Cardiac Dysfunction in Rheumatoid Arthritis: The Role of Inflammation
Abstract
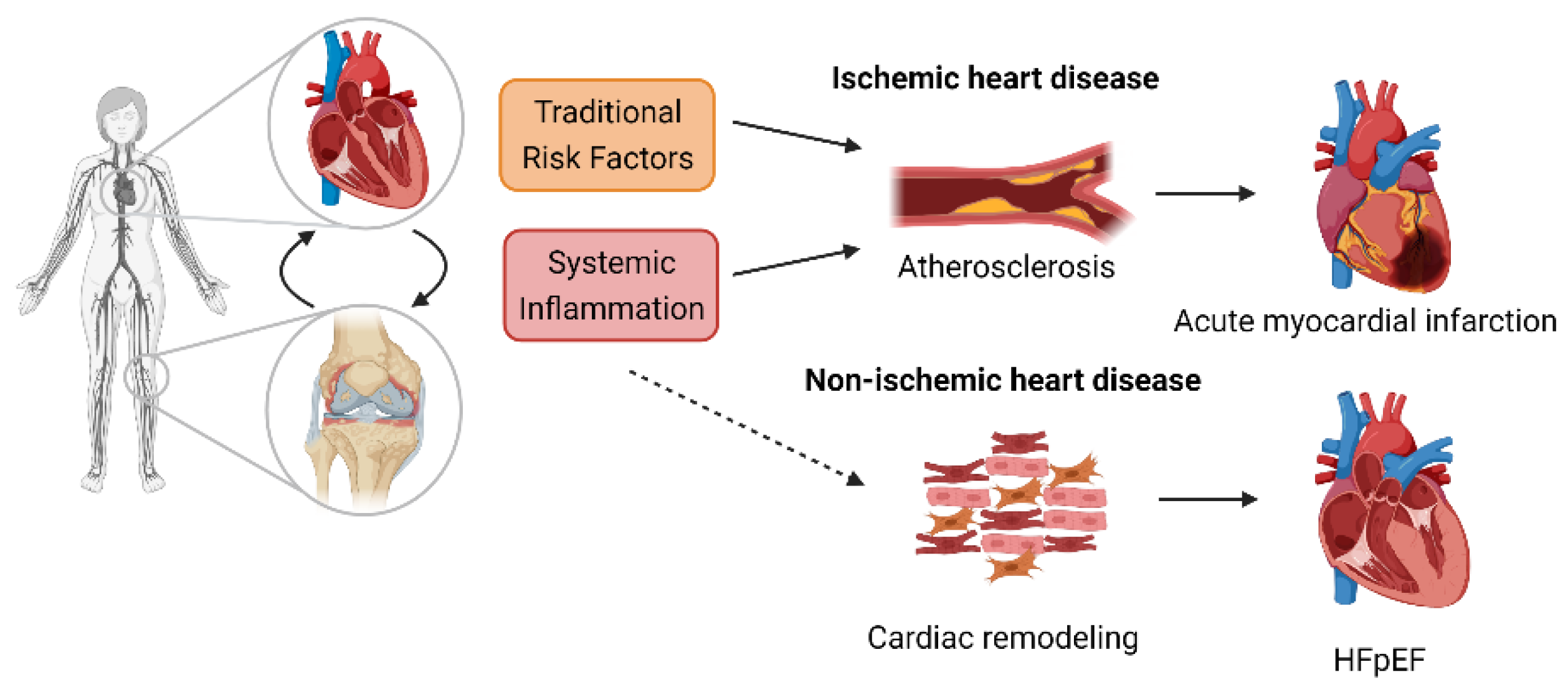
:1. Cardiovascular Disease in Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA): Impact on the RA Population
