Abstract
The epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) contributes to tumor malignancy via gene amplification and protein overexpression. Previously, we developed an anti-human EGFR (hEGFR) monoclonal antibody, namely EMab-134, which detects hEGFR and dog EGFR (dEGFR) with high sensitivity and specificity. In this study, we produced a defucosylated mouse–dog chimeric anti-EGFR monoclonal antibody, namely E134Bf. In vitro analysis revealed that E134Bf highly exerted antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity and complement-dependent cytotoxicity against a canine osteosarcoma cell line (D-17) and a canine fibroblastic cell line (A-72), both of which express endogenous dEGFR. Moreover, in vivo administration of E134Bf significantly suppressed the development of D-17 and A-72 compared with the control dog IgG in mouse xenografts. These results indicate that E134Bf exerts antitumor effects against dEGFR-expressing canine cancers and could be valuable as part of an antibody treatment regimen for dogs.
1. Introduction
The epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) is a member of the receptor tyrosine kinases, which can form homo- or heterodimers with other EGFR family members, including HER2 (ErbB2/neu), HER3 (ErbB3), and HER4 (ErbB4) [1,2]. These dimers promote cell proliferation through the activation of several signaling pathways, such as the PI3K-AKT-mTOR, Ras-Raf-MEK-ERK, and JAK-STAT pathways [3]. EGFR overexpression is observed in various tumors—including lung [4], breast [5], and colorectal carcinomas [6]; glioblastomas [7]; and osteosarcomas [8,9]—and contributes to tumor malignancy by augmenting the aforementioned signaling pathways.
Osteosarcoma is the most common primary bone tumor in dogs and leads to metastasis [10]. Canine osteosarcoma has only a 45% 1-year survival rate, and its incidence is 27 times higher than that in humans [11]. The therapeutic measures for canine osteosarcoma include surgery, radiotherapy, and chemotherapy [12,13]. However, they are not sufficiently effective. Thus, new therapeutic strategies for canine osteosarcoma need to be developed.
By immunizing mice with purified recombinant hEGFR ectodomain (hEGFRec) from cultures of hEGFRec-overexpressed human glioblastoma, LN229, cells, we previously developed a novel anti-human EGFR (hEGFR) monoclonal antibody (mAb), namely EMab-134 [14]. EMab-134 can be used in Western blotting, flow cytometry, and immunohistochemistry. The mouse IgG2a version of EMab-134 (134-mG2a) demonstrates antitumor activities in mouse xenograft models of hEGFR-expressing oral squamous cell carcinoma [15]. In addition, we produced the defucosylated version of 134-mG2a (134-mG2a-f) to augment antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity (ADCC) [16]. The 134-mG2a-f exhibits ADCC and complement-dependent cytotoxicity (CDC) in dog EGFR (dEGFR)-overexpressed CHO-K1 (CHO/dEGFR) cells and antitumor activities in mouse xenograft models of CHO/dEGFR cells [16]. In this study, we investigated the antitumor activities of a defucosylated mouse–dog anti-EGFR mAb (E134Bf) against D-17 and A-72 xenografts, both of which endogenously express dEGFR.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cell Lines
CHO-K1, a canine osteosarcoma cell line (D-17 [17]), and a canine fibroblast cell line (A-72 [18]) were obtained from the American Type Culture Collection (Manassas, VA, USA). CHO/dEGFR was established in our previous study [16]. CHO-K1 and CHO/dEGFR were cultured in RPMI medium (Nacalai Tesque, Inc., Kyoto, Japan), D-17 in Minimum Essential Medium (Nacalai Tesque, Inc., Kyoto, Japan), and A-72 in Dulbecco’s Modified Eagle Medium (DMEM; Nacalai Tesque, Inc., Kyoto, Japan). Those media were supplemented with 10% heat-inactivated fetal bovine serum (FBS; Thermo Fisher Scientific Inc., Waltham, MA, USA), 1 mM of sodium pyruvate, 100 units/mL of penicillin, 100 μg/mL of streptomycin, and 0.25 μg/mL of amphotericin B (Nacalai Tesque, Inc., Kyoto, Japan). The cells were cultured at 37 °C in a humidified atmosphere containing 5% CO2. The negativity for mycoplasma infection was confirmed using the TaKaRa Mycoplasma Detection Set (Takara Bio, Shiga, Japan).
2.2. Animals
All animal experiments were conducted according to relevant guidelines and regulations to minimize animal suffering and distress in the laboratory. Animal experiments for antitumor activity were approved by the Institutional Committee for Experiments of the Institute of Microbial Chemistry (permit No. 2021-021). The mice were maintained in a specific pathogen-free environment (23 ± 2 °C, 55 ± 5% humidity) on an 11 h light/13 h dark cycle with food and water supplied ad libitum throughout the experimental period. In addition, the mice were monitored for health and weight every 2–5 days during the 3-week period for each experiment. We determined the loss of original body weight of more than 25% or a maximum tumor size greater than 3000 mm3 as humane endpoints for euthanasia. The mice were euthanized by cervical dislocation and death was verified by respiratory and cardiac arrest.
2.3. Antibodies
The anti-hEGFR mAb, EMab-134, was developed as previously described [14]. To produce E134B, we subcloned the VH cDNA of EMab-134 and CH cDNA of dog IgGB into the pCAG-Ble vector (FUJIFILM Wako Pure Chemical Corporation, Osaka, Japan), along with the VL cDNA of EMab-134 and CL cDNA of dog kappa light chain into the pCAG-Neo vector (FUJIFILM Wako Pure Chemical Corporation). Two vectors of E134B were transfected into BINDS-09 cells (FUT8-deficient ExpiCHO-S cells) using the ExpiCHO Expression System (Thermo Fisher Scientific Inc., Waltham, MA, USA) [16]. The resulting mAb, E134Bf, was purified with Protein G-Sepharose (GE Healthcare Biosciences, Pittsburgh, PA, USA) [16]. Dog IgG was purchased from Jackson ImmunoResearch Inc. (West Grove, PA, USA).
2.4. Flow Cytometry
The D-17 and A-72 cells (1 × 105 cells/sample) were harvested by brief exposure to 0.25% trypsin in 1 mM ethylenediamine tetraacetic acid (EDTA, Nacalai Tesque, Inc.). After washing with a blocking buffer of 0.1% bovine serum albumin (BSA) in phosphate-buffered saline (PBS), the cells were treated with 1 μg/mL of E134Bf or control blocking buffer for 30 min at 4 °C. The cells were then incubated in FITC-conjugated anti-dog IgG at a dilution of 1:1000 (Thermo Fisher Scientific Inc.) for 30 min at 4 °C. Fluorescence data were collected using 488 nm laser and 525/50 bandpass filter of the EC800 Cell Analyzer (Sony Corp., Tokyo, Japan). No gating was used for the data analysis. All experiments were conducted in triplicate.
