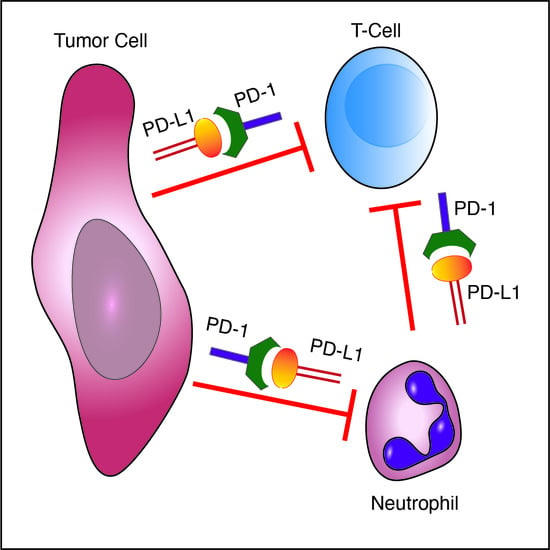
The PD-L1/PD-1 Axis Blocks Neutrophil Cytotoxicity in Cancer
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals
2.2. Cell Lines
2.3. Plasmids
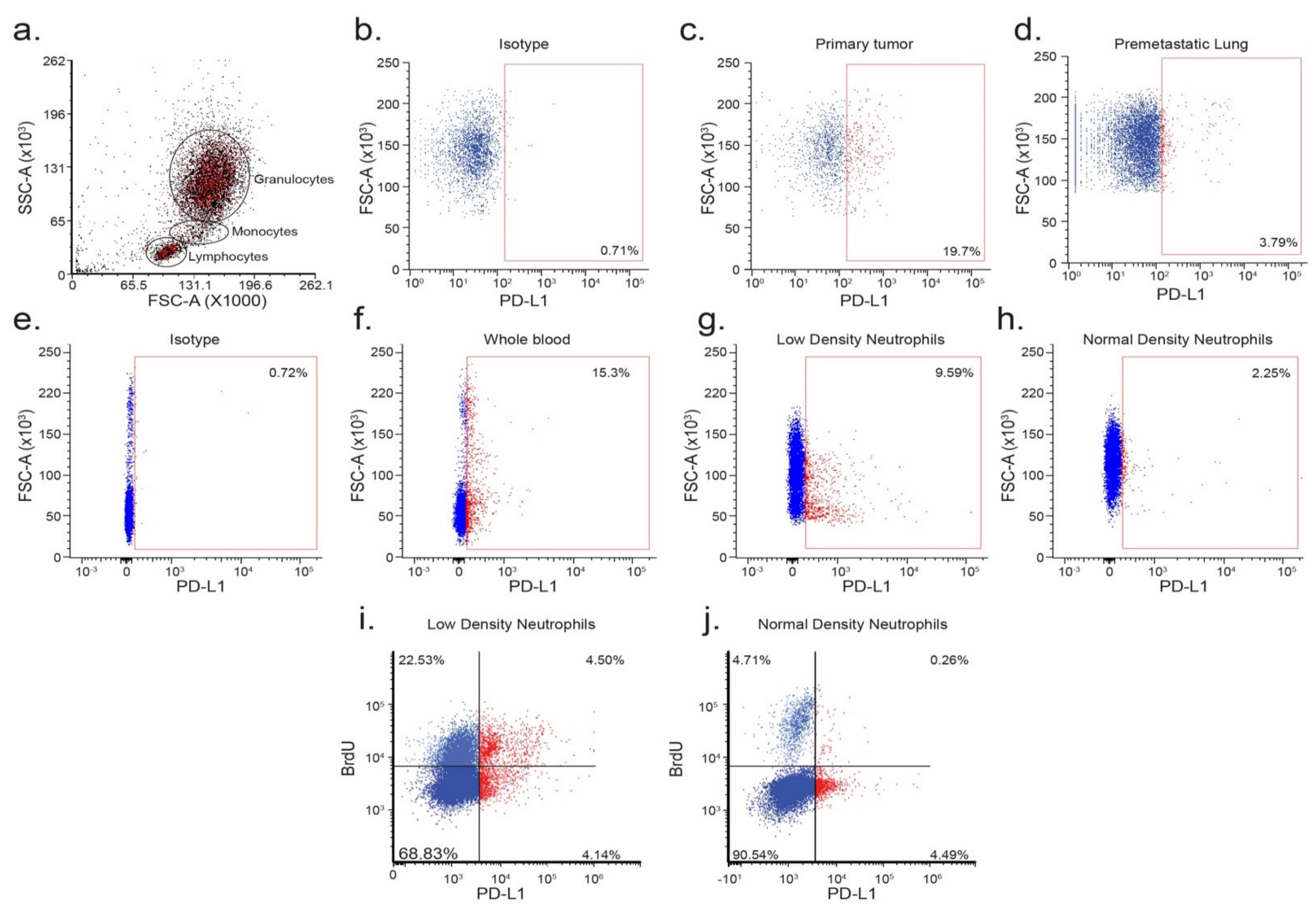
2.4. Neutrophil Purification
2.5. Primary Tumor and Metastasis Formation In Vivo Assay
2.6. qPCR
2.7. Peritonitis
2.8. ROS Production Assay
2.9. In Vitro Killing Assay
2.10. BrdU Labeling
2.11. Antibodies
2.12. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
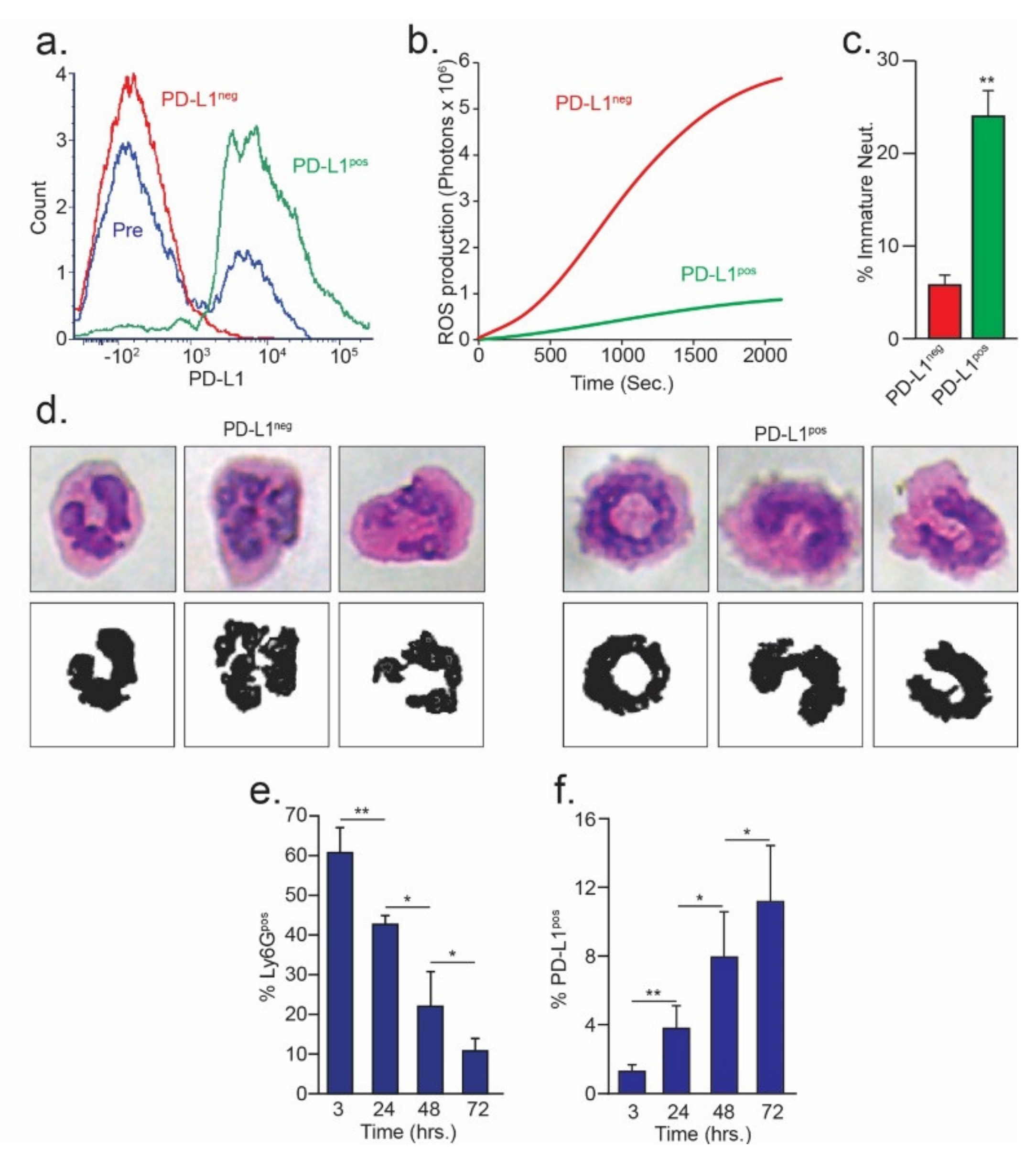
3.1. Immature Low-Density Neutrophils Express Higher Levels of PD-L1
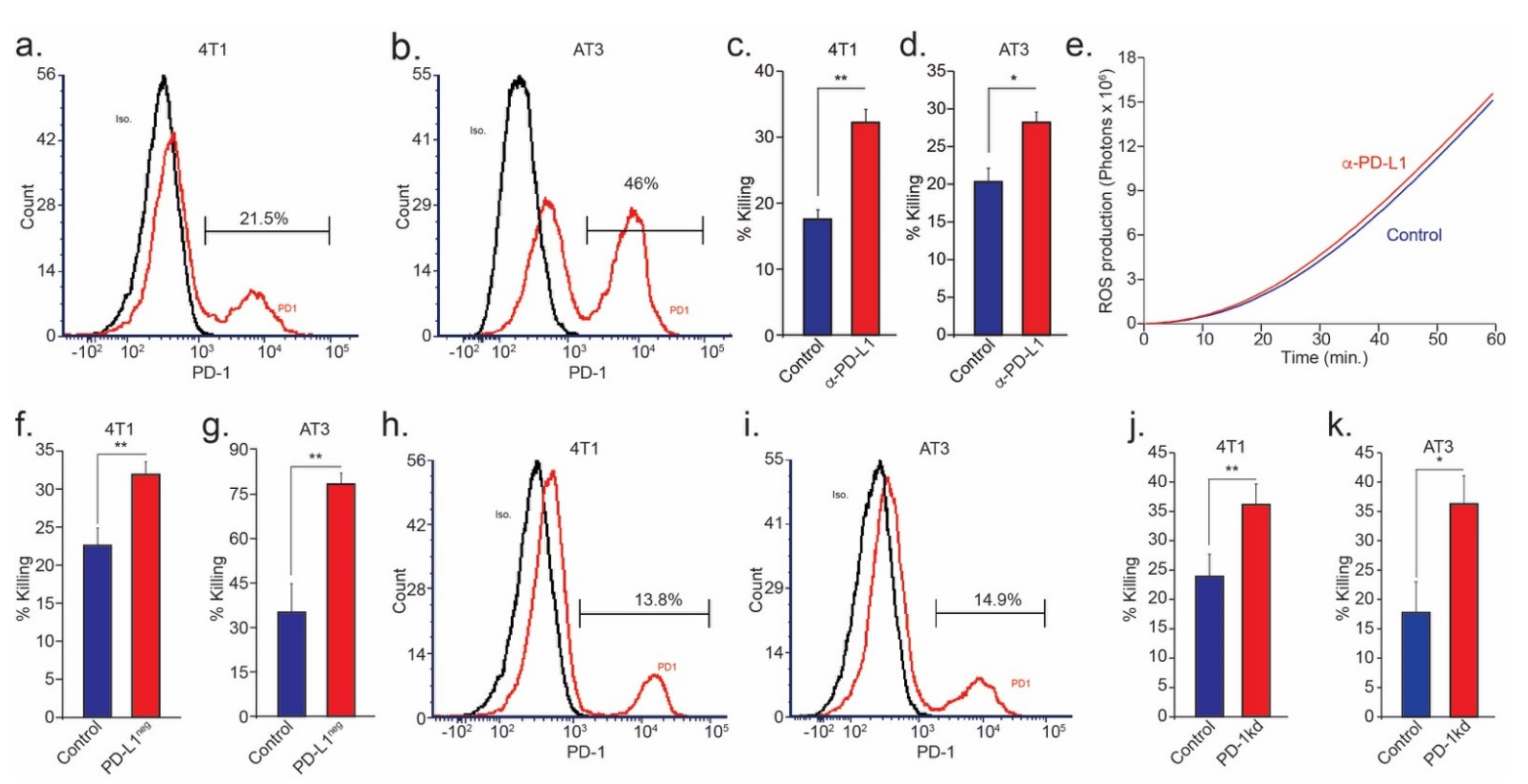
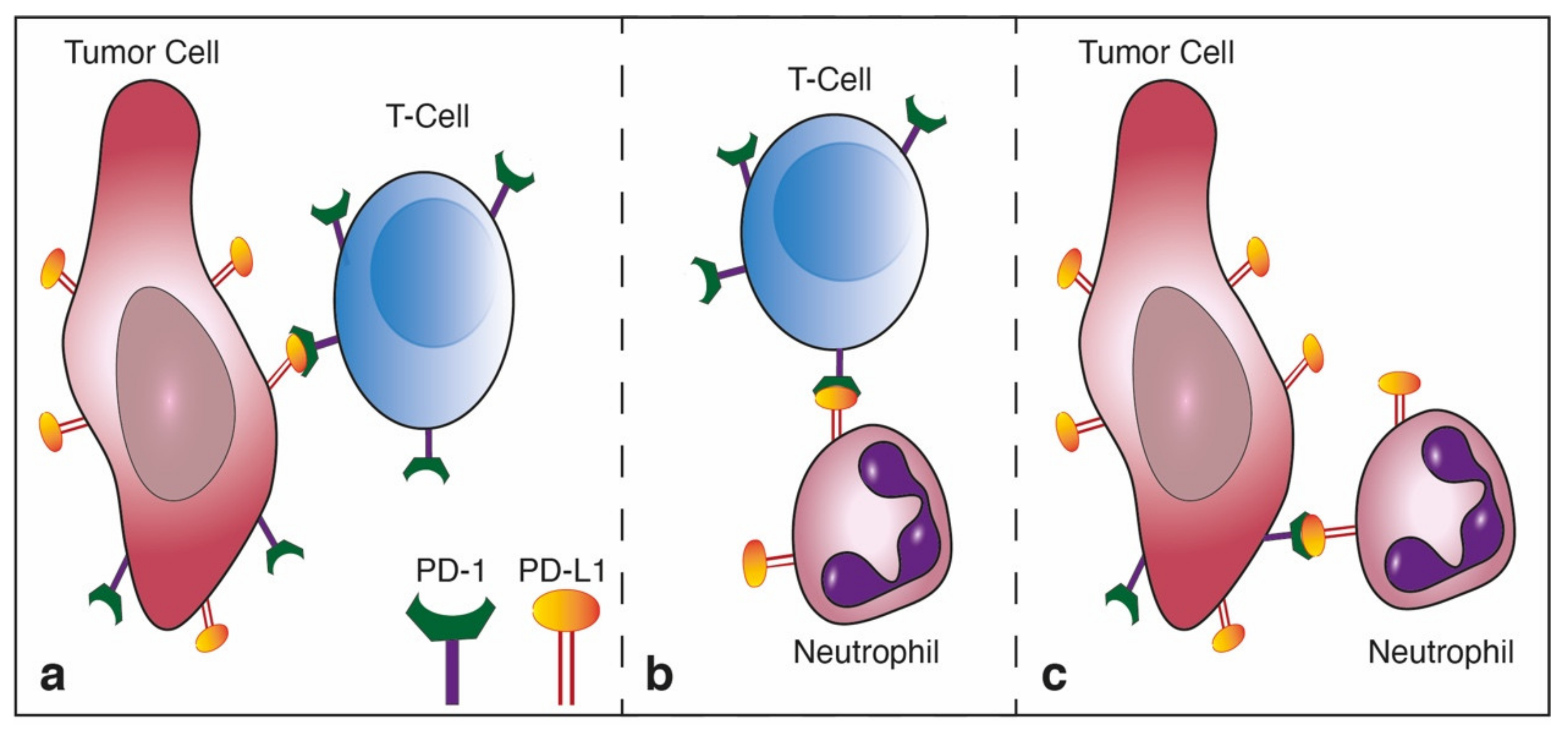
3.2. PD-1-Expressing Tumor Cells Inhibit Neutrophil Cytotoxicity via the PD-L1/PD-1 Axis
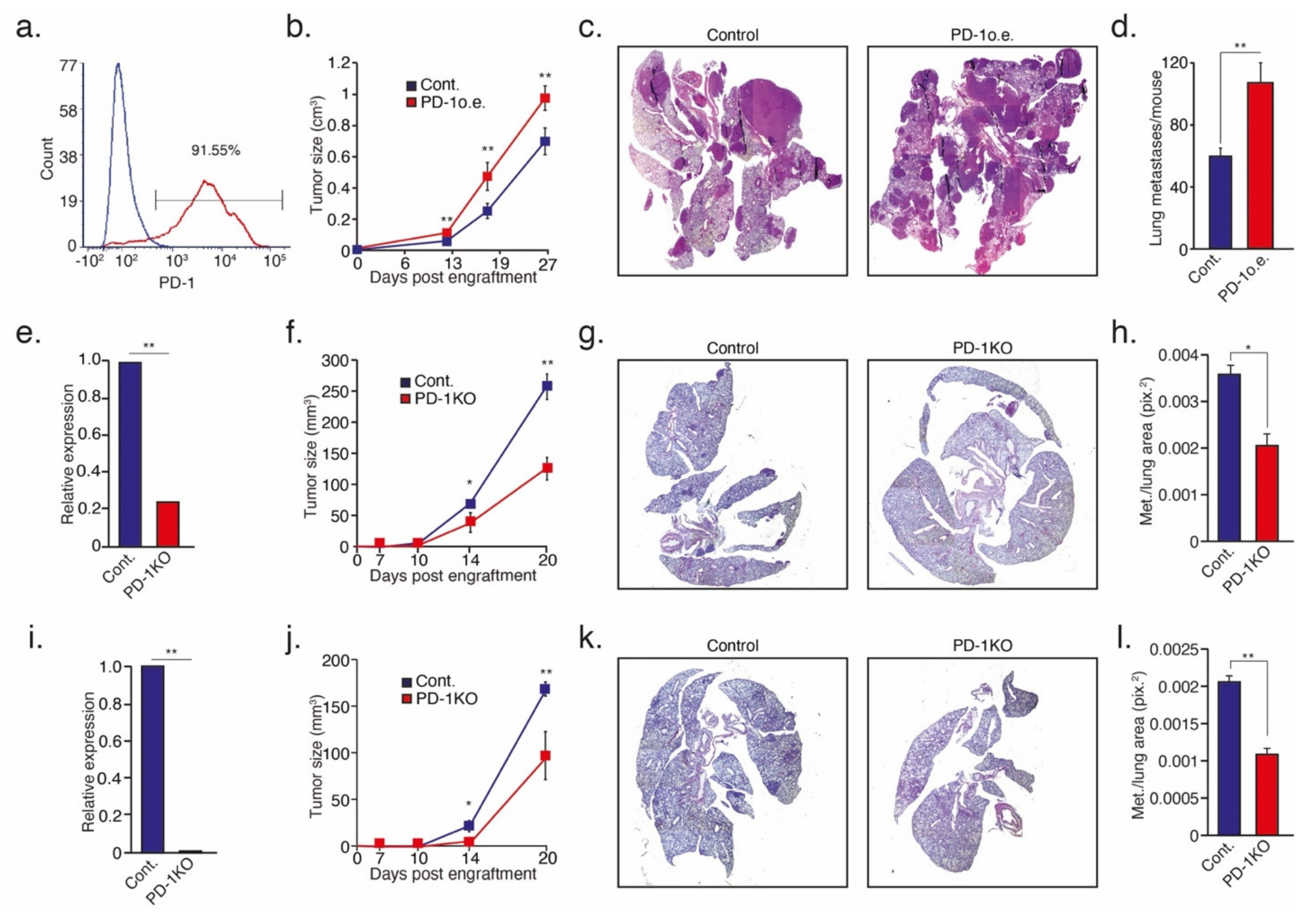
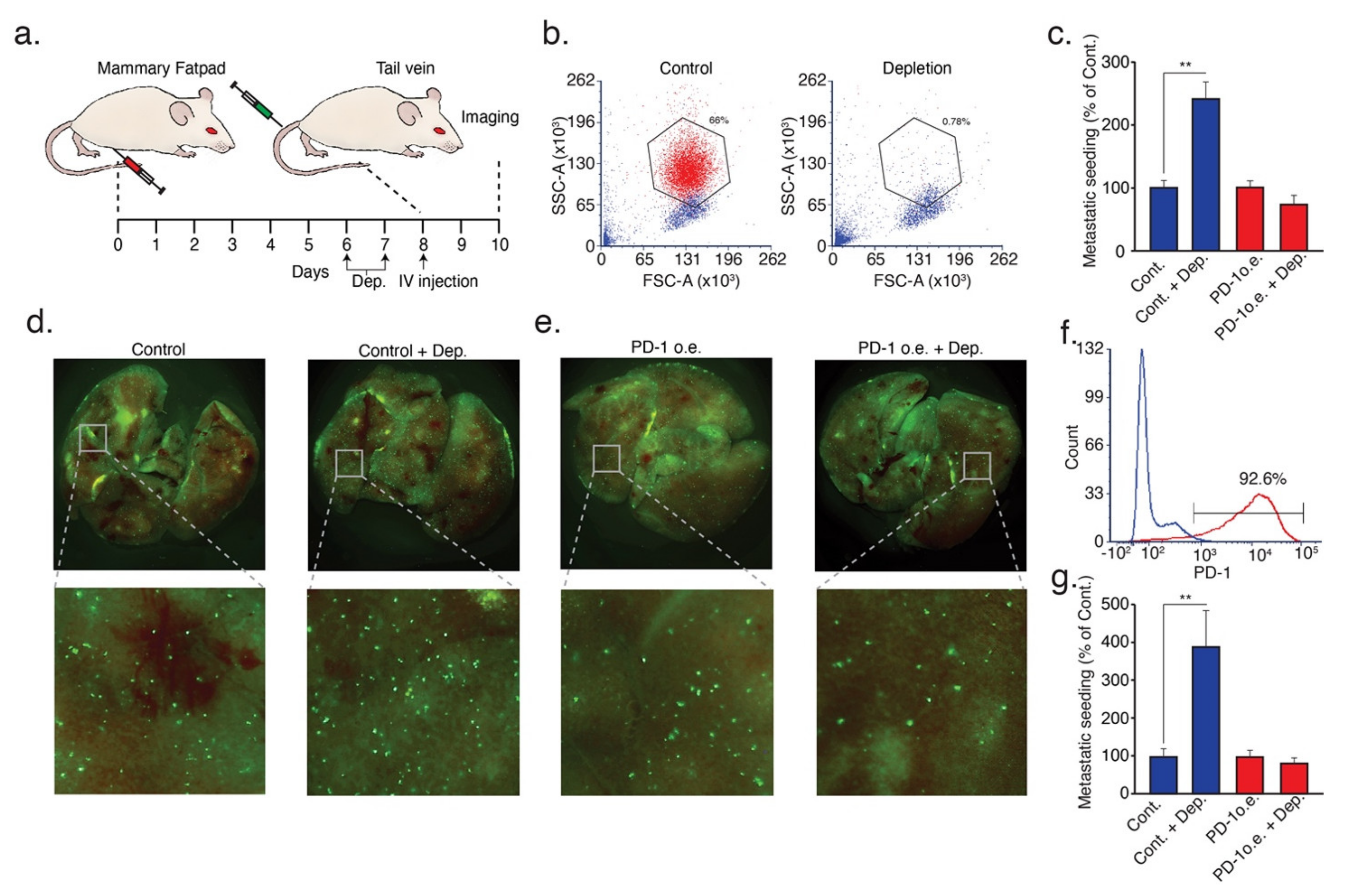
3.3. Tumor Cell PD-1 Inhibits Neutrophil Cytotoxicity and Increases Metastatic Potential
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hanahan, D.; Coussens, L.M. Accessories to the crime: Functions of cells recruited to the tumor microenvironment. Cancer Cell 2012, 21, 309–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nanda, N.K.; Sercarz, E.E. Induction of anti-self-immunity to cure cancer. Cell 1995, 82, 13–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, D.S.; Mellman, I. Oncology meets