Protein Kinase A-Mediated Septin7 Phosphorylation Disrupts Septin Filaments and Ciliogenesis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. DNA Constructs, Cell Culture, and Transfection
2.2. Immunoprecipitation Assay and Western Blot Analysis
2.3. Immunofluorescence
2.4. ClustalW multiple Sequence Alignment
2.5. Examining Primary Cilia Formation
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Conservation of the SEPT7 Phosphorylation Site among Species
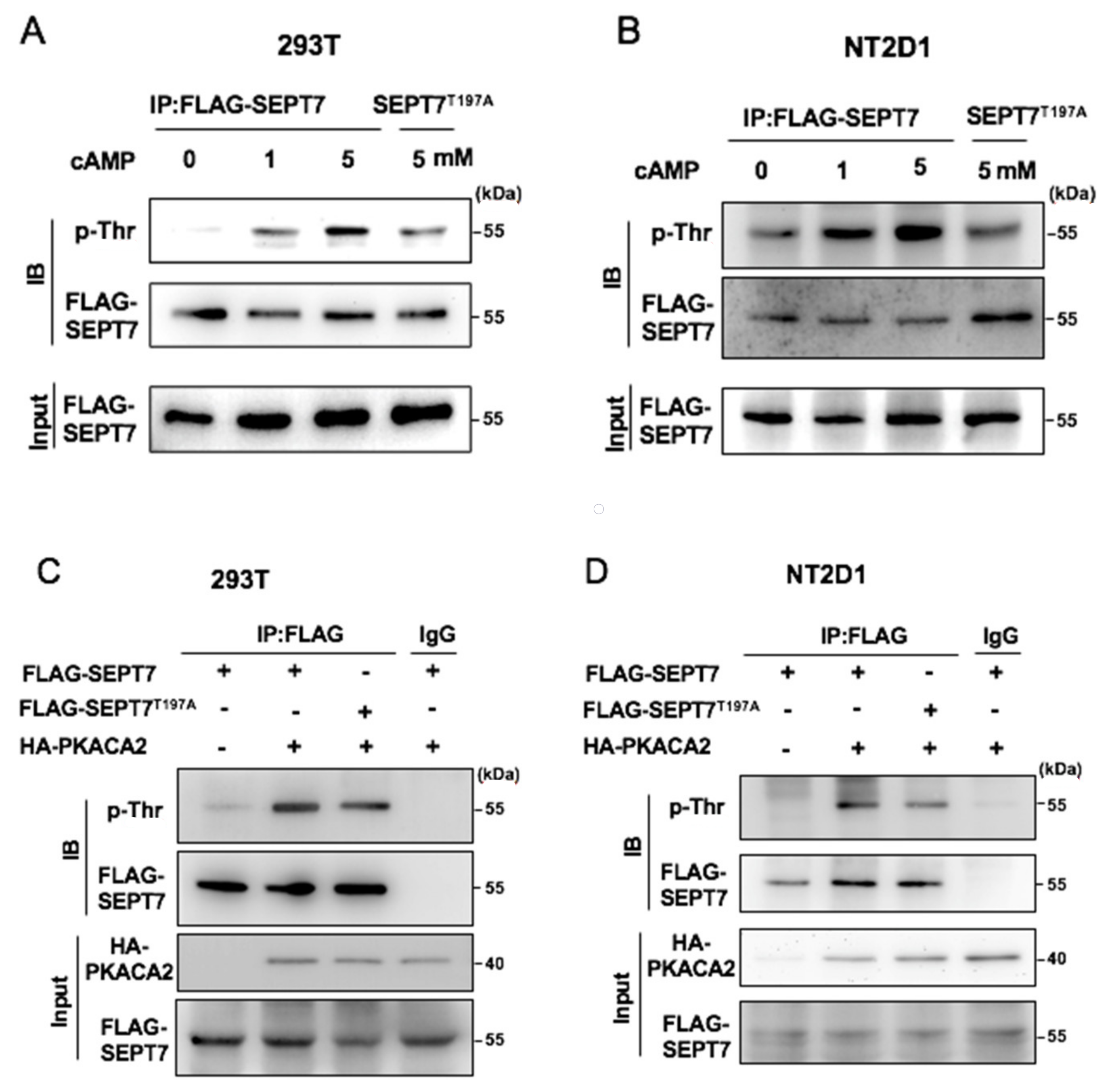
3.2. SEPT7 Is Phosphorylated by PKA
3.3. SEPT7 Interacts with PKA via the GTP-Binding Domain
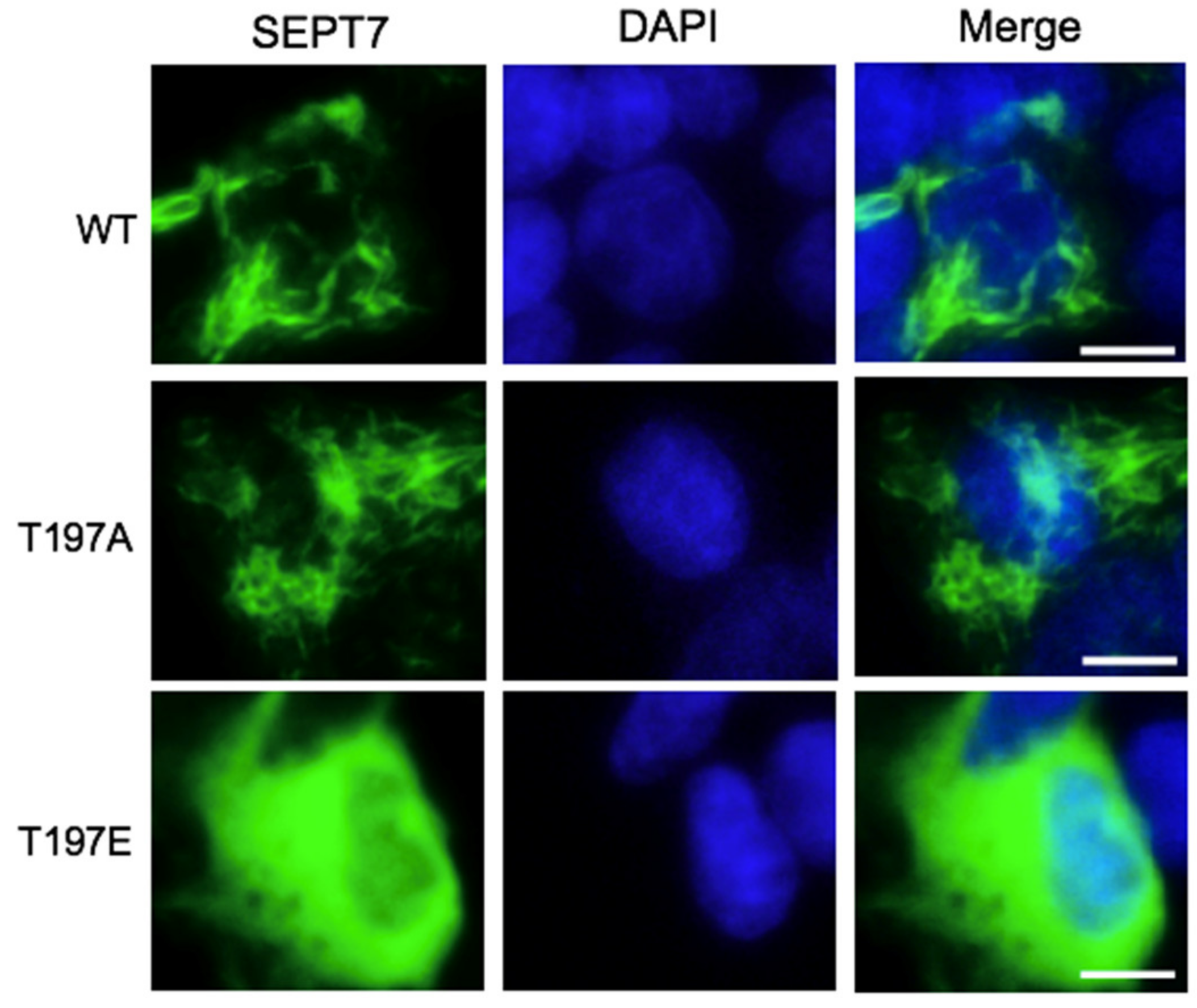
3.4. SEPT7 Phosphorylation Disrupts Septin Filament Formation
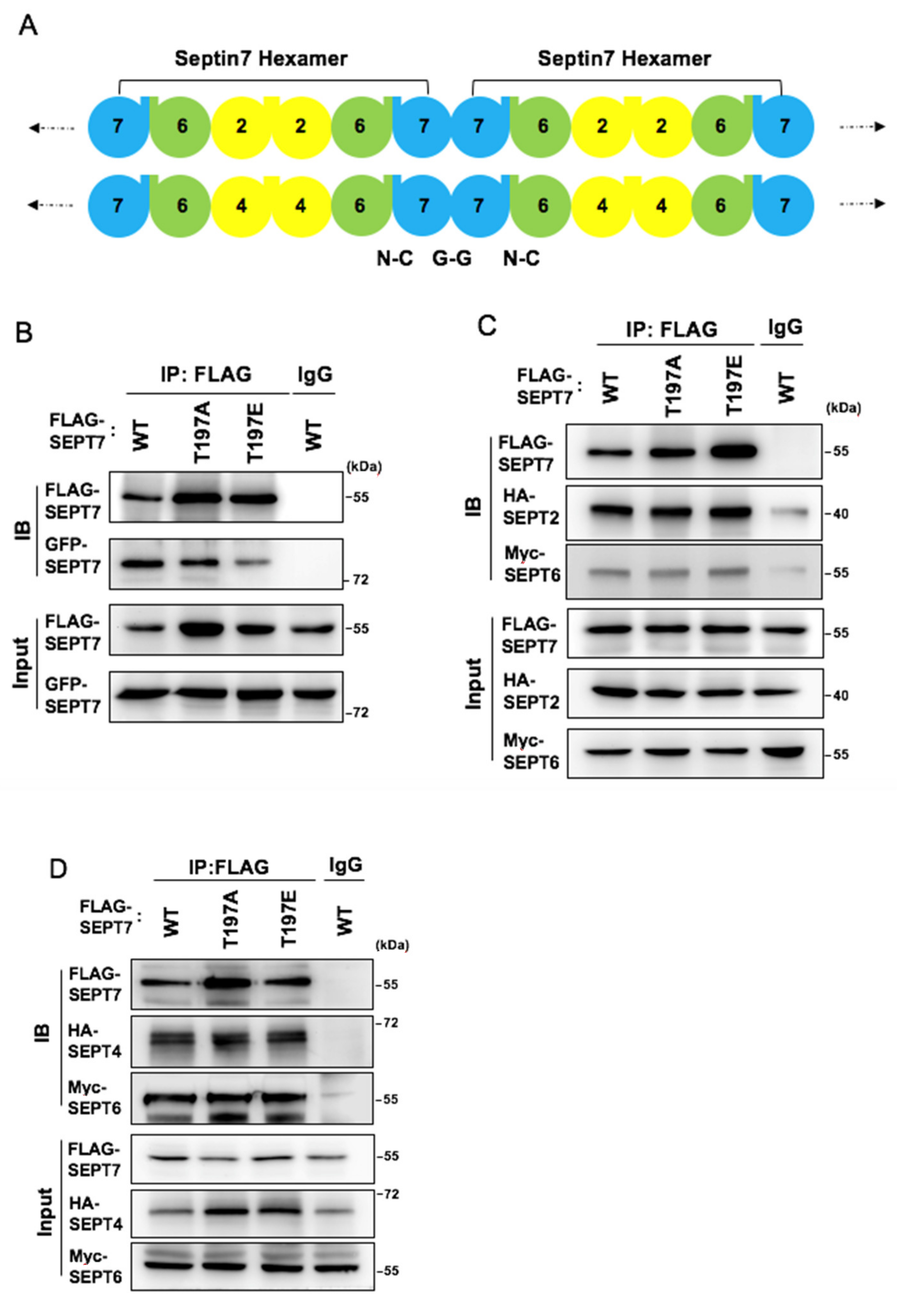
3.5. SEPT7 Phosphorylation Disrupts SEPT7‒SEPT7 Interaction
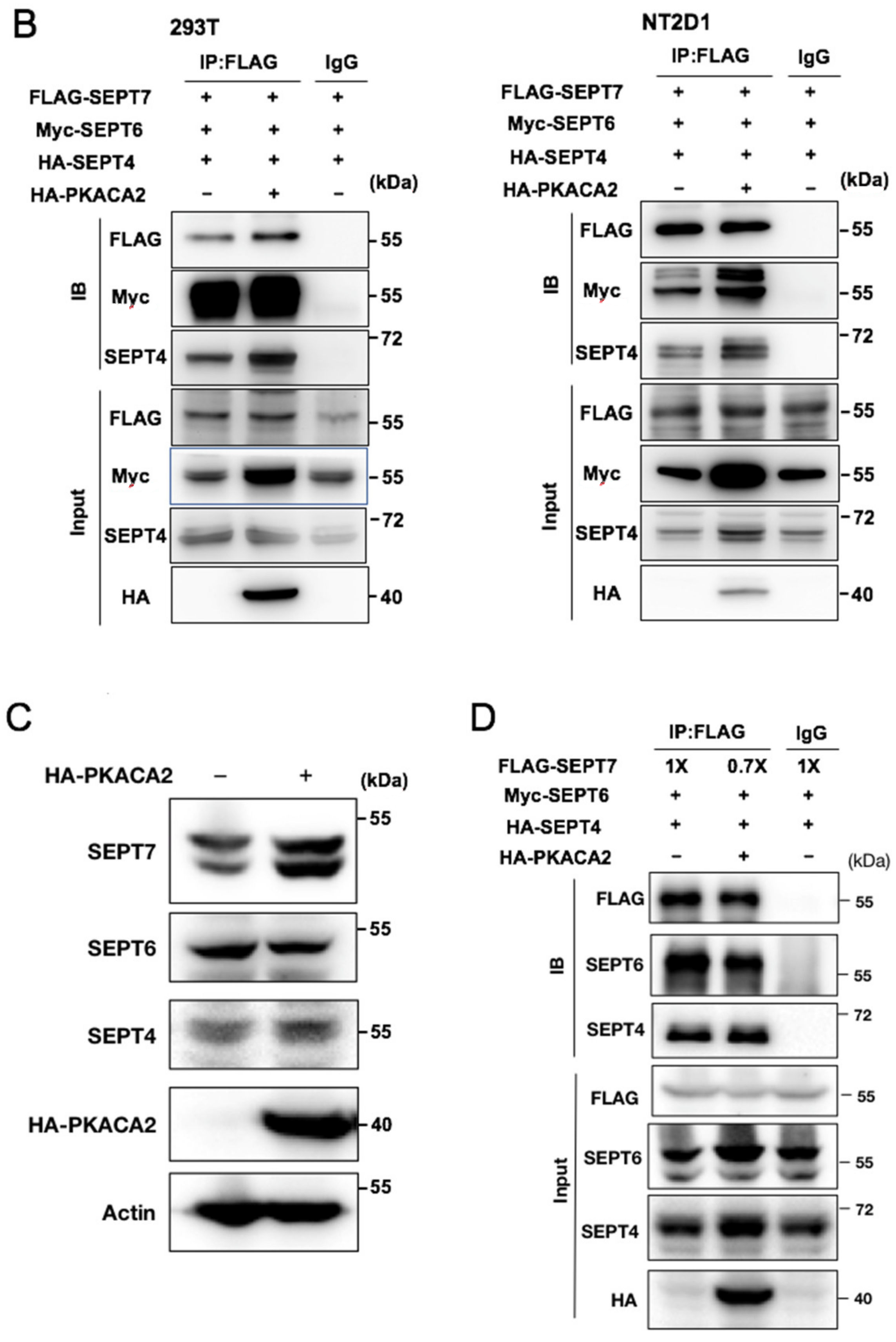
3.6. Overexpression of PKA Disrupts SEPT7‒SEPT7 Interaction
3.7. PKA-Mediated SEPT7 Phosphorylation Affected Ciliogenesis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Abbey, M.; Hakim, C.; Anand, R.; Lafera, J.; Schambach, A.; Kispert, A.; Taft, M.H.; Kaever, V.; Kotlyarov, A.; Gaestel, M.; et al. GTPase domain driven dimerization of SEPT7 is dispensable for the critical role of septins in fibroblast cytokinesis. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 20007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kremer, B.E.; Adang, L.A.; Macara, I.G. Septins regulate actin organization and cell-cycle arrest through nuclear accumulation of NCK mediated by SOCS7. Cell 2007, 130, 837–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, Y.H.; Kuo, Y.C.; Chiang, H.S.; Kuo, P.L. The role of the septin family in