The Alpha-Synuclein RT-QuIC Products Generated by the Olfactory Mucosa of Patients with Parkinson’s Disease and Multiple System Atrophy Induce Inflammatory Responses in SH-SY5Y Cells
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
3.1. αSyn_RT-QuIC Analysis of OM Samples and Biochemical Characterization of Reaction Products
3.2. Inflammatory Profile of Neuronal-like SH-SY5Y Cells Exposed to αSyn_RT-QuIC Products Generated by OM-MSA and OM-PD
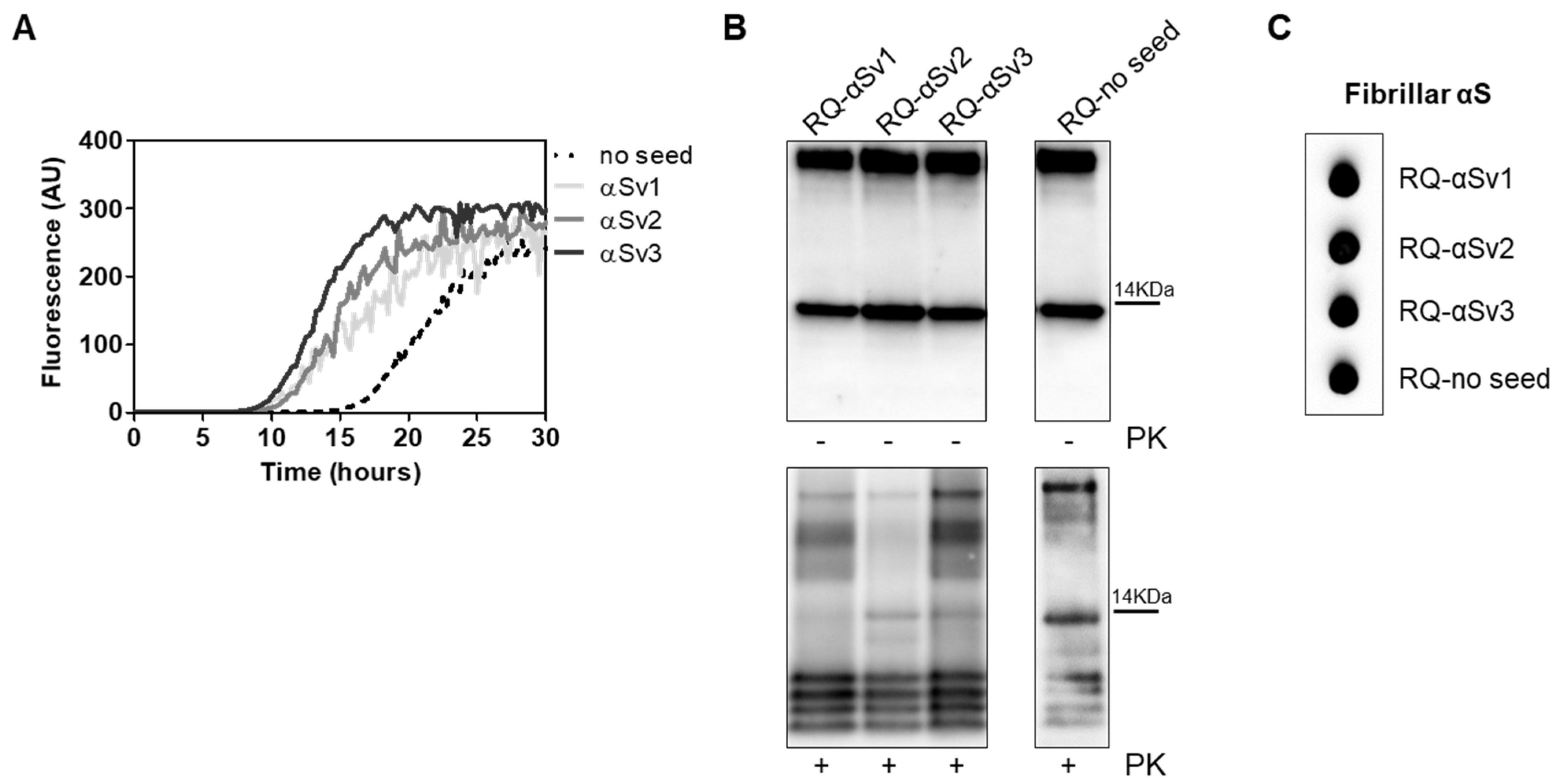
3.3. Generation and Morphological Characterization of Recombinant α-Synuclein Aggregates
3.4. αSyn_RT-QuIC Analysis of Recombinant α-Synuclein Aggregates and Characterization of Final Reaction Products
3.5. Inflammatory Profile of SH-SY5Y Cells Exposed to αSv1, αSv2, αSv3 and Their αSyn_RT-QuIC Reaction Products
3.6. αSyn_RT-QuIC Analysis of Lysates from Cells Stimulated with αSv1, αSv2, αSv3 and RQ-MSA and RQ-PD
4. Discussions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Postuma, R.B.; Berg, D.; Stern, M.; Poewe, W.; Olanow, C.W.; Oertel, W.; Obeso, J.; Marek, K.; Litvan, I.; Lang, A.E.; et al. MDS clinical diagnostic criteria for Parkinson’s disease. Mov. Disord. 2015, 30, 1591–1601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gilman, S.; Wenning, G.; Low, P.A.; Brooks, D.; Mathias, C.J.; Trojanowski, J.Q.; Wood, N.; Colosimo, C.; Durr, A.; Fowler, C.J.; et al. Second consensus statement on the diagnosis of multiple system atrophy. Neurology 2008, 71, 670–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dickson, D.W. Parkinson’s Disease and Parkinsonism: Neuropathology. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 2012, 2, a009258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Peelaerts, W.; Bousset, L.; Baekelandt, V.; Melki, R. ɑ-Synuclein strains and seeding in Parkinson’s disease, incidental Lewy body disease, dementia with Lewy bodies and multiple system atrophy: Similarities and differences. Cell Tissue Res. 2018, 373, 195–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamasaki, T.R.; Holmes, B.; Furman, J.L.; Dhavale, D.; Su, B.W.; Song, E.-S.; Cairns, N.J.; Kotzbauer, P.T.; Diamond, M.I. Parkinson’s disease and multiple system atrophy have distinct α-synuclein seed characteristics. J. Biol. Chem. 2019, 294, 1045–1058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Peelaerts, W.; Bousset, L.; Van der Perren, A.; Moskalyuk, A.; Pulizzi, R.; Giugliano, M.; Van den Haute, C.; Melki, R.; Baekelandt, V. α-Synuclein strains cause distinct synucleinopathies after local and systemic administration. Nature 2015, 522, 340–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jan, A.; Gonçalves, N.; Vaegter, C.; Jensen, P.; Ferreira, N. The Prion-Like Spreading of Alpha-Synuclein in Parkinson’s Disease: Update on Models and Hypotheses. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 8338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, J.; Gao, J.; Wang, J.; Xie, A. Prion-Like Mechanisms in Parkinson’s Disease. Front Neurosci. 2019, 13, 552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woerman, A.L.; Watts, J.C.; Aoyagi, A.; Giles, K.; Middleton, L.T.; Prusiner, S.B. α-Synuclein: Multiple System Atrophy Prions. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 2018, 8, a024588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prusiner, S.B.; Woerman, A.L.; Mordes, D.A.; Watts, J.C.; Rampersaud, R.; Berry, D.B.; Patel, S.; Oehler, A.; Lowe, J.K.; Kravitz, S.N.; et al. Evidence for α-synuclein prions causing multiple system atrophy in humans with parkinsonism. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, E5308–E5317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Volpicelli-Daley, L.; Brundin, P. Prion-like propagation of pathology in Parkinson disease. Handb. Clin. Neurol. 2018, 153, 321–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kouli, A.; Horne, C.; Williams-Gray, C. Toll-like receptors and their therapeutic potential in Parkinson’s disease and α-synucleinopathies. Brain Behav. Immun. 2019, 81, 41–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dzamko, N.; Gysbers, A.; Perera, G.; Bahar, A.; Shankar, A.; Gao, J.; Fu, Y.; Halliday, G.M. Toll-like receptor 2 is increased in neurons in Parkinson’s disease brain and may contribute to alpha-synuclein pathology. Acta Neuropathol. 2017, 133, 303–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Caplan, I.F.; Maguire-Zeiss, K.A. Toll-like receptor 2 signaling and current approaches for therapeutic modulation in synucle-inopathies. Front. Pharmacol. 2018, 9, 417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kim, C.; Rockenstein, E.; Spencer, B.; Kim, H.-K.; Adame, A.; Trejo, M.; Stafa, K.; Lee, H.-J.; Lee, S.-J.; Masliah, E. Antagonizing Neuronal Toll-like Receptor 2 Prevents Synucleinopathy by Activating Autophagy. Cell Rep. 2015, 13, 771–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chao, Y.; Wong, S.C.; Tan, E.K. Evidence of Inflammatory System Involvement in Parkinson’s Disease. BioMed Res. Int. 2014, 2014, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaufman, E.; Hall, S.; Surova, Y.; Widner, H.; Hansson, O.; Lindqvist, D. Proinflammatory Cytokines Are Elevated in Serum of Patients with Multiple System Atrophy. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e62354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sanchez-Guajardo, V.; Tentillier, N.; Romero-Ramos, M. The relation between α-synuclein and microglia in Parkinson’s disease: Recent developments. Neuroscience 2015, 302, 47–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prinz, M.; Priller, J.; Sisodia, S.S.; Ransohoff, R.M. Heterogeneity of CNS myeloid cells and their roles in neurodegeneration. Nat. Neurosci. 2011, 14, 1227–1235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fairfoul, G.; McGuire, L.I.; Pal, S.; Ironside, J.W.; Neumann, J.; Christie, S.; Joachim, C.; Esiri, M.; Evetts, S.G.; Rolinski, M.; et al. Alpha-synuclein RT-QuIC in the CSF of patients with alpha-synucleinopathies. Ann. Clin. Transl. Neurol. 2016, 3, 812–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iranzo, A.; Fairfoul, G.; Ayudhaya, A.C.N.; Serradell, M.; Gelpi, E.; Vilaseca, I.; Sanchez-Valle, R.; Gaig, C.; Santamaria, J.; Tolosa, E.; et al. Detection of α-synuclein in CSF by RT-QuIC in patients with isolated rapid-eye-movement sleep behaviour disorder: A longitudinal observational study. Lancet Neurol. 