Diverse Mechanisms of Resistance against Osimertinib, a Third-Generation EGFR-TKI, in Lung Adenocarcinoma Cells with an EGFR-Activating Mutation
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cell Lines and Reagents
2.2. Establishment of Acquired Osimertinib-Resistant PC-9 Cells Harboring a 15 bp Deletion in EGFR Exon 19 as Front-Line Therapy
2.3. Cell Viability Assay
2.4. Immunoblotting, Immunoprecipitation, and Antibodies
2.5. Subcellular Fractionation
2.6. RAS Pull-Down Assay
2.7. RNA Interference
2.8. Quantitative PCR
2.9. EGFR, KRAS, and PTPN11 Sequence Analysis
2.10. Droplet Digital PCR Analysis for EGFR Allele Quantification
2.11. PCR Analysis of EGFR Exon 19
2.12. Xenograft Studies on Tumor Growth
2.13. Cell-Based Insulin-like Growth Factor 1 Receptor (IGF1R) Phosphorylation Assay
2.14. Next-Generation Sequencing and nCounter Analysis
2.15. Caspase-3/7 Activity Assay
2.16. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
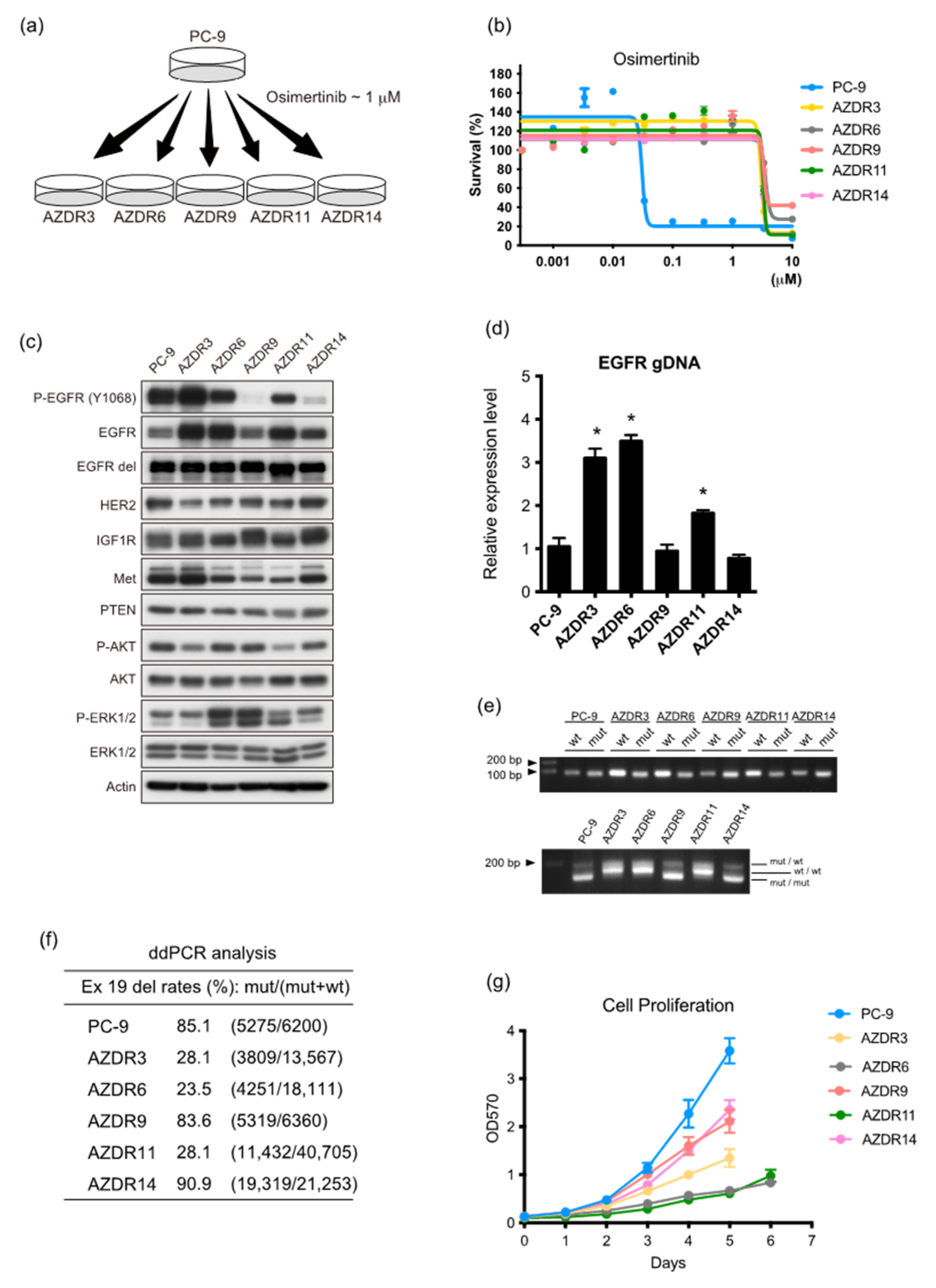
3.1. Characteristics of Clones with Acquired Resistance against Osimertinib
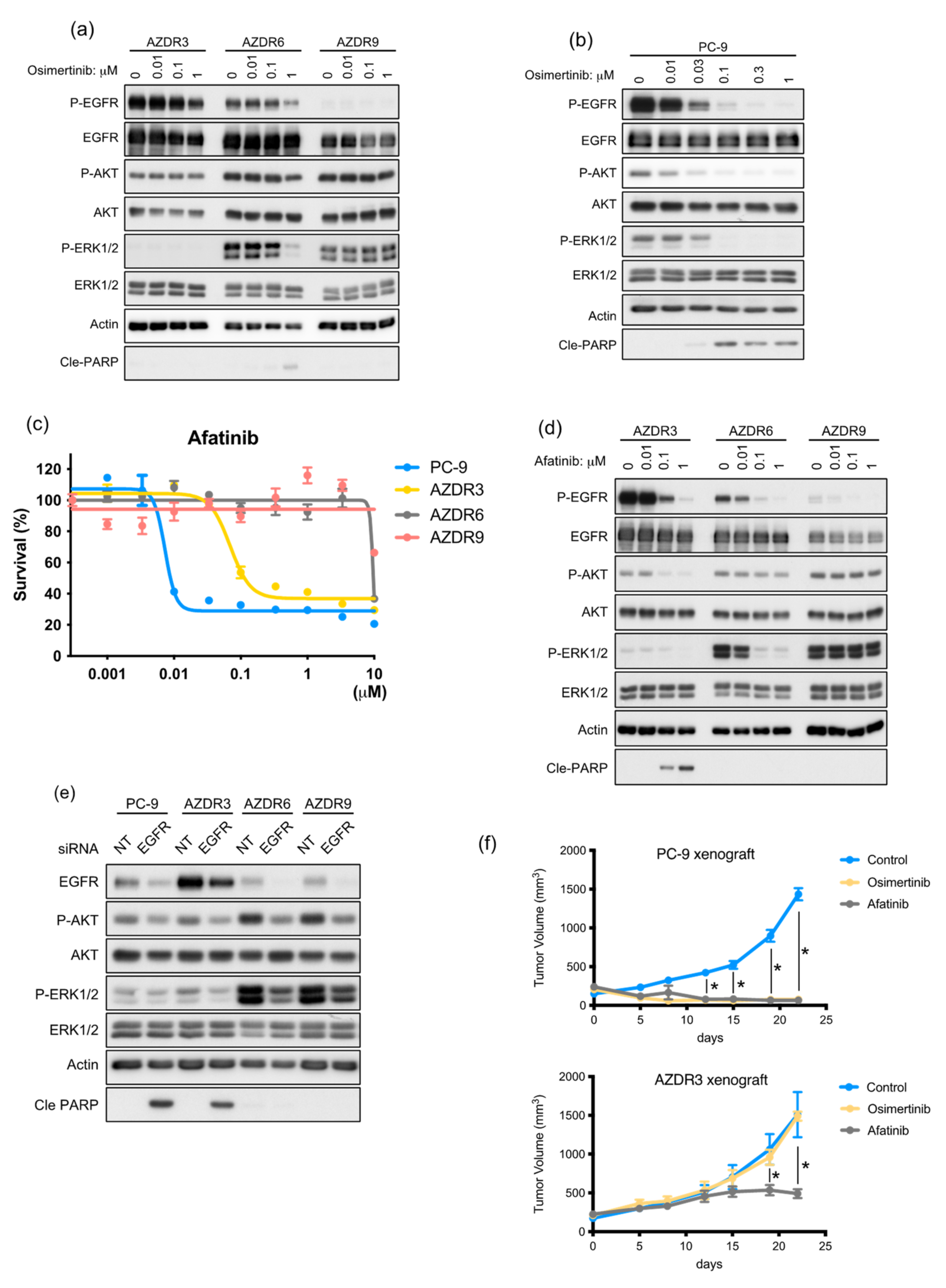
3.2. AZDR3 Cells Exhibit EGFR Amplification and Loss of EGFR Exon 19 Deletion
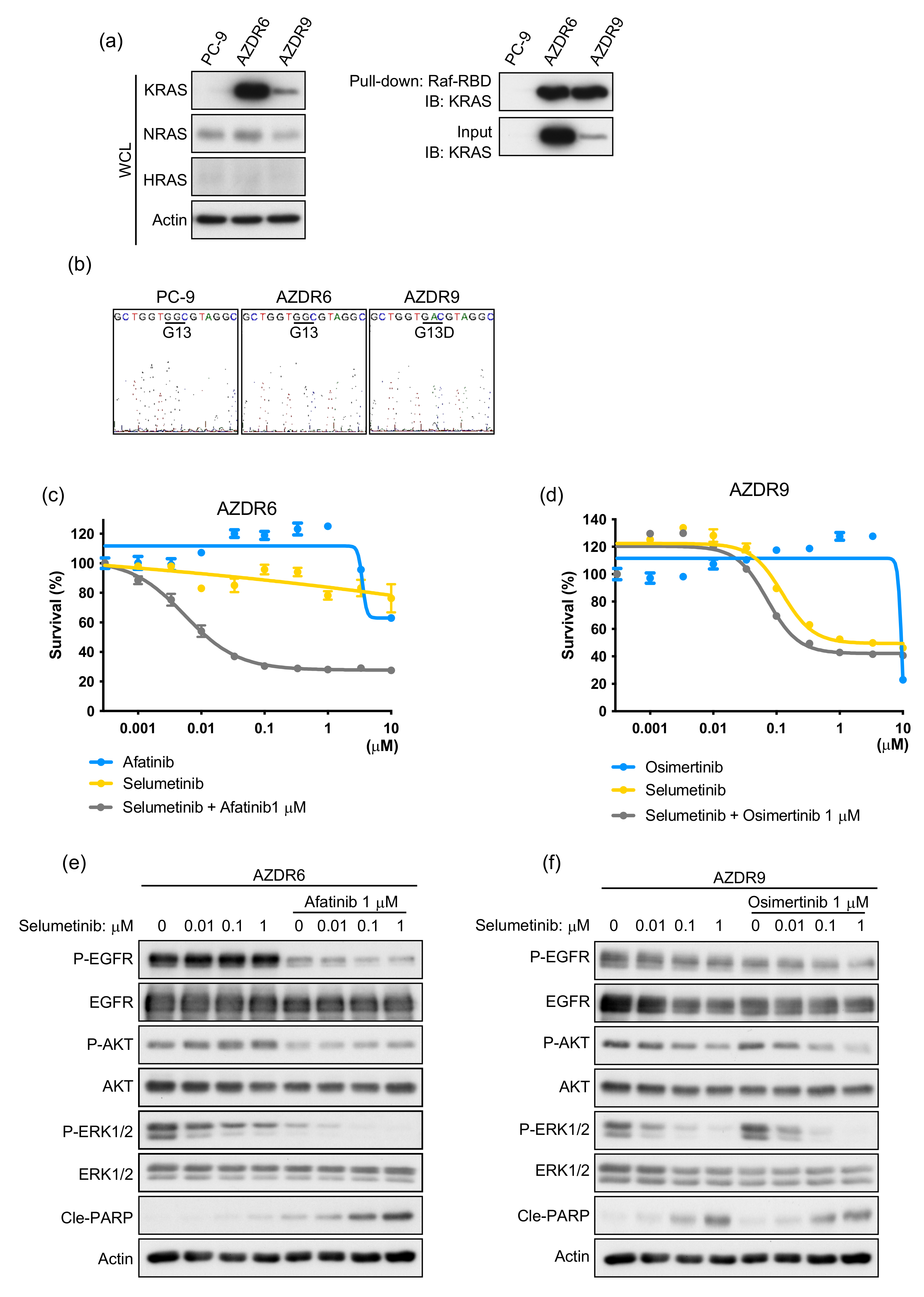
