New Onset of Autoimmune Diseases Following COVID-19 Diagnosis
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Search Strategy
3. Results
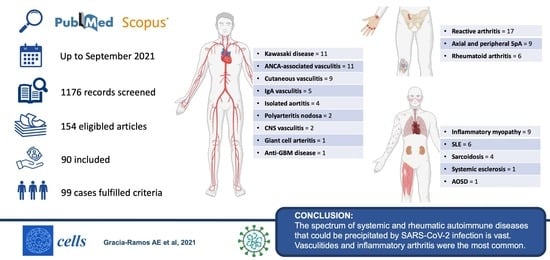
3.1. Vasculitis
3.2. Arthritis
3.3. Idiopathic Inflammatory Myopathies
3.4. Systemic Lupus Erythematosus
3.5. Other Rheumatic Autoimmune Diseases
3.6. Antiphospholipid Syndrome
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Winchester, N.E.; Calabrese, C.; Calabrese, L. The intersection of COVID-19 and autoimmunity: What is our current understanding? Pathog. Immun. 2021, 6, 31–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smatti, M.K.; Cyprian, F.S.; Nasrallah, G.K.; Al Thani, A.A.; Almishal, R.O.; Yassine, H.M. Viruses and Autoimmunity: A Review on the Potential Interaction and Molecular Mechanisms. Viruses 2019, 11, 762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hussein, H.M.; Rahal, E.A. The role of viral infections in the development of autoimmune diseases. Crit. Rev. Microbiol. 2019, 45, 394–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Getts, D.R.; Chastain, E.M.L.; Terry, R.L.; Miller, S.D. Virus infection, antiviral immunity, and autoimmunity. Immunol. Rev. 2013, 255, 197–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Münz, C.; Lünemann, J.D.; Getts, M.T.; Miller, S.D. Antiviral immune responses: Triggers of or triggered by autoimmunity? Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2009, 9, 246–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gazzaruso, C.; Stella, N.C.; Mariani, G.; Nai, C.; Coppola, A.; Naldani, D.; Gallotti, P. High prevalence of antinuclear antibodies and lupus anticoagulant in patients hospitalized for SARS-CoV2 pneumonia. Clin. Rheumatol. 2020, 39, 2095–2097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Han, T.; Chen, J.; Hou, C.; Hua, L.; He, S.; Guo, Y.; Zhang, S.; Wang, Y.; Yuan, J.; et al. Clinical and Autoimmune Characteristics of Severe and Critical Cases of COVID-19. Clin. Transl. Sci. 2020, 13, 1077–1086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woodruff, M.C.; Ramonell, R.P.; Saini, A.S.; Haddad, N.S.; Anam, F.A.; Rudolph, M.E.; Bugrovsky, R.; Hom, J.; Cashman, K.S.; Nguyen, D.C.; et al. Relaxed Peripheral Tolerance Drives Broad de Novo Autoreactivity in Severe COVID-19. medRxiv 2021. preprint. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bastard, P.; Rosen, L.B.; Zhang, Q.; Michailidis, E.; Hoffmann, H.-H.; Zhang, Y.; Dorgham, K.; Philippot, Q.; Rosain, J.; Béziat, V.; et al. Auto-antibodies against type I IFNs in patients with life-threatening COVID-19. Science 2020, 370, eabd4585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohkhedkar, M.; Venigalla, S.S.K.; Janakiraman, V. Untangling COVID-19 and autoimmunity: Identification of plausible targets suggests multi organ involvement. Mol. Immunol. 2021, 137, 105–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, S.; Danda, D.; Kavadichanda, C.; Das, S.; Adarsh, M.B.; Negi, V.S. Autoimmune and rheumatic musculoskeletal diseases as a consequence of SARS-CoV-2 infection and its treatment. Rheumatol. Int. 2020, 40, 1539–1554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zacharias, H.; Dubey, S.; Koduri, G.; D’Cruz, D. Rheumatological complications of Covid-19. Autoimmun. Rev. 2021, 20, 102883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramos-Casals, M.; Brito-Zerón, P.; Mariette, X. Systemic and organ-specific immune-related manifestations of COVID-19. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2021, 17, 315–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Page, M.J.; McKenzie, J.E.; Bossuyt, P.M.; Boutron, I.; Hoffmann, T.C.; Mulrow, C.D.; Shamseer, L.; Tetzlaff, J.M.; Akl, E.A.; Brennan, S.E.; et al. The PRISMA 2020 statement: An updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. BMJ 2021, 372, n71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aletaha, D.; Neogi, T.; Silman, A.J.; Funovits, J.; Felson, D.; Bingham, C.O., III; Birnbaum, N.S.; Burmester, G.R.; Bykerk, V.P.; Cohen, M.D.; et al. 2010 Rheumatoid arthritis classification criteria: An American College of Rheumatology/European League Against Rheumatism collaborative initiative. Arthritis Rheum. 2010, 62, 2569–2581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sieper, J.; Braun, J.; Kingsley, G.H. Report on the fourth International workshop on reactive arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 2000, 43, 720–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jennette, J.C.; Falk, R.J.; Bacon, P.A.; Basu, N.; Cid, M.C.; Ferrario, F.; Flores-Suarez, L.F.; Gross, W.L.; Guillevin, L.; Hagen, E.C.; et al. 2012 Revised International Chapel Hill Consensus Conference Nomenclature of Vasculitides. Arthritis Rheum. 2013, 65, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunder, G.G.; Bloch, D.A.; Michel, B.A.; Stevens, M.B.; Arend, W.P.; Do, L.H.C.; Edworthy, S.M.; Fauci, A.S.; Leavitt, R.Y.; Lie, J.T.; et al. The American College of Rheumatology 1990 criteria for the classification of giant cell arteritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1990, 33, 1122–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lightfoot, R.W., Jr.; Michel, B.A.; Bloch, D.A.; Hunder, G.G.; Zvaifler, N.J.; McShane, D.J.; Arend, W.P.; Do, L.H.C.; Leavitt, R.Y.; Lie, J.T.; et al. The American college of rheumatology 1990 criteria for the classification of polyarteritis nodosa. Arthritis Rheum. 1990, 33, 1088–1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watts, R.; Lane, S.; Hanslik, T.; Hauser, T.; Hellmich, B.; Koldingsnes, W.; Mahr, A.; Segelmark, M.; Cohen-Tervaert, J.W.; Scott, D. Development and validation of a consensus methodology for the classification of the ANCA-associated vasculitides and polyarteritis nodosa for epidemiological studies. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2006, 66, 222–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawasaki Disease Case Definition. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/kawasaki/case-definition.html (accessed on 13 October 2021).
