Comprehensive Integrative Analysis Reveals the Association of KLF4 with Macrophage Infiltration and Polarization in Lung Cancer Microenvironment
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Identification of NSCLC-Specific DEGs, DEMs and Pathway Enrichment Analysis
2.2. Extraction of Significant NSCLC-Specific miRNAs and TFs
2.3. Overall Survival (OS) Analysis
2.4. Validation of KLF4 and IL-1β Using UALCAN and cBioPortal
2.5. Tumor Immune Infiltration Analysis
2.6. Cell Culture, Macrophage Differentiation, and Transient Transfection
2.7. Co-Culture
2.8. Quantitative Real-Time PCR (qRT-PCR)
2.9. One-Step qRT-PCR
2.10. Western Blotting
2.11. Flow Cytometry
2.12. Cell Viability and Cell Proliferation
2.13. Clonogenic Assay
2.14. In Vitro Scratch Assay
2.15. Nitrite Assay
2.16. Dual-Luciferase Assay
2.17. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Identification of NSCLC-Specific DEGs, DEMs and Pathway Enrichment Analysis
3.2. NSCLC-Specific 3-Node miRNA FFL and OS Analyses
3.3. Validation of KLF4 and IL-1β Using UALCAN and cBioPortal
3.4. Evaluation of Tumor Immune Cell Infiltration
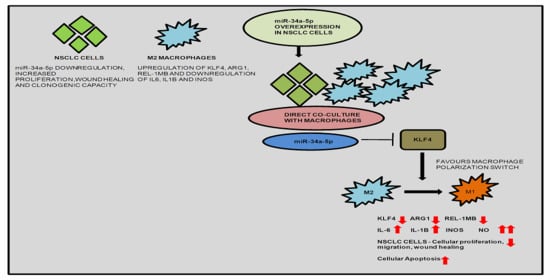
3.5. KLF4, IL-1β and miR-34a-5p Is Associated with Macrophage Polarization
3.6. KLF4—Acting as an Oncogene in NSCLC
3.7. miR-34a-5p/KLF4 Mediated Macrophage Polarization Reduce Tumorigenesis
3.8. KLF4 and Tumor Inversion in NSCLC Microenvironment
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Iqbal, M.A.; Arora, S.; Prakasam, G.; Calin, G.A.; Syed, M.A. MicroRNA in Lung Cancer: Role, Mechanisms, Pathways and Therapeutic Relevance. Mol. Asp. Med. 2019, 70, 3–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, M.; Li, Y.; Li, W.; Zhao, Q.; Zhang, Q.; Le, K.; Huang, Z.; Yi, P. Immune and Stroma Related Genes in Breast Cancer: A Comprehensive Analysis of Tumor Microenvironment Based on the Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA) Database. Front. Med. 2020, 7, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weisser, S.B.; McLarren, K.W.; Kuroda, E.; Sly, L.M. Generation and Characterization of Murine Alternatively Activated Macrophages. Methods Mol. Biol. Clifton NJ 2013, 946, 225–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Öjlert, Å.K.; Halvorsen, A.R.; Nebdal, D.; Lund-Iversen, M.; Solberg, S.; Brustugun, O.T.; Lingjaerde, O.C.; Helland, Å. The Immune Microenvironment in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Is Predictive of Prognosis after Surgery. Mol. Oncol. 2019, 13, 1166–1179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yuan, X.; Li, Y.; Zhang, A.Z.; Jiang, C.H.; Li, F.P.; Xie, Y.F.; Li, J.F.; Liang, W.H.; Zhang, H.J.; Liu, C.X.; et al. Tumour-Associated Macrophage Polarisation Promotes Progression of Esophageal Carcinoma. Aging 2020, 13, 2049–2072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mantovani, A.; Sica, A.; Sozzani, S.; Allavena, P.; Vecchi, A.; Locati, M. The Chemokine System in Diverse Forms of Macrophage Activation and Polarization. Trends Immunol. 2004, 25, 677–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sica, A.; Mantovani, A. Macrophage Plasticity and Polarization: In Vivo Veritas. J. Clin. Investig. 2012, 122, 787–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atri, C.; Guerfali, F.; Laouini, D. Role of Human Macrophage Polarization in Inflammation during Infectious Diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 1801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, L.-X.; Zhang, S.-X.; Wu, H.-J.; Rong, X.-L.; Guo, J. M2b Macrophage Polarization and Its Roles in Diseases. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2019, 106, 345–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, N.; Liang, H.; Zen, K. Molecular Mechanisms That Influence the Macrophage M1–M2 Polarization Balance. Front. Immunol. 2014, 5, 614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Biswas, S.K.; Mantovani, A. Macrophage Plasticity and Interaction with Lymphocyte Subsets: Cancer as a Paradigm. Nat. Immunol. 