Identification of the Novel Tumor Suppressor Role of FOCAD/miR-491-5p to Inhibit Cancer Stemness, Drug Resistance and Metastasis via Regulating RABIF/MMP Signaling in Triple Negative Breast Cancer
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Cell Culture and Sphere Forming Assay
2.2. Transwell Migration and Invasion Assay
2.3. Western Blotting Analysis
2.4. Short Interfering RNA (siRNA), Expression Vector of RABIF and Their Transfection
2.5. Soft Agar Assay
2.6. MTS Cell Proliferation Assay
2.7. In Vitro Cytotoxicity Assay
2.8. ELISA Analysis
2.9. In Vivo Metastasis Assays
2.10. Web Server Survival Analysis
2.11. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
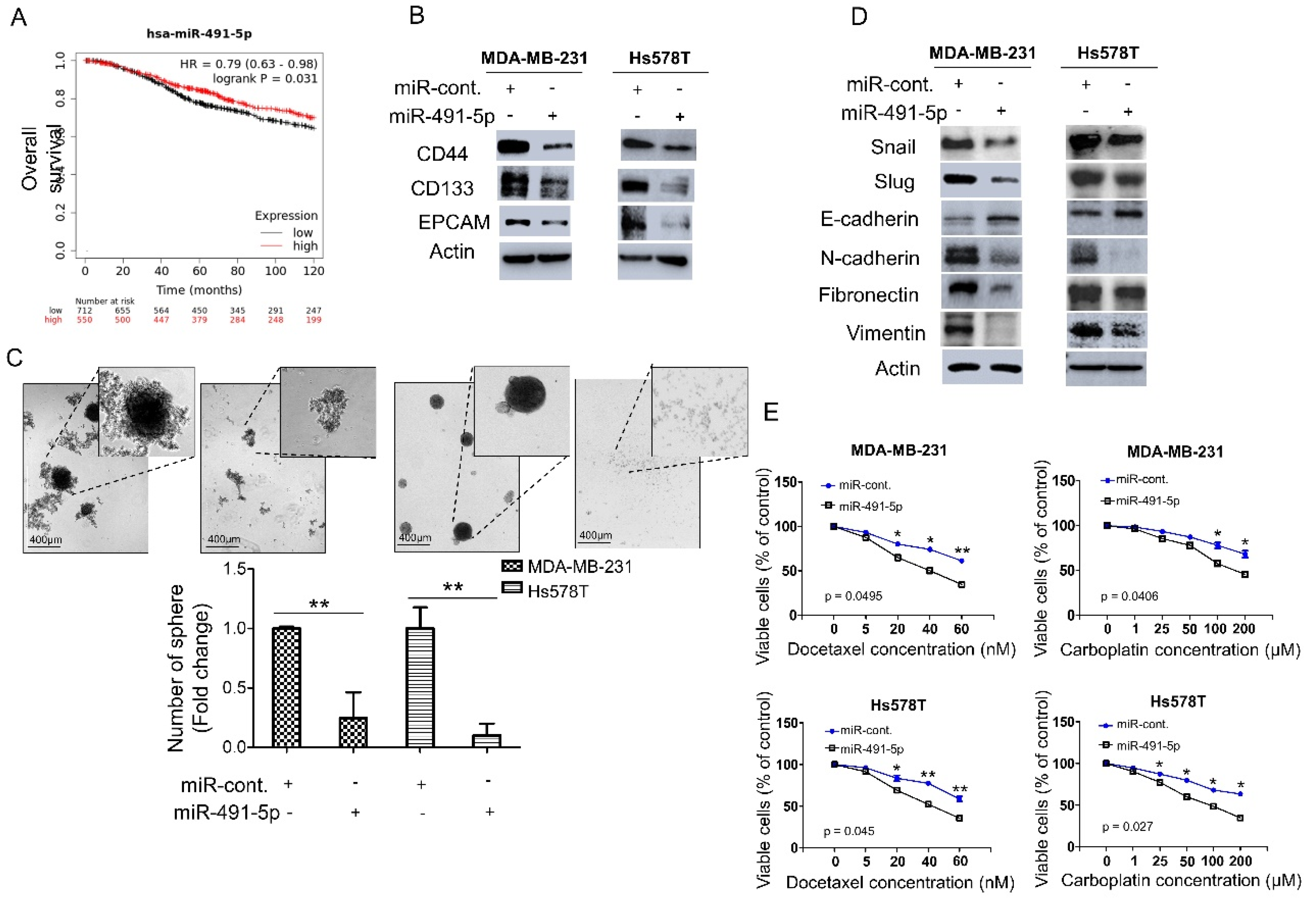
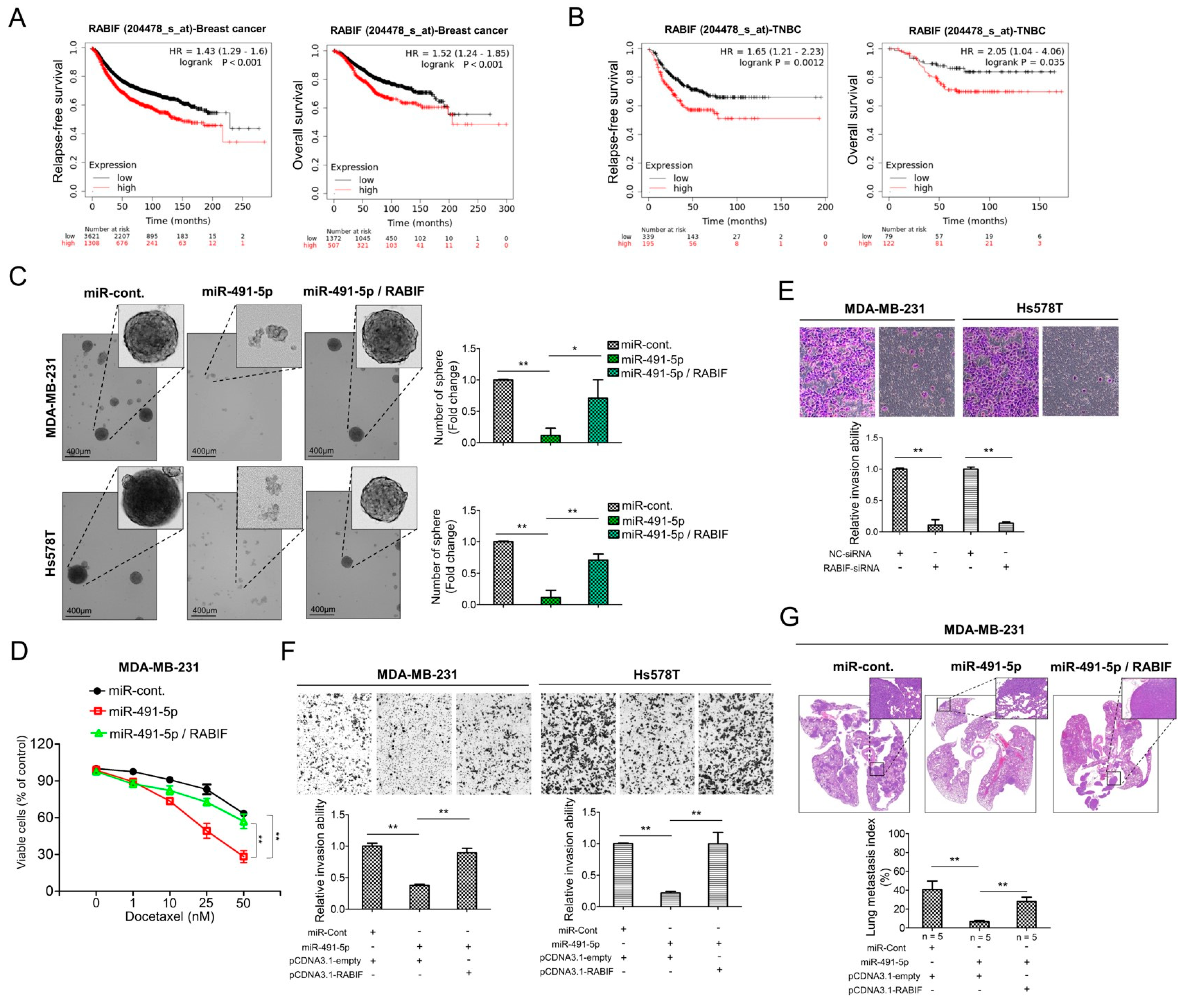
3.1. MiR-491-5p Correlates with Longer Overall Survival and Suppresses Cancer Stemness, Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition (EMT) and Drug Resistance in TNBC
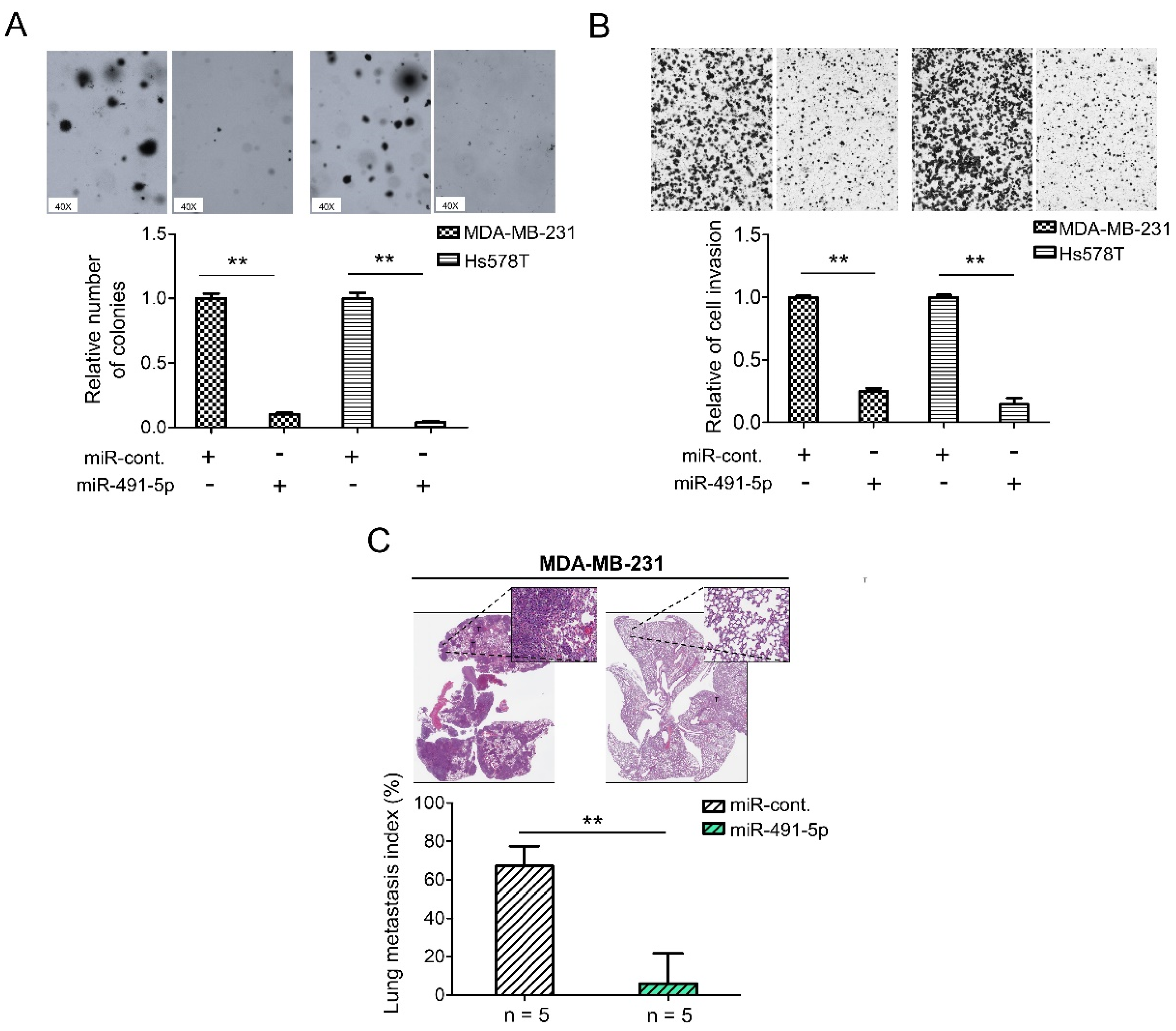
3.2. MiR-491-5p Significantly Inhibits TNBC Anchorage-Independent Growth, Cell Invasion and Pulmonary Metastasis in TNBC
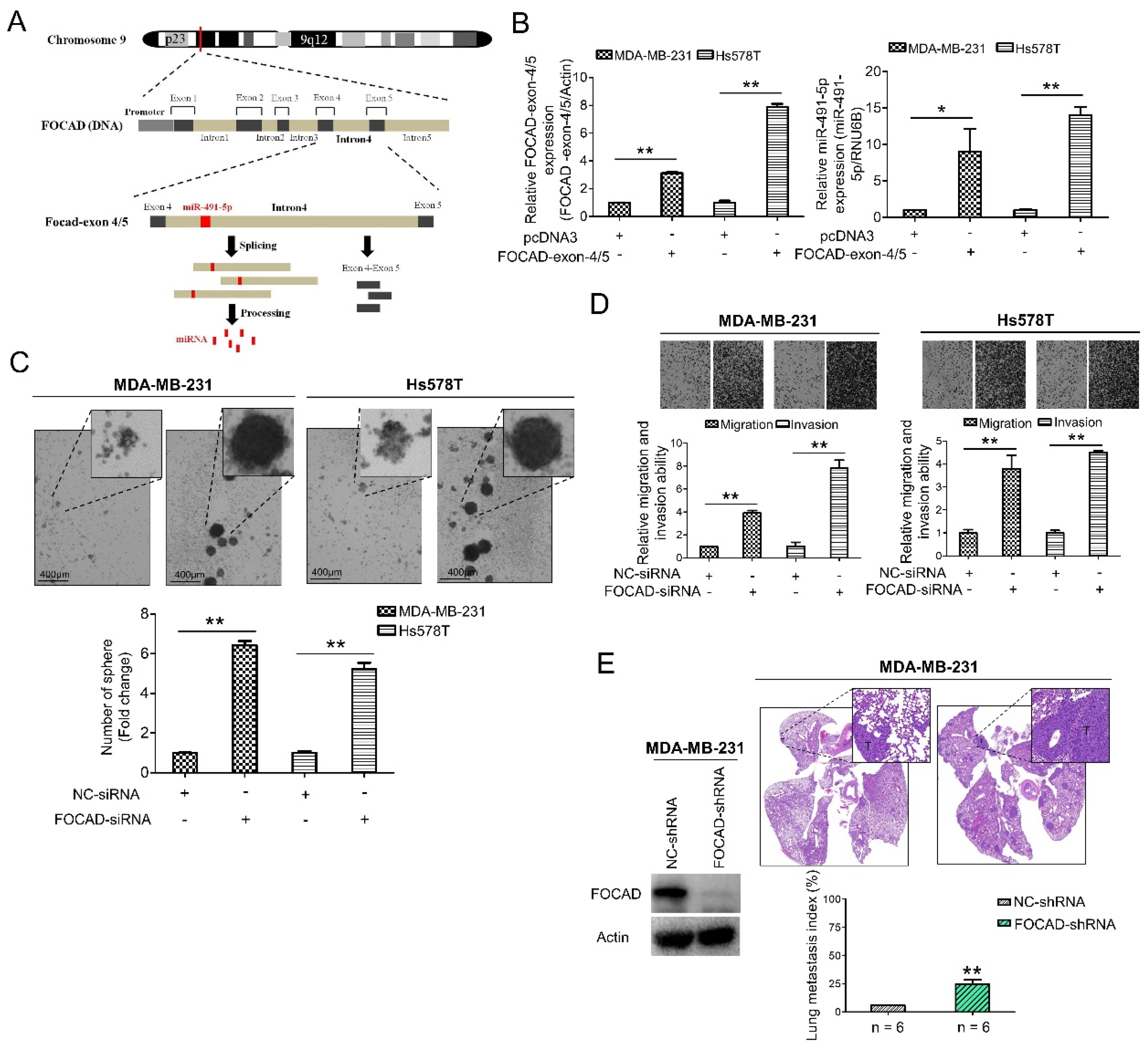
3.3. MiR-491-5p Could Be an Intronic miRNA Processed from FOCAD Gene and FOCAD Regulates Cancer Stemness, Migration/Invasion and Lung Metastasis in TNBC
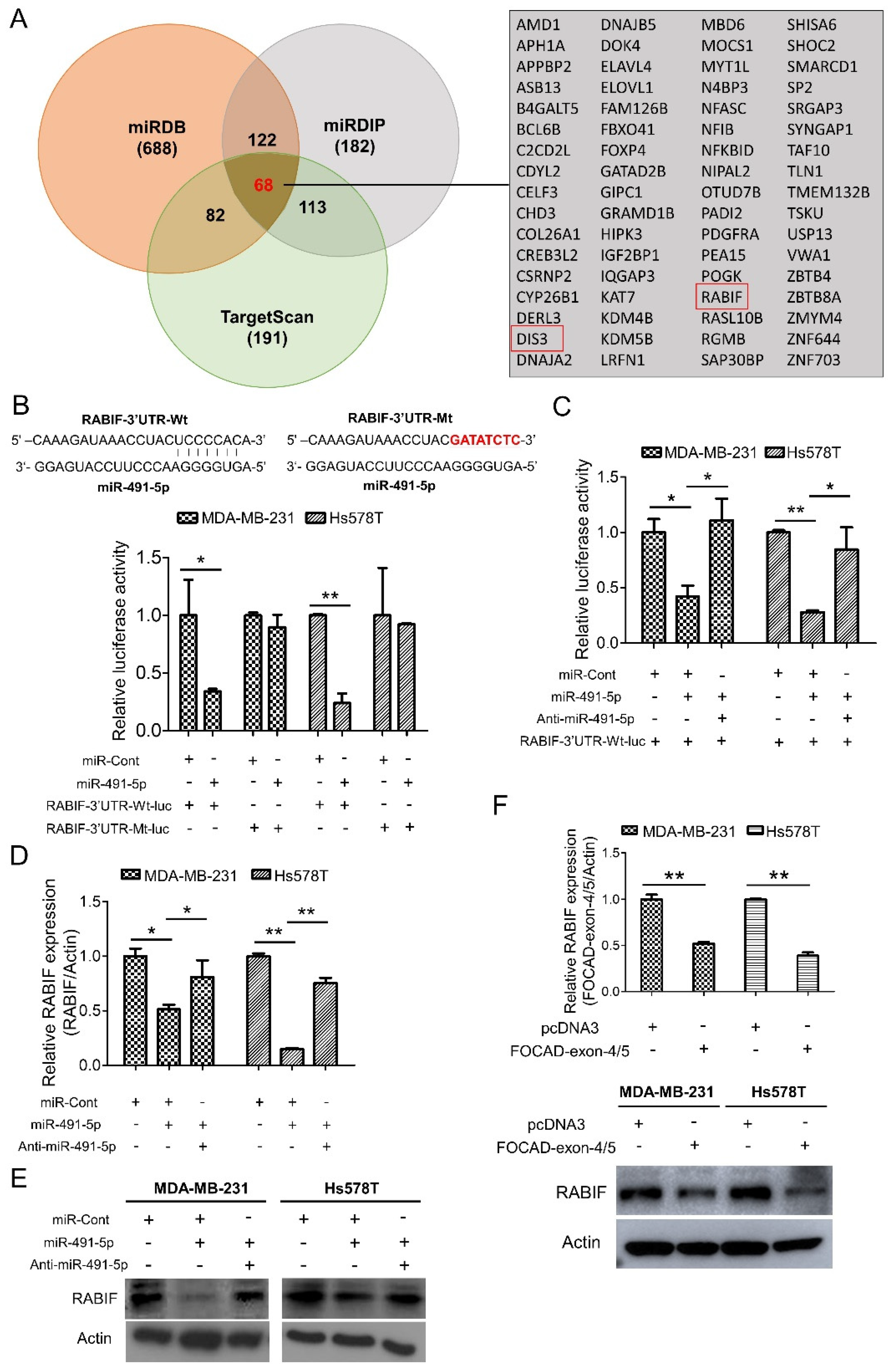
3.4. RABIF Is a Direct Target of MiR-491-5p
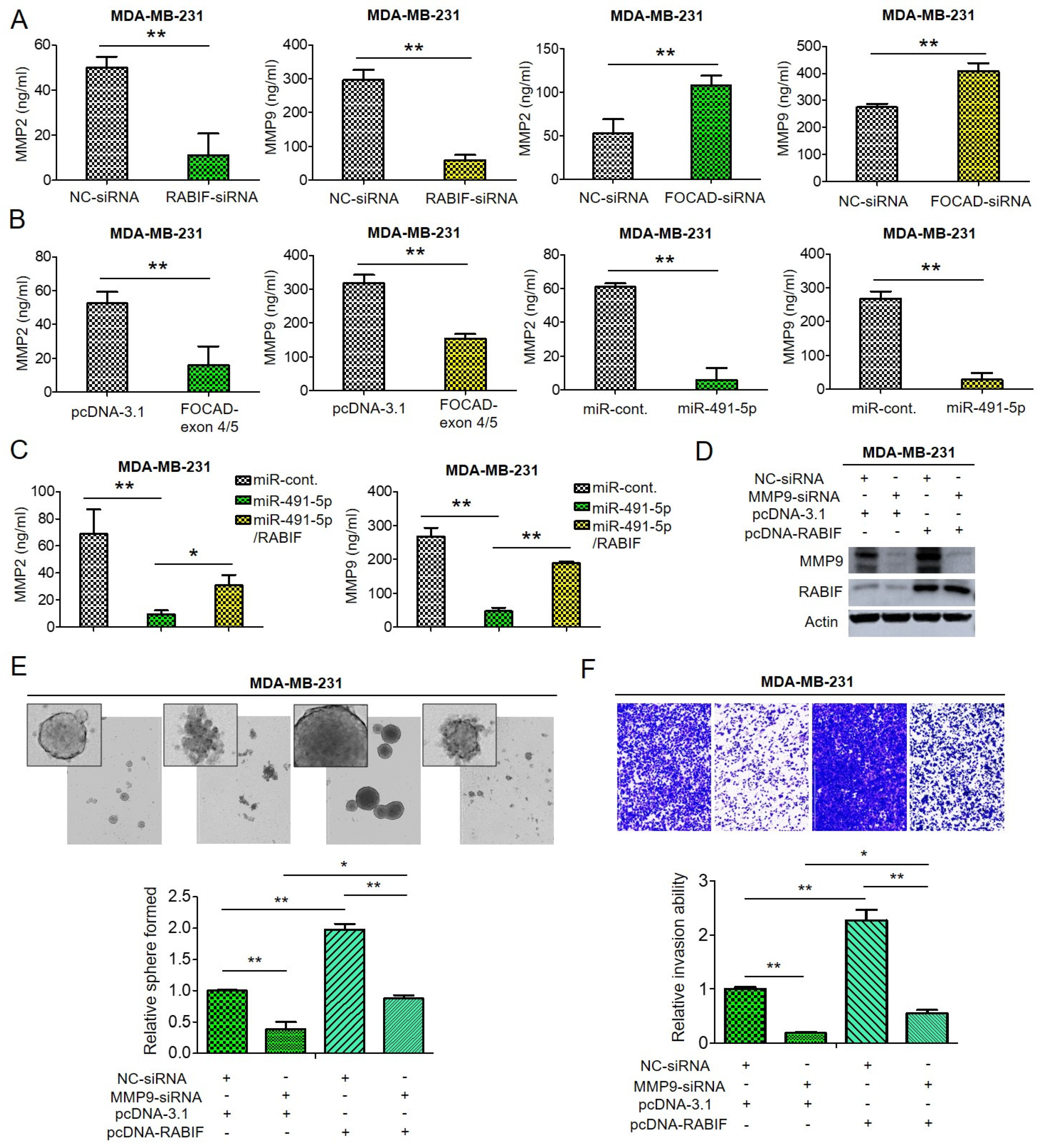
3.5. RABIF Correlates with Poor Clinical Outcomes and Promotes TNBC Cancer Stemness, Drug Resistance, Cell Invasion and Pulmonary Metastasis, Which Are Inhibited by MiR-491-5p
3.6. Matrix Metalloproteinase (MMP)-2 and MMP-9 Are Downstream Signaling Molecules of FOCAD/MiR-491-5p/RABIF Axis
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Siegel, R.L.; Miller, K.D.; Fuchs, H.E.; Jemal, A. Cancer Statistics, 2021. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2021, 71, 7–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, P.; Aggarwal, R. An overview of triple-negative breast cancer. Arch. Gynecol. Obs. 2016, 293, 247–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loh, H.-Y.; Norman, B.P.; Lai, K.-S.; Rahman, N.M.A.N.A.; Alitheen, N.B.M.; Osman, M.A. The Regulatory Role of MicroRNAs in Breast Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 4940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramezani, M.; Siami, S.; Rezaei, M.; Khazaei, S.; Sadeghi, M. An immunohistochemical study of HER2 expression in primary brain tumors. BioMedicine 2020, 10, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Ruijter, T.C.; Veeck, J.; de Hoon, J.P.J.; van Engeland, M.; Tjan-Heijnen, V.C. Characteristics of triple-negative breast cancer. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 2011, 137, 183–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Reilly, E.A.; Gubbins, L.; Sharma, S.; Tully, R.; Guang, M.H.Z.; Weiner-Gorzel, K.; McCaffrey, J.; Harrison, M.; Furlong, F.; Kell, M.; et al. The fate of chemoresistance in triple negative breast cancer (TNBC). BBA Clin. 2015, 3, 257–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krol, J.; Loedige, I.; Filipowicz, W. The widespread regulation of microRNA biogenesis, function and decay. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2010, 11, 597–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esquela-Kerscher, A.; Slack, F.J. Oncomirs—microRNAs with a role in cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2006, 6, 259–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hui, Z.; Yiling, C.; Wenting, Y.; XuQun, H.; ChuanYi, Z.; Hui, L. miR-491-5p functions as a tumor suppressor by targeting JMJD2B in ERα-positive breast cancer. FEBS Lett. 2015, 589, 812–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; Luo, C.; Yang, Y. MiR-491-5p, as a Tumor Suppressor, Prevents Migration and Invasion of Breast Cancer by Targeting ZNF-703 to Regulate AKT/mTOR Pathway. Cancer Manag. Res. 2021, 13, 403–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, G.Z.; Li, M.; Tan, X.; Shi, M.L.; Mou, K. MiR-491 suppresses migration and invasion via directly targeting TPX2 in breast cancer. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharm. Sci. 2019, 23, 9996–10004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wu, Z.; Li, Y.; Zheng, Z.; Yan, J.; Tian, S.; Han, L. Long Non-Coding RNA H19 Promotes Proliferation, Migration and Invasion and Inhibits Apoptosis of Breast Cancer Cells by Targeting miR-491-5p/ZNF703 Axis. Cancer Manag. Res. 2020, 12, 9247–9258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Q.; Zhai, Y.X.; Liu, H.Q.; Shi, Y.A.; Li, X.B. MicroRNA-491-5p suppresses cervical cancer cell growth by targeting hTERT. Oncol. Rep. 2015, 34, 979–986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Wang, Y.; Xie, Z.; Hu, H. JMJD2A facilitates growth and inhibits apoptosis of cervical cancer cells by downregulating tumor suppressor miR-491-5p. Mol. Med. Rep. 2019, 19, 