An Electrophysiological and Pharmacological Study of the Properties of Human iPSC-Derived Neurons for Drug Discovery
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
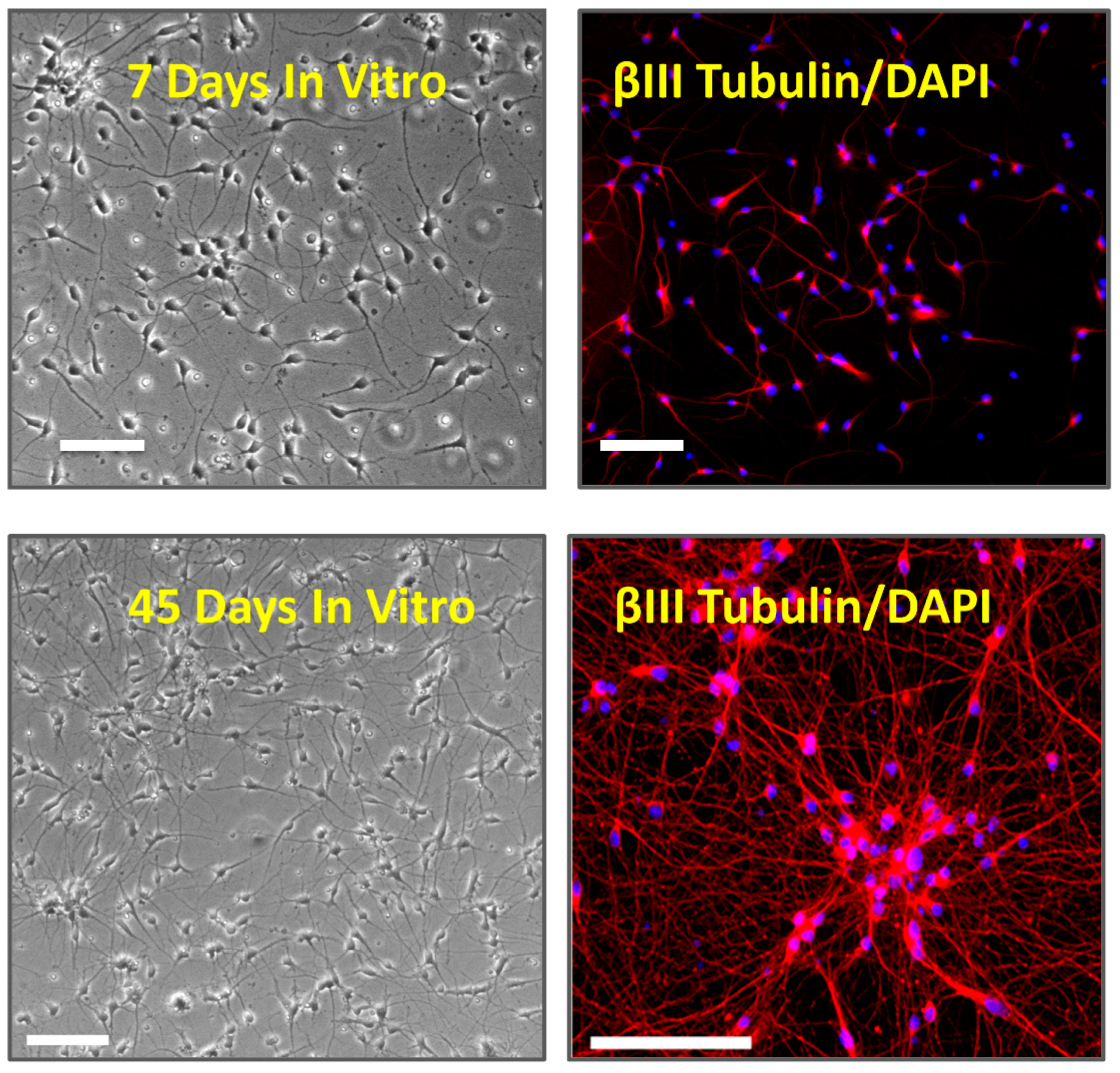
2.1. Cell Culture
2.2. Immunocytochemistry
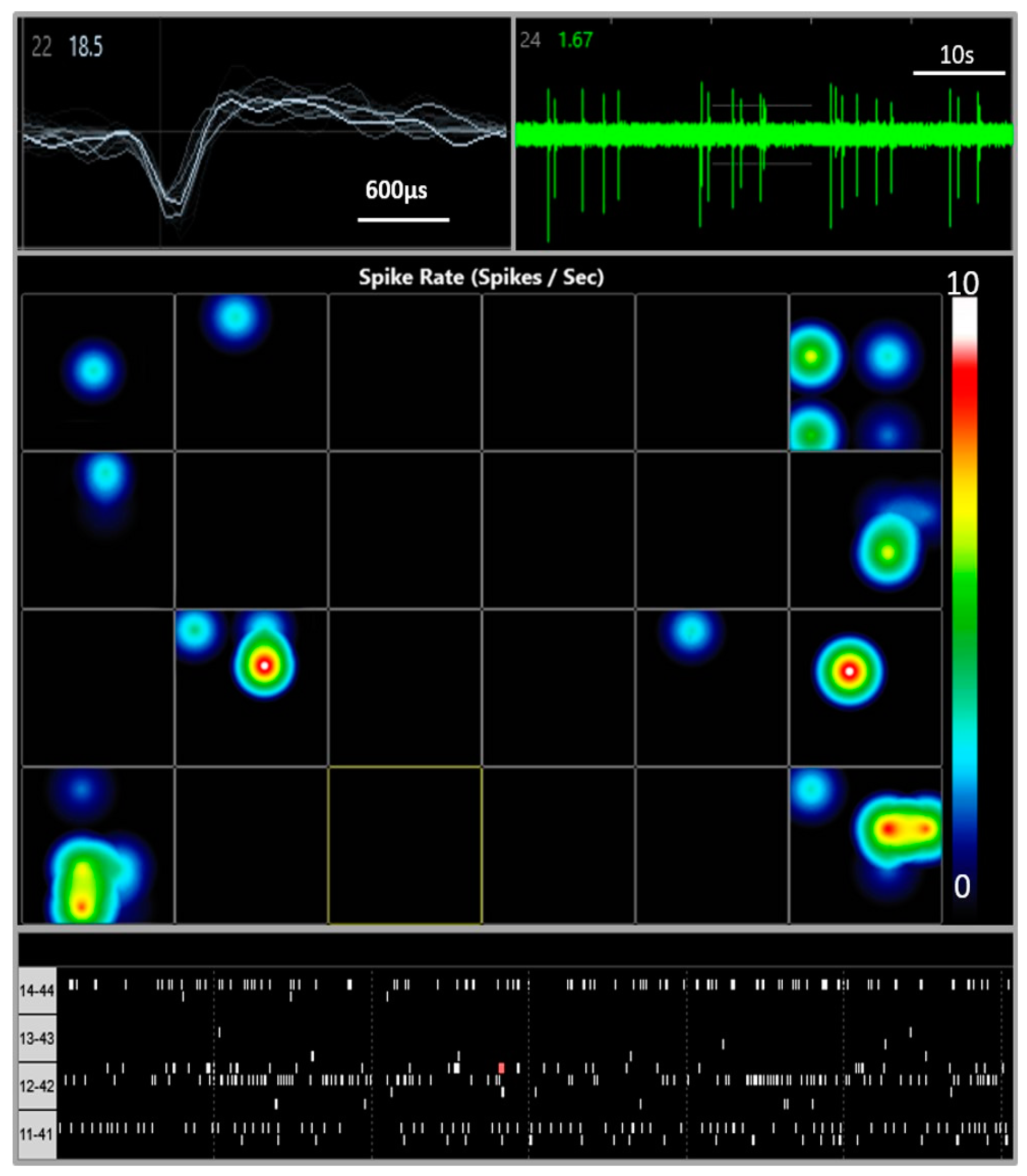
2.3. Multi-Electrode Array Electrophysiology
2.4. Patch-Clamp Electrophysiology
2.5. Drugs and Their Application
2.6. Data Analysis
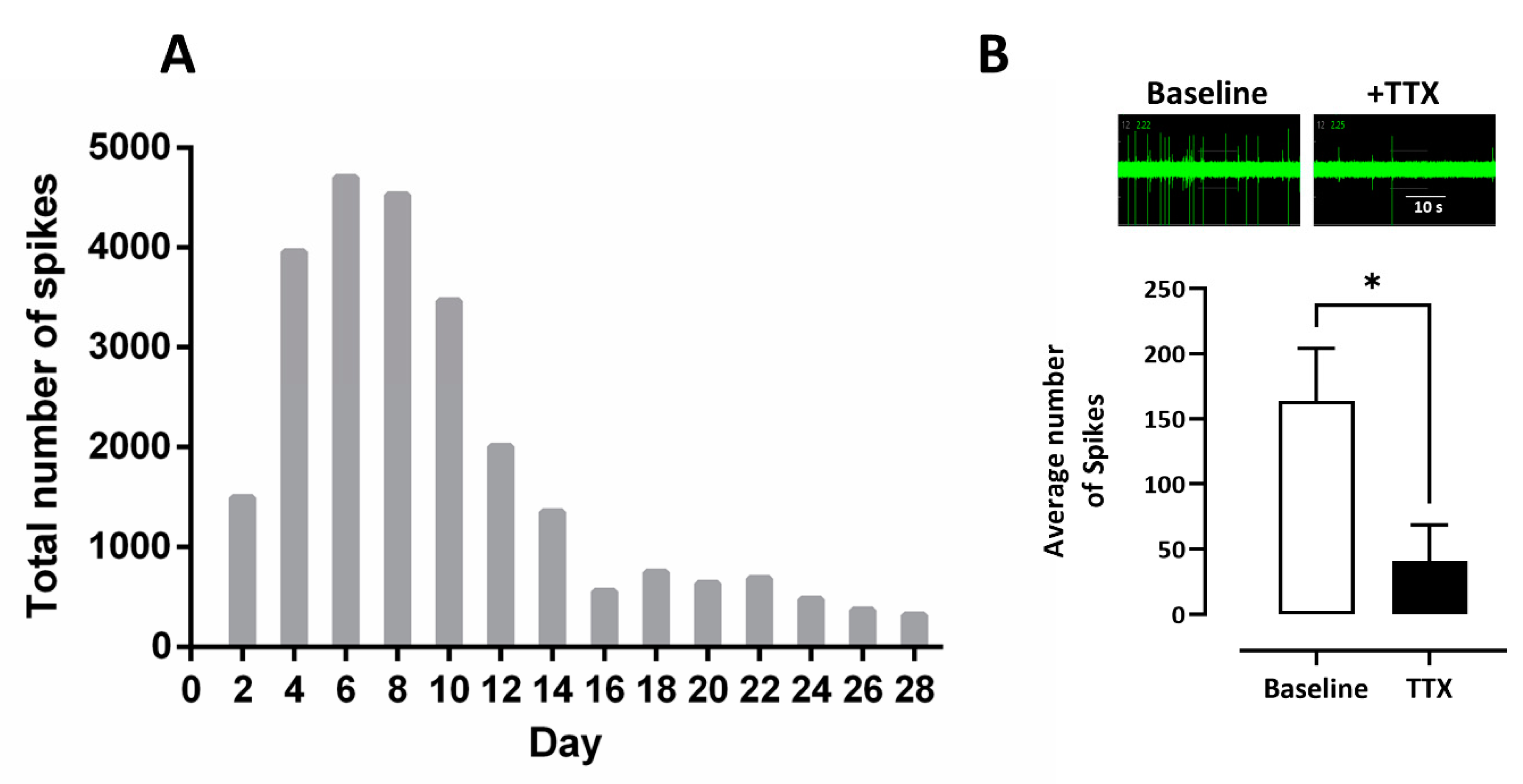
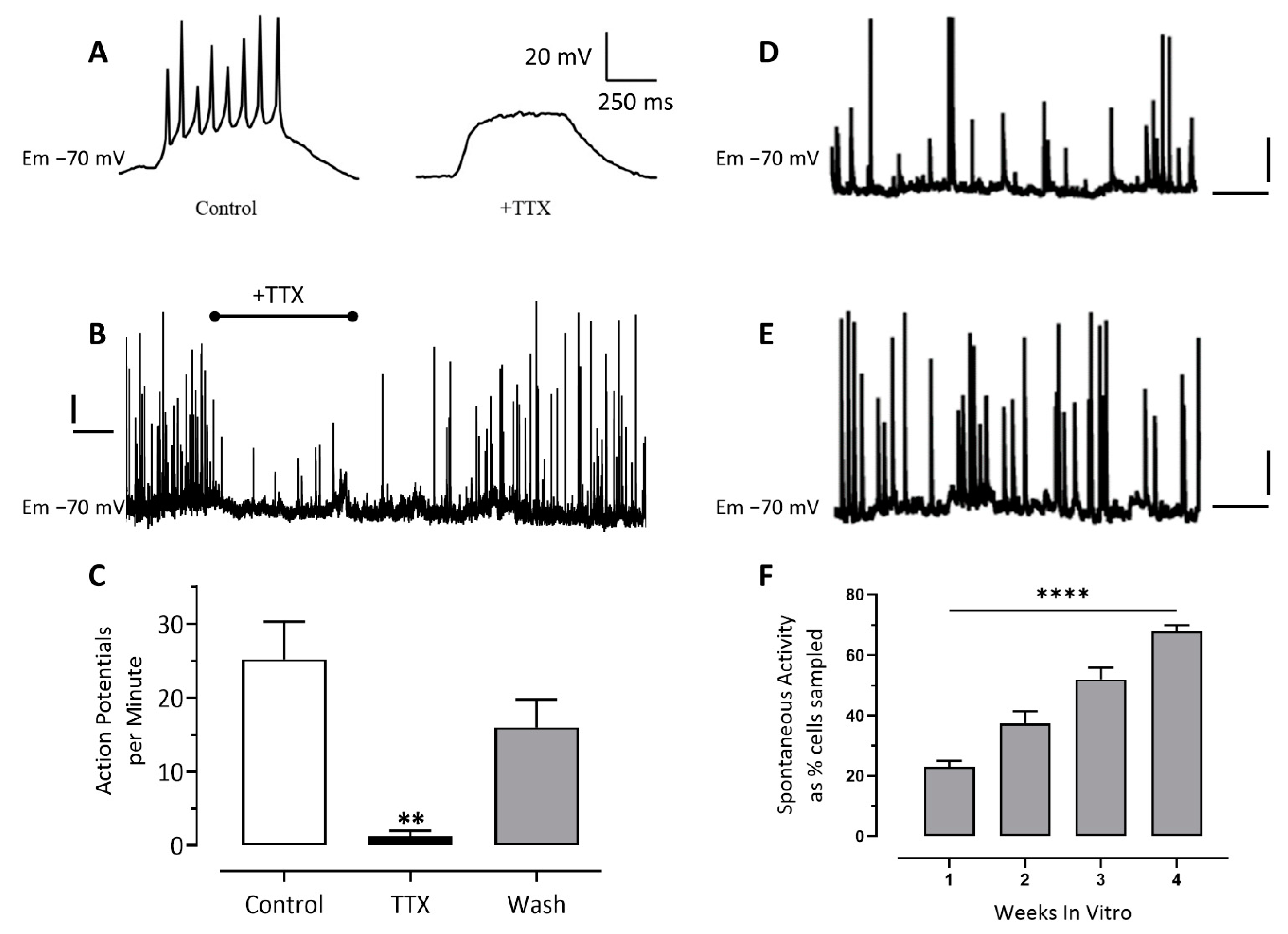
3. Results
3.1. Multi Electrode Array
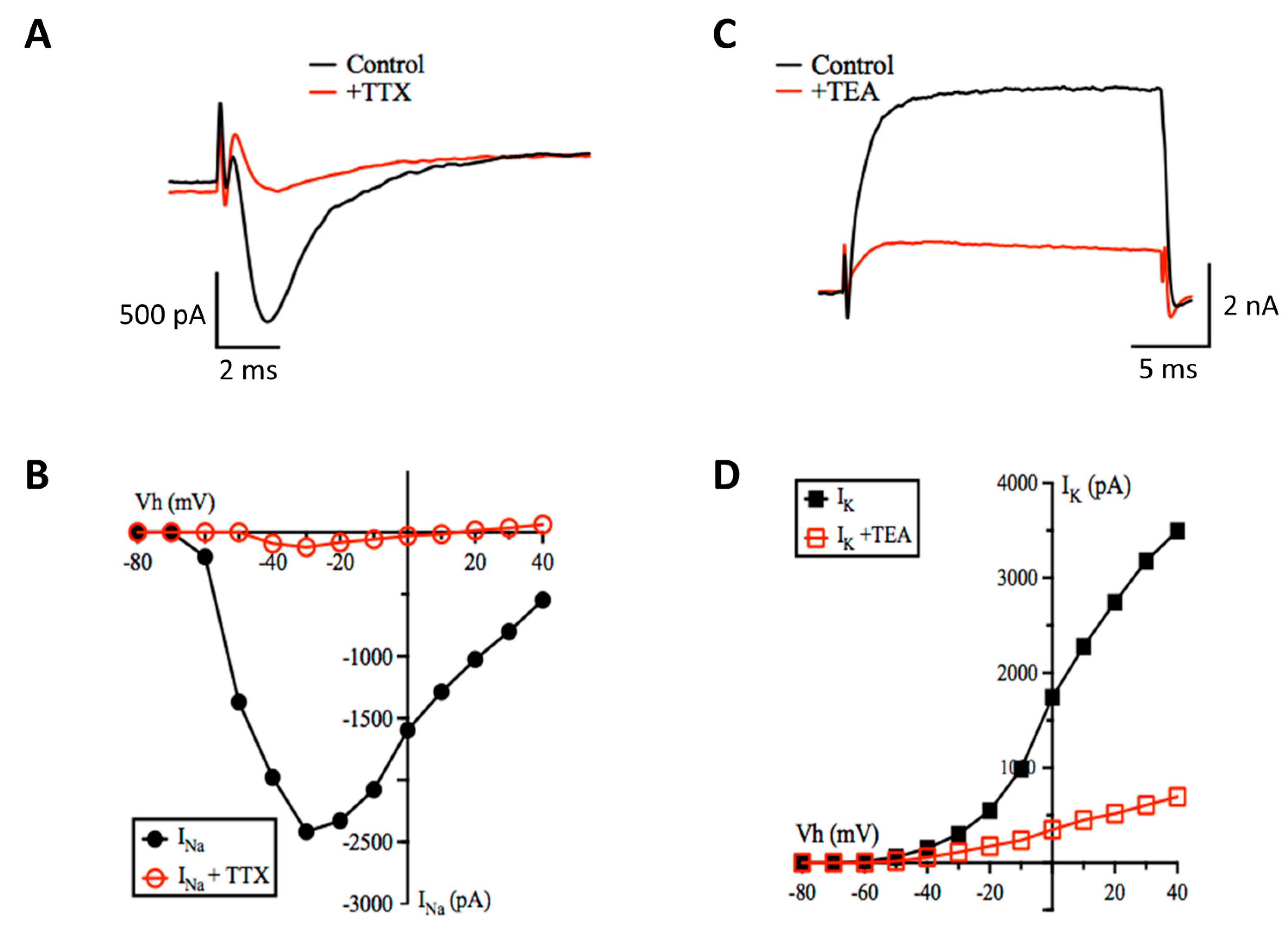
3.2. Patch-Clamp Electrophysiology
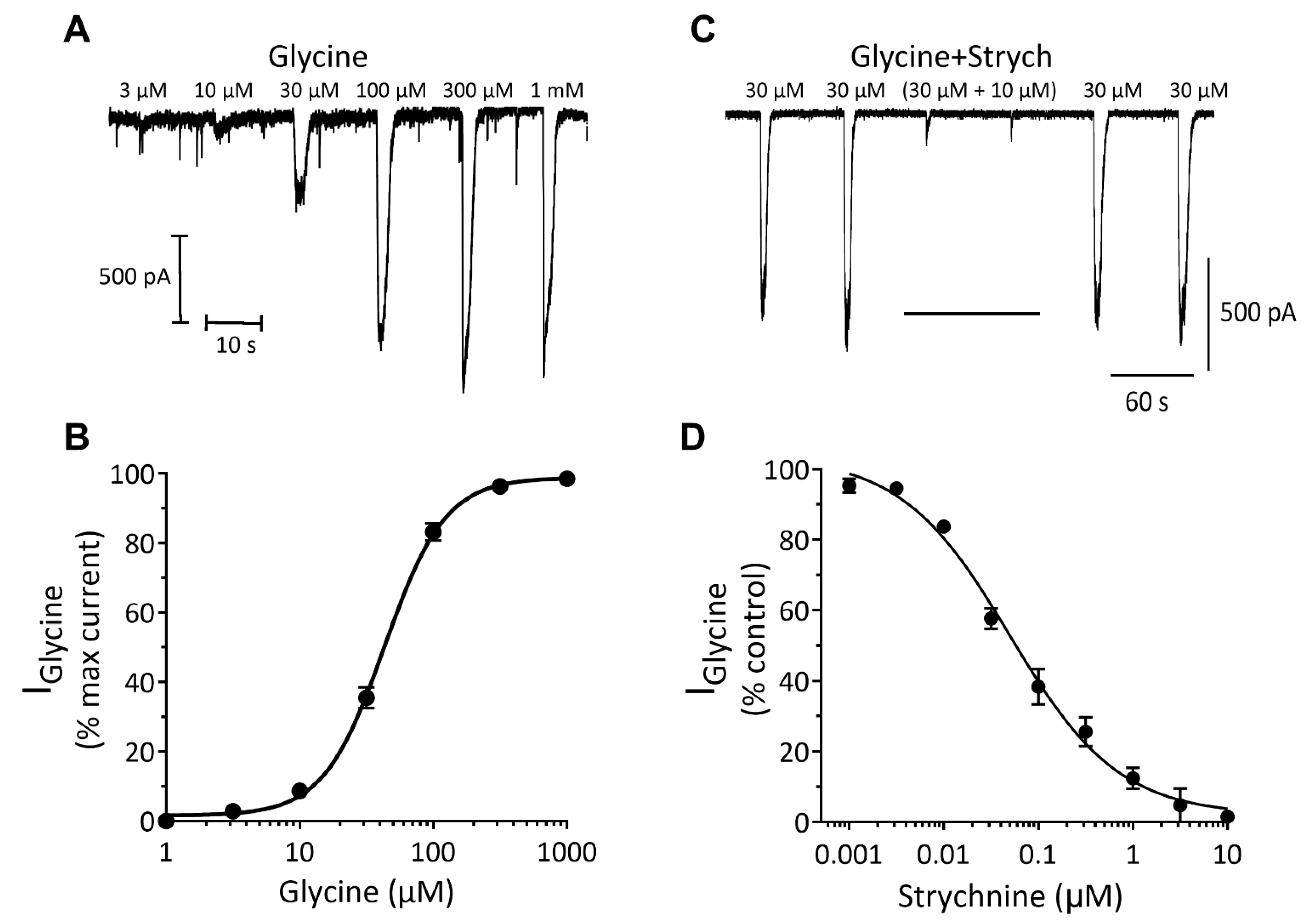
Inhibitory Ligand-Gated Currents
3.3. Excitatory Ligand-Gated Currents
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Piccolino, M. Animal Electricity and the Birth of Electrophysiology: The Legacy of Luigi Galvani. Brain Res. Bull. 1998, 46, 381–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rai, J.; Kaushik, K. Reduction of Animal Sacrifice in Biomedical Science & Research through Alternative Design of Animal Experiments. Saudi Pharm. J. 2018, 26, 896–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avoli, M.; Williamson, A. Functional and Pharmacological Properties of Human Neocortical Neurons Maintained in Vitro. Prog. Neurobiol. 1996, 48, 519–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halliwell, R.F.; Thomas, P.; Patten, D.; James, C.H.; Martinez-Torres, A.; Miledi, R.; Smart, T.G. Subunit-Selective Modulation of GABAA Receptors by the Non-Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Agent, Mefenamic Acid. Eur. J. Neurosci. 