2.5. Determination of Binding Affinity
The D-17 and A-72 cells (1 × 105 cells/sample) were suspended in 100 μL of serially diluted E134Bf (0.006–100 μg/mL), followed by FITC-conjugated anti-dog IgG (1:200). Fluorescence data were collected using 488 nm laser and 525/50 bandpass filter of the EC800 Cell Analyzer. No gating was used for the data analysis. All experiments were conducted in triplicate. The dissociation constant (KD) was calculated by fitting the binding isotherms to built-in one-site binding models in GraphPad Prism 8 (GraphPad Software, Inc., La Jolla, CA, USA).
2.6. Immunocytochemistry
The D-17 and A-72 cells (1 × 105 cells/sample) were fixed with 4% paraformaldehyde in PBS for 10 min and quenched with 50 mM NH4Cl in PBS containing 0.2 mM Ca2+ and 2 mM Mg2+ (PBSc/m) for 10 min. The cells were treated with blocking buffer (PBSc/m supplemented with 0.5% BSA) for 30 min and incubated with 10 µg/mL of E134Bf or the control blocking buffer for 1 h. The cells were then incubated with Alexa Fluor 488-conjugated anti-dog IgG (1:400; Jackson ImmunoResearch Laboratories, Inc., West Grove, PA, USA) and DAPI (Thermo Fisher Scientific Inc.) for 45 min. Fluorescence images were obtained using a BZ-X800 digital microscope (Keyence, Osaka, Japan) at a magnification of 40× with a GFP filter channel (green) and a DAPI filter channel (blue). All experiments were conducted in triplicate.
2.7. ADCC
ADCC assay was performed as previously described [16,19,20,21,22,23,24,25,26]. Briefly, canine mononuclear cells derived from dog blood were obtained from Yamaguchi University and resuspended in DMEM with 10% FBS to be used as effector cells. Target cells (D-17 and A-72) were labeled with 10 μg/mL calcein AM (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Inc.) and resuspended in the same medium. The target cells (2 × 104 cells/well) were plated in 96-well plates and mixed with effector cells (effector/target cells ratio, 50:1), 100 μg/mL of E134Bf or the control dog IgG. After 4.5 h of incubation at 37 °C, the release of calcein into the supernatant was measured in each well. The fluorescence intensity was determined using a microplate reader (PowerScan HT; BioTek Instruments, Inc., Winooski, VT, USA) with excitation and emission wavelengths of 485 and 538 nm. Cytolytic activity (% lysis) was calculated as follows: % lysis = (E − S)/(M − S) × 100, where E denotes the fluorescence measured of the combined cultures of the target and effector cells; S, the spontaneous fluorescence of the target cells only; and M, the maximum fluorescence measured following the lysis of all cells with a buffer containing 0.5% Triton X-100, 10 mM Tris-HCl (pH 7.4), and 10 mM EDTA. All experiments were conducted in triplicate.
2.8. CDC
The CDC assay was performed as described previously [27,28,29]. Briefly, D-17 and A-72 cells were labeled with 10 μg/mL calcein AM and resuspended in the medium. They were then plated in 96-well plates at 2 × 104 cells/well with rabbit complement (final dilution 1:10; Low-Tox-M Rabbit Complement; Cedarlane Laboratories, Hornby, ON, Canada) and 100 μg/mL of E134Bf or control dog IgG. After 4 h of incubation at 37 °C, we measured the release of calcein into the supernatant of each well. The fluorescence intensity was calculated as described in Section 2.7. All experiments were conducted in triplicate.
2.9. Influence of E134Bf on EGF-Stimulated Cell Growth
A-72 cells (1 × 104 cells/well) were plated in each well of a 96-well plate. The cells were either left untreated or treated with 1 ng/mL of canine recombinant EGF (SinoBiological Inc., Beijing, China) with or without 20 μg/mL of normal dog IgG or E134Bf (n = 3 in each group). After 36 h of incubation, cell growth was determined using the CellTiter 96 Aqueous One Solution Cell Proliferation Assay Kit (Promega, Madison, WI, USA), according to the manufacturer’s protocol.
2.10. Antitumor Activity of E134Bf in Xenografts of D-17 and A-72 Cells
A total of 16 female BALB/c nude mice (5 weeks old, weighing 14–17 g) were purchased from Charles River Laboratories, Inc (Kanagawa, Japan)., and used in experiments once they reached 7 weeks old. D-17 or A-72 cells (0.3 mL of 1.33 × 108 cells/mL in DMEM) were mixed with 0.5 mL BD Matrigel Matrix Growth Factor Reduced (BD Biosciences, San Jose, CA, USA); 100 μL of this suspension (5 × 106 cells) was subcutaneously injected into the left flank of the mice.
On day 7 post-inoculation, 100 μg of E134Bf (n = 8) or control dog IgG (n = 8) in 100 μL PBS was intraperitoneally injected. Additional antibody inoculations were performed on days 14 and 21. This regimen was selected based on prior studies [15,30]. Canine mononuclear cells, which were obtained from Yamaguchi University, were injected surrounding the tumors on days 7, 14, and 21. At 25 days following cell implantation, all mice were euthanized by cervical dislocation. The tumor diameters and volumes were determined as previously described [16].
2.11. Immunohistochemistry
Immunohistochemistry was conducted as previously described [30]. Briefly, paraffin-embedded xenograft tumor tissues were sectioned and placed on glass microscope slides. After the sections were deparaffinized, they were boiled in buffered sodium citrate solution (0.01 mol/L, pH 6.0) for 10 min and subjected to immunohistochemical staining with anti-Ki-67 antibody (ab15580, 1:1000; Abcam, Cambridge, UK), followed by horseradish peroxidase-conjugated secondary antibody for rabbit IgG for 30 min. Then, the tissues were stained with 3,3′-diaminobenzidine using the ChemMate EnVision Kit (Agilent Technologies, Inc., Santa Clara, CA, USA). The slides were briefly immersed in hematoxylin for counterstaining and then observed under a Nikon Biophot microscope (Nikon, Tokyo, Japan) and photographed using a digital camera (Nikon Digital Sight DS-Ri1, Nikon). The photographs were taken under 400× magnification (Supplementary Figure S3A). Ki-67-positive cells were counted from five randomly selected fields (Supplementary Figure S3B).
2.12. Statistical Analyses
All data are expressed as mean ± standard error of the mean (SEM). Statistical analysis was conducted with Tukey’s test for ADCC and CDC and Welch’s t-test for tumor weight. ANOVA and Sidak’s multiple comparisons tests were conducted for tumor volume and mouse weight. All calculations were performed using GraphPad Prism 8. A p-value of <0.05 was considered statistically significant.
