Long Noncoding RNAs Regulate the Inflammatory Responses of Macrophages
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Proinflammatory Macrophage-Targeting lncRNAs
2.1. Carlr
2.2. CHRF
2.3. FENDRR
2.4. FIRRE
2.5. GAS5
2.6. HOTAIR
2.7. H19
2.8. Maclpil
2.9. MALAT1
2.10. MIR155HG
2.11. PACER
2.12. PTPRE-AS1
2.13. RAPIA
2.14. ROCKI
2.15. SNHG16
3. Anti-Inflammatory Macrophage-Associated lncRNAs
3.1. ANCR
3.2. LncRNA-AK085865
3.3. LncRNA-CCL2
3.4. Dnmt3aos
3.5. LincRNA-EPS
3.6. Kcnq1ot1
3.7. Lethe
3.8. Mirt2
3.9. MIST
3.10. LncRNA-Mm2pr
3.11. NEAT1
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Guttman, M.; Amit, I.; Garber, M.; French, C.; Lin, M.F.; Feldser, D.; Huarte, M.; Zuk, O.; Carey, B.W.; Cassady, J.P.; et al. Chromatin signature reveals over a thousand highly conserved large non-coding RNAs in mammals. Nat. Cell Biol. 2009, 458, 223–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Wang, W.; Zhu, W.; Dong, J.; Cheng, Y.; Yin, Z.; Shen, F. Mechanisms and Functions of Long Non-Coding RNAs at Multiple Regulatory Levels. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 5573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rinn, J.L.; Kertesz, M.; Wang, J.K.; Squazzo, S.L.; Xu, X.; Brugmann, S.A.; Goodnough, L.H.; Helms, J.A.; Farnham, P.J.; Segal, E.; et al. Functional Demarcation of Active and Silent Chromatin Domains in Human HOX Loci by Noncoding RNAs. Cell 2007, 129, 1311–1323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, X.; Arai, S.; Song, X.; Reichart, D.; Du, K.; Pascual, G.; Tempst, P.; Rosenfeld, M.G.; Glass, C.K.; Kurokawa, R. Induced ncRNAs allosterically modify RNA-binding proteins in cis to inhibit transcription. Nat. Cell Biol. 2008, 454, 126–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.-Y.; Li, S.; Wang, G.-X.; Yu, Q.; Lin, J.D. A Long Noncoding RNA Transcriptional Regulatory Circuit Drives Thermogenic Adipocyte Differentiation. Mol. Cell 2014, 55, 372–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gong, C.; Maquat, L.E. lncRNAs transactivate STAU1-mediated mRNA decay by duplexing with 3′ UTRs via Alu elements. Nat. Cell Biol. 2011, 470, 284–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rapicavoli, N.A.; Qu, K.; Zhang, J.; Mikhail, M.; Laberge, R.-M.; Chang, H.Y. A mammalian pseudogene lncRNA at the interface of inflammation and anti-inflammatory therapeutics. Elife 2013, 2, e00762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boliar, S.; Gludish, D.W.; Jambo, K.C.; Kamng’Ona, R.; Mvaya, L.; Mwandumba, H.C.; Russell, D.G. Inhibition of the lncRNA SAF drives activation of apoptotic effector caspases in HIV-1–infected human macrophages. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 7431–7438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zur Bruegge, J.; Einspanier, R.; Sharbati, S. A long journey ahead: Long non-coding RNAs in bacterial infections. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2017, 7, 95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, C.-H.; Shi, H.-H.; Chen, L.-H.; Li, X.-L.; Cao, G.-L.; Hu, X.-F. Identification of key lncRNAs associated with atherosclerosis progression based on public datasets. Front. Genet. 2019, 10, 123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Haemmig, S.; Simion, V.; Feinberg, M.W. Long Non-Coding RNAs in Vascular Inflammation. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2018, 5, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luan, A.; Hu, M.S.; Leavitt, T.; Brett, E.A.; Wang, K.C.; Longaker, M.T.; Wan, D.C. Noncoding RNAs in Wound Healing: A New and Vast Frontier. Adv. Wound Care 2018, 7, 19–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhao, X.-Y.; Lin, J.D. Long Noncoding RNAs: A New Regulatory Code in Metabolic Control. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2015, 40, 586–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sica, A.; Mantovani, A. Macrophage plasticity and polarization: In vivo veritas. J. Clin. Investig. 2012, 122, 787–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Smith, W.; Hao, D.; He, B.; Kong, L. M1 and M2 macrophage polarization and potentially therapeutic naturally occurring compounds. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2019, 70, 459–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fok, E.T.; Davignon, L.; Fanucchi, S.; Mhlanga, M.M. The lncRNA Connection Between Cellular Metabolism and Epigenetics in Trained Immunity. Front. Immunol. 