The HPSE Gene Insulator—A Novel Regulatory Element That Affects Heparanase Expression, Stem Cell Mobilization, and the Risk of Acute Graft versus Host Disease
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Population
2.2. Cell Lines
2.3. SNPs Analysis
2.4. DNA Constructs
2.5. Luciferase Reporter Assay
2.6. Electromobility Shift Assay (EMSA)
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Detection of Insulator Activity in Cancer Cell Lines of Hematological and Non-Hematological Origin
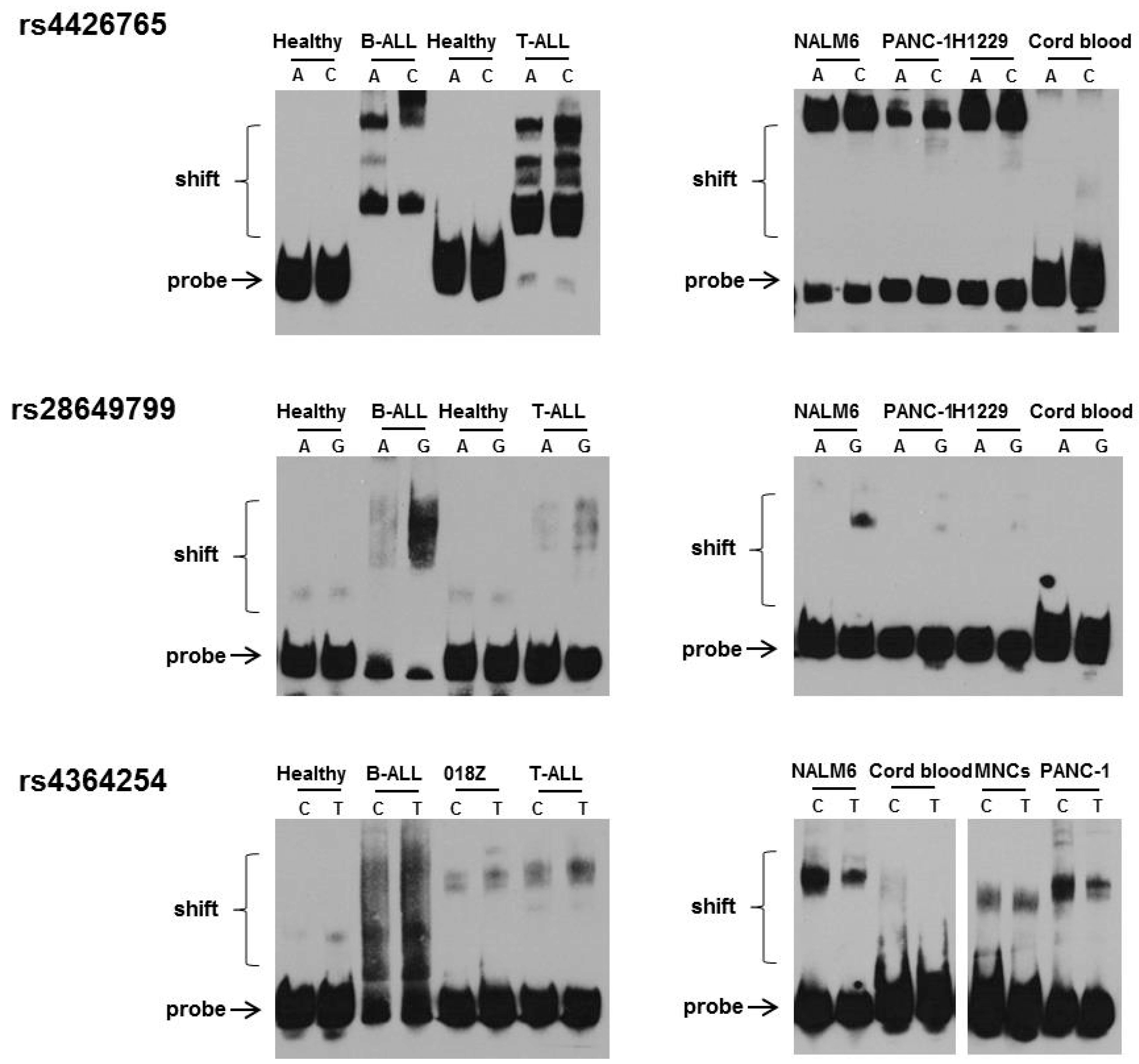
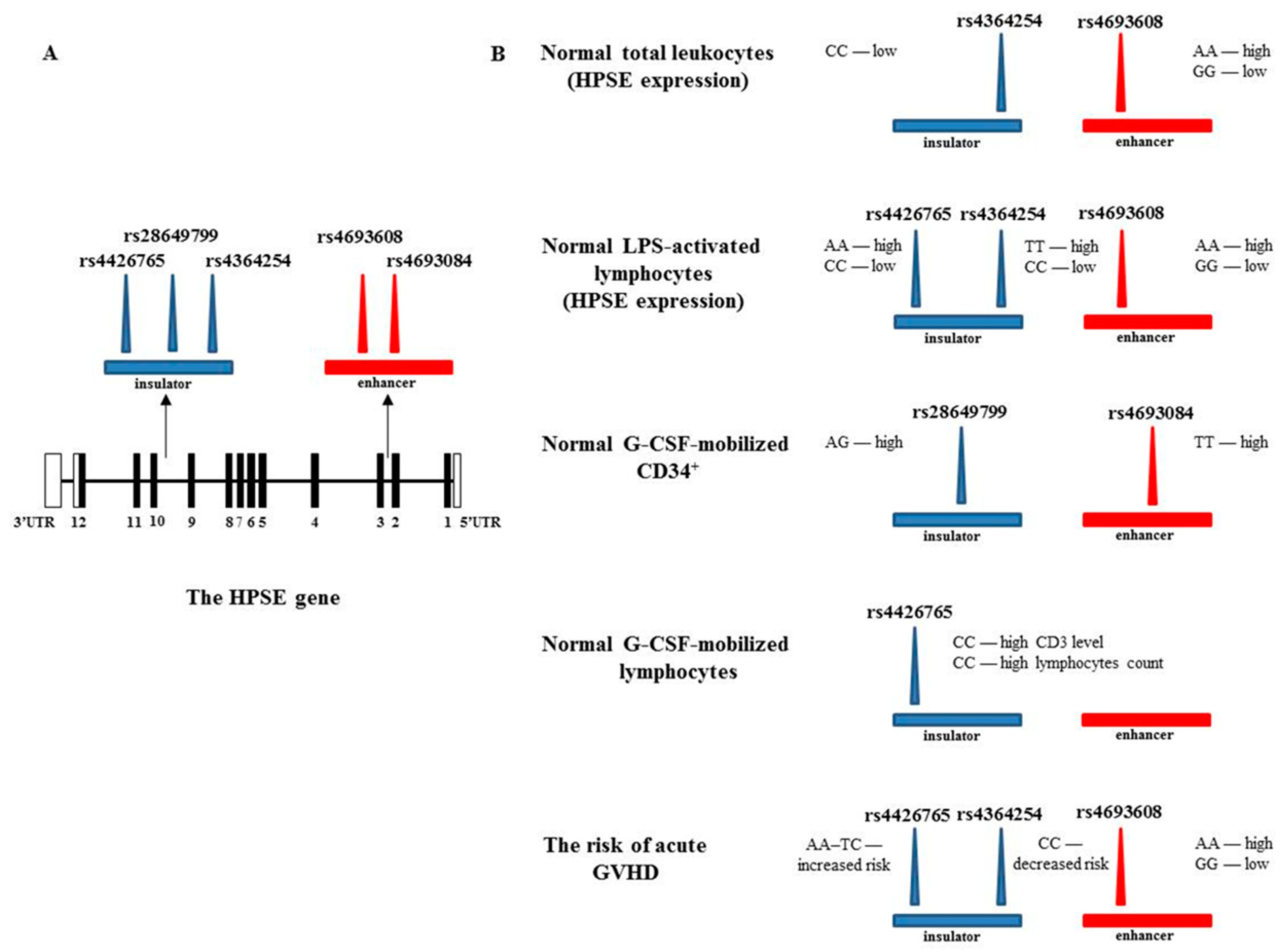
3.2. Effect of rs4426765, rs28649799, and rs4364254 SNPs on the Binding of Nuclear Proteins to the Insulator Region
3.3. Acute GVHD
3.4. Correlation between Enhancer and Insulator HPSE SNPs and Heparanase mRNA Levels in MNCs before and after LPS Treatment
3.5. Association between Enhancer and Insulator HPSE Gene SNPs and the Levels of HPSE mRNA in Normal Leukocytes
3.6. G-CSF-Mediated Peripheral Blood Stem Cell Mobilization
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Vlodavsky, I.; Ilan, N.; Sanderson, R.D. Forty years of basic and translational heparanase research. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2020, 1221, 3–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Purushothaman, A.; Sanderson, R.D. Heparanase: A dynamic promoter of myeloma progression. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2020, 1221, 331–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koganti, R.; Suryawanshi, R.; Shukla, D. Heparanase, cell signaling, and viral infections. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2020, 77, 5059–5077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jayatilleke, K.M.; Hulett, M.D. Heparanase and the hallmarks of cancer. J. Transl. Med. 2020, 18, 1–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ilan, N.; Elkin, M.; Vlodavsky, I. Regulation, function and clinical significance of heparanase in cancer metastasis and angiogenesis. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2006, 38, 2018–2039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vlodavsky, I.; Gross-Cohen, M.; Weissmann, M.; Ilan, N.; Sanderson, R.D. Opposing Functions of heparanase-1 and heparanase-2 in cancer progression. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2018, 43, 18–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khanna, M.; Parish, C.R. Heparanase: Historical aspects and future perspectives. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2020, 1221, 71–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayfosh, A.; Baschuk, N.; Hulett, M.D. Leukocyte heparanase: A double-edged sword in tumor progression. Front. Oncol. 2019, 9, 331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ostrovsky, O.; Shimoni, A.; Baryakh, P.; Morgulis, Y.; Mayorov, M.; Beider, K.; Shteingauz, A.; Ilan, N.; Vlodavsky, I.; Nagler, A. Modification of heparanase gene expression in response to conditioning and LPS treatment: Strong correlation to rs4693608 SNP. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2014, 95, 677–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaskin, S.M.; da Costa, T.P.S.; Hulett, M.D. Heparanase: Cloning, function and regulation. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2020, 1221, 189–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shteper, P.J.; Zcharia, E.; Ashhab, Y.; Peretz, T.; Vlodavsky, I.; Ben-Yehuda, D. Role of promoter methylation in regulation of the mammalian heparanase gene. Oncogene 2003, 22, 7737–7749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ogishima, T.; Shiina, H.; Breault, J.E.; Tabatabai, L.; Bassett, W.W.; Enokida, H.; Li, L.C.; Kawakami, T.; Urakami, S.; Ribeiro-Filho, L.A.; et al. Increased heparanase expression is caused by promoter hypomethylation and up-regulation of transcriptional factor early growth response-1 in human prostate cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2005, 11, 1028–1036. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Jiao, F.; Bai, S.-Y.; Ma, Y.; Yan, Z.-H.; Yue, Z.; Yu, Y.; Wang, X.; Wang, J. DNA methylation of heparanase promoter influences its expression and associated with the progression of human breast cancer. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e92190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, P.; Kumar, A.; Parrillo, J.E.; Dempsey, L.A.; Platt, J.L.; Prinz, R.A.; Xu, X. Cloning and characterization of the human heparanase-1 (hpr1) gene promoter. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 8989–8998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Mestre, A.; Khachigian, L.; Santiago, F.S.; Staykova, M.A.; Hulett, M. Regulation of inducible heparanase gene transcription in activated T cells by early growth response 1. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 50377–50385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, W.C.; Liu, Y.N.; Kang, B.B.; Chen, J.H. Trans-activation of heparanase promoter by ETS transcription factors. Oncogene 2003, 22, 919–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, H.; Zheng, L.; Jiao, W.; Mei, H.; Li, D.; Song, H.; Fang, E.; Wang, X.; Li, S.; Huang, K.; et al. Smad4 suppresses the tumorigenesis and aggressiveness of neuroblastoma through repressing the expression of heparanase. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 32628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baraz, L.; Haupt, Y.; Elkin, M.; Peretz, T.; Vlodavsky, I. Tumor suppressor p53 regulates heparanase gene expression. Oncogene 2006, 25, 3939–3947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elkin, M.; Cohen, I.; Zcharia, E.; Orgel, A.; Guatta-Rangini, Z.; Peretz, T.; Vlodavsky, I.; Kleinman, H.K. Regulation of hepa-ranase gene expression by estrogen in breast cancer. Cancer Res. 2003, 63, 8821–8826. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Sullivan, P.S.; Goodman, J.C.; Gunaratne, P.H.; Marchetti, D. MicroRNA-1258 suppresses breast cancer brain metastasis by targeting heparanase. Cancer Res. 2011, 71, 645–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maxhimer, J.B.; Somenek, M.; Rao, G.; Pesce, C.E.; Baldwin, D.; Gattuso, P.; Schwartz, M.M.; Lewis, E.J.; Prinz, R.A.; Xu, X. Heparanase-1 gene expression and regulation by high glucose in renal epithelial cells: A potential role in the pathogenesis of proteinuria in diabetic patients. Diabetes 2005, 54, 2172–2178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ostrovsky, O.; Grushchenko-Polaq, A.H.; Beider, K.; Mayorov, M.; Canaani, J.; Shimoni, A.; Vlodavsky, I.; Nagler, A. Identification of strong intron enhancer in the heparanase gene: Effect of functional rs4693608 variant on HPSE enhancer activity in hematological and solid malignancies. Oncogenesis 2018, 7, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ostrovsky, O.; Korostishevsky, M.; Levite, I.; Leiba, M.; Galski, H.; Gazit, E.; Vlodavsky, I.; Nagler, A. Characterization of HPSE gene single nucleotide polymorphisms in Jewish populations of Israel. Acta Haematol. 2006, 117, 57–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ostrovsky, O.; Korostishevsky, M.; Levite, I.; Leiba, M.; Galski, H.; Vlodavsky, I.; Nagler, A. Association of heparanase gene (HPSE) single nucleotide polymorphisms with hematological malignancies. Leukemia 2007, 21, 2296–2303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ostrovsky, O.; Korostishevsky, M.; Shafat, I.; Mayorov, M.; Ilan, N.; Vlodavsky, I.; Nagler, A. Inverse correlation between HPSE gene single nucleotide polymorphisms and heparanase expression: Possibility of multiple levels of heparanase regulation. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2009, 86, 445–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ostrovsky, O.; Shimoni, A.; Rand, A.; Vlodavsky, I.; Nagler, A. Genetic variations in the heparanase gene (HPSE) associate with increased risk of GVHD following allogeneic stem cell transplantation: Effect of discrepancy between recipients and donors. Blood 2010, 115, 2319–2328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ostrovsky, O.; Vlodavsky, I.; Nagler, A. Mechanism of HPSE gene SNPs function: From normal processes to inflammation, cancerogenesis and tumor progression. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2020, 1221, 231–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brasset, E.; Vaury, C. Insulators are fundamental components of the eukaryotic genomes. Heredity 2005, 94, 571–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Vicente-García, C.; Seruggia, D.; Moltó, E.; Fernandez-Miñán, A.; Neto, A.; Lee, E.; Gómez-Skarmeta, J.L.; Montoliu, L.; Lunyak, V.; et al. MIR retrotransposon sequences provide insulators to the human genome. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, E4428–E4437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tomblyn, M.; Chiller, T.; Einsele, H.; Gress, R.; Sepkowitz, K.; Storek, J.; Wingard, J.R.; Young, J.-A.; Boeckh, M.A. Guidelines for preventing infectious complications among hematopoietic cell transplantation recipients: A global perspective. Biol. Blood Marrow Transplant. 2009, 15, 1143–1238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmitt, M.; Publicover, A.; Orchard, K.H.; Görlach, M.; Wang, L.; Schmitt, A.; Mani, J.; Tsirigotis, P.; Kuriakose, R.; Nagler, A. Biosimilar G-CSF based mobilization of peripheral blood hematopoietic stem cells for autologous and allogeneic stem cell transplantation. Theranostics 2014, 4, 280–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Glucksberg, H.; Storb, R.; Fefer, A.; Buckner, C.D.; Neiman, P.E.; Clift, R.A.; Lerner, K.G.; Thomas, E.D. Clinical manifestations of graft-versus-host disease in human recipients of marrow from hl-a-matched sibling donor, s. Transplantation 1974, 18, 295–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gooley, T.A.; Leisenring, W.; Crowley, J.; Storer, B.E. Estimation of failure probabilities in the presence of competing risk: New representations of old estimators. Stat. Med. 1999, 18, 695–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moog, R. Mobilization and harvesting of peripheral blood stem cells. Curr. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2006, 1, 189–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- West, A.; Gaszner, M.; Felsenfeld, G. Insulators: Many functions, many mechanisms. Genes Dev. 2002, 16, 271–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matharu, N.K.; Ahanger, S.H. Chromatin insulators and topological domains: Adding new dimensions to 3D genome architecture. Genes 2015, 6, 790–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsieh, S.; Lintell, N.; Hunter, K. Germline polymorphisms are potential metastasis risk and prognosis markers in breast cancer. Breast Dis. 2007, 26, 157–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, E.; Palmieri, C.; Tilley, W.D. Renewed interest in the progesterone receptor in breast cancer. Br. J. Cancer 2016, 115, 909–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seifert, C.; Wittig, S.; Arndt, C.; Gruhn, B. Heparanase polymorphisms: Influence on incidence of hepatic sinusoidal obstruction syndrome in children undergoing allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 2014, 141, 877–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lerner, I.; Baraz, L.; Pikarsky, E.; Meirovitz, A.; Edovitsky, E.; Peretz, T.; Vlodavsky, I.; Elkin, M. Function of heparanase in prostate tumorigenesis: Potential for therapy. Clin. Cancer Res. 2008, 14, 668–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyango, I.; Barash, U.; Naroditsky, I.; Li, J.