3. Results
3.1. Flow Cytometry Analysis against D-17 and A-17 Cells Using E134Bf
In our previous study, an anti-hEGFR mAb (EMab-134) recognized dEGFR-overexpressed CHO/dEGFR cells, indicating that EMab-134 crossreacts with dEGFR [16]. In this study, we produced a defucosylated mouse–dog chimeric anti-EGFR mAb (E134Bf) by combining the VH and VL of EMab-134 with the CH and CL of dog IgG, respectively (Figure 1). E134Bf also detected canine cell lines, such as D-17 and A-72 cells, although the endogenous dEGFR expression level is lower than that of CHO/dEGFR cells (Figure 2A).
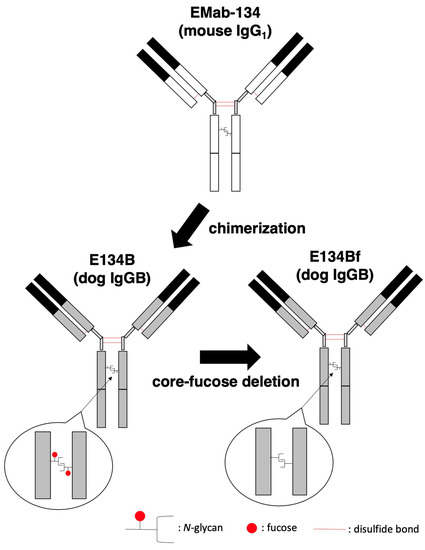
Figure 1.
Production of E134Bf (core-fucose-deficient dog IgGB) from EMab-134 (mouse IgG1).
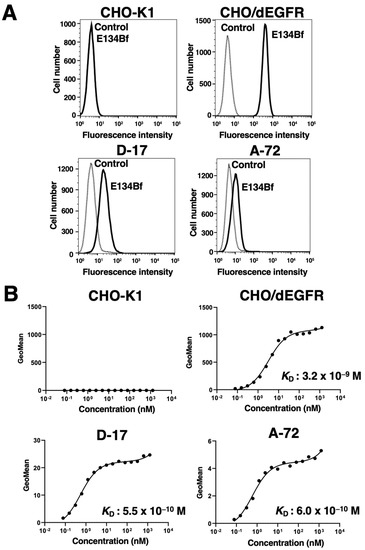
Figure 2.
Flow cytometry using E134Bf. (A) CHO-K1, CHO/dEGFR, D-17, and A-72 cells were treated with E134Bf or buffer control, followed by FITC-conjugated anti-dog IgG. (B) Determination of the binding affinity of E134Bf for CHO-K1, CHO/dEGFR, D-17, and A-72 cells via flow cytometry. The cells were suspended in 100 μL of serially diluted E134Bf, followed by the addition of FITC-conjugated anti-dog IgG. Fluorescence data were collected using the EC800 Cell Analyzer.
Kinetic analysis of the interactions of E134Bf with the D-17 and A-72 cells was conducted via flow cytometry. As presented in Figure 2B, the KD for the interaction of E134Bf with the D-17 and A-72 cells was 5.5 × 10−10 M and 6.0 × 10−10 M, respectively, indicating that E134Bf exhibits high affinity for D-17 and A-72 cells. On the contrary, the KD for the interaction between the E134Bf and CHO/dEGFR cells was 3.2 × 10−9 M, indicating that the binding affinity of E134Bf for endogenous dEGFR in canine cancer cells is higher than that for exogenous dEGFR in CHO/dEGFR. Since dEGFR was not detected in CHO-K1 cells, we could not determine the binding affinity of E134Bf for CHO-K1 cells.
3.2. Immunocytochemistry against the D-17 and A-72 Cells Using E134Bf
Here, we investigated whether E134Bf was applicable for immunocytochemistry. At first, we evaluated the specificity of E134Bf using the CHO-K1 and CHO/dEGFR cells. As a result, E134Bf detected dEGFR on the CHO/dEGFR cells but not the CHO-K1 cells (Figure 3A,B). The buffer control detected no signal for both the CHO-K1 and CHO/dEGFR cells. Next, we examined the binding of E134Bf to endogenous dEGFR on the D-17 and A-72 cells and found that E134Bf specifically detected endogenous dEGFR (Figure 3C,D). These results indicate that E134Bf recognizes endogenous and exogenous dEGFR in immunocytochemistry.
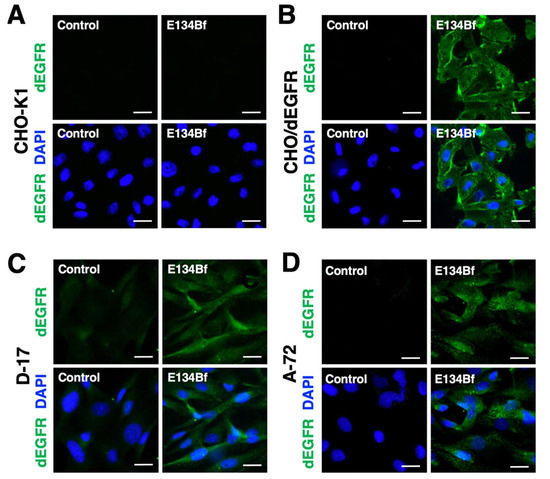
Figure 3.
Immunocytochemistry using E134Bf. CHO-K1 (A), CHO/dEGFR (B), D-17 (C), and A-72 (D) cells were incubated with a buffer control or 10 µg/mL of E134Bf for 1 h, followed by incubation with Alexa Fluor 488-conjugated anti-dog IgG and DAPI for 45 min. Fluorescence images were taken using a fluorescence microscope BZ-X800. Scale bars, 20 µm.
3.3. E134Bf-Mediated ADCC and CDC in the D-17 and A-72 Cells
We investigated whether E134Bf was capable of mediating ADCC against the D-17 and A-72 cells. As presented in Figure 4A, E134Bf showed ADCC (14.0% cytotoxicity) against D-17 cells more effectively than did the control dog IgG (4.7% cytotoxicity; p < 0.05) and the control PBS (4.3% cytotoxicity; p < 0.05). E134Bf also showed ADCC (23.6% cytotoxicity) against A-72 cells more effectively than did the control dog IgG (9.2% cytotoxicity; p < 0.05) and the control PBS (7.4% cytotoxicity; p < 0.05). On the contrary, E134Bf did not show ADCC against CHO-K1 cells, which are EGFR-negative cells (Supplementary Figure S1A).