immunology: The cancer-immunity cycle. Immunity 2013, 39, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Barberis, I.; Myles, P.; Ault, S.K.; Bragazzi, N.L.; Martini, M. History and evolution of influenza control through vaccination: From the first monovalent vaccine to universal vaccines. J. Prev. Med. Hyg. 2016, 57, E115–E120. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Drake, C.G.; Jaffee, E.; Pardoll, D.M. Mechanisms of immune evasion by tumors. Adv. Immunol. 2006, 90, 51–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ribas, A. Adaptive Immune Resistance: How Cancer Protects from Immune Attack. Cancer Discov. 2015, 5, 915–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Topalian, S.L.; Drake, C.G.; Pardoll, D.M. Immune checkpoint blockade: A common denominator approach to cancer therapy. Cancer Cell 2015, 27, 450–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sharma, P.; Allison, J.P. The future of immune checkpoint therapy. Science 2015, 348, 56–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trivedi, M.S.; Hoffner, B.; Winkelmann, J.L.; Abbott, M.E.; Hamid, O.; Carvajal, R.D. Programmed death 1 immune checkpoint inhibitors. Clin. Adv. Hematol. Oncol. 2015, 13, 858–868. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Chikuma, S. Basics of PD-1 in self-tolerance, infection, and cancer immunity. Int J. Clin. Oncol. 