2019, 9, 3184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quintin, J.; Saeed, S.; Martens, J.; Giamarellos-Bourboulis, E.; Ifrim, D.C.; Logie, C.; Jacobs, L.; Jansen, T.; Kullberg, B.-J.; Wijmenga, C.; et al. Candida albicans Infection Affords Protection against Reinfection via Functional Reprogramming of Monocytes. Cell Host Microbe 2012, 12, 223–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kleinnijenhuis, J.; Quintin, J.; Preijers, F.; Joosten, L.A.; Jacobs, C.; Xavier, R.J.; van der Meer, J.W.; van Crevel, R.; Netea, M.G. BCG-induced trained immunity in NK cells: Role for non-specific protection to infection. Clin. Immunol. 2014, 155, 213–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kaufmann, E.; Sanz, J.; Dunn, J.L.; Khan, N.; Mendonça, L.E.; Pacis, A.; Tzelepis, F.; Pernet, E.; Dumaine, A.; Grenier, J.-C.; et al. BCG Educates Hematopoietic Stem Cells to Generate Protective Innate Immunity against Tuberculosis. Cell 2018, 172, 176–190.e19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hole, C.; Wager, C.M.L.; Castro-Lopez, N.; Campuzano, A.; Cai, H.; Wozniak, K.L.; Wang, Y.; Wormley, F.L., Jr. Induction of memory-like dendritic cell responses in vivo. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 2955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Engreitz, J.M.; Haines, J.E.; Perez, E.; Munson, G.; Chen, J.; Kane, M.; McDonel, P.E.; Guttman, M.; Lander, E.S. Local regulation of gene expression by lncRNA promoters, transcription and splicing. Nat. Cell Biol. 2016, 539, 452–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melé, M.; Rinn, J.L. “Cat’s Cradling” the 3D Genome by the Act of LncRNA Transcription. Mol. Cell. 2016, 62, 657–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mantovani, A.; Sozzani, S.; Locati, M.; Allavena, P.; Sica, A. Macrophage polarization: Tumor-associated macrophages as a paradigm for polarized M2 mononuclear phagocytes. Trends Immunol. 2002, 23, 549–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, J.; Dong, R.; Jiang, L.; Gong, Y.; Yuan, M.; You, J.; Meng, W.; Chen, Z.; Zhang, N.; Weng, Q. LncRNA-MM2P identified as a modulator of macrophage M2 polarization. Cancer. Immunol. Res. 2019, 7, 292–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez, F.O.; Gordon, S. The M1 and M2 paradigm of macrophage activation: Time for reassessment. F1000Prime Rep. 2014, 6, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Murray, P.J.; Allen, J.E.; Biswas, S.K.; Fisher, E.A.; Gilroy, D.W.; Goerdt, S.; Gordon, S.; Hamilton, J.A.; Ivashkiv, L.B.; Lawrence, T.; et al. Macrophage Activation and Polarization: Nomenclature and Experimental Guidelines. Immunity 2014, 41, 14–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Carpenter, S.; Aiello, D.; Atianand, M.K.; Ricci, E.P.; Gandhi, P.; Hall, L.L.; Byron, M.; Monks, B.; Henry-Bezy, M.; Lawrence, J.B.; et al. A Long Noncoding RNA Mediates Both Activation and Repression of Immune Response Genes. Science 2013, 341, 789–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Castellanos-Rubio, A.; Kratchmarov, R.; Sebastian, M.; Garcia-Etxebarria, K.; Garcia, L.; Irastorza, I.; Ghosh, S. Cytoplasmic form of Carlr lncRNA facilitates inflammatory gene expression upon NF-κB Activation. J. Immunol. 2017, 199, 581–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Liu, F.; Zhou, L.-Y.; Long, B.; Yuan, S.-M.; Wang, Y.; Liu, C.-Y.; Sun, T.; Zhang, X.-J.; Li, P.-F. The Long Noncoding RNA CHRF Regulates Cardiac Hypertrophy by Targeting miR-489. Circ. Res. 2014, 114, 1377–1388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wu, Q.; Han, L.; Yan, W.; Ji, X.; Han, R.; Yang, J.; Yuan, J.; Ni, C. miR-489 inhibits silica-induced pulmonary fibrosis by targeting MyD88 and Smad3 and is negatively regulated by lncRNA CHRF. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 30921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Grote, P.; Wittler, L.; Hendrix, D.; Koch, F.; Währisch, S.; Beisaw, A.; Macura, K.; Bläss, G.; Kellis, M.; Werber, M.; et al. The Tissue-Specific lncRNA Fendrr Is an Essential Regulator of Heart and Body Wall Development in the Mouse. Dev. Cell 2013, 24, 206–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xu, T.-P.; Huang, M.-D.; Xia, R.; Liu, X.-X.; Sun, M.; Yin, L.; Chen, W.-M.; Han, L.; Zhang, E.-B.; Kong, R. Decreased expression of the long non-coding RNA FENDRR is associated with poor prognosis in gastric cancer and FENDRR regulates gastric cancer cell metastasis by affecting fibronectin1 expression. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2014, 7, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munteanu, M.C.; Huang, C.; Liang, Y.; Sathiaseelan, R.; Zeng, X.; Liu, L. Long non-coding RNA FENDRR regulates IFNγ-induced M1 phenotype in macrophages. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 13672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hacisuleyman, E.; Goff, L.; Trapnell, C.; Williams, A.; Henao-Mejia, J.; Sun, L.; McClanahan, P.; Hendrickson, D.G.; Sauvageau, M.; Kelley, D.R.; et al. Topological organization of multichromosomal regions by the long intergenic noncoding RNA Firre. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2014, 21, 198–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, R.-W.; Wang, Y.; Chen, L.-L. Cellular functions of long noncoding RNAs. Nat. Cell Biol. 2019, 21, 542–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shyu, A.-B.; Wilkinson, M.F. The Double Lives of Shuttling mRNA Binding Proteins. Cell 2000, 102, 135–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lu, Y.; Liu, X.; Xie, M.; Liu, M.; Ye, M.; Li, M.; Chen, X.-M.; Li, X.; Zhou, R. The NF-κB–responsive long noncoding RNA FIRRE regulates posttranscriptional regulation of inflammatory gene expression through interacting with hnRNPU. J. Immunol. 2017, 199, 3571–3582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Asai, A.; Nakamura, K.; Kobayashi, M.; Herndon, D.N.; Suzuki, F. CCL1 released from M2b macrophages is essentially required for the maintenance of their properties. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2012, 92, 859–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Q.; Wang, N.; Qi, J.; Gu, Z.; Shen, H. Long non-coding RNA-GAS5 acts as a tumor suppressor in bladder transitional cell carcinoma via regulation of chemokine (C-C motif) ligand 1 expression. Mol. Med. Rep. 2015, 13, 27–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ito, I.; Asai, A.; Suzuki, S.; Kobayashi, M.; Suzuki, F. M2b macrophage polarization accompanied with reduction of long noncoding RNA GAS5. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2017, 493, 170–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Zhang, L.; Liechty, C.; Zgheib, C.; Hodges, M.M.; Liechty, K.W.; Xu, J. Long Noncoding RNA GAS5 Regulates Macrophage Polarization and Diabetic Wound Healing. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2020, 140, 1629–1638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chi, X.; Ding, B.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, J.; Wang, J.; Zhang, W. lncRNA GAS5 promotes M1 macrophage polarization via miR-455-5p/SOCS3 pathway in childhood pneumonia. J. Cell. Physiol. 2019, 234, 13242–13251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, J.; Wang, C.; Wang, D.; Yuan, H. LncRBA GSA5, up-regulated by ox-LDL, aggravates inflammatory response and MMP expression in THP-1 macrophages by acting like a sponge for miR-221. Exp. Cell Res. 2018, 369, 348–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Obaid, M.; Udden, S.M.N.; Deb, P.; Shihabeddin, N.; Zaki, H.; Mandal, S.S. LncRNA HOTAIR regulates lipopolysaccharide-induced cytokine expression and inflammatory response in macrophages. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 15670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fujisaka, Y.; Iwata, T.; Tamai, K.; Nakamura, M.; Mochizuki, M.; Shibuya, R.; Yamaguchi, K.; Shimosegawa, T.; Satoh, K. Long non-coding RNA HOTAIR up-regulates chemokine (C-C motif) ligand 2 and promotes proliferation of macrophages and myeloid-derived suppressor cells in hepatocellular carcinoma cell lines. Oncol. Lett. 2017, 15, 509–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Subuddhi, A.; Kumar, M.; Majumder, D.; Sarkar, A.; Ghosh, Z.; Vasudevan, M.; Kundu, M.; Basu, J. Unraveling the role of H3K4 trimethylation and lncRNA HOTAIR in SATB1 and DUSP4-dependent survival of virulent Mycobacterium tuberculosis in macrophages. Tuberculosis 2020, 120, 101897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, M.-C.; Manor, O.; Wan, Y.; Mosammaparast, N.; Wang, J.K.; Lan, F.; Shi, Y.; Segal, E.; Chang, H.Y. Long Noncoding RNA as Modular Scaffold of Histone Modification Complexes. Science 2010, 329, 689–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gabory, A.; Jammes, H.; Dandolo, L. The H19 locus: Role of an imprinted non-coding RNA in growth and development. BioEssays 2010, 32, 473–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.-T.; Ye, H.; Wei, P.-P.; Han, B.-W.; He, B.; Chen, Z.-H.; Chen, Y.