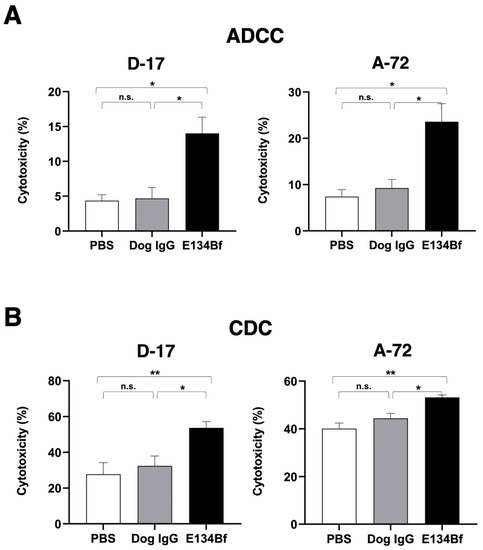
Figure 4.
Evaluation of ADCC and CDC elicited by E134Bf. (A) ADCC elicited by E134Bf, control dog IgG, or control PBS targeting the D-17 and A-72 cells. (B) CDC elicited by E134Bf, control dog IgG, or control PBS targeting the D-17 and A-72 cells. The values are expressed as mean ± SEM. Asterisks indicate statistical significance (** p < 0.01; * p < 0.05; n.s., not significant; Tukey’s post hoc test). ADCC, antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity; CDC, complement-dependent cytotoxicity.
We then investigated whether E134Bf could mediate CDC against D-17 cells. As presented in Figure 4B, E134Bf elicited a higher degree of CDC (53.6% cytotoxicity) in D-17 cells compared with that elicited by the control dog IgG (32.4% cytotoxicity; p < 0.05) and the control PBS (27.7% cytotoxicity; p < 0.01). E134Bf also elicited a higher degree of CDC (53.2% cytotoxicity) in the A-72 cells compared with that elicited by control dog IgG (44.4% cytotoxicity; p < 0.05) and the control PBS (40.0% cytotoxicity; p < 0.01). On the contrary, E134Bf did not show CDC against CHO-K1 (Supplementary Figure S1B). These results indicated that E134Bf promoted significantly higher levels of ADCC and CDC against the dEGFR-expressing D-17 and A-72 cells.
3.4. E134Bf Did Not Inhibit the EGF-Stimulated Cell Growth of A-72
We next determined whether E134Bf could inhibit the EGF-stimulated EGFR activation, which leads to cell growth. As presented in Supplementary Figure S2, we identified A-72 as an EGF-responsive cell line. Although the addition of EGF resulted in cell growth and survival of A-72, E134Bf did not inhibit the cell growth of A-72, similar to the control dog IgG. These results indicated that E134Bf did not inhibit the activation of EGFR in response to EGF stimulation.
3.5. Antitumor Activities of E134Bf in the Mouse Xenografts of D-17 and A-72 Cells
In the D-17 xenograft models, E134Bf (100 μg) and dog IgG (100 μg) were injected intraperitoneally into mice on days 7, 14, and 21, following the injection of the D-17 cells. The tumor volume was measured on days 7, 11, 14, 18, 21, and 25 post-injection. The administration of E134Bf resulted in a significant reduction in tumor development on days 11 (p < 0.05), 14 (p < 0.01), 18 (p < 0.01), 21 (p < 0.01), and 25 (p < 0.01) compared with that of the dog IgG (Figure 5A). The administration of E134Bf resulted in a 37% reduction in tumor volume compared with that of the control dog IgG on day 25 post-injection.
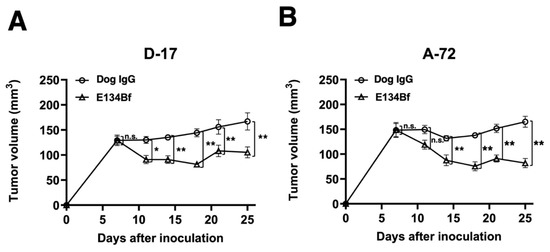
Figure 5.
Evaluation of tumor volume in the D-17 and A-72 xenograft models. (A) D-17 cells (5 × 106 cells) were subcutaneously injected into the left flank. On day 7, 100 μg of E134Bf (n = 8) or control dog IgG (n = 8) in 100 μL PBS was intraperitoneally injected into the mice; additional antibodies were then injected on days 14 and 21. The tumor volume was measured on days 7, 11, 14, 18, 21, and 25 after the injection. (B) The A-72 cells (5 × 106 cells) were subcutaneously injected into the left flank. On day 7, 100 μg of E134Bf (n = 8) or control dog IgG (n = 8) in 100 μL PBS was intraperitoneally injected into the mice; additional antibodies were then injected on days 14 and 21. The tumor volume was measured on days 7, 11, 14, 18, 21, and 25 after the injection. The values are expressed as mean ± SEM. Asterisks indicate statistical significance (** p < 0.01; * p < 0.05; n.s., not significant; ANOVA and Sidak’s multiple comparisons test).
In the A-72 xenograft models, the administration of the antibody treatment and monitoring of the tumor volume were performed the same with the D-17 cells. The administration of E134Bf resulted in a significant reduction in tumor development on days 14 (p < 0.01), 18 (p < 0.01), 21 (p < 0.01), and 25 (p < 0.01) compared with that of the dog IgG (Figure 5B). The administration of E134Bf resulted in a 50% reduction in tumor volume compared with that of the dog IgG on day 25 post-injection.
The tumors of D-17 that were resected from mice on day 25 are presented in Figure 6A. The D-17 tumors from the E134Bf-treated mice weighed significantly less than those from the control dog IgG-treated mice (42% reduction; p < 0.01, Figure 6B). Consistent with these results, Ki-67 staining revealed a markedly reduced proliferation index in E134Bf-treated tumors (Supplementary Figure S3). The A-72 tumors that were resected from mice on day 25 are demonstrated in Figure 6A. The A-72 tumors from the E134Bf-treated mice weighed significantly less than those from the dog IgG-treated mice (42% reduction; p < 0.05, Figure 6B).
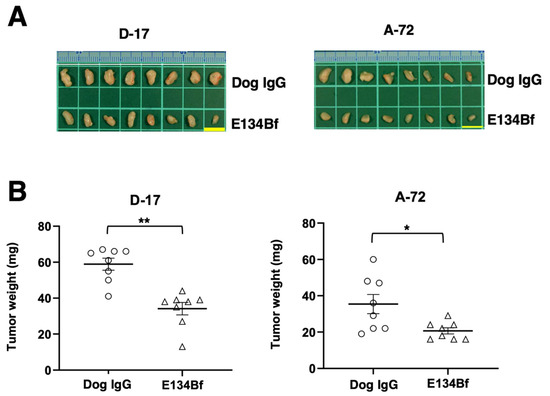
Figure 6.
