Role of Irisin in Myocardial Infarction, Heart Failure, and Cardiac Hypertrophy
Abstract
:1. Introduction
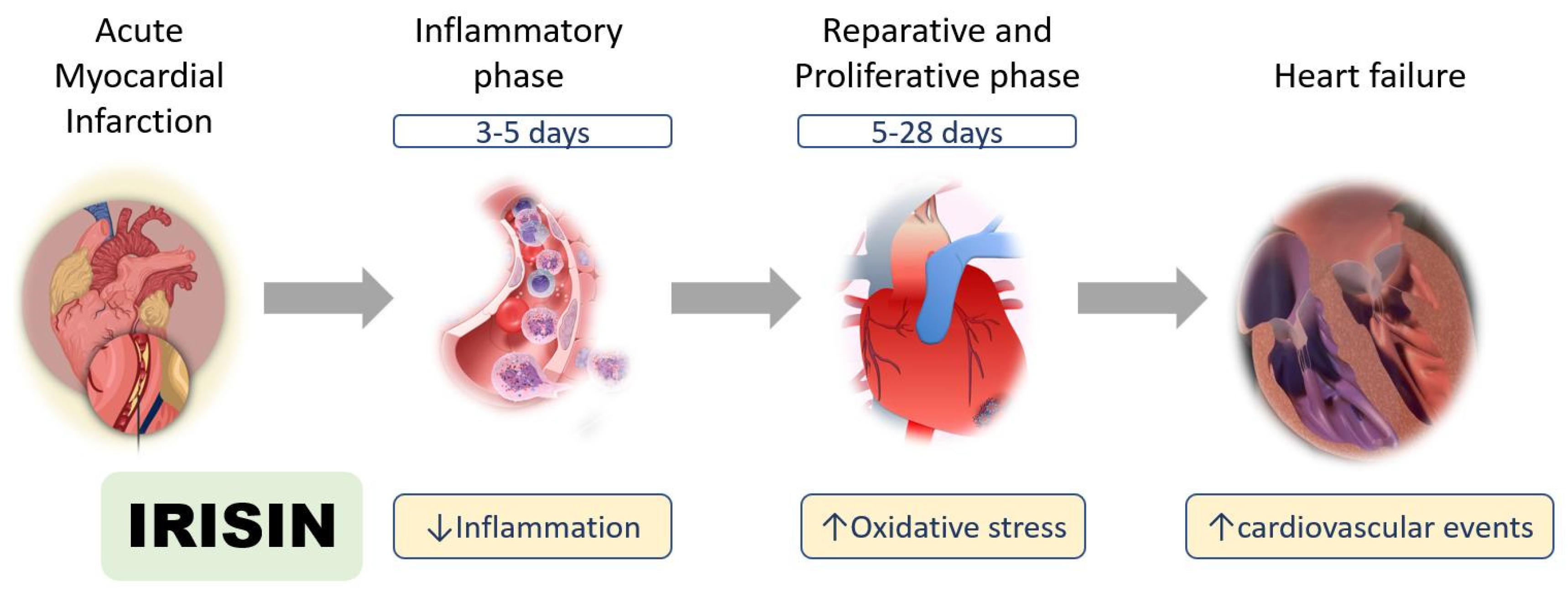
2. Acute Myocardial Infarction
2.1. Inflammatory Phase after Myocardial Infarction
2.2. Reparative and Proliferative Phase after Myocardial Infarction
3. Heart Failure
3.1. Oxidative Stress and Mitochondria Dysfunction in Heart Failure
3.2. Irisin in Patients with Heart Failure
4. Hypertension and Ventricular Hypertrophy
5. Perspectives and Conclusions
- The adequate therapeutic level of irisin in myocardial infarction
- The optimal timing of irisin administration during heart failure
- The role of irisin as a biomarker in acute myocardial infarction and heart failure
- The mechanism of irisin during heart failure repair (trigger or consequence)
- The further response of irisin in vascular disease and hypertension
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ferrer-Martínez, A.; Ruiz-Lozano, P.; Chien, K.R. Mouse PeP: A novel peroxisomal protein linked to myoblast differentiation and development. Dev. Dyn. 2002, 224, 154–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farahabadi, S.H.; Ghaedi, K.; Zadegan, F.G.; Karbalaie, K.; Rabiee, F.; Nematollahi, M.; Baharvand, H.; Nasr-Esfahani, M.H. Erk1/2 Is a Key Regulator of Fndc5 and Pgc1alpha Expression during Neural Differentiation of Mescs. Neuroscience 2015, 297, 252–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boström, P.; Wu, J.; Jedrychowski, M.P.; Korde, A.; Ye, L.; Lo, J.C.; Rasbach, K.A.; Boström, E.A.; Choi, J.H.; Long, J.Z.; et al. A Pgc1-Alpha-Dependent Myokine That Drives Brown-Fat-Like Development of White Fat and Thermogenesis. Nature 2012, 481, 463–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pedersen, B.K.; Febbraio, M.A. Muscles, exercise and obesity: Skeletal muscle as a secretory organ. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2012, 8, 457–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- So, B.; Kim, H.-J.; Kim, J.-S.; Song, W. Exercise-induced myokines in health and metabolic diseases. Integr. Med. Res. 2014, 3, 172–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brenmoehl, J.; Albrecht, E.; Komolka, K.; Schering, L.; Langhammer, M.; Hoeflich, A.; Maak, S. Irisin Is Elevated in Skeletal Muscle and Serum of Mice Immediately after Acute Exercise. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2014, 10, 338–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Aydin, S.; Kuloglu, T.; Ogeturk, M.; Dabak, O.; Aydin, S.; Eren, M.N.; Celik, A.; Yilmaz, M.; Kalayci, M.; Sahin, I.; et al. Cardiac, skeletal muscle and serum irisin responses to with or without water exercise in young and old male rats: Cardiac muscle produces more irisin than skeletal muscle. Peptides 2014, 52, 68–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.T.; Wang, J.; Yano, N.; Zhang, L.X.; Wang, H.; Zhang, S.; Qin, G.; Dubielecka, P.M.; Zhuang, S.; Liu, P.Y.; et al. Irisin promotes cardiac progenitor cell-induced myocardial repair and functional improvement in infarcted heart. J. Cell. Physiol. 2019, 234, 1671–1681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, G.; Wang, J.; Song, M.; Zhou, F.; Fu, D.; Ruan, G.; Zhu, X.; Bai, Y.; Huang, L.; Pang, R.; et al. Irisin Increased the Number and Improved the Function of Endothelial Progenitor Cells in Diabetes Mellitus Mice. J. Cardiovasc. Pharmacol. 2016, 68, 67–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shen, S.; Gao, R.; Bei, Y.; Li, J.; Zhang, H.; Zhou, Y.; Yao, W.; Xu, D.; Zhou, F.; Jin, M.; et al. Serum Irisin Predicts Mortality Risk in Acute Heart Failure Patients. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2017, 42, 615–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, L.; Xiang, G.; Yue, L.; Zhang, J.; Zhao, L. Circulating irisin levels are positively associated with endothelium-dependent vasodilation in newly diagnosed type 2 diabetic patients without clinical angiopathy. Atherosclerosis 2014, 235, 328–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, J.; Han, Y.; Wang, J.; Liu, Y.; Zheng, S.; Zhou, L.; Jose, P.A.; Zeng, C. Irisin Lowers Blood Pressure by Improvement of Endothelial Dysfunction Via Ampk-Akt-Enos-No Pathway in the Spontaneously Hypertensive Rat. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2016, 5, e003433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mazur-Bialy, A.I. Irisin acts as a regulator of macrophages host defense. Life Sci. 2017, 176, 21–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsieh, I.-C.; Ho, M.-Y.; Wen, M.-S.; Chen, C.-C.; Hsieh, M.-J.; Lin, C.-P.; Yeh, J.-K.; Tsai, M.-L.; Yang, C.-H.; Wu, V.C.-C.; et al. Serum irisin levels are associated with adverse cardiovascular outcomes in patients with acute myocardial infarction. Int. J. Cardiol. 2018, 261, 12–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khorasani, Z.M.; Bagheri, R.K.; Yaghoubi, M.A.; Chobkar, S.; Aghaee, M.A.; Abbaszadegan, M.R.; Sahebkar, A. The association between serum irisin levels and cardiovascular disease in diabetic patients. Diabetes Metab. Syndr. Clin. Res. Rev. 2019, 13, 786–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, W.; Zhang, B.; Wang, X. Lower Irisin Levels in Coronary Artery Disease: A Meta-Analysis. Minerva Endocrinol. 2020, 45, 61–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benjamin, E.J.; Muntner, P.; Alonso, A.; Bittencourt, M.S.; Callaway, C.W.; Carson, A.P.; Chamberlain, A.M.; Chang, A.R.; Cheng, S.; Das, S.R.; et al. Heart disease and stroke statistics—2019 update: A report from the American heart association. Circulation 2019, 139, e56–e528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sesti, G.; Andreozzi, F.; Fiorentino, T.V.; Mannino, G.C.; Sciacqua, A.; Marini, M.A.; Perticone, F. High circulating irisin levels are associated with insulin resistance and vascular atherosclerosis in a cohort of nondiabetic adult subjects. Acta Diabetol. 2014, 51, 705–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Efe, T.H.; Açar, B.; Ertem, A.G.; Yayla, K.G.; Algül, E.; Yayla, Ç.; Ünal, S.; Bilgin, M.; Çimen, T.; Kirbaş, Ö.; et al. Serum Irisin Level Can Predict the Severity of Coronary Artery Disease in Patients with Stable Angina. Korean Circ. J. 2017, 47, 44–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Aronis, K.N.; Moreno, M.; Polyzos, S.A.; Moreno-Navarrete, J.M.; Ricart, W.; Delgado, E.; De La Hera, J.; Sahin-Efe, A.; Chamberland, J.P.; Berman, R.; et al. Circulating Irisin Levels and Coronary Heart Disease: Association with Future Acute Coronary Syndrome and Major Adverse Cardiovascular Events. Int. J. Obes. 2015, 39, 156–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Mu, Q.; Shao, L.; Wang, X.; Li, S.; Yang, L.; Wu, Q.; Zhang, M.; Tang, D.; Zhou, Z.; et al. Protective Effect of Irisin on Atherosclerosis via Suppressing Oxidized Low Density Lipoprotein Induced Vascular Inflammation and Endothelial Dysfunction. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0158038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Song, H.