1999, 11, 2897–2905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halliwell, R.F. Electrophysiological Properties of Neurons Derived from Human Stem Cells and INeurons in Vitro. Neurochem. Int. 2017, 106, 37–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonaventura, G.; Iemmolo, R.; Attaguile, G.A.; La Cognata, V.; Pistone, B.S.; Raudino, G.; D’Agata, V.; Cantarella, G.; Barcellona, M.L.; Cavallaro, S. IPSCs: A Preclinical Drug Research Tool for Neurological Disorders. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 4596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dage, J.L.; Colvin, E.M.; Fouillet, A.; Langron, E.; Roell, W.C.; Li, J.; Mathur, S.X.; Mogg, A.J.; Schmitt, M.G.; Felder, C.C.; et al. Pharmacological Characterisation of Ligand- and Voltage-Gated Ion Channels Expressed in Human IPSC-Derived Forebrain Neurons. Psychopharmacology 2014, 231, 1105–1124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neagoe, I.; Liu, C.; Stumpf, A.; Lu, Y.; He, D.; Francis, R.; Chen, J.; Reynen, P.; Alaoui-Ismaili, M.H.; Fukui, H. The GluN2B Subunit Represents a Major Functional Determinant of NMDA Receptors in Human Induced Pluripotent Stem Cell-Derived Cortical Neurons. Stem Cell Res. 2018, 28, 105–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haythornthwaite, A.; Stoelzle, S.; Hasler, A.; Kiss, A.; Mosbacher, J.; George, M.; Brüggemann, A.; Fertig, N. Characterizing Human Ion Channels in Induced Pluripotent Stem Cell-Derived Neurons. J. Biomol. Screen. 