Evaluation of tumor weight in the D-17 and A-72 xenograft models. The tumors of the D-17 and A-72 xenografts were resected from the control dog IgG and E134Bf groups. (A) Appearance of resected tumors of the D-17 and A-72 xenografts from the control dog IgG and E134Bf groups on day 25. Scale bar, 1 cm. (B) The tumor weight on day 25 was measured from the excised D-17 and A-72 xenografts. The values are expressed as mean ± SEM. Asterisk indicates statistical significance (** p < 0.01, * p < 0.05, Welch’s t-test).
The total body weights of the D-17 xenograft mice did not significantly differ among the two groups (Figure 7A). The body appearance of the D-17 xenograft mice on day 25 is presented in Figure 7B. In the same way, the total body weights of the A-72 xenograft mice did not significantly differ among the two groups (Figure 7A). The body appearance of the A-72 xenograft mice on day 25 is demonstrated in Figure 7B.
Figure 7.
Body weights and appearance of the mice implanted with the D-17 and A-72 xenografts. (A) Body weights of mice implanted with the D-17 and A-72 xenografts were recorded on days 7, 11, 14, 18, 21, and 25 (n.s.: not significant). (B) Body appearance of the D-17 and A-72 xenograft mice on day 25. Scale bar, 1 cm. n.s., not significant.
Taken together, these results indicate that the administration of E134Bf effectively reduced the growth of D-17 and A-72 xenografts.
4. Discussion
Among canine cancers, osteosarcoma is a highly metastatic and intractable cancer, and about 80% of dogs with osteosarcoma die from lung metastases [10,31,32]. Because canine osteosarcoma shares various molecular and clinical similarities with human osteosarcoma, canine osteosarcoma can be used for identifying biomarkers and developing treatments for human osteosarcoma [11]. Therefore, the development of therapeutic strategies for canine osteosarcoma will also improve the clinical response rate of human osteosarcoma. In canine osteosarcoma, surgery is a first-line treatment. Chemotherapy, including carboplatin, cisplatin, and doxorubicin, is also used for adjuvant and/or neoadjuvant therapy [33,34,35,36]. These treatments have been shown to result in longer survival times than amputation alone [37]. Because the toxicity of chemotherapy often causes severe adverse effects, such as vomiting, diarrhea, anorexia, and myelosuppression, which lead to a significant reduction in the canine’s quality of life, it is important to establish a new therapeutic modality.
Canine fibrosarcoma is a malignant, infiltrating, mesenchymal tumor that mainly affects the oral cavity of medium to large dogs [38]. In addition to surgery and radiotherapy, chemotherapy has been used as adjuvant treatment for oral fibrosarcoma. Doxorubicin is the most commonly administered drug in association with surgery and/or radiation. However, the ability to control local disease still represents the major challenge. Recently, the effect of two tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKI), imatinib (BCR-ABL inhibitor) and masitinib (c-KIT and PDGF inhibitor), on canine fibrosarcoma cells was investigated [39]. However, there are no reports on the use of anti-EGFR drugs, including TKI or antibody drugs, for the treatment of canine oral fibrosarcoma.
Antibody therapies are successful against various diseases and generally well tolerated in humans [40]. Original antibody therapies for dogs have not been established for most diseases, including osteosarcoma; therefore, antibody drugs for humans have been used as alternatives. For example, several tumor antigens that have been used for targeted therapies in human cancers are also identified in canine malignancies, including EGFR, HER2, VEGFR2, CD20, podoplanin, PD-1, and PD-L1 [16,41,42,43,44,45,46,47,48,49]. Particularly, the hEGFR and dEGFR amino acid sequences are 91% identical, and some anti-hEGFR mAbs are effective against canine tumors that overexpress dEGFR in vitro and/or in vivo [16,50].
Although it has been reported that the aberrant expression of EGFR in human osteosarcoma is associated with poor response to chemotherapy, distant metastasis, and reduced survival time of patients [51,52], precise information on EGFR expression and its association with clinical features in canine osteosarcoma has not been elucidated. In addition, the prognostic and clinicopathological significance of the EGFR expression of canine osteosarcoma and its relevance to EGFR-targeted drugs have not been fully elucidated. Further exploring these relationships could provide new insights into the efficacy of EGFR-targeted therapies for both humans and dogs.
D-17 is a canine osteosarcoma cell line commonly used for various studies [53,54,55,56,57]. Since the D-17 cells express EGFR [58,59], Mantovani et al. applied an EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitor to suppress D-17 cell proliferation [58]. On the contrary, there has been no study on the application of an anti-EGFR mAb to EGFR-expressing canine osteosarcoma cell lines. In this study, we demonstrated that E134Bf could recognize the endogenous dEGFR of D-17 cells via flow cytometry and immunocytochemistry (Figure 2A and Figure 3). The most critical aim of the present study was to investigate the antitumor activity of E134Bf for endogenous dEGFR-expressing canine tumor cells. E134Bf demonstrated growth inhibition of endogenous dEGFR-expressing D-17 cells without body weight loss and skin abnormality (Figure 5, Figure 6 and Figure 7).
A canine fibroblast cell line, A-72, was established from a tumor surgically removed from a golden retriever and mainly used for virus research [18]. Although the histology of the original tumor has not been identified, the A-72 cells expressed EGFR (Figure 2 and Figure 3), and its growth was promoted by EGF (Supplementary Figure S2). Furthermore, E134Bf could suppress xenograft growth (Figure 5 and Figure 6), most likely through ADCC activity (Figure 4). Furthermore, through immunocytochemistry (Figure 3), the cytosolic dot-like staining of dEGFR was preferentially observed in the A-72 cells, suggesting that the internalized dEGFR abundantly accumulates in the cytoplasm. Previously, we developed the mouse–canine chimeric anti-dog podoplanin mAb P38B, conjugated with emtansine as the payload, which demonstrated an antitumor effect against dog podoplanin -overexpressed cells [60]. It would be interesting to examine the sensitivity of an E134Bf-drug conjugate to the A-72 cells.
These results suggest that E134Bf may be useful for an antibody treatment regimen for dEGFR-expressing canine tumors, which would lead to the establishment of EGFR-targeted immunotherapy. However, this study was limited by the number of canine tumor samples. Future investigations are needed to test the antitumor effects of E134Bf against spontaneously developed canine tumors and its efficacy compared to other caninized monoclonal antibodies.
