Characterization of Severity in Zellweger Spectrum Disorder by Clinical Findings: A Scoping Review, Meta-Analysis and Medical Chart Review
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Literature Review
2.2. Review of Medical Charts from Our Longitudinal Natural History Study on PBD-ZSD
2.3. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Literature Search Results
3.2. Severity Designation in Cohort and Case Studies
3.3. Severity Designation in Natural History Study
3.4. Characterization of Severe Patients
3.4.1. Cohort and Case Study Meta-Analysis
3.4.2. Natural History Study
3.5. Characterization of Intermediate Patients
3.5.1. Cohort and Case Study Meta-Analysis
3.5.2. Natural History Study
3.6. Characterization of Mild Patients
3.6.1. Cohort and Case Study Meta-Analysis
3.6.2. Natural History Study
3.7. Other Clinical Findings
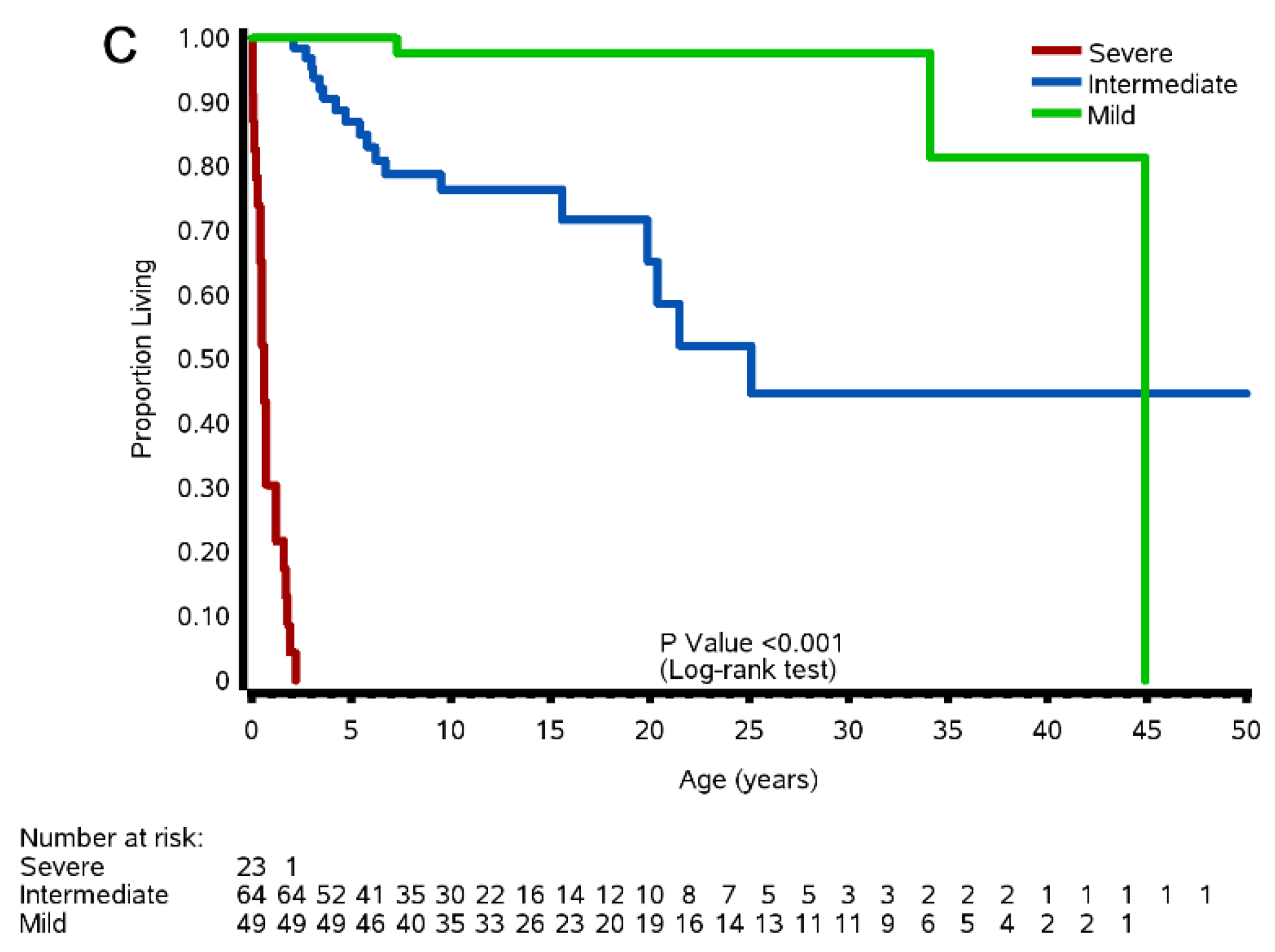
3.8. Survival of Severe, Intermediate, and Mild Patients
3.8.1. Cohort and Case Studies
3.8.2. Natural History Study
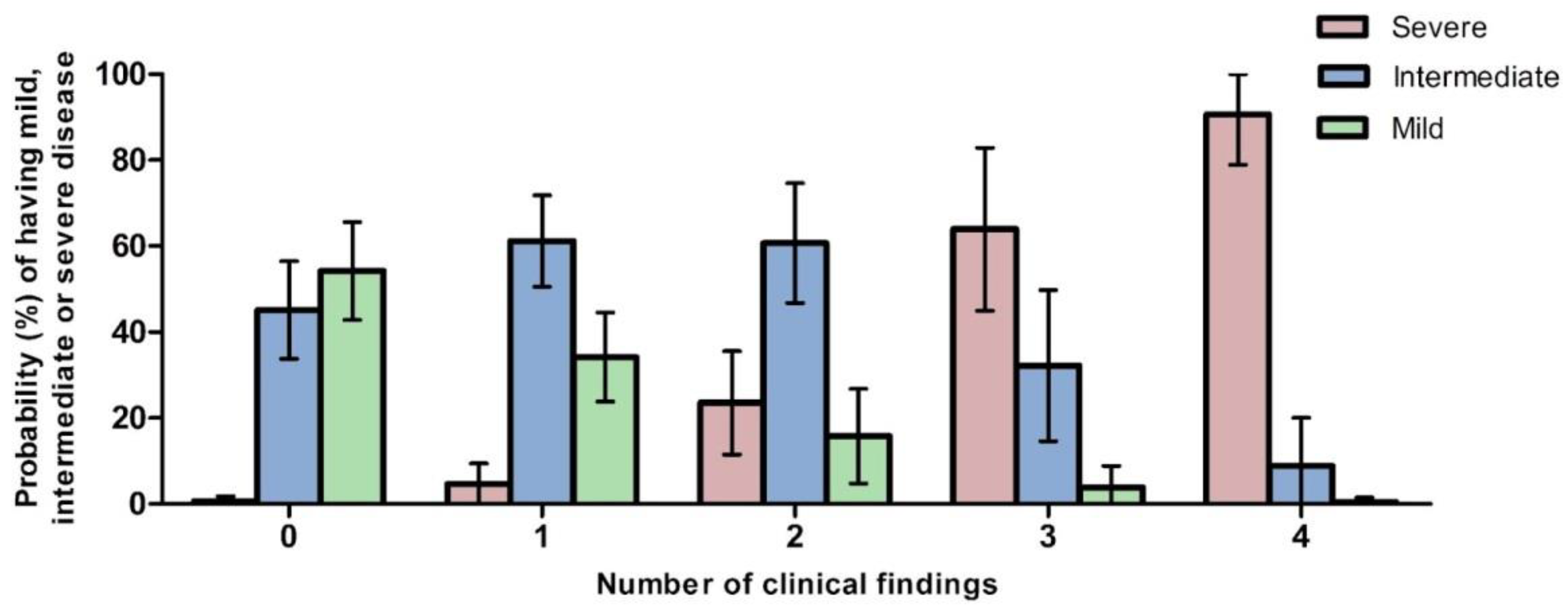
3.9. Predictions of Severity in ZSD
3.9.1. Predicted Probabilities of Disease Severity by Number of Clinical Findings
3.9.2. Predicted Probabilities of Disease Severity by Plasma C26:0 VLCFA Levels
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wanders, R.J.A.; Waterham, H.R. Biochemistry of Mammalian Peroxisomes Revisited. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2006, 75, 295–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steinberg, S.J.; Dodt, G.; Raymond, G.V.; Braverman, N.E.; Moser, A.B.; Moser, H.W. Peroxisome Biogenesis Disorders. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA)-Mol. Cell Res. 2006, 1763, 1733–1748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Braverman, N.E.; Steinberg, S.J.; Fallatah, W.; Duker, A.; Bober, M. Rhizomelic Chondrodysplasia Punctata Type 1. In GeneReviews®; Adam, M.P., Ardinger, H.H., Pagon, R.A., Wallace, S.E., Bean, L.J., Gripp, K.W., Mirzaa, G.M., Amemiya, A., Eds.; University of Washington: Seattle, WA, USA, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Steinberg, S.J.; Raymond, G.V.; Braverman, N.E.; Moser, A.B. Zellweger Spectrum Disorder. In GeneReviews®; Adam, M.P., Ardinger, H.H., Pagon, R.A., Wallace, S.E., Bean, L.J., Gripp, K.W., Mirzaa, G.M., Amemiya, A., Eds.; University of Washington: Seattle, WA, USA, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Scriver, C.R. (Ed.) The Metabolic & Molecular Bases of Inherited Disease, 8th ed.; McGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 2001; ISBN 978-0-07-913035-8. [Google Scholar]
- Acharya, B.S.; Ritwik, P.; Velasquez, G.M.; Fenton, S.J. Medical-Dental Findings and Management of a Child with Infantile Refsum Disease: A Case Report: Infantile Refsum Disease-Dental Management. Spec. Care Dent. 2012, 32, 112–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alhazmi, H. Renal Oxalate Stones in Children with Zellweger Spectrum Disorders. Saudi J. Anaesth. 2018, 12, 332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bader, P.I.; Dougherty, S.; Cangany, N.; Raymond, G.; Jackson, C.E. Infantile Refsum Disease in Four Amish Sibs. Am. J. Med. Genet. 2000, 90, 110–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berendse, K.; Engelen, M.; Linthorst, G.E.; van Trotsenburg, A.P.; Poll-The, B.T. High Prevalence of Primary Adrenal Insufficiency in Zellweger Spectrum Disorders. Orphanet J. Rare Dis. 2014, 9, 133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bose, M.; Cuthbertson, D.D.; Fraser, M.A.; Roullet, J.-B.; Gibson, K.M.; Schules, D.R.; Gawron, K.M.; Gamble, M.B.; Sacra, K.M.; Lopez, M.J.; et al. Zellweger Spectrum Disorder: A Cross-Sectional Study of Symptom Prevalence Using Input from Family Caregivers. Mol. Genet. Metab. Rep. 2020, 25, 100694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choksi, V.; Hoeffner, E.; Karaarslan, E.; Yalcinkaya, C.; Cakirer, S. Infantile Refsum Disease: Case Report. Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2003, 24, 2082. [Google Scholar]
- Gootjes, J.; Schmohl, F.; Mooijer, P.A.W.; Dekker, C.; Mandel, H.; Topcu, M.; Huemer, M.; von Schütz, M.; Marquardt, T.; Smeitink, J.A.; et al. Identification of the Molecular Defect in Patients with Peroxisomal Mosaicism Using a Novel Method Involving Culturing of Cells at 40 °C: Implications for Other Inborn Errors of Metabolism. Hum. Mutat. 2004, 24, 130–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lertsirivorakul, J.; Wongswadiwat, M.; Treesuwan, P. Oral Manifestations and Dental Management of a Child with Zellweger Syndrome. Spec. Care Dent. 2014, 34, 46–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasrallah, F.; Zidi, W.; Feki, M.; Kacem, S.; Tebib, N.; Kaabachi, N. Biochemical and Clinical Profiles of 52 Tunisian Patients Affected by Zellweger Syndrome. Pediatrics Neonatol. 2017, 58, 484–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ong, K.R.; Visram, S.; McKaig, S.; Brueton, L.A. Sensorineural Deafness, Enamel Abnormalities and Nail Abnormalities: A Case Report of Heimler Syndrome in Identical Twin Girls. Eur. J. Med. Genet. 2006, 49, 187–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poll-The, B.T.; Gootjes, J.; Duran, M.; de Klerk, J.B.C.; Maillette de Buy Wenniger-Prick, L.J.; Admiraal, R.J.C.; Waterham, H.R.; Wanders, R.J.A.; Barth, P.G. Peroxisome Biogenesis Disorders with Prolonged Survival: Phenotypic Expression in a Cohort of 31 Patients. Am. J. Med. Genet. 2004, 126A, 333–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rush, E.T.; Goodwin, J.L.; Braverman, N.E.; Rizzo, W.B. Low Bone Mineral Density Is a Common Feature of Zellweger Spectrum Disorders. Mol. Genet. Metab. 2016, 117, 33–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Theil, A.C.; Schutgens, R.B.H.; Wanders, R.J.A.; Heymans, H.S.A. Clinical Recognition of Patients Affected by a Peroxisomal Disorder: A Retrospective Study in 40 Patients. Eur. J. Pediatrics 1992, 151, 117–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Woerden, C.S.; Groothoff, J.W.; Wijburg, F.A.; Duran, M.; Wanders, R.J.A.; Barth, P.G.; Poll-The, B.T. High Incidence of Hyperoxaluria in Generalized Peroxisomal Disorders. Mol. Genet. Metab. 