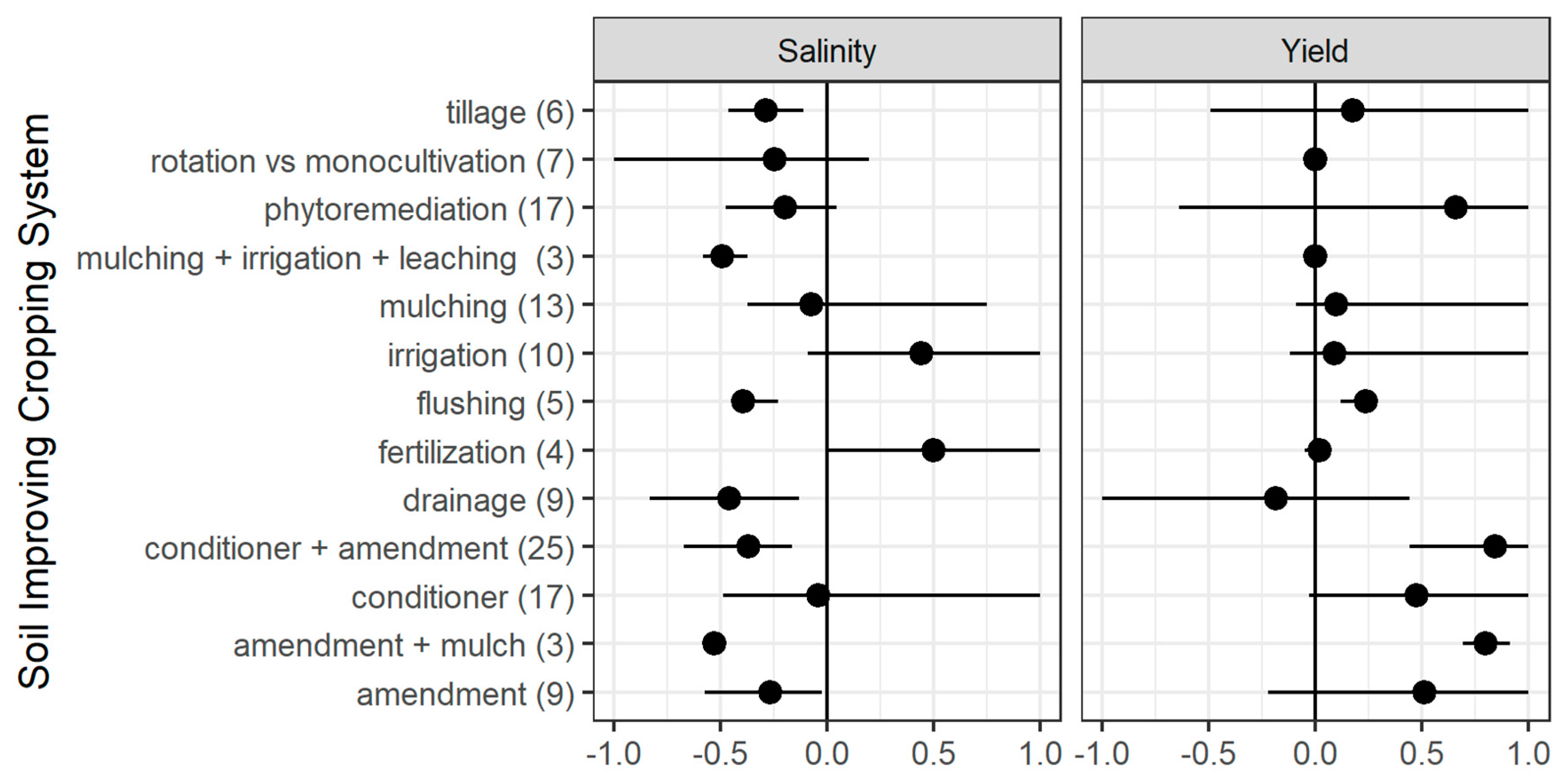
The effects of the above-mentioned soil improving crop systems on agronomic, economic, and environmental aspects regarding the salinization of soils are described in Figure 3.
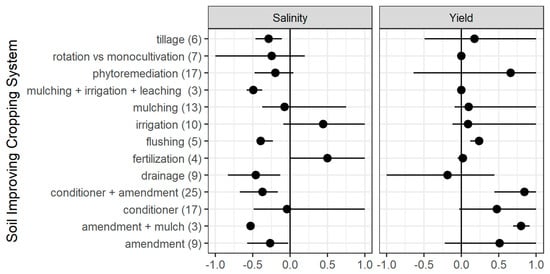
Figure 3.
Effect size of different soil improving cropping systems for reported data on soil salinity and corresponding reported crop yields from the studies mentioned in Table 1.
2.3. Reversing Salinization: Removing Salt from the System
Halophytes are plants capable to live in salty environments since they are the natural vegetation of saline soils. The natural existence of this kind of plants—true halophytes—could be useful for reducing the amount of salts present in the root zone. Plants cope with the problems of salinity in various ways; some of them avoid salinity by completing their cycle when salinity is lower (rainy periods), some others resist salinity, and a few others tolerate salinity [114,137]. These latter plants accumulate salts in their cells and/or secrete it through specials organs and are thus useful for reversing salinization. The idea implies the continuous growing and later disposal of the above ground plant tissues of halophytes in order to reverse salinization levels and eventually reclaim the desalinized lands for a new agricultural use. The knowledge of how halophytes have evolved to adapt to saline soils is also of great interest for breeding new cultivars able to tolerate higher levels of salinity.
Biosaline agriculture is a relatively new way to deal with salinity in agriculture. It develops cropping systems for saline environments, using the capacity of certain plants to grow under saline conditions in combination with the use of saline soil and alternative water-resources [137]. In order to become reliable, biosaline agriculture requires improved soil and water management, but most importantly new genetic resources (new genotypes or more salt-tolerant species). High global variation in salinity, availability, and ionic composition of saline water and soil conditions renders any single plant unsuitable for all systems, so a high number of crops will be needed for the success of biosaline agriculture.