- McCrindle, B.W.; Rowley, A.H.; Newburger, J.W.; Burns, J.C.; Bolger, A.F.; Gewitz, M.; Baker, A.L.; Jackson, M.A.; Takahashi, M.; Shah, P.B.; et al. Diagnosis, Treatment, and Long-Term Management of Kawasaki Disease: A Scientific Statement for Health Professionals From the American Heart Association. Circulation 2017, 135, 927–999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanegaye, J.T.; Wilder, M.S.; Molkara, D.; Frazer, J.R.; Pancheri, J.; Tremoulet, A.H.; Watson, V.E.; Best, B.M.; Burns, J.C. Recognition of a Kawasaki Disease Shock Syndrome. Pediatrics 2009, 123, e783–e789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Multisystem Inflammatory Syndrome in Adults (MIS-A) Case Definition. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/mis/mis-a/hcp.html (accessed on 13 October 2021).
- Multisystem Inflammatory Syndrome in Children (MIS-C) Case Definition. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/mis/mis-c.html (accessed on 13 October 2021).
- Bohan, A.; Peter, J.B. Polymyositis and Dermatomyositis (First of Two Parts). N. Engl. J. Med. 1975, 292, 344–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bohan, A.; Peter, J.B. Polymyositis and Dermatomyositis (Second of Two Parts). N. Engl. J. Med. 1975, 292, 403–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lundberg, E.I.; Tjärnlund, A.; Bottai, M.; Werth, V.P.; Pilkington, C.; De Visser, M.; Alfredsson, L.; Amato, A.; Barohn, R.J.; Liang, M.H.; et al. 2017 European League Against Rheumatism/American College of Rheumatology classification criteria for adult and juvenile idiopathic inflammatory myopathies and their major subgroups. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2017, 76, 1955–1964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aringer, M.; Costenbader, K.; Daikh, D.; Brinks, R.; Mosca, M.; Ramsey-Goldman, R.; Smolen, J.S.; Wofsy, D.; Boumpas, D.T.; Kamen, D.L.; et al. 2019 European League Against Rheumatism/American College of Rheumatology Classification Criteria for Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019, 71, 1400–1412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shiboski, C.H.; Shiboski, S.C.; Seror, R.; Criswell, L.A.; Labetoulle, M.; Lietman, T.M.; Rasmussen, A.; Scofield, H.; Vitali, C.; Bowman, S.J.; et al. 2016 American College of Rheumatology/European League Against Rheumatism classification criteria for primary Sjögren’s syndrome: A Consensus and Data-Driven Methodology Involving Three International Patient Cohorts. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2017, 76, 9–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamaguchi, M.; Ohta, A.; Tsunematsu, T.; Kasukawa, R.; Mizushima, Y.; Kashiwagi, H.; Kashiwazaki, S.; Tanimoto, K.; Matsumoto, Y.; Ota, T. Preliminary criteria for classification of adult Still’s disease. J. Rheumatol. 1992, 19, 424–430. [Google Scholar]
- Rudwaleit, M.; Van Der Heijde, D.; Landewé, R.; Listing, J.; Akkoç, N.; Brandt, J.; Braun, J.; Chou, C.T.; Estévez, E.C.; Dougados, M.; et al. The development of Assessment of SpondyloArthritis international Society classification criteria for axial spondyloarthritis (part II): Validation and final selection. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2009, 68, 777–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Statement on Sarcoidosis. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 1999, 160, 736–755. [CrossRef]
- Miyakis, S.; Lockshin, M.D.; Atsumi, T.; Branch, D.W.; Brey, R.L.; Cervera, R.; Derksen, R.H.W.M.; De Groot, P.G.; Koike, T.; Meroni, P.L.; et al. International consensus statement on an update of the classification criteria for definite antiphospholipid syndrome (APS). J. Thromb. Haemost. 2006, 4, 295–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caputo, V.; Schroeder, J.; Rongioletti, F. A generalized purpuric eruption with histopathologic features of leucocytoclastic vasculitis in a patient severely ill with COVID-19. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2020, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayor-Ibarguren, A.; Feito-Rodriguez, M.; Castanedo, L.Q.; Ruiz-Bravo, E.; Vega, D.M.; Herranz-Pinto, P. Cutaneous small vessel vasculitis secondary to COVID-19 infection: A case report. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2020, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iraji, F.; Galehdari, H.; Siadat, A.H.; Jazi, S.B. Cutaneous leukocytoclastic vasculitis secondary to COVID-19 infection: A case report. Clin. Case Rep. 2021, 9, 830–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dominguez-Santas, M.; Diaz-Guimaraens, B.; Abellas, P.G.; Del Real, C.M.; Burgos-Blasco, P.; Suarez-Valle, A. Cutaneous small-vessel vasculitis associated with novel 2019 coronavirus SARS-CoV-2 infection (COVID-19). J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2020, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kösters, K.; Schwarzer, S.; Labuhn, A.; Rübben, A.; Yang, S.; Hessler, F.; Assaf, C. Cutaneous Vasculitis in a Patient With COVID-19. Open Forum Infect. Dis. 2020, 7, ofaa474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaigany, S.; Gnirke, M.; Guttmann, A.; Chong, H.; Meehan, S.; Raabe, V.; Louie, E.; Solitar, B.; Femia, A. An adult with Kawasaki-like multisystem inflammatory syndrome associated with COVID-19. Lancet 2020, 396, e8–e10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Negrini, S.; Guadagno, A.; Greco, M.; Parodi, A.; Burlando, M. An unusual case of bullous haemorrhagic vasculitis in a COVID-19 patient. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2020, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duran, T.I.; Turkmen, E.; Dilek, M.; Sayarlioglu, H.; Arik, N. ANCA-associated vasculitis after COVID-19. Rheumatol. Int. 2021, 41, 1523–1529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussein, A.; Al Khalil, K.; Bawazir, Y.M. Anti-Neutrophilic Cytoplasmic Antibody (ANCA) Vasculitis Presented as Pulmonary Hemorrhage in a Positive COVID-19 Patient: A Case Report. Cureus 2020, 12, e9643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oda, R.; Inagaki, T.; Ishikane, M.; Hotta, M.; Shimomura, A.; Sato, M.; Nakamoto, T.; Akiyama, Y.; Yamamoto, K.; Minamimoto, R.; et al. Case of adult large vessel vasculitis after SARS-CoV-2 infection. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2020, 2020, 218440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Timmons, G.M.; Rempe, T.; Bevins, E.A.; Goodwill, V.; Miner, A.; Kavanaugh, A.; Ritter, M.; Graves, J.S. CNS Lymphocytic Vasculitis in a Young Woman With COVID-19 Infection. Neurol.-Neuroimmunol. Neuroinflamm. 2021, 8, e1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chérif, M.Y.; de Filette, J.M.; André, S.; Kamgang, P.; Richert, B.; Clevenbergh, P. Coronavirus disease 2019–related Kawasaki-like disease in an adult: A case report. JAAD Case Rep. 2020, 6, 780–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sokolovsky, S.; Soni, P.; Hoffman, T.; Kahn, P.; Scheers-Masters, J. COVID-19 associated Kawasaki-like multisystem inflammatory disease in an adult. Am. J. Emerg. Med. 2021, 39, 253.e1–253.e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vacchi, C.; Meschiari, M.; Milic, J.; Marietta, M.; Tonelli, R.; Alfano, G.; Volpi, S.; Faltoni, M.; Franceschi, G.; Ciusa, G.; et al. COVID-19-associated vasculitis and thrombotic complications: From pathological findings to multidisciplinary discussion. Rheumatology 2020, 59, e147–e150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Selvaraj, V.; Moustafa, A.; Dapaah-Afriyie, K.; Birkenbach, M.P. COVID-19-induced granulomatosis with polyangiitis. BMJ Case Rep. 2021, 14, e242142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allez, M.; Denis, B.; Bouaziz, J.; Battistella, M.; Zagdanski, A.; Bayart, J.; Lazaridou, I.; Gatey, C.; Pillebout, E.; Baudier, M.C.; et al. COVID-19–Related IgA Vasculitis. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2020, 72, 1952–1953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, N.L.; Papini, A.B.; Shao, T.; Girard, L. Immunoglobulin-A Vasculitis With Renal Involvement in a Patient With COVID-19: A Case Report and Review of Acute Kidney Injury Related to SARS-CoV-19. Can. J. Kidney Health Dis. 2021, 8, 205435812199168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kudose, S.; Batal, I.; Santoriello, D.; Xu, K.; Barasch, J.; Peleg, Y.; Canetta, P.; Ratner, L.E.; Marasa, M.; Gharavi, A.G.; et al. Kidney Biopsy Findings in Patients with COVID-19. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2020, 31, 1959–1968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uppal, N.N.; Kello, N.; Shah, H.H.; Khanin, Y.; De Oleo, I.R.; Epstein, E.; Sharma, P.; Larsen, C.P.; Bijol, V.; Jhaveri, K.D. De Novo ANCA-Associated Vasculitis With Glomerulonephritis in COVID. Kidney Int. Rep. 2020, 5, 2079–2083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lind, E.; Jameson, A.; Kurban, E. Fulminant granulomatosis with polyangiitis presenting with diffuse alveolar haemorrhage following COVID. BMJ Case Rep. 2021, 14, e242628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbetta, L.; Filocamo, G.; Passoni, E.; Boggio, F.; Folli, C.; Monzani, V. Henoch-Schönlein Purpura with Renal and Gastro-intestinal Involvement in Course of COVID-19: A Case Report. Clin. Exp. Rheumatol. 2021, 39 (Suppl. S129), 191–192. [Google Scholar]
- Suso, A.S.; Mon, C.; Alonso, I.O.; Romo, K.G.; Juarez, R.C.; Ramírez, C.L.; Sánchez, M.S.; Valdivia, V.M.; Librero, M.O.; Pala, A.O.; et al. IgA Vasculitis With Nephritis (Henoch−Schönlein Purpura) in a COVID-19 Patient. Kidney Int. Rep. 2020, 5, 2074–2078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, P.; DeCuir, J.; Abrams, J.; Campbell, A.P.; Godfred-Cato, S.; Belay, E.D. Clinical Characteristics of Multisystem Inflammatory Syndrome in Adults. JAMA Netw. Open 2021, 4, e2126456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dixon, L.; Coughlan, C.; Karunaratne, K.; Gorgoraptis, N.; Varley, J.; Husselbee, J.; Mallon, D.; Carroll, R.; Jones, B.; Boynton, C.; et al. Immunosuppression for intracranial vasculitis associated with SARS-CoV-2: Therapeutic implications for COVID-19 cerebrovascular pathology. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2021, 92, 103–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cogan, E.; Foulon, P.; Cappeliez, O.; Dolle, N.; Vanfraechem, G.; De Backer, D. Multisystem Inflammatory Syndrome With Complete Kawasaki Disease Features Associated With SARS-CoV-2 Infection in a Young Adult. A Case Report. Front. Med. 2020, 7, 428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bressler, M.Y.; Pathak, N.; Cervellione, K.; Bagheri, F.; Epstein, E.; Mir, A.; Tamez, R. New Onset Granulomatosis with Polyangiitis Associated with COVID-19. Case Rep. Dermatol. Med. 2021, 2021, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moeinzadeh, F.; Dezfouli, M.; Naimi, A.; Shahidi, S.; Moradi, H. Newly Diagnosed Glomerulonephritis During COVID-19 Infection Undergoing Immunosuppression Therapy, a Case Report. Iran J. Kidney Dis. 2020, 14, 239–242. [Google Scholar]