2489–2496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denoyelle, C.; Lambert, B.; Meryet-Figuière, M.; Vigneron, N.; Brotin, E.; Lecerf, C.; Abeilard, E.; Giffard, F.; Louis, M.H.; Gauduchon, P.; et al. miR-491-5p-induced apoptosis in ovarian carcinoma depends on the direct inhibition of both BCL-XL and EGFR leading to BIM activation. Cell Death Dis. 2014, 5, e1445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, R.; Liu, Z.; Tong, D.; Yang, Y.; Guo, B.; Wang, X.; Zhao, L.; Huang, C. miR-491-5p, mediated by Foxi1, functions as a tumor suppressor by targeting Wnt3a/β-catenin signaling in the development of gastric cancer. Cell Death Dis. 2017, 8, e2714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, R.; Wang, Y.; Shi, W.-Y.; Liu, B.; Hou, S.-Q.; Liu, L. MicroRNA miR-491-5p targeting both TP53 and Bcl-XL induces cell apoptosis in SW1990 pancreatic cancer cells through mitochondria mediated pathway. Molecules 2012, 17, 14733–14747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Zhang, H.; Xie, F.; Tao, D.; Xiao, X.; Huang, C.; Wang, M.; Gu, C.; Zhang, X.; Jiang, G. Hsa_circ_0001361 promotes bladder cancer invasion and metastasis through miR-491-5p/MMP9 axis. Oncogene 2020, 39, 1696–1709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.-C.; Chan, S.-H.; Jang, T.-H.; Chang, J.-W.; Ko, Y.-C.; Yen, T.-C.; Chiang, S.-L.; Chiang, W.-F.; Shieh, T.-Y.; Liao, C.-T.; et al. miRNA-491-5p and GIT1 Serve as Modulators and Biomarkers for Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma Invasion and Metastasis. Cancer Res. 2014, 74, 751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, Z.; Ding, H.; He, E.; Chen, J.; Li, M. Up-regulation of microRNA-491-5p suppresses cell proliferation and promotes apoptosis by targeting FOXP4 in human osteosarcoma. Cell Prolif. 2017, 50, e12308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Touchot, N.; Chardin, P.; Tavitian, A. Four additional members of the ras gene superfamily isolated by an oligonucleotide strategy: Molecular cloning of YPT-related cDNAs from a rat brain library. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1987, 84, 8210–8214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burton, J.; Roberts, D.; Montaldi, M.; Novick, P.; Camilli, P.D. A mammalian guanine-nucleotide-releasing protein enhances function of yeast secretory protein Sec4. Nature 1993, 361, 464–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miyazaki, A.; Sasaki, T.; Araki, K.; Ueno, N.; Imazumi, K.; Nagano, F.; Takahashi, K.; Takai, Y. Comparison of kinetic properties between