Transmembrane and Tetratricopeptide Repeat Containing 4 Is a Novel Diagnostic Marker for Prostate Cancer with High Specificity and Sensitivity
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Upregulation of TMTC4 in Prostate Cancer Cells
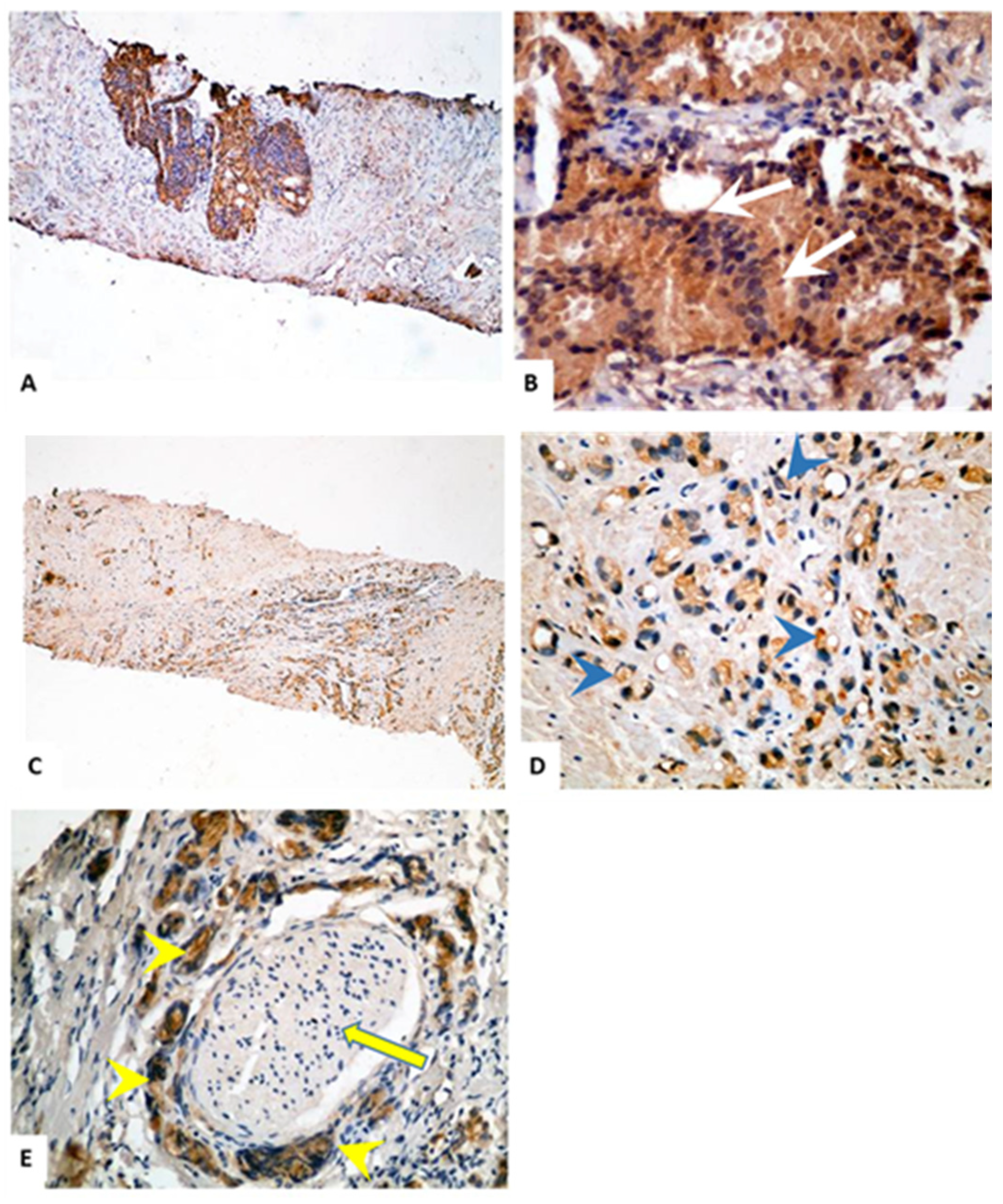
2.2. Immunohistochemical Staining of TMTC4 in BPH and PCa Tissue Specimens
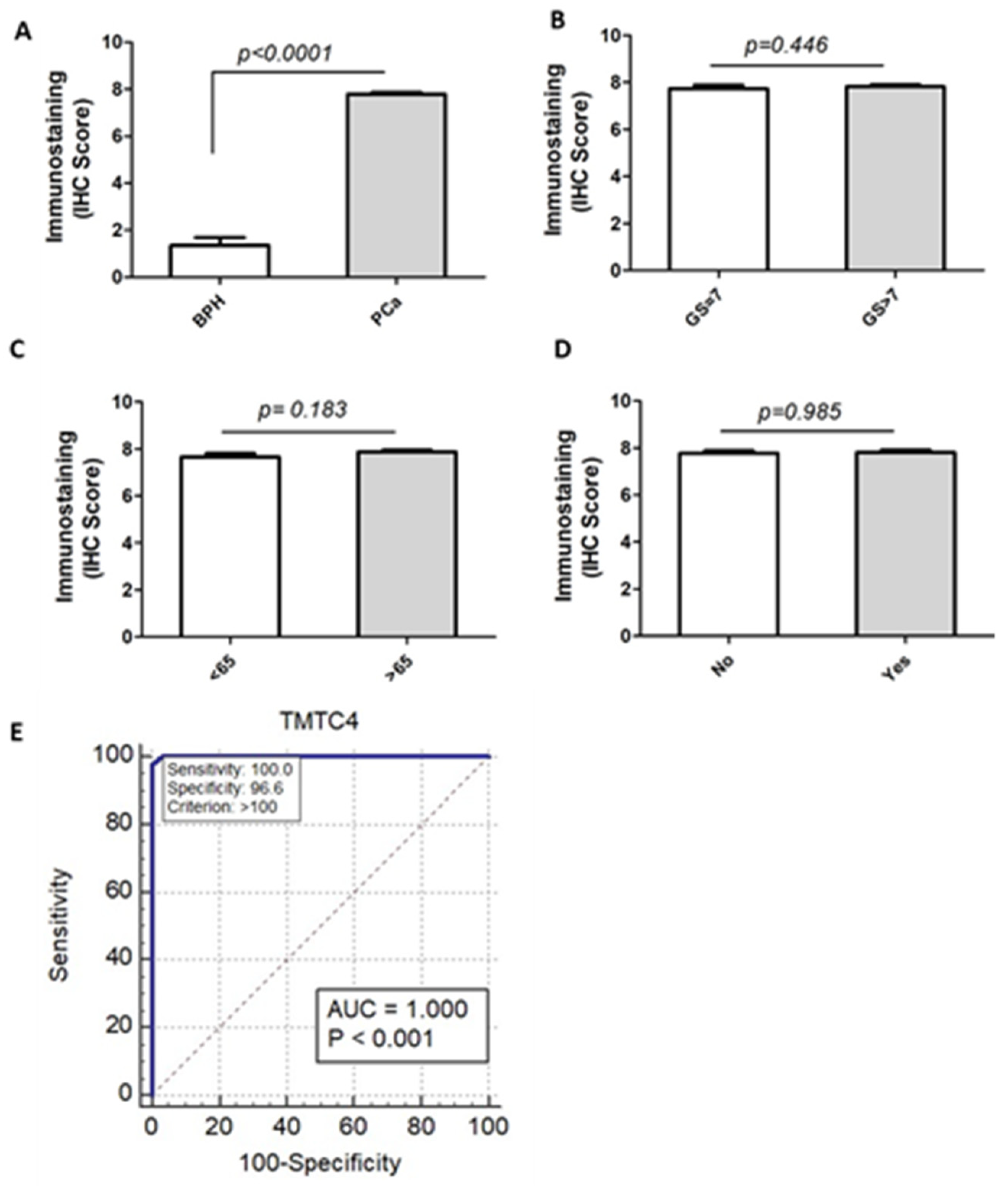
2.3. TMTC4 Expression Discriminates PCa from BPH Patients with High Accuracy
2.4. Upregulation of tmtc4 Transcript in an Independent Cohort of PCa
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Patients and Specimens
4.2. Cell Culture
4.3. Gene Expression Analysis in PCa Cells
4.4. Western Blot Analysis
4.5. Immunohistochemical Staining
4.6. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Siegel, R.L.; Miller, K.D.; Fuchs, H.E.; Jemal, A. Cancer Statistics, 2021. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2021, 71, 7–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murillo-Garzon, V.; Kypta, R. WNT signalling in prostate cancer. Nat. Rev. Urol. 2017, 14, 683–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prensner, J.R.; Rubin, M.A.; Wei, J.T.; Chinnaiyan, A.M. Beyond PSA: The next generation of prostate cancer biomarkers. Sci. Transl. Med. 2012, 4, 127rv123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caram, M.E.; Skolarus, T.A.; Cooney, K.A. Limitations of Prostate-specific Antigen Testing After a Prostate Cancer Diagnosis. Eur. Urol. 2016, 70, 209–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kretschmer, A.; Tilki, D. Biomarkers in prostate cancer—Current clinical utility and future perspectives. Crit. Rev. Oncol. Hematol. 2017, 120, 180–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jakobsen, N.A.; Hamdy, F.C.; Bryant, R.J. Novel biomarkers for the detection of prostate cancer. J. Clin. Urol. 2016, 9, 3–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Magi-Galluzzi, C. Prostate cancer: Diagnostic criteria and role of immunohistochemistry. Mod. Pathol. 2018, 31, 12–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerhard, D.S.; Wagner, L.; Feingold, E.A.; Shenmen, C.M.; Grouse, L.H.; Schuler, G.; Klein, S.L.; Old, S.; Rasooly, R.; Good, P.; et al. The status, quality, and expansion of the NIH full-length cDNA project: The Mammalian Gene Collection (MGC). Genome Res. 2004, 14, 2121–2127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ota, T.; Suzuki, Y.; Nishikawa, T.; Otsuki, T.; Sugiyama, T.; Irie, R.; Wakamatsu, A.; Hayashi, K.; Sato, H.; Nagai, K.; et al. Complete sequencing and characterization of 21,243 full-length human cDNAs. Nat. Genet. 