2006, 88, 346–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeynelabidin, S.; Klouwer, F.C.C.; Meijers, J.C.M.; Suijker, M.H.; Engelen, M.; Poll-The, B.T.; van Ommen, C.H. Coagulopathy in Zellweger Spectrum Disorders: A Role for Vitamin K. J. Inherit. Metab. Dis. 2018, 41, 249–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Braverman, N.E.; Raymond, G.V.; Rizzo, W.B.; Moser, A.B.; Wilkinson, M.E.; Stone, E.M.; Steinberg, S.J.; Wangler, M.F.; Rush, E.T.; Hacia, J.G.; et al. Peroxisome Biogenesis Disorders in the Zellweger Spectrum: An Overview of Current Diagnosis, Clinical Manifestations, and Treatment Guidelines. Mol. Genet. Metab. 2016, 117, 313–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Walter, C.; Gootjes, J.; Mooijer, P.A.; Portsteffen, H.; Klein, C.; Waterham, H.R.; Barth, P.G.; Epplen, J.T.; Kunau, W.H.; Wanders, R.J.; et al. Disorders of Peroxisome Biogenesis due to Mutations in PEX1: Phenotypes and PEX1 Protein Levels. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2001, 69, 35–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rosewich, H.; Ohlenbusch, A.; Gärtner, J. Genetic and Clinical Aspects of Zellweger Spectrum Patients with PEX1 Mutations. J. Med. Genet. 2005, 42, e58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Preuss, N.; Brosius, U.; Biermanns, M.; Muntau, A.C.; Conzelmann, E.; Gartner, J. PEX1 Mutations in Complementation Group 1 of Zellweger Spectrum Patients Correlate with Severity of Disease. Pediatric Res. 2002, 51, 706–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zellweger, H. Peroxisomes and Peroxisomal Disorders. Ala. J. Med. Sci. 1988, 25, 54–58. [Google Scholar]
- Ratbi, I.; Jaouad, I.C.; Elorch, H.; Al-Sheqaih, N.; Elalloussi, M.; Lyahyai, J.; Berraho, A.; Newman, W.G.; Sefiani, A. Severe Early Onset Retinitis Pigmentosa in a Moroccan Patient with Heimler Syndrome due to Novel Homozygous Mutation of PEX1 Gene. Eur. J. Med. Genet. 2016, 59, 507–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Klouwer, F.C.C.; Ferdinandusse, S.; van Lenthe, H.; Kulik, W.; Wanders, R.J.A.; Poll-The, B.T.; Waterham, H.R.; Vaz, F.M. Evaluation of C26:0-Lysophosphatidylcholine and C26:0-Carnitine as Diagnostic Markers for Zellweger Spectrum Disorders. J. Inherit. Metab. Dis. 2017, 40, 875–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kelley, R.I.; Datta, N.S.; Dobyns, W.B.; Hajra, A.K.; Moser, A.B.; Noetzel, M.J.; Zackai, E.H.; Moser, H.W.; Opitz, J.M.; Reynolds, J.F. Neonatal Adrenoleukodystrophy: New Cases, Biochemical Studies, and Differentiation from Zellweger and Related Peroxisomal Polydystrophy Syndromes. Am. J. Med. Genet. 1986, 23, 869–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steinberg, S.J.; Elçioglu, N.; Slade, C.M.; Sankaralingam, A.; Dennis, N.; Mohammed, S.N.; Fensom, A.H. Peroxisomal Disorders: Clinical and Biochemical Studies in 15 Children and Prenatal Diagnosis in 7 Families. Am. J. Med. Genet. 1999, 85, 502–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bose, M.; Mahadevan, M.; Schules, D.R.; Coleman, R.K.; Gawron, K.M.; Gamble, M.B.; Roullet, J.-B.; Gibson, K.M.; Rizzo, W.B. Emotional Experience in Parents of Children with Zellweger Spectrum Disorders: A Qualitative Study. Mol. Genet. Metab. Rep. 2019, 19, 100459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maldergem, L.V.; Moser, A.B.; Vincent, M.-F.; Roland, D.; Reding, R.; Otte, J.-B.; Wanders, R.J.; Sokal, E. Orthotopic Liver Transplantation from a Living-Related Donor in an Infant with a Peroxisome Biogenesis Defect of the Infantile Refsum Disease Type. J. Inherit. Metab. Dis. 2005, 28, 593–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsunami, M.; Shimozawa, N.; Fukuda, A.; Kumagai, T.; Kubota, M.; Chong, P.F.; Kasahara, M. Living-Donor Liver Transplantation From a Heterozygous Parent for Infantile Refsum Disease. Pediatrics 2016, 137, e20153102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Heubi, J.E.; Bove, K.E.; Setchell, K.D.R. Oral Cholic Acid Is Efficacious and Well Tolerated in Patients With Bile Acid Synthesis and Zellweger Spectrum Disorders. J. Pediatric Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2017, 65, 321–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Heubi, J.E.; Setchell, K.D.R. Open-Label Phase 3 Continuation Study of Cholic Acid in Patients With Inborn Errors of Bile Acid Synthesis. J. Pediatric Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2020, 70, 423–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klouwer, F.C.C.; Koot, B.G.P.; Berendse, K.; Kemper, E.M.; Ferdinandusse, S.; Koelfat, K.V.K.; Lenicek, M.; Vaz, F.M.; Engelen, M.; Jansen, P.L.M.; et al. The Cholic Acid Extension Study in Zellweger Spectrum Disorders: Results and Implications for Therapy. J. Inherit. Metab. Dis. 2019, 42, 303–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Martínez, M.; Vázquez, E.; García-Silva, M.T.; Manzanares, J.; Bertran, J.M.; Castelló, F.; Mougan, I. Therapeutic Effects of Docosahexaenoic Acid Ethyl Ester in Patients with Generalized Peroxisomal Disorders. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2000, 71, 376s–385s. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Noguer, M.T.; Martinez, M. Visual Follow-Up in Peroxisomal-Disorder Patients Treated with Docosahexaenoic Acid Ethyl Ester. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2010, 51, 2277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Paker, A.M.; Sunness, J.S.; Brereton, N.H.; Speedie, L.J.; Albanna, L.; Dharmaraj, S.; Moser, A.B.; Jones, R.O.; Raymond, G.V. Docosahexaenoic Acid Therapy in Peroxisomal Diseases: Results of a Double-Blind, Randomized Trial. Neurology 2010, 75, 826–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gootjes, J.; Mooijer, P.A.W.; Dekker, C.; Barth, P.G.; Poll-The, B.T.; Waterham, H.R.; Wanders, R.J.A. Biochemical Markers Predicting Survival in Peroxisome Biogenesis Disorders. Neurology 2002, 59, 1746–1749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stradomska, T.J.; Syczewska, M.; Jamroz, E.; Pleskaczyńska, A.; Kruczek, P.; Ciara, E.; Tylki-Szymanska, A. Serum Very Long-Chain Fatty Acids (VLCFA) Levels as Predictive Biomarkers of Diseases Severity and Probability of Survival in Peroxisomal Disorders. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0238796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moser, A.B.; Kreiter, N.; Bezman, L.; Lu, S.-E.; Raymond, G.V.; Naidu, S.; Moser, H.W. Plasma Very Long Chain Fatty Acids in 3000 Peroxisome Disease Patients and 29,000 Controls. Ann. Neurol. 1999, 45, 100–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berendse, K.; Engelen, M.; Ferdinandusse, S.; Majoie, C.B.L.M.; Waterham, H.R.; Vaz, F.M.; Koelman, J.H.T.M.; Barth, P.G.; Wanders, R.J.A.; Poll-The, B.T. Zellweger Spectrum Disorders: Clinical Manifestations in Patients Surviving into Adulthood. J. Inherit. Metab. Dis. 2016, 39, 93–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Klouwer, F.C.C.; Meester-Delver, A.; Vaz, F.M.; Waterham, H.R.; Hennekam, R.C.M.; Poll-The, B.T. Development and Validation of a Severity Scoring System for Zellweger Spectrum Disorders. Clin. Genet. 2018, 93, 613–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, J.; Yergeau, C.; Kawai, K.; Braverman, N.; Géléoc, G.S.G. A Retrospective Study of Hearing Loss in Patients Diagnosed with Peroxisome Biogenesis Disorders in the Zellweger Spectrum. Ear Hear. 2022, 43, 582–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peters, M.D.J.; Godfrey, C.M.; Khalil, H.; McInerney, P.; Parker, D.; Soares, C.B. Guidance for Conducting Systematic Scoping Reviews. Int. J. Evid.-Based Healthc. 2015, 13, 141–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Klouwer, F.C.C.; Berendse, K.; Ferdinandusse, S.; Wanders, R.J.A.; Engelen, M.; Poll-The, B.T. Zellweger Spectrum Disorders: Clinical Overview and Management Approach. Orphanet J. Rare Dis. 2015, 10, 151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Moser, H.W. Komrower Lecture. Adrenoleukodystrophy: Natural History, Treatment and Outcome. J. Inherit. Metab. Dis. 1995, 18, 435–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Geel, B.M.; Assies, J.; Wanders, R.J.; Barth, P.G. X Linked Adrenoleukodystrophy: Clinical Presentation, Diagnosis, and Therapy. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 1997, 63, 4–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engelen, M.; Kemp, S.; de Visser, M.; van Geel, B.M.; Wanders, R.J.A.; Aubourg, P.; Poll-The, B.T. X-Linked Adrenoleukodystrophy (X-ALD): Clinical Presentation and Guidelines for Diagnosis, Follow-up and Management. Orphanet J. Rare Dis. 2012, 7, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, K.R.; Buckley, M.B. Using a Synthesis Matrix to Plan a Literature Review. Radiol. Technol. 2017, 88, 354–357. [Google Scholar]
- Roscher, A.A.; Hoefler, S.; Hoefler, G.; Paschke, E.; Paltauf, F.; Moser, A.; Moser, H. Genetic and Phenotypic Heterogeneity in Disorders of Peroxisome Biogenesis—A Complementation Study Involving Cell Lines from 19 Patients. Pediatric Res. 1989, 26, 67–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Al-Essa, M.; Dhaunsi, G.S.; Rashed, M.; Ozand, P.T.; Rahbeeni, Z. Zellweger Syndrome in Saudi Arabia and Its Distinct Features. Clin. Pediatrics 1999, 38, 77–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barkovich, A.J.; Peck, W.W. MR of Zellweger Syndrome. AJNR Am. J. Neuroradiol. 1997, 18, 1163–1170. [Google Scholar]
- Govaerts, L.; Monnens, L.; Tegelaers, W.; Trijbels, F.; van Raay-Selten, A. Cerebro-Hepato-Renal Syndrome of Zellweger: Clinical Symptoms and Relevant Laboratory Findings in 16 Patients. Eur. J. Pediatrics 1982, 139, 125–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Govaerts, L.; Colon, E.; Rotteveel, J.; Monnens, L. A Neurophysiological Study of Children with the Cerebro-Hepato-Renal Syndrome of Zellweger. Neuropediatrics 1985, 16, 185–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamel, A.; Houdou, S.; Takashima, S.; Suzuki, Y.; Becker, L.E.; Armstrong, D.L. Peroxisomal Disorders in Children: Immunohistochemistry and Neuropathology. J. Pediatrics 1993, 122, 573–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Powers, J.M.; Tummons, R.C.; Moser, A.B.; Moser, H.W.; Huff, D.S.; Kelley, R.I. Neuronal Lipidosis and Neuroaxonal Dystrophy in Cerebro-Hepato-Renal (Zellweger) Syndrome. Acta Neuropathol. 1987, 73, 333–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, Y.; Suzuki, Y.; Kumazaki, K.; Tanabe, Y.; Akaboshi, S.; Miura, K.; Shimozawa, N.; Kondo, N.; Nishiguchi, T.; Terada, K.; et al. Epilepsy in Peroxisomal Diseases. Epilepsia 1997, 38, 182–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolff, J.; Nyhan, W.L.; Powell, H.; Takahashi, D.; Hutzler, J.; Hajra, A.K.; Datta, N.S.; Singh, I.; Moser, H.W. Myopathy in an Infant with a Fatal Peroxisomal Disorder. Pediatric Neurol. 1986, 2, 141–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vamecq, J.; Draye, J.P.; Van Hoof, F.; Misson, J.P.; Evrard, P.; Verellen, G.; Eyssen, H.J.; Van Eldere, J.; Schutgens, R.B.; Wanders, R.J. Multiple Peroxisomal Enzymatic Deficiency Disorders. A Comparative Biochemical and Morphologic Study of Zellweger Cerebrohepatorenal Syndrome and Neonatal Adrenoleukodystrophy. Am. J. Pathol. 1986, 125, 524–535. [Google Scholar]
- Glasgow, B.J.; Brown, H.H.; Hannah, J.B.; Foos, R.Y. Ocular Pathologic Findings in Neonatal Adrenoleukodystrophy. Ophthalmology 1987, 94, 1054–1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaffe, R.; Crumrine, P.; Hashida, Y.; Moser, H.W. Neonatal Adrenoleukodystrophy: Clinical, Pathologic, and Biochemical Delineation of a Syndrome Affecting Both Males and Females. Am. J. Pathol. 1982, 108, 100–111. [Google Scholar]