2016, 21, 448–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blank, C.; Brown, I.; Peterson, A.C.; Spiotto, M.; Iwai, Y.; Honjo, T.; Gajewski, T.F. PD-L1/B7H-1 inhibits the effector phase of tumor rejection by T cell receptor (TCR) transgenic CD8+ T cells. Cancer Res. 2004, 64, 1140–1145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Amarnath, S.; Mangus, C.W.; Wang, J.C.; Wei, F.; He, A.; Kapoor, V.; Foley, J.E.; Massey, P.R.; Felizardo, T.C.; Riley, J.L.; et al. The PDL1-PD1 axis converts human TH1 cells into regulatory T cells. Sci. Transl. Med. 2011, 3, 111ra120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Butte, M.J.; Keir, M.E.; Phamduy, T.B.; Sharpe, A.H.; Freeman, G.J. Programmed death-1 ligand 1 interacts specifically with the B7-1 costimulatory molecule to inhibit T cell responses. Immunity 2007, 27, 111–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gibbons Johnson, R.M.; Dong, H. Functional Expression of Programmed Death-Ligand 1 (B7-H1) by Immune Cells and Tumor Cells. Front. Immunol 2017, 8, 961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, G.; Zhang, H.; Zhou, J.; Wang, B.; Chen, Y.; Kong, Y.; Xie, X.; Wang, X.; Fei, R.; Wei, L.; et al. Peritumoural neutrophils negatively regulate adaptive immunity via the PD-L1/PD-1 signalling pathway in hepatocellular carcinoma. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2015, 34, 141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, T.T.; Zhao, Y.L.; Peng, L.S.; Chen, N.; Chen, W.; Lv, Y.P.; Mao, F.Y.; Zhang, J.Y.; Cheng, P.; Teng, Y.S.; et al. Tumour-activated neutrophils in gastric cancer foster immune suppression and disease progression through GM-CSF-PD-L1 pathway. Gut 2017, 66, 1900–1911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sionov, R.V.; Fridlender, Z.G.; Granot, Z. The Multifaceted Roles Neutrophils Play in the Tumor Microenvironment. Cancer Microenviron. 2015, 8, 125–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Katoh, H.; Wang, D.; Daikoku, T.; Sun, H.; Dey, S.K.; Dubois, R.N. CXCR2-expressing myeloid-derived suppressor cells are essential to promote colitis-associated tumorigenesis. Cancer Cell 2013, 24, 631–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Houghton, A.M.; Rzymkiewicz, D.M.; Ji, H.; Gregory, A.D.; Egea, E.E.; Metz, H.E.; Stolz, D.B.; Land, S.R.; Marconcini, L.A.; Kliment, C.R.; et al. Neutrophil elastase-mediated degradation of IRS-1 accelerates lung tumor growth. Nat. Med. 2010, 16, 219–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jablonska, J.; Leschner, S.; Westphal, K.; Lienenklaus, S.; Weiss, S. Neutrophils responsive to endogenous IFN-beta regulate tumor angiogenesis and growth in a mouse tumor model. J. Clin. Investig. 