MSS4 and Rab3A GRF GDP/GTP exchange proteins. FEBS Lett. 1994, 350, 333–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller-Pillasch, F.; Zimmerhackl, F.; Lacher, U.; Schultz, N.; Hameister, H.; Varga, G.; Friess, H.; Büchler, M.; Adler, G.; Gress, T.M. Cloning of novel transcripts of the human guanine-nucleotide-exchange factor Mss4: In situ chromosomal mapping and expression in pancreatic cancer. Genomics 1997, 46, 389–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miolo, G.; Giuffrida, M.G.; Corona, G.; Capalbo, A.; Pivetta, B.; Tessitori, G.; Bernardini, L. A novel mosaic 1q32.1 microduplication identified through Chromosome Microarray Analysis: Narrowing the smallest critical region including KDM5B gene found associated with neurodevelopmetal disorders. Eur. J. Med. Genet. 2019, 62, 103558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gulbranson, D.R.; Davis, E.M.; Demmitt, B.A.; Ouyang, Y.; Ye, Y.; Yu, H.; Shen, J. RABIF/MSS4 is a Rab-stabilizing holdase chaperone required for GLUT4 exocytosis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, E8224–E8233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moissoglu, K.; Stueland, M.; Gasparski, A.N.; Wang, T.; Jenkins, L.M.; Hastings, M.L.; Mili, S. RNA localization and co-translational interactions control RAB13 GTPase function and cell migration. EMBO J. 2020, 39, e104958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walter, B.M.; Nordhoff, C.; Varga, G.; Goncharenko, G.; Schneider, S.W.; Ludwig, S.; Wixler, V. Mss4 protein is a regulator of stress response and apoptosis. Cell Death Dis. 2012, 3, e297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knoblauch, A.; Will, C.; Goncharenko, G.; Ludwig, S.; Wixler, V. The binding of Mss4 to alpha-integrin subunits regulates matrix metalloproteinase activation and fibronectin remodeling. FASEB J. 2007, 21, 497–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brockschmidt, A.; Trost, D.; Peterziel, H.; Zimmermann, K.; Ehrler, M.; Grassmann, H.; Pfenning, P.N.; Waha, A.; Wohlleber, D.; Brockschmidt, F.F.; et al. KIAA1797/FOCAD encodes a novel focal adhesion protein with tumour suppressor function in gliomas. Brain 2012, 135, 1027–1041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, H.; Zhang, G.; Zhang, L.; Wang, Q.; Li, H.; Han, Y.; Xie, L.; Yan, Z.; Li, Y.; An, Y.; et al. Comprehensive Review of Web Servers and Bioinformatics Tools for Cancer Prognosis Analysis. Front. Oncol. 