2. Inflammation: The Link between RA and CVD
2.1. Ischemic Heart Disease
2.2. Cardiac Dysfunction/CHF
3. CVD Risk Factors in the RA Population
Inflammation as a CV Risk Factor
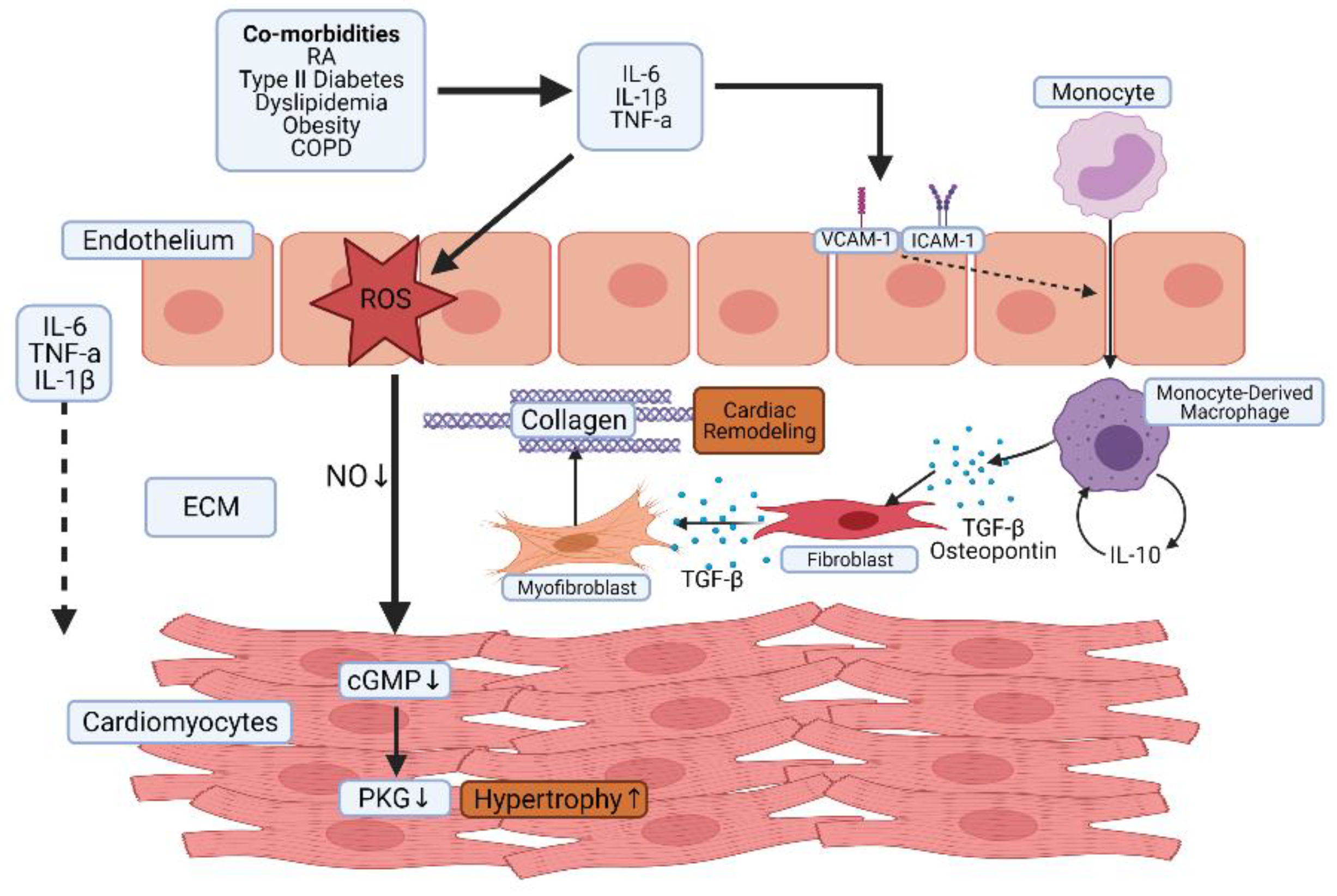
4. The Role of Inflammation in Heart Failure
5. Effect of Current RA Therapies on CVD
5.1. Synthetic DMARDs
5.2. Biological DMARDs
5.3. Nonsteroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs) and Corticosteroids
6. Is the Heightened Cardiovascular Risk a Result of Failed Resolution Pathways?
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ACR | American College of Rheumatology |
| ADMA | asymmetric dimethylarginine |
| AMI | acute myocardial infarction |
| AnxA1 | annexinA1 |
| bDMARDs | biological DMARDs |
| CANTOS | canakinumab anti-inflammatory outcome study |
| cGMP | cyclic guanosine monophosphate |
| CHF | congestive heart failure |
| CIRT | cardiovascular inflammation reduction trial |
| COMORA | comorbidities in rheumatoid arthritis |
| CORRONA | Consortium of Rheumatology Researchers of North America |
| COX-2 | cyclooxygenase-2 |
| CRP | C-reactive protein |
| csDMARDs | conventional synthetic DMARDs |
| CVD | cardiovascular disease |
| CIRT | cardiovascular inflammation reduction trial |
| DMARDs | disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs |
| eNOS | endothelial nitric oxide synthase |
| ESR | erythrocyte sedimentation rate |
| EULAR | European League Against Rheumatism |
| FPR2 | N-formyl peptide receptor 2 |
| GPCR | G protein-coupled receptor |
| HDL | high-density lipoprotein |
| HFpEF | HF with preserved ejection fraction |
| HFrEF | HF with reduced ejection fraction |
| ICAM-1 | intercellular adhesion molecule-1 |
| IL | interleukin |
| iNOS | inducible nitric oxide synthase |
| Jak | Janus kinase |
| LDL-C | low-density lipoprotein cholesterol |
| LPS | lipopolysaccharide |
| LX | lipoxin |
| MACE | major adverse cardiac events |
| MCTR1 | maresin conjugates in tissue regeneration 1 |
| MHCII | major histocompatibility complex class II |
| MI | myocardial infarction |
| MTX | methotrexate |
| NO | nitric oxide |
| NSAIDs | nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs |
| NT-proBNP | N-terminal probrain natriuretic peptide |
| PKG | protein kinase G |
| PRECISION | Prospective Randomized Evaluation of Celecoxib Integrated Safety versus Ibuprofen or Naproxen |
| RA | rheumatoid arthritis |
| RvD3 | resolvin D3 |
| RvT | 13-series resolvins |
| SPMs | specialised pro-resolving mediators |
| TGF | transforming growth factor |
| TNF | tumour necrosis factor |
| tsDMARDs | targeted synthetic DMARDs |
References
- Smolen, J.S.; Aletaha, D.; Barton, A.; Burmester, G.R.; Emery, P.; Firestein, G.S.; Kavanaugh, A.; McInnes, I.B.; Solomon, D.H.; Strand, V.; et al. Rheumatoid arthritis. Nat. Rev. Dis. Prim. 2018, 4, 18001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dadoun, S.; Zeboulon-Ktorza, N.; Combescure, C.; Elhai, M.; Rozenberg, S.; Gossec, L.; Fautrel, B. Mortality in rheumatoid arthritis over the last fifty years: Systematic review and meta-analysis. Jt. Bone Spine 2013, 80, 29–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lassere, M.N.; Rappo, J.; Portek, I.J.; Sturgess, A.; Edmonds, J.P. How many life years are lost in patients with rheumatoid arthritis? Secular cause-specific and all-cause mortality in rheumatoid arthritis, and their predictors in a long-term Australian cohort study. Intern. Med. J. 2013, 43, 66–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van den Hoek, J.; Boshuizen, H.C.; Roorda, L.D.; Tijhuis, G.J.; Nurmohamed, M.T.; van den Bos, G.A.M.; Dekker, J. Mortality in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: A 15-year prospective cohort study. Rheumatol. Int. 2017, 37, 487–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Piepoli, M.F.; Hoes, A.W.; Agewall, S.; Albus, C.; Brotons, C.; Catapano, A.L.; Cooney, M.T.; Corra, U.; Cosyns, B.; Deaton, C.; et al. 2016 European Guidelines on cardiovascular disease prevention in clinical practice: The Sixth Joint Task Force of the European Society of Cardiology and Other Societies on Cardiovascular Disease Prevention in Clinical Practice (constituted by representatives of 10 societies and by invited experts)Developed with the special contribution of the European Association for Cardiovascular Prevention & Rehabilitation (EACPR). Eur. Heart J. 2016, 37, 2315–2381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agca, R.; Heslinga, S.C.; Rollefstad, S.; Heslinga, M.; McInnes, I.B.; Peters, M.J.L.; Kvien, T.K.; Dougados, M.; Radner, H.; Atzeni, F.; et al. EULAR recommendations for cardiovascular disease risk management in patients with rheumatoid arthritis and other forms of inflammatory joint disorders: 2015/2016 update. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2017, 76, 17–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Combe, B.; Landewe, R.; Daien, C.I.; Hua, C.; Aletaha, D.; Álvaro-Gracia, J.M.; Bakkers, M.; Brodin, N.; Burmester, G.R.; Codreanu, C.; et al. 2016 update of the EULAR recommendations for the management of early arthritis. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2017, 76, 948–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Provan, S.A.; Lillegraven, S.; Sexton, J.; Angel, K.; Austad, C.; Haavardsholm, E.A.; Kvien, T.K.; Uhlig, T. Trends in all-cause and cardiovascular mortality in patients with incident rheumatoid arthritis: A 20-year follow-up matched case-cohort study. Rheumatology 2019, 59, 505–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lacaille, D.; Avina-Zubieta, J.A.; Sayre, E.C.; Abrahamowicz, M. Improvement in 5-year mortality in incident rheumatoid arthritis compared with the general population—closing the mortality gap. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2017, 76, 1057–1063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Myasoedova, E.; Davis, J.M.; Roger, V.L.; Achenbach, S.J.; Crowson, C.S. Improved Incidence of Cardiovascular Disease in Patients with Incident Rheumatoid Arthritis in the 2000s: A Population-Based Cohort Study. J. Rheumatol. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dougados, M.; Soubrier, M.; Antunez, A.; Balint, P.; Balsa, A.; Buch, M.H.; Casado, G.; Detert, J.; El-Zorkany, B.; Emery, P.; et al. Prevalence of comorbidities in rheumatoid arthritis and evaluation of their monitoring: Results of an international, cross-sectional study (COMORA). Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2014, 73, 62–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bandyopadhyay, D.; Banerjee, U.; Hajra, A.; Chakraborty, S.; Amgai, B.; Ghosh, R.K.; Haddadin, F.I.; Modi, V.A.; Sinha, K.; Aronow, W.S.; et al. Trends of Cardiac Complications in Patients With Rheumatoid Arthritis: Analysis of the United States National Inpatient Sample; 2005-2014. Curr. Probl. Cardiol. 2021, 46, 100455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nikiphorou, E.; De Lusignan, S.; Mallen, C.D.; Khavandi, K.; Bedarida, G.; Buckley, C.D.; Galloway, J.; Raza, K. Cardiovascular risk factors and outcomes in early rheumatoid arthritis: A population-based study. Heart 2020, 106, 1566–1572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Libby, P. Inflammation in Atherosclerosis. Arter. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2012, 32, 2045–2051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ridker, P.M. Testing the inflammatory hypothesis of atherothrombosis: Scientific rationale for the cardiovascular inflammation reduction trial (CIRT). J. Thromb. Haemost. 2009, 7 (Suppl. 