2010, 120, 1151–1164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nozawa, H.; Chiu, C.; Hanahan, D. Infiltrating neutrophils mediate the initial angiogenic switch in a mouse model of multistage carcinogenesis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 12493–12498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gabrilovich, D.I.; Ostrand-Rosenberg, S.; Bronte, V. Coordinated regulation of myeloid cells by tumours. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2012, 12, 253–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- De Kleijn, S.; Langereis, J.D.; Leentjens, J.; Kox, M.; Netea, M.G.; Koenderman, L.; Ferwerda, G.; Pickkers, P.; Hermans, P.W. IFN-gamma-stimulated neutrophils suppress lymphocyte proliferation through expression of PD-L1. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e72249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cools-Lartigue, J.; Spicer, J.; McDonald, B.; Gowing, S.; Chow, S.; Giannias, B.; Bourdeau, F.; Kubes, P.; Ferri, L. Neutrophil extracellular traps sequester circulating tumor cells and promote metastasis. J. Clin. Investig. 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spicer, J.D.; McDonald, B.; Cools-Lartigue, J.J.; Chow, S.C.; Giannias, B.; Kubes, P.; Ferri, L.E. Neutrophils promote liver metastasis via Mac-1-mediated interactions with circulating tumor cells. Cancer Res. 2012, 