spermiogenesis. Spermatogenesis 2011, 1, 298–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boubakar, L.; Falk, J.; Ducuing, H.; Thoinet, K.; Reynaud, F.; Derrington, E.; Castellani, V. Molecular Memory of Morphologies by Septins during Neuron Generation Allows Early Polarity Inheritance. Neuron 2017, 95, 834–851.e835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palander, O.; El-Zeiry, M.; Trimble, W.S. Uncovering the Roles of Septins in Cilia. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2017, 5, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gilden, J.; Krummel, M.F. Control of cortical rigidity by the cytoskeleton: Emerging roles for septins. Cytoskeleton 2010, 67, 477–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kinoshita, M. Assembly of mammalian septins. J. Biochem. 2003, 134, 491–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mostowy, S.; Cossart, P. Septins: The fourth component of the cytoskeleton. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2012, 13, 183–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, L.; Ding, X.; Yu, W.; Yang, X.; Shen, S.; Yu, L. Phylogenetic and evolutionary analysis of the septin protein family in metazoan. FEBS Lett. 2007, 581, 5526–5532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dolat, L.; Hu, Q.; Spiliotis, E.T. Septin functions in organ system physiology and pathology. Biol. Chem. 2014, 395, 123–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menon, M.B.; Sawada, A.; Chaturvedi, A.; Mishra, P.; Schuster-Gossler, K.; Galla, M.; Schambach, A.; Gossler, A.; Förster, R.; Heuser, M.; et al. Genetic deletion of SEPT7 reveals a cell type-specific role of septins in microtubule destabilization for the completion of cytokinesis. PLoS Genet. 