-Q. LncRNAs H19 and HULC, activated by oxidative stress, promote cell migration and invasion in cholangiocarcinoma through a ceRNA manner. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2016, 9, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, D.Y.; Busch, A.; Jin, H.; Chernogubova, E.; Pelisek, J.; Karlsson, J.; Sennblad, B.; Liu, S.; Lao, S.; Hofmann, P.; et al. H19 Induces Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm Development and Progression. Circulation 2018, 138, 1551–1568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.; Ma, J.; Wang, J.; Wang, L. Silencing of H19 inhibits the adipogenesis and inflammation response in ox-LDL-treated Raw264.7 cells by up-regulating miR-130b. Mol. Immunol. 2018, 93, 107–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Liu, R.; Wang, Y.; Zhu, W.; Zhao, D.; Wang, X.; Yang, H.; Gurley, E.C.; Chen, W.; Hylemon, P.B.; et al. Cholangiocyte-Derived Exosomal lncRNA H19 Promotes Macrophage Activation and Hepatic Inflammation under Cholestatic Conditions. Cells 2020, 9, 190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, Y.; Luo, Y.; Yao, Y.; Ji, Y.; Feng, L.; Du, F.; Zheng, X.; Tao, T.; Zhai, X.; Li, Y.; et al. Silencing the lncRNA Maclpil in pro-inflammatory macrophages attenuates acute experimental ischemic stroke via LCP1 in mice. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2020, 40, 747–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, P.; Diederichs, S.; Wang, W.; Böing, S.; Metzger, R.; Schneider, P.M.; Tidow, N.; Brandt, B.; Buerger, H.; Bulk, E.; et al. MALAT-1, a novel noncoding RNA, and thymosin β4 predict metastasis and survival in early-stage non-small cell lung cancer. Oncogene 2003, 22, 8031–8041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhao, G.; Su, Z.; Song, D.; Mao, Y.; Mao, X. The long noncoding RNA MALAT1 regulates the lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammatory response through its interaction with NF-κB. FEBS Lett. 2016, 590, 2884–2895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cui, H.; Banerjee, S.; Guo, S.; Xie, N.; Ge, J.; Jiang, D.; Zörnig, M.; Thannickal, V.J.; Liu, G. Long noncoding RNA Malat1 regulates differential activation of macrophages and response to lung injury. JCI Insight 2019, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, N.; Liu, Y.; Cai, J. LncRNA MIR155HG regulates M1/M2 macrophage polarization in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2019, 117, 109015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, R.C.; Vardinogiannis, I.; Gilmore, T.D. Identification of an NF-κB p50/p65-responsive site in the human MIR155HG promoter. BMC Mol. Biol. 2013, 14, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Krawczyk, M.; Emerson, B.M. p50-associated COX-2 extragenic RNA (PACER) activates COX-2 gene expression by occluding repressive NF-κB complexes. Elife 2014, 3, e01776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sully, V.; Pownall, S.; Vincan, E.; Bassal, S.; Borowski, A.H.; Hart, P.H.; Rockman, S.P.; Phillips, W. Functional Abnormalities in Protein Tyrosine Phosphatase ε-Deficient Macrophages. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2001, 286, 184–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, X.; Huang, S.; Xue, P.; Fu, J.; Liu, L.; Zhang, C.; Yang, L.; Xia, L.; Sun, L.; Huang, S.-K.; et al. LncRNA PTPRE-AS1 modulates M2 macrophage activation and inflammatory diseases by epigenetic promotion of PTPRE. Sci. Adv. 2019, 5, eaax9230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sun, C.; Fu, Y.; Gu, X.; Xi, X.; Peng, X.; Wang, C.; Sun, Q.; Wang, X.; Qian, F.; Qin, Z. Macrophage-enriched lncRNA RAPIA: A novel therapeutic target for atherosclerosis. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2020, 40, 1464–1478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.-M.; Yuk, J.-M.; Shin, D.-M.; Yang, C.-S.; Kim, K.-K.; Choi, D.-K.; Liang, Z.-L.; Kim, J.-M.; Jeon, B.H.; Kim, C.D.; et al. Apurinic/Apyrimidinic Endonuclease 1 Is a Key Modulator of Keratinocyte Inflammatory Responses. J. Immunol. 2009, 183, 6839–6848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lykke-Andersen, S.; Chen, Y.; Ardal, B.R.; Lilje, B.; Waage, J.; Sandelin, A.; Jensen, T.H. Human nonsense-mediated RNA decay initiates widely by endonucleolysis and targets snoRNA host genes. Genes Dev. 2014, 28, 2498–2517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- An, J.; Chen, Z.; Ma, Q.; Wang, H.; Zhang, J.; Shi, F. LncRNA SNHG16 promoted proliferation and inflammatory response of macrophages through miR-17-5p/NF-κB signaling pathway in patients with atherosclerosis. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2019, 23, 8665–8677. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, W.; Lou, C.; Gao, J.; Zhang, X.; Du, Y. LncRNA SNHG16 reverses the effects of miR-15a/16 on LPS-induced inflammatory pathway. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2018, 106, 1661–1667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kretz, M.; Webster, D.E.; Flockhart, R.J.; Lee, C.S.; Zehnder, A.; Lopez-Pajares, V.; Qu, K.; Zheng, G.X.; Chow, J.; Kim, G.E.; et al. Suppression of progenitor differentiation requires the long noncoding RNA ANCR. Genes Dev. 2012, 26, 338–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fatica, A.; Bozzoni, I. Long non-coding RNAs: New players in cell differentiation and development. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2014, 15, 7–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, C.; Guo, Y.; Lou, S. LncRNA ANCR Promotes Invasion and Migration of Gastric Cancer by Regulating FoxO1 Expression to Inhibit Macrophage M1 Polarization. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2020, 65, 2863–2872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pei, W.; Zhang, Y.; Li, X.; Luo, M.; Chen, T.; Zhang, M.; Zhong, M.; Lv, K. LncRNA AK085865 depletion ameliorates asthmatic airway inflammation by modulating macrophage polarization. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2020, 83, 106450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, X.; Kong, X.; Zhang, M.; Wang, D.; Liu, Y.; Lv, K. Long non-coding RNA AK085865 ablation confers susceptibility to viral myocarditis by regulating macrophage polarization. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2020, 24, 5542–5554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, X.; Wang, C.; Zhang, M.; Yang, H.; Lv, K. lncRNA AK085865 Promotes Macrophage M2 Polarization in CVB3-Induced VM by Regulating ILF2-ILF3 Complex-Mediated miRNA-192 Biogenesis. Mol. Ther. Nucleic Acids 2020, 21, 441–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khyzha, N.; Khor, M.; DiStefano, P.V.; Wang, L.; Matic, L.; Hedin, U.; Wilson, M.D.; Maegdefessel, L.; Fish, J.E. Regulation of CCL2 expression in human vascular endothelial cells by a neighboring divergently transcribed long noncoding RNA. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 2019, 116, 16410–16419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Stout, R.D.; Jiang, C.; Matta, B.; Tietzel, I.; Watkins, S.K.; Suttles, J. Macrophages Sequentially Change Their Functional Phenotype in Response to Changes in Microenvironmental Influences. J. Immunol. 2005, 175, 342–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, Y.; Li, Z.; Cai, W.; Xiao, D.; Han, S.; Han, F.; Bai, X.; Wang, K.; Liu, Y.; Li, X.; et al. SIRT1 regulates inflammation response of macrophages in sepsis mediated by long noncoding RNA. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA) Mol. Basis Dis. 2018, 1864, 784–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, H.-L.; Mostoslavsky, R.; Saito, S.; Manis, J.P.; Gu, Y.; Patel, P.; Bronson, R.; Appella, E.; Alt, F.W.; Chua, K.F. Developmental defects and p53 hyperacetylation in Sir2 homolog (SIRT1)-deficient mice. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 2003, 100, 10794–10799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, X.; Zhang, Y.; Pei, W.; Zhang, M.; Yang, H.; Zhong, M.; Kong, X.; Xu, Y.; Zhu, X.; Chen, T.; et al. LncRNA Dnmt3aos regulates Dnmt3a expression leading to aberrant DNA methylation in macrophage polarization. FASEB J. 2020, 34, 5077–5091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Atianand, M.K.; Hu, W.; Satpathy, A.T.; Shen, Y.; Ricci, E.P.; Alvarez-Dominguez, J.R.; Bhatta, A.; Schattgen, S.A.; McGowan, J.D.; Blin, J. A long noncoding RNA lincRNA-EPS acts as a transcriptional brake to restrain inflammation. Cell 2016, 165, 1672–1685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hu, W.; Yuan, B.; Flygare, J.; Lodish, H.F. Long noncoding RNA-mediated anti-apoptotic activity in murine erythroid terminal differentiation. Genes Dev. 2011, 25, 2573–2578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sunamura, N.; Ohira, T.; Kataoka, M.; Inaoka, D.; Tanabe, H.; Nakayama, Y.; Oshimura, M.; Kugoh, H. Regulation of functional KCNQ1OT1 lncRNA by β-catenin. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 20690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gao, X.; Ge, J.; Li, W.; Zhou, W.; Xuren, G. LncRNA KCNQ1OT1 ameliorates particle-induced osteolysis through inducing macrophage polarization by inhibiting miR-21a-5p. Biol. Chem. 2018, 399, 375–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, R.R.; Mondal, T.; Mohammad, F.; Enroth, S.; Redrup, L.; Komorowski, J.; Nagano, T.; Mancini-DiNardo, D.; Kanduri, C. Kcnq1ot1 Antisense Noncoding RNA Mediates Lineage-Specific Transcriptional Silencing through Chromatin-Level Regulation. Mol. Cell 2008, 32, 232–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammad, F.; Mondal, T.; Guseva, N.; Pandey, G.K.; Kanduri, C. Kcnq1ot1 noncoding RNA mediates transcriptional gene silencing by interacting with Dnmt1. Development 2010, 137, 2493–2499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zgheib, C.; Hodges, M.M.; Hu, J.; Liechty, K.W.; Xu, J. Long non-coding RNA Lethe regulates hyperglycemia-induced reactive oxygen species production in macrophages. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0177453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, M.; Yuan, L.; Tan, X.; Huang, D.; Wang, X.; Zheng, Z.; Mao, X.; Li, X.; Yang, L.; Huang, K.; et al. The LPS-inducible lncRNA Mirt2 is a negative regulator of inflammation. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 2049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stapleton, K.; Das, S.; Reddy, M.A.; Leung, A.; Amaram, V.; Lanting, L.; Chen, Z.; Zhang, L.; Palanivel, R.; Deiuliis, J.A.; et al. Novel Long Noncoding RNA, Macrophage Inflammation-Suppressing Transcript (MIST), Regulates Macrophage Activation During Obesity. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2020, 40, 914–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.; Tang, A.; Wang, X.; Chen, X.; Zhao, L.; Xiao, Z.; Shen, S. Inhibition of lncRNA NEAT1 suppresses the inflammatory response in IBD by modulating the intestinal epithelial barrier and by exosome-mediated polarization of macrophages. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2018, 42, 2903–2913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Clemson, C.M.; Hutchinson, J.N.; Sara, S.A.; Ensminger, A.W.; Fox, A.H.; Chess, A.; Lawrence, J.B. An Architectural Role for a Nuclear Noncoding RNA: NEAT1 RNA Is Essential for the Structure of Paraspeckles. Mol. Cell 2009, 33, 717–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gao, Y.; Fang, P.; Li, W.-J.; Zhang, J.; Wang, G.-P.; Jiang, D.-F.; Chen, F.-P. LncRNA NEAT1 sponges miR-214 to regulate M2 macrophage polarization by regulation of B7-H3 in multiple myeloma. Mol. Immunol. 2020, 117, 20–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imamura, K.; Imamachi, N.; Akizuki, G.; Kumakura, M.; Kawaguchi, Y.; Nagata, K.; Kato, A.; Sato, H.; Yoneda, M.; Kai, C.; et al. Long Noncoding RNA NEAT1-Dependent SFPQ Relocation from Promoter Region to Paraspeckle Mediates IL8 Expression upon Immune Stimuli. Mol. Cell 2014, 53, 393–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gast, M.; Rauch, B.; Haghikia, A.; Nakagawa, S.; Haas, J.; Stroux, A.; Schmidt, D.; Schumann, P.; Weiss, S.; Jensen, L.; et al. Long noncoding RNA NEAT1 modulates immune cell functions and is suppressed in early onset myocardial infarction patients. Cardiovasc. Res. 2019, 115, 1886–1906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.C.; Chang, H.Y. Molecular Mechanisms of Long Noncoding RNAs. Mol. Cell 2011, 43, 904–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tripathi, V.; Ellis, J.D.; Shen, Z.; Song, D.Y.; Pan, Q.; Watt, A.T.; Freier, S.M.; Bennett, C.F.; Sharma, A.; Bubulya, P.A.; et al. The Nuclear-Retained Noncoding RNA MALAT1 Regulates Alternative Splicing by Modulating SR Splicing Factor Phosphorylation. Mol. Cell 2010, 39, 925–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ilik, I.A.; Quinn, J.J.; Georgiev, P.; Tavares-Cadete, F.; Maticzka, D.; Toscano, S.; Wan, Y.; Spitale, R.C.; Luscombe, N.; Backofen, R.; et al. Tandem Stem-Loops in roX RNAs Act Together to Mediate X Chromosome Dosage Compensation in Drosophila. Mol. Cell 2013, 51, 156–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vance, K.W.; Ponting, C.P. Transcriptional regulatory functions of nuclear long noncoding RNAs. Trends Genet. 2014, 30, 348–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kanduri, C. Long noncoding RNAs: Lessons from genomic imprinting. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA) Bioenerg. Mech. 2016, 1859, 102–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dykes, I.M.; Emanueli, C. Transcriptional and Post-transcriptional Gene Regulation by Long Non-coding RNA. Genom. Proteom. Bioinform. 