72, 3919–3927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Casbon, A.J.; Reynaud, D.; Park, C.; Khuc, E.; Gan, D.D.; Schepers, K.; Passegue, E.; Werb, Z. Invasive breast cancer reprograms early myeloid differentiation in the bone marrow to generate immunosuppressive neutrophils. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, E566–E575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gershkovitz, M.; Caspi, Y.; Fainsod-Levi, T.; Katz, B.; Michaeli, J.; Khawaled, S.; Lev, S.; Polyansky, L.; Shaul, M.E.; Sionov, R.V.; et al. TRPM2 Mediates Neutrophil Killing of Disseminated Tumor Cells. Cancer Res. 2018, 78, 2680–2690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Granot, Z.; Henke, E.; Comen, E.A.; King, T.A.; Norton, L.; Benezra, R. Tumor entrained neutrophils inhibit seeding in the premetastatic lung. Cancer Cell 2011, 20, 300–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Simon, S.; Labarriere, N. PD-1 expression on tumor-specific T cells: Friend or foe for immunotherapy? Oncoimmunology 2017, 7, e1364828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kleffel, S.; Posch, C.; Barthel, S.R.; Mueller, H.; Schlapbach, C.; Guenova, E.; Elco, C.P.; Lee, N.; Juneja, V.R.; Zhan, Q.; et al. Melanoma Cell-Intrinsic PD-1 Receptor Functions Promote Tumor Growth. Cell 2015, 162, 