The first patent for a halophyte crop was issued less than 20 years ago, and currently halophyte crops are being developed by classical breeding, biotechnology, tissue culture, and plant exploration [112,138,139]. Quinoa (Chenopodium quinoa Wild.), an ancient species and now the new wonder crop, is a facultative halophyte that can be part of this basket, since the most tolerant varieties are able to cope with salinity levels as high as those present in sea water [140]. There is also a special interest on the cultivation of halophytes using saline waters and soils in desert ecosystems and their use as fodder [141]. Kochia (Bassia scoparia A.J.Scott) is a salt- and drought-tolerant species, an annual plant of the family Chenopodiaceae, which can be a valuable source of fodder. The results reported by Kafi et al. [141] suggest that Kochia may be a candidate species for cultivation in areas where salinity cannot be diminished to acceptable limits by other means. This plant has a high potential to grow on soils under irrigation with saline water in summer. Kochia can produce considerable dry mass, and a reduction of up to 20% in its water requirements has no significant effect on its fodder production.
Baig et al. [142] compared the base scenario of keeping land and crops management as usual with bioremediation by growing salt-tolerant fodder, such as Sudan grass (Sorghum x drummondii Millsp. and Chase) and Berseem clover (Trifolium alexandrinum L.), with the strategy of optimum land allocation with different crops. The results show that in comparison with a base scenario, bioremediation techniques are helpful in reducing the salt balance of the root zone in the long term, while optimum crop allocation was found to be more effective as a short-term solution, but less effective on reducing salt content in the soil. Despite these encouraging experiences, cultivating halophytes is so far unusual and its effects on soil salinity likely minimal according to Barrett-Lennard [70].
The last strategy is the mechanical removal of salts from the surface of the soil using appropriate machinery [41]. This strategy consists of surface flushing or mechanical removal of salts from salt crusts at the surface by different means. This could be the last solution where drainage is inadequate, and leaching is restricted by the presence of a shallow water table or highly impermeable profile. This strategy seems rarely affordable.
3. Synthesis
Table 1 provides an overview of all SICS that were studied in 30 studies. Some studies reported on more than one treatment, so that in total 128 treatments were studied. Studies are grouped based on the type of treatment used and may therefore appear more than once on the list.

Table 1.
Soil-improving cropping systems (SICS) used in the meta-analysis. A: amendment (chemical, other than conditioner); M: mulching; C: conditioner (biological); D: drainage; Fe: fertilization; Fl: flushing; I: irrigation; P: phytoremediation; R: rotation instead of monocultivation; T: tillage.
For all 128 treatments the effect of the SICS treatment was expressed in a change in soil salinity, either expressed in Electrical Conductivity (EC) levels [dS m−1], Sodium Adsorption Ratio (SAR; ((mmol/L−1)0.5)), in total salt content (%) or Cl−/Na+ ion concentration [meq/100 g]. Figure 3 presents the effect size, ES (%), as the change in salinity due to the SICS treatment relative to the reference case: a negative value for ES indicates a decrease (in this case an improvement) of the soil salinity level. Yield is expressed as t ha−1, g plant−1, or g container−1, depending on experimental design.

Table 2.
Qualitative assessment of salinization specific soil improving cropping systems (SICS) regarding the achieved change in yield (ΔY) and change in soil salinity (ΔS).
- Soil amendments (chemical) typically reduce salinity but have a great variability in yield increase (may also cause a decrease in yield).
- Mulching, alone or in combination with amendments, generally preserve productivity (but have also caused a decrease in certain applications) with very satisfactory results reducing salinity.
- Biological soil conditioners increase yield while reducing salinity and may act better in combination with other soil amendments.
- Drainage increases yield but its effect on soil salinity depends on location and procedure.
- Fertilization increases salinity and yield.
- Flushing is always advisable.
- Irrigation management measures are typically aiming at sustaining production while maintaining soil salinity in tolerable levels. Therefore, it is not really a SICS, but rather a last resort for water-saving.
- Phytoremediation increases yield (typically because of the additional biomass generated), but does not guarantee positive effects on soil salinity.
- Rotation systems are always advisable (rather than monocultivation).
- Reduced tillage decreases salinity and increases yield.
- Most promising for salinity is a combination of amendments, conditioners, and mulching, while performing flushing and maintaining cover crops or some sort of rotation.
- Most promising for yield is phytoremediation (but this depends on yield requirements) and biological conditioners while maintain cover crops or some sort of rotation.
4. Conclusions
Salinization-specific SICS prevent salinization and/or lower the accumulation of unwanted salts and contribute to improving soil structure. Salinization-specific SICS are highly site-specific and may involve three mechanisms. The first mechanism involves improved drainage through groundwater level control and channeling, reduced evaporation, less fertilizers, and irrigation with low EC water. The second mechanism involves high frequency localized irrigation instead of surface irrigation. The third mechanism includes ridging, mulching, and growing tolerant crops.
Most promising salinization specific SICS reduce the input of unwanted salts into the soil, decrease the content of unwanted salts in the soil, and minimize the impact of unwanted salts on soil functioning. As Shabala S. and Munns [23] state, there is no easy solution to soil salinization. Where man-induced secondary salinization appears, then changes in land management are needed. This implies changes in drainage, irrigation, and fertilization, as well as selection of crop genotypes able to tolerate higher levels of salts in soil. If, on the contrary, salts are a natural part of the soil or if salinization is due to seawater intrusion, then growing more tolerant varieties is the best way to sustain crop productivity. In this sense, biotechnology can help by breeding new salt-tolerant crops. Different biotechnological tools now permit linking genes to their biological function thus helping us to select more salt-tolerant genotypes.
Once the problem of salinization is well-established, farmers may adopt different decisions to minimize the impact of salinization. Among them, we may select the management of irrigation and fertilization as the most crucial techniques for halting further degradation of soils. Selection of crops tolerant to moderate levels of salts can be considered as far as the cash obtained by their cultivation does not lessen their acceptance by farmers. Biosaline agriculture seems, so far, the last resort when the soil accumulates large amounts of salts in the root zone. In the near future, we may expect some help from biotechnology for reclaiming salinized lands. Screening germplasm of halophytes plants could be of interest for recovering lands heavily affected by the problem of salinization. The use of tolerant rootstocks and varieties is foreseen to increase in the years to come. Transgenic crops have also been proposed as a solution to deal with salinized soils. Nonetheless, whatever the approach planned for halting salinization of agricultural lands, the measures proposed should also unavoidably consider stakeholders’ willingness to adopt them.