2010, 11, 889–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wynn, T.A.; Chawla, A.; Pollard, J.W. Macrophage Biology in Development, Homeostasis and Disease. Nature 2013, 496, 445–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arora, S.; Dev, K.; Agarwal, B.; Das, P.; Syed, M.A. Macrophages: Their Role, Activation and Polarization in Pulmonary Diseases. Immunobiology 2018, 223, 383–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Song, Y.; Du, W.; Gong, L.; Chang, H.; Zou, Z. Tumor-Associated Macrophages: An Accomplice in Solid Tumor Progression. J. Biomed. Sci. 2019, 26, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, C.; Liu, X.-J.; Xie, J.; Ma, T.-T.; Meng, X.-M.; Li, J. MiR-146a Modulates Macrophage Polarization by Inhibiting Notch1 Pathway in RAW264.7 Macrophages. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2016, 32, 46–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, C.; Jeong, H.; Bae, Y.; Shin, K.; Kang, S.; Kim, H.; Oh, J.; Bae, H. Targeting of M2-like Tumor-Associated Macrophages with a Melittin-Based pro-Apoptotic Peptide. J. Immunother. Cancer 2019, 7, 147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Petty, A.J.; Yang, Y. Tumor-Associated Macrophages: Implications in Cancer Immunotherapy. Immunotherapy 2017, 9, 289–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Arora, S.; Ahmad, S.; Irshad, R.; Goyal, Y.; Rafat, S.; Siddiqui, N.; Dev, K.; Husain, M.; Ali, S.; Mohan, A.; et al. TLRs in Pulmonary Diseases. Life Sci. 2019, 233, 116671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tetreault, M.-P.; Yang, Y.; Katz, J.P. Krüppel-like Factors in Cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2013, 13, 701–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fadous-Khalifé, M.C.; Aloulou, N.; Jalbout, M.; Hadchity, J.; Aftimos, G.; Paris, F.; Hadchity, E. Krüppel-like Factor 4: A New Potential Biomarker of Lung Cancer. Mol. Clin. Oncol. 2016, 5, 35–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Soufi, A.; Donahue, G.; Zaret, K.S. Facilitators and Impediments of the Pluripotency Reprogramming Factors’ Initial Engagement with the Genome. Cell 2012, 151, 994–1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, Q.; Jia, Z.; Wang, L.; Kong, X.; Li, Q.; Guo, K.; Tan, D.; Le, X.; Wei, D.; Huang, S.; et al. Disruption of Klf4 in Villin-Positive Gastric Progenitor Cells Promotes Formation and Progression of Tumors of the Antrum in Mice. Gastroenterology 2012, 142, 531–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nishi, M.; Sakai, Y.; Akutsu, H.; Nagashima, Y.; Quinn, G.; Masui, S.; Kimura, H.; Perrem, K.; Umezawa, A.; Yamamoto, N.; et al. Induction of Cells with Cancer Stem Cell Properties from Nontumorigenic Human Mammary Epithelial Cells by Defined Reprogramming Factors. Oncogene 2014, 33, 643–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liu, M.; Li, X.; Peng, K.-Z.; Gao, T.; Cui, Y.; Ma, N.; Zhou, Y.; Hou, G. Subcellular Localization of Klf4 in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer and Its Clinical Significance. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2018, 99, 480–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.; Hisamuddin, I.M.; Nandan, M.O.; Babbin, B.A.; Lamb, N.E.; Yang, V.W. Identification of Krüppel-like Factor 4 as a Potential Tumor Suppressor Gene in Colorectal Cancer. Oncogene 2004, 23, 395–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wei, D.; Kanai, M.; Huang, S.; Xie, K. Emerging Role of KLF4 in Human Gastrointestinal Cancer. Carcinogenesis 2006, 27, 23–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nakahara, Y.; Northcott, P.A.; Li, M.; Kongkham, P.N.; Smith, C.; Yan, H.; Croul, S.; Ra, Y.