2012, 17, 1264–1272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Berry, B.J.; Akanda, N.; Smith, A.S.T.; Long, C.J.; Schnepper, M.T.; Guo, X.; Hickman, J.J. Morphological and Functional Characterization of Human Induced Pluripotent Stem Cell-Derived Neurons (ICell Neurons) in Defined Culture Systems. Biotechnol. Prog. 2015, 31, 1613–1622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, N.Y.; Poe, M.M.; Witzigmann, C.; Cook, J.M.; Stafford, D.; Arnold, L.A. Characterization of GABAA Receptor Ligands with Automated Patch-Clamp Using Human Neurons Derived from Pluripotent Stem Cells. J. Pharmacol. Toxicol. Methods 2016, 82, 109–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, M.A.; Weick, J.P.; Pearce, R.A.; Zhang, S.-C. Functional Neural Development from Human Embryonic Stem Cells: Accelerated Synaptic Activity via Astrocyte Coculture. J. Neurosci. 2007, 27, 3069–3077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Risner-Janiczek, J.R.; Ungless, M.A.; Li, M. Electrophysiological Properties of Embryonic Stem Cell-Derived Neurons. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e24169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olsen, R.W. Allosteric Ligands and Their Binding Sites Define γ-Aminobutyric Acid (GABA) Type A Receptor Subtypes. Adv. Pharmacol. 2015, 73, 167–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olsen, R.W.; Sieghart, W. International Union of Pharmacology. LXX. Subtypes of γ-Aminobutyric AcidA Receptors: Classification on the Basis of Subunit Composition, Pharmacology, and Function. Update. Pharmacol. Rev. 2008, 60, 243–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burgos, C.F.; Yévenes, G.E.; Aguayo, L.G. Structure and Pharmacologic Modulation of Inhibitory Glycine Receptors. Mol. Pharmacol. 