- Aydemir, O.; Kavurt, S.; Esin, S.; Kandemir, O.; Bas, A.Y.; Demirel, N. Fetal Echogenic Bowel in Association with Zellweger Syndrome: Fetal Echogenic Bowel in ZS. J. Obstet. Gynaecol. Res. 2014, 40, 1799–1802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bamford, N.S. Chondrodysplasia Punctata: A Clue to the Zellweger Spectrum Disorders. Pediatric Neurol. 2019, 95, 84–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brun, A.; Gilboa, M.; Meeuwisse, G.W.; Nordgren, H. The Zellweger Syndrome: Subcellular Pathology, Neuropathology, and the Demonstration of Pneumocystis Carinii Pneumonitis in Two Siblings. Eur. J. Pediatrics 1978, 127, 229–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dursun, A.; Gucer, S.; Ebberink, M.S.; Yigit, S.; Wanders, R.J.A.; Waterham, H.R. Zellweger Syndrome with Unusual Findings: Non-Immune Hydrops Fetalis, Dermal Erythropoiesis and Hypoplastic Toe Nails. J. Inherit. Metab. Dis. 2009, 32, 345–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garner, A.; Fielder, A.R.; Primavesi, R.; Stevens, A. Tapetoretinal Degeneration in the Cerebro-Hepato-Renal (Zellweger’s) Syndrome. Br. J. Ophthalmol. 1982, 66, 422–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Groenendaal, F.; Cristina Bianchi, M.; Battini, R.; Tosetti, M.; Boldrini, A.; de Vries, L.; Cioni, G. Proton Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy (1H-MRS) of the Cerebrum in Two Young Infants with Zellweger Syndrome. Neuropediatrics 2001, 32, 23–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haddad, R.; Font, R.L.; David, S. Friendly Cerebro-Hepato-Renal Syndrome of Zellweger: Ocular Histopathologic Findings. Arch. Ophthalmol. 1976, 94, 1927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Havali, C.; Dorum, S.; Akbaş, Y.; Görükmez, O.; Hirfanoglu, T. Two Different Missense Mutations of PEX Genes in Two Similar Patients with Severe Zellweger Syndrome: An Argument on the Genotype-Phenotype Correlation. J. Pediatric Endocrinol. Metab. 2020, 33, 437–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konkoľová, J.; Petrovič, R.; Chandoga, J.; Halasová, E.; Jungová, P.; Böhmer, D. A Novel Mutation in the PEX12 Gene Causing a Peroxisomal Biogenesis Disorder. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2015, 42, 1359–1363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Suthar, R.; Sharda, S.; Panigrahi, I.; Marwaha, R.K. Zellweger Syndrome: Prenatal and Postnatal Growth Failure with Epiphyseal Stippling. J. Pediatric Endocrinol. Metab. 2014, 27, 185–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.F.; Mak, S.C.; Wu, F.W.; Chi, C.S.; Huang, S.C. Zellweger Syndrome: Report of One Case. Acta Paediatr. Taiwan 2001, 42, 53–56. [Google Scholar]
- Lindhard, A.; Graem, N.; Skovby, F.; Jeppesen, D. Postmortem Findings and Prenatal Diagnosis of Zellweger Syndrome. APMIS 1993, 101, 226–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luisiri, A.; Sotelo-Avila, C.; Silberstein, M.J.; Graviss, E.R. Sonography of the Zellweger Syndrome. J. Ultrasound Med. 1988, 7, 169–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, S.; El-Meleagy, E.; Nasr, A.; Ebberink, M.S.; Wanders, R.J.A.; Waterham, H.R. A Mutation in PEX19 Causes a Severe Clinical Phenotype in a Patient with Peroxisomal Biogenesis Disorder. Am. J. Med. Genet. 2010, 152A, 2318–2321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohebbi, M.R.; Rush, E.T.; Rizzo, W.B.; Banagale, R.C. Zellweger Syndrome and Associated Brain Malformations: Report of a Novel Peroxin1 (PEX1) Mutation in a Native American Infant. J. Child Neurol. 2012, 27, 1589–1592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muntau, A.C.; Mayerhofer, P.U.; Paton, B.C.; Kammerer, S.; Roscher, A.A. Defective Peroxisome Membrane Synthesis due To Mutations in Human PEX3 Causes Zellweger Syndrome, Complementation Group G. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2000, 67, 967–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Naritomi, K.; Izumikawa, Y.; Ohshiro, S.; Yoshida, K.; Shimozawa, N.; Suzuki, Y.; Orii, T.; Hirayama, K. Gene Assignment of Zellweger Syndrome to 7q11.23: Report of the Second Case Associated with a Pericentric Inversion of Chromosome 7. Hum. Genet. 1989, 84, 79–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panjan, D.P.; Meglič, N.P.; Meglič, N.P.; Neubauer, D. A Case of Zellweger Syndrome with Extensive MRI Abnormalities and Unusual EEG Findings. Clin. Electroencephalogr. 2001, 32, 28–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfeifer, C.M.; Martinot, C.A. Zellweger Syndrome: Depiction of MRI Findings in Early Infancy at 3.0 Tesla. Neuroradiol. J. 2017, 30, 442–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quintas-Neves, M.; Carvalho, R.; Soares-Fernandes, J.P. Brain MRI in a Newborn with Zellweger Syndrome: ADC Quantitation in White Matter Disease. Childs Nerv. Syst. 2018, 34, 1103–1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raas-Rothschild, A.; Wanders, R.J.A.; Mooijer, P.A.W.; Gootjes, J.; Waterham, H.R.; Gutman, A.; Suzuki, Y.; Shimozawa, N.; Kondo, N.; Eshel, G.; et al. A PEX6-Defective Peroxisomal Biogenesis Disorder with Severe Phenotype in an Infant, versus Mild Phenotype Resembling Usher Syndrome in the Affected Parents. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2002, 70, 1062–1068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rife, E.; Dunbar, A.E.; Nelson, S.L.; Andersson, H.C. Stippled Chondral Calcifications of the Patella in Zellweger Syndrome. J. Pediatrics 2018, 192, 265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Setchell, K.D.R.; Bragetti, P.; Zimmer-Nechemias, L.; Daugherty, C.; Pelli, M.A.; Vaccaro, R.; Gentili, G.; Distrutti, E.; Dozzini, G.; Morelli, A.; et al. Oral Bile Acid Treatment and the Patient with Zellweger Syndrome. Hepatology 1992, 15, 198–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferdinandusse, S.; Ebberink, M.S.; Vaz, F.M.; Waterham, H.R.; Wanders, R.J.A. The Important Role of Biochemical and Functional Studies in the Diagnostics of Peroxisomal Disorders. J. Inherit. Metab. Dis. 2016, 39, 531–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nakai, A.; Shigematsu, Y.; Nishida, K.; Kikawa, Y.; Konishi, Y. MRI Findings of Zellweger Syndrome. Pediatric Neurol. 1995, 13, 346–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smitthimedhin, A.; Otero, H.J. Scimitar-like Ossification of Patellae Led to Diagnosis of Zellweger Syndrome in Newborn: A Case Report. Clin. Imaging 2018, 49, 128–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strenge, S.; Froster, U.G.; Wanders, R.J.A.; Gartner, J.; Maier, E.M.; Muntau, A.C.; Faber, R. First-Trimester Increased Nuchal Translucency as a Prenatal Sign of Zellweger Syndrome. Prenat. Diagn. 