2020, 10, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clara, J.A.; Monge, C.; Yang, Y.; Takebe, N. Targeting signalling pathways and the immune microenvironment of cancer stem cells—A clinical update. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2020, 17, 204–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saygin, C.; Matei, D.; Majeti, R.; Reizes, O.; Lathia, J.D. Targeting Cancer Stemness in the Clinic: From Hype to Hope. Cell Stem. Cell 2019, 24, 25–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Brien, C.A.; Kreso, A.; Jamieson, C.H.M. Cancer stem cells and self-renewal. Clin. Cancer Res. 2010, 16, 3113–3120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karamboulas, C.; Ailles, L. Developmental signaling pathways in cancer stem cells of solid tumors. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA) Gen. Subj. 2013, 1830, 2481–2495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Fan, D. The epithelial-mesenchymal transition and cancer stem cells: Functional and mechanistic links. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2015, 21, 1279–1291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.-S.; Jiang, J.; Liang, X.-H.; Tang, Y.-L. Links between cancer stem cells and epithelial-mesenchymal transition. OncoTargets Ther. 2015, 8, 2973–2980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeisberg, M.; Neilson, E.G. Biomarkers for epithelial-mesenchymal transitions. J. Clin. Investig. 2009, 119, 1429–1437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wahba, H.A.; El-Hadaad, H.A. Current approaches in treatment of triple-negative breast cancer. Cancer Biol. Med. 2015, 12, 106–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foulkes, W.D.; Smith, I.E.; Reis-Filho, J.S. Triple-negative breast cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2010, 363, 1938–1948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Conor, C.J.; Chen, T.; González, I.; Cao, D.; Peng, Y. Cancer stem cells in triple-negative breast cancer: A potential target and prognostic marker. Biomark. Med. 2018, 12, 813–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qi, Z.; Cai, S.; Cai, J.; Chen, L.; Yao, Y.; Chen, L.; Mao, Y. miR-491 regulates glioma cells proliferation by targeting TRIM28 in vitro. BMC Neurol. 