-S.; Eberhart, C.; Huang, A.; et al. Genetic and Epigenetic Inactivation of Kruppel-like Factor 4 in Medulloblastoma. Neoplasia 2010, 12, 20–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yasunaga, J.; Taniguchi, Y.; Nosaka, K.; Yoshida, M.; Satou, Y.; Sakai, T.; Mitsuya, H.; Matsuoka, M. Identification of Aberrantly Methylated Genes in Association with Adult T-Cell Leukemia. Cancer Res. 2004, 64, 6002–6009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, N.; Liu, Z.-H.; Ding, F.; Wang, X.-Q.; Zhou, C.-N.; Wu, M. Down-Regulation of Gut-Enriched Kruppel-like Factor Expression in Esophageal Cancer. World J. Gastroenterol. 2002, 8, 966–970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, W.; Hofstetter, W.L.; Li, H.; Zhou, Y.; He, Y.; Pataer, A.; Wang, L.; Xie, K.; Swisher, S.G.; Fang, B. Putative Tumor-Suppressive Function of Krüppel-Like Factor 4 in Primary Lung Carcinoma. Clin. Cancer Res. 2009, 15, 5688–5695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ohnishi, S.; Ohnami, S.; Laub, F.; Aoki, K.; Suzuki, K.; Kanai, Y.; Haga, K.; Asaka, M.; Ramirez, F.; Yoshida, T. Downregulation and Growth Inhibitory Effect of Epithelial-Type Krüppel-like Transcription Factor KLF4, but Not KLF5, in Bladder Cancer. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2003, 308, 251–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foster, K.W.; Frost, A.R.; McKie-Bell, P.; Lin, C.Y.; Engler, J.A.; Grizzle, W.E.; Ruppert, J.M. Increase of GKLF Messenger RNA and Protein Expression during Progression of Breast Cancer. Cancer Res. 2000, 60, 6488–6495. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.-J.; Wu, C.-Y.; Chang, C.-C.; Ma, C.-J.; Li, M.-C.; Chen, C.-M. Nuclear Krüppel-like Factor 4 Expression Is Associated with Human Skin Squamous Cell Carcinoma Progression and Metastasis. Cancer Biol. Ther. 2008, 7, 777–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Taracha-Wisniewska, A.; Kotarba, G.; Dworkin, S.; Wilanowski, T. Recent Discoveries on the Involvement of Krüppel-Like Factor 4 in the Most Common Cancer Types. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 8843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Wu, Y.; Lin, L.; Liu, X. Transcription Factor KLF4: A Potential Biomarker of Non-Small Cell Lung Cancertranscription Factor KLF4: A Potential Biomarker of Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. BMC Microbiol. 2020. In Review. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, X.; Sharma, N.; Kapadia, F.; Zhou, G.; Lu, Y.; Hong, H.; Paruchuri, K.; Mahabeleshwar, G.H.; Dalmas, E.; Venteclef, N.; et al. Krüppel-like Factor 4 Regulates Macrophage Polarization. J. Clin. Investig. 2011, 121, 2736–2749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Clough, E.; Barrett, T. The Gene Expression Omnibus Database. Methods Mol. Biol. Clifton NJ 2016, 1418, 93–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, G.-M.; Goyal, H.; Song, L.-L. Bioinformatics Analysis of Differentially Expressed MiRNA-Related MRNAs and Their Prognostic Value in Breast Carcinoma. Oncol. Rep. 2018, 39, 2865–2872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuleshov, M.V.; Jones, M.R.; Rouillard, A.D.; Fernandez, N.F.; Duan, Q.; Wang, Z.; Koplev, S.; Jenkins, S.L.; Jagodnik, K.M.; Lachmann, A.; et al. Enrichr: A Comprehensive Gene Set Enrichment Analysis Web Server 2016 Update. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016, 44, W90–W97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhou, K.-R.; Liu, S.; Sun, W.-J.; Zheng, L.-L.; Zhou, H.; Yang, J.-H.; Qu, L.-H. ChIPBase v2.0: Decoding Transcriptional Regulatory Networks of Non-Coding RNAs and Protein-Coding Genes from ChIP-Seq Data. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017, 45, D43–D50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sticht, C.; De La Torre, C.; Parveen, A.; Gretz, N. MiRWalk: An Online Resource for Prediction of MicroRNA Binding Sites. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0206239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Açıcı, K.; Terzi, Y.K.; Oğul, H. Retrieving Relevant Experiments: The Case of MicroRNA Microarrays. Biosystems 2015, 134, 71–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.