2021, 20, 203–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossi, M.; Candelise, N.; Baiardi, S.; Capellari, S.; Giannini, G.; Orrù, C.D.; Antelmi, E.; Mammana, A.; Hughson, A.G.; Calandra-Buonaura, G.; et al. Ultrasensitive RT-QuIC assay with high sensitivity and specificity for Lewy body-associated synucleinopathies. Acta Neuropathol. 2020, 140, 49–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bongianni, M.; Ladogana, A.; Capaldi, S.; Klotz, S.; Baiardi, S.; Cagnin, A.; Perra, D.; Fiorini, M.; Poleggi, A.; Legname, G.; et al. α-Synuclein RT-QuIC assay in cerebrospinal fluid of patients with dementia with Lewy bodies. Ann. Clin. Transl. Neurol. 2019, 6, 2120–2126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Groveman, B.R.; Orrù, C.D.; Hughson, A.G.; Raymond, L.D.; Zanusso, G.; Ghetti, B.; Campbell, K.J.; Safar, J.; Galasko, D.; Caughey, B. Rapid and ultra-sensitive quantitation of dis-ease-associated α-synuclein seeds in brain and cerebrospinal fluid by αSyn RT-QuIC. Acta Neuropathol. Commun. 2018, 6, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perra, D.; Bongianni, M.; Novi, G.; Janes, F.; Bessi, V.; Capaldi, S.; Sacchetto, L.; Tagliapietra, M.; Schenone, G.; Morbelli, S.; et al. Alpha-synuclein seeds in olfactory mucosa and cerebrospinal fluid of patients with dementia with Lewy bodies. Brain Commun. 2021, 3, fcab045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bargar, C.; Wang, W.; Gunzler, S.A.; LeFevre, A.; Wang, Z.; Lerner, A.J.; Singh, N.; Tatsuoka, C.; Appleby, B.; Zhu, X.; et al. Streamlined alpha-synuclein RT-QuIC assay for various biospecimens in Parkinson’s disease and dementia with Lewy bodies. Acta Neuropathol. Commun. 2021, 9, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Becker, K.; Donadio, V.; Siedlak, S.; Yuan, J.; Rezaee, M.; Incensi, A.; Kuzkina, A.; Orrú, C.D.; Tatsuoka, C.; et al. Skin α-Synuclein Aggregation Seeding Activity as a Novel Biomarker for Parkinson Disease. JAMA Neurol. 2021, 78, 30–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donadio, V.; Wang, Z.; Incensi, A.; Rizzo, G.; Fileccia, E.; Vacchiano, V.; Capellari, S.; Magnani, M.; Scaglione, C.; Stanzani Maserati, M.; et al. In Vivo Diagnosis of Synucleinopathies. Neurology 2021, 96, e2513–e2524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mammana, A.; Baiardi, S.; Quadalti, C.; Rossi, M.; Donadio, V.; Capellari, S.; Liguori, R.; Parchi, P. RT-QuIC Detection of Pathological α-Synuclein in Skin Punches of Patients with Lewy Body Disease. Mov. Disord. 2021, 36, 2173–2177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manne, S.; Kondru, N.; Jin, H.; Anantharam, V.; Huang, X.; Kanthasamy, A.; Kanthasamy, A.G. α-Synuclein Real-Time Quaking-Induced Conversion in the Submandibular Glands of Parkinson’s Disease Patients. Mov. Disord. 