3.3. Increase in Acquired WT KRAS Expression in AZDR6 Cells, and KRASG13D Mutation in AZDR9 Cells Results in Differential Sensitivity to MEK Inhibitor
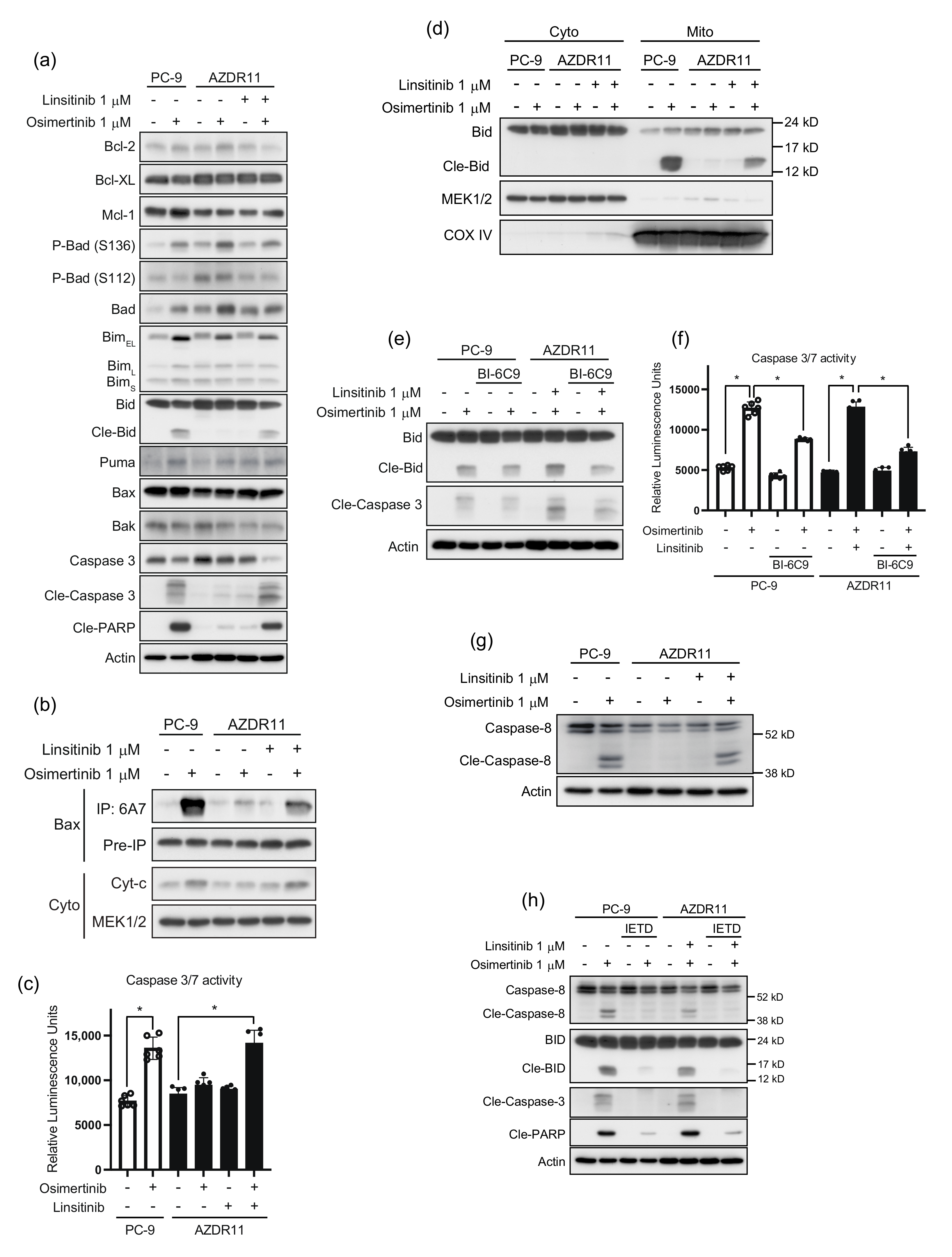
3.4. Bypass Signal of IGF1R to AKT Requires Ligand(s) Stimulation in AZDR11 and AZDR14 Cells
3.5. Bid Cleavage by Caspase-8 Is Required for Apoptosis Induction in AZDR11 Cells
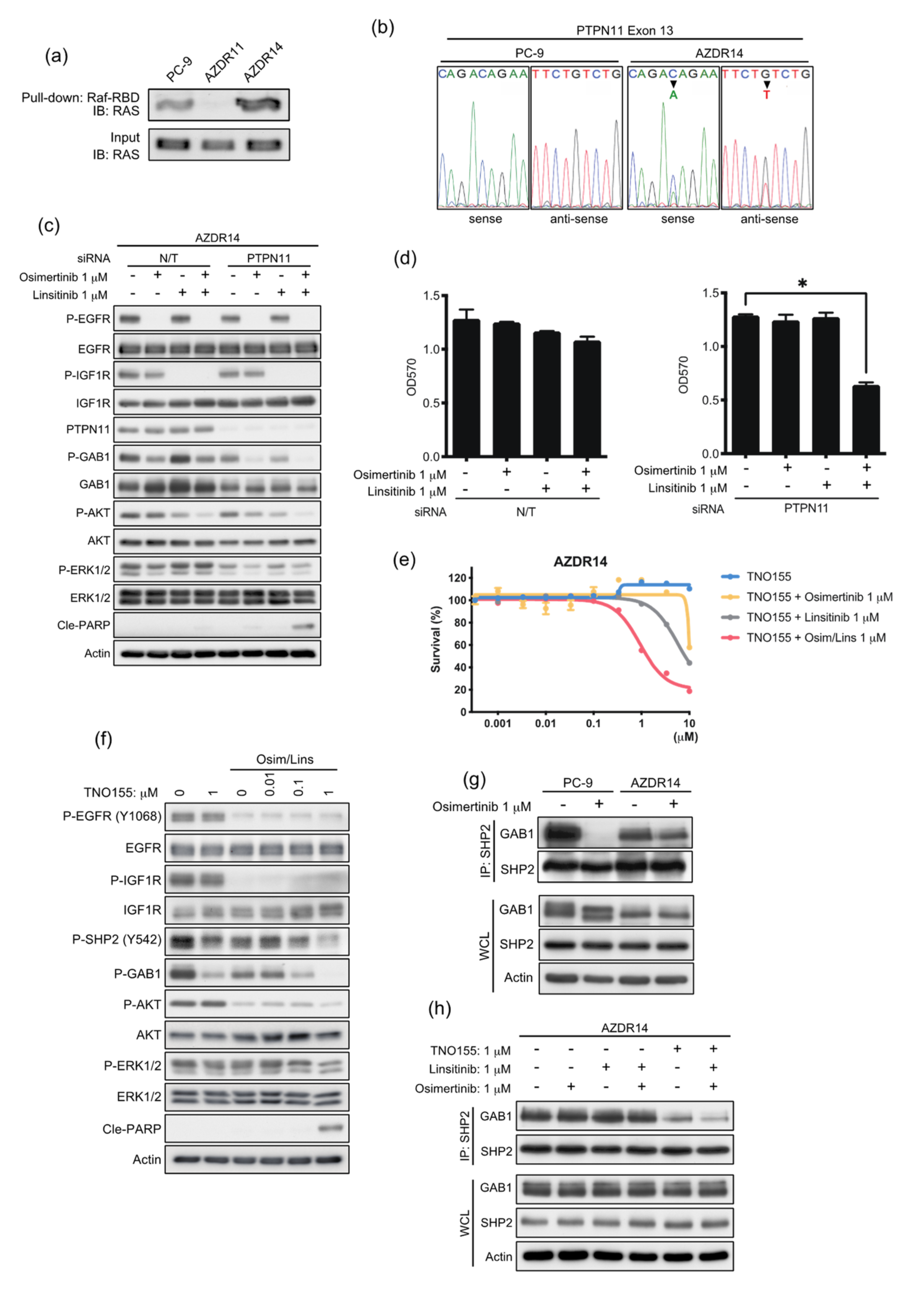
3.6. An Acquired Novel Mutation, T507K PTPN11 Detected in AZDR14 Cells Activates ERK1/2 Signal via Association with SHP2/GAB1
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rosell, R.; Moran, T.; Queralt, C.; Porta, R.; Cardenal, F.; Camps, C.; Majem, M.; Lopez-Vivanco, G.; Isla, D.; Provencio, M.; et al. Screening for epidermal growth factor receptor mutations in lung cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2009, 361, 958–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shi, Y.; Au, J.S.; Thongprasert, S.; Srinivasan, S.; Tsai, C.M.; Khoa, M.T.; Heeroma, K.; Itoh, Y.; Cornelio, G.; Yang, P.C. A prospective, molecular epidemiology study of EGFR mutations in Asian patients with advanced non-small-cell lung cancer of adenocarcinoma histology (PIONEER). J. Thorac. Oncol. 