Nucleofection of Adipose Mesenchymal Stem/Stromal Cells: Improved Transfection Efficiency for GMP Grade Applications
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cell Isolation, Expansion, and Characterization
2.2. Nucleofection
2.3. Calculations:
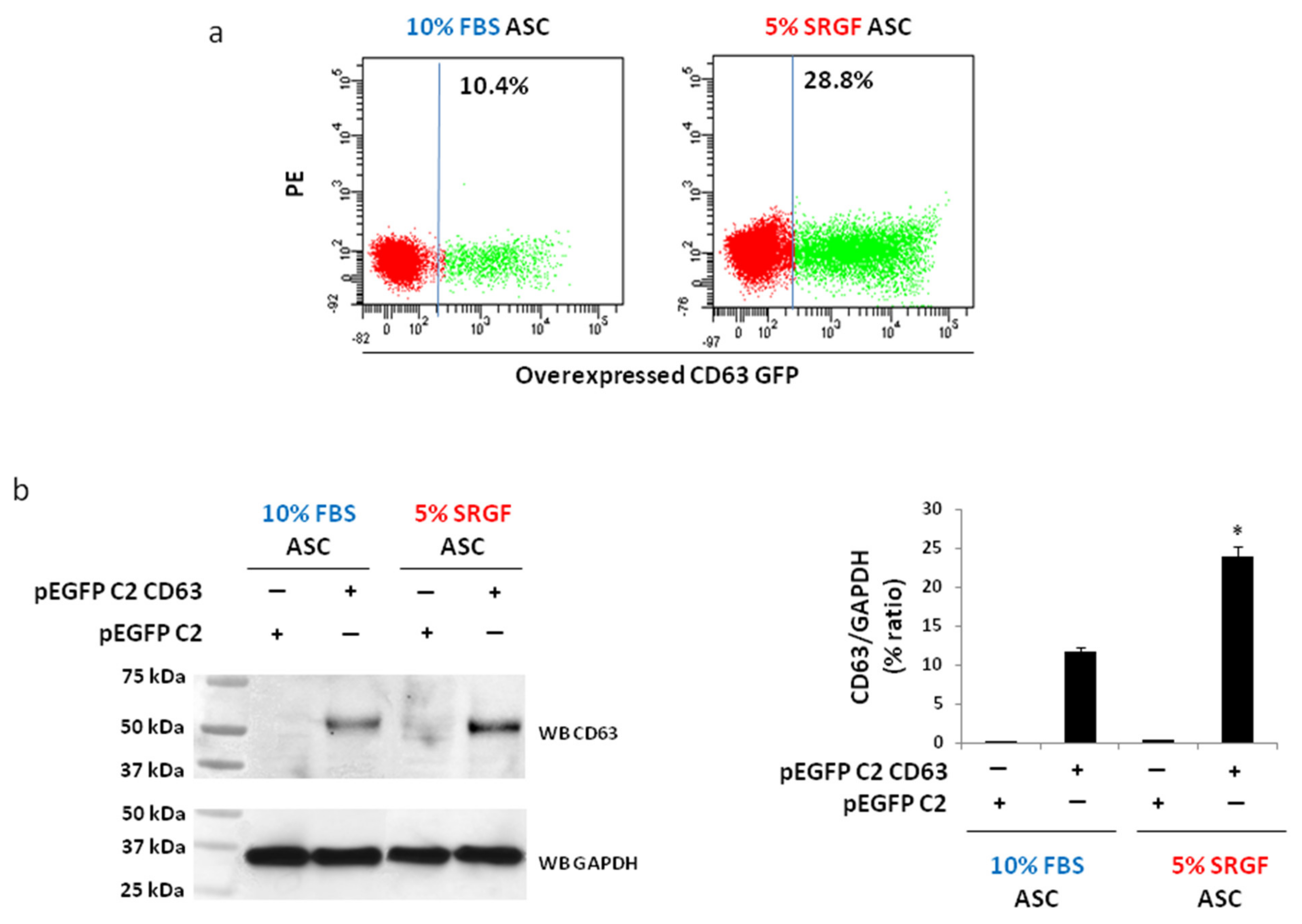
2.4. Overexpression of CD63
2.5. Intracellular Vesicle Labelling
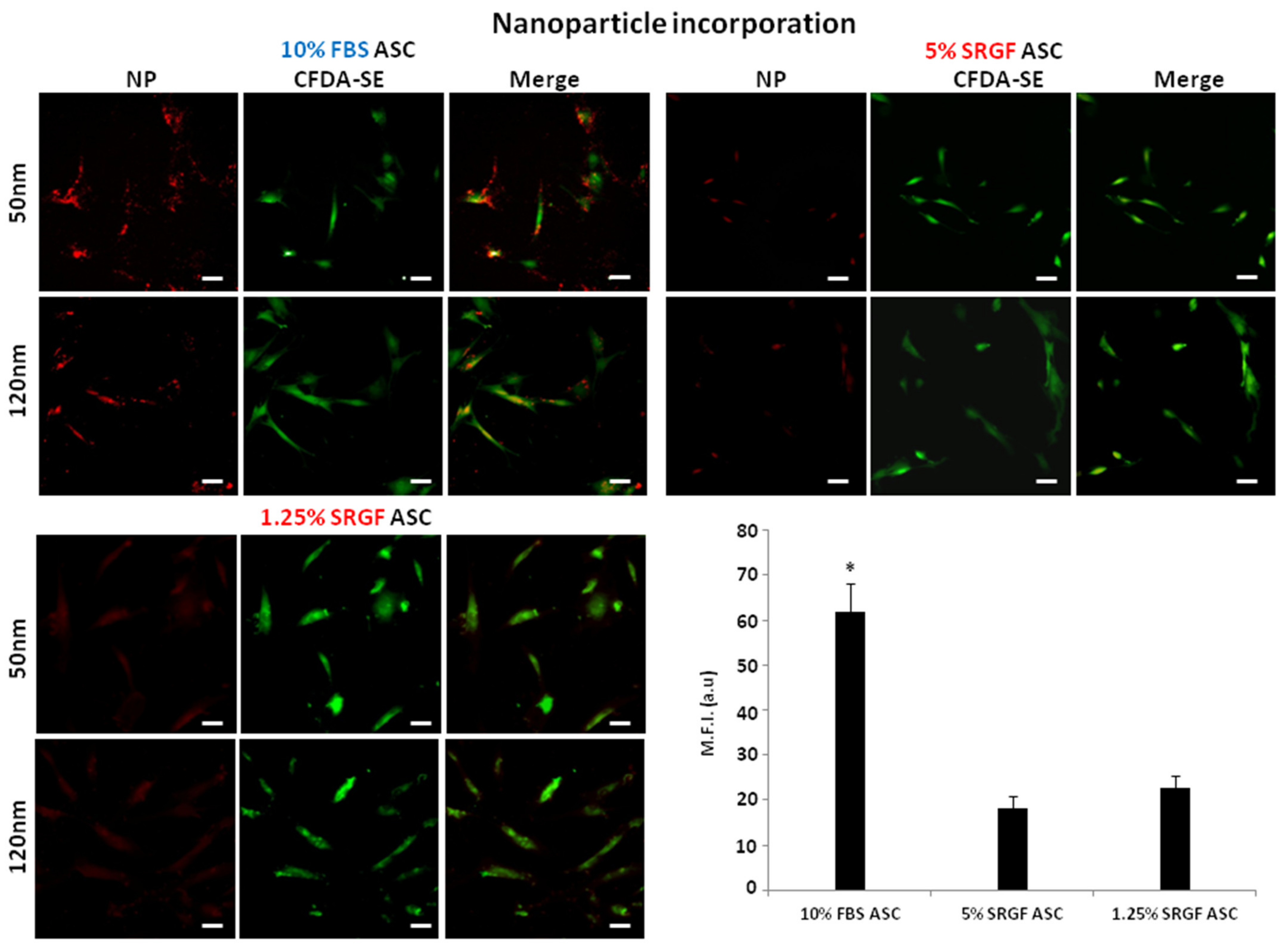
2.6. Phagocytosis
2.7. Supplementation of Expanded ASC
2.8. ASC Membrane Composition
2.9. Labelling and Quantification of Lipid Rafts on Cell Membrane
2.10. Intracellular Actin Labelling
2.11. Total and Membrane Protein Analysis
2.12. Statistics
3. Results
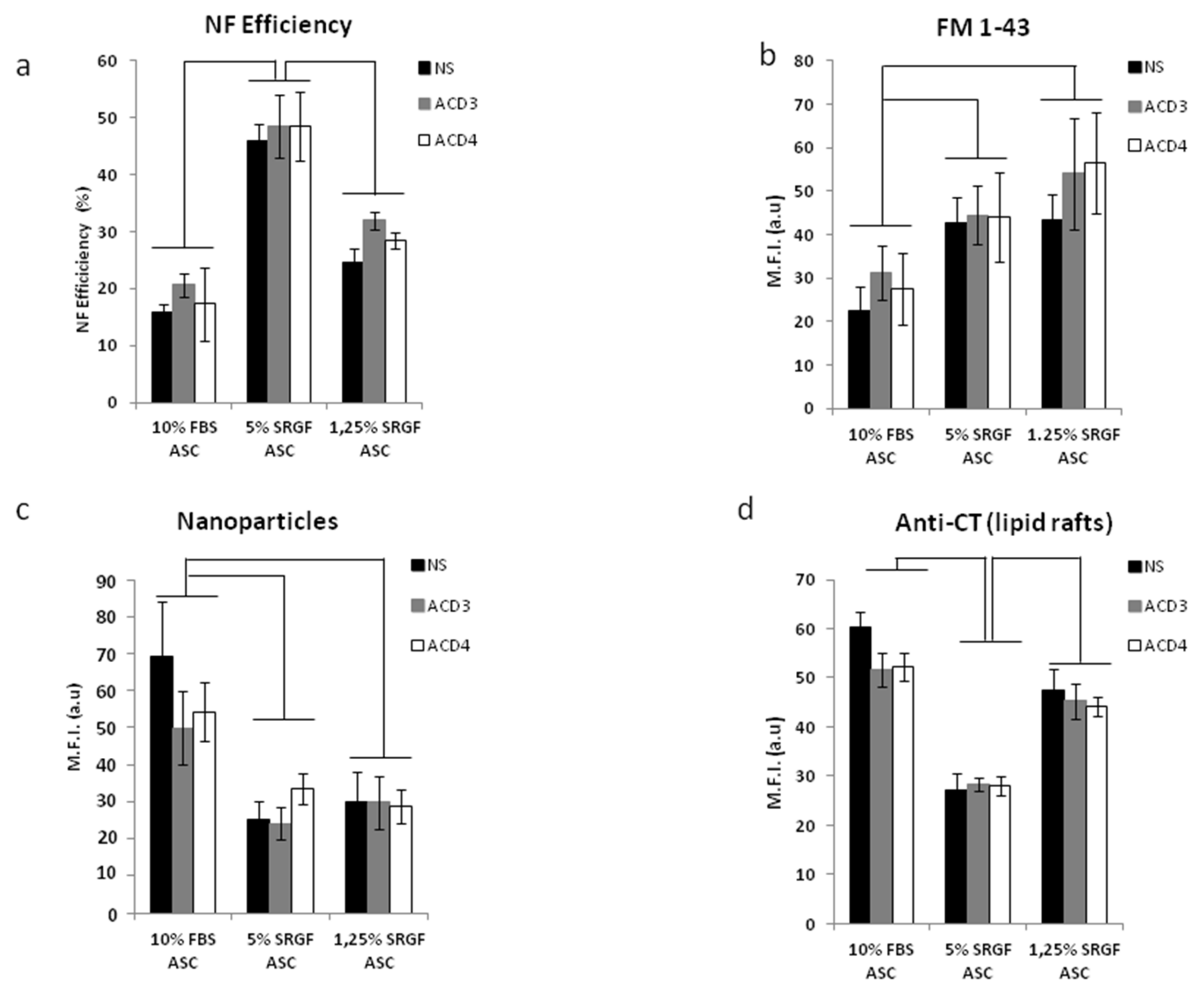
3.1. SRGF Expanded ASC Can Be Efficiently Nucleoporated by the C-17 Program
3.2. Method Validation: Overexpression of CD63 Gene
3.3. SRGF Impact on ASC Endocytosis and Phagocyotis Properties
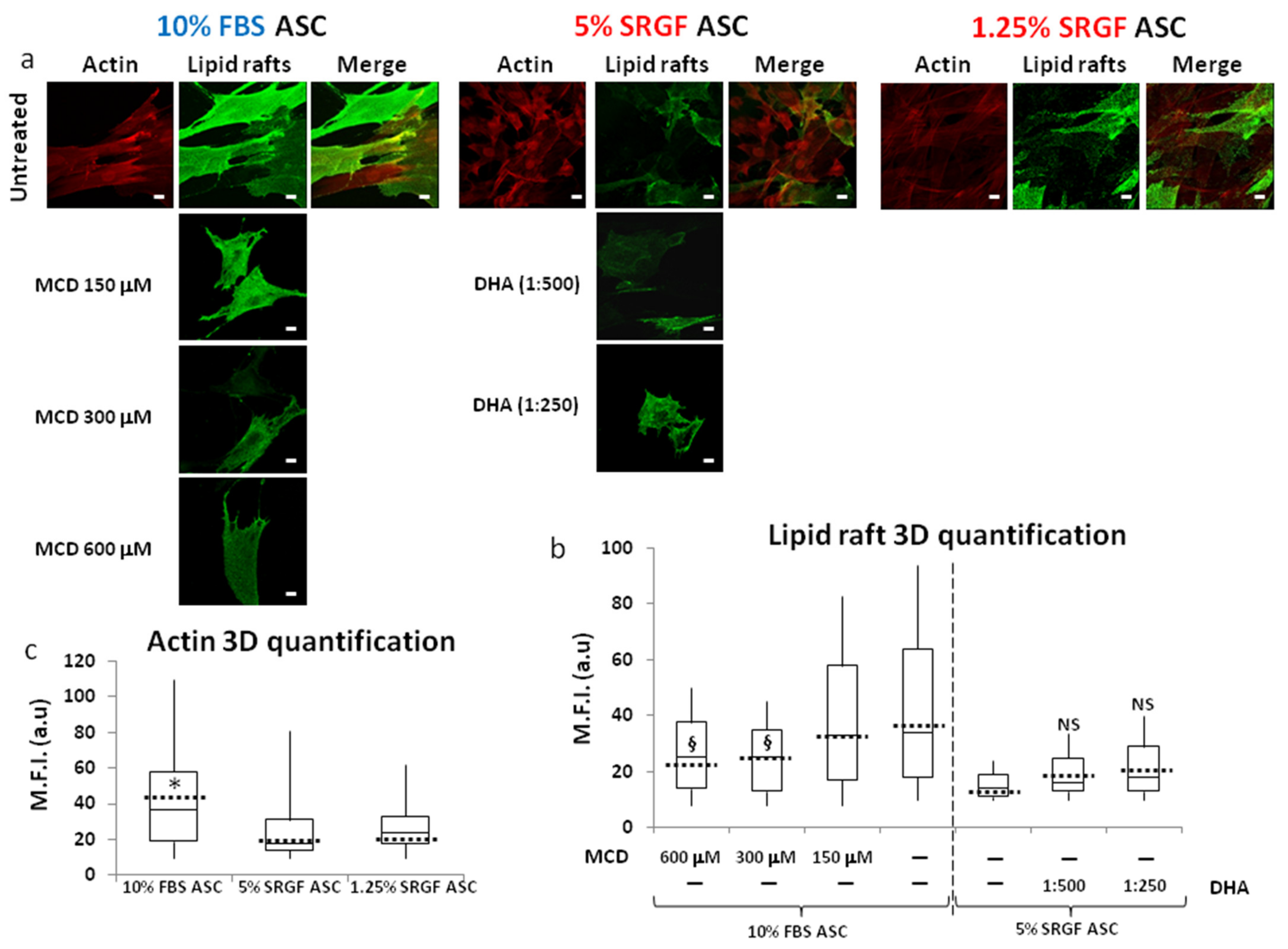
3.4. SRGF Impact on Membrane Fatty Acid Composition and on Lipid Raft Formation
3.5. n-3 or n-6 Fatty Acid Supplementation and MCD Addition at Appropriate Concentrations
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
6. Patents
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Friedenstein, A.J.; Chailakhjan, R.K.; Lalykina, K.S. The Development of Fibroblast Colonies in Monolayer Cultures of Guinea-Pig Bone Marrow and Spleen Cells. Cell Tissue Kinet 1970, 3, 393–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zuk, P.A.; Zhu, M.; Ashjian, P.; De Ugarte, D.A.; Huang, J.I.; Mizuno, H.; Alfonso, Z.C.; Fraser, J.K.; Benhaim, P.; Hedrick, M.H. Human Adipose Tissue Is a Source of Multipotent Stem Cells. Mol. Biol. Cell 2002, 13, 4279–4295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Samsonraj, R.M.; Raghunath, M.; Nurcombe, V.; Hui, J.H.; van Wijnen, A.J.; Cool, S.M. Concise Review: Multifaceted Characterization of Human Mesenchymal Stem Cells for Use in Regenerative Medicine. Stem Cells Transl. Med. 2017, 6, 2173–2185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zuk, P.A.; Zhu, M.; Mizuno, H.; Huang, J.; Futrell, J.W.; Katz, A.J.; Benhaim, P.; Lorenz, H.P.; Hedrick, M.H. Multilineage Cells from Human Adipose Tissue: Implications for Cell-Based Therapies. Tissue Eng. 2001, 7, 211–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ra, J.C.; Shin, I.S.; Kim, S.H.; Kang, S.K.; Kang, B.C.; Lee, H.Y.; Kim, Y.J.; Jo, J.Y.; Yoon, E.J.; Choi, H.J.; et al. Safety of Intravenous Infusion of Human Adipose Tissue-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells in Animals and Humans. Stem Cells Dev. 2011, 20, 1297–1308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, M.; Mei, S.H.J.; Wolfe, D.; Champagne, J.; Fergusson, D.; Stewart, D.J.; Sullivan, K.J.; Doxtator, E.; Lalu, M.; English, S.W.; et