1), 332–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ridker, P.M.; Thuren, T.; Zalewski, A.; Libby, P. Interleukin-1β inhibition and the prevention of recurrent cardiovascular events: Rationale and Design of the Canakinumab Anti-inflammatory Thrombosis Outcomes Study (CANTOS). Am. Heart J. 2011, 162, 597–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agca, R.; Blanken, A.B.; van Sijl, A.M.; Smulders, Y.M.; Voskuyl, A.E.; van der Laken, C.; Boellaard, R.; Nurmohamed, M.T. Arterial wall inflammation is increased in rheumatoid arthritis compared with osteoarthritis, as a marker of early atherosclerosis. Rheumatology 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geraldino-Pardilla, L.; Zartoshti, A.; Ozbek, A.B.; Giles, J.T.; Weinberg, R.; Kinkhabwala, M.; Bokhari, S.; Bathon, J.M. Arterial Inflammation Detected With 18 F-Fluorodeoxyglucose–Positron Emission Tomography in Rheumatoid Arthritis. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2018, 70, 30–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Arts, E.E.; Fransen, J.; Broeder, A.A.D.; Popa, C.D.; Van Riel, P.L. The effect of disease duration and disease activity on the risk of cardiovascular disease in rheumatoid arthritis patients. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2015, 74, 998–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crepaldi, G.; Scirè, C.A.; Carrara, G.; Sakellariou, G.; Caporali, R.; Hmamouchi, I.; Dougados, M.; Montecucco, C. Cardiovascular Comorbidities Relate More than Others with Disease Activity in Rheumatoid Arthritis. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0146991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Myasoedova, E.; Chandran, A.; Ilhan, B.; Major, B.T.; Michet, C.J.; Matteson, E.L.; Crowson, C.S. The role of rheumatoid arthritis (RA) flare and cumulative burden of RA severity in the risk of cardiovascular disease. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2016, 75, 560–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Karpouzas, G.A.; Malpeso, J.; Choi, T.-Y.; Li, D.; Munoz, S.; Budoff, M.J. Prevalence, extent and composition of coronary plaque in patients with rheumatoid arthritis without symptoms or prior diagnosis of coronary artery disease. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2014, 73, 1797–1804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maradit-Kremers, H.; Crowson, C.S.; Nicola, P.J.; Ballman, K.V.; Roger, V.L.; Jacobsen, S.J.; Gabriel, S.E. Increased unrecognized coronary heart disease and sudden deaths in rheumatoid arthritis: A population-based cohort study. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2005, 52, 402–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- del Rincon, I.D.; Williams, K.; Stern, M.P.; Freeman, G.L.; Escalante, A. High incidence of cardiovascular events in a rheumatoid arthritis cohort not explained by traditional cardiac risk factors. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2001, 44, 2737–2745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solomon, D.H.; Karlson, E.W.; Rimm, E.B.; Cannuscio, C.C.; Mandl, L.A.; Manson, J.E.; Stampfer, M.J.; Curhan, G.C. Cardiovascular Morbidity and Mortality in Women Diagnosed With Rheumatoid Arthritis. Circulation 2003, 107, 1303–1307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lindhardsen, J.; Ahlehoff, O.; Gislason, G.H.; Madsen, O.R.; Olesen, J.B.; Torp-Pedersen, C.; Hansen, P.R. The risk of myocardial infarction in rheumatoid arthritis and diabetes mellitus: A Danish nationwide cohort study. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2011, 70, 929–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Agca, R.; Hopman, L.H.; Laan, K.J.; Van Halm, V.P.; Peters, M.J.; Smulders, Y.M.; Dekker, J.M.; Nijpels, G.; Stehouwer, C.D.; Voskuyl, A.E.; et al. Cardiovascular Event Risk in Rheumatoid Arthritis Compared with Type 2 Diabetes: A 15-year Longitudinal Study. J. Rheumatol. 2020, 47, 316–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCoy, S.S.; Crowson, C.S.; Maradit-Kremers, H.; Therneau, T.M.; Roger, V.L.; Matteson, E.L.; Gabriel, S.E. Longterm outcomes and treatment after myocardial infarction in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. J. Rheumatol. 2013, 40, 605–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gabriel, S.E.; Crowson, C.S.; O’Fallon, W.M. Comorbidity in arthritis. J. Rheumatol. 1999, 26, 2475–2479. [Google Scholar]
- Khalid, Y.; Dasu, N.; Shah, A.; Brown, K.; Kaell, A.; Levine, A.; Dasu, K.; Raminfard, A. Incidence of congestive heart failure in rheumatoid arthritis: A review of literature and meta-regression analysis. ESC Heart Fail. 2020, 7, 3745–3753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mantel, Ä.; Holmqvist, M.; Andersson, D.C.; Lund, L.H.; Askling, J. Association Between Rheumatoid Arthritis and Risk of Ischemic and Nonischemic Heart Failure. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2017, 69, 1275–1285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicola, P.J.; Maradit-Kremers, H.; Roger, V.L.; Jacobsen, S.J.; Crowson, C.S.; Ballman, K.V.; Gabriel, S.E. The risk of congestive heart failure in rheumatoid arthritis: A population-based study over 46 years. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2005, 52, 412–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, M.B.; Fonseca, T.; Costa, R.; Marinhoc, A.; Carvalho, H.C.; Oliveira, J.C.; Zannad, F.; Rossignol, P.; Gottenberg, J.-E.; Saraiva, F.A.; et al. Prevalence, risk factors and proteomic bioprofiles associated with heart failure in rheumatoid arthritis: The RA-HF study. Eur. J. Intern. Med. 2021, 85, 41–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunlay, S.M.; Roger, V.L.; Redfield, M.M. Epidemiology of heart failure with preserved ejection fraction. Nat. Rev. Cardiol. 2017, 14, 591–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahlers, M.J.; Lowery, B.D.; Farber-Eger, E.; Wang, T.J.; Bradham, W.; Ormseth, M.J.; Chung, C.P.; Stein, C.M.; Gupta, D.K. Heart Failure Risk Associated With Rheumatoid Arthritis–Related Chronic Inflammation. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2020, 9, e014661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Conceição, G.; Heinonen, I.; Lourenço, A.P.; Duncker, D.J.; Falcão-Pires, I. Animal models of heart failure with preserved ejection fraction. Neth. Heart J. 2016, 24, 275–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Alex, L.; Russo, I.; Holoborodko, V.; Frangogiannis, N.G. Characterization of a mouse model of obesity-related fibrotic cardiomyopathy that recapitulates features of human heart failure with preserved ejection fraction. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 2018, 315, H934–H949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wijk, S.S.-V.; Tromp, J.; Beussink-Nelson, L.; Hage, C.; Svedlund, S.; Saraste, A.; Swat, S.A.; Sanchez, C.; Njoroge, J.; Tan, R.-S.; et al. Proteomic Evaluation of the Comorbidity-Inflammation Paradigm in Heart Failure With Preserved Ejection Fraction: Results From the PROMIS-HFpEF Study. Circulation 2020, 142, 2029–2044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shuai, W.; Wen, J.; Li, X.; Wang, D.; Li, Y.; Xiang, J. High-Choline Diet Exacerbates Cardiac Dysfunction, Fibrosis, and Inflammation in a Mouse Model of Heart Failure with Preserved Ejection Fraction. J. Card. Fail. 2020, 26, 694–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hage, C.; Michaëlsson, E.; Linde, C.; Donal, E.; Daubert, J.-C.; Gan, L.-M.; Lund, L.H. Inflammatory Biomarkers Predict Heart Failure Severity and Prognosis in Patients With Heart Failure With Preserved Ejection Fraction: A Holistic Proteomic Approach. Circ. Cardiovasc. Genet. 2017, 10, e001633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Baghdadi, L.R.; Woodman, R.J.; Shanahan, E.M.; Mangoni, A.A. The Impact of Traditional Cardiovascular Risk Factors on Cardiovascular Outcomes in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0117952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gonzalez, A.; Kremers, H.M.; Crowson, C.S.; Ballman, K.V.; Roger, V.L.; Jacobsen, S.J.; O’Fallon, W.M.; Gabriel, S.E. Do cardiovascular risk factors confer the same risk for cardiovascular outcomes in rheumatoid arthritis patients as in non-rheumatoid arthritis patients? Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2008, 67, 64–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giles, J.T.; Wasko, M.C.M.; Chung, C.P.; Szklo, M.; Blumenthal, R.S.; Kao, A.; Bokhari, S.; Zartoshti, A.; Stein, C.M.; Bathon, J.M. Exploring the Lipid Paradox Theory in Rheumatoid Arthritis: Associations of Low Circulating Low-Density Lipoprotein Concentration With Subclinical Coronary Atherosclerosis. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019, 71, 1426–1436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, N.; Zhang, Z.; Wu, H.; Jiang, Y.; Meng, L.; Xiong, J.; Zhao, Z.; Zhou, X.; Li, J.; Li, H.; et al. Recognition of H3K9 methylation by GLP is required for efficient establishment of H3K9 methylation, rapid target gene repression, and mouse viability. Genes Dev. 2015, 29, 379–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Myasoedova, E.; Crowson, C.S.; Kremers, H.M.; Roger, V.L.; Fitz-Gibbon, P.D.; Therneau, T.M.; Gabriel, S.E. Lipid paradox in rheumatoid arthritis: The impact of serum lipid measures and systemic inflammation on the risk of cardiovascular disease. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2011, 70, 482–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liao, K.P.; Cai, T.; Gainer, V.S.; Cagan, A.; Murphy, S.N.; Liu, C.; Churchill, S.; Shaw, S.Y.; Kohane, I.; Solomon, D.H.; et al. Lipid and Lipoprotein Levels and Trend in Rheumatoid Arthritis Compared to the General Population. Arthritis Care Res. 2013, 65, 2046–2050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myasoedova, E.; Crowson, C.S.; Kremers, H.M.; Fitz-Gibbon, P.D.; Therneau, T.M.; Gabriel, S.E. Total cholesterol and LDL levels decrease before rheumatoid arthritis. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2009, 69, 1310–1314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Charles-Schoeman, C.; Fleischmann, R.; Davignon, J.; Schwartz, H.; Turner, S.M.; Beysen, C.; Milad, M.; Hellerstein, M.K.; Luo, Z.; Kaplan, I.V.; et al. Potential Mechanisms Leading to the Abnormal Lipid Profile in Patients With Rheumatoid Arthritis Versus Healthy Volunteers and Reversal by Tofacitinib. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2015, 67, 616–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myasoedova, E. Lipids and lipid changes with synthetic and biologic disease-modifying antirheumatic drug therapy in rheumatoid arthritis: Implications for cardiovascular risk. Curr. Opin. Rheumatol. 2017, 29, 277–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solomon, D.H.; Goodson, N.J.; Katz, J.N.; Weinblatt, M.E.; Avorn, J.; Setoguchi, S.; Canning, C.; Schneeweiss, S. Patterns of cardiovascular risk in rheumatoid arthritis. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2006, 65, 1608–1612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Meissner, Y.; Zink, A.; Kekow, J.; Rockwitz, K.; Liebhaber, A.; Zinke, S.; Gerhold, K.; Richter, A.; Listing, J.; Strangfeld, A. Impact of disease activity and treatment of comorbidities on the risk of myocardial infarction in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Res. 2016, 18, 183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mong, N.; Tarjanyi, Z.; Tothfalusi, L.; Bartykowszki, A.; Nagy, A.I.; Szekely, A.; Becker, D.; Maurovich-Horvat, P.; Merkely, B.; Nagy, G. Largely Accelerated Arterial Aging in Rheumatoid Arthritis Is Associated With Inflammatory Activity and Smoking in the Early Stage of the Disease. Front. Pharmacol. 2020, 11, 523962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solomon, D.H.; Reed, G.W.; Kremer, J.M.; Curtis, J.R.; Farkouh, M.E.; Harrold, L.R.; Hochberg, M.C.; Tsao, P.; Greenberg, J.D. Disease Activity in Rheumatoid Arthritis and the Risk of Cardiovascular Events. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2015, 67, 1449–1455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amigues, I.; Tugcu, A.; Russo, C.; Giles, J.T.; Morgenstein, R.; Zartoshti, A.; Schulze, C.; Flores, R.; Bokhari, S.; Bathon, J.M. Myocardial Inflammation, Measured Using 18-Fluorodeoxyglucose Positron Emission Tomography With Computed Tomography, Is Associated With Disease Activity in Rheumatoid Arthritis. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019, 71, 496–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ntusi, N.A.; Piechnik, S.K.; Francis, J.M.; Ferreira, V.M.; Matthews, P.M.; Robson, M.D.; Wordsworth, P.B.; Neubauer, S.; Karamitsos, T.D. Diffuse Myocardial Fibrosis and Inflammation in Rheumatoid Arthritis: Insights From CMR T1 Mapping. JACC Cardiovasc. Imaging 2015, 8, 526–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mavrogeni, S.; Karabela, G.; Stavropoulos, E.; Gialafos, E.; Sfendouraki, E.; Kyrou, L.; Kolovou, G. Imaging patterns of heart failure in rheumatoid arthritis evaluated by cardiovascular magnetic resonance. Int. J. Cardiol. 2013, 168, 4333–4335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grundtman, C.; Hollan, I.; Førre, Ø.T.; Saatvedt, K.; Mikkelsen, K.; Lundberg, I.E. Cardiovascular disease in patients with inflammatory rheumatic disease is associated with up-regulation of markers of inflammation in cardiac microvessels and cardiomyocytes. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2010, 62, 667–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, R.B.; Shah, S.J. Drug Targets for Heart Failure with Preserved Ejection Fraction: A Mechanistic Approach and Review of Contemporary Clinical Trials. Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2019, 59, 41–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanghera, C.; Wong, L.M.; Panahi, M.; Sintou, A.; Hasham, M.; Sattler, S. Cardiac phenotype in mouse models of systemic autoimmunity. Dis. Model. Mech. 2019, 12, dmm036947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Paulus, W.J.; Tschöpe, C. A Novel Paradigm for Heart Failure with Preserved Ejection Fraction: Comorbidities drive myocardial dysfunction and remodeling through coronary microvascular endothelial inflammation. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2013, 62, 263–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schiattarella, G.G.; Sequeira, V.; Ameri, P. Distinctive patterns of inflammation across the heart failure syndrome. Heart Fail. Rev. 2020, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abernethy, A.; Raza, S.; Sun, J.; Anstrom, K.J.; Tracy, R.; Steiner, J.; VanBuren, P.; LeWinter, M.M. Pro-Inflammatory Biomarkers in Stable Versus Acutely Decompensated Heart Failure With Preserved Ejection Fraction. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2018, 7, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collier, P.; Watson, C.J.; Voon, V.; Phelan, D.; Jan, A.; Mak, G.; Martos, R.; Baugh, J.A.; Ledwidge, M.T.; McDonald, K.M. Can emerging biomarkers of myocardial remodelling identify asymptomatic hypertensive patients at risk for diastolic dysfunction and diastolic heart failure? Eur. J. Heart Fail. 2011, 13, 1087–1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Glezeva, N.; Voon, V.; Watson, C.; Horgan, S.; McDonald, K.; Ledwidge, M.; Baugh, J. Exaggerated Inflammation and Monocytosis Associate With Diastolic Dysfunction in Heart Failure With Preserved Ejection Fraction: Evidence of M2 Macrophage Activation in Disease Pathogenesis. J. Card. Fail. 2015, 21, 167–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wijk, S.S.-V.; Van Empel, V.; Davarzani, N.; Maeder, M.T.; Handschin, R.; Pfisterer, M.E.; Rocca, H.-P.B.-L.; for the TIME-CHF Investigators. Circulating biomarkers of distinct pathophysiological pathways in heart failure with preserved vs. reduced left ventricular ejection fraction. Eur. J. Heart Fail. 2015, 17, 1006–1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tromp, J.; Khan, M.A.F.; Klip, I.T.; Meyer, S.; de Boer, R.A.; Jaarsma, T.; Hillege, H.; van Veldhuisen, D.J.; van der Meer, P.; Voors, A.A. Biomarker Profiles in Heart Failure Patients with Preserved and Reduced Ejection Fraction. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2017, 6, e003989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Westermann, D.; Lindner, D.; Kasner, M.; Zietsch, C.; Savvatis, K.; Escher, F.; Von Schlippenbach, J.; Skurk, C.; Steendijk, P.; Riad, A.; et al. Cardiac Inflammation Contributes to Changes in the Extracellular Matrix in Patients With Heart Failure and Normal Ejection Fraction. Circ. Heart Fail. 2011, 4, 44–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Scherzer, R.; Shah, S.J.; Secemsky, E.; Butler, J.; Grunfeld, C.; Shlipak, M.G.; Hsue, P.Y. Association of Biomarker Clusters With Cardiac Phenotypes and Mortality in Patients With HIV Infection. Circ. Heart Fail. 2018, 11, e004312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, J.M.; Lin, G.; Oh, J.K.; Crowson, C.S.; Achenbach, S.J.; Therneau, T.M.; Matteson, E.L.; Rodeheffer, R.J.; Gabriel, S.E. Five-year changes in cardiac structure and function in patients with rheumatoid arthritis compared with the general population. Int. J. Cardiol. 2017, 240, 379–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sattar, N.; McCarey, D.W.; Capell, H.; McInnes, I.B. Explaining How “High-Grade” Systemic Inflammation Accelerates Vascular Risk in Rheumatoid Arthritis. Circulation 2003, 108, 2957–2963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doyama, K.; Fujiwara, H.; Fukumoto, M.; Tanaka, M.; Fujiwara, Y.; Oda, T.; Inada, T.; Ohtani, S.; Hasegawa, K.; Fujiwara, T.; et al. Tumour necrosis factor is expressed in cardiac tissues of patients with heart failure. Int. J. Cardiol. 1996, 54, 217–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riehle, C.; Bauersachs, J. Key inflammatory mechanisms underlying heart failure. Herz 2019, 44, 96–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hulsmans, M.; Sager, H.B.; Roh, J.D.; Valero-Muñoz, M.; Houstis, N.E.; Iwamoto, Y.; Sun, Y.; Wilson, R.M.; Wojtkiewicz, G.; Tricot, B.; et al. Cardiac macrophages promote diastolic dysfunction. J. Exp. Med. 2018, 215, 423–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pironti, G.; Bersellini-Farinotti, A.; Agalave, N.M.; Sandor, K.; Fernandez-Zafra, T.; Jurczak, A.; Lund, L.H.; Svensson, C.I.; Andersson, D.C. Cardiomyopathy, oxidative stress and impaired contractility in a rheumatoid arthritis mouse model. Heart 2018, 104, 2026–2034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bryant, D.; Becker, L.; Richardson, J.; Shelton, J.; Franco, F.; Peshock, R.; Thompson, M.; Giroir, B. Cardiac Failure in Transgenic Mice With Myocardial Expression of Tumor Necrosis Factor-α. Circulation 1998, 97, 1375–1381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhou, Z.; Miao, Z.; Luo, A.; Zhu, D.; Lu, Y.; Li, P.; Feng, X.; Tan, W.; Wang, F. Identifying a marked inflammation mediated cardiac dysfunction during the development of arthritis in collagen-induced arthritis mice. Clin. Exp. Rheumatol. 2020, 38, 203–211. [Google Scholar]
- Bordy, R.; Moretto, J.; Devaux, S.; Wendling, D.; Moretto-Riedweg, K.; Demougeot, C.; Totoson, P. Adjuvant-induced arthritis is a relevant model to mimic coronary and myocardial impairments in rheumatoid arthritis. Jt. Bone Spine 2021, 88, 105069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mokotedi, L.; Michel, F.S.; Mogane, C.; Gomes, M.; Woodiwiss, A.J.; Norton, G.R.; Millen, A.M.E. Associations of inflammatory markers with impaired left ventricular diastolic and systolic function in collagen-induced arthritis. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0230657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Binstadt, B.A.; Hebert, J.L.; Ortiz-Lopez, A.; Bronson, R.; Benoist, C.; Mathis, D. The same systemic autoimmune disease provokes arthritis and endocarditis via distinct mechanisms. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 16758–16763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Anceyab, C.; Corbic, P.; Frogerd, J.; Delwailb, A.; Wijdenese, J.; Gascand, H.; Potreaua, D.; Lecron, J.-C. Secretion of IL-6, IL-11 and LIF by human cardiomyocytes in primary culture. Cytokine 2002, 18, 199–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martini, E.; Kunderfranco, P.; Peano, C.; Carullo, P.; Cremonesi, M.; Schorn, T.; Carriero, R.; Termanini, A.; Colombo, F.S.; Jachetti, E.; et al. Single-Cell Sequencing of Mouse Heart Immune Infiltrate in Pressure Overload–Driven Heart Failure Reveals Extent of Immune Activation. Circulation 2019, 140, 2089–2107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shioi, T.; Matsumori, A.; Kihara, Y.; Inoko, M.; Ono, K.; Iwanaga, Y.; Yamada, T.; Iwasaki, A.; Matsushima, K.; Sasayama, S. Increased Expression of Interleukin-1β and Monocyte Chemotactic and Activating Factor/Monocyte Chemoattractant Protein-1 in the Hypertrophied and Failing Heart With Pressure Overload. Circ. Res. 1997, 81, 664–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kallikourdis, M.; Martini, E.; Carullo, P.; Sardi, C.; Roselli, G.; Greco, C.M.; Vignali, D.; Riva, F.; Berre, A.M.O.; Stølen, T.O.; et al. T cell costimulation blockade blunts pressure overload-induced heart failure. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 14680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sorop, O.; Heinonen, I.; Van Kranenburg, M.; Van De Wouw, J.; De Beer, V.J.; Nguyen, I.T.N.; Octavia, Y.; Van Duin, R.W.B.; Stam, K.; Van Geuns, R.-J.; et al. Multiple common comorbidities produce left ventricular diastolic dysfunction associated with coronary microvascular dysfunction, oxidative stress, and myocardial stiffening. Cardiovasc. Res. 2018, 114, 954–964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Franssen, C.; Chen, S.; Unger, A.; Korkmaz, H.I.; De Keulenaer, G.W.; Tschöpe, C.; Leite-Moreira, A.F.; Musters, R.; Niessen, H.W.; Linke, W.A.; et al. Myocardial Microvascular Inflammatory Endothelial Activation in Heart Failure with Preserved Ejection Fraction. JACC Heart Fail. 2016, 4, 312–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borbély, A.; Falcao-Pires, I.; van Heerebeek, L.; Hamdani, N.; Édes, I.; Gavina, C.; Leite-Moreira, A.F.; Bronzwaer, J.G.; Papp, Z.; van der Velden, J.; et al. Hypophosphorylation of the Stiff N2B Titin Isoform Raises Cardiomyocyte Resting Tension in Failing Human Myocardium. Circ. Res. 2009, 104, 780–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gevaert, A.B.; Shakeri, H.; Leloup, A.J.; Van Hove, C.E.; De Meyer, G.R.; Vrints, C.J.; Lemmens, K.; Van Craenenbroeck, E.M. Endothelial Senescence Contributes to Heart Failure With Preserved Ejection Fraction in an Aging Mouse Model. Circ. Heart Fail. 2017, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schiattarella, G.G.; Altamirano, F.; Tong, D.; French, K.M.; Villalobos, E.; Kim, S.Y.; Luo, X.; Jiang, N.; May, H.I.; Wang, Z.V.; et al. Nitrosative stress drives heart failure with preserved ejection fraction. Nature 2019, 568, 351–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bordy, R.; Totoson, P.; Prati, C.; Marie, C.; Wendling, D.; Demougeot, C. Microvascular endothelial dysfunction in rheumatoid arthritis. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2018, 14, 404–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prati, C.; Berthelot, A.; Wendling, D.; Demougeot, C. Endothelial dysfunction in rat adjuvant-induced arthritis: Up-regulation of the vascular arginase pathway. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2011, 63, 2309–2317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandrasekharan, U.M.; Wang, Z.; Wu, Y.; Tang, W.H.W.; Hazen, S.L.; Wang, S.; Husni, M.E. Elevated levels of plasma symmetric dimethylarginine and increased arginase activity as potential indicators of cardiovascular comorbidity in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2018, 20, 123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Haruna, Y.; Morita, Y.; Komai, N.; Yada, T.; Sakuta, T.; Tomita, N.; Fox, D.A.; Kashihara, N. Endothelial dysfunction in rat adjuvant-induced arthritis: Vascular superoxide production by NAD(P)H oxidase and uncoupled endothelial nitric oxide synthase. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2006, 54, 1847–1855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mäki-Petäjä, K.M.; Cheriyan, J.; Booth, A.D.; Hall, F.C.; Brown, J.; Wallace, S.M.; Ashby, M.J.; McEniery, C.M.; Wilkinson, I.B. Inducible nitric oxide synthase activity is increased in patients with rheumatoid arthritis and contributes to endothelial dysfunction. Int. J. Cardiol. 2008, 129, 399–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tozzato, G.P.Z.; Taipeiro, E.F.; Spadella, M.A.; Filho, P.M.; De Assis, M.R.; Carlos, C.P.; Girol, A.P.; Chies, A.B. Collagen-induced arthritis increases inducible nitric oxide synthase not only in aorta but also in the cardiac and renal microcirculation of mice. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2015, 183, 341–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Edelmann, F.; Holzendorf, V.; Wachter, R.; Nolte, K.; Schmidt, A.G.; Kraigher-Krainer, E.; Duvinage, A.; Unkelbach, I.; Düngen, H.-D.; Tschöpe, C.; et al. Galectin-3 in patients with heart failure with preserved ejection fraction: Results from the Aldo-DHF trial. Eur. J. Heart Fail. 2015, 17, 214–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, U.C.; Pokharel, S.; Van Brakel, T.J.; Van Berlo, J.H.; Cleutjens, J.P.M.; Schroen, B.; André, S.; Crijns, H.J.; Gabius, H.-J.; Maessen, J.; et al. Galectin-3 Marks Activated Macrophages in Failure-Prone Hypertrophied Hearts and Contributes to Cardiac Dysfunction. Circulation 2004, 110, 3121–3128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Issa, S.F.; Christensen, A.F.; Lindegaard, H.M.; Hetland, M.L.; Hørslev-Petersen, K.; Stengaard-Pedersen, K.; Ejbjerg, B.J.; Lottenburger, T.; Ellingsen, T.; Pedersen, J.K.; et al. Galectin-3 is Persistently Increased in Early Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA) and Associates with Anti-CCP Seropositivity and MRI Bone Lesions, While Early Fibrosis Markers Correlate with Disease Activity. Scand. J. Immunol. 2017, 86, 471–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Issa, S.F.; Duer, A.; Østergaard, M.; Hørslev-Petersen, K.; Hetland, M.L.; Hansen, M.S.; Junker, K.; Lindegaard, H.M.; Møller, J.M.; Junker, P. Increased galectin-3 may serve as a serologic signature of pre-rheumatoid arthritis while markers of synovitis and cartilage do not differ between early undifferentiated arthritis subsets. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2017, 19, 80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ohshima, S.; Kuchen, S.; Seemayer, C.A.; Kyburz, D.; Hirt, A.; Klinzing, S.; Michel, B.A.; Gay, R.E.; Liu, F.-T.; Gay, S.; et al. Galectin 3 and its binding protein in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2003, 48, 2788–2795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anyfanti, P.; Gkaliagkousi, E.; Gavriilaki, E.; Triantafyllou, A.; Dolgyras, P.; Galanopoulou, V.; Aslanidis, S.; Douma, S. Association of galectin-3 with markers of myocardial function, atherosclerosis, and vascular fibrosis in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Clin. Cardiol. 2019, 42, 62–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Filer, A.; Bik, M.; Parsonage, G.N.; Fitton, J.; Trebilcock, E.; Howlett, K.; Cook, M.; Raza, K.; Simmons, D.L.; Thomas, A.M.C.; et al. Galectin 3 induces a distinctive pattern of cytokine and chemokine production in rheumatoid synovial fibroblasts via selective signaling pathways. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2009, 60, 1604–1614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Forsman, H.; Islander, U.; Andréasson, E.; Andersson, A.; Önnheim, K.; Karlström, A.; Sävman, K.; Magnusson, M.; Brown, K.L.; Karlsson, A. Galectin 3 aggravates joint inflammation and destruction in antigen-induced arthritis. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2011, 63, 445–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ismaili, H.; Ismaili, L.; Rexhepi, M. Values and Correlations between C-Reactive Protein and Apolipoprotein B after Treatment with Methotrexate at Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis. Open Access Maced. J. Med. Sci. 2019, 7, 1293–1298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pope, J.E.; Choy, E.H. C-reactive protein and implications in rheumatoid arthritis and associated comorbidities. Semin. Arthritis Rheum. 2021, 51, 219–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smolen, J.S.; Aletaha, D.; McInnes, I.B. Rheumatoid arthritis. Lancet 2016, 388, 2023–2038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aletaha, D.; Smolen, J.S. Diagnosis and Management of Rheumatoid Arthritis: A Review. JAMA 2018, 320, 1360–1372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, H.K.; Hernán, M.A.; Seeger, J.D.; Robins, J.M.; Wolfe, F. Methotrexate and mortality in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: A prospective study. Lancet 2002, 359, 1173–1177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ridker, P.M.; Everett, B.M.; Pradhan, A.; MacFadyen, J.G.; Solomon, D.H.; Zaharris, E.; Mam, V.; Hasan, A.; Rosenberg, Y.; Iturriaga, E.; et al. Low-Dose Methotrexate for the Prevention of Atherosclerotic Events. N. Engl. J. Med. 2019, 380, 752–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naranjo, A.; Sokka, T.; Descalzo, M.A.; Calvo-Alén, J.; Hørslev-Petersen, K.; Luukkainen, R.K.; Combe, B.; Burmester, G.R.; Devlin, J.; Ferraccioli, G.; et al. Cardiovascular disease in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: Results from the QUEST-RA study. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2008, 10, R30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Van Halm, V.P.; Nurmohamed, M.T.; Twisk, J.W.R.; Dijkmans, B.A.C.; Voskuyl, A.E. Disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs are associated with a reduced risk for cardiovascular disease in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: A case control study. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2006, 8, R151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Suissa, S.; Bernatsky, S.; Hudson, M. Antirheumatic drug use and the risk of acute myocardial infarction. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2006, 55, 531–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatre, C.; Roubille, F.; Vernhet, H.; Jorgensen, C.; Pers, Y.-M. Cardiac Complications Attributed to Chloroquine and Hydroxychloroquine: A Systematic Review of the Literature. Drug Saf. 2018, 41, 919–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tselios, K.; Deeb, M.; Gladman, D.D.; Harvey, P.; Akhtari, S.; Mak, S.; Butany, J.; Urowitz, M.B. Antimalarial-induced Cardiomyopathy in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus: As Rare as Considered? J. Rheumatol. 2019, 46, 391–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roubille, C.; Richer, V.; Starnino, T.; McCourt, C.; McFarlane, A.; Fleming, P.; Siu, S.; Kraft, J.; Lynde, C.; Pope, J.; et al. The effects of tumour necrosis factor inhibitors, methotrexate, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs and corticosteroids on cardiovascular events in rheumatoid arthritis, psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2015, 74, 480–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, E.S.; Packer, M.; Lo, K.H.; Fasanmade, A.A.; Willerson, J.T. Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled, Pilot Trial of Infliximab, a Chimeric Monoclonal Antibody to Tumor Necrosis Factor-α, in Patients With Moderate-to-Severe Heart Failure: Results of the anti-TNF Therapy Against Congestive Heart Failure (ATTACH) trial. Circulation 2003, 107, 3133–3140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Singh, J.A.; Saag, K.G.; Bridges, S.L., Jr.; Akl, E.A.; Bannuru, R.R.; Sullivan, M.C.; Vaysbrot, E.; McNaughton, C.; Osani, M.; Shmerling, R.H.; et al. 2015 American College of Rheumatology Guideline for the Treatment of Rheumatoid Arthritis. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2016, 68, 1–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Suha, C.; Gokhan, V.M.; Ekrem, Y.; Mehmet, D.; Goksal, K.; Akif, O.M. Infliximab, an anti-TNF-alpha agent, improves left atrial abnormalities in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: Preliminary results. Cardiovasc. J. Afr. 2014, 25, 168–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kotyla, P.J.; Owczarek, A.; Rakoczy, J.; Lewicki, M.; Kucharz, E.J.; Emery, P. Infliximab Treatment Increases Left Ventricular Ejection Fraction in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis: Assessment of Heart Function by Echocardiography, Endothelin 1, Interleukin 6, and NT-pro Brain Natriuretic Peptide. J. Rheumatol. 2012, 39, 701–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baniaamam, M.; Handoko, M.L.; Agca, R.; Heslinga, S.C.; Konings, T.C.; Van Halm, V.P.; Nurmohamed, M.T. The Effect of Anti-TNF Therapy on Cardiac Function in Rheumatoid Arthritis: An Observational Study. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 3145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giles, J.T.; Sattar, N.; Gabriel, S.; Ridker, P.M.; Gay, S.; Warne, C.; Musselman, D.; Brockwell, L.; Shittu, E.; Klearman, M.; et al. Cardiovascular Safety of Tocilizumab Versus Etanercept in Rheumatoid Arthritis: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2020, 72, 31–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, S.; Fumery, M.; Singh, A.G.; Singh, N.; Prokop, L.J.; Dulai, P.S.; Sandborn, W.J.; Curtis, J.R. Comparative Risk of Cardiovascular Events With Biologic and Synthetic Disease-Modifying Antirheumatic Drugs in Patients With Rheumatoid Arthritis: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Arthritis Care Res. 2020, 72, 561–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kobayashi, H.; Kobayashi, Y.; Yokoe, I.; Kitamura, N.; Nishiwaki, A.; Takei, M.; Giles, J.T. Heart Rate–corrected QT Interval Duration in Rheumatoid Arthritis and Its Reduction with Treatment with the Interleukin 6 Inhibitor Tocilizumab. J. Rheumatol. 2018, 45, 1620–1627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ikonomidis, I.; Tzortzis, S.; Lekakis, J.; Paraskevaidis, I.; Andreadou, I.; Nikolaou, M.; Kaplanoglou, T.; Katsimbri, P.; Skarantavos, G.; Soucacos, P.; et al. Lowering interleukin-1 activity with anakinra improves myocardial deformation in rheumatoid arthritis. Heart 2009, 95, 1502–1507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Everett, B.M.; Cornel, J.H.; Lainscak, M.; Anker, S.D.; Abbate, A.; Thuren, T.; Libby, P.; Glynn, R.J.; Ridker, P.M. Anti-Inflammatory Therapy With Canakinumab for the Prevention of Hospitalization for Heart Failure. Circulation 2019, 139, 1289–1299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ljung, L.; Rantapää-Dahlqvist, S.; Jacobsson, L.T.H.; Askling, J. Response to biological treatment and subsequent risk of coronary events in rheumatoid arthritis. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2016, 75, 2087–2094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dixon, W.G.; Watson, K.D.; Lunt, M.; Hyrich, K.L.; Silman, A.J.; Symmons, D.P.M. Reduction in the incidence of myocardial infarction in patients with rheumatoid arthritis who respond to anti–tumor necrosis factor α therapy: Results from the British Society for Rheumatology Biologics Register. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2007, 56, 2905–2912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Rincón, I.; Battafarano, D.F.; Restrepo, J.F.; Erikson, J.M.; Escalante, A. Glucocorticoid Dose Thresholds Associated With All-Cause and Cardiovascular Mortality in Rheumatoid Arthritis. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2014, 66, 264–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lindhardsen, J.; Gislason, G.H.; Jacobsen, S.; Ahlehoff, O.; Olsen, A.-M.S.; Madsen, O.R.; Torp-Pedersen, C.; Hansen, P.R. Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs and risk of cardiovascular disease in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: A nationwide cohort study. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2014, 73, 1515–1521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pujades-Rodriguez, M.; Morgan, A.W.; Cubbon, R.M.; Wu, J. Dose-dependent oral glucocorticoid cardiovascular risks in people with immune-mediated inflammatory diseases: A population-based cohort study. PLoS Med. 2020, 17, e1003432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crane, M.M.; Juneja, M.; Allen, J.K.; Kurrasch, R.H.; Chu, M.E.; Quattrocchi, E.; Manson, S.C.; Chang, D.J. Epidemiology and Treatment of New-Onset and Established Rheumatoid Arthritis in an Insured US Population. Arthritis Care Res. 2015, 67, 1646–1655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nissen, S.E.; Yeomans, N.D.; Solomon, D.H.; Lüscher, T.F.; Libby, P.; Husni, M.E.; Graham, D.Y.; Borer, J.S.; Wisniewski, L.M.; Wolski, K.E.; et al. Cardiovascular Safety of Celecoxib, Naproxen, or Ibuprofen for Arthritis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2016, 375, 2519–2529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Perretti, M.; Cooper, D.; Dalli, J.; Norling, L.V. Immune resolution mechanisms in inflammatory arthritis. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2017, 13, 87–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schett, G. Resolution of inflammation in arthritis. Semin. Immunopathol. 2019, 41, 675–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arnardottir, H.H.; Dalli, J.; Norling, L.V.; Colas, R.A.; Perretti, M.; Serhan, C.N. Resolvin D3 Is Dysregulated in Arthritis and Reduces Arthritic Inflammation. J. Immunol. 2016, 197, 2362–2368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gomez, E.A.; Colas, R.A.; Souza, P.R.; Hands, R.; Lewis, M.J.; Bessant, C.; Pitzalis, C.; Dalli, J. Blood pro-resolving mediators are linked with synovial pathology and are predictive of DMARD responsiveness in rheumatoid arthritis. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 5420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Norling, L.V.; Headland, S.E.; Dalli, J.; Arnardottir, H.H.; Haworth, O.; Jones, H.R.; Irimia, D.; Serhan, C.N.; Perretti, M. Proresolving and cartilage-protective actions of resolvin D1 in inflammatory arthritis. JCI Insight 2016, 1, e85922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krönke, G.; Katzenbeisser, J.; Uderhardt, S.; Zaiss, M.M.; Scholtysek, C.; Schabbauer, G.; Zarbock, A.; Koenders, M.I.; Axmann, R.; Zwerina, J.; et al. 12/15-Lipoxygenase Counteracts Inflammation and Tissue Damage in Arthritis. J. Immunol. 2009, 183, 3383–3389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kao, W.; Gu, R.; Jia, Y.; Wei, X.; Fan, H.; Harris, J.; Zhang, Z.; Quinn, J.; Morand, E.F.; Yang, Y.H. A formyl peptide receptor agonist suppresses inflammation and bone damage in arthritis. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2014, 171, 4087–4096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Perretti, M.; Godson, C. Formyl peptide receptor type 2 agonists to kick-start resolution pharmacology. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2020, 177, 4595–4600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.; Xiong, M.; Zong, X.; Ge, Y.; Zhang, H.; Wang, M.; Han, G.W.; Yi, C.; Ma, L.; Ye, R.D.; et al. Structural basis of ligand binding modes at the human formyl peptide receptor 2. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 1208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Amico, M.D.; Di Filippo, C.; La, M.; Solito, E.; McLean, P.G.; Jflower, R.J.; Oliani, S.M.; Perretti, M. Lipocortin 1 reduces myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury by affecting local leukocyte recruitment. FASEB J. 2000, 14, 1867–1869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kain, V.; Ingle, K.A.; Colas, R.A.; Dalli, J.; Prabhu, S.D.; Serhan, C.N.; Joshi, M.D.; Halade, G.V. Resolvin D1 activates the inflammation resolving response at splenic and ventricular site following myocardial infarction leading to improved ventricular function. J. Mol. Cell. Cardiol. 