2014, 9, 154–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sequist, L.V.; Waltman, B.A.; Dias-Santagata, D.; Digumarthy, S.; Turke, A.B.; Fidias, P.; Bergethon, K.; Shaw, A.T.; Gettinger, S.; Cosper, A.K.; et al. Genotypic and histological evolution of lung cancers acquiring resistance to EGFR inhibitors. Sci. Transl. Med. 2011, 3, 75ra26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cheng, H.; Nair, S.K.; Murray, B.W. Recent progress on third generation covalent EGFR inhibitors. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2016, 26, 1861–1868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mok, T.S.; Wu, Y.L.; Ahn, M.J.; Garassino, M.C.; Kim, H.R.; Ramalingam, S.S.; Shepherd, F.A.; He, Y.; Akamatsu, H.; Theelen, W.S.; et al. Osimertinib or Platinum-Pemetrexed in EGFR T790M-Positive Lung Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 376, 629–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Soria, J.C.; Ohe, Y.; Vansteenkiste, J.; Reungwetwattana, T.; Chewaskulyong, B.; Lee, K.H.; Dechaphunkul, A.; Imamura, F.; Nogami, N.; Kurata, T.; et al. Osimertinib in Untreated EGFR-Mutated Advanced Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 378, 113–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramalingam, S.S.; Vansteenkiste, J.; Planchard, D.; Cho, B.C.; Gray, J.E.; Ohe, Y.; Zhou, C.; Reungwetwattana, T.; Cheng, Y.; Chewaskulyong, B.; et al. Overall Survival with Osimertinib in Untreated, EGFR-Mutated Advanced NSCLC. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 382, 41–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leonetti, A.; Sharma, S.; Minari, R.; Perego, P.; Giovannetti, E.; Tiseo, M. Resistance mechanisms to osimertinib in EGFR-mutated non-small cell lung cancer. Br. J. Cancer 2019, 121, 725–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakatani, K.; Yamaoka, T.; Ohba, M.; Fujita, K.I.; Arata, S.; Kusumoto, S.; Taki-Takemoto, I.; Kamei, D.; Iwai, S.; Tsurutani, J.; et al. KRAS and EGFR Amplifications Mediate Resistance to Rociletinib and Osimertinib in Acquired Afatinib-Resistant NSCLC Harboring Exon 19 Deletion/T790M in EGFR. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2019, 18, 112–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yamaoka, T.; Ohmori, T.; Ohba, M.; Arata, S.; Kishino, Y.; Murata, Y.; Kusumoto, S.; Ishida, H.; Shirai, T.; Hirose, T.; et al. Acquired Resistance Mechanisms to Combination Met-TKI/EGFR-TKI Exposure in Met-Amplified EGFR-TKI-Resistant Lung Adenocarcinoma Harboring an Activating EGFR Mutation. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2016, 15, 3040–3054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ando, K.; Ohmori, T.; Inoue, F.; Kadofuku, T.; Hosaka, T.; Ishida, H.; Shirai, T.; Okuda, K.; Hirose, T.; Horichi, N.; et al. Enhancement of sensitivity to tumor necrosis factor alpha in non-small cell lung cancer cells with acquired resistance to gefitinib. Clin. Cancer Res. 2005, 11, 8872–8879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yamaoka, T.; Ohmori, T.; Ohba, M.; Arata, S.; Murata, Y.; Kusumoto, S.; Ando, K.; Ishida, H.; Ohnishi, T.; Sasaki, Y. Distinct Afatinib Resistance Mechanisms Identified in Lung Adenocarcinoma Harboring an EGFR Mutation. Mol. Cancer Res. 2017, 15, 915–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tabara, K.; Kanda, R.; Sonoda, K.; Kubo, T.; Murakami, Y.; Kawahara, A.; Azuma, K.; Abe, H.; Kage, M.; Yoshinaga, A.; et al. Loss of activating EGFR mutant gene contributes to acquired resistance to EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitors in lung cancer cells. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e41017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nukaga, S.; Yasuda, H.; Tsuchihara, K.; Hamamoto, J.; Masuzawa, K.; Kawada, I.; Naoki, K.; Matsumoto, S.; Mimaki, S.; Ikemura, S.; et al. Amplification of EGFR Wild-Type Alleles in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Cells