Author Contributions
J.C. led the team, contributed to the selection of papers for the review, wrote first drafts and edited late version of the manuscript. I.N.D. contributed in the selection of papers for the review, conducted the metanalysis, and helped in the writing and editing of the manuscript. F.d.M. contributed in the selection of papers for the review, the extraction of data for formal analysis and helping in the writing and editing of the manuscript. J.J.H. contributed in the selection of papers for the review and helped in the original writing. I.K.T. contributed to the planning of the manuscript and provided resources and funds for some of the research experimentation performed by the Greek team.
Funding
This study was funded by the European Union’s Horizon 2020 Research and Innovation Program, Project SoilCare, grant agreement 677407.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Keesstra, S.D.; Bouma, J.; Wallinga, J.; Tittonell, P.; Smith, P.; Cerdà, A.; Montanarella, L.; Quinton, J.N.; Pachepsky, Y.; van der Putten, W.H.; et al. The significance of soils and soil science towards realization of the United Nations Sustainable Development Goals. SOIL 2016, 2, 111–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- United Nations General Assembly. Transforming Our World: The 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development; United Nations General Assembly: New York, NY, USA, 2015; p. 35. [Google Scholar]
- Nafziger, E. Cropping Systems. Dep. Crop Sci. 2010, 49–63. Available online: http://extension.cropsciences.illinois.edu/handbook/pdfs/chapter05.pdf (accessed on 5 June 2019).
- Reeves, D.W. The role of soil organic matter in maintaining soil quality in continuous cropping systems. Soil Tillage Res. 1997, 43, 131–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, A.; Panagos, P.; Barcelo, S.; Bouraoui, F.; Bosco, C.; Dewitte, O.; Gardi, C.; Hervás, J.; Hiederer, R.; Jeffery, S.; et al. The State of Soil in Europe-a Contribution of the JRC to the European Environment Agency’s Environment State and Outlook Report–SOER 2010. 2012. Available online: http://publications.jrc.ec.europa.eu/repository/bitstream/JRC68418/lbna25186enn.pdf (accessed on 5 June 2019).
- Rockström, J.; Steffen, W.; Noone, K.; Persson, Å.; Chapin, F.S., III; Lambin, E.; Lenton, T.; Scheffer, M.; Folke, C.; Schellnhuber, H.J.; et al. Planetary boundaries: Exploring the safe operating space for humanity. Ecol. Soc. 2009, 14, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Attard, E.; Recous, S.; Chabbi, A.; De Berranger, C.; Guillaumaud, N.; Labreuche, J.; Philippot, L.; Schmid, B.; Le Roux, X. Soil environmental conditions rather than denitrifier abundance and diversity drive potential denitrification after changes in land uses. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2011, 17, 1975–1989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cassman, K.G. Ecological intensification of cereal production systems: Yield potential, soil quality, and precision agriculture. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1999, 96, 5952–5959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gasso, V.; Sørensen, C.A.G.; Oudshoorn, F.W.; Green, O. Controlled traffic farming: A review of the environmental impacts. Eur. J. Agron. 2013, 48, 66–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sapkota, T.B.; Mazzoncini, M.; Bàrberi, P.; Antichi, D.; Silvestri, N. Fifteen years of no till increase soil organic matter, microbial biomass and arthropod diversity in cover crop-based arable cropping systems. Agron. Sustain. Dev. 2012, 32, 853–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pittelkow, C.M.; Liang, X.; Linquist, B.A.; van Groenigen, K.J.; Lee, J.; Lundy, M.E.; van Gestel, N.; Six, J.; Venterea, R.T.; van Kessel, C. Productivity limits and potentials of the principles of conservation agriculture. Nature 2015, 517, 365–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daliakopoulos, I.N.; Tsanis, I.K.; Koutroulis, A.G.; Kourgialas, N.; Varouchakis, E.A.; Karatzas, G.P.; Ritsema, C.J. The threat of soil salinity: A European scale review. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 573, 727–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Beek, C.L.; Tóth, G. Risk Assessment Methodologies of Soil Threats in Europe. 2012. Available online: http://citeseerx.ist.psu.edu/viewdoc/download?doi=10.1.1.397.1303&rep=rep1&type=pdf (accessed on 5 June 2019).
- Wallender, W.W.; Tanji, K.K. Nature and extent of agricultural salinity and sodicity. In Agricultural Salinity Assessment and Management; Wallender, W.W., Tanji, K.K., Eds.; American Society of Civil Engineers: New York, NY, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Suarez, D.L. Sodic soil reclamation: Modelling and field study. Aust. J. Soil Res. 2001, 39, 1225–1246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pitman, M.G.; Läuchli, A. Global Impact of Salinity and Agricultural Ecosystems. In Salinity: Environment - Plants - Molecules; Kluwer Academic Publishers: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2002; Volume 3, pp. 3–20. [Google Scholar]
- Qadir, M.; Noble, A.D.; Schubert, S.; Thomas, R.J.; Arslan, A. Sodicity-induced land degradation and its sustainable management: Problems and prospects. Land Degrad. Dev. 2006, 17, 661–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rengasamy, P. World salinization with emphasis on Australia. J. Exp. Bot. 2006, 57, 1017–1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aquastat. FAO’s Information System on Water and Agriculture; Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) of the United Nation: Roma, Italy; Available online: http://www.fao.org/nr/water/aquastat (accessed on 1 June 2016).
- Ghassemi, F.; Jakeman, A.J.; Nix, H.A. Salinisation of Land and Water Resources: Human Causes, Extent, Management and Case Studies; CAB International: Wallingford, UK, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Wichelns, D.; Qadir, M. Achieving sustainable irrigation requires effective management of salts, soil salinity, and shallow groundwater. Agric. Water Manag. 2014, 157, 31–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bridges, E.M.; Oldeman, L.R. Global Assessment of Human-Induced Soil Degradation. Arid Soil Res. Rehabil. 1999, 13, 319–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shabala, S.; Munns, R. Salinity Stress: Physiological Constraints and Adaptive Mechanisms. In Plant Stress Physiology; CABI: Boston, MA, USA, 2017; pp. 24–63. ISBN 9781780647296. [Google Scholar]
- Chesworth, W. Encyclopedia of Soil Science; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2008; ISBN 1-4020-3994-8. [Google Scholar]
- Maas, E.V. Salt tolerance of plants. Appl. Agric. Res. 1986, 1, 12–26. [Google Scholar]
- Mateo-Sagasta, J.; Burke, J. Agriculture and Water Quality Interactions: A Global Overview. SOLAW Background Thematic Report-TR08. 2011, p. 46. Available online: http://www.fao.org/3/a-bl092e.pdf (accessed on 5 June 2019).