2004, 36, 40–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D’Andrea, L.D.; Regan, L. TPR proteins: The versatile helix. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2003, 28, 655–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sunryd, J.C.; Cheon, B.; Graham, J.B.; Giorda, K.M.; Fissore, R.A.; Hebert, D.N. TMTC1 and TMTC2 are novel endoplasmic reticulum tetratricopeptide repeat-containing adapter proteins involved in calcium homeostasis. J. Biol. Chem. 2014, 289, 16085–16099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Akil, O.; Rouse, S.L.; McLaughlin, C.W.; Matthews, I.R.; Lustig, L.R.; Chan, D.K.; Sherr, E.H. Deletion of Tmtc4 activates the unfolded protein response and causes postnatal hearing loss. J. Clin. Investig. 2018, 128, 5150–5162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Larsen, I.S.B.; Narimatsu, Y.; Joshi, H.J.; Siukstaite, L.; Harrison, O.J.; Brasch, J.; Goodman, K.M.; Hansen, L.; Shapiro, L.; Honig, B.; et al. Discovery of an O-mannosylation pathway selectively serving cadherins and protocadherins. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, 11163–11168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvalho, S.; Oliveira, T.; Bartels, M.F.; Miyoshi, E.; Pierce, M.; Taniguchi, N.; Carneiro, F.; Seruca, R.; Reis, C.A.; Strahl, S.; et al. O-mannosylation and N-glycosylation: Two coordinated mechanisms regulating the tumour suppressor functions of E-cadherin in cancer. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 65231–65246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, Y.; Saatcioglu, F. Targeting the Unfolded Protein Response in Hormone-Regulated Cancers. Trends Cancer 2020, 6, 160–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martelli, A.M.; Paganelli, F.; Chiarini, F.; Evangelisti, C.; McCubrey, J.A. The Unfolded Protein Response: A Novel Therapeutic Target in Acute Leukemias. Cancers 2020, 12, 333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandrashekar, D.S.; Bashel, B.; Balasubramanya, S.A.H.; Creighton, C.J.; Ponce-Rodriguez, I.; Chakravarthi, B.; Varambally, S. UALCAN: A Portal for Facilitating Tumor Subgroup Gene Expression and Survival