2014, 10, e1004558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.; Ou, X.H.; Wei, L.; Wang, Z.B.; Zhang, Q.H.; Ouyang, Y.C.; Hou, Y.; Schatten, H.; Sun, Q.Y. Septin 7 is required for orderly meiosis in mouse oocytes. Cell Cycle 2012, 11, 3211–3218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.; Vessey, J.P.; Konecna, A.; Dahm, R.; Macchi, P.; Kiebler, M.A. The GTP-binding protein Septin 7 is critical for dendrite branching and dendritic-spine morphology. Curr. Biol. 2007, 17, 1746–1751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sirajuddin, M.; Farkasovsky, M.; Hauer, F.; Kühlmann, D.; Macara, I.G.; Weyand, M.; Stark, H.; Wittinghofer, A. Structural insight into filament formation by mammalian septins. Nature 2007, 449, 311–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koch, S.; Acebron, S.P.; Herbst, J.; Hatiboglu, G.; Niehrs, C. Post-transcriptional Wnt Signaling Governs Epididymal Sperm Maturation. Cell 2015, 163, 1225–1236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sitz, J.H.; Baumgärtel, K.; Hämmerle, B.; Papadopoulos, C.; Hekerman, P.; Tejedor, F.J.; Becker, W.; Lutz, B. The Down syndrome candidate dual-specificity tyrosine phosphorylation-regulated kinase 1A phosphorylates the neurodegeneration-related septin 4. Neuroscience 2008, 157, 596–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, J.; Wang, X.; Malladi, C.S.; Kinoshita, M.; Milburn, P.J.; Lengyel, I.; Rostas, J.A.; Robinson, P.J. Phosphorylation of a new brain-specific septin, G-septin, by cGMP-dependent protein kinase. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 10047–10056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Estey, M.P.; Di Ciano-Oliveira, C.; Froese, C.D.; Fung, K.Y.; Steels, J.D.; Litchfield, D.W.; Trimble, W.S. Mitotic regulation of SEPT9 protein by cyclin-dependent kinase 1 (Cdk1) and Pin1 protein is important for the completion of cytokinesis. J. Biol. Chem. 2013, 288, 30075–30086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hildebrandt, F.; Benzing, T.; Katsanis, N. Ciliopathies. N. Engl. J. Med. 2011, 364, 1533–1543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fliegauf, M.; Kahle, A.; Häffner, K.; Zieger, B. Distinct localization of septin proteins to ciliary sub-compartments in airway epithelial cells. Biol. Chem. 2014, 395, 151–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghossoub, R.; Hu, Q.; Failler, M.; Rouyez, M.C.; Spitzbarth, B.; Mostowy, S.; Wolfrum, U.; Saunier, S.; Cossart, P.; Jamesnelson, W.; et al. Septins 2, 7 and 9 and MAP4 colocalize along the axoneme in the primary cilium and control ciliary length. J. Cell Sci. 2013, 126, 2583–2594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Q.; Milenkovic, L.; Jin, H.; Scott, M.P.; Nachury, M.V.; Spiliotis, E.T.; Nelson, W.J. A septin diffusion barrier at the base of the primary cilium maintains ciliary membrane protein distribution. Science 2010, 329, 436–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.K.; Shindo, A.; Park, T.J.; Oh, E.C.; Ghosh, S.; Gray, R.S.; Lewis, R.A.; Johnson, C.A.; Attie-Bittach, T.; Katsanis, N.; et al. Planar cell polarity acts through septins to control collective cell movement and ciliogenesis. Science 2010, 329, 1337–1340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keeling, J.; Tsiokas, L.; Maskey, D. Cellular