2004, 24, 151–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takashima, S.; Chan, F.; Becker, L.E.; Houdou, S.; Suzuki, Y. Cortical Cytoarchitectural and Immunohistochemical Studies on Zellweger Syndrome. Brain Dev. 1991, 13, 158–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takenouchi, T.; Raju, G.P. Germinal Matrix Hemorrhage in Zellweger Syndrome. J. Child Neurol. 2010, 25, 1398–1400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, K.; Shimizu, T.; Ohtsuka, Y.; Yamashiro, Y.; Oshida, K. Early Dietary Treatments with Lorenzo’s Oil and Docosahexaenoic Acid for Neurological Development in a Case with Zellweger Syndrome. Brain Dev. 2007, 29, 586–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, G.N.; Holmes, R.G.; Custer, J.; Lipkowitz, J.L.; Stover, J.; Datta, N.; Hajra, A.; Reynolds, J.F. Zellweger Syndrome: Diagnostic Assays, Syndrome Delineation, and Potential Therapy. Am. J. Med. Genet. 1986, 24, 69–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ünay, B.; Kendirli, T.; Atac, K.; Gül, D.; Akın, R.; Gökc Ay, E. Caudothalamic Groove Cysts in Zellweger Syndrome. Clin. Dysmorphol. 2005, 14, 165–167. [Google Scholar]
- Müller-Höcker, J.; Walther, J.U.; Bise, K.; Pongratz, D.; Hübner, G. Mitochondrial Myopathy with Loosely Coupled Oxidative Phosphorylation in a Case of Zellweger Syndrome: A Cytochemical-Ultrastructural Study. Virchows Arch. B Cell Pathol. 1984, 45, 125–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maeda, K.; Kimura, A.; Yamato, Y.; Nittono, H.; Takei, H.; Sato, T.; Mitsubuchi, H.; Murai, T.; Kurosawa, T. Oral Bile Acid Treatment in Two Japanese Patients With Zellweger Syndrome. J. Pediatric Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2002, 35, 227–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moser, A.B.; Jones, D.S.; Raymond, G.V.; Moser, H.W. Plasma and Red Blood Cell Fatty Acids in Peroxisomal Disorders. Neurochem. Res. 1999, 24, 187–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aubourg, P.; Scotto, J.; Rocchiccioli, F.; Feldmann-Pautrat, D.; Robain, O. Neonatal Adrenoleukodystrophy. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 1986, 49, 77–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Budden, S.S.; Kennaway, N.G.; Buist, N.R.M.; Poulos, A.; Weleber, R.G. Dysmorphic Syndrome with Phytanic Acid Oxidase Deficiency, Abnormal Very Long Chain Fatty Acids, and Pipecolic Acidemia: Studies in Four Children. J. Pediatrics 1986, 108, 33–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wangler, M.F.; Hubert, L.; Donti, T.R.; Ventura, M.J.; Miller, M.J.; Braverman, N.; Gawron, K.; Bose, M.; Moser, A.B.; Jones, R.O.; et al. A Metabolomic Map of Zellweger Spectrum Disorders Reveals Novel Disease Biomarkers. Genet. Med. 2018, 20, 1274–1283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cohen, S.M.Z.; Moser, H.W.; Brown, F.R.; Green, W.R.; Zenaida, C.; Luckenbach, M.W.; Dove, D.J.; Maumenee, I.H. Ocular Histopathologic Studies of Neonatal and Childhood Adrenoleukodystrophy. Am. J. Ophthalmol. 1983, 95, 82–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, F.R.; McAdams, A.J.; Cummins, J.W.; Konkol, R.; Singh, I.; Moser, A.B.; Moser, H.W. Cerebro-Hepato-Renal (Zellweger) Syndrome and Neonatal Adrenoleukodystrophy: Similarities in Phenotype and Accumulation of Very Long Chain Fatty Acids. Johns Hopkins Med. J. 1982, 151, 344–351. [Google Scholar]
- Chang, Y.-C.; Huang, C.-C.; Huang, S.-C.; Hung, F.-C. Neonatal Adrenoleukodystrophy Presenting With Seizure at Birth: A Case Report and Review of the Literature. Pediatric Neurol. 2008, 38, 137–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez, M.; Pineda, M.; Vidal, R.; Conill, J.; Martin, B. Docosahexaenoic Acid–A New Therapeutic Approach to Peroxisomal-disorder Patients: Experience with Two Cases. Neurology 1993, 43, 1389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mito, T.; Takada, K.; Akaboshi, S.; Takashima, S.; Takeshita, K.; Origuchi, Y. A Pathological Study of a Peripheral Nerve in a Case of Neonatal Adrenoleukodystrophy. Acta Neuropathol. 1989, 77, 437–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paul, D.A.; Goldsmith, L.S.; Miles, D.K.; Moser, A.B.; Spiro, A.J.; Grover, W.D. Neonatal Adrenoleukodystrophy Presenting as Infantile Progressive Spinal Muscular Atrophy. Pediatric Neurol. 1993, 9, 496–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, N.P.; Hart, Z.H.; Nigro, M. Electrophysiologic Studies in Neonatal Adrenoleukodystrophy. Electroencephalogr. Clin. Neurophysiol. 1985, 60, 7–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huybrechts, S.J.; Van Veldhoven, P.P.; Hoffman, I.; Zeevaert, R.; de Vos, R.; Demaerel, P.; Brams, M.; Jaeken, J.; Fransen, M.; Cassiman, D. Identification of a Novel PEX14 Mutation in Zellweger Syndrome. J. Med. Genet. 2008, 45, 376–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komatsuzaki, S.; Ogawa, E.; Shimozawa, N.; Sakamoto, O.; Haginoya, K.; Uematsu, M.; Hasegawa, Y.; Matsubara, Y.; Ohura, T. First Japanese Case of Zellweger Syndrome with a Mutation in PEX14: First Japanese Case of PEX14 Deficiency. Pediatrics Int. 2015, 57, 1189–1192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, P.R.; Raymond, G.V. Child Neurology: Zellweger Syndrome. Neurology 2013, 80, e207–e210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cardoso, P.; Amaral, M.E.; Lemos, S.; Garcia, P. Zellweger Syndrome with Severe Malnutrition, Immunocompromised State and Opportunistic Infections. BMJ Case Rep. 2016, 2016, bcr2015214283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pineda, M.; Girós, M.; Roels, F.; Espeel, M.; Ruiz, M.; Moser, A.; Moser, H.W.; Wanders, R.J.A.; Pavia, C.; Conill, J.; et al. Diagnosis and Follow-Up of a Case of Peroxisomal Disorder with Peroxisomal Mosaicism. J. Child Neurol. 1999, 14, 434–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanesu-Segal, B.; Evrard, P. Zellweger Syndrome, Retinal Involvement. Metab. Pediatric Syst. Ophthalmol. 1989, 12, 96–99. [Google Scholar]