Supplementary Materials
The following are available online at https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/cells10123599/s1. Figure S1: Evaluation of ADCC and CDC by E134Bf against CHO-K1, EGFR-negative cells elicited., Figure S2: E134Bf did not inhibit the cell growth of A-72 stimulated by EGF., Figure S3: Ki-67 staining in the xenograft tumor tissues.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, M.K. and Y.K.; methodology, M.K.K., T.M., and H.S.; validation, J.T. and H.S.; investigation, G.L., T.O., and M.S.; resources, T.M.; writing, G.L. and T.O.; funding acquisition, Y.K. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was supported in part by Japan Agency for Medical Research and Development (AMED) under grant numbers JP21am0401013 (to Y.K.) and JP21am0101078 (to Y.K.) and by the Japan Society for the Promotion of Science (JSPS) Grants-in-Aid for Scientific Research (KAKENHI) under grant numbers 21K07168 (to M.K.K.) and 19K07705 (to Y.K.).
Institutional Review Board Statement
All animal experiments were carried out in accordance with the guidelines and regulation to minimize animal suffering and distress in the laboratory. Animal experiments for antitumor activity were approved by the Institutional Committee for Experiments of the Institute of Microbial Chemistry (permit No. 2021-021).
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank Akiko Harakawa (Institute of Microbial Chemistry (BIKAKEN), Numazu, Microbial Chemistry Research Foundation) for technical assistance in the animal experiment.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest associated with this manuscript.
References
- Viola, P. The biology of Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor (EGFR) from regulating cell cycle to promoting carcinogenesis: The state of art including treatment options. Ann. Cytol. Pathol. 2020, 5, 048–053. [Google Scholar]
- Lemmon, M.A.; Schlessinger, J.; Ferguson, K.M. The EGFR Family: Not So Prototypical Receptor Tyrosine Kinases. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2014, 6, a020768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wee, P.; Wang, Z. Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor Cell Proliferation Signaling Pathways. Cancers 2017, 9, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bethune, G.; Bethune, D.; Ridgway, N.; Xu, Z. Epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) in lung cancer: An overview and update. J. Thorac. Dis. 2010, 2, 48–51. [Google Scholar]
- Gonzalez-Conchas, G.A.; Rodriguez-Romo, L.; Hernandez-Barajas, D.; Gonzalez-Guerrero, J.F.; Rodriguez-Fernandez, I.A.; Verdines-Perez, A.; Templeton, A.J.; Ocana, A.; Seruga, B.; Tannock, I.F.; et al. Epidermal growth factor receptor overexpression and outcomes in early breast cancer: A systematic review and a meta-analysis. Cancer Treat. Rev. 2018, 62, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spano, J.P.; Fagard, R.; Soria, J.-C.; Rixe, O.; Khayat, D.; Milano, G. Epidermal growth factor receptor signaling in colorectal cancer: Preclinical data and therapeutic perspectives. Ann. Oncol. 2005, 16, 189–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Zong, H.; Ma, C.; Ming, S.; Shang, M.; Hailiang, Z.; He, X.; Du, H.; Cao, L. Epidermal growth factor receptor in glioblastoma. Oncol. Lett. 2017, 14, 512–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, Y.H.; Koeppen, H.; Garcia, R.; Chiriboga, L.; Tarlow, B.; Peters, B.; Eigenbrot, C.; Yee, H.; Steiner, G.; Greco, M.A. Epidermal growth factor receptor in osteosarcoma: Expression and mutational analysis. Hum. Pathol. 2007, 38, 1184–1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kersting, C.; Gebert, C.; Agelopoulos, K.; Schmidt, H.; van Diest, P.J.; Juergens, H.; Winkelmann, W.; Kevric, M.; Gosheger, G.; Brandt, B.; et al. Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor Expression in High-Grade Osteosarcomas Is Associated with a Good Clinical Outcome. Clin. Cancer Res. 2007, 13, 2998–3005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szewczyk, M.; Lechowski, R.; Zabielska, K. What do we know about canine osteosarcoma treatment?—Review. Vet. Res. Commun. 2014, 39, 61–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simpson, S.; Dunning, M.D.; de Brot, S.; Grau-Roma, L.; Mongan, N.P.; Rutland, C.S. Comparative review of human and canine osteosarcoma: Morphology, epidemiology, prognosis, treatment and genetics. Acta Vet. Scand. 2017, 59, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boston, S.E.; Ehrhart, N.P.; Dernell, W.S.; Lafferty, M.; Withrow, S.J. Evaluation of survival time in dogs with stage III osteosarcoma that undergo treatment: 90 cases (1985–2004). J. Am. Vet. Med. Assoc. 2006, 228, 1905–1908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selmic, L.; Burton, J.; Thamm, D.; Withrow, S.; Lana, S. Comparison of Carboplatin and Doxorubicin-Based Chemotherapy Protocols in 470 Dogs after Amputation for Treatment of Appendicular Osteosarcoma. J. Vet. Intern. Med. 2014, 28, 554–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Itai, S.; Yamada, S.; Kaneko, M.K.; Chang, Y.-W.; Harada, H.; Kato, Y. Establishment of EMab-134, a Sensitive and Specific Anti-Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor Monoclonal Antibody for Detecting Squamous Cell Carcinoma Cells of the Oral Cavity. Monoclon. Antibodies Immunodiagn. Immunother. 2017, 36, 272–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosono, H.; Takei, J.; Ohishi, T.; Sano, M.; Asano, T.; Sayama, Y.; Nakamura, T.; Yanaka, M.; Kawada, M.; Harada, H.; et al. Anti-EGFR monoclonal antibody 134-mG2a exerts antitumor effects in mouse xenograft models of oral squamous cell carcinoma. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2020, 46, 1443–1452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tateyama, N.; Nanamiya, R.; Ohishi, T.; Takei, J.; Nakamura, T.; Yanaka, M.; Hosono, H.; Saito, M.; Asano, T.; Tanaka, T.; et al. Defucosylated Anti-Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor Monoclonal Antibody 134-mG2a-f Exerts Antitumor Activities in Mouse Xenograft Models of Dog Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor-Overexpressed Cells. Monoclon. Antibodies Immunodiagn. Immunother. 2021, 40, 177–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riggs, J.L.; McAllister, R.M.; Lennette, E.H. Immunofluorescent Studies of RD-114 Virus Replication in Cell Culture. J. Gen. Virol. 