-P.; Hammond, E.; Ilan, N.; Vlodavsky, I. Heparanase cooperates with Ras to drive breast and skin tumorigenesis. Cancer Res. 2014, 74, 4504–4514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shu, J.; Santulli, G. Heparanase in health and disease: The neglected housekeeper of the cell? Atherosclerosis 2019, 283, 124–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruszkowska-Ciastek, B.; Bielawski, K.; Zarychta, E.; Rhone, P. Impact of adjuvant treatment on heparanase concentration in invasive, unilateral breast cancer patients: Results of a prospective single-centre cohort study. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 2184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vlodavsky, I.; Singh, P.; Boyango, I.; Gutter-Kapon, L.; Elkin, M.; Sanderson, R.D.; Ilan, N. Heparanase: From basic research to therapeutic applications in cancer and inflammation. Drug Resist. Updat. 2016, 29, 54–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Secchi, M.F.; Masola, V.; Zaza, G.; Lupo, A.; Gambaro, G.; Onisto, M. Recent data concerning heparanase: Focus on fibrosis, inflammation and cancer. Biomol. Concepts 2015, 6, 415–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parish, C.; Freeman, C.; Ziolkowski, A.; He, Y.; Sutcliffe, E.; Zafar, A.; Rao, S.; Simeonovic, C. Unexpected new roles for heparanase in type 1 diabetes and immune gene regulation. Matrix Biol. 2013, 32, 228–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabelink, T.; van der Berg, B.M.; Garsen, M.; Wang, G.; Elkin, M.; van der Vlag, J. Heparanase: Roles in cell survival, extracellular matrix remodelling and the development of kidney disease. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2017, 13, 201–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barash, U.; Rangappa, S.; Mohan, C.; Vishwanath, D.; Boyango, I.; Basappa, B.; Vlodavsky, I.; Rangappa, K. New heparanase-inhibiting triazolo-thiadiazoles attenuate primary tumor growth and metastasis. Cancers 2021, 13, 2959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parate, S.; Kumar, V.; Danishuddin; Hong, J.C.; Lee, K.W. Computational investigation identified potential chemical scaffolds for heparanase as anticancer therapeutics. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 5311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noda, K.; Philips, B.J.; Snyder, M.E.; Phillippi, J.A.; Sullivan, M.; Stolz, D.B.; Ren, X.; Luketich, J.D.; Sanchez, P.G. Heparanase inhibition preserves the endothelial glycocalyx in lung grafts and improves lung preservation and transplant outcomes. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matharu, N.; Ahituv, N. Modulating gene regulation to treat genetic disorders. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2020, 19, 757–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Cell Lines | Relative Luciferase Activity | p Value | Relative Luciferase Activity | p Value | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sense (%) | A-A-T/C-A-C | Antisense (%) | A-A-T/C-A-C | |||||
| A-A-T /A-G-C | A-A-T /A-G-C | |||||||
| A-A-T | C-A-C | A-G-C | C-A-C/A-G-C | A-A-T | C-A-C | A-G-C | C-A-C/A-G-C | |
| Solid tumors: | ||||||||
| HT1080 | 455 | 552 | 590 | <0.01; <0.01; 0.051 | 2188 | 1471 | 2226 | <0.01; NS; <0.01 |
| H1229 | 134 | 131 | 182 | NS; <0.01; <0.01 | 261 | 184 | 181 | <0.01; <0.01; NS |