Mechanisms of Ciliary Length Control. Cells 2016, 5, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Avasthi, P.; Marshall, W.F. Stages of ciliogenesis and regulation of ciliary length. Differ. Res. Biol. Divers. 2012, 83, S30–S42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tilley, A.E.; Walters, M.S.; Shaykhiev, R.; Crystal, R.G. Cilia dysfunction in lung disease. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 2015, 77, 379–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuo, Y.C.; Shen, Y.R.; Chen, H.I.; Lin, Y.H.; Wang, Y.Y.; Chen, Y.R.; Wang, C.Y.; Kuo, P.L. SEPT12 orchestrates the formation of mammalian sperm annulus by organizing core octameric complexes with other SEPT proteins. J. Cell Sci. 2015, 128, 923–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, Y.R.; Wang, H.Y.; Kuo, Y.C.; Shih, S.C.; Hsu, C.H.; Chen, Y.R.; Wu, S.R.; Wang, C.Y.; Kuo, P.L. SEPT12 phosphorylation results in loss of the septin ring/sperm annulus, defective sperm motility and poor male fertility. PLoS Genet. 2017, 13, e1006631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, Z.; Lin, M.G.; Stowe, T.R.; Chen, S.; Zhu, M.; Stearns, T.; Franco, B.; Zhong, Q. Autophagy promotes primary ciliogenesis by removing OFD1 from centriolar satellites. Nature 2013, 502, 254–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia, G., 3rd; Bertin, A.; Li, Z.; Song, Y.; McMurray, M.A.; Thorner, J.; Nogales, E. Subunit-dependent modulation of septin assembly: Budding yeast septin Shs1 promotes ring and gauze formation. J. Cell Biol. 2011, 195, 