- Cocks, P.S. Ecology of herbaceous perennial legumes: A review of characteristics that may provide management options for the control of salinity and waterlogging in dryland cropping systems. Aust. J. Agric. Res. 2001, 52, 137–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ritzema, H.P. Drain for Gain: Managing salinity in irrigated lands—A review. Agric. Water Manag. 2016, 176, 18–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crescimanno, G.; Garofalo, P. Management of Irrigation with Saline Water in Cracking Clay Soils. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2006, 70, 1774–1787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhutta, M.N.; Smedema, L.K. One hundred years of waterlogging and salinity control in the Indus Valley, Pakistan: A historical review. Irrig. Drain. 2007, 56, S81–S90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oron, G.; DeMalach, Y.; Gillerman, L.; David, I.; Lurie, S. SW—Soil and Water. Biosyst. Eng. 2002, 81, 237–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, H.-C.; Li, Y.-Y.; Yang, J.-S.; Liang, Y.-S. Effect of brackish water irrigation and straw mulching on soil salinity and crop yields under monsoonal climatic conditions. Agric. Water Manag. 2010, 97, 1971–1977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sørensen, C.G.; Halberg, N.; Oudshoorn, F.W.; Petersen, B.M.; Dalgaard, R. Energy inputs and GHG emissions of tillage systems. Biosyst. Eng. 2014, 120, 2–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lahmar, R. Adoption of conservation agriculture in Europe. Land Use Policy 2010, 27, 4–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jensen, H.G.; Jacobsen, L.-B.; Pedersen, S.M.; Tavella, E. Socioeconomic impact of widespread adoption of precision farming and controlled traffic systems in Denmark. Precis. Agric. 2012, 13, 661–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deike, S.; Pallutt, B.; Melander, B.; Strassemeyer, J.; Christen, O. Long-term productivity and environmental effects of arable farming as affected by crop rotation, soil tillage intensity and strategy of pesticide use: A case-study of two long-term field experiments in Germany and Denmark. Eur. J. Agron. 2008, 29, 191–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devita, P.; Dipaolo, E.; Fecondo, G.; Difonzo, N.; Pisante, M. No-tillage and conventional tillage effects on durum wheat yield, grain quality and soil moisture content in southern Italy. Soil Tillage Res. 2007, 92, 69–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darwish, T.; Atallah, T.; El Moujabber, M.; Khatib, N. Salinity evolution and crop response to secondary soil salinity in two agro-climatic zones in Lebanon. Agric. Water Manag. 2005, 78, 152–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitamura, Y.; Yano, T.; Honna, T.; Yamamoto, S.; Inosako, K. Causes of farmland salinization and remedial measures in the Aral Sea Basin-Research on water management to prevent secondary salinization in rice-based cropping system in arid land. Agric. Water Manag. 2006, 85, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finlayson, J.; Bathgate, A.; Nordblom, T.; Theiveyanathan, T.; Farquharson, B.; Crosbie, R.; Mitchell, D.; Hoque, Z. Balancing land use to manage river volume and salinity: Economic and hydrological consequences for the Little River catchment in Central West, New South Wales, Australia. Agric. Syst. 2010, 103, 161–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qadir, M.; Schubert, S.; Noble, A.D.; Saqib, M.; Saifullah, M. Amelioration strategies for salinity-induced land degradation. CAB Reviews: Perspectives in Agriculture, Veterinary Science. Nutr. Nat. Resour. 2006, 1, 69. [Google Scholar]
- Kara, T.; Willardson, L. Leaching requirements to prevent soil salinization. J. Appl. Sci. 2006, 6, 1481–1489. [Google Scholar]
- Munns, R.; James, R.A.; Läuchli, A. Approaches to increasing the salt tolerance of wheat and other cereals. J. Exp. Bot. 2006, 57, 1025–1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiconato, D.A.; da Silveira Sousa Junior, G.; dos Santos, D.M.M.; Munns, R. Adaptation of sugarcane plants to saline soil. Environ. Exp. Bot. 2019, 162, 201–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mujeeb-Kazi, A.; Munns, R.; Rasheed, A.; Ogbonnaya, F.C.; Alí, N.; Hollington, P.; Dundas, I.; Saeed, N.; Wang, R.; Rengasamy, P.; et al. Chapter four-Breeding strategies for structuring salinity tolerance in wheat. Adv. Agron. 2019, 155, 121–187. [Google Scholar]
- Young, R. Determining the Economic Value of Water: Concepts and Methods; Resources for the Future: Washington, DC, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.; Pu, L.; Zhu, M.; Zhang, R. The present situation and hot issues in the salt-affected soil research. Acta Geogr. Sin. 2012, 67, 1233–1245. [Google Scholar]
- Gabriel, J.L.; Vanclooster, M.; Quemada, M. Integrating water, nitrogen, and salinity in sustainable irrigated systems: cover crops versus fallow. J. Irrig. Drain. Eng. 2014, 140, A4014002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wichelns, D.; Oster, J.D. Sustainable irrigation is necessary and achievable, but direct costs and environmental impacts can be substantial. Agric. Water Manag. 2006, 86, 114–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castanheira, P.J.N.; Serralheiro, R.P. Impact of mole drains on salinity of a vertisoil under irrigation. Biosyst. Eng. 2010, 105, 25–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diez, J.A.; Caballero, R.; Roman, R.; Tarquis, A.; Cartagena, M.C.; Vallejo, A. Integrated fertilizer and irrigation management to reduce nitrate leaching in Central Spain. J. Environ. Qual. 2000, 29, 1539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matthews, N.; Grové, B.; Barnard, J.H.; Van Rensburg, L.D. Modelling the economic tradeoffs between allocating water for crop production or leaching for salinity management. Water SA 2010, 36, 37–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Abliz, A.; Tiyip, T.; Ghulam, A.; Halik, Ü.; Ding, J.; Sawut, M.; Zhang, F.; Nurmemet, I.; Abliz, A. Effects of shallow groundwater table and salinity on soil salt dynamics in the Keriya Oasis, Northwestern China. Environ. Earth Sci. 2016, 75, 260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daliakopoulos, I.N.; Apostolakis, A.; Wagner, K.; Deligianni, A.; Koutskoudis, D.; Stamatakis, A.; Tsanis, I.K. Effectiveness