| PC3 | 189 | 219 | 167 | 0.021; 0.054; <0.01 | 355 | 273 | 229 | <0.01; <0.01; 0.023 |
| MCF7 | 159 | 113 | 160 | <0.01; NS; <0.01 | 259 | 138 | 117 | <0.01; <0.01; NS |
| Hematological malignancies: | ||||||||
| RPMI8226 | 154 | 101 | 206 | <0.01; <0.01; <0.01 | 220 | 225 | 134 | NS; <0.01; <0.01 |
| SU-DHL4 | 199 | 125 | 167 | <0.01; 0.17; <0.01 | 400 | 211 | 146 | <0.01; <0.01; <0.01 |
| KG1 | 100 | 115 | 164 | NS; <0.01; <0.01 | 129 | 160 | 224 | 0.019; <0.01; <0.01 |
| Jurkat | 164 | 124 | 72 | <0.01; <0.01; <0.01 | 102 | 77 | 90 | 0.038; NS; NS |
| CEM | 56 | 56 | 72 | NS; NS; NS | 101 | 59 | 73 | <0.01; <0.01; 0.051 |
| NALM6 | 97 | 79 | 160 | 0.013; <0.01; <0.01 | 115 | 138 | 117 | 0.048; NS; NS |
| MOLT3 | 87 | 78 | 89 | NS; NS; NS | 86 | 85 | 54 | NS; <0.01; <0.01 |
| SNPs | Genotype | Cumulative Incidence, (95% CI), % | χ2, p Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| rs4693608 (enhancer) | AA | 47.9 (41.2–55.5) | 15.55 |
| AG | 39.4 (34.2–45.4) | ||
| GG | 29.1 (22.4–37.8) | 0.00042 | |
| rs4693084 (enhancer) | GG | 42.0 (37.2–47.4) | 5.4 |
| GT | 38.8 (32.3–46.5) | ||
| TT | 17.5 (7.9–38.9) | 0.067 | |
| rs4426765 (insulator) | AA | 42.2 (37.1–47.9) | 2.97 |
| AC | 37.1 (31.1–44.1) | ||
| CC | 34.6 (23.5–50.9) | 0.23 | |
| rs28649799 (insulator) | AA | 38.5 (34.4–43.1) | 3.78 |
| AG | 42.8 (34.2–53.6) | ||
| GG | 60.0 (29.3–100) | 0.15 | |
| rs4364254 (insulator) | TT | 39.3 (34.1–45.4) | 5.16 |
| TC | 43.7 (37.9–50.4) | ||
| CC | 28.5 (20.3–39.9) | 0.076 | |
| rs4693608 | HR | 47.1 (40.4–55.1) | 18.04 |
| rs4364254 | MR | 41.1 (35.5–47.5) | |
| LR | 27.6 (21.6–35.3) | 0.00012 | |
| rs4693608 | N-HR | 49.2 (43.1–56.0) | 30.67 |
| rs4426765 | N-MR | 39.6 (33.9–46.4) | |
| rs4364254 | N-LR | 22.5 (16.5–30.7) | <0.00001 |
| Discrepancy | D1: N-HR/N-MR | 56.9 (47.6–68.1) | 33.67 |
| N-HR/N-LR | |||
| D2: N-HR/N-HR | 42.1 (36.8–48.0) | <0.00001 | |
| N-MR/N-MR | |||
| N-MR/N-HR | |||
| N-MR/N-LR | |||
| D3: N-LR/N-LR | 23.2 (17.1–31.5) | ||
| N-LR/N-MR | |||
| N-LR/N-HR |
| rs4693608-rs4426765-rs4364254 | Cumulative Incidence, (95% CI), % |
|---|---|
| AA-AA-TT | 45.5 (37.2–55.6) |
| AA-AA-TC | 44.4 (21.4–92.3) |
| AA-AC-TT | 50.0 (28.4–88.0) |
| AA-AC-TC | 45.8 (31.6–66.6) |
| AA-NN-NN | 66.7 (46.6–95.4) |
| AG-AA-TT | 39.0 (30.3–50.2) |
| AG-AA-TC | 55.2 (42.0–72.4) |
| AG-AC-TT | 36.8 (20.5–66.4) |
| AG-AC-TC | 39.0 (29.9–50.7) |
| AG-CC-TC | 40.4 (21.6–75.6) |
| AG-NN-CC | 20.7 (10.2–42.2) |
| GG-AA-TT | 18.8 (8.5–41.5) |
| GG-AA-TC | 46.7 (30.2–72.0) |
| GG-AC-TT | 16.7 (2.8–99.7) |
| GG-AC-TC | 29.2 (15.6–54.4) |
| GG-AA-CC | 25.0 (7.5–83.0) |
| GG-AC-CC | 32.9 (15.9–68.1) |
| GG-CC-CC | 23.4 (10.8–50.2) |
| SNPs | Treatment | Genotype | No. | mRNA Level | Comparisons to Carriers | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (AV ± SE) | ||||||
| rs4693608 (enhancer) | Pre-treatment | AA | 33 | 11.3 ± 3.1 | AA to GG | 0.123 |
| AG | 53 | 9.5 ± 1.3 | AA to others | 0.25 | ||
| Post-treatment | GG | 23 | 6.3 ± 1.1 | GG to others | 0.028 | |
| AA | 47.3 ± 15.6 | AA to GG | 0.033 | |||
| Ratio | AG | 41.8 ± 10 | AA to others | 0.4 | ||
| GG | 12.2 ± 2.5 | GG to others | 0.00054 | |||
| AA | 10.5 ± 4.1 | AA to GG | 0.047 | |||
| AG | 5.6 ± 1.3 | AA to others | 0.16 | |||
| GG | 2.0 ± 0.25 | GG to others | 0.0029 | |||
| rs4426765 (insulator) | Pre-treatment | AA | 60 | 10.2 ± 1.7 | AA to CC | 0.43 |
| AC | 35 | 7.7 ± 1.7 | AA to others | 0.28 | ||
| Post-treatment | CC | 8 | 7.7 ± 2.5 | CC to others | 0.59 | |
| AA | 48.4 ± 11.7 | AA to CC | 0.0078 | |||
| Ratio | AC | 21.7 ± 5.3 | AA to others | 0.027 | ||
| CC | 14.0 ± 4.5 | CC to others | 0.0078 | |||
| AA | 8.8 ± 2.5 | AA to CC | 0.0059 | |||
| AC | 3.5 ± 0.6 | AA to others | 0.026 | |||