Analyses. Neoplasia 2017, 19, 649–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, E.J.; Fang, J.; Metter, E.J.; Partin, A.W.; Landis, P.; Chan, D.; Carter, H. Prostate specific antigen predicts the long-term risk of prostate enlargement: Results from the Baltimore Longitudinal Study of Aging. J. Urol. 2002, 167, 2484–2487, discussion 2487–2488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peyromaure, M.; Ravery, V.; Messas, A.; Toublanc, M.; Boccon-Gibod, L.; Boccon-Gibod, L. Pain and morbidity of an extensive prostate 10-biopsy protocol: A prospective study in 289 patients. J. Urol. 2002, 167, 218–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hooker, S.E., Jr.; Woods-Burnham, L.; Bathina, M.; Lloyd, S.; Gorjala, P.; Mitra, R.; Nonn, L.; Kimbro, K.S.; Kittles, R.A. Genetic Ancestry Analysis Reveals Misclassification of Commonly Used Cancer Cell Lines. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomark. Prev. 2019, 28, 1003–1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Epstein, J.I.; Egevad, L.; Humphrey, P.A.; Montironi, R. Best practices recommendations in the application of immunohistochemistry in the prostate: Report from the International Society of Urologic Pathology consensus conference. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 2014, 38, e6–e19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wadosky, K.M.; Shourideh, M.; Goodrich, D.W.; Koochekpour, S. Riluzole induces AR degradation via endoplasmic reticulum stress pathway in androgen-dependent and castration-resistant prostate cancer cells. Prostate 2019, 79, 140–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Periasamy, M.; Kalyanasundaram, A. SERCA pump isoforms: Their role in calcium transport and disease. Muscle Nerve 2007, 35, 430–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monteith, G.R.; McAndrew, D.; Faddy, H.M.; Roberts-Thomson, S.J. Calcium and cancer: Targeting Ca2+ transport. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2007, 7, 519–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, J.A.; Kim, B.; Dhanasekaran, D.N.; Tsang, B.K.; Song, Y.S. Curcumin induces apoptosis by inhibiting sarco/endoplasmic reticulum Ca2+ ATPase activity in ovarian cancer cells. Cancer Lett. 2016, 371, 30–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paredes, J.; Figueiredo, J.; Albergaria, A.; Oliveira, P.; Carvalho, J.; Ribeiro, A.S.; Caldeira, J.; Costa, A.M.; Simoes-Correia, J.; Oliveira, M.J.; et al. Epithelial E- and P-cadherins: Role and clinical significance in cancer. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2012, 1826, 297–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Epstein, J.I.; Egevad, L.; Amin, M.B.; Delahunt, B.; Srigley, J.R.; Humphrey, P.A. The 2014 International Society of Urological Pathology (ISUP) Consensus Conference on Gleason Grading of Prostatic Carcinoma: Definition of Grading Patterns and Proposal for a New Grading System. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 2016, 40, 244–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Theodore, S.; Sharp, S.; Zhou, J.; Turner, T.; Li, H.; Miki, J.; Ji, Y.; Patel, V.; Yates, C.; Rhim, J.S. Establishment and characterization of a pair of non-malignant and malignant tumor derived cell lines from an African American prostate cancer patient. Int. J. Oncol. 2010, 37, 1477–1482. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Gokce, A.; Abd Elmageed, Z.Y.; Lasker, G.F.; Bouljihad, M.; Kim, H.; Trost, L.W.; Kadowitz, P.J.; Abdel-Mageed, A.B.; Sikka, S.C.; Hellstrom, W.J. Adipose tissue-derived stem cell therapy for prevention and treatment of erectile dysfunction in a rat model of Peyronie’s disease. Andrology 2014, 2, 244–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaballa, R.; Ali, H.E.A.; Mahmoud, M.O.; Rhim, J.S.; Ali, H.I.; Salem, H.F.; Saleem, M.; Kandeil, M.A.; Ambs, S.; Abd Elmageed, Z.Y. Exosomes-Mediated Transfer of Itga2 Promotes Migration and Invasion of Prostate Cancer Cells by Inducing Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition. Cancers 2020, 12, 2300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abd Elmageed, Z.Y.; Moroz, K.; Srivastav, S.K.; Fang, Z.; Crawford, B.E.; Moparty, K.; Thomas, R.; Abdel-Mageed, A.B. High circulating estrogens and selective expression of ERbeta in prostate tumors of Americans: Implications for racial disparity of prostate cancer. Carcinogenesis 2013, 34, 2017–2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| Variables | Frequency | Percent (%) |
|---|---|---|
| BPH | ||
| Cases (N) | 29 | 100 |
| Age (average ± SD) | 67.3 ± 7.7 | |
| PSA (ng/mL) | 6.9 ± 5.6 | |
| PCa | ||
| Cases (N) | 43 | 100 |
| Age (average ± SD) | 70.3 ± 9.3 | |
| PSA (ng/mL) | 14.7 ± 8.6 | |
| Gleason score | ||
| 7 | 14 | 32.5 |
| 8 | 10 | 23.3 |
| 9 | 19 | 44.2 |