- Sandhu, S.; Chand, S.; Bhatnagar, A.; Dabas, R.; Bhat, S.; Kumar, H.; Dixit, P.K. Possible association between IgA vasculitis and COVID-19. Dermatol. Ther. 2021, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riera-Martí, N.; Romaní, J.; Calvet, J. SARS-CoV-2 infection triggering a giant cell arteritis. Med. Clínica 2021, 156, 253–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nasiri, S.; Dadkhahfar, S.; Abasifar, H.; Mortazavi, N.; Gheisari, M. Urticarial vasculitis in a COVID-19 recovered patient. Int. J. Dermatol. 2020, 59, 1285–1286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Perosanz-Lobo, D.; Fernandez-Nieto, D.; Burgos-Blasco, P.; Selda-Enriquez, G.; Carretero, I.; Moreno, C.; Fernández-Guarino, M. Urticarial vasculitis in COVID-19 infection: A vasculopathy-related symptom? J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2020, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhakal, P.; Khadka, S.; Clowes, J.A.; Chakinala, R.C. Aortitis in COVID-19. IDCases 2021, 24, e01063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shergill, S.; Davies, J.; Bloomfield, J. Florid aortitis following SARS-CoV-2 infection. Eur. Heart J. 2020, 41, 4286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuriyama, Y.; Shimizu, A.; Oka, H.; Sato, M.; Makioka, K.; Ikota, H.; Yanagisawa, K.; Tokue, Y.; Tsukagoshi, H.; Motegi, S. Erythema nodosum-like eruption in coronavirus disease 2019: A case report and literature review of Asian countries. J. Dermatol. 2021, 48, 1588–1592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lidder, A.K.; Pandit, S.A.; Lazzaro, D.R. An adult with COVID-19 kawasaki-like syndrome and ocular manifestations. Am. J. Ophthalmol. Case Rep. 2020, 20, 100875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malangu, B.; Quintero, J.A.; Capitle, E.M. Adult Inflammatory Multi-System Syndrome Mimicking Kawasaki Disease in a Patient With COVID-19. Cureus 2020, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vergnano, S.; Alders, N.; Armstrong, C.; Bamber, A.R.; Bandi, S.; Evans, A.J.; Hajiani, N.; Kenny, J.; Kucera, F.; Tometzki, A.; et al. Severe refractory Kawasaki disease in seven infants in the COVID-19 era. Lancet Rheumatol. 2020, 2, e520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kofman, A.D.; Sizemore, E.K.; Detelich, J.F.; Albrecht, B.; Piantadosi, A.L. A young adult with COVID-19 and multisystem inflammatory syndrome in children (MIS-C)-like illness: A case report. BMC Infect. Dis. 2020, 20, 716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ventura, M.J.; Guajardo, E.; Clark, E.H.; Bhairavarasu, K.; Kherallah, R.Y.; Dinardo, A.R.; Ye, X.; Piedra, A.P.; Atmar, R.L.; Agarwal, S.K. Correspondence on ‘Paediatric multisystem inflammatory syndrome temporally associated with SARS-CoV-2 mimicking Kawasaki disease (Kawa-COVID-19): A multicentre cohort’ by Pouletty et al. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2020, 2020, 218959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, I.; Bell, L.C.K.; Manson, J.J.; Last, A. An adult presentation consistent with PIMS-TS. Lancet Rheumatol. 2020, 2, e520–e521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parker, A.; Louw, E.H.; Lalla, U.; Koegelenberg, C.F.N.; Allwood, B.W.; Rabie, H.; Sibeko, I.S.; Taljaard, J.J.; Lahri, S. Multisystem inflammatory syndrome in adult COVID-19 patients. S. Afr. Med. J. 2020, 110, 957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagra, D.; Russell, M.D.; Rosmini, S.; Sado, D.; Buazon, A.; Shafi, T.; Hamlyn, E.; Sandhu, G.; Rutherford, I.A.; Galloway, J.B. A Kawasaki-like illness in an adult with recent SARS-CoV-2 infection. Rheumatol. Adv. Pract. 2021, 5, rkab035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lechien, J.R.; Hervochon, R.; Hans, S. Post-COVID-19 Kawasaki-Like Syndrome. Ear Nose Throat J. 2021, 014556132110060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Novelli, L.; Motta, F.; Ceribelli, A.; Guidelli, G.M.; Luciano, N.; Isailovic, N.; Vecellio, M.; Caprioli, M.; Clementi, N.; Clementi, M.; et al. A case of psoriatic arthritis triggered by SARS-CoV-2 infection. Rheumatology 2021, 60, e21–e23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liew, I.Y.; Mak, T.M.; Cui, L.; Vasoo, S.; Lim, X.R. A Case of Reactive Arthritis Secondary to Coronavirus Disease 2019 Infection. JCR: J. Clin. Rheumatol. 2020, 26, 233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuschner, Z.; Do, A.O.; Mukherji, P. A case of SARS-CoV-2-associated arthritis with detection of viral RNA in synovial fluid. J. Am. Coll. Emerg. Phys. Open 2021, 2, e12452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cincinelli, G.; Di Taranto, R.; Orsini, F.; Rindone, A.; Murgo, A.; Caporali, R. A case report of monoarthritis in a COVID-19 patient and literature review. Medicine 2021, 100, e26089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baimukhamedov, C.; Barskova, T.; Matucci-Cerinic, M. Arthritis after SARS-CoV-2 infection. Lancet Rheumatol. 2021, 3, e324–e325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Hasbani, G.; Jawad, A.; Uthman, I. Axial and peripheral spondyloarthritis triggered by sars-cov-2 infection: A report of two cases. Reumatismo 2021, 73, 59–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Carlo, M.; Tardella, M.; Salaffi, F. Can SARS-CoV-2 Induce Reactive Arthritis? Clin. Exp. Rheumatol. 2021, 39 (Suppl. S128), 25–26. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Fragata, I.; Mourão, A.F. Coronavirus Disease 19 (COVID-19) complicated with post-viral arthritis. Acta Reum. Port 2021, 45, 278–280. [Google Scholar]
- Roongta, R.; Chattopadhyay, A.; Ghosh, A. Correspondence on ‘Onset of rheumatoid arthritis after COVID-19: Coincidence or connected?’. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2021, 2021, 220479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Derksen, V.F.A.M.; Kissel, T.; Lamers-Karnebeek, F.B.G.; van der Bijl, E.A.; Venhuizen, A.C.; Huizinga, T.W.J.; Toes, R.E.M.; Roukens, E.A.H.; van der Woude, D. Onset of rheumatoid arthritis after COVID-19: Coincidence or connected? Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2021, 80, 1096–1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gasparotto, M.; Framba, V.; Piovella, C.; Doria, A.; Iaccarino, L. Post-COVID-19 arthritis: A case report and literature review. Clin. Rheumatol. 2021, 40, 3357–3362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hønge, B.L.; Hermansen, M.