-H.; Liu, S.; Zhou, H.; Qu, L.-H.; Yang, J.-H. StarBase v2.0: Decoding MiRNA-CeRNA, MiRNA-NcRNA and Protein–RNA Interaction Networks from Large-Scale CLIP-Seq Data. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014, 42, D92–D97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sun, J.; Gong, X.; Purow, B.; Zhao, Z. Uncovering MicroRNA and Transcription Factor Mediated Regulatory Networks in Glioblastoma. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2012, 8, e1002488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shannon, P.; Markiel, A.; Ozier, O.; Baliga, N.S.; Wang, J.T.; Ramage, D.; Amin, N.; Schwikowski, B.; Ideker, T. Cytoscape: A Software Environment for Integrated Models of Biomolecular Interaction Networks. Genome Res. 2003, 13, 2498–2504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagy, Á.; Munkácsy, G.; Győrffy, B. Pancancer Survival Analysis of Cancer Hallmark Genes. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 6047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chandrashekar, D.S.; Bashel, B.; Balasubramanya, S.A.H.; Creighton, C.J.; Ponce-Rodriguez, I.; Chakravarthi, B.V.S.K.; Varambally, S. UALCAN: A Portal for Facilitating Tumor Subgroup Gene Expression and Survival Analyses. Neoplasia 2017, 19, 649–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cerami, E.; Gao, J.; Dogrusoz, U.; Gross, B.E.; Sumer, S.O.; Aksoy, B.A.; Jacobsen, A.; Byrne, C.J.; Heuer, M.L.; Larsson, E.; et al. The CBio Cancer Genomics Portal: An Open Platform for Exploring Multidimensional Cancer Genomics Data. Cancer Discov. 2012, 2, 401–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gao, J.; Aksoy, B.A.; Dogrusoz, U.; Dresdner, G.; Gross, B.; Sumer, S.O.; Sun, Y.; Jacobsen, A.; Sinha, R.; Larsson, E.; et al. Integrative Analysis of Complex Cancer Genomics and Clinical Profiles Using the CBioPortal. Sci. Signal. 2013, 6, pl1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, T.; Fu, J.; Zeng, Z.; Cohen, D.; Li, J.; Chen, Q.; Li, B.; Liu, X.S. TIMER2.0 for Analysis of Tumor-Infiltrating Immune Cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 2020, 48, W509–W514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szanto, A.; Balint, B.L.; Nagy, Z.S.; Barta, E.; Dezso, B.; Pap, A.; Szeles, L.; Poliska, S.; Oros, M.; Evans, R.M.; et al. STAT6 Transcription Factor Is a Facilitator of the Nuclear Receptor PPARγ-Regulated Gene Expression in Macrophages and Dendritic Cells. Immunity 2010, 33, 699–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Parisi, L.; Gini, E.; Baci, D.; Tremolati, M.; Fanuli, M.; Bassani, B.; Farronato, G.; Bruno, A.; Mortara, L. Macrophage Polarization in Chronic Inflammatory Diseases: Killers or Builders? J. Immunol. Res. 2018, 2018, 8917804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luanpitpong, S.; Chanvorachote, P. Nitric Oxide and Aggressive Behavior of Lung Cancer Cells. Anticancer Res. 2015, 35, 4585–4592. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Colakogullari, M.; Ulukaya, E.; Yilmaztepe, A.; Ocakoglu, G.; Yilmaz, M.; Karadag, M.; Tokullugil, A. Higher Serum Nitrate Levels Are Associated with Poor Survival in Lung Cancer Patients. Clin. Biochem. 2006, 39, 898–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fukumura, D.; Kashiwagi, S.; Jain, R.K. The Role of Nitric Oxide in Tumour Progression. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2006, 6, 521–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kitamura, T.; Qian, B.-Z.; Pollard, J.W. Immune Cell Promotion of Metastasis. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2015, 15, 73–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, S.; Liu, T.; Cheng, Y.; Bai, Y.; Liang, G. Immune Cell Infiltration as a Biomarker for the Diagnosis and Prognosis of Digestive System Cancer. Cancer Sci. 2019, 110, 3639–3649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mao, Y.; Feng, Q.; Zheng, P.; Yang, L.; Liu, T.; Xu, Y.; Zhu, D.; Chang, W.; Ji, M.; Ren, L.; et al. Low Tumor Purity Is Associated with Poor Prognosis, Heavy Mutation Burden, and Intense Immune Phenotype in Colon Cancer. Cancer Manag. Res. 2018, 10, 3569–3577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yuan, X.; Li, Z.; Zhao, H.; Bai, J.; Zhang, J. Accurate Inference of Tumor Purity and Absolute Copy Numbers From High-Throughput Sequencing Data. Front. Genet. 2020, 11, 458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karn, T.; Jiang, T.; Hatzis, C.; Sänger, N.; El-Balat, A.; Rody, A.; Holtrich, U.; Becker, S.; Bianchini, G.; Pusztai, L. Association Between Genomic Metrics and Immune Infiltration in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer. JAMA Oncol. 2017, 3, 1707–1711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Safonov, A.; Jiang, T.; Bianchini, G.; Győrffy, B.; Karn, T.; Hatzis, C.; Pusztai, L. Immune Gene Expression Is Associated with Genomic Aberrations in Breast Cancer. Cancer Res. 2017, 77, 3317–3324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, L.; Shen, F.; Stroehlein, J.R.; Wei, D. Context-Dependent Functions of KLF4 in Cancers: Could Alternative Splicing Isoforms Be the Key? Cancer Lett. 2018, 438, 10–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferralli, J.; Chiquet-Ehrismann, R.; Degen, M. KLF4α Stimulates Breast Cancer Cell Proliferation by Acting as a KLF4 Antagonist. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 45608–45621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Park, C.S.; Shen, Y.; Lewis, A.; Lacorazza, H.D. Role of the Reprogramming Factor KLF4 in Blood Formation. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2016, 99, 673–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rowland, B.D.; Peeper, D.S. KLF4, P21 and Context-Dependent Opposing Forces in Cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2006, 6, 11–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]







| Relationship | No. of Edges | No. of miRNAs | No. of TFs | No. of Genes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| miRNA-gene a | 22 | 22 | - | 4 |
| TF-gene b | 37 | - | 23 | 4 |
| miRNA-TF c | 183 | 22 | 23 | - |
| Items | Low Expression Cohort (Months) | High Expression Cohort (Months) |
|---|---|---|
| KLF4 | 51.03 | 34.77 |
| IL-1β (ns) | 42.27 | 59.27 |
| miR-34a-5p | 48.47 | 59.27 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Arora, S.; Singh, P.; Ahmad, S.; Ahmad, T.; Dohare, R.; Almatroodi, S.A.; Alrumaihi, F.; Rahmani, A.H.; Syed, M.A. Comprehensive Integrative Analysis Reveals the Association of KLF4 with Macrophage Infiltration and Polarization in Lung Cancer Microenvironment. Cells 2021, 10, 2091. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells10082091
Arora S, Singh P, Ahmad S, Ahmad T, Dohare R, Almatroodi SA, Alrumaihi F, Rahmani AH, Syed MA. Comprehensive Integrative Analysis Reveals the Association of KLF4 with Macrophage Infiltration and Polarization in Lung Cancer Microenvironment. Cells. 2021; 10(8):2091. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells10082091
Chicago/Turabian StyleArora, Shweta, Prithvi Singh, Shaniya Ahmad, Tanveer Ahmad, Ravins Dohare, Saleh A. Almatroodi, Faris Alrumaihi, Arshad Husain Rahmani, and Mansoor Ali Syed. 2021. "Comprehensive Integrative Analysis Reveals the Association of KLF4 with Macrophage Infiltration and Polarization in Lung Cancer Microenvironment" Cells 10, no. 8: 2091. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells10082091
APA StyleArora, S., Singh, P., Ahmad, S., Ahmad, T., Dohare, R., Almatroodi, S. A., Alrumaihi, F., Rahmani, A. H., & Syed, M. A. (2021). Comprehensive Integrative Analysis Reveals the Association of KLF4 with Macrophage Infiltration and Polarization in Lung Cancer Microenvironment. Cells, 10(8), 2091. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells10082091