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, F.; Mu, Q.; Jiang, M.; Wang, F.; Zhang, W.; Li, L.; Shao, L.; et al. Irisin Inhibits Atherosclerosis by Promoting Endothelial Proliferation Through microRNA126-5p. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2016, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tang, H.; Yu, R.; Liu, S.; Huwatibieke, B.; Li, Z.; Zhang, W. Irisin Inhibits Hepatic Cholesterol Synthesis via AMPK-SREBP2 Signaling. EBioMedicine 2016, 6, 139–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, H.; Shen, J.; Wu, T.; Kuang, J.; Liu, Q.; Cheng, S.; Pu, S.; Chen, L.; Li, R.; Li, Y.; et al. Irisin Is Controlled by Farnesoid X Receptor and Regulates Cholesterol Homeostasis. Front. Pharmacol. 2019, 10, 548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bashar, S.M.; El-Sherbeiny, S.M.S.; Boraie, M.Z. Correlation between the blood level of irisin and the severity of acute myocardial infarction in exercise-trained rats. J. Basic Clin. Physiol. Pharmacol. 2018, 30, 59–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Mottaleb, N.A.A.; Galal, H.M.; El Maghraby, K.M.; Gadallah, A.I. Serum irisin level in myocardial infarction patients with or without heart failure. Can. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 2019, 97, 932–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Eltzschig, H.K.; Eckle, T. Ischemia and reperfusion—From mechanism to translation. Nat. Med. 2011, 17, 1391–1401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Prabhu, S.D.; Frangogiannis, N.G. The Biological Basis for Cardiac Repair after Myocardial infarction: From Inflammation to Fibrosis. Circ. Res. 2016, 119, 91–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miller, E.J.; Li, J.; Leng, L.; McDonald, C.; Atsumi, T.; Bucala, R.; Young, L.H. Macrophage migration inhibitory factor stimulates AMP-activated protein kinase in the ischaemic heart. Nat. Cell Biol. 2008, 451, 578–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qi, D.; Hu, X.; Wu, X.; Merk, M.; Leng, L.; Bucala, R.; Young, L.H. Cardiac macrophage migration inhibitory factor inhibits JNK pathway activation and injury during ischemia/reperfusion. J. Clin. Investig. 2009, 119, 3807–3816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, K.; Xu, Z.; Liu, Y.; Wang, Z.; Li, Y.; Xu, X.; Chen, C.; Xia, T.; Liao, Q.; Yao, Y.; et al. Irisin protects mitochondria function during pulmonary ischemia/reperfusion injury. Sci. Transl. Med. 2017, 9, eaao6298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ho, M.-Y.; Wen, M.-S.; Yeh, J.-K.; Hsieh, I.-C.; Chen, C.-C.; Hsieh, M.-J.; Tsai, M.-L.; Yang, C.-H.; Wu, V.C.-C.; Hung, K.-C.; et al. Excessive irisin increases oxidative stress and apoptosis in murine heart. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2018, 503, 2493–2498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiong, M.; Wang, Z.; Pedrozo, Z.; Cao, D.J.; Troncoso, R.; Ibacache, M.; Criollo, A.; Nemchenko, A.; Hill, J.A.; Lavandero, S. Cardiomyocyte death: Mechanisms and translational implications. Cell Death Dis. 2011, 2, e244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frangogiannis, N.G. Regulation of the Inflammatory Response in Cardiac Repair. Circ. Res. 2012, 110, 159–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Zhao, Y.T.; Zhang, S.; Dubielecka, P.M.; Du, J.; Yano, N.; Chin, Y.E.; Zhuang, S.; Qin, G.; Zhao, T.C. Irisin plays a pivotal role to protect the heart against ischemia and reperfusion injury. J. Cell. Physiol. 