- Kulkarni, K.S.; Baranano, K.W.; Lin, D.D.M.; Raymond, G.V. Contrast Enhancement of Brainstem Tracts in Zellweger Spectrum Disorder: Evidence of Inflammatory Demyelination? Neuropediatrics 2011, 42, 32–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mandel, H.; Berant, M.; Meiron, D.; Aizin, A.; Oiknine, J.; Brook, J.G.; Aviram, M. Plasma Lipoproteins and Monocyte-Macrophages in a Peroxisome-Deficient System: Study of a Patient with Infantile Refsum Disease. J. Inherit. Metab. Dis. 1992, 15, 774–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kılıç, M.; Karlı-Oğuz, K.; Haliloğlu, G.; Topçu, M.; Wanders, R.J.; Coşkun, T. Conventional and Advanced MR Imaging in Infantile Refsum Disease. Turk. J. Pediatrics 2015, 57, 294–299. [Google Scholar]
- Falkenberg, K.D.; Braverman, N.E.; Moser, A.B.; Steinberg, S.J.; Klouwer, F.C.C.; Schlüter, A.; Ruiz, M.; Pujol, A.; Engvall, M.; Naess, K.; et al. Allelic Expression Imbalance Promoting a Mutant PEX6 Allele Causes Zellweger Spectrum Disorder. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2017, 101, 965–976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ebberink, M.S.; Csanyi, B.; Chong, W.K.; Denis, S.; Sharp, P.; Mooijer, P.A.W.; Dekker, C.J.M.; Spooner, C.; Ngu, L.H.; De Sousa, C.; et al. Identification of an Unusual Variant Peroxisome Biogenesis Disorder Caused by Mutations in the PEX16 Gene. J. Med. Genet. 2010, 47, 608–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Smith, C.E.L.; Poulter, J.A.; Levin, A.V.; Capasso, J.E.; Price, S.; Ben-Yosef, T.; Sharony, R.; Newman, W.G.; Shore, R.C.; Brookes, S.J.; et al. Spectrum of PEX1 and PEX6 Variants in Heimler Syndrome. Eur. J. Hum. Genet. 2016, 24, 1565–1571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renaud, M.; Guissart, C.; Mallaret, M.; Ferdinandusse, S.; Cheillan, D.; Drouot, N.; Muller, J.; Claustres, M.; Tranchant, C.; Anheim, M.; et al. Expanding the Spectrum of PEX10-Related Peroxisomal Biogenesis Disorders: Slowly Progressive Recessive Ataxia. J. Neurol. 2016, 263, 1552–1558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bjørgo, K.; Fjær, R.; Mørk, H.H.; Ferdinandusse, S.; Falkenberg, K.D.; Waterham, H.R.; Øye, A.-M.; Sikiric, A.; Amundsen, S.S.; Kulseth, M.A.; et al. Biochemical and Genetic Characterization of an Unusual Mild PEX3- Related Zellweger Spectrum Disorder. Mol. Genet. Metab. 2017, 121, 325–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barillari, M.R.; Karali, M.; Di Iorio, V.; Contaldo, M.; Piccolo, V.; Esposito, M.; Costa, G.; Argenziano, G.; Serpico, R.; Carotenuto, M.; et al. Mild Form of Zellweger Spectrum Disorders (ZSD) due to Variants in PEX1: Detailed Clinical Investigation in a 9-Years-Old Female. Mol. Genet. Metab. Rep. 2020, 24, 100615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barth, P.G.; Schutgens, R.B.H.; Bakkeren, J.A.J.M.; Dingemans, K.P.; Heymans, H.S.A.; Douwes, A.C.; van der Klei-van Moorsel, J.M. A Milder Variant of Zellweger Syndrome. Eur. J. Pediatrics 1985, 144, 338–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bleeker-Wagemakers, E.M. Long Term Survival of a Patient with the Cerebro-Hepato-Renal (Zellweger) Syndrome. Clin. Genet. 1986, 29, 160–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blomqvist, M.; Ahlberg, K.; Lindgren, J.; Ferdinandusse, S.; Asin-Cayuela, J. Identification of a Novel Mutation in PEX10 in a Patient with Attenuated Zellweger Spectrum Disorder: A Case Report. J. Med. Case Rep. 2017, 11, 218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cakirer, S.; Savas, M.R. Infantile Refsum Disease: Serial Evaluation with MRI. Pediatric Radiol. 2005, 35, 212–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dubois, J.; Sebag, G.; Argyropoulou, M.; Brunelle, F. MR Findings in Infantile Refsum Disease: Case Report of Two Family Members. AJNR Am. J. Neuroradiol. 1991, 12, 1159–1160. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Karaman, Y.; Goktay, A.; Agin, H.; Karaarslan, U. Propofol Infusion Syndrome or Adrenoleukodystrophy? Paediatric Anaesth. 2013, 23, 368–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lima, L.H.; Barbazetto, I.A.; Chen, R.; Yannuzzi, L.A.; Tsang, S.H.; Spaide, R.F. Macular Dystrophy in Heimler Syndrome. Ophthalmic Genet. 2011, 32, 97–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lipiński, P.; Stawiński, P.; Rydzanicz, M.; Wypchło, M.; Płoski, R.; Stradomska, T.J.; Jurkiewicz, E.; Ferdinandusse, S.; Wanders, R.J.A.; Vaz, F.M.; et al. Mild Zellweger Syndrome due to Functionally Confirmed Novel PEX1 Variants. J. Appl. Genet. 2020, 61, 87–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Majewski, J.; Wang, Z.; Lopez, I.; Al Humaid, S.; Ren, H.; Racine, J.; Bazinet, A.; Mitchel, G.; Braverman, N.; Koenekoop, R.K. A New Ocular Phenotype Associated with an Unexpected but Known Systemic Disorder and Mutation: Novel Use of Genomic Diagnostics and Exome Sequencing. J. Med. Genet. 2011, 48, 593–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manson, J.I.; Pollard, A.C.; Poulos, A.; Carter, R.F. Infantile Refsum’s Disease: A Peroxisomal Storage Disorder? Clin. Exp. Neurol. 1985, 21, 283–287. [Google Scholar]
- Maxit, C.; Denzler, I.; Marchione, D.; Agosta, G.; Koster, J.; Wanders, R.J.A.; Ferdinandusse, S.; Waterham, H.R. Novel PEX3 Gene Mutations Resulting in a Moderate Zellweger Spectrum Disorder. In JIMD Reports; Morava, E., Baumgartner, M., Patterson, M., Rahman, S., Zschocke, J., Peters, V., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2016; Volume 34, pp. 71–75. ISBN 978-3-662-55585-9. [Google Scholar]