1974, 25, 21–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Binn, L.N.; Marchwicki, R.H.; Stephenson, E.H. Establishment of a canine cell line: Derivation, characterization, and viral spectrum. Am. J. Vet. Res. 1980, 41, 855–860. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Tateyama, N.; Asano, T.; Ohishi, T.; Takei, J.; Hosono, H.; Nanamiya, R.; Tanaka, T.; Sano, M.; Saito, M.; Kawada, M.; et al. An Anti-HER2 Monoclonal Antibody H2Mab-41 Exerts Antitumor Activities in Mouse Xenograft Model Using Dog HER2-Overexpressed Cells. Monoclon. Antibodies Immunodiagn. Immunother. 2021, 40, 184–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asano, T.; Ohishi, T.; Takei, J.; Nakamura, T.; Nanamiya, R.; Hosono, H.; Tanaka, T.; Sano, M.; Harada, H.; Kawada, M.; et al. Anti-HER3 monoclonal antibody exerts antitumor activity in a mouse model of colorectal adenocarcinoma. Oncol. Rep. 2021, 46, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, T.; Ohishi, T.; Asano, T.; Takei, J.; Nanamiya, R.; Hosono, H.; Sano, M.; Harada, H.; Kawada, M.; Kaneko, M.K.; et al. An anti-TROP2 monoclonal antibody TrMab-6 exerts antitumor activity in breast cancer mouse xenograft models. Oncol. Rep. 2021, 46, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosono, H.; Ohishi, T.; Takei, J.; Asano, T.; Sayama, Y.; Kawada, M.; Kaneko, M.K.; Kato, Y. The anti-epithelial cell adhesion molecule (EpCAM) monoclonal antibody EpMab-16 exerts antitumor activity in a mouse model of colorectal adenocarcinoma. Oncol. Lett. 2020, 20, 383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaneko, M.K.; Ohishi, T.; Takei, J.; Sano, M.; Nakamura, T.; Hosono, H.; Yanaka, M.; Asano, T.; Sayama, Y.; Harada, H.; et al. Anti-EpCAM monoclonal antibody exerts antitumor activity against oral squamous cell carcinomas. Oncol. Rep. 2020, 44, 2517–2526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaneko, M.K.; Ohishi, T.; Kawada, M.; Kato, Y. A cancer-specific anti-podocalyxin monoclonal antibody (60-mG2a-f) exerts antitumor effects in mouse xenograft models of pancreatic carcinoma. Biochem. Biophys. Rep. 2020, 24, 100826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaneko, M.K.; Ohishi, T.; Nakamura, T.; Inoue, H.; Takei, J.; Sano, M.; Asano, T.; Sayama, Y.; Hosono, H.; Suzuki, H.; et al. Development of Core-Fucose-Deficient Humanized and Chimeric Anti-Human Podoplanin Antibodies. Monoclon. Antibodies Immunodiagn. Immunother. 2020, 39, 167–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takei, J.; Kaneko, M.K.; Ohishi, T.; Hosono, H.; Nakamura, T.; Yanaka, M.; Sano, M.; Asano, T.; Sayama, Y.; Kawada, M.; et al. A defucosylated anti-CD44 monoclonal antibody 5-mG2a-f exerts antitumor effects in mouse xenograft models of oral squamous cell carcinoma. Oncol. Rep. 2020, 44, 1949–1960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takei, J.; Kaneko, M.K.; Ohishi, T.; Kawada, M.; Harada, H.; Kato, Y. H2Mab-19, an anti-human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 monoclonal antibody exerts antitumor activity in mouse oral cancer xenografts. Exp. Ther. Med. 2020, 20, 846–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takei, J.; Kaneko, M.K.; Ohishi, T.; Kawada, M.; Harada, H.; Kato, Y. A novel anti-EGFR monoclonal antibody (EMab-17) exerts antitumor activity against oral squamous cell carcinomas via antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity and complement-dependent cytotoxicity. Oncol. Lett. 2020, 19, 2809–2816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Itai, S.; Ohishi, T.; Kaneko, M.K.; Yamada, S.; Abe, S.; Nakamura, T.; Yanaka, M.; Chang, Y.-W.; Ohba, S.-I.; Nishioka, Y.; et al. Anti-podocalyxin antibody exerts antitumor effects via antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity in mouse xenograft models of oral squamous cell carcinoma. Oncotarget 2018, 9, 22480–22497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Ohishi, T.; Kato, Y.; Kaneko, M.K.; Ohba, S.-I.; Inoue, H.; Harakawa, A.; Kawada, M. Anti-Metastatic Activity of an Anti-EGFR Monoclonal Antibody against Metastatic Colorectal Cancer with KRAS p.G13D Mutation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 6037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, V.; Evans, K.M.; Sampson, J.; Wood, J.L.N. Methods and mortality results of a health survey of purebred dogs in the UK. J. Small Anim. Pract. 2010, 51, 512–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lewis, T.W.; Wiles, B.M.; Llewellyn-Zaidi, A.M.; Evans, K.M.; O’Neill, D.G. Longevity and mortality in Kennel Club registered dog breeds in the UK in 2014. Canine Genet. Epidemiol. 2018, 5, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phillips, B.; Powers, B.E.; Dernell, W.S.; Straw, R.C.; Khanna, C.; Hogge, G.S.; Vail, D.M. Use of Single-Agent Carboplatin as Adjuvant or Neoadjuvant Therapy in Conjunction With Amputation for Appendicular Osteosarcoma in Dogs. J. Am. Anim. Hosp. Assoc. 2009, 45, 33–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Withrow, S.J.; Thrall, D.E.; Straw, R.C.; Powers, B.E.; Wrigley, R.H.; LaRue, S.M.; Page, R.L.; Richardson, D.C.; Bissonette, K.W.; Betts, C.W.; et al. Intra-arterial cisplatin with or without radiation in limb-sparing for canine osteosarcoma. Cancer 1993, 71, 2484–2490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berg, J.; Weinstein, M.J.; Springfield, D.S.; Rand, W.M. Results of surgery and doxorubicin chemotherapy in dogs with osteosarcoma. J. Am. Vet. Med. Assoc. 1995, 206, 1555–1560. [Google Scholar]