1242–1256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Minn, A.J.; Kang, Y.; Serganova, I.; Gupta, G.P.; Giri, D.D.; Doubrovin, M.; Ponomarev, V.; Gerald, W.L.; Blasberg, R.; Massague, J. Distinct organ-specific metastatic potential of individual breast cancer cells and primary tumors. J. Clin. Investig. 2005, 115, 44–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sionov, R.V.; Assi, S.; Gershkovitz, M.; Sagiv, J.Y.; Polyansky, L.; Mishalian, I.; Fridlender, Z.G.; Granot, Z. Isolation and Characterization of Neutrophils with Anti-Tumor Properties. J. Vis. Exp. JoVE 2015, e52933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gershkovitz, M.; Fainsod-Levi, T.; Khawaled, S.; Shaul, M.E.; Sionov, R.V.; Cohen-Daniel, L.; Aqeilan, R.I.; Shaul, Y.D.; Fridlender, Z.G.; Granot, Z. Microenvironmental Cues Determine Tumor Cell Susceptibility to Neutrophil Cytotoxicity. Cancer Res. 2018, 78, 5050–5059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sagiv, J.Y.; Michaeli, J.; Assi, S.; Mishalian, I.; Kisos, H.; Levy, L.; Damti, P.; Lumbroso, D.; Polyansky, L.; Sionov, R.V.; et al. Phenotypic diversity and plasticity in circulating neutrophil subpopulations in cancer. Cell Rep. 2015, 10, 562–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yang, X.D.; Ai, W.; Asfaha, S.; Bhagat, G.; Friedman, R.A.; Jin, G.; Park, H.; Shykind, B.; Diacovo, T.G.; Falus, A.; et al. Histamine deficiency