of T. harzianum in soil and yield conservation of tomato crops under saline irrigation. Catena 2019, 175, 153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forkutsa, I.; Sommer, R.; Shirokova, Y.I.; Lamers, J.P.A.; Kienzler, K.; Tischbein, B.; Martius, C.; Vlek, P.L.G. Modeling irrigated cotton with shallow groundwater in the Aral Sea Basin of Uzbekistan: II. Soil salinity dynamics. Irrig. Sci. 2009, 27, 319–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashraf, M.; Saeed, M.M. Effect of improved cultural practices on crop yield and soil salinity under relatively saline groundwater applications. Irrig. Drain. Syst. 2006, 20, 111–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panagea, I.S.; Daliakopoulos, I.N.; Tsanis, I.K.; Schwilch, G. Evaluation of promising technologies for soil salinity amelioration in Timpaki (Crete): A participatory approach. Solid Earth 2016, 7, 177–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dandekar, C.B.; Chougule, B.A. Drainage of Irrigated Lands. In Proceedings of the 9th International Drainage Symposium Held Jointly with CIGR and CSBE/SCGAB Proceedings, Québec, QC, Canada, 13−16 June 2010; American Society of Agricultural and Biological Engineers: St. Joseph, MI, USA, 2010; p. 1. [Google Scholar]
- Kotb, T.H.; Watanabe, T.; Ogino, Y.; Tanji, K.K. Soil salinization in the Nile Delta and related policy issues in Egypt. Agric. Water Manag. 2000, 43, 239–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konukcu, F.; Gowing, J.W.; Rose, D.A. Dry drainage: A sustainable solution to waterlogging and salinity problems in irrigation areas? Agric. Water Manag. 2006, 83, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heuperman, A. Hydraulic gradient reversal by trees in shallow water table areas and repercussions for the sustainability of tree-growing systems. Agric. Water Manag. 1999, 39, 153–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhutta, M.N.; Chaudhary, M.R. Biological control of waterlogging. In Proceedings of the Eighth ICID International Drainage Workshop, New Delhi, India, 31 January–4 February 2000; pp. 33–45. [Google Scholar]
- Kapoor, A.S.; Denecke, H.W. L’experience du Rajasthan en matiere de biodrainage et de bioelimination. Grid 2001, 17, 3–4. [Google Scholar]
- Heuperman, A.F.; Kapoor, A.S.; Denecke, H.W. Biodrainage: Principles, Experiences and Applications; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Akram, S.; Kashkouli, H.A.; Pazira, E. Sensitive variables controlling salinity and water table in a bio-drainage system. Irrig. Drain. Syst. 2008, 22, 271–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morris, J.D.; Collopy, J.J. Water use and salt accumulation by Eucalyptus camaldulensis and Casuarina cunninghamiana on a site with shallow saline groundwater. Agric. Water Manag. 1999, 39, 205–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slavich, P.G.; Smith, K.S.; Tyerman, S.D.; Walker, G.R. Water use of grazed salt bush plantations with saline water table. Agric. Water Manag. 1999, 39, 169–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamazaki, F. Farmland Engineering; Tokyo University Publication: Tokyo, Japan, 1976; Volume 1. [Google Scholar]
- Sharma, P.K.; Bhagat, R.M. Puddling and compaction effects on water permeability of texturally different soils. J. Indian Soc. Soil Sci. 1993, 41, 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Barrett-Lennard, E.G. Restoration of saline land through revegetation. Agric. Water Manag. 2002, 53, 213–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Connor, D.J. Designing cropping systems for efficient use of limited water in southern Australia. Eur. J. Agron. 2004, 21, 419–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jobbágy, E.B.; Jackson, R.B. Groundwater use and salinization with grassland afforestation. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2004, 10, 1299–1312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendes, J.P.; Carvalho, M.C. Controlo da salinidade do solo com recurso à sementeira directa. Rev. Ciências Agrárias 2009, 32, 360–369. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, Q.; Wu, F.; Zhang, Q. Is irrigation water price an effective leverage for water management? An empirical study in the middle reaches of the Heihe River basin. Phys. Chem. Earth Parts A/B/C 2015, 89–90, 25–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alcon, F.; Tapsuwan, S.; Brouwer, R.; de Miguel, M.D. Adoption of irrigation water policies to guarantee water supply: A choice experiment. Environ. Sci. Policy 2014, 44, 226–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- English, M.J.; Solomon, K.H.; Hoffman, G.J. A paradigm shift in irrigation management. J. Irrig. Drain. Eng. 2002, 128, 267–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffman, G.J.; Shannon, M.C. 4. Salinity. Dev. Agric. Eng. 2007, 13, 131–160. [Google Scholar]
- Marchand, M.; Abd El Hadi, H. Long-term experiments comparing the impact on soils and field crops of potassium chloride vs. potassium sulfate. Acta Hortic. 2002, 573, 49–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanson, B.; Hopmans, J.W.; Šimůnek, J. Leaching with subsurface drip irrigation under saline, shallow groundwater conditions. Vadose Zone J. 2008, 7, 810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fereres, E.; Soriano, M.A. Deficit irrigation for reducing agricultural water use. J. Exp. Bot. 2006, 58, 147–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cuevas, J.; Cañete, M.L.; Pinillos, V.; Zapata, A.J.; Fernández, M.D.; González, M.; Hueso, J.J. Optimal dates for regulated deficit irrigation in “Algerie” loquat (Eriobotrya japonica Lindl.) cultivated in Southeast Spain. Agric. Water Manag. 2007, 89, 131–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hueso, J.J.; Cuevas, J. Ten consecutive years of regulated deficit irrigation probe the sustainability and profitability of this water saving strategy in loquat. Agric. Water Manag. 2010, 97, 645–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hueso, J.J.; Cuevas, J. Loquat as a crop model for successful deficit irrigation. Irrig. Sci. 2008, 26, 269–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinillos, V.; Chiamolera, F.M.; Ortiz, J.F.; Hueso, J.J.; Cuevas, J. Post-veraison regulated deficit irrigation in ‘Crimson Seedless’ table grape saves water and improves berry skin color. Agric. Water Manag. 2016, 165, 181–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aragüés, R.; Medina, E.T.; Martínez-Cob, A.; Faci, J. Effects of deficit irrigation strategies on soil salinization and sodification in a semiarid drip-irrigated peach orchard. Agric. Water Manag. 2014, 142, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Mokh, F.; Nagaz, K. Impact of deficit irrigation with saline water on yield, soil salinization and water productivity of barley in arid regions of Tunisia. Rev. des Régions Arid. Pagination 2014, 35, 1217–1225. [Google Scholar]