-L.F.; Storgaard, M. Reactive arthritis after COVID-19. BMJ Case Rep. 2021, 14, e241375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kocyigit, B.F.; Akyol, A. Reactive arthritis after COVID-19: A case-based review. Rheumatol. Int. 2021, 41, 2031–2039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danssaert, Z.; Raum, G.; Hemtasilpa, S. Reactive Arthritis in a 37-Year-Old Female With SARS-CoV2 Infection. Cureus 2020, 12, e9698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ono, K.; Kishimoto, M.; Shimasaki, T.; Uchida, H.; Kurai, D.; Deshpande, A.G.; Komagata, Y.; Kaname, S. Reactive arthritis after COVID-19 infection. RMD Open 2020, 6, e001350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sureja, N.P.; Nandamuri, D. Reactive arthritis after SARS-CoV-2 infection. Rheumatol. Adv. Pract. 2021, 5, rkab001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schenker, H.M.; Hagen, M.; Simon, D.; Schett, G.; Manger, B. Reactive arthritis and cutaneous vasculitis after SARS-CoV-2 infection. Rheumatology 2021, 60, 479–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salvatierra, J.; Martínez-Peñalver, D.; Salvatierra-Velasco, L. CoVid-19 related dactyitis. Jt. Bone Spine 2020, 87, 660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jali, I. Reactive Arthritis After COVID-19 Infection. Cureus 2020, 12, e11761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Talarico, R.; Stagnaro, C.; Ferro, F.; Carli, L.; Mosca, M. Symmetric peripheral polyarthritis developed during SARS-CoV-2 infection. Lancet Rheumatol. 2020, 2, e518–e519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saikali, W.; Gharib, S. The first non-radiographic axial spondyloarthrits with COVID-19. Immunity Inflamm. Dis. 2021, 9, 628–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Stefano, L.; Rossi, S.; Montecucco, C.; Bugatti, S. Transient monoarthritis and psoriatic skin lesions following COVID-19. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2020, 2020, 218520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parisi, S.; Borrelli, R.; Bianchi, S.; Fusaro, E. Viral arthritis and COVID-19. Lancet Rheumatol. 2020, 2, e655–e657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alivernini, S.; Cingolani, A.; Gessi, M.; Paglionico, A.; Pasciuto, G.; Tolusso, B.; Fantoni, M.; Gremese, E. Comparative analysis of synovial inflammation after SARS-CoV-2 infection. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2021, 80, e91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukarram, M.S. Jinnah Medical College Hospital Post COVID-19 Reactive Arthritis: An Emerging Existence In The Spectrum Of Musculoskeletal Complications Of SARS-CoV-2 Infection. Clin. Stud. Med Case Rep. 2020, 7, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yokogawa, N.; Minematsu, N.; Katano, H.; Suzuki, T. Case of acute arthritis following SARS-CoV-2 infection. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2021, 80, e101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perrot, L.; Hemon, M.; Busnel, J.-M.; Muis-Pistor, O.; Picard, C.; Zandotti, C.; Pham, T.; Roudier, J.; Desplat-Jego, S.; Balandraud, N. First flare of ACPA-positive rheumatoid arthritis after SARS-CoV-2 infection. Lancet Rheumatol. 2021, 3, 6–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibson, M.; Sampat, K.; Coakley, G. EP15 A self-limiting symmetrical polyarthritis following COVID-19 infection. Rheumatol. Adv. Pr. 2020, 4, rkaa052.014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uslu, S. Myositis due to COVID-19. Postgrad. Med. J. 2021, 97, 399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beydon, M.; Chevalier, K.; Al Tabaa, O.; Hamroun, S.; Delettre, A.-S.; Thomas, M.; Herrou, J.; Riviere, E.; Mariette, X. Myositis as a manifestation of SARS-CoV-19. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2021, 80, e42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shabbir, A.; Camm, C.F.; Elkington, A.; Tilling, L.; Stirrup, J.; Chan, A.; Bull, S. Myopericarditis and myositis in a patient with COVID-19: A case report. Eur. Hearth J.Case Rep. 2020, 4, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lokineni, S.; Mortezavi, M. Delayed-onset Necrotizing Myositis following COVID-19 Infection. Eur. J. Case Rep. Intern. Med. 2021, 8, 002461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Charmchi, Z.; Seidman, R.J.; Anziska, Y.; Do, V.V.; Perk, J. COVID -19–associated myositis with severe proximal and bulbar weakness. Muscle Nerve 2020, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veyseh, M.; Koyoda, S.; Ayesha, B. COVID-19 IgG-related autoimmune inflammatory necrotizing myositis. BMJ Case Rep. 2021, 14, e239457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sacchi, M.C.; Tamiazzo, S.; Lauritano, E.C.; Bonometti, R. Case Report of COVID-19 in an Elderly Patient: Could SARS-CoV2 Trigger Myositis? Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2020, 24, 11960–11963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gokhale, Y.; Patankar, A.; Holla, U.; Shilke, M.; Kalekar, L.; Karnik, N.D.; Bidichandani, K.; Baveja, S.; Joshi, A. Dermatomy-ositis during COVID-19 Pandemic (A Case Series): Is There a Cause Effect Relationship? J. Assoc. Physicians. India 2020, 68, 20–24. [Google Scholar]
- Hali, F.; Jabri, H.; Chiheb, S.; Hafiani, Y.; Nsiri, A. A concomitant diagnosis of COVID-19 infection and systemic lupus erythematosus complicated by a macrophage activation syndrome: A new case report. Int. J. Dermatol. 2021, 60, 1030–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gracia-Ramos, A.E.; Saavedra-Salinas, M. Ángel Can the SARS-CoV-2 infection trigger systemic lupus erythematosus? A case-based review. Rheumatol. Int. 2021, 41, 799–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cardoso, E.M.; Hundal, J.; Feterman, D.; Magaldi, J. Concomitant new diagnosis of systemic lupus erythematosus and COVID-19 with possible antiphospholipid syndrome. Just a coincidence? A case report and review of intertwining pathophysiology. Clin. Rheumatol. 2020, 39, 2811–2815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slimani, Y.; Abbassi, R.; El Fatoiki, F.; Barrou, L.; Chiheb, S. Systemic lupus erythematosus and varicella-like rash following COVID-19 in a previously healthy patient. J. Med. Virol. 