- Michelakakis, H.M.; Zafeiriou, D.I.; Moraitou, M.S.; Gootjes, J.; Wanders, R.J.A. PEX1 Deficiency Presenting as Leber Congenital Amaurosis. Pediatric Neurol. 2004, 31, 146–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Bryhim, B.E.; Kozel, B.A.; Lueder, G.T. Novel Retinal Findings in Peroxisomal Biogenesis Disorders. Ophthalmic Genet. 2018, 39, 377–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pakzad-Vaezi, K.L.; Maberley, D.A.L. Infantile Refsum disease in a young adult: Case presentation and brief review. Retinal Cases Brief Rep. 2014, 8, 56–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Régal, L.; Ebberink, M.S.; Goemans, N.; Wanders, R.J.; De Meirleir, L.; Jaeken, J.; Schrooten, M.; Van Coster, R.; Waterham, H.R. Mutations in PEX10 Are a Cause of Autosomal Recessive Ataxia. Ann. Neurol. 2010, 68, 259–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rydzanicz, M.; Stradomska, T.J.; Jurkiewicz, E.; Jamroz, E.; Gasperowicz, P.; Kostrzewa, G.; Płoski, R.; Tylki-Szymańska, A. Mild Zellweger Syndrome due to a Novel PEX6 Mutation: Correlation between Clinical Phenotype and in Silico Prediction of Variant Pathogenicity. J. Appl. Genet. 2017, 58, 475–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steinberg, S.J.; Snowden, A.; Braverman, N.E.; Chen, L.; Watkins, P.A.; Clayton, P.T.; Setchell, K.D.R.; Heubi, J.E.; Raymond, G.V.; Moser, A.B.; et al. A PEX10 Defect in a Patient with No Detectable Defect in Peroxisome Assembly or Metabolism in Cultured Fibroblasts. J. Inherit. Metab. Dis. 2009, 32, 109–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vandana, V.P.; Bindu, P.S.; Nagappa, M.; Sinha, S.; Taly, A.B. Audiological Findings in Infantile Refsum Disease. Int. J. Pediatric Otorhinolaryngol. 2015, 79, 1366–1369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ventura, M.J.; Wheaton, D.; Xu, M.; Birch, D.; Bowne, S.J.; Sullivan, L.S.; Daiger, S.P.; Whitney, A.E.; Jones, R.O.; Moser, A.B.; et al. Diagnosis of a Mild Peroxisomal Phenotype with Next-Generation Sequencing. Mol. Genet. Metab. Rep. 2016, 9, 75–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wangtiraumnuay, N.; Alnabi, W.A.; Tsukikawa, M.; Thau, A.; Capasso, J.; Sharony, R.; Inglehearn, C.F.; Levin, A.V. Ophthalmic Manifestations of Heimler Syndrome due to PEX6 Mutations. Ophthalmic Genet. 2018, 39, 384–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Warren, M.; Mierau, G.; Wartchow, E.P.; Shimada, H.; Yano, S. Histologic and Ultrastructural Features in Early and Advanced Phases of Zellweger Spectrum Disorder (Infantile Refsum Disease). Ultrastruct. Pathol. 2018, 42, 220–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeharia, A.; Ebberink, M.S.; Wanders, R.J.A.; Waterham, H.R.; Gutman, A.; Nissenkorn, A.; Korman, S.H. A Novel PEX12 Mutation Identified as the Cause of a Peroxisomal Biogenesis Disorder with Mild Clinical Phenotype, Mild Biochemical Abnormalities in Fibroblasts and a Mosaic Catalase Immunofluorescence Pattern, Even at 40 °C. J. Hum. Genet. 2007, 52, 599–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Zhan, F.-X.; Tian, W.-T.; Xu, Y.-Q.; Zhu, Z.-Y.; Wang, Y.; Song, X.; Cao, L. Ataxia with Novel Compound Heterozygous PEX10 Mutations and a Literature Review of PEX10-Related Peroxisome Biogenesis Disorders. Clin. Neurol. Neurosurg. 2019, 177, 92–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goez, H.; Meiron, D.; Horowitz, J.; Schutgens, R.H.; Wanders, R.J.; Berant, M.; Mandel, H. Infantile Refsum Disease: Neonatal Cholestatic Jaundice Presentation of a Peroxisomal Disorder. J. Pediatric Gastroenterol. Nutr. 1995, 20, 98–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capalbo, D.; Moracas, C.; Cappa, M.; Balsamo, A.; Maghnie, M.; Wasniewska, M.G.; Greggio, N.A.; Baronio, F.; Bizzarri, C.; Ferro, G.; et al. Primary Adrenal Insufficiency in Childhood: Data From a Large Nationwide Cohort. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2021, 106, 762–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martinez, M. Restoring the DHA Levels in the Brains of Zellweger Patients. J. Mol. Neurosci. 2001, 16, 309–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, J.N.; Ammous, Z.; Eroglu, Y.; Hernandez, E.; Heubi, J.; Himes, R.; Palle, S. Cholbam® and Zellweger Spectrum Disorders: Treatment Implementation and Management. Orphanet J. Rare Dis. 2021, 16, 388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Budgell, B. Guidelines to the Writing of Case Studies. J. Can. Chiropr. Assoc. 2008, 52, 199–204. [Google Scholar]



| Severe (9 Studies Total) | Intermediate (10 Studies Total) | Mild (10 Studies Total) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Clinical Finding | Studies | % Subjects with Clinical Finding | Studies | % Subjects with Clinical Finding | Studies | % Subjects with Clinical Finding |
| Neurological findings | ||||||
| Seizure disorder | 9 | 70.8 (51/72) | 6 | 51.0 (26/51) * | 5 | 15.9 (10/63) ^^ |
| Abnormal EEG | 5 | 51.2 (21/41) | 1 | 100.0 (2/2) | 1 | 0 (0/3) |
| Brain abnormalities | 6 | 69.4 (34/49) | 4 | 15.4 (4/26) ** | 3 | 70.6 (24/34) ^^ |
| Ataxia | 0 | n/a | 2 | 66.7 (10/15) | 6 | 64.3 (18/39) |
| Hypotonia | 5 | 94.6 (35/37) | 7 | 97.6 (40/41) | 4 | 50 (21/42) ^^ |
| Gastrointestinal findings | ||||||
| Feeding difficulties | 5 | 71.1 (32/45) | 3 | 52.9 (9/17) | 3 | 14.8 (8/54) ^ |
| Gastroesophageal reflux | 0 | n/a | 1 | 63.6 (7/11) | 1 | 14.3 (1/7) |
| Abnormal liver function/structure | 8 | 81.5 (53/65) | 7 | 79.0 (30/38) | 5 | 54.3 (38/70) ^^ |
| Other clinical findings | ||||||
| Vision loss | 6 | 58.5 (31/53) | 6 | 92.1 (35/38) ** | 7 | 92.7 (63/68) |
| Hearing loss | 2 | 36.8 (7/19) | 5 | 77.5 (31/40) * | 7 | 52.0 (39/75) ^ |
| Renal cortical microcysts | 5 | 41.9 (18/43) | 1 | 0 (0/24) ** | 0 | n/a |
| Adrenal insufficiency | 1 | 7.1 (1/14) | 3 | 57.1 (16/28) * | 3 | 11.8 (4/34) ^^ |
| Developmental outcomes | ||||||
| Global developmental delay | 3 | 76.9 (30/39) | 6 | 89.2 (33/37) | 5 | 84.6 (33/39) |
| Reduced verbal communication | 0 | n/a | 3 | 63.2 (12/19) | 4 | 36.9 (24/65) |
| Reduced mobility | 0 | n/a | 5 | 70.8 (17/24) | 4 | 35.7 (25/70) ^ |
| Other | ||||||
| Shortened lifespan (died ≤ 2 years) | 7 | 83.3 (45/54) | 3 | 24.4 (11/45) ** | 0 | 0 (0/77) ^^ |
| Severe (38 Studies) | Intermediate (18 Studies) | Mild (31 Studies) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Clinical Finding | % Subjects with Clinical Finding | % Subjects with Clinical Finding | % Subjects with Clinical Finding |
| Neurological findings | |||
| Seizure disorder | 97.0 (32/33) | 83.3 (10/12) | 50.0 (4/8) |
| Abnormal EEG | 81.3 (13/16) | 72.7 (8/11) | 80.0 (4/5) |
| Brain abnormalities | 85.3 (29/34) | 76.9 (10/13) | 66.7 (12/18) |
| Ataxia | 100.0 (1/1) | 100.0 (1/1) | 83.3 (5/6) |
| Hypotonia | 100.0 (42/42) | 100.0 (17/17) | 85.7 (12/14) |
| Gastrointestinal findings | |||
| Feeding difficulties | 95.8 (23/24) | 100.0 (5/5) | 90.0 (9/10) |