| CC | 1.8 ± 0.3 | CC to others | 0.0019 | |||
| rs28649799 (insulator) | Pre-treatment | AA | 83 | 8.9 ± 1.2 | AA to AG | 0.71 |
| Post-treatment | AG | 19 | 10.6 ± 3.4 | |||
| Ratio | AA | 37.8 ± 8 | AA to AG | 0.72 | ||
| AG | 32.4 ± 16.2 | |||||
| AA | 5.7 ± 1.3 | AA to AG | 0.53 | |||
| AG | 9.3 ± 5.1 | |||||
| rs4364254 (insulator) | Pre-treatment | TT | 47 | 9.4 ± 1.8 | TT to CC | 0.35 |
| TC | 45 | 9.4 ± 1.9 | TT to others | 0.84 | ||
| Post-treatment | CC | 12 | 6.9 ± 1.8 | CC to others | 0.29 | |
| TT | 50.2 ± 13.4 | TT to CC | 0.012 | |||
| Ratio | TC | 27.6 ± 7.7 | TT to others | 0.089 | ||
| CC | 14.2 ± 3.1 | CC to others | 0.0039 | |||
| TT | 7.5 ± 2.3 | TT to CC | 0.04 | |||
| TC | 6.1 ± 2.2 | TT to others | 0.45 | |||
| CC | 2.6 ± 0.6 | CC to others | 0.013 | |||
| rs4693608 & rs4364254 (enhancer & Insulator) | Pre-treatment | HR | 31 | 11.6 ± 4.8 | HR to LR | 0.17 |
| MR | 46 | 8.9 ± 1.3 | HR to others | 0.31 | ||
| Post-treatment | LR | 27 | 6.7 ± 1.1 | LR to others | 0.087 | |
| HR | 46.8 ± 16.4 | HR to LR | 0.047 | |||
| Ratio | MR | 43.5 ± 11.2 | HR to others | 0.42 | ||
| LR | 12.5 ± 2.2 | LR to others | 0.011 | |||
| HR | 10.5 ± 4.1 | HR to LR | 0.049 | |||
| MR | 6.0 ± 1.4 | HR to others | 0.16 | |||
| LR | 2.1 ± 0.3 | LR to others | 0.0034 | |||
| rs4693608 & rs4364254 & rs4426765 (enhancer & Insulator) | Pre-treatment | N-HR | 44 | 11.2 ± 2.4 | N-HR to N-LR | 0.16 |
| N-MR | 38 | 7.8 ± 1.3 | N-HR to others | 0.23 | ||
| Post-treatment | N-LR | 22 | 7.2 ± 1.3 | N-LR to others | 0.17 | |
| N-HR | 46.0 ± 13.1 | N-HR to N-LR | 0.017 | |||
| Ratio | N-MR | 39.0 ± 11.7 | N-HR to others | 0.28 | ||
| N-LR | 13.0 ± 2.3 | N-LR to others | 0.0016 | |||
| N-HR | 9.2 ± 3.1 | N-HR to N-LR | 0.028 | |||
| N-MR | 5.5 ± 1.5 | N-HR to others | 0.13 | |||
| N-LR | 2.1 ± 0.3 | N-LR to others | 0.0041 |
| SNPs Interaction | Genotype | No. | mRNA Level (AV ± SE) | Comparisons to Carriers | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| rs4426765 | Group 1:AA-TT | 39 | 56.7 ± 16.0 | AA-TT to AA-TC | 0.3 |
| rs4364254 | AA-TC | 19 | 33.4 ± 15.3 | AC-TT to AC-TC | 0.67 |
| AC-CC to CC-CC | 0.79 | ||||
| into insulator | Group 2:AC-TT | 7 | 19.2 ± 8.0 | ||
| AC-TC | 24 | 23.9 ± 7.3 | |||
| Group1 to Group3 | 0.0052 | ||||
| Group 3:CC-TC | 1 | 7.3 | Group1 to others | 0.025 | |
| CC-CC | 7 | 15.0 ± 5.1 | Group3 to others | 0.0029 | |
| AC-CC | 4 | 13.2 ± 4.0 | |||
| AA-CC | 1 | 12.2 | |||
| rs4693608 | AA-1 | 23 | 49.8 ± 20.6 | AA-1 to AA-2 | 0.95 |
| rs4426765 | AA-2 | 5 | 47.5 ± 28.9 | ||
| rs4364254 | AA-3 | 1 | 7.3 | ||
| enhancer-insulator | AG-1 | 29 | 56.7 ± 17.1 | AG-1 to AG-3 | 0.023 |
| AG-2 | 17 | 21.1 ± 6.3 | AG-1 to others | 0.047 | |
| AG-3 | 4 | 14.2 ± 5.0 | AG-3 to others | 0.021 | |
| GG-1 | 6 | 9.2 ± 5.6 | GG-1 to GG-3 | 0.49 | |
| GG-2 | 9 | 12.4 ± 3.8 | GG-1 to others | 0.54 | |
| GG-3 | 8 | 14.2 ± 4.2 | GG-3 to others | 0.57 |
| SNPs | Location | Genotype | No. | mRNA Level | Comparisons to Carriers | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (AV ± SE) | ||||||
| rs4693608 | Enhancer | AA | 27 | 13.9 ± 2.3 | AA to GG | 0.01 |
| AG | 62 | 11.7 ± 1.6 | AA to others | 0.2 | ||
| GG | 19 | 7.2 ± 1.1 | GG to others | 0.0028 | ||
| rs4426765 | Insulator | AA | 59 | 13 ± 1.7 | AA to CC | 0.56 |
| AC | 36 | 9.3 ± 1.4 | AA to others | 0.14 | ||
| CC | 12 | 11.3 ± 2.2 | CC to others | 0.91 | ||
| rs28649799 | Insulator | AA | 84 | 11.4 ± 1.2 | AA to AG | 0.73 |
| AG | 22 | 12.5 ± 2.8 | ||||
| rs4364254 | Insulator | TT | 49 | 12.7 ± 1.8 | TT to CC | 0.0029 |
| TC | 50 | 11.3 ± 1.5 | TT to others | 0.32 | ||
| CC | 9 | 6.1 ± 1 | CC to others | 0.00049 | ||
| rs4693608 & rs4364254 | Enhancer & Insulator | HR | 25 | 14.6 ± 2.4 | HR to LR | 0.007 |