2021, 93, 1184–1187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zamani, B.; Taba, S.-M.M.; Shayestehpour, M. Systemic lupus erythematosus manifestation following COVID-19: A case report. J. Med. Case Rep. 2021, 15, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonometti, R.; Sacchi, M.C.; Stobbione, P.; Lauritano, E.C.; Tamiazzo, S.; Marchegiani, A.; Novara, E.; Molinaro, E.; Benedetti, I.; Massone, L.; et al. The first case of systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) triggered by COVID-19 infection. Eur. Rev. Med Pharmacol. Sci. 2020, 24, 9695–9697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fineschi, S. Case Report: Systemic Sclerosis After Covid-19 Infection. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 686699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bamidis, A.D.; Koehler, P.; di Cristanziano, V.; Rasche, K.; Demirel, B.; Bacher, P.; Hallek, M.; Kochanek, M.; Klein, F.; Hofmann, S.C.; et al. First manifestation of adult-onset Still’s disease after COVID-19. Lancet Rheumatol. 2021, 3, e319–e321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ekinci, A.P.; Büyükbabani, N.; Meşe, S.; Pehlivan, G.; Okumuş, N.; Ağaçfidan, A.; Özkaya, E. COVID-19-triggered sarcoidal granulomas mimicking scar sarcoidosis. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2021, 35, e477–e480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mertz, P.; Jeannel, J.; Guffroy, A.; Lescuyer, S.; Korganow, A.S.; Rondeau-Lutz, M.; Weber, J.C. Granulomatous manifestations associated with COVID19 infection: Is there a link between these two diseases? Autoimmun. Rev. 2021, 20, 102824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behbahani, S.; Baltz, J.O.; Droms, R.; Deng, A.C.; Amano, S.U.; Levin, N.A.; O’Brien, M.C.; Wiss, K. Sarcoid-like reaction in a patient recovering from coronavirus disease 19 pneumonia. JAAD Case Rep. 2020, 6, 915–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colmenero, I.; Santonja, C.; Alonso-Riaño, M.; Noguera-Morel, L.; Hernández-Martín, A.; Andina, D.; Wiesner, T.; Rodríguez-Peralto, J.; Requena, L.; Torrelo, A. SARS-CoV-2 endothelial infection causes COVID-19 chilblains: Histopathological, immunohistochemical and ultrastructural study of seven paediatric cases. Br. J. Dermatol. 2020, 183, 729–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McGonagle, D.; Bridgewood, C.; Ramanan, A.V.; Meaney, J.F.M.; Watad, A. COVID-19 vasculitis and novel vasculitis mimics. Lancet Rheumatol. 2021, 3, e224–e233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verdoni, L.; Mazza, A.; Gervasoni, A.; Martelli, L.; Ruggeri, M.; Ciuffreda, M.; Bonanomi, E.; D’Antiga, L. An outbreak of severe Kawasaki-like disease at the Italian epicentre of the SARS-CoV-2 epidemic: An observational cohort study. Lancet 2020, 395, 1771–1778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pouletty, M.; Borocco, C.; Ouldali, N.; Caseris, M.; Basmaci, R.; Lachaume, N.; Bensaid, P.; Pichard, S.; Kouider, H.; Morelle, G.; et al. Paediatric multisystem inflammatory syndrome temporally associated with SARS-CoV-2 mimicking Kawasaki disease (Kawa-COVID-19): A multicentre cohort. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2020, 79, 999–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feldstein, L.R.; Rose, E.B.; Horwitz, S.M.; Collins, J.P.; Newhams, M.M.; Son, M.B.F.; Newburger, J.W.; Kleinman, L.C.; Heidemann, S.M.; Martin, A.A.; et al. Multisystem Inflammatory Syndrome in U.S. Children and Adolescents. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 383, 334–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roncati, L.; Ligabue, G.; Fabbiani, L.; Malagoli, C.; Gallo, G.; Lusenti, B.; Nasillo, V.; Manenti, A.; Maiorana, A. Type 3 hypersensitivity in COVID-19 vasculitis. Clin. Immunol. 2020, 217, 108487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fraison, J.-B.; Sève, P.; Dauphin, C.; Mahr, A.; Gomard-Mennesson, E.; Varron, L.; Pugnet, G.; Landron, C.; Roblot, P.; Oziol, E.; et al. Kawasaki disease in adults: Observations in France and literature review. Autoimmun. Rev. 2016, 15, 242–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, L.-Y.; Lu, C.-Y.; Shao, P.-L.; Lee, P.-I.; Lin, M.-T.; Fan, T.-Y.; Cheng, A.-L.; Lee, W.-L.; Hu, J.-J.; Yeh, S.-J.; et al. Viral infections associated with Kawasaki disease. J. Formos. Med. Assoc. 2014, 113, 148–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Turnier, J.L.; Anderson, M.S.; Heizer, H.R.; Jone, P.-N.; Glodé, M.P.; Dominguez, S.R. Concurrent Respiratory Viruses and Kawasaki Disease. Pediatrics 2015, 136, e609–e614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Guleria, S.; Jindal, A.K.; Pandiarajan, V.; Singh, M.P.; Singh, S. Dengue-Triggered Kawasaki Disease: A Report of 2 Cases. JCR J. Clin. Rheumatol. 2018, 24, 401–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toubiana, J.; Cohen, J.F.; Brice, J.; Poirault, C.; Bajolle, F.; Curtis, W.; Moulin, F.; Matczak, S.; Leruez, M.; Casanova, J.-L.; et al. Distinctive Features of Kawasaki Disease Following SARS-CoV-2 Infection: A Controlled Study in Paris, France. J. Clin. Immunol. 2021, 41, 526–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yener, G.O.; Kısaarslan, A.P.; Ulu, K.; Atalay, E.; Haşlak, F.; Özdel, S.; Yücel, B.B.; Yıldırım, D.G.; Çakmak, F.; Öztürk, K.; et al. Differences and similarities of multisystem inflammatory syndrome in children, Kawasaki disease and macrophage activating syndrome due to systemic juvenile idiopathic arthritis: A comparative study. Rheumatol. Int. 2021, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Consiglio, C.R.; Cotugno, N.; Sardh, F.; Pou, C.; Amodio, D.; Rodriguez, L.; Tan, Z.; Zicari, S.; Ruggiero, A.; Pascucci, G.R.; et al. The Immunology of Multisystem Inflammatory Syndrome in Children with COVID-19. Cell 2020, 183, 968–981.e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez-Smith, J.J.; Verweyen, E.L.; Clay, G.M.; Esteban, Y.M.; de Loizaga, S.R.; Baker, E.J.; Do, T.; Dhakal, S.; Lang, S.M.; Grom, A.A.; et al. Inflammatory biomarkers in COVID-19-associated multisystem inflammatory syndrome in children, Kawasaki disease, and macrophage activation syndrome: A cohort study. Lancet Rheumatol. 