| Abnormal liver function/structure | 95.1 (39/41) | 93.8 (15/16) | 77.8 (14/18) |
| Other clinical findings | |||
| Renal cortical microcysts | 90.5 (19/21) | 0 (0/2) * | 0 (0/5) |
| Adrenal insufficiency | 100.0 (4/4) | 62.5 (5/8) | 66.7 (2/3) |
| Developmental outcomes | |||
| Global developmental delay | 100.0 (9/9) | 100.0 (17/17) | 90.5 (19/21) |
| Reduced verbal communication | 100.0 (1/1) | 100.0 (6/6) | 77.8 (14/18) |
| Reduced mobility | 100.0 (1/1) | 83.3 (5/6) | 86.7 (13/15) |
| Other | |||
| Shortened lifespan (died ≤ 2 years) | 93.0(40/43) | 31.3 (5/16) ** | 5.7 (2/35) ^ |
| % of Patients with Clinical Finding (Total n) | Median Age of Onset * (Q1–Q3) (y) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Clinical Findings | Severe | Intermediate | Mild | Total All Severities | Severe | Intermediate | Mild |
| Neurological findings | |||||||
| Seizure disorder | 100 (23) | 41.3 (63) ** | 16.3 (49) ^ | 42.2 (135) | 0 (0–0.2) | 3.3 (1.0–8.3) ** | 6.2 (4.0–21.3) ^^ |
| Abnormal EEG | 100 (17) | 72.2 (36) * | 40.0 (10) | 74.6 (63) | 0 (0–0.1) | 2.3 (0.9–5.3) ** | 5.8 (2.3–36.6) ^^ |
| Brain MRI abnormalities | 95.0 (20) | 81.0 (42) | 75.0 (36) | 81.6 (98) | 0 (0–0.1) | 2.0 (0.4–3.8) ** | 6 (2.8–19.9) ^^ |
| Hypotonia | 100 (23) | 98.2 (56) | 72.1 (43) ^ | 89.3 (122) | 0.1 (0.1–0.3) | 1.5 (0.4–3.6) ** | 4.9 (1.6–8.2) ^^ |
| Gastrointestinal findings | |||||||
| Feeding difficulties | 90.0 (20) | 71.9 (57) | 0 (48) ^^ | 47.2 (125) | 0.1 (0–0.1) | 2.2 (1.3–4.7) ** | n/a |
| Failure to thrive | 100 (1) | 94.1 (17) | 5.3 (19) ^^ | 48.7 (37) | 0.2 (0–0.9) | 0.5 | |
| Gastroesophageal reflux | 28.6 (21) | 51.7 (58) | 11.1 (45) ^^ | 33.1 (124) | 0.3 (0.3–0.6) | 2.4 (1.0–10.6) * | 6.5 (2.0–9.2) ^ |
| Abnormal liver functions | 94.4 (18) | 92.9 (56) | 65.9 (44) ^^ | 83.1 (118) | 0.1 (0–0.2) | 1.3 (0.3–4.2) ** | 3.1 (1.3–6.1) ^^ |
| Abnormal liver structure | 33.3 (21) | 61.4 (57) | 31.0 (42) ^ | 45.8 (120) | 0.1 (0.1–0.5) | 1.3 (0.6–2.0) ** | 2.9 (1.1–5.1) ^^ |
| Other clinical findings | |||||||
| Vision loss | 100 (9) | 89.1 (55) | 67.4 (46) ^ | 80.9 (110) | 0.4 (0.2–0.5) | 1.8 (0.8–3.6) ** | 4.4 (1.9–8.2) ^^ |
| Renal cortical microcysts | 79.0 (19) | 0 (37) ** | 0 (29) | 17.7 (85) | 0 (0–0.1) | n/a | n/a |
| Adrenal insufficiency | 14.3 (21) | 54.2 (59) * | 10.4 (48) ^^ | 31.3 (128) | 0.1 (0–0.1) | 3.8 (2.2–11.0) ** | 20.7 (16.7–23.8) ^^ |
| Cardiac abnormalities | 81.3 (16) | 17.7 (34) ** | 20.0 (25) | 32 (75) | 0 (0–0.1) | 0.1 (0–0.8) | 26.4 (24.0–27.0) ^^ |
| Bone fractures | 0 (3) | 51.2 (41) | 27.6 (29) | 39.7 (73) | n/a | 5.4 (3.0–12.0) | 5.4 (4.9–14.0) |
| Developmental outcomes | |||||||
| Global developmental delay | 100 (7) | 97.5 (40) | 33.3 (36) ^^ | 69.9 (83) | 0.5 (0.2–0.7) | 3.3 (1.5–5.0) ** | 4.2 (2.6–6.8) ^^ |
| Not sitting independently | 100 (1) | 28.8 (59) | 0 (49) ^^ | 16.5 (109) | 1.8 | 2.8 (2.3–3.9) | n/a |
| Walking with support | n/a | 33.9 (59) | 12.2 (49) ^ | 24.1 (108) | n/a | 4 (2.8–7.0) | 2.3 (1.6–3.0) |
| Walking independently | n/a | 23.7 (59) | 87.8 (49) ^^ | 52.8 (108) | n/a | 2.6 (1.9–3.5) | 1.5 (1.3–2.5) ^ |
| No words | 100 (5) | 71.7 (53) | 0 (46) ^^ | 41.4 (104) | 1 (0.5–1.2) | 3.5 (2.8–8.3) ** | n/a |
| 2–3 words together | 0 (5) | 5.7 (53) | 26.1 (46) ^^ | 14.4 (104) | n/a | 4.1 (2.0–15.5) | 4.4 (2.7–6.2) |
| Full sentences | n/a | 1.9 (53) | 71.7 (46) ^^ | 34.3 (99) | n/a | 8.3 | 9.8 (6.0–14.8) |
| Intellectual disability | n/a | 100 (23) | 30.0 (30) ^^ | 62.3 (53) | n/a | 7.0 (3.9–18.0) | 14.6 (10.5–16.2) |
| Peroxisome metabolites | |||||||
| Decreased C16:0/C16:0 DMA | 100 (4) | 83.3 (24) | 23.5 (17) ^^ | 62.2 (45) | 0 (0–0.1) | 2.6 (0.9–5.3) ** | 6.7 (4.0–15.8) ^^ |
| Decreased C18:0/C18:0 DMA | 100 (4) | 91.7 (24) | 35.3 (17) ^^ | 71.1 (45) | 0 (0–0.1) | 2.6 (0.9–5.3) ** | 6.7 (4.0–15.8) ^^ |
| Others | |||||||
| Shortened lifespan (died at age ≤ 2 years) | 95.7 (23) | 0 (64) ** | 0 (49) | 16.2 (136) | |||
| Reference Range [41,97] | Severe | Intermediate | Mild | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Median plasma C26:0 fatty acid levels, Q1–Q3 (μg/mL) | 0.14–0.31 | 3.9 ** 2.7–5.6 (n = 8) | 2.0 ** 1.3–2.8 (n = 44) | 0.6 ** 0.4–0.9 (n = 36) |
| Median serum DHCA levels, Q1–Q3 (μmol/L) | 0–0.1 | 3.1 * (n = 1) | 3.2 * 0.5–9.7 (n = 17) | 0.0 * 0.0–0.8 (n = 13) |
| Median serum THCA levels, Q1–Q3 (μmol/L) | 0–1.3 | 22.5 * (n = 1) | 0.6 * 0.2–1.5 (n = 17) | 0.2 * 0.2–0.4 (n = 14) |
| Median RBC membrane C16:0 DMA/C16:0 ratio, Q1–Q3 | 0.08–0.13 | 0.007 ** 0.005–0.01 (n = 4) | 0.056 ** 0.04–0.07 (n = 24) | 0.094 ** 0.087–0.108 (n = 17) |
| Median RBC membrane C18:0 DMA/C18:0 ratio, Q1–Q3 | 0.20–0.28 | 0.006 ** 0.004–0.008 (n = 4) | 0.122 ** 0.1–0.16 (n = 24) | 0.215 ** 0.182–0.23 (n = 17) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bose, M.; Yergeau, C.; D’Souza, Y.; Cuthbertson, D.D.; Lopez, M.J.; Smolen, A.K.; Braverman, N.E. Characterization of Severity in Zellweger Spectrum Disorder by Clinical Findings: A Scoping Review, Meta-Analysis and Medical Chart Review. Cells 2022, 11, 1891. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells11121891
Bose M, Yergeau C, D’Souza Y, Cuthbertson DD, Lopez MJ, Smolen AK, Braverman NE. Characterization of Severity in Zellweger Spectrum Disorder by Clinical Findings: A Scoping Review, Meta-Analysis and Medical Chart Review. Cells. 2022; 11(12):1891. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells11121891
Chicago/Turabian StyleBose, Mousumi, Christine Yergeau, Yasmin D’Souza, David D. Cuthbertson, Melisa J. Lopez, Alyssa K. Smolen, and Nancy E. Braverman. 2022. "Characterization of Severity in Zellweger Spectrum Disorder by Clinical Findings: A Scoping Review, Meta-Analysis and Medical Chart Review" Cells 11, no. 12: 1891. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells11121891
APA StyleBose, M., Yergeau, C., D’Souza, Y., Cuthbertson, D. D., Lopez, M. J., Smolen, A. K., & Braverman, N. E. (2022). Characterization of Severity in Zellweger Spectrum Disorder by Clinical Findings: A Scoping Review, Meta-Analysis and Medical Chart Review. Cells, 11(12), 1891. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells11121891