2017, 232, 3775–3785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, J.; Zhang, N.; Chen, F.; Yang, C.; Ning, H.; Xiao, C.; Sun, K.; Liu, Y.; Yang, M.; Hu, T.; et al. Irisin ameliorates high glucose-induced cardiomyocytes injury via AMPK/mTOR signal pathway. Cell Biol. Int. 2020, 44, 2315–2325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xin, C.; Zhang, Z.; Gao, G.; Ding, L.; Yang, C.; Wang, C.; Liu, Y.; Guo, Y.; Yang, X.; Zhang, L.; et al. Irisin Attenuates Myocardial Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury and Improves Mitochondrial Function through AMPK Pathway in Diabetic Mice. Front. Pharmacol. 2020, 11, 565160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Chen, K.; Han, Y.; Zhu, H.; Zhou, X.; Tan, T.; Zeng, J.; Zhang, J.; Liu, Y.; Li, Y.; et al. Irisin Protects Heart Against Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury Through a SOD2-Dependent Mitochondria Mechanism. J. Cardiovasc. Pharmacol. 2018, 72, 259–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, W.; Wang, P.; Chen, Q.; Li, C. Exercise enhances mitochondrial fission and mitophagy to improve myopathy following critical limb ischemia in elderly mice via the PGC1a/FNDC5/irisin pathway. Skelet. Muscle 2020, 10, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, L.; Ma, J.; Tang, J.; Liu, Y.; Zheng, Q.; Chen, S.; Gao, E.; Ren, J.; Yang, L.; Yang, J. Irisin attenuates myocardial ischemia/reperfusion-induced cardiac dysfunction by regulating ER-mitochondria interaction through a mitochondrial ubiquitin ligase-dependent mechanism. Clin. Transl. Med. 2020, 10, 166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aydin, S.; Aydin, S.; Baydas, A.; Kobat, M.A.; Kalayci, M.; Eren, M.N.; Yilmaz, M.; Kuloglu, T.; Gul, E.; Secen, O.; et al. Decreased saliva/serum irisin concentrations in the acute myocardial infarction promising for being a new candidate biomarker for diagnosis of this pathology. Peptides 2014, 56, 141–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, J.; Xiang, G.; Liu, M.; Mei, W.; Xiang, L.; Dong, J. Irisin protects against endothelial injury and ameliorates atherosclerosis in apolipoprotein E-Null diabetic mice. Atherosclerosis 2015, 243, 438–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lörchner, H.; Pöling, J.; Gajawada, P.; Hou, Y.; Polyakova, V.; Kostin, S.; Adrian-Segarra, J.M.; Boettger, T.; Wietelmann, A.; Warnecke, H.; et al. Myocardial Healing Requires Reg3beta-Dependent Accumulation of Macrophages in the Ischemic Heart. Nat. Med. 2015, 21, 353–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.; Qiao, X.; Ma, Y.; Deng, H.; Xu, C.C.; Xu, L. Disordered metabolism in mice lacking irisin. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 17368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taylor, C.J.; Ordóñez-Mena, J.M.; Roalfe, A.K.; Lay-Flurrie, S.; Jones, N.; Marshall, T.; Hobbs, F.D.R. Trends in survival after a diagnosis of heart failure in the United Kingdom 2000–2017: Population based cohort study. BMJ 2019, 364, l223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhou, B.; Tian, R. Mitochondrial dysfunction in pathophysiology of heart failure. J. Clin. Investig. 2018, 128, 3716–3726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Porter, G.A.; Hom, J.R.; Hoffman, D.L.; Quintanilla, R.A.; Bentley, K.L.D.M.; Sheu, S.-S. Bioenergetics, mitochondria, and cardiac myocyte differentiation. Prog. Pediatr. Cardiol. 2011, 31, 75–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rosca, M.; Hoppel, C.L. Mitochondrial dysfunction in heart failure. Heart Fail. Rev. 2013, 18, 607–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhao, Q.; Sun, Q.; Zhou, L.; Liu, K.; Jiao, K. Complex Regulation of Mitochondrial Function during Cardiac Development. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2019, 8, e012731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menshikova, E.V.; Ritov, V.B.; Fairfull, L.; Ferrell, R.E.; Kelley, D.E.; Goodpaster, B.H. Effects of Exercise on Mitochondrial Content and Function in Aging Human Skeletal Muscle. J. Gerontol. Ser. A Boil. Sci. Med. Sci. 2006, 61, 534–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- White, A.T.; Schenk, S. NAD+/NADH and skeletal muscle mitochondrial adaptations to exercise. Am. J. Physiol. Metab. 2012, 303, E308–E321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Puigserver, P.; Spiegelman, B.M. Peroxisome Proliferator-Activated Receptor-Gamma Coactivator 1 Alpha (Pgc-1 Alpha): Transcriptional Coactivator and Metabolic Regulator. Endocr. Rev. 2003, 24, 78–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gureev, A.P.; Shaforostova, E.A.; Popov, V.N. Regulation of Mitochondrial Biogenesis as a Way for Active Longevity: Interaction Between the Nrf2 and PGC-1α Signaling Pathways. Front. Genet. 2019, 10, 435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Riehle, C.; Abel, E.D. PGC-1 Proteins and Heart Failure. Trends Cardiovasc. Med. 2012, 22, 98–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Oka, S.-I.; Sabry, A.D.; Cawley, K.M.; Warren, J.S. Multiple Levels of PGC-1α Dysregulation in Heart Failure. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2020, 7, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, S.; Fu, C.; Wang, H.; Shi, Y.; Xu, X.; Chen, J.; Song, X.; Sun, K.; Wang, J.; Fan, X.; et al. Polymorphisms of the Peroxisome Proliferator-Activated Receptor-Gamma Coactivator-1alpha Gene Are Associated with Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy and Not with Hypertension Hypertrophy. Clin. Chem. Lab. Med. 2007, 45, 962–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arhire, L.I.; Mihalache, L.; Covasa, M. Irisin: A Hope in Understanding and Managing Obesity and Metabolic Syndrome. Front. Endocrinol. 2019, 10, 524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Perakakis, N.; Triantafyllou, G.A.; Fernández-Real, J.M.; Huh, J.Y.; Park, K.H.; Seufert, J.; Mantzoros, C.S. Physiology and role of irisin in glucose homeostasis. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2017, 13, 324–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rosen, E.D.; Spiegelman, B.M. Adipocytes as regulators of energy balance and glucose homeostasis. Nat. Cell Biol. 2006, 444, 847–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xiong, X.-Q.; Chen, D.; Sun, H.-J.; Ding, L.; Wang, J.-J.; Chen, Q.; Li, Y.-H.; Zhou, Y.-B.; Han, Y.; Zhang, F.; et al. FNDC5 overexpression and irisin ameliorate glucose/lipid metabolic derangements and enhance lipolysis in obesity. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Basis Dis. 2015, 1852, 1867–1875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kurdiova, T.; Balaz, M.; Vician, M.; Maderova, D.; Vlcek, M.; Valkovic, L.; Srbecky, M.; Imrich, R.; Kyselovicova, O.; Belan, V.; et al. Effects of Obesity, Diabetes and Exercise on Fndc5 Gene Expression and Irisin Release in Human Skeletal Muscle and Adipose Tissue: In Vivo and In Vitro Studies. J. Physiol. 2014, 592, 1091–1107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vaughan, R.A.; Gannon, N.P.; Barberena, M.A.; Garcia-Smith, R.; Bisoffi, M.; Mermier, C.M.; Conn, C.A.; Trujillo, K.A. Characterization of the Metabolic Effects of Irisin on Skeletal Muscle In Vitro. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2014, 16, 711–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Belviranlı, M.; Okudan, N. Exercise training increases cardiac, hepatic and circulating levels of brain-derived neurotrophic factor and irisin in young and aged rats. Horm. Mol. Biol. Clin. Investig. 2018, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsuo, Y.; Gleitsmann, K.; Mangner, N.; Werner, S.; Fischer, T.; Bowen, T.S.; Kricke, A.; Matsumoto, Y.; Kurabayashi, M.; Schuler, G.; et al. Fibronectin type III domain containing 5 expression in skeletal muscle in chronic heart failure-relevance of inflammatory cytokines. J. Cachex Sarcopenia Muscle 2015, 6, 62–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, Q.; Ding, R.; Wang, X.; Yang, P.; Jiang, F.; Chen, X. Effect of Irisin on Pressure Overload–Induced Cardiac Remodeling. Arch. Med. Res. 2021, 52, 182–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, Q.; Wang, X.; Wu, K.; Liu, K.; Wang, S.; Chen, X. Irisin attenuates H2O2-induced apoptosis in cardiomyocytes via microRNA-19b/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Pathol. 2017, 10, 7707–7717. [Google Scholar]
- Li, R.; Wang, X.; Wu, S.; Wu, Y.; Chen, H.; Xin, J.; Li, H.; Lan, J.; Xue, K.; Li, X.; et al. Irisin ameliorates angiotensin II-induced cardiomyocyte apoptosis through autophagy. J. Cell. Physiol. 2019, 234, 17578–17588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lecker, S.H.; Zavin, A.; Cao, P.; Arena, R.; Allsup, K.; Daniels, K.M.; Joseph, J.; Schulze, P.C.; Forman, D.E. Expression of the Irisin Precursor FNDC5 in Skeletal Muscle Correlates with Aerobic Exercise Performance in Patients with Heart Failure. Circ. Heart Fail. 2012, 5, 812–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sobieszek, G.; Powrózek, T.; Mazurek, M.; Skwarek-Dziekanowska, A.; Małecka-Massalska, T. Electrical and Hormonal Biomarkers in Cachectic Elderly Women with Chronic Heart Failure. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mansur, A.J. Adropin and Irisin in Patients with Cardiac Cachexia. Arq. Bras. Cardiol. 2018, 111, 48–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Keulenaer, G.W.; Brutsaert, D.L. Systolic and Diastolic Heart Failure Are Overlapping Phenotypes within the Heart Failure Spectrum. Circulation 2011, 123, 1996–2005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Silvestrini, A.; Bruno, C.; Vergani, E.; Venuti, A.; Favuzzi, A.M.R.; Guidi, F.; Nicolotti, N.; Meucci, E.; Mordente, A.; Mancini, A. Circulating irisin levels in heart failure with preserved or reduced ejection fraction: A pilot study. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0210320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosendorff, C.; Lackland, D.T.; Allison, M.; Aronow, W.S.; Black, H.R.; Blumenthal, R.S.; Cannon, C.P.; De Lemos, J.A.; Elliott, W.J.; Findeiss, L.; et al. Treatment of Hypertension in Patients with Coronary Artery Disease: A Scientific Statement from the American Heart Association, American College of Cardiology, and American Society of Hypertension. Circulation 2015, 131, e435–e470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lamprea-Montealegre, J.A.; Zelnick, L.; Hall, Y.N.; Bansal, N.; De Boer, I.H. Prevalence of Hypertension and Cardiovascular Risk According to Blood Pressure Thresholds Used for Diagnosis. Hypertension 2018, 72, 602–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campbell, N.R.; Burgess, E.; Choi, B.C.; Taylor, G.; Wilson, E.; Cléroux, J.; Fodor, J.G.; Leiter, L.A.; Spence, D. Lifestyle modifications to prevent and control hypertension. 1. Methods and an overview of the Canadian recommendations. Canadian Hypertension Society, Canadian Coalition for High Blood Pressure Prevention and Control, Laboratory Centre for Disease Control at Health Canada, Heart and Stroke Foundation of Canada. Can. Med. Assoc. J. 1999, 160, S1–S6. [Google Scholar]