promotes inflammation-associated carcinogenesis through reduced myeloid maturation and accumulation of CD11b+Ly6G+ immature myeloid cells. Nat. Med. 2011, 17, 87–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhang, X.; Xu, W. Neutrophils diminish T-cell immunity to foster gastric cancer progression: The role of GM-CSF/PD-L1/PD-1 signalling pathway. Gut 2017, 66, 1878–1880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yajuk, O.; Baron, M.; Toker, S.; Zelter, T.; Fainsod-Levi, T.; Granot, Z. The PD-L1/PD-1 Axis Blocks Neutrophil Cytotoxicity in Cancer. Cells 2021, 10, 1510. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells10061510
Yajuk O, Baron M, Toker S, Zelter T, Fainsod-Levi T, Granot Z. The PD-L1/PD-1 Axis Blocks Neutrophil Cytotoxicity in Cancer. Cells. 2021; 10(6):1510. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells10061510
Chicago/Turabian StyleYajuk, Olga, Maya Baron, Sapir Toker, Tamir Zelter, Tanya Fainsod-Levi, and Zvi Granot. 2021. "The PD-L1/PD-1 Axis Blocks Neutrophil Cytotoxicity in Cancer" Cells 10, no. 6: 1510. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells10061510
APA StyleYajuk, O., Baron, M., Toker, S., Zelter, T., Fainsod-Levi, T., & Granot, Z. (2021). The PD-L1/PD-1 Axis Blocks Neutrophil Cytotoxicity in Cancer. Cells, 10(6), 1510. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells10061510