2015, 84, 24–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- La, M.; D’Amico, M.; Bandiera, S.; Di Filippo, C.; Oliani, S.M.; Gavins, F.N.E.; Flower, R.J.; Perretti, M. Annexin 1 peptides protect against experimental myocardial ischemia-reperfusion: Analysis of their mechanism of action. FASEB J. 2001, 15, 2247–2256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flower, R.J.; Blackwell, G.J. Anti-inflammatory steroids induce biosynthesis of a phospholipase A2 inhibitor which prevents prostaglandin generation. Nature 1979, 278, 456–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, C.X.; May, L.T.; Li, R.; Cao, N.; Rosli, S.; Deo, M.; Alexander, A.E.; Horlock, D.; Bourke, J.E.; Yang, Y.H.; et al. Small-molecule-biased formyl peptide receptor agonist compound 17b protects against myocardial ischaemia-reperfusion injury in mice. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 14232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asahina, Y.; Wurtz, N.R.; Arakawa, K.; Carson, N.; Fujii, K.; Fukuchi, K.; Garcia, R.A.; Hsu, M.-Y.; Ishiyama, J.; Ito, B.; et al. Discovery of BMS-986235/LAR-1219: A Potent Formyl Peptide Receptor 2 (FPR2) Selective Agonist for the Prevention of Heart Failure. J. Med. Chem. 2020, 63, 9003–9019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- García, R.A.; Ito, B.R.; Lupisella, J.A.; Carson, N.A.; Hsu, M.-Y.; Fernando, G.; Heroux, M.; Bouvier, M.; Dierks, E.; Kick, E.K.; et al. Preservation of Post-Infarction Cardiac Structure and Function via Long-Term Oral Formyl Peptide Receptor Agonist Treatment. JACC: Basic Transl. Sci. 2019, 4, 905–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferraro, B.; Leoni, G.; Hinkel, R.; Ormanns, S.; Paulin, N.; Ortega-Gomez, A.; Viola, J.R.; de Jong, R.; Bongiovanni, D.; Bozoglu, T.; et al. Pro-Angiogenic Macrophage Phenotype to Promote Myocardial Repair. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2019, 73, 2990–3002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fredman, G.; Hellmann, J.; Proto, J.D.; Kuriakose, G.; Colas, R.A.; Dorweiler, B.; Connolly, E.S.; Solomon, R.; Jones, D.M.; Heyer, E.J.; et al. An imbalance between specialized pro-resolving lipid mediators and pro-inflammatory leukotrienes promotes instability of atherosclerotic plaques. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 12859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hasturk, H.; Abdallah, R.; Kantarci, A.; Nguyen, D.; Giordano, N.; Hamilton, J.; Van Dyke, T.E. Resolvin E1 (RvE1) Attenuates Atherosclerotic Plaque Formation in Diet and Inflammation-Induced Atherogenesis. Arter. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2015, 35, 1123–1133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tourki, B.; Kain, V.; Pullen, A.B.; Norris, P.C.; Patel, N.; Arora, P.; Leroy, X.; Serhan, C.N.; Halade, G.V. Lack of resolution sensor drives age-related cardiometabolic and cardiorenal defects and impedes inflammation-resolution in heart failure. Mol. Metab. 2020, 31, 138–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gobbetti, T.; Coldewey, S.M.; Chen, J.; McArthur, S.; Le Faouder, P.; Cenac, N.; Flower, R.J.; Thiemermann, C.; Perretti, M. Nonredundant protective properties of FPR2/ALX in polymicrobial murine sepsis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 18685–18690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, J.; Purvis, G.S.D.; Collotta, D.; Al Zoubi, S.; Sugimoto, M.A.; Cacace, A.; Martin, L.; Colas, R.A.; Collino, M.; Dalli, J.; et al. RvE1 Attenuates Polymicrobial Sepsis-Induced Cardiac Dysfunction and Enhances Bacterial Clearance. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 2080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Xiao, J.; Tian, Y.; Ma, M.; Li, X.; Li, L.; Zhang, P.; Li, M.; Wang, J.; et al. Maresin conjugates in tissue regeneration 1 prevents lipopolysaccharide-induced cardiac dysfunction through improvement of mitochondrial biogenesis and function. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2020, 177, 114005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiurchiù, V.; Leuti, A.; Saracini, S.; Fontana, D.; Finamore, P.; Giua, R.; Padovini, L.; Incalzi, R.A.; Maccarrone, M. Resolution of inflammation is altered in chronic heart failure and entails a dysfunctional responsiveness of T lymphocytes. FASEB J. 2019, 33, 909–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, K.J.; Spite, M.; Owens, C.D.; Lancero, H.; Kroemer, A.H.; Pande, R.; Creager, M.A.; Serhan, C.N.; Conte, M.S. Aspirin-Triggered Lipoxin and Resolvin E1 Modulate Vascular Smooth Muscle Phenotype and Correlate with Peripheral Atherosclerosis. Am. J. Pathol. 2010, 177, 2116–2123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colas, R.A.; Souza, P.R.; Walker, M.E.; Burton, M.; Zasłona, Z.; Curtis, A.M.; Marques, R.M.; Dalli, J. Impaired Production and Diurnal Regulation of Vascular RvD n-3 DPA Increase Systemic Inflammation and Cardiovascular Disease. Circ. Res. 2018, 122, 855–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soulaidopoulos, S.; Nikiphorou, E.; Dimitroulas, T.; Kitas, G.D. The Role of Statins in Disease Modification and Cardiovascular Risk in Rheumatoid Arthritis. Front. Med. 2018, 5, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bedi, O.; Dhawan, V.; Sharma, P.L.; Kumar, P. Pleiotropic effects of statins: New therapeutic targets in drug design. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch. Pharmacol. 2016, 389, 695–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oesterle, A.; Liao, J.K. The Pleiotropic Effects of Statins—From Coronary Artery Disease and Stroke to Atrial Fibrillation and Ventricular Tachyarrhythmia. Curr. Vasc. Pharmacol. 2019, 17, 222–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCarey, D.W.; McInnes, I.B.; Madhok, R.; Hampson, R.; Scherbakova, O.; Ford, I.; Capell, H.A.; Sattar, N. Trial of Atorvastatin in Rheumatoid Arthritis (TARA): Double-blind, randomised placebo-controlled trial. Lancet 2004, 363, 2015–2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalli, J.; Chiang, N.; Serhan, C.N. Elucidation of novel 13-series resolvins that increase with atorvastatin and clear infections. Nat. Med. 2015, 21, 1071–1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walker, M.E.; Souza, P.R.; Colas, R.A.; Dalli, J. 13-Series resolvins mediate the leukocyte-platelet actions of atorvastatin and pravastatin in inflammatory arthritis. FASEB J. 2017, 31, 3636–3648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Birnbaum, Y.; Ye, Y.; Lin, Y.; Freeberg, S.Y.; Nishi, S.P.; Martinez, J.D.; Huang, M.-H.; Uretsky, B.F.; Perez-Polo, J.R. Augmentation of Myocardial Production of 15-Epi-Lipoxin-A4by Pioglitazone and Atorvastatin in the Rat. Circulation 2006, 114, 929–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xing, B.; Yin, Y.-F.; Zhao, L.-D.; Wang, L.; Zheng, W.-J.; Chen, H.; Wu, Q.-J.; Tang, F.-L.; Zhang, F.-C.; Shan, G.; et al. Effect of 3-Hydroxy-3-Methylglutaryl-Coenzyme A Reductase Inhibitor on Disease Activity in Patients With Rheumatoid Arthritis: A meta-analysis. Medicine 2015, 94, e572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Serhan, C.N.; Brain, S.D.; Buckley, C.D.; Gilroy, D.W.; Haslett, C.; O’Neill, L.A.J.; Perretti, M.; Rossi, A.G.; Wallace, J.L. Resolution of in flammation: State of the art, definitions and terms. FASEB J. 2007, 21, 325–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, J.; Norling, L.V.; Cooper, D. Cardiac Dysfunction in Rheumatoid Arthritis: The Role of Inflammation. Cells 2021, 10, 881. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells10040881
Chen J, Norling LV, Cooper D. Cardiac Dysfunction in Rheumatoid Arthritis: The Role of Inflammation. Cells. 2021; 10(4):881. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells10040881
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Jianmin, Lucy V. Norling, and Dianne Cooper. 2021. "Cardiac Dysfunction in Rheumatoid Arthritis: The Role of Inflammation" Cells 10, no. 4: 881. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells10040881