- Saam, D.E.; Liptak, J.; Stalker, M.J.; Chun, R. Predictors of outcome in dogs treated with adjuvant carboplatin for appendicular osteosarcoma: 65 cases (1996–2006). J. Am. Vet. Med. Assoc. 2011, 238, 195–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berg, J. Canine osteosarcoma: Amputation and chemotherapy. Vet. Clin. N. Am. Small Anim. Pract. 1996, 26, 111–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martano, M.; Iussich, S.; Morello, E.; Buracco, P. Canine oral fibrosarcoma: Changes in prognosis over the last 30 years? Vet. J. 2018, 241, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milovancev, M.; Helfand, S.C.; Marley, K.; Goodall, C.P.; Löhr, C.V.; Bracha, S. Antiproliferative effects of masitinib and imatinib against canine oral fibrosarcoma in vitro. BMC Vet. Res. 2016, 12, 85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beckman, R.A.; von Roemeling, R.; Scott, A.M. Monoclonal antibody dose determination and biodistribution into solid tumors. Ther. Deliv. 2011, 2, 333–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabattini, S.; Mancini, F.R.; Marconato, L.; Bacci, B.; Rossi, F.; Vignoli, M.; Bettini, G. EGFR overexpression in canine primary lung cancer: Pathogenetic implications and impact on survival. Vet. Comp. Oncol. 2012, 12, 237–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singer, J.; Fazekas, J.; Wang, W.; Weichselbaumer, M.; Matz, M.; Mader, A.; Steinfellner, W.; Meitz, S.; Mechtcheriakova, D.; Sobanov, Y.; et al. Generation of a Canine Anti-EGFR (ErbB-1) Antibody for Passive Immunotherapy in Dog Cancer Patients. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2014, 13, 1777–1790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Veloso, E.S.; Gonçalves, I.N.N.; Arantes, J.A.; De Abreu, R.V.S.; Cassali, G.D.; Ferreira, E. Quantification of EGFR family in canine mammary ductal carcinomas in situ: Implications on the histological graduation. Vet. Res. Commun. 2019, 43, 123–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Millanta, F.; Silvestri, G.; Vaselli, C.; Citi, S.; Pisani, G.; Lorenzi, D.; Poli, A. The role of vascular endothelial growth factor and its receptor Flk-1/KDR in promoting tumour angiogenesis in feline and canine mammary carcinomas: A preliminary study of autocrine and paracrine loops. Res. Vet. Sci. 2006, 81, 350–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jubala, C.M.; Wojcieszyn, J.W.; Valli, V.E.O.; Getzy, D.M.; Fosmire, S.P.; Coffey, D.; Bellgrau, D.; Modiano, J.F. CD20 Expression in Normal Canine B Cells and in Canine non-Hodgkin Lymphoma. Vet. Pathol. 2005, 42, 468–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mizuno, T.; Kato, Y.; Kaneko, M.K.; Sakai, Y.; Shiga, T.; Kato, M.; Tsukui, T.; Takemoto, H.; Tokimasa, A.; Baba, K.; et al. Generation of a canine anti-canine CD20 antibody for canine lymphoma treatment. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 11476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrasco-Ramirez, P.; Greening, D.W.; Andres, G.; Gopal, S.K.; Martin-Villar, E.; Renart, J.; Simpson, R.J.; Quintanilla, M. Podoplanin is a component of extracellular vesicles that reprograms cell-derived exosomal proteins and modulates lymphatic vessel formation. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 16070–16089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamoto, S.; Shinada, M.; Kato, D.; Yoshimoto, S.; Ikeda, N.; Tsuboi, M.; Yoshitake, R.; Eto, S.; Hashimoto, Y.; Takahashi, Y.; et al. Phase I/II Clinical Trial of the Anti-Podoplanin Monoclonal Antibody Therapy in Dogs with Malignant Melanoma. Cells 2020, 9, 2529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maekawa, N.; Konnai, S.; Okagawa, T.; Nishimori, A.; Ikebuchi, R.; Izumi, Y.; Takagi, S.; Kagawa, Y.; Nakajima, C.; Suzuki, Y.; et al. Immunohistochemical Analysis of PD-L1 Expression in Canine Malignant Cancers and PD-1 Expression on Lymphocytes in Canine Oral Melanoma. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0157176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singer, J.; Weichselbaumer, M.; Stockner, T.; Mechtcheriakova, D.; Sobanov, Y.; Bajna, E.; Wrba, F.; Horvat, R.; Thalhammer, J.G.; Willmann, M.; et al. Comparative oncology: ErbB-1 and ErbB-2 homologues in canine cancer are susceptible to cetuximab and trastuzumab targeting. Mol. Immunol. 2012, 50, 200–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Zhong, G.; Wang, X.-X.; Yu, F.; Weng, D.; Lin, J. Prognostic significance of the expression of HER family members in primary osteosarcoma. Oncol. Lett. 2018, 16, 2185–2194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Z.; Wang, S.-L.; Chen, H.; Shen, R.-K.; Li, X.-D.; Huang, Q.-S.; Wu, C.-Y.; Weng, D.-F.; Lin, J.-H. Clinicopathological and prognostic values of ErbB receptor family amplification in primary osteosarcoma. Scand. J. Clin. Lab. Investig. 2019, 79, 601–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gentschev, I.; Patil, S.S.; Adelfinger, M.; Weibel, S.; Geissinger, U.; Frentzen, A.; Chen, N.G.; Yu, Y.A.; Zhang, Q.; Ogilvie, G.; et al. Characterization and evaluation of a new oncolytic Vaccinia Virus strain LIVP6.1.1 for canine cancer therapy. Bioengineered 2013, 4, 84–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, H.; Park, S.; Bazer, F.W.; Lim, W.; Song, G. Myricetin treatment induces apoptosis in canine osteosarcoma cells by inducing DNA fragmentation, disrupting redox homeostasis, and mediating loss of mitochondrial membrane potential. J. Cell. Physiol. 2018, 233, 7457–7466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, R.; Thamm, D.H.; Misra, V. The effect of Zhangfei/CREBZF on cell growth, differentiation, apoptosis, migration, and the unfolded protein response in several canine osteosarcoma cell lines. BMC Vet. Res. 2015, 11, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Massimini, M.; Palmieri, C.; De Maria, R.; Romanucci, M.; Malatesta, D.; DE Martinis, M.; Maniscalco, L.; Ciccarelli, A.; Ginaldi, L.; Buracco, P.; et al. 17-AAG and Apoptosis, Autophagy, and Mitophagy in Canine Osteosarcoma Cell Lines. Vet. Pathol. 2016, 54, 405–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gebhard, C.; Miller, I.; Hummel, K.; Ondrovics, M.N.N.; Schlosser, S.; Walter, I. Comparative proteome analysis of monolayer and spheroid culture of canine osteosarcoma cells. J. Proteom. 2018, 177, 124–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mantovani, F.B.; Morrison, J.A.; Mutsaers, A.J. Effects of epidermal growth factor receptor kinase inhibition on radiation response in canine osteosarcoma cells. BMC Vet. Res. 2016, 12, 82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selvarajah, G.T.; Verheije, M.H.; Kik, M.; Slob, A.; Rottier, P.J.; Mol, J.A.; Kirpensteijn, J. Expression of epidermal growth factor receptor in canine osteosarcoma: Association with clinicopathological parameters and prognosis. Vet. J. 2012, 193, 412–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kato, Y.; Ito, Y.; Ohishi, T.; Kawada, M.; Nakamura, T.; Sayama, Y.; Sano, M.; Asano, T.; Yanaka, M.; Okamoto, S.; et al. Antibody–Drug Conjugates Using Mouse–Canine Chimeric Anti-Dog Podoplanin Antibody Exerts Antitumor Activity in a Mouse Xenograft Model. Monoclon. Antibodies Immunodiagn. Immunother. 2020, 39, 37–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).