993–1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chih, B.; Liu, P.; Chinn, Y.; Chalouni, C.; Komuves, L.G.; Hass, P.E.; Sandoval, W.; Peterson, A.S. A ciliopathy complex at the transition zone protects the cilia as a privileged membrane domain. Nat. Cell Biol. 2011, 14, 61–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwitny, S.; Klaus, A.V.; Hunnicutt, G.R. The annulus of the mouse sperm tail is required to establish a membrane diffusion barrier that is engaged during the late steps of spermiogenesis. Biol. Reprod. 2010, 82, 669–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowen, J.R.; Hwang, D.; Bai, X.; Roy, D.; Spiliotis, E.T. Septin GTPases spatially guide microtubule organization and plus end dynamics in polarizing epithelia. J. Cell Biol. 2011, 194, 187–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagata, K.; Kawajiri, A.; Matsui, S.; Takagishi, M.; Shiromizu, T.; Saitoh, N.; Izawa, I.; Kiyono, T.; Itoh, T.J.; Hotani, H.; et al. Filament formation of MSF-A, a mammalian septin, in human mammary epithelial cells depends on interactions with microtubules. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 18538–18543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Estey, M.P.; Di Ciano-Oliveira, C.; Froese, C.D.; Bejide, M.T.; Trimble, W.S. Distinct roles of septins in cytokinesis: SEPT9 mediates midbody abscission. J. Cell Biol. 2010, 191, 741–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Founounou, N.; Loyer, N.; Le Borgne, R. Septins regulate the contractility of the actomyosin ring to enable adherens junction remodeling during cytokinesis of epithelial cells. Dev. Cell 2013, 24, 242–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joo, E.; Tsang, C.W.; Trimble, W.S. Septins: Traffic control at the cytokinesis intersection. Traffic 2005, 6, 626–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ewers, H.; Tada, T.; Petersen, J.D.; Racz, B.; Sheng, M.; Choquet, D. A Septin-Dependent Diffusion Barrier at Dendritic Spine Necks. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e113916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caudron, F.; Barral, Y. Septins and the lateral compartmentalization of eukaryotic membranes. Dev. Cell 2009, 16, 493–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]





Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, H.-Y.; Lin, C.-H.; Shen, Y.-R.; Chen, T.-Y.; Wang, C.-Y.; Kuo, P.-L. Protein Kinase A-Mediated Septin7 Phosphorylation Disrupts Septin Filaments and Ciliogenesis. Cells 2021, 10, 361. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells10020361
Wang H-Y, Lin C-H, Shen Y-R, Chen T-Y, Wang C-Y, Kuo P-L. Protein Kinase A-Mediated Septin7 Phosphorylation Disrupts Septin Filaments and Ciliogenesis. Cells. 2021; 10(2):361. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells10020361
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Han-Yu, Chun-Hsiang Lin, Yi-Ru Shen, Ting-Yu Chen, Chia-Yih Wang, and Pao-Lin Kuo. 2021. "Protein Kinase A-Mediated Septin7 Phosphorylation Disrupts Septin Filaments and Ciliogenesis" Cells 10, no. 2: 361. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells10020361
APA StyleWang, H.-Y., Lin, C.-H., Shen, Y.-R., Chen, T.-Y., Wang, C.-Y., & Kuo, P.-L. (2021). Protein Kinase A-Mediated Septin7 Phosphorylation Disrupts Septin Filaments and Ciliogenesis. Cells, 10(2), 361. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells10020361