2021, 3, e574–e584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henderson, L.A.; Canna, S.W.; Friedman, K.G.; Gorelik, M.; Lapidus, S.K.; Bassiri, H.; Behrens, E.M.; Ferris, A.; Kernan, K.F.; Schulert, G.S.; et al. American College of Rheumatology Clinical Guidance for Multisystem Inflammatory Syndrome in Children Associated With SARS–CoV-2 and Hyperinflammation in Pediatric COVID-19: Version 2. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2021, 73, e13–e29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santoriello, D.; Khairallah, P.; Bomback, A.S.; Xu, K.; Kudose, S.; Batal, I.; Barasch, J.; Radhakrishnan, J.; D’Agati, V.; Markowitz, G. Postmortem Kidney Pathology Findings in Patients with COVID-19. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2020, 31, 2158–2167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, R.; Amrutiya, V.; Baghal, M.; Shah, M.; Lo, A. Life-Threatening Diffuse Alveolar Hemorrhage as an Initial Presentation of Microscopic Polyangiitis: COVID-19 as a Likely Culprit. Cureus 2021, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Löffler, C.; Mahrhold, J.; Fogarassy, P.; Beyer, M.; Hellmich, B. Two Immunocompromised Patients With Diffuse Alveolar Hemorrhage as a Complication of Severe Coronavirus Disease. Chest 2020, 158, e215–e219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gelzo, M.; Cacciapuoti, S.; Pinchera, B.; De Rosa, A.; Cernera, G.; Scialò, F.; Comegna, M.; Mormile, M.; Gallicchio, A.; Fabbrocini, G.; et al. A Transient Increase in the Serum ANCAs in Patients with SARS-CoV-2 Infection: A Signal of Subclinical Vasculitis or an Epiphenomenon with No Clinical Manifestations? A Pilot Study. Viruses 2021, 13, 1718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vlachoyiannopoulos, P.G.; Magira, E.; Alexopoulos, H.; Jahaj, E.; Theophilopoulou, K.; Kotanidou, A.; Tzioufas, A.G. Autoantibodies related to systemic autoimmune rheumatic diseases in severely ill patients with COVID-19. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2020, 79, 1661–1663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dotan, A.; Muller, S.; Kanduc, D.; David, P.; Halpert, G.; Shoenfeld, Y. The SARS-CoV-2 as an instrumental trigger of autoimmunity. Autoimmun. Rev. 2021, 20, 102792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pastuszczak, M.; Celińska-Löwenhoff, M.; Sułowicz, J.; Wojas-Pelc, A.; Musiał, J. Clinical study on single-organ cutaneous small vessels vasculitis (SoCSVV). Medicine 2017, 96, e6376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loricera, J.; Blanco, R.; Ortiz-Sanjuán, F.; Hernández, J.L.; Pina, T.; González-Vela, M.C.; Calvo-Río, V.; Rueda-Gotor, J.; Alvarez, L.; González-López, M.A.; et al. Single-organ cutaneous small-vessel vasculitis according to the 2012 revised International Chapel Hill Consensus Conference Nomenclature of Vasculitides: A study of 60 patients from a series of 766 cutaneous vasculitis cases. Rheumatology 2015, 54, 77–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sollini, M.; Ciccarelli, M.; Cecconi, M.; Aghemo, A.; Morelli, P.; Gelardi, F.; Chiti, A. Vasculitis changes in COVID-19 survivors with persistent symptoms: An [18F] FDG-PET/CT study. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2021, 48, 1460–1466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dudouet, P.; Cammilleri, S.; Guedj, E.; Jacquier, A.; Raoult, D.; Eldin, C. Aortic 18F-FDG PET/CT hypermetabolism in patients with long COVID: A retrospective study. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2021, 27, 1873–1875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Hu, B.; Hu, C.; Zhu, F.; Liu, X.; Zhang, J.; Wang, B.; Xiang, H.; Cheng, Z.; Xiong, Y.; et al. Clinical Characteristics of 138 Hospitalized Patients With 2019 Novel Coronavirus-Infected Pneumonia in Wuhan, China. JAMA 2020, 323, 1061–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joob, B.; Wiwanitkit, V. Arthralgia as an initial presentation of COVID-19: Observation. Rheumatol. Int. 2020, 40, 823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fujinami, R.S.; von Herrath, M.G.; Christen, U.; Whitton, J.L. Molecular Mimicry, Bystander Activation, or Viral Persistence: Infections and Autoimmune Disease. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2006, 19, 80–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Vassilopoulos, D.; Calabrese, L.H. Virally associated arthritis 2008: Clinical, epidemiologic, and pathophysiologic considerations. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2008, 10, 215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stavropoulos, P.; Soura, E.; Kanelleas, A.; Katsambas, A.; Antoniou, C. Reactive Arthritis. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2014, 29, 415–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riebeling-Navarro, C.; Nava, A. Patogenia de las miopatías inflamatorias idiopáticas. Reumatol. Clín. 2009, 5, 6–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adler, B.; Christopher-Stine, L.; Cristopher-Stine, L. Triggers of inflammatory myopathy: Insights into pathogenesis. Discov. Med. 2018, 25, 75–83. [Google Scholar]