2020, 35, 268–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chahine, L.M.; Beach, T.G.; Brumm, M.C.; Adler, C.H.; Coffey, C.S.; Mosovsky, S.; Caspell-Garcia, C.; Serrano, G.E.; Munoz, D.G.; White, C.L.; et al. In vivo distribution of α-synuclein in multiple tissues and biofluids in Parkinson disease. Neurology 2020, 95, e1267–e1284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stefani, A.; Iranzo, A.; Holzknecht, E.; Perra, D.; Bongianni, M.; Gaig, C.; Heim, B.; Serradell, M.; Sacchetto, L.; Garrido, A.; et al. Alpha-synuclein seeds in olfactory mucosa of patients with isolated REM sleep behaviour disorder. Brain 2021, 144, 1118–1126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Luca, C.M.G.; Elia, A.E.; Portaleone, S.M.; Cazzaniga, F.A.; Rossi, M.; Bistaffa, E.; De Cecco, E.; Narkiewicz, J.; Salzano, G.; Carletta, O.; et al. Efficient RT-QuIC seeding activity for α-synuclein in olfactory mucosa samples of patients with Parkinson’s disease and multiple system atrophy. Transl. Neurodegener. 2019, 8, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bargar, C.; De Luca, C.M.G.; Devigili, G.; Elia, A.E.; Cilia, R.; Portaleone, S.M.; Wang, W.; Tramacere, I.; Bistaffa, E.; Cazzaniga, F.A.; et al. Discrimination of MSA-P and MSA-C by RT-QuIC analysis of olfactory mucosa: The first assessment of assay reproducibility between two specialized laboratories. Mol. Neurodegener. 2021, 16, 82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shahnawaz, M.; Mukherjee, A.; Pritzkow, S.; Mendez, N.; Rabadia, P.; Liu, X.; Hu, B.; Schmeichel, A.; Singer, W.; Wu, G.; et al. Discriminating α-synuclein strains in Parkinson’s disease and multiple system atrophy. Nature 2020, 578, 273–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aulić, S.; Le, T.T.N.; Moda, F.; Abounit, S.; Corvaglia, S.; Casalis, L.; Gustincich, S.; Zurzolo, C.; Tagliavini, F.; Legname, G. Defined α-synuclein prion-like molecular assemblies spreading in cell culture. BMC Neurosci. 2014, 15, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ross, A.; Xing, V.; Wang, T.T.; Bureau, S.C.; Link, G.A.; Fortin, T.; Zhang, H.; Hayley, S.; Sun, H. Alleviating toxic α-Synuclein accumulation by membrane de-polarization: Evidence from an in vitro model of Parkinson’s disease. Mol. Brain. 2020, 13, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bousset, L.; Pieri, L.; Ruiz-Arlandis, G.; Gath, J.; Jensen, P.H.; Habenstein, B.; Madiona, K.; Olieric, V.; Böckmann, A.; Meier, B.H.; et al. Structural and functional characterization of two alpha-synuclein strains. Nat. Commun. 2013, 4, 2575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Alam, P.; Bousset, L.; Melki, R.; Otzen, D.E. α-synuclein oligomers and fibrils: A spectrum of species, a spectrum of toxicities. J. Neurochem. 2019, 150, 522–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, J.; Li, X.; Li, J.-D. The Roles of Post-translational Modifications on α-Synuclein in the Pathogenesis of Parkinson’s Diseases. Front. Neurosci. 2019, 13, 381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huang, C.; Ren, G.; Zhou, H.; Wang, C.-C. A new method for purification of recombinant human α-synuclein in Escherichia coli. Protein Expr. Purif. 