al. Cell Therapy with Intravascular Administration of Mesenchymal Stromal Cells Continues to Appear Safe: An Updated Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. EClinicalMedicine 2020, 19, 100249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mendicino, M.; Bailey, A.M.; Wonnacott, K.; Puri, R.K.; Bauer, S.R. MSC-Based Product Characterization for Clinical Trials: An FDA Perspective. Cell Stem Cell 2014, 14, 141–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Expert Committee of European Commission. Good Manufacturing Practice—Volume 4. In The Rules Governing Medicinal Products in the European Union; Expert Committee of European Commission: Brussels, Belgium, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Committeee for Medicinal Products for Human Use. Note for Guidance on the Use of Bovine Serum in the Manufacture of Human Biological Products; European Medicines Agency: Amsterdam, Netherlands, 2012; Volume 1, pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Durante, C.; Agostini, F.; Abbruzzese, L.; Toffola, R.T.; Zanolin, S.; Suine, C.; Mazzucato, M. Growth Factor Release from Platelet Concentrates: Analytic Quantification and Characterization for Clinical Applications. Vox Sang. 2013, 105, 129–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agostini, F.; Rossi, F.M.; Aldinucci, D.; Battiston, M.; Lombardi, E.; Zanolin, S.; Massarut, S.; Parodi, P.C.; Da Ponte, A.; Tessitori, G.; et al. Improved GMP Compliant Approach to Manipulate Lipoaspirates, to Cryopreserve Stromal Vascular Fraction, and to Expand Adipose Stem Cells in Xeno-Free Media. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2018, 9, 130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Agostini, F.; Vicinanza, C.; Di Cintio, F.; Battiston, M.; Lombardi, E.; Golinelli, G.; Durante, C.; Toffoli, G.; Dominici, M.; Mazzucato, M. Adipose Mesenchymal Stromal/Stem Cells Expanded by a GMP Compatible Protocol Displayed Improved Adhesion on Cancer Cells in Flow Conditions. Ann. Transl. Med. 2020, 8, 533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oggu, G.S.; Sasikumar, S.; Reddy, N.; Ella, K.K.R.; Rao, C.M.; Bokara, K.K. Gene Delivery Approaches for Mesenchymal Stem Cell Therapy: Strategies to Increase Efficiency and Specificity. Stem Cell Rev. 2017, 13, 725–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rothe, M.; Modlich, U.; Schambach, A. Biosafety Challenges for Use of Lentiviral Vectors in Gene Therapy. Curr. Gene Ther. 2013, 13, 453–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Halim, N.S.S.A.; Fakiruddin, K.S.; Ali, S.A.; Yahaya, B.H. A Comparative Study of Non-Viral Gene Delivery Techniques to Human Adipose-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cell. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2014, 15, 15044–15060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Helledie, T.; Nurcombe, V.; Cool, S.M. A Simple and Reliable Electroporation Method for Human Bone Marrow Mesenchymal Stem Cells. Stem Cells Dev. 2008, 17, 837–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zaragosi, L.-E.; Billon, N.; Ailhaud, G.; Dani, C. Nucleofection Is a Valuable Transfection Method for Transient and Stable Transgene Expression in Adipose Tissue-Derived Stem Cells. Stem Cells 2007, 25, 790–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murovec, T.; Sweeney, D.C.; Latouche, E.; Davalos, R.V.; Brosseau, C. Modeling of Transmembrane Potential in Realistic Multicellular Structures before Electroporation. Biophys. J. 2016, 111, 2286–2295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Napotnik, T.B.; Miklavčič, D. In Vitro Electroporation Detection Methods—An Overview. Bioelectrochemistry 2018, 120, 166–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reigada, R. Electroporation of Heterogeneous Lipid Membranes. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2014, 1838, 814–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kanduser, M.; Sentjurc, M.; Miklavcic, D. Cell Membrane Fluidity Related to Electroporation and Resealing. Eur. Biophys. J. 2006, 35, 196–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanduser, M.; Sentjurc, M.; Miklavcic, D. The Temperature Effect during Pulse Application on Cell Membrane Fluidity and Permeabilization. Bioelectrochemistry 2008, 74, 52–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maulucci, G.; Cohen, O.; Daniel, B.; Sansone, A.; Petropoulou, P.I.; Filou, S.; Spyridonidis, A.; Pani, G.; De Spirito, M.; Chatgilialoglu, C.; et al. Fatty Acid-Related Modulations of Membrane Fluidity in Cells: Detection and Implications. Free Radic. Res. 2016, 50, S40–S50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Simons, K.; Ikonen, E. Functional Rafts in Cell Membranes. Nature 1997, 387, 569–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levental, K.R.; Surma, M.A.; Skinkle, A.D.; Lorent, J.H.; Zhou, Y.; Klose, C.; Chang, J.T.; Hancock, J.F.; Levental, I. ω-3 Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids Direct Differentiation of the Membrane Phenotype in Mesenchymal Stem Cells to Potentiate Osteogenesis. Sci. Adv. 2017, 3, 1193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tisza, M.J.; Zhao, W.; Fuentes, J.S.R.; Prijic, S.; Chen, X.; Levental, I.; Chang, J.T. Motility and Stem Cell Properties Induced by the Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition Require Destabilization of Lipid Rafts. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 51553–51568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ben Gedalya, T.; Loeb, V.; Israeli, E.; Altschuler, Y.; Selkoe, D.J.; Sharon, R. α–Synuclein and PolyUnsaturated Fatty Acids Promote Clathrin Mediated Endocytosis and Synaptic Vesicle Recycling. Traffic 2009, 10, 218–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fuhrmann, H.; Miles, E.A.; West, A.L.; Calder, P.C. Membrane Fatty Acids, Oxidative Burst and Phagocytosis after Enrichment of P388D1 Monocyte/Macrophages with Essential 18-Carbon Fatty Acids. Ann. Nutr. Metab. 2007, 51, 155–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kasper, J.; Hermanns, M.; Bantz, C.; Koshkina, O.; Lang, T.; Maskos, M.; Pohl, C.; Unger, R.E.; Kirkpatrick, C.J. Interactions of Silica Nanoparticles with Lung Epithelial Cells and the Association to Flotillins. Arch. Toxicol. 2013, 87, 1053–1065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Vercauteren, D.; Piest, M.; van der Aa, L.J.; Al Soraj, M.; Jones, A.T.; Engbersen, J.F.J.; De Smedt, S.C.; Braeckmans, K. Flotillin-Dependent Endocytosis and a Phagocytosis-like Mechanism for Cellular Internalization of Disulfide-Based Poly(Amido Amine)/DNA Polyplexes. Biomaterials 2011, 32, 3072–3084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chatgilialoglu, A.; Rossi, M.; Alviano, F.; Poggi, P.; Zannini, C.; Marchionni, C.; Ricci, F.; Tazzari, P.L.; Taglioli, V.; Calder, P.C.; et al. Restored in Vivo-like Membrane Lipidomics Positively Influence In Vitro Features of Cultured Mesenchymal Stromal/Stem Cells Derived from Human Placenta. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2017, 8, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yaqoob, P.; Newsholme, E.A.; Calder, P.C. Influence of Cell Culture Conditions on Diet-Induced Changes in Lymphocyte Fatty Acid Composition. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1995, 1255, 333–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dominici, M.; Le Blank, K.; Mueller, I.; Slaper-Cortenbach, I.; Marini, F.; Krause, D.; Deans, R.; Keating, A.; Prockop, D.; Horwitz, E. Minimal Criteria for Defining Multipotent Mesenchymal Stromal Cells. The International Society for Cellular Therapy Position Statement. Cytotherapy 2006, 8, 315–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazzucco, S.; Agostini, F.; Biolo, G. Inactivity-Mediated Insulin Resistance Is Associated with Upregulated pro-Inflammatory Fatty Acids in Human Cell Membranes. Clin. Nutr. 2010, 29, 386–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zidovetzki, R.; Levitan, I. Use of Cyclodextrins to Manipulate Plasma Membrane Cholesterol Content: Evidence, Misconceptions and Control Strategies. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2007, 1768, 1311–1324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Noack, A.; Noack, S.; Hoffmann, A.; Maalouf, K.; Buettner, M.; Couraud, P.-O.; Romero, I.A.; Weksler, B.; Alms, D.; Römermann, K.; et al. Drug-Induced Trafficking of p-Glycoprotein in Human Brain Capillary Endothelial Cells as Demonstrated by Exposure to Mitomycin, C. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e88154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Si, Z.; Wang, X.; Sun, C.; Kang, Y.; Xu, J.; Wang, X.; Hui, Y. Adipose-Derived Stem Cells: Sources, Potency, and Implications for Regenerative Therapies. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2019, 114, 108765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grisendi, G.; Bussolari, R.; Cafarelli, L.; Petak, I.; Rasini, V.; Veronesi, E.; De Santis, G.; Spano, C.; Tagliazzucchi, M.; Barti-Juhasz, H.; et al. Adipose-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells as Stable Source of Tumor Necrosis Factor-Related Apoptosis-Inducing Ligand Delivery for Cancer Therapy. Cancer Res. 2010, 70, 3718–3729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Park, J.S.; Suryaprakash, S.; Lao, Y.-H.; Leong, K.W. Engineering Mesenchymal Stem Cells for Regenerative Medicine and Drug Delivery. Methods 2015, 84, 3–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhuang, W.-Z.; Lin, Y.-H.; Su, L.-J.; Wu, M.-S.; Jeng, H.-Y.; Chang, H.-C.; Huang, Y.-H.; Ling, T.-Y. Mesenchymal Stem/Stromal Cell-Based Therapy: Mechanism, Systemic Safety and Biodistribution for Precision Clinical Applications. J. Biomed. Sci. 2021, 28, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haleem-Smith, H.; Derfoul, A.; Okafor, C.; Tuli, R.; Olsen, D.; Hall, D.J.; Tuan, R.S. Optimization of High-Efficiency Transfection of Adult Human Mesenchymal Stem Cells in Vitro. Mol. Biotechnol. 2005, 30, 9–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magnani, C.F.; Mezzanotte, C.; Cappuzzello, C.; Bardini, M.; Tettamanti, S.; Fazio, G.; Cooper, L.J.N.; Dastoli, G.; Cazzaniga, G.; Biondi, A.; et al. Preclinical Efficacy and Safety of CD19CAR Cytokine-Induced Killer Cells Transfected with Sleeping Beauty Transposon for the Treatment of Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. Hum. Gene Ther. 2018, 29, 602–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olmedillas López, S.; Garcia-Arranz, M.; Garcia-Olmo, D.; Liras, A. Preliminary Study on Non-Viral Transfection of F9 (Factor IX) Gene by Nucleofection in Human Adipose-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells. PeerJ 