Confers Acquired Resistance to Mutation-Selective EGFR Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors. Cancer Res. 2017, 77, 2078–2089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cortot, A.B.; Repellin, C.E.; Shimamura, T.; Capelletti, M.; Zejnullahu, K.; Ercan, D.; Christensen, J.G.; Wong, K.K.; Gray, N.S.; Janne, P.A. Resistance to irreversible EGF receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitors through a multistep mechanism involving the IGF1R pathway. Cancer Res. 2013, 73, 834–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Manabe, T.; Yasuda, H.; Terai, H.; Kagiwada, H.; Hamamoto, J.; Ebisudani, T.; Kobayashi, K.; Masuzawa, K.; Ikemura, S.; Kawada, I.; et al. IGF2 Autocrine-Mediated IGF1R Activation Is a Clinically Relevant Mechanism of Osimertinib Resistance in Lung Cancer. Mol. Cancer Res. 2020, 18, 549–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Friedbichler, K.; Hofmann, M.H.; Kroez, M.; Ostermann, E.; Lamche, H.R.; Koessl, C.; Borges, E.; Pollak, M.N.; Adolf, G.; Adam, P.J. Pharmacodynamic and antineoplastic activity of BI 836845, a fully human IGF ligand-neutralizing antibody, and mechanistic rationale for combination with rapamycin. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2014, 13, 399–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, H.G.; Rapp, U.R.; Reed, J.C. Bcl-2 targets the protein kinase Raf-1 to mitochondria. Cell 1996, 87, 629–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Adams, J.M.; Cory, S. The Bcl-2 apoptotic switch in cancer development and therapy. Oncogene 2007, 26, 1324–1337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hsu, Y.T.; Youle, R.J. Nonionic detergents induce dimerization among members of the Bcl-2 family. J. Biol. Chem. 1997, 272, 13829–13834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gross, A.; Yin, X.M.; Wang, K.; Wei, M.C.; Jockel, J.; Milliman, C.; Erdjument-Bromage, H.; Tempst, P.; Korsmeyer, S.J. Caspase cleaved BID targets mitochondria and is required for cytochrome c release, while BCL-XL prevents this release but not tumor necrosis factor-R1/Fas death. J. Biol. Chem. 1999, 274, 1156–1163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hengartner, M.O. The biochemistry of apoptosis. Nature 2000, 407, 770–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neel, B.G.; Gu, H.; Pao, L. The ‘Shp’ing news: SH2 domain-containing tyrosine phosphatases in cell signaling. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2003, 28, 284–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.