2017, 15, 177–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.; Wang, M.; Tian, J.; Li, X.; Yang, M.; Zhang, K.; Tan, S.; Luo, L.; Luo, C.; Peng, L.; et al. Long non-coding RNA expressed in macrophage co-varies with the inflammatory phenotype during macrophage development and polarization. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2019, 23, 6530–6542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Yang, W.; Guo, Y.; Chen, W.; Zheng, P.; Zeng, J.; Tong, W. Exosomal lncRNA GAS5 regulates the apoptosis of macrophages and vascular endothelial cells in atherosclerosis. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0185406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Wang, L.; Mao, Y.; Nan, G. Long Noncoding RNA-H19 Contributes to Atherosclerosis and Induces Ischemic Stroke via the Upregulation of Acid Phosphatase 5. Front. Neurol. 2019, 10, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Song, J.; Wang, Q.; Zong, L. LncRNA MIR155HG contributes to smoke-related chronic obstructive pulmonary disease by targeting miR-128-5p/BRD4 axis. Biosci. Rep. 2020, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhang, Q.; Chao, T.; Patil, V.S.; Qin, Y.; Tiwari, S.K.; Chiou, J.; Dobin, A.; Tsai, C.; Li, Z.; Dang, J.; et al. The long noncoding RNA ROCKI regulates inflammatory gene expression. EMBO J. 2019, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, C.-W.; Luo, T.; Zou, S.-S.; Wu, A.-S. The Role of Long Noncoding RNAs in Central Nervous System and Neurodegenerative Diseases. Front. Behav. Neurosci. 2018, 12, 175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, J.; Cao, X. Long noncoding RNAs in the metabolic control of inflammation and immune disorders. Cell. Mol. Immunol. 2018, 16, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Carrillo, J.L.M.; García, F.P.C.; Coronado, O.G.; García, M.A.M.; Cordero, J.F.C. Physiology and Pathology of Innate Immune Response against Pathogens; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Takeda, K.; Akira, S. Regulation of innate immune responses by Toll-like receptors. Jpn. J. Infect. Dis. 2001, 54, 209–219. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Djebali, S.; Davis, C.A.; Merkel, A.; Dobin, A.; Lassmann, T.; Mortazavi, A.; Tanzer, A.; Lagarde, J.; Lin, W.; Schlesinger, F.; et al. Landscape of transcription in human cells. Nature 2012, 489, 101–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wu, X.; Kriz, A.J.; Sharp, P.A. Target specificity of the CRISPR-Cas9 system. Quant. Biol. 2014, 2, 59–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Covarrubias, S.; Robinson, E.K.; Shapleigh, B.; Vollmers, A.; Katzman, S.; Hanley, N.; Fong, N.; McManus, M.T.; Carpenter, S. CRISPR/Cas-based screening of long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs) in macrophages with an NF-κB reporter. J. Biol. Chem. 2017, 292, 20911–20920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
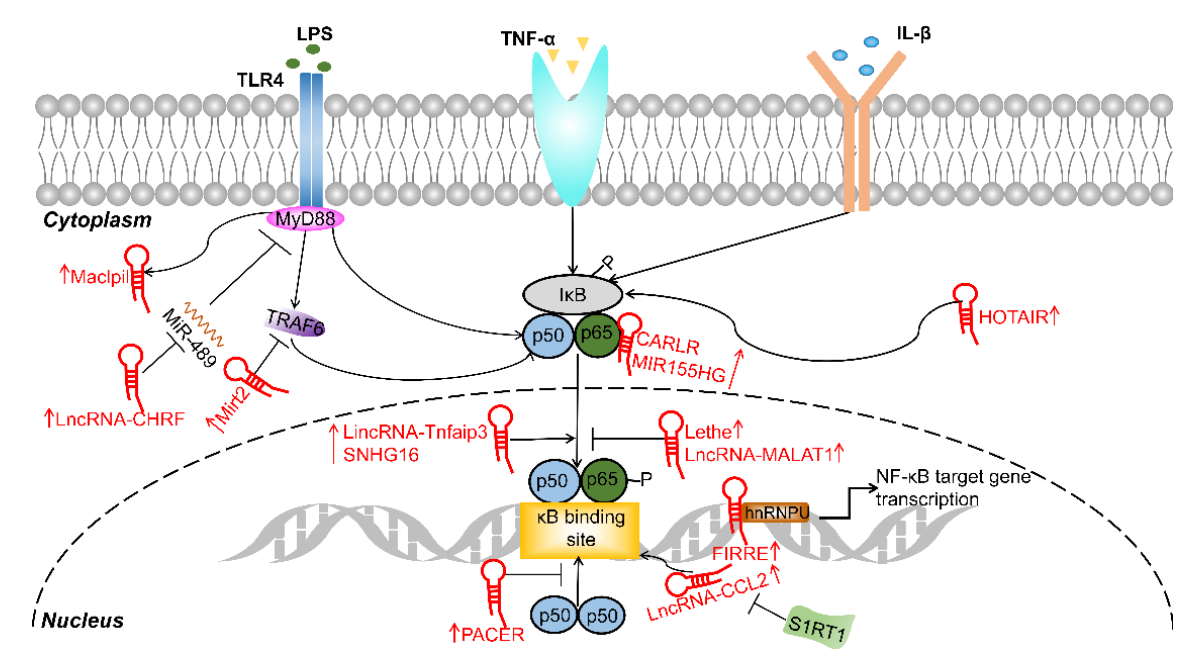
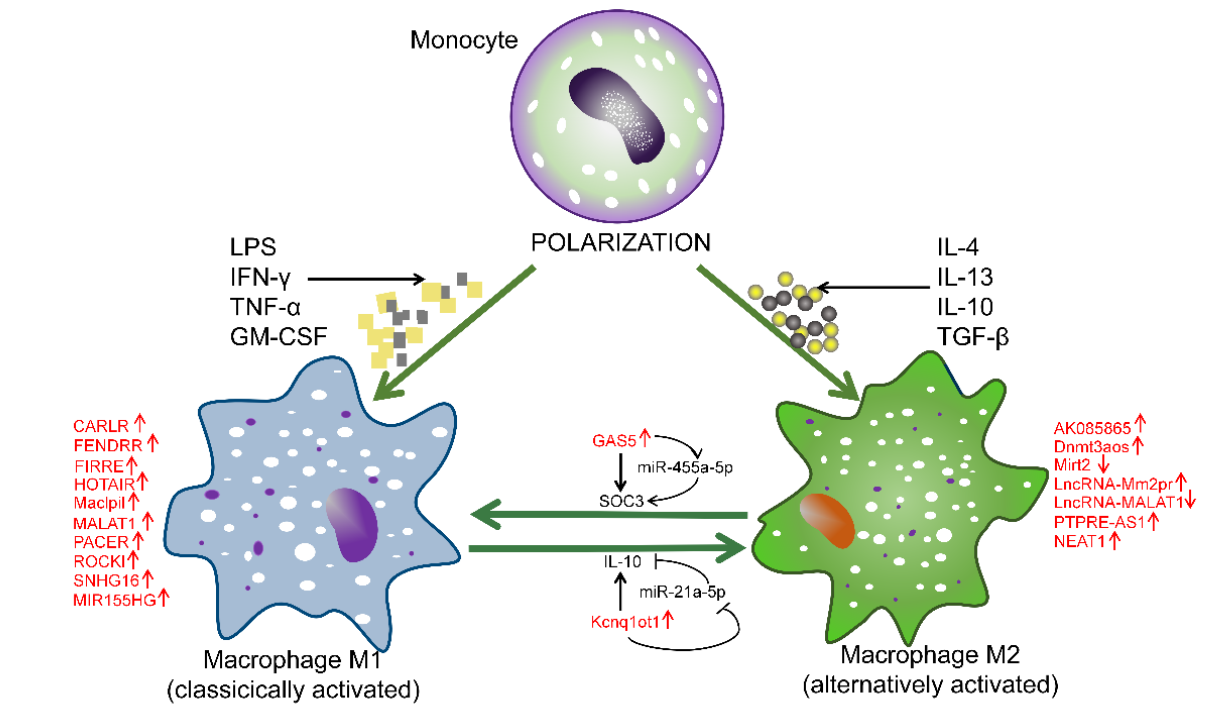
| LncRNA Names | Species | Classification | Localization | Role and Function in Macrophages | Possible Mechanism | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CARLR | Mouse | intergenic | Cytoplasm | Increased after activation of NF-κB in macrophage | Binds to p65 and lets it Released from IκBα | [28] |
| CHRF | Mouse | intergenic | Cytoplasm | Acts as the endogenous “sponge” of miR-489 | Changes the expression of MyD88 | [29] |
| FENDRR | Human Mouse | intergenic | Nucleus | Overexpression of FENDRR increases mRNA expression of M1 markers induced by IFN-γ in primary mouse BMDMs | Enhances IFN-γ induced M1 macrophage polarization via the STAT1 pathway. | [33] |
| FIRRE | Human | intergenic | Nucleus | Induces inflammatory gene expression in macrophages | Inhibits chromatin state through interaction with hnRNPU | [34,35] |
| GAS5 | Human Mouse | antisense | Nucleus | Induces polarization of M1 macrophages and aggravates inflammation | Acts as the ceRNA of miR-455-5p and a sponge of miR-221 | [42,43] |
| HOTAIR | Human | antisense | Cytoplasm | Upregulated after LPS stimulation in RAW264.7 cells and BMDM | Degrades expression of IκBα, activates NF-κB, and translocates the position of nucleus | [45] |
| H19 | Human Mouse | intergenic | Nucleus | Upregulates the expression of IL-6, IL-1β, COX-2, CCL-5 | Promotes the differentiation and activation of pro-inflammatory M1 macrophages | [52,53] |