| ISUP group | ||
| 2 | 10 | 23.3 |
| 3 | 4 | 9.3 |
| 4 | 10 | 23.3 |
| 5 | 19 | 44.2 |
| Perineural invasion | ||
| Positive | 16 | −37.2 |
| negative | 27 | −62.8 |
| Variables | TMTC4 Expression (Mean ± SD) (Percent × Intensity) | p-Value * |
|---|---|---|
| BPH | 16.69 ± 34.4 | <0.001 2 |
| PCa | 278.12 ± 41.54 | |
| PCa based on Gleason score | ||
| 7 | 271.54 ± 45.79 | 0.88 1 |
| 8 | 281.55 ± 40.32 | |
| 9 | 280.63 ± 40.99 | |
| ISUP Grade | ||
| 2 | 284.00 ± 35.02 | 0.62 1 |
| 3 | 247.50 ± 60.75 | |
| 4 | 279.70 ± 42.01 | |
| 5 | 280.63 ± 40.99 | |
| Perineural invasion | ||
| Positive | 275.31 ± 42.87 | 0.97 2 |
| negative | 279.78 ± 41.47 | |
| TMTC4 Marker Cutoff Point | Sensitivity | Specificity | Positive Predictive Value | Negative Predictive Value | AUC | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ≥100 | 100% | 96.55% | 97.7% | 100% | 1.0 | <0.001 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Makboul, R.; Abdelkawi, I.F.; Badary, D.M.; Hussein, M.R.A.; Rhim, J.S.; Toraih, E.A.; Zerfaoui, M.; Abd Elmageed, Z.Y. Transmembrane and Tetratricopeptide Repeat Containing 4 Is a Novel Diagnostic Marker for Prostate Cancer with High Specificity and Sensitivity. Cells 2021, 10, 1029. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells10051029
Makboul R, Abdelkawi IF, Badary DM, Hussein MRA, Rhim JS, Toraih EA, Zerfaoui M, Abd Elmageed ZY. Transmembrane and Tetratricopeptide Repeat Containing 4 Is a Novel Diagnostic Marker for Prostate Cancer with High Specificity and Sensitivity. Cells. 2021; 10(5):1029. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells10051029
Chicago/Turabian StyleMakboul, Rania, Islam F. Abdelkawi, Dalia M. Badary, Mahmoud R. A. Hussein, Johng S. Rhim, Eman A. Toraih, Mourad Zerfaoui, and Zakaria Y. Abd Elmageed. 2021. "Transmembrane and Tetratricopeptide Repeat Containing 4 Is a Novel Diagnostic Marker for Prostate Cancer with High Specificity and Sensitivity" Cells 10, no. 5: 1029. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells10051029
APA StyleMakboul, R., Abdelkawi, I. F., Badary, D. M., Hussein, M. R. A., Rhim, J. S., Toraih, E. A., Zerfaoui, M., & Abd Elmageed, Z. Y. (2021). Transmembrane and Tetratricopeptide Repeat Containing 4 Is a Novel Diagnostic Marker for Prostate Cancer with High Specificity and Sensitivity. Cells, 10(5), 1029. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells10051029