2016, 16, 248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agarwal, V.; Bell, G.W.; Nam, J.W.; Bartel, D.P. Predicting effective microRNA target sites in mammalian mRNAs. Elife 2015, 4, e05005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Wang, X. miRDB: An online database for prediction of functional microRNA targets. Nucleic Acids Res. 2020, 48, D127–D131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tokar, T.; Pastrello, C.; Rossos, A.E.M.; Abovsky, M.; Hauschild, A.C.; Tsay, M.; Lu, R.; Jurisica, I. mirDIP 4.1-integrative database of human microRNA target predictions. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018, 46, D360–D370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laurin, M.; Huber, J.; Pelletier, A.; Houalla, T.; Park, M.; Fukui, Y.; Haibe-Kains, B.; Muller, W.J.; Côté, J.-F. Rac-specific guanine nucleotide exchange factor DOCK1 is a critical regulator of HER2-mediated breast cancer metastasis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 7434–7439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ojala, V.K.; Knittle, A.M.; Kirjalainen, P.; Merilahti, J.A.M. The guanine nucleotide exchange factor VAV3 participates in ERBB4-mediated cancer cell migration. J. Biol. Chem. 2020, 295, 11559–11571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, D.; Asiedu, M.; Wei, Q. Myosin-interacting guanine exchange factor (MyoGEF) regulates the invasion activity of MDA-MB-231 breast cancer cells through activation of RhoA and RhoC. Oncogene 2009, 28, 2219–2230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roskelley, C.D.; Bissell, M.J. Dynamic reciprocity revisited: A continuous, bidirectional flow of information between cells and the extracellular matrix regulates mammary epithelial cell function. Biochem. Cell Biol. 1995, 73, 391–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacob, A.; Jing, J.; Lee, J.; Schedin, P.; Gilbert, S.M.; Peden, A.A.; Junutula, J.R.; Prekeris, R. Rab40b regulates trafficking of MMP2 and MMP9 during invadopodia formation and invasion of breast cancer cells. J. Cell Sci. 2013, 126, 4647–4658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Ma, J.; Guo, Q.; Duan, F.; Tang, F.; Zheng, P.; Zhao, Z.; Lu, G. Overexpression of MMP-2 and MMP-9 in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Dis. Esophagus 2009, 22, 664–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dean, M.; Fojo, T.; Bates, S. Tumour stem cells and drug resistance. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2005, 5, 275–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garofalo, M.; Croce, C.M. Role of microRNAs in maintaining cancer stem cells. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2015, 81, 53–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimono, Y.; Mukohyama, J.; Nakamura, S.; Minami, H. MicroRNA Regulation of Human Breast Cancer Stem Cells. J. Clin. Med. 2016, 5, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimono, Y.; Zabala, M.; Cho, R.W.; Lobo, N.; Dalerba, P.; Qian, D.; Diehn, M.; Liu, H.; Panula, S.P.; Chiao, E.; et al. Downregulation of miRNA-200c links breast cancer stem cells with normal stem cells. Cell 2009, 138, 592–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Ye, J.; Yan, H.; Tang, Z.; Shen, J.; Zhang, J.; Yang, L. MiR-491 attenuates cancer stem cells-like properties of hepatocellular carcinoma by inhibition of GIT-1/NF-κB-mediated EMT. Tumour Biol. 2016, 37, 201–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Jiang, F.; Liu, Q.; Shen, J.; Wang, X.; Li, Z.; Zhang, J.; Lu, X. Inhibition of the cancer stem cells-like properties by arsenic trioxide, involved in the attenuation of endogenous transforming growth factor beta signal. Toxicol. Sci. 2015, 143, 156–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Liu, Y.; Granberg, K.J.; Wang, Q.; Moore, L.M.; Ji, P.; Gumin, J.; Sulman, E.P.; Calin, G.A.; Haapasalo, H.; et al. Two mature products of MIR-491 coordinate to suppress key cancer hallmarks in glioblastoma. Oncogene 2015, 34, 1619–1628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, T.; Wang, L.N.; Li, W.; Zuo, Q.F.; Li, M.M.; Zou, Q.M.; Xiao, B. Downregulation of miR-491-5p promotes gastric cancer metastasis by regulating SNAIL and FGFR4. Cancer Sci. 2018, 109, 1393–1403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krepischi, A.C.V.; Achatz, M.I.W.; Santos, E.M.M.; Costa, S.S.; Lisboa, B.C.G.; Brentani, H.; Santos, T.M.; Gonçalves, A.; Nóbrega, A.F.; Pearson, P.L.; et al. Germline DNA copy number variation in familial and early-onset breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res. 2012, 14, R24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venkatachalam, R.; Verwiel, E.T.; Kamping, E.J.; Hoenselaar, E.; Görgens, H.; Schackert, H.K.; van Krieken, J.H.; Ligtenberg, M.J.; Hoogerbrugge, N.; van Kessel, A.G.; et al. Identification of candidate predisposing copy number variants in familial and early-onset colorectal cancer patients. Int. J. Cancer 2011, 129, 1635–1642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brand, F.; Förster, A.; Christians, A.; Bucher, M.; Thomé, C.M.; Raab, M.S.; Westphal, M.; Pietsch, T.; von Deimling, A.; Reifenberger, G.; et al. FOCAD loss impacts microtubule assembly, G2/M progression and patient survival in astrocytic gliomas. Acta Neuropathol. 