2016, 4, e1907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Borghese, C.; Agostini, F.; Durante, C.; Colombatti, A.; Mazzucato, M.; Aldinucci, D. Clinical-Grade Quality Platelet-Rich Plasma Releasate (PRP-R/SRGF) from CaCl2 -Activated Platelet Concentrates Promoted Expansion of Mesenchymal Stromal Cells. Vox Sang. 2016, 111, 197–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Von der Haar, K.; Jonczyk, R.; Lavrentieva, A.; Weyand, B.; Vogt, P.; Jochums, A.; Stahl, F.; Scheper, T.; Blume, C.A. Electroporation: A Sustainable and Cell Biology Preserving Cell Labeling Method for Adipogenous Mesenchymal Stem Cells. BioRes. Open Access 2019, 8, 32–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Flanagan, M.; Gimble, J.M.; Yu, G.; Wu, X.; Xia, X.; Hu, J.; Yao, S.; Li, S. Competitive Electroporation Formulation for Cell Therapy. Cancer Gene Ther. 2011, 18, 579–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hurwitz, S.N.; Cheerathodi, M.R.; Nkosi, D.; York, S.B.; Meckes, D.G. Tetraspanin CD63 Bridges Autophagic and Endosomal Processes to Regulate Exosomal Secretion and Intracellular Signaling of Epstein–Barr Virus LMP1. J. Virol. 2018, 12, e01969-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Winkel, A.; Jaimes, Y.; Melzer, C.; Dillschneider, P.; Hartwig, H.; Stiesch, M.; von der Ohe, J.; Strauss, S.; Vogt, P.M.; Hamm, A.; et al. Cell Culture Media Notably Influence Properties of Human Mesenchymal Stroma/Stem-like Cells from Different Tissues. Cytotherapy 2020, 22, 653–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Sayed, A.; Harashima, H. Endocytosis of Gene Delivery Vectors: From Clathrin-Dependent to Lipid Raft-Mediated Endocytosis. Mol. Ther. 2013, 21, 1118–1130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Madeira, C.; Mendes, R.D.; Ribeiro, S.C.; Boura, J.S.; Aires-Barros, M.R.; da Silva, C.L.; Cabral, J.M.S. Nonviral Gene Delivery to Mesenchymal Stem Cells Using Cationic Liposomes for Gene and Cell Therapy. J. Biomed. Biotechnol. 2010, 2010, 735349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, G.; Bao, P.; Zhang, Y.; Deng, A.; Chen, N.; Wen, T. Enhancing Electro-Transformation Competency of Recalcitrant Bacillus Amyloliquefaciens by Combining Cell-Wall Weakening and Cell-Membrane Fluidity Disturbing. Anal. Biochem. 2011, 409, 130–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibarguren, M.; López, D.J.; Escribá, P.V. The Effect of Natural and Synthetic Fatty Acids on Membrane Structure, Microdomain Organization, Cellular Functions and Human Health. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2014, 1838, 1518–1528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gunn, P.J.; Green, C.J.; Pramfalk, C.; Hodson, L. In Vitro Cellular Models of Human Hepatic Fatty Acid Metabolism: Differences between Huh7 and HepG2 Cell Lines in Human and Fetal Bovine Culturing Serum. Physiol. Rep. 2017, 5, e13532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patterson, E.; Wall, R.; Fitzgerald, G.F.; Ross, R.P.; Stanton, C. Health Implications of High Dietary Omega-6 Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids. J. Nutr. Metab. 2012, 2012, 539426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmitz, G.; Ecker, J. The Opposing Effects of N-3 and n-6 Fatty Acids. Prog. Lipid Res. 2008, 47, 147–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calder, P.C. N-3 PUFA and Inflammation: From Membrane to Nucleus and from Bench to Bedside. Proc. Nutr. Soc. 2020, 79, 404–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, Y.; Li, F.; Li, L.; Fan, J.; Sun, X.; Yin, Y. N-6:N-3 PUFA Ratio Is Involved in Regulating Lipid Metabolism and Inflammation in Pigs. Br. J. Nutr. 2014, 111, 445–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zaloga, G.P.; Marik, P. Lipid Modulation and Systemic Inflammation. Crit. Care Clin. 2001, 17, 201–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, J.; Li, K.; Wang, F.; Yang, B.; Fu, Y.; Zheng, J.; Li, D. Effect of Marine-Derived n-3 Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids on Major Eicosanoids: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis from 18 Randomized Controlled Trials. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0147351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kew, S.; Banerjee, T.; Minihane, A.; Finnegann, Y.; Williams, C.; Calder, P. Relation between the Fatty Acid Composition of Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells and Measures of Immune Cell Function in Healthy, Free-Living Subjects Aged 25–72 y. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2003, 77, 1278–1286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sezgin, E.; Levental, I.; Mayor, S.; Eggeling, C. The Mystery of Membrane Organization: Composition, Regulation and Roles of Lipid Rafts. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2017, 18, 361–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Grosse, S.; Aron, Y.; Thévenot, G.; François, D.; Monsigny, M.; Fajac, I. Potocytosis and Cellular Exit of Complexes as Cellular Pathways for Gene Delivery by Polycations. J. Gene Med. 2005, 7, 1275–1286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Halloran, T.J.; Anderson, R.G. Clathrin Heavy Chain Is Required for Pinocytosis, the Presence of Large Vacuoles, and Development in Dictyostelium. J. Cell Biol. 1992, 118, 1371–1377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holguin, S.Y.; Anderson, C.F.; Thadhani, N.N.; Prausnitz, M.R. Role of Cytoskeletal Mechanics and Cell Membrane Fluidity in the Intracellular Delivery of Molecules Mediated by Laser-Activated Carbon Nanoparticles. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2017, 114, 2390–2399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| 10% FBS ASC | 5% SRGF ASC | 1.25% SRGF ASC | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NS | ACD3 | ACD4 | NS | ACD3 | ACD4 | NS | ACD3 | ACD4 | |
| SFA | 44.7 ± 0.7 | 68.6 ± 7.3 a | 66.6 ± 4.8 a | 48.6 ± 1.6 | 60.4 ± 4.2 a | 63.4 ± 4.6 a | 72.4 ± 2.7 b.c | 65.0 ± 3.2 | 68.1 ± 1.5 |
| MUFA | 26.6 ± 1.0 | 9.4 ± 3.1 a | 13.3 ± 3.3 a | 24.4 ± 1.5 | 9.8 ± 1.6 a | 11.7 ± 2.7 a | 12.8 ± 1.6 b.c | 6.8 ± 0.7 a | 7.6 ± 0.1 a |
| n-3 PUFA | 7.9 ± 0.3 | 2.1 ± 0.7 a | 10.1 ± 2.1 a | 1.5 ± 0.1 b | 0.9 ± 0.3 | 14.7 ± 0.9 a | 1.4 ± 0.3 b | 1.1 ± 0.8 | 16.4 ± 0.7 a |
| n-6 PUFA | 15.3 ± 0.7 | 20.0 ± 4.9 a | 10.0 ± 1.4 a | 22.3 ± 1.3 b.d | 29.0 ± 4.1 a | 10.2 ± 2.1 a | 13.4 ± 1.0 | 27.1 ± 5.0 a | 7.9 ± 1.2 a |
| SFA/UFA | 0.9 ± 0.2 | 2.2 ± 0.6 a | 2.0 ± 0.4 a | 1.0 ± 0.8 | 1.9 ± 0.7 a | 2.1 ± 0.9 a | 2.6 ± 0.3 b | 1.9 ± 0.3 a | 2.1 ± 0.4 a |
| n-6/n-3 | 1.9 ± 0.2 | 9.5 ± 2.1 a | 1.0 ± 0.1 | 14.3 ± 3.5 b | 33.1 ± 7.1 a | 0.7 ± 0.1 a | 9.7 ± 3.0 b | 24.0 ± 6.1 a | 0.5 ± 0.3 a |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Agostini, F.; Vicinanza, C.; Biolo, G.; Spessotto, P.; Da Ros, F.; Lombardi, E.; Durante, C.; Mazzucato, M. Nucleofection of Adipose Mesenchymal Stem/Stromal Cells: Improved Transfection Efficiency for GMP Grade Applications. Cells 2021, 10, 3412. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells10123412
Agostini F, Vicinanza C, Biolo G, Spessotto P, Da Ros F, Lombardi E, Durante C, Mazzucato M. Nucleofection of Adipose Mesenchymal Stem/Stromal Cells: Improved Transfection Efficiency for GMP Grade Applications. Cells. 2021; 10(12):3412. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells10123412
Chicago/Turabian StyleAgostini, Francesco, Carla Vicinanza, Gianni Biolo, Paola Spessotto, Francesco Da Ros, Elisabetta Lombardi, Cristina Durante, and Mario Mazzucato. 2021. "Nucleofection of Adipose Mesenchymal Stem/Stromal Cells: Improved Transfection Efficiency for GMP Grade Applications" Cells 10, no. 12: 3412. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells10123412
APA StyleAgostini, F., Vicinanza, C., Biolo, G., Spessotto, P., Da Ros, F., Lombardi, E., Durante, C., & Mazzucato, M. (2021). Nucleofection of Adipose Mesenchymal Stem/Stromal Cells: Improved Transfection Efficiency for GMP Grade Applications. Cells, 10(12), 3412. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells10123412