- Aragüés, R.; Medina, E.T.; Clavería, I.; Martínez-Cob, A.; Faci, J. Regulated deficit irrigation, soil salinization and soil sodification in a table grape vineyard drip-irrigated with moderately saline waters. Agric. Water Manag. 2014, 134, 84–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mousavi, S.F.; Mostafazadeh-Fard, B.; Farkhondeh, A.; Feizi, M. Effects of deficit irrigation with saline water on yield, fruit quality and water use efficiency of cantaloupe in an arid region. J. Agric. Sci. Technol. 2009, 11, 469–479. [Google Scholar]
- González Vázquez, J.C.; Grande, J.A.; Barragán, F.J.; Ocaña, J.A.; De La Torre, M.L. Nitrate accumulation and other components of the groundwater in relation to cropping system in an aquifer in Southwestern Spain. Water Resour. Manag. 2005, 19, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crisosto, C.H.; Johnson, R.S.; DeJong, T.; Day, K.R. Orchard factors affecting postharvest stone fruit quality. HortScience 1997, 32, 820–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subbarao, G.V.; Johansen, C. Strategies and scope for improving salinity tolerance in crop plants. In Handbook of Plant and Crop Stress; Pessarakli, M., Ed.; MARCEL DEKKER AG: New York, NY, USA, 1999; pp. 1069–1088. [Google Scholar]
- Grattan, S.; Grieve, C. Mineral nutrient acquisition and response by plants grown in saline environments. In Handbook of Plant and Crop; Pessarakli, M., Ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1999; pp. 203–229. [Google Scholar]
- Canellas, L.P.; Olivares, F.L.; Aguiar, N.O.; Jones, D.L.; Nebbioso, A.; Mazzei, P.; Piccolo, A. Humic and fulvic acids as biostimulants in horticulture. Sci. Hortic. 2015, 196, 15–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashraf, M.; Akram, N.A.; Arteca, R.N.; Foolad, M.R. The physiological, biochemical and molecular roles of brassinosteroids and salicylic acid in plant processes and salt tolerance. CRC. Crit. Rev. Plant Sci. 2010, 29, 162–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayakannan, M.; Bose, J.; Babourina, O.; Rengel, Z.; Shabala, S. Salicylic acid in plant salinity stress signalling and tolerance. Plant Growth Regul. 2015, 76, 25–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; Zheng, J.; Zhang, X.; Hu, Q.; Qian, R. Salicylic acid alleviates the adverse effects of salt stress on Dianthus superbus (Caryophyllaceae) by activating photosynthesis, protecting morphological structure, and enhancing the antioxidant system. Front. Plant Sci. 2017, 8, 600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, J.; Ma, X.; Zhang, X.; Hu, Q.; Qian, R. Salicylic acid promotes plant growth and salt-related gene expression in Dianthus superbus L. (Caryophyllaceae) grown under different salt stress conditions. Physiol. Mol. Biol. Plants 2018, 24, 231–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, K.; Lei, Y. Integrated effect of water, fertilize and salinity on the wheat yield in desalinized fluvo-aquic soil in Heilonggang Region. Res. Agric. Mod 1994, 15, 364–368. [Google Scholar]
- Pang, H.; Xu, F. Study on the tillage methods under straw mulching in Weibei Arid Area. Res. Agric. Mod 1998, 19, 249–251. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, Q.; Yin, Z.; Tian, C. Effect of two different straw mulching methods on soil solute salt concentration. Arid Land Geogr. 2001, 24, 52–56. [Google Scholar]
- Deng, L.; Chen, M.; Liu, Z.; Shen, Q.; Wang, H.; Wang, J. Effects of different ground covers on soil physical properties and crop growth on saline-alkaline soil. Chin. J. Soil Sci. 2003, 34, 93–97. [Google Scholar]
- Qiao, H.; Liu, X.; Li, W.; Huang, W.; Li, C.; Li, Z. Effect of deep straw mulching on soil water and salt movement and wheat growth. Chin. J. Soil Sci. 2006, 37, 885–889. [Google Scholar]
- Pang, H. The effect of straw mulching on the soil environment and wheat yield traits. Chin. J. Soil Sci. 1999, 30, 174–175. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; Zhang, Z. Effect of straw mulching on soil water and salt movement. Chin. J. Soil Sci. 1999, 30, 257–258. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, X.; Li, Y. Effect of straw mulching on soil water and salt movement. J. Shandong Agric. Univ. 2000, 31, 38–40. [Google Scholar]
- Hira, G.S.; Thind, H.S. A plantation technique for salt-affected soils with shallow water table. Landsc. Urban Plan. 1987, 14, 445–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greiner, R. Optimal farm management responses to emerging soil salinisation in a dryland catchment in eastern Australia. Land Degrad. Dev. 1997, 8, 281–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weaver, T.B.; Hulugalle, N.R.; Ghadiri, H.; Harden, S. Quality of Drainage Water Under Irrigated Cotton In Vertisols of the Lower Namoi Valley, New South Wales, Australia. Irrig. Drain. 2013, 62, 107–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Z.H.; Huang, J.F.; Zhang, C.S.; Li, A.F. Soil Quality Evolution After Land Use Change from Paddy Soil to Vegetable Land. Environ. Geochem. Health 2004, 26, 97–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, S.; O’Connel, N.; Rana, T.; Xevi, E. Hydrologic–Economic model for managing irrigation intensity in irrigation areas under watertable and soil salinity targets. Environ. Model. Assess. 2008, 13, 115–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lefroy, E.C.; Stirzaker, R.J. Agroforestry for water management in the cropping zone of southern Australia. Agrofor. Syst. 1999, 45, 277–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yensen, N.P.; Biel, K.Y. Soil remediation via salt-conduction and the hypotheses of halosynthesis and photoprotection. In Ecophysiology of High Salinity Tolerant Plants; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2008; pp. 313–344. [Google Scholar]