- Park, K.H.; Zaichenko, L.; Brinkoetter, M.; Thakkar, B.; Sahin-Efe, A.; Joung, K.E.; Tsoukas, M.; Geladari, E.V.; Huh, J.Y.; Dincer, F.; et al. Circulating Irisin in Relation to Insulin Resistance and the Metabolic Syndrome. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2013, 98, 4899–4907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.-J.; Xie, Q.; Tang, C.-S.; Zhang, A.-H. Expressions of irisin and urotensin II and their relationships with blood pressure in patients with preeclampsia. Clin. Exp. Hypertens. 2017, 39, 460–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Çelik, H.T.; Akkaya, N.; Erdamar, H.; Gok, S.; Kazanci, F.; DemirCelik, B.; Cakmak, M.; Yigitoglu, R. The Effects of Valsartan and Amlodipine on the Levels of Irisin, Adropin, and Perilipin. Clin. Lab. 2015, 61, 1889–1895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, M.; Wan, F.; Wang, F.; Wu, Q. Irisin relaxes mouse mesenteric arteries through endothelium-dependent and endothelium-independent mechanisms. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2015, 468, 832–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Chang, L.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, R.; Li, Z.; Chai, B.; Li, J.; Chen, E.; Mulholland, M. Central and Peripheral Irisin Differentially Regulate Blood Pressure. Cardiovasc. Drugs Ther. 2015, 29, 121–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Carling, D.; Viollet, B. Beyond Energy Homeostasis: The Expanding Role of AMP-Activated Protein Kinase in Regulating Metabolism. Cell Metab. 2015, 21, 799–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Han, F.; Zhang, S.; Hou, N.; Wang, D.; Sun, X. Irisin Improves Endothelial Function in Obese Mice through the Ampk-Enos Pathway. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 2015, 309, H1501–H1508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wu, J.; Spiegelman, B.M. Irisin ERKs the Fat. Diabetes 2014, 63, 381–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Levy, D.; Larson, M.G.; Vasan, R.S.; Kannel, W.B.; Ho, K.K. The progression from hypertension to congestive heart failure. JAMA 1996, 275, 1557–1562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delezie, J.; Handschin, C. Endocrine Crosstalk Between Skeletal Muscle and the Brain. Front. Neurol. 2018, 9, 698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.L.; Wu, S.S.; Wu, Y.; Wang, X.X.; Chen, H.Y.; Xin, J.J.; Li, H.; Lan, J.; Xue, K.Y.; Li, X.; et al. Irisin Alleviates Pressure Overload-Induced Cardiac Hypertrophy by Inducing Protective Autophagy via Mtor-Independent Activation of the Ampk-Ulk1 Pathway. J. Mol. Cell. Cardiol. 2018, 121, 242–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huo, C.-J.; Yu, X.-J.; Sun, Y.-J.; Li, H.-B.; Su, Q.; Bai, J.; Li, Y.; Liu, K.-L.; Qi, J.; Zhou, S.-W.; et al. Irisin lowers blood pressure by activating the Nrf2 signaling pathway in the hypothalamic paraventricular nucleus of spontaneously hypertensive rats. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2020, 394, 114953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, N.; Chen, Y.; Fan, Y.; Chang, J.; Gao, X.; Zhao, Y.; Sun, H.; Wang, Z.; Gu, X.; Tian, J.; et al. Plasma irisin levels are associated with hemodynamic and clinical outcome in idiopathic pulmonary arterial hypertension patients. Intern. Emerg. Med. 2021, 16, 625–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrie, J.; Guzik, T.J.; Touyz, R.M. Diabetes, Hypertension, and Cardiovascular Disease: Clinical Insights and Vascular Mechanisms. Can. J. Cardiol. 