2020, 139, 175–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, W.; Zhang, J.; Huang, T.; Zhou, Y.; Wong, C.C.; Chan, R.C.K.; Dong, Y.; Wu, F.; Zhang, B.; Wu, W.K.K.; et al. NOTCH3, a crucial target of miR-491-5p/miR-875-5p, promotes gastric carcinogenesis by upregulating PHLDB2 expression and activating Akt pathway. Oncogene 2021, 40, 1578–1594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Świtnicki, M.P.; Juul, M.; Madsen, T.; Sørensen, K.D.; Pedersen, J.S. PINCAGE: Probabilistic integration of cancer genomics data for perturbed gene identification and sample classification. Bioinformatics 2016, 32, 1353–1365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amson, R.; Pece, S.; Marine, J.C.; Di Fiore, P.P.; Telerman, A. TPT1/TCTP-regulated pathways in phenotypic reprogramming. Trends Cell Biol. 2013, 23, 37–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Huang, W.-C.; Chi, H.-C.; Tung, S.-L.; Chen, P.-M.; Shih, Y.-C.; Huang, Y.-C.; Chu, P.-Y. Identification of the Novel Tumor Suppressor Role of FOCAD/miR-491-5p to Inhibit Cancer Stemness, Drug Resistance and Metastasis via Regulating RABIF/MMP Signaling in Triple Negative Breast Cancer. Cells 2021, 10, 2524. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells10102524
Huang W-C, Chi H-C, Tung S-L, Chen P-M, Shih Y-C, Huang Y-C, Chu P-Y. Identification of the Novel Tumor Suppressor Role of FOCAD/miR-491-5p to Inhibit Cancer Stemness, Drug Resistance and Metastasis via Regulating RABIF/MMP Signaling in Triple Negative Breast Cancer. Cells. 2021; 10(10):2524. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells10102524
Chicago/Turabian StyleHuang, Wei-Chieh, Hsiang-Cheng Chi, Shiao-Lin Tung, Po-Ming Chen, Ya-Chi Shih, Yi-Ching Huang, and Pei-Yi Chu. 2021. "Identification of the Novel Tumor Suppressor Role of FOCAD/miR-491-5p to Inhibit Cancer Stemness, Drug Resistance and Metastasis via Regulating RABIF/MMP Signaling in Triple Negative Breast Cancer" Cells 10, no. 10: 2524. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells10102524
APA StyleHuang, W.-C., Chi, H.-C., Tung, S.-L., Chen, P.-M., Shih, Y.-C., Huang, Y.-C., & Chu, P.-Y. (2021). Identification of the Novel Tumor Suppressor Role of FOCAD/miR-491-5p to Inhibit Cancer Stemness, Drug Resistance and Metastasis via Regulating RABIF/MMP Signaling in Triple Negative Breast Cancer. Cells, 10(10), 2524. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells10102524