- Khan, M.A.; Ansari, R.; Ali, H.; Gul, B.; Nielsen, B.L. Panicum turgidum, a potentially sustainable cattle feed alternative to maize for saline areas. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2009, 129, 542–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanji, K.K.; Kielen, N.C. Agricultural Drainage Water Management in Arid and Semi-arid Areas; FAO Irrigation and Drainage paper 61, Annex 1: Crop Salt Tolerance Data; United Nations Food Agric: Rome, Italy, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Chartzoulakis, K.S. Salinity and olive: Growth, salt tolerance, photosynthesis and yield. Agric. Water Manag. 2005, 78, 108–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paranychianakis, N.V.; Chartzoulakis, K.S. Irrigation of Mediterranean crops with saline water: From physiology to management practices. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2005, 106, 171–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuazo, V.H.D.; Raya, A.M.; Ruiz, J.A. Impact of salinity on the fruit yield of mango (Mangifera indica L. cv. ‘Osteen’). Eur. J. Agron. 2004, 21, 323–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagner, K.; Apostolakis, A.; Daliakopoulos, I.N.; Tsanis, I. Can tomato inoculation with Trichoderma compensate yield and soil health deficiency due to soil salinity? EGU Gen. Assem. Conf. Abstr. 2016, 18, 1007. [Google Scholar]
- Apostolakis, A.; Daliakopoulos, I.; Tsanis, I. Effectiveness of T. harzianum and humate amendment in soil salinity restoration. Geophys. Res. Abstr. EGU Gen. Assem. 2017, 19, 15797. [Google Scholar]
- Cabot, C.; Sibole, J.V.; Barceló, J.; Poschenrieder, C. Lessons from crop plants struggling with salinity. Plant Sci. 2014, 226, 2–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koubouris, G.C.; Tzortzakis, N.; Kourgialas, N.N.; Darioti, M.; Metzidakis, I. Growth, photosynthesis and pollen performance in saline water treated olive plants under high temperature. Int. J. Plant Biol. 2015, 6, 28–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, S.J.; Negrao, S.; Tester, M. Salt resistant crop plants. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2014, 26, 115–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- National Research Council. Saline Agriculture: Salt-tolerant Plants for Developing Countries; The National Academies Press: Washington, DC, USA, 1990; pp. 11–16. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; Yang, J.; Liu, G.; Yao, R.; Yu, S. Impact of irrigation volume and water salinity on winter wheat productivity and soil salinity distribution. Agric. Water Manag. 2015, 149, 44–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qadir, M.; Tubeileh, A.; Akhtar, J.; Larbi, A.; Minhas, P.S.; Khan, M.A. Productivity enhancement of salt-affected environments through crop diversification. Land Degrad. Dev. 2008, 19, 429–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Tian, Y.; Gao, L.; Peng, X.; Tong, E. Effects of straw biological reactor and microbial agents on physicochemical properties and microbial diversity of tomato soil in solar greenhouse. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2014, 30, 153–164. [Google Scholar]
- Mudge, K.; Janick, J.; Scofield, S.; Goldschmidt, E.E. A History of grafting. Hortic. Rev. 2009, 35, 437–493. [Google Scholar]
- Colla, G.; Rouphael, Y.; Leonardi, C.; Bie, Z. Role of grafting in vegetable crops grown under saline conditions. Sci. Hortic. 2010, 127, 147–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinod, K.K.; Krishnan, S.G.; Babu, N.N.; Nagarajan, M.; Singh, A.K. Improving salt tolerance in rice: Looking beyond the conventional. In Salt Stress in Plants; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2013; pp. 219–260. [Google Scholar]
- Bacilio, M.; Moreno, M.; Bashan, Y. Mitigation of negative effects of progressive soil salinity gradients by application of humic acids and inoculation with Pseudomonas stutzeri in a salt-tolerant and a salt-susceptible pepper. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2016, 107, 394–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mbarki, S.; Cerdà, A.; Brestic, M.; Mahendra, R.; Abdelly, C.; Pascual, J.A. Vineyard compost supplemented with Trichoderma harzianum T78 improve saline soil quality. Land Degrad. Dev. 2017, 28, 1028–1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abebe, T.; Guenzi, A.C.; Martin, B.; Cushman, J.C. Tolerance of mannitol-accumulating transgenic wheat to water stress and salinity. Plant Physiol. 2003, 131, 1748–1755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, L.; Lu, H.; Liu, Q.; Chen, X.; Jiang, X. Overexpression of mtl D gene in transgenic Populus tomentosa improves salt tolerance through accumulation of mannitol. Tree Physiol. 2005, 25, 1273–1281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, N.; Si, H.-J.; Wen, G.; Du, H.-H.; Liu, B.-L.; Wang, D. Enhanced drought and salinity tolerance in transgenic potato plants with a BADH gene from spinach. Plant Biotechnol. Rep. 2011, 5, 71–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colmer, T.D.; Flowers, T.J.; Munns, R. Use of wild relatives to improve salt tolerance in wheat. J. Exp. Bot. 2006, 57, 1059–1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nevo, E.; Chen, G. Drought and salt tolerances in wild relatives for wheat and barley improvement. Plant. Cell Environ. 2010, 33, 670–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brini, F.; Masmoudi, K. Biotechnology for drought and salinity tolerance of crops. In Physiological Mechanisms and Adaptation Strategies in Plants under Changing Environment; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2014; pp. 97–113. [Google Scholar]
- Qureshi, A.S.; Qadir, M.; Heydari, N.; Turral, H.; Javadi, A. A Review of Management Strategies for Salt-prone Land and Water Resources in Iran; IWMI: Colombo, Sri Lanka, 2007; Volume 125. [Google Scholar]