| Maclpil | Mouse | - | - | Upregulates its expression under the stimulation of LPS in MoDM and MiDM | Polarizes pro-inflammatory macrophages | [54] |
| MALAT1 | Human Mouse | intergenic | Nucleus | Upregulated after the action of LPS and in PMA-induced THP-1 cells and RAW264.7 cells | Binds NF-κB subunit p65/50 | [56] |
| MIR155HG | Mouse | - | Nucleus | Upregulated in macrophages induced by GM-CSF | Induced polarization of M1 macrophages | [59] |
| PACER | Human | antisense | Nucleus | Upregulated following stimulation of LPS in U937 monocyte derived macrophage | Regulates chromatin acetylation | [60] |
| PTPRE-AS1 | Human Mouse | antisense | Nucleus Cytoplasm | Upregulated in IL-4 induced macrophages and inhibit the expression of IL-10, Arg-1, and CD206 | Inhibits the activation of MAPK/ERK1/2 signal pathway | [61] |
| RAPIA | Mouse | - | Cytoplasm | Promotes proliferation and reduces apoptosis of macrophages | Combines with miR-183-5p and regulates downstream ITGB1 | [63] |
| ROCKI | Human | Nucleus | Induces a variety of cytokines and inflammatory genes | HDAC1 binds to the Marcks promoter, reducing the expression of H3K27ac and Marcks | [64] | |
| SNHG16 | Human | intergenic | Cytoplasm | Induces IL-6, TNF-α, and IL-1β expression in THP-1 cells | Acts as a ceRNA to absorb miR-17-5p to promote IKKβ, p-IκBα, and p-P65 in NF-κB pathway | [66] |
| ANCR | Human | intergenic | Cytoplasm | Anti-differentiation function | Downregulates the expression of FoxO1 and inhibits the polarization of M1 macrophages | [69] |
| LncRNA- AK085865 | Mouse | - | Nucleus | Highly expressed in asthmatic mice and closely related to M2 macrophages | Regulates ILF2-ILF3 complex-mediated miRNA-192 biogenesis | [73] |
| LncRNA- CCL2 | Mouse | - | Cytoplasm | Leads to downregulation of inflammatory cytokines in macrophages | Inhibits Sirt2 homolog 1 (SIRT1) | [76] |
| Dnmt3aos | Mouse | antisense | Nucleus | Upregulated in M (IL-4) macrophages | DNA methylation caused by the Dnmt3aos-DNMT3A axis | [78] |
| LincRNA- EPS | Mouse | intergenic | Nucleus | Downregulated under the stimulation of TLR2 in BMDMs | Binds to chromatin hnRNPL through the CANACA motif located at the 3′ end of EPS | [79] |
| Kcnq1ot1 | Mouse | antisense | Cytoplasm | Downregulated under the stimulation of PMMA in primary mouse BMDMand RAW264.7 cells | Acts as a ceRNA to absorb miR-21a-5p to M2 macrophage polarization | [83] |
| Lethe | Mouse | - | Nucleus | Induced by pro-inflammatory cytokines (TNF-α, IL-1β) leads to upregulation ofits expression in BMDMs | Interacts with p65 to repress the activation of NF-κB | [85] |
| Mirt2 | Mouse | antisense | Cytoplasm | Prevents the abnormal activation of inflammation in peritoneal macrophages | Associates with TRAF6 and weakens the ubiquitination of its connection with lys63, thus inhibiting the activation of NF-κB and MAPK pathways | [86] |
| MIST | Human Mouse | intergenic | Nucleus | Downregulated in obese mice induced by high-fat diet | Interacts with PARP1 to block recruitment of PARP1 on the promoter of inflammatory gene | [87] |
| LncRNA- Mm2pr | Mouse | - | Nucleus | Upregulated after IL-13 and IL-4 stimulation in BMDM and RAW264.7 cells | Through the phosphorylation of STAT6 to promotes the occurrence and development of tumor | [5,24] |
| NEAT1 | Human Mouse | intergenic | Nucleus | Promotes its target molecule miR-214 interacts with B7-H3 | Via JAK2/STAT3 signal pathway to promote the occurrence of multiple myeloma | [90] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhao, Q.; Pang, G.; Yang, L.; Chen, S.; Xu, R.; Shao, W. Long Noncoding RNAs Regulate the Inflammatory Responses of Macrophages. Cells 2022, 11, 5. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells11010005
Zhao Q, Pang G, Yang L, Chen S, Xu R, Shao W. Long Noncoding RNAs Regulate the Inflammatory Responses of Macrophages. Cells. 2022; 11(1):5. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells11010005
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhao, Qing, Gaozong Pang, Lin Yang, Shu Chen, Ruiyao Xu, and Wei Shao. 2022. "Long Noncoding RNAs Regulate the Inflammatory Responses of Macrophages" Cells 11, no. 1: 5. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells11010005
APA StyleZhao, Q., Pang, G., Yang, L., Chen, S., Xu, R., & Shao, W. (2022). Long Noncoding RNAs Regulate the Inflammatory Responses of Macrophages. Cells, 11(1), 5. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells11010005