2016, 90, 318–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siebler, M.; Pekel, M.; Köller, H.; Müller, H.W. Strychnine-Sensitive Glycine Receptors in Cultured Primary Neurons from Rat Neocortex. Brain Res. Dev. Brain Res. 1993, 73, 289–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Li, W.-G.; Huang, C.; Zhu, M.X.; Xu, T.-L.; Wu, D.-Z.; Li, Y. Subunit-Specific Inhibition of Glycine Receptors by Curcumol. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2012, 343, 371–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mayer, M.L. Structural Biology of Glutamate Receptor Ion Channel Complexes. Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol. 2016, 41, 119–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kew, J.N.C.; Kemp, J.A. Ionotropic and Metabotropic Glutamate Receptor Structure and Pharmacology. Psychopharmacology 2005, 179, 4–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, C.-Y.; Ting, H.-C.; Liu, C.-A.; Su, H.-L.; Chiou, T.-W.; Lin, S.-Z.; Harn, H.-J.; Ho, T.-J. Induced Pluripotent Stem Cell (IPSC)-Based Neurodegenerative Disease Models for Phenotype Recapitulation and Drug Screening. Molecules 2020, 25, 2000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, M.C.; Haggarty, S.J. Human Pluripotent Stem Cell-Derived Models and Drug Screening in CNS Precision Medicine. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2020, 1471, 18–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, L.; Tcw, J. Human IPSC-Based Modeling of Central Nerve System Disorders for Drug Discovery. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 1203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stewart, R.; Coyne, L.; Lako, M.; Halliwell, R.F.; Przyborski, S.A. Human Embryonal Carcinoma Stem Cells Expressing Green Fluorescent Protein Form Functioning Neurons in Vitro: A Research Tool for Co-Culture Studies. Stem Cells Dev. 2004, 13, 646–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coyne, L.; Shan, M.; Przyborski, S.A.; Hirakawa, R.; Halliwell, R.F. Neuropharmacological Properties of Neurons Derived from Human Stem Cells. Neurochem. Int. 2011, 59, 404–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tukker, A.M.; de Groot, M.W.G.D.M.; Wijnolts, F.M.J.; Kasteel, E.E.J.; Hondebrink, L.; Westerink, R.H.S. Is the Time Right for in Vitro Neurotoxicity Testing Using Human IPSC-Derived Neurons? ALTEX Altern. Anim. Exp. 2016, 33, 261–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Odawara, A.; Saitoh, Y.; Alhebshi, A.H.; Gotoh, M.; Suzuki, I. Long-Term Electrophysiological Activity and Pharmacological Response of a Human Induced Pluripotent Stem Cell-Derived Neuron and Astrocyte Co-Culture. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2014, 443, 1176–1181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kasteel, E.E.J.; Westerink, R.H.S. Comparison of the Acute Inhibitory Effects of Tetrodotoxin (TTX) in Rat and Human Neuronal Networks for Risk Assessment Purposes. Toxicol. Lett. 2017, 270, 12–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hille, B. Ion Channels of Excitable Membranes, 3rd ed.; Sinauer Associates Inc.: Sunderland, MA, USA, 2001; p. 11. [Google Scholar]