- Rabhi, M.; Ferchichi, S.; Jouini, J.; Hamrouni, M.H.; Koyro, H.W.; Ranieri, A.; Abdelly, C.; Smaoui, A. Phytodesalination of a salt-affected soil with the halophyte Sesuvium portulacastrum L. to arrange in advance the requirements for the successful growth of a glycophytic crop. Bioresour. Technol. 2010, 101, 6822–6828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adolf, V.I.; Jacobsen, S.-E.; Shabala, S. Salt tolerance mechanisms in quinoa (Chenopodium quinoa Willd.). Environ. Exp. Bot. 2013, 92, 43–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kafi, M.; Asadi, H.; Ganjeali, A. Possible utilization of high-salinity waters and application of low amounts of water for production of the halophyte Kochia scoparia as alternative fodder in saline agroecosystems. Agric. Water Manag. 2010, 97, 139–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baig, M.A.; Adamowski, J.; Prasher, S. Development and application of a decision support system for optimizing cropping patterns under saline agriculture conditions in Rechna Doab, Pakistan. In Proceedings of the 2015 ASABE International Meeting American Society of Agricultural and Biological Engineers, New Orleans, LA, USA, 26–29 July 2015; pp. 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Qadir, M.; Qureshi, R.H.; Ahmad, N.; Ilyas, M. Salt-tolerant forage cultivation on a saline-sodic field for biomass production and soil reclamation. Land Degrad. Dev. 1996, 7, 11–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, S.; Ghafoor, A.; Akhtar, M.E.; Khan, M.Z. Ionic displacement and reclamation of saline-sodic soils using chemical amendments and crop rotation. Land Degrad. Dev. 2013, 24, 170–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahdy, A.M. Comparative effects of different soil amendments on amelioration of saline-sodic soils. Soil Water Res. 2011, 6, 205–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adnan, M.; Zia-ur-Rehman, M.; Yousaf, B.; Murtaza, G.; Yousaf, A.; Latif, M.A.; Khan, A.M. The evaluation of various soil conditioners effects on the amelioration of saline-sodic soil. J. Environ. Earth Sci. 2014, 4, 22–29. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmad, M.J.; Arif, M.; Iqbal, A.; Khalid, M.; Akhtar, N. Rice production in salt-affected soils of Pakistan using different reclamation techniques. In Developments in Soil Salinity Assessment and Reclamation; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2013; pp. 283–293. [Google Scholar]
- Pedreño, J.N.; Gómez, I.; Moral, R.; Mataix, J. Improving the agricultural value of a semi-arid soil by addition of sewage sludge and almond residue. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 1996, 58, 115–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaaban, M.; Abid, M.; Abou-Shanab, R. Amelioration of salt affected soils in rice paddy system by application of organic and inorganic amendments. Plant Soil Environ. 2013, 59, 227–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, D.P.; Gupta, S.K. Subsurface drainage for reversing degradation of waterlogged saline lands. Land Degrad. Dev. 2006, 17, 605–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satyanarayana, T.V.; Lakshmi, G.V.; Hanumanthaiah, C.V.; Srinivasulu, A.; Ratnam, M. Feasible Subsurface Drainage Strategies to Combat Water Logging and Salinity in Irrigated Agricultural Lands in Andhra Pradesh; Technical Document; Indo-Dutch Network Project: Bapatla, India, 2003; p. 32. [Google Scholar]
- Ritzema, H.P.; Satyanarayana, T.V.; Raman, S.; Boonstra, J. Subsurface drainage to combat waterlogging and salinity in irrigated lands in India: Lessons learned in farmers’ fields. Agric. Water Manag. 2008, 95, 179–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nayak, A.K.; Sharma, D.K.; Mishra, V.K.; Minhas, P.S.; Verma, C.L. Reclamation of saline-sodic soil under a rice-wheat system by horizontal surface flushing. Soil Use Manag. 2008, 24, 337–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, R.; Paul, M.; Malik, R. Impact assessment and recommendation of alternative conjunctive water use strategies for salt affected agricultural lands through a field scale decision support system—A case study. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2007, 129, 257–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aragüés, R.; Medina, E.T.; Zribi, W.; Clavería, I.; Álvaro-Fuente, J.; Faci, J. Soil Salinization as a threat to the sustainability of deficit irrigation under present and expected climate change scenarios. Irrig. Sci. 2015, 33, 67–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-dhuhli, H.S.; Al-rawahy, S.A.; Prathapar, S. Effectiveness of mulches to control soil salinity in Sorghum fields irrigated with saline water. Manag. Salt-Affect. Soils Water Sustain. Agric. 2010, 46, 41–46. [Google Scholar]
- Bezborodov, G.A.; Shadmanov, D.K.; Mirhashimov, R.T.; Yuldashev, T.; Qureshi, A.S.; Noble, A.D.; Qadir, M. Mulching and water quality effects on soil salinity and sodicity dynamics and cotton productivity in Central Asia. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2010, 138, 95–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, N.; Qureshi, R.H.; Qadir, M. Amelioration of a calcareous saline-sodic soil by gypsum and forage plants. Land Degrad. Dev. 1990, 2, 277–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ado, M.N.; Guero, Y.; Michot, D.; Soubeiga, B.; Senga Kiesse, T.; Walter, C. Phytodesalinization of irrigated saline Vertisols in the Niger Valley by Echinochloa stagnina. Agric. Water Manag. 2016, 177, 229–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuccarini, P. Ion uptake by halophytic plants to mitigate saline stress in Solarium lycopersicon L., and different effect of soil and water salinity. Soil Water Res. 2008, 3, 62–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Ma, L.-Y.; Wang, X.-F.; Wei, M.; Shi, Q.-H.; Yang, F.-J. Effects of short-term summer fallow and rotations on soil quality under plastic greenhouse cultivation. J. Food Agric. Environ. 2012, 10, 1106–1110. [Google Scholar]
- Young, R.; Huth, N.; Harden, S.; McLeod, R. Impact of rain-fed cropping on the hydrology and fertility of alluvial clays in the more arid areas of the upper Darling Basin, eastern Australia. Soil Res. 2014, 52, 388–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pulatov, A.; Egamberdiev, O.; Karimov, A.; Tursunov, M.; Kienzler, S.; Sayre, K.; Tursunov, L.; Lamers, J.P.A.; Martius, C. Introducing conservation agriculture on irrigated meadow alluvial soils (Arenosols) in Khorezm, Uzbekistan. In Cotton, Water, Salts and Soums; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2012; pp. 195–217. [Google Scholar]
- Lozano-García, B.; Parras-Alcántara, L.; Muriel-Fernández, J.L. Soil tillage effects on monovalent cations (Na+ and K+) in vertisols soil solution. Catena 2011, 84, 61–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).