- Grant, M.C.; Geoghegan, L.; Arbyn, M.; Mohammed, Z.; McGuinness, L.; Clarke, E.L.; Wade, R.G. The prevalence of symptoms in 24,410 adults infected by the novel coronavirus (SARS-CoV-2; COVID-19): A systematic review and meta-analysis of 148 studies from 9 countries. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0234765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berth, S.H.; Lloyd, T.E. Secondary Causes of Myositis. Curr. Treat. Options Neurol. 2020, 22, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsivgoulis, G.; Palaiodimou, L.; Katsanos, A.H.; Caso, V.; Köhrmann, M.; Molina, C.; Cordonnier, C.; Fischer, U.; Kelly, P.; Sharma, V.; et al. Neurological manifestations and implications of COVID-19 pandemic. Ther. Adv. Neurol. Disord. 2020, 13, 175628642093203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saud, A.; Naveen, R.; Aggarwal, R.; Gupta, L. COVID-19 and Myositis: What We Know So Far. Curr. Rheumatol. Rep. 2021, 23, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gracia-Ramos, A.E. Is the ACE2 Overexpression a Risk Factor for COVID-19 Infection? Arch. Med. Res. 2020, 51, 345–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paliwal, V.K.; Garg, R.K.; Gupta, A.; Tejan, N. Neuromuscular presentations in patients with COVID-19. Neurol. Sci. 2020, 41, 3039–3056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rigante, D.; Mazzoni, M.B.; Esposito, S. The cryptic interplay between systemic lupus erythematosus and infections. Autoimmun. Rev. 2014, 13, 96–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujii, H.; Tsuji, T.; Yuba, T.; Tanaka, S.; Suga, Y.; Matsuyama, A.; Omura, A.; Shiotsu, S.; Takumi, C.; Ono, S.; et al. High levels of anti-SSA/Ro antibodies in COVID-19 patients with severe respiratory failure: A case-based review: High Levels of Anti-SSA/Ro Antibodies in COVID-19. Clin. Rheumatol. 2020, 39, 3171–3175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, C.; Wang, Y.; Li, X.; Ren, L.; Zhao, J.; Hu, Y.; Zhang, L.; Fan, G.; Xu, J.; Gu, X.; et al. Clinical features of patients infected with 2019 novel coronavirus in Wuhan, China. Lancet 2020, 395, 497–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sun, Z.; Zhang, N.; Li, Y.; Xu, X. A systematic review of chest imaging findings in COVID-19. Quant. Imaging Med. Surg. 2020, 10, 1058–1079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nadim, M.K.; Forni, L.G.; Mehta, R.L.; Connor, M.J.; Liu, K.D.; Ostermann, M.; Rimmelé, T.; Zarbock, A.; Bell, S.; Bihorac, A.; et al. COVID-19-associated acute kidney injury: Consensus report of the 25th Acute Disease Quality Initiative (ADQI) Workgroup. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2020, 16, 747–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Small-Vessel Vasculitis (n = 28) | Medium-Vessel Vasculitis (n = 13) | Large-Vessel Vasculitis (n = 5) | RA (n = 6) | SpA (n = 9) | Reactive Arthritis (n = 17) | Inflammatory Myopathies (n = 9) | SLE (n = 6) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age, mean ± SD, years | 49.9 ± 18 | 37.3 ± 13.5 | 64.8 ± 7.9 | 58.8 ± 14.4 | 44.1 ± 13.5 | 50 ± 14.1 | 55.6 ± 11.5 | 39.2 ± 24.7 |
| Male, n (%) | 17 (60.1) | 7 (53.8) | 4 (80) | 3 (50) | 6 (66.6) | 9 (52.9) | 3 (33.3) | 2 (33.3) |
| Geographical distribution | ||||||||
| Europe, n (%) | 10 (35.7) | 6 (46.2) | 3 (60) | 6 (100) | 6 (66.6) | 9 (52.9) | 4 (44.4) | 1 (16.7) |
| Asia, n (%) | 8 (28.6) | 1 (7.7) | 1 (20) | 0 | 2 (22.2) | 6 (35.2) | 2 (22.2) | 1 (16.7) |
| North America, n (%) | 10 (35.7) | 6 (46.2) | 1 (29) | 0 | 1 (11.1) | 2 (11.7) | 3 (33.3) | 2 (33.3) |
| South America, n (%) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Other, n (%) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2 (33.3) |
| COVID-19 severity | ||||||||
| Asymptomatic, n (%) | 2 (8) | 1 (7.7) | 1 (20) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| Mild, n (%) | 6 (24) | 7 (53.8) | 2 (40) | 3 (50) | 7 (77.7) | 11 (64.7) | 1 (11.1) | 0 |
| Moderate, n (%) | 10 (40) | 4 (30.8) | 2 (40) | 1 (16) | 1 (11.1) | 1 (5,8) | 1 (11.1) | 2 (33.3) |
| Severe, n (%) | 4 (16) | 1 (7.7) | 0 | 2 (33.3) | 1 (11.1) | 4 (23.5) | 4 (44.4) | 0 |
| Critical, n (%) | 3 (12) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 (5.8) | 1 (11.1) | 2 (33.3) |
| COVID-19 diagnostic method | ||||||||
| Nasopharyngeal swab (RT-PCR or other method) n (%) | 21 (77.8) | 10 (76.9) | 2 (40) | 2 (66) | 8 (88.8) | 16 (94.1) | 8 (88.8) | 4 (66.7) |
| Serology, n (%) | 3 (11.1) | 3 (23.1) | 3 (60) | 1 (33.3) | 3 (33.3) | 0 | 1 (11.1) | 2 (33.3) |
| Imaging, n (%) | 2 (7.4) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| Epidemiological background, n (%) | 1 (3.7) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| RAD onset at acute phase of COVID-19, n (%) | 11 (44) | 7/12 | 3 (60) | 2 (33.3) | 0 | 1 (5.8) | 6 (66.6) | 4 (66.7) |
| RAD onset after the acute phase of COVID-19, n (%) | 14 (56) | 5 (38.5) | 2 (40) | 4 (66.6) | 9 (100) | 16 (94.1) | 3 (33.3) | 2 (33.3) |
| Days from COVID-19 to ARD onset, mean ± SD, days | 28.2 ± 17.7 | 29.8 ± 8.2 | 44 ± 16 | 25.6 ± 12.6 | 20.7 ± 6.6 | 19 ± 11.4 | 30.1 ± 27 | 24.5 ± 25 |
| COVID-19 outcome | ||||||||
| Resolved, n (%) | 23 (92) | 13 (100) | 5 (100) | 3 (50) | 9 (100) | 16 (94.1) | 8 (88.8) | 4 (66.7) |
| Death, n (%) | 2 (8) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 (5.8) | 1 (11.1) | 2 (33.3) |
| RAD outcome | ||||||||
| Improved or resolved *, n (%) | 21 (87.5) | 12 (100) | 4 (100) | 3 (100) | 7 (77.7) | 16 (94.1) | 8 (88.8)) | 4 (66.7) |
| Death, n (%) | 3 (12.5) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 (6.2) | 1 (11.1) | 2 (33.3) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gracia-Ramos, A.E.; Martin-Nares, E.; Hernández-Molina, G. New Onset of Autoimmune Diseases Following COVID-19 Diagnosis. Cells 2021, 10, 3592. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells10123592
Gracia-Ramos AE, Martin-Nares E, Hernández-Molina G. New Onset of Autoimmune Diseases Following COVID-19 Diagnosis. Cells. 2021; 10(12):3592. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells10123592
Chicago/Turabian StyleGracia-Ramos, Abraham Edgar, Eduardo Martin-Nares, and Gabriela Hernández-Molina. 2021. "New Onset of Autoimmune Diseases Following COVID-19 Diagnosis" Cells 10, no. 12: 3592. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells10123592
APA StyleGracia-Ramos, A. E., Martin-Nares, E., & Hernández-Molina, G. (2021). New Onset of Autoimmune Diseases Following COVID-19 Diagnosis. Cells, 10(12), 3592. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells10123592