2005, 42, 173–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schindelin, J.; Arganda-Carreras, I.; Frise, E.; Kaynig, V.; Longair, M.; Pietzsch, T.; Preibisch, S.; Rueden, C.; Saalfeld, S.; Schmid, B.; et al. Fiji: An open-source platform for biological-image analysis. Nat. Methods 2012, 9, 676–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- González-Sanmiguel, J.; Schuh, C.M.A.P.; Muñoz-Montesino, C.; Contreras-Kallens, P.; Aguayo, L.G.; Aguayo, S. Complex Interaction between Resident Microbiota and Misfolded Proteins: Role in Neuroinflammation and Neurodegeneration. Cells 2020, 9, 2476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nonaka, T.; Watanabe, S.T.; Iwatsubo, T.; Hasegawa, M. Seeded Aggregation and Toxicity of α-Synuclein and Tau. J. Biol. Chem. 2010, 285, 34885–34898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]








| αSyn Variant | Aggregation Buffer | Biochemical Properties of the Fibrils | Morphological Properties of the Fibrils | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Length | Over-Twists | Note | |||
| αSv1 | H2O | Completely digested by PK | Short | No | Arranged side-by-side |
| αSv2 | 5 mM Tris + 100 mM NaCl | Partially resistant to digestion (4 PK resistant bands detected) | Long | Yes, although few fibrils without over-twists were also found | Arranged in a net-like structure |
| αSv3 | 5 mM Tris | Partially resistant to digestion (2 PK resistant bands detected) | Mainly short | Yes, although several fibrils without over-twists were also found | Arranged either side-by-side or in a net-like structure. Presence of amorphous material |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
De Luca, C.M.G.; Consonni, A.; Cazzaniga, F.A.; Bistaffa, E.; Bufano, G.; Quitarrini, G.; Celauro, L.; Legname, G.; Eleopra, R.; Baggi, F.; et al. The Alpha-Synuclein RT-QuIC Products Generated by the Olfactory Mucosa of Patients with Parkinson’s Disease and Multiple System Atrophy Induce Inflammatory Responses in SH-SY5Y Cells. Cells 2022, 11, 87. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells11010087
De Luca CMG, Consonni A, Cazzaniga FA, Bistaffa E, Bufano G, Quitarrini G, Celauro L, Legname G, Eleopra R, Baggi F, et al. The Alpha-Synuclein RT-QuIC Products Generated by the Olfactory Mucosa of Patients with Parkinson’s Disease and Multiple System Atrophy Induce Inflammatory Responses in SH-SY5Y Cells. Cells. 2022; 11(1):87. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells11010087
Chicago/Turabian StyleDe Luca, Chiara Maria Giulia, Alessandra Consonni, Federico Angelo Cazzaniga, Edoardo Bistaffa, Giuseppe Bufano, Giorgia Quitarrini, Luigi Celauro, Giuseppe Legname, Roberto Eleopra, Fulvio Baggi, and et al. 2022. "The Alpha-Synuclein RT-QuIC Products Generated by the Olfactory Mucosa of Patients with Parkinson’s Disease and Multiple System Atrophy Induce Inflammatory Responses in SH-SY5Y Cells" Cells 11, no. 1: 87. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells11010087
APA StyleDe Luca, C. M. G., Consonni, A., Cazzaniga, F. A., Bistaffa, E., Bufano, G., Quitarrini, G., Celauro, L., Legname, G., Eleopra, R., Baggi, F., Giaccone, G., & Moda, F. (2022). The Alpha-Synuclein RT-QuIC Products Generated by the Olfactory Mucosa of Patients with Parkinson’s Disease and Multiple System Atrophy Induce Inflammatory Responses in SH-SY5Y Cells. Cells, 11(1), 87. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells11010087