2018, 34, 575–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, X.; Mujahid, H.; Rong, B.; Lu, Q.-H.; Zhang, W.; Li, P.; Li, N.; Liang, E.-S.; Wang, Q.; Tang, D.-Q.; et al. Irisin inhibits high glucose-induced endothelial-to-mesenchymal transition and exerts a dose-dependent bidirectional effect on diabetic cardiomyopathy. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2017, 22, 808–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
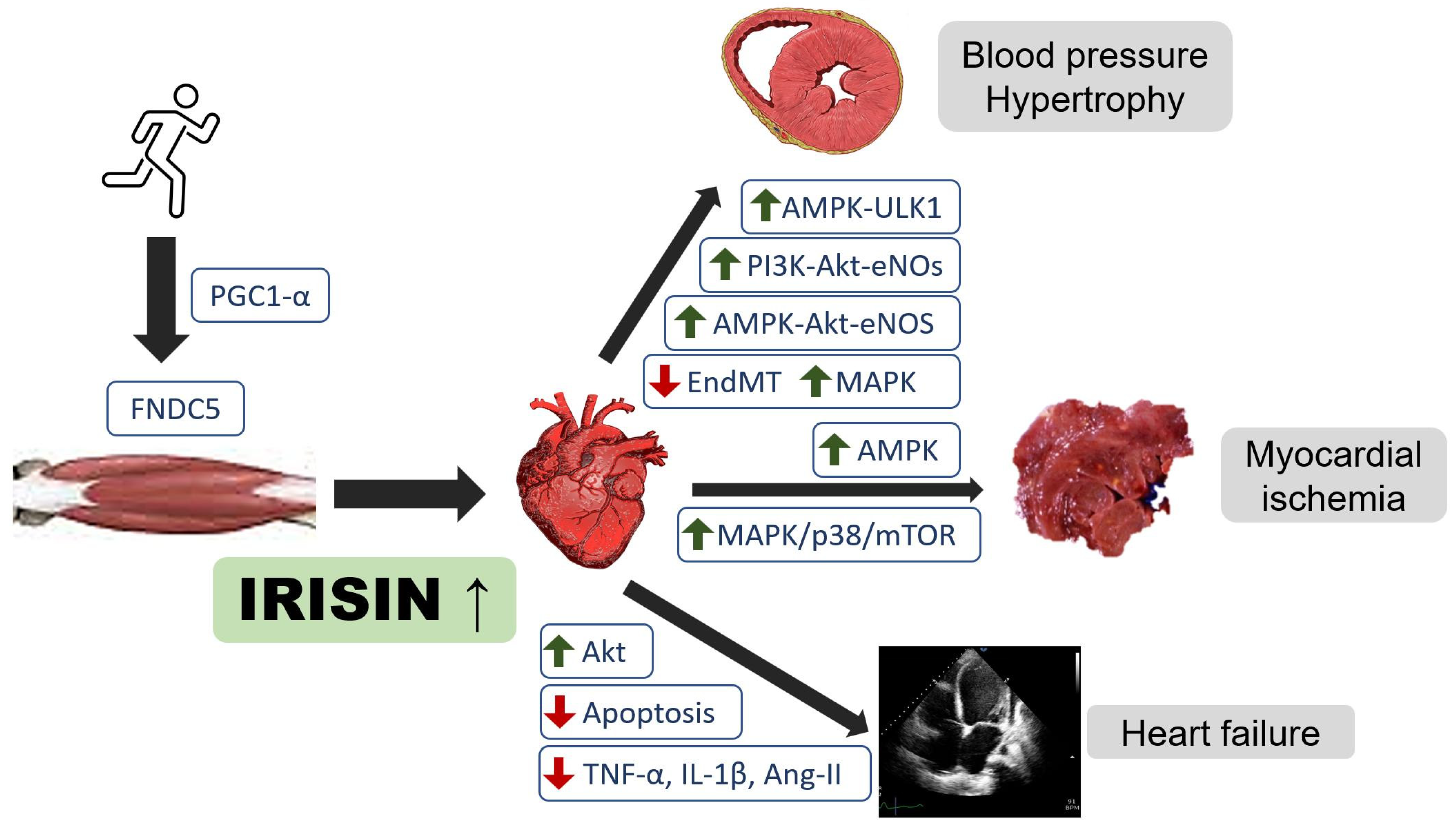
| Signaling Pathway | Irisin Source/Dose | Target Cells/Tissues | Animal Model | Cardiovascular Effect | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PI3K/Akt/eNOS | Recombinant Irisin 0.5 mg/kg | Blood/Bone marrow Endothelial progenitor cell | STZ-induced Diabetic Mice | Improved the function of endothelial progenitor cells | [9] |
| AMPK-Akt-eNOS-NO | Recombinant Irisin 0.1, 1, 10 µg/kg | Human coronary endothelial cell | Spontaneously hypertensive rats | Lowers blood pressure | [12] |
| MAPK/p38 | Recombinant Irisin 100 mg/kg | Cardiomyocyte | Ischemia/Reperfusion Mice | Protect the heart against ischemia and reperfusion injury | [35] |
| AMPK/mTOR | Irisin to cell | Cardiomyocyte | High glucose-induced cardiomyocytes of rats | Ameliorates high glucose-induced cardiomyocytes injury | [36] |
| AMPK | Recombinant Irisin 0.5 µg/g | Cardiomyocyte | High fat diet-induced Diabetic Mice with ischemia/reperfusion | Attenuates myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury and improves mitochondrial function | [37] |
| Akt | Recombinant Irisin 10 µg/kg | Cardiomyocyte | TAC-induced cardiac hypertrophic rat | Improve cardiac remodeling | [65] |
| MicroRNA-19b/AKT/mTOR | Irisin to cell | Oxidative stress-induced injury rat cardiac myoblast cell | Attenuates H2O2-induced apoptosis | [66] | |
| Angiotensin II | Irisin transgenic mice | Cardiomyocyte | TAC-induced cardiac hypertrophic mice | Ameliorates apoptosis through autophagy | [67] |
| AMPK-ULK1 | Recombinant Irisin | Cardiomyocyte | TAC-induced Cardiac hypertrophic Mice | Inducing protective autophagy and improves cardiac hypertrophy | [68] |
| Nrf2 | Recombinant Irisin 10 µg/kg | Hypothalamic paraventricular nucleus | Spontaneously hypertensive rats | Lowers blood pressure | [87] |
| EndMT MAPK | Recombinant Irisin 0.5, 1.5 µg/g | Cardiomyocyte | STZ-induced Diabetic Mice | Dose-dependent bidirectional effect on myocardial fibrosis | [90] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ho, M.-Y.; Wang, C.-Y. Role of Irisin in Myocardial Infarction, Heart Failure, and Cardiac Hypertrophy. Cells 2021, 10, 2103. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells10082103
Ho M-Y, Wang C-Y. Role of Irisin in Myocardial Infarction, Heart Failure, and Cardiac Hypertrophy. Cells. 2021; 10(8):2103. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells10082103
Chicago/Turabian StyleHo, Ming-Yun, and Chao-Yung Wang. 2021. "Role of Irisin in Myocardial Infarction, Heart Failure, and Cardiac Hypertrophy" Cells 10, no. 8: 2103. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells10082103
APA StyleHo, M. -Y., & Wang, C. -Y. (2021). Role of Irisin in Myocardial Infarction, Heart Failure, and Cardiac Hypertrophy. Cells, 10(8), 2103. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells10082103