| MR | 59 | 11.9 ± 1.7 | HR to others | 0.16 | ||
| LR | 22 | 7.1 ± 0.9 | LR to others | 0.00098 | ||
| rs4693608 & rs4364254 & rs4426765 | Enhancer & Insulator | N-HR | 35 | 14. 7 ± 2.3 | N-HR to N-LR | 0.0014 |
| N-MR | 55 | 11.1 ± 1.5 | N-HR to others | 0.082 | ||
| N-LR | 16 | 6.4 ± 0.7 | N-LR to others | 0.000076 |
| Parameters | rs4693608 | rs4693084 | rs4426765 | rs28649799 | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Genotype | Median (Range) | p * | Genotype | Median (Range) | p * | Genotype | Median (Range) | p * | Genotype | Median (Range) | p | |
| CD34+ × 106 total yield | AA (89) | 753.9 | 0.12 | GG (175) | 691.9 | 0.011 | AA (139) | 659.7 | 0.54 | AA (204) | 656.7 | 0.34 |
| (631.7–812.5) | (620.6–768.0) | (549.0–755.4) | (549.4–729.4) | |||||||||
| AG (125) | 634 | 0.12 | GT (78) | 561 | 0.26 | AC (90) | 675.6 | 0.67 | AG (41) | 682.5 | ||
| (545.9–711.3) | (479.1–651.4) | (521.3–758.9) | (495.8–988.7) | |||||||||
| GG (61) | 598.9 | 0.28 | TT (8) | 1022.3 | 0.0068 | CC (15) | 524.9 | 0.55 | ||||
| (493.1–727.1) | (598.9–1196.6) | (431.4–866.1) | ||||||||||
| CD34+ × 106/kg | AA (64) | 8.9 | 0.82 | GG (138) | 7.9 | 0.026 | AA (106) | 7.9 | 0.85 | AA (172) | 7.7 | 0.039 |
| (7.0–10.7) | (7.2–9.1) | (7.0–9.4) | (7.3–9.1) | |||||||||
| AG (105) | 7.7 | 0.86 | GT (66) | 8.2 | 0.53 | AC (82) | 8.4 | 0.52 | AG (32) | 10.9 | ||
| (7.4–9.1) | (7.5–9.5) | (7.3–10.7) | (7.5–13.1) | |||||||||
| GG (53) | 8.3 | 0.54 | TT (7) | 11.9 | 0.025 | CC (15) | 7.4 | 0.99 | ||||
| (6.9–10.0) | (7.6–23.5) | (5.5–11.9) | ||||||||||
| % CD34+ | AA (89) | 0.84 | 0.29 | GG (175) | 0.75 | 0.22 | AA (138) | 0.75 | 0.9 | AA (203) | 0.72 | 0.081 |
| (0.69–0.92) | (0.7–0.84) | (0.65–0.83) | (0.66–0.77) | |||||||||
| AG (126) | 0.72 | 0.08 | GT (78) | 0.68 | 0.38 | AC (91) | 0.72 | 0.9 | AG (42) | 0.84 | ||
| (0.62–0.77) | (0.57–0.76) | (0.66–0.77) | (0.69–1) | |||||||||
| GG (59) | 0.74 | 0.83 | TT (8) | 0.85 | 0.17 | CC (15) | 0.77 | 0.94 | ||||
| (0.64–0.84) | (0.49–1.29) | (0.59–0.85) | ||||||||||
| CD3+ × 108 total yield | AA (88) | 270.7 | 0.99 | GG (173) | 276 | 0.73 | AA (138) | 273.7 | 0.054 | AA (202) | 275.2 | 0.41 |
| (255.4–300.0) | (262.8–300.2) | (258.3–297.8) | (264.6–300.0) | |||||||||
| AG (124) | 289.1 | 0.54 | GT (78) | 274.5 | 0.58 | AC (89) | 266.6 | 0.87 | AG (41) | 268.4 | ||
| (266.6–307.5) | (258.3–305.4) | (247.0–298.9) | (222.4–306.9) | |||||||||
| GG (61) | 268.9 | 0.67 | TT (8) | 266.2 | 0.77 | CC (15) | 336 | 0.044 | ||||
| (241.3–299.2) | (187.1–425.5) | (270.6–378.1) | ||||||||||
| CD3+ × 108/kg | AA (64) | 3.6 | 0.44 | GG (137) | 3.8 | 0.63 | AA (105) | 3.6 | 0.039 | AA (171) | 3.7 | 0.72 |
| (3.1–4.0) | (3.4–4.0) | (3.2–3.9) | (3.5–4.0) | |||||||||
| AG (104) | 3.9 | 0.69 | GT (66) | 3.8 | 0.83 | AC (82) | 3.9 | 0.37 | AG (32) | 3.8 | ||
| (3.5–4.3) | (3.2–4.3) | (3.3–4.2) | (3.0–4.7) | |||||||||
| GG (53) | 3.8 | 0.33 | TT (7) | 4 | 0.61 | CC (15) | 4.16 | 0.039 | ||||
| (3.4–4.2) | (2.2–5.5) | (3.5–5.9) | ||||||||||
| % CD3+ | AA (88) | 31.3 | 0.63 | GG (174) | 31.3 | 0.04 | AA (138) | 31.8 | 0.0042 | AA (202) | 31.4 | 0.97 |
| (28.9–33.9) | (29.6–32.4) | (30.3–33.6) | (29.8–32.7) | |||||||||
| AG (126) | 32.3 | 0.65 | GT (78) | 33.9 | 0.58 | AC (90) | 29.5 | 0.98 | AG (42) | 31.7 | ||
| (29.6–34.0) | (30.6–36.9) | (27.7–32.0) | (28.1–34.3) | |||||||||
| GG (59) | 31.9 | 0.76 | TT (8) | 26 | 0.03 | CC (15) | 39.9 | 0.0026 | ||||
| (29.8–35.9) | (10.8–29.8) | (32.4–43.9) | ||||||||||
| Neutrophils abs., 103/µL | AA (90) | 13.9 | 0.66 | GG (175) | 14.3 | 0.032 | AA (140) | 14.9 | 0.25 | AA (205) | 14.4 | 0.41 |
| (11.2–17.0) | (12.5–17.0) | (12.5–19.2) | (12.5–17.0) | |||||||||
| AG (124) | 15.6 | 0.37 | GT (79) | 14.1 | 0.45 | AC (91) | 16.1 | 0.56 | AG (42) | 17.1 | ||
| (12.4–20.6) | (11.3–17.4) | (12.0–19.2) | (12.6–25.2) | |||||||||
| GG (61) | 13.6 | 0.91 | TT (8) | 24.8 | 0.042 | CC (15) | 13 | 0.25 | ||||
| (11.4–19.1) | (10.0–42.7) | (4.5–20.6) | ||||||||||
| Neutrophils, % | AA (90) | 43.4 | 0.77 | GG (176) | 41.5 | 0.12 | AA (140) | 43.1 | 0.017 | AA (206) | 40.6 | 0.54 |
| (37.5–49.5) | (35.7–47.3) | (37.3–47.6) | (33.2–44.8) | |||||||||
| AG (126) | 37 | 0.48 | GT (80) | 37.7 | 0.95 | AC (92) | 40.7 | 0.59 | AG (42) | 43.7 | ||
| (31.6–46.9) | (29.2–44.3) | (31.9–52.6) | (32.1–55.0) | |||||||||
| GG (61) | 38.7 | 0.82 | TT (8) | 56.8 | 0.12 | CC (15) | 28.2 | 0.015 | ||||
| (31.2–53.3) | (33–71.7) | (12.5–44.3) | ||||||||||
| Lymphocytes abs., 103/µL | AA (90) | 9.8 | 0.75 | GG (175) | 9.9 | 0.12 | AA (140) | 9.9 | 0.017 | AA (205) | 10 | 0.94 |
| (7.4–12.3) | (8.8–12.2) | (8.4–12.2) | (9.4–12.2) | |||||||||
| AG (124) | 10 | 0.57 | GT (79) | 10.8 | 0.95 | AC (91) | 10 | 0.64 | AG (42) | 11.2 | ||
| (8.5–12.1) | (8.1–13.9) | (7.5–12.2) | (6.6–15.8) | |||||||||
| GG (60) | 10.3 | 0.99 | TT (8) | 3.7 | 0.1 | CC (15) | 21.5 | 0.013 | ||||
| (6.6–13.9) | (0.48–15.8) | (10.3–29.0) | ||||||||||
| Lymphocytes, % | AA (90) | 31.8 | 0.77 | GG (176) | 26.5 | 0.049 | AA (140) | 23.5 | 0.026 | AA (206) | 26.3 | 0.91 |
| (19.7–38.8) | (19.7–34.4) | (18.8–32.1) | (19.7–34.3) | |||||||||
| AG (126) | 22.4 | 0.66 | GT (80) | 26.4 | 0.83 | AC (92) | 25.6 | 0.54 | AG (42) | 24.4 | ||
| (17.8–26.8) | (19.7–38.6) | (17.3–35.4) | (15.2–38.6) | |||||||||
| GG (61) | 30.4 | 0.47 | TT (8) | 9.5 | 0.049 | CC (15) | 55.9 | 0.023 | ||||
| (19.9–40.8) | (0.65–29.64) | (29.0–63.9) | ||||||||||
| Platelets, 103/µL | AA (89) | 297.8 | 0.32 | GG (175) | 323.7 | 0.24 | AA (138) | 323.9 | 0.068 | AA (204) | 324 | 0.22 |
| (258.6–326.5) | (303.9–339.9) | (300.2–349.8) | (304.7–345.8) | |||||||||
| AG (125) | 349 | 0.018 | GT (79) | 324.7 | 0.29 | AC (92) | 311.9 | 0.98 | AG (42) | 327.9 | ||
| (323.7–371.3) | (282.3–366.0) | (269.8–349.0) | (286.1–426.6) | |||||||||
| GG (61) | 324.7 | 0.72 | TT (8) | 369.5 | 0.29 | CC (15) | 375.6 | 0.059 | ||||
| (274.4–342.8) | (209.0–485.7) | (304.7–485.7) | ||||||||||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ostrovsky, O.; Baryakh, P.; Morgulis, Y.; Mayorov, M.; Bloom, N.; Beider, K.; Shimoni, A.; Vlodavsky, I.; Nagler, A. The HPSE Gene Insulator—A Novel Regulatory Element That Affects Heparanase Expression, Stem Cell Mobilization, and the Risk of Acute Graft versus Host Disease. Cells 2021, 10, 2523. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells10102523
Ostrovsky O, Baryakh P, Morgulis Y, Mayorov M, Bloom N, Beider K, Shimoni A, Vlodavsky I, Nagler A. The HPSE Gene Insulator—A Novel Regulatory Element That Affects Heparanase Expression, Stem Cell Mobilization, and the Risk of Acute Graft versus Host Disease. Cells. 2021; 10(10):2523. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells10102523
Chicago/Turabian StyleOstrovsky, Olga, Polina Baryakh, Yan Morgulis, Margarita Mayorov, Nira Bloom, Katia Beider, Avichai Shimoni, Israel Vlodavsky, and Arnon Nagler. 2021. "The HPSE Gene Insulator—A Novel Regulatory Element That Affects Heparanase Expression, Stem Cell Mobilization, and the Risk of Acute Graft versus Host Disease" Cells 10, no. 10: 2523. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells10102523
APA StyleOstrovsky, O., Baryakh, P., Morgulis, Y., Mayorov, M., Bloom, N., Beider, K., Shimoni, A., Vlodavsky, I., & Nagler, A. (2021). The HPSE Gene Insulator—A Novel Regulatory Element That Affects Heparanase Expression, Stem Cell Mobilization, and the Risk of Acute Graft versus Host Disease. Cells, 10(10), 2523. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells10102523