- Prè, D.; Nestor, M.W.; Sproul, A.A.; Jacob, S.; Koppensteiner, P.; Chinchalongporn, V.; Zimmer, M.; Yamamoto, A.; Noggle, S.A.; Arancio, O. A Time Course Analysis of the Electrophysiological Properties of Neurons Differentiated from Human Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells (IPSCs). PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e103418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.J.; Hibbs, R.E. Direct Structural Insights into GABAA Receptor Pharmacology. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2021, 46, 502–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pritchett, D.B.; Sontheimer, H.; Shivers, B.D.; Ymer, S.; Kettenmann, H.; Schofield, P.R.; Seeburg, P.H. Importance of a Novel GABAA Receptor Subunit for Benzodiazepine Pharmacology. Nature 1989, 338, 582–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sigel, E.; Baur, R.; Trube, G.; Möhler, H.; Malherbe, P. The Effect of Subunit Composition of Rat Brain GABAA Receptors on Channel Function. Neuron 1990, 5, 703–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coyne, L.; Su, J.; Patten, D.; Halliwell, R.F. Characterization of the Interaction between Fenamates and Hippocampal Neuron GABA(A) Receptors. Neurochem. Int. 2007, 51, 440–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Castellano, D.; Shepard, R.D.; Lu, W. Looking for Novelty in an “Old” Receptor: Recent Advances toward Our Understanding of GABAARs and Their Implications in Receptor Pharmacology. Front. Neurosci. 2020, 14, 616298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, A.B.; Snyder, S.H. Strychnine Binding Associated with Glycine Receptors of the Central Nervous System. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1973, 70, 2832–2836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Betz, H.; Laube, B. Glycine Receptors: Recent Insights into Their Structural Organization and Functional Diversity. J. Neurochem. 2006, 97, 1600–1610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dutertre, S.; Becker, C.-M.; Betz, H. Inhibitory Glycine Receptors: An Update. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 40216–40223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mayer, M.L.; Westbrook, G.L.; Guthrie, P.B. Voltage-Dependent Block by Mg2+ of NMDA Responses in Spinal Cord Neurones. Nature 1984, 309, 261–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, J.W.; Ascher, P. Glycine Potentiates the NMDA Response in Cultured Mouse Brain Neurons. Nature 1987, 325, 529–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, H.; Chen, Z.; Josephson, L.; Li, Z.; Liang, S.H. Positron Emission Tomography (PET) Ligand Development for Ionotropic Glutamate Receptors: Challenges and Opportunities for Radiotracer Targeting N-Methyl-d-Aspartate (NMDA), α-Amino-3-Hydroxy-5-Methyl-4-Isoxazolepropionic Acid (AMPA), and Kainate Receptors. J. Med. Chem. 2019, 62, 403–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, H.; Low, C.-M.; Moody, O.A.; Jenkins, A.; Traynelis, S.F. Ionotropic GABA and Glutamate Receptor Mutations and Human Neurologic Diseases. Mol. Pharmacol. 2015, 88, 203–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wing, C.; Komatsu, M.; Delaney, S.M.; Krause, M.; Wheeler, H.E.; Dolan, M.E. Application of Stem Cell Derived Neuronal Cells to Evaluate Neurotoxic Chemotherapy. Stem Cell Res. 2017, 22, 79–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, L.; Koo, Y.; Russell, T.; Gay, E.; Li, Y.; Yun, Y. Three-Dimensional Brain-on-Chip Model Using Human IPSC-Derived GABAergic Neurons and Astrocytes: Butyrylcholinesterase Post-Treatment for Acute Malathion Exposure. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0230335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tukker, A.M.; Wijnolts, F.M.J.; de Groot, A.; Westerink, R.H.S. Applicability of HiPSC-Derived Neuronal Cocultures and Rodent Primary Cortical Cultures for In Vitro Seizure Liability Assessment. Toxicol. Sci. 2020, 178, 71–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Halliwell, R.F.; Salmanzadeh, H.; Coyne, L.; Cao, W.S. An Electrophysiological and Pharmacological Study of the Properties of Human iPSC-Derived Neurons for Drug Discovery. Cells 2021, 10, 1953. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells10081953
Halliwell RF, Salmanzadeh H, Coyne L, Cao WS. An Electrophysiological and Pharmacological Study of the Properties of Human iPSC-Derived Neurons for Drug Discovery. Cells. 2021; 10(8):1953. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells10081953
Chicago/Turabian StyleHalliwell, Robert F., Hamed Salmanzadeh, Leanne Coyne, and William S. Cao. 2021. "An Electrophysiological and Pharmacological Study of the Properties of Human iPSC-Derived Neurons for Drug Discovery" Cells 10, no. 8: 1953. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells10081953
APA StyleHalliwell, R. F., Salmanzadeh, H., Coyne, L., & Cao, W. S. (2021). An Electrophysiological and Pharmacological Study of the Properties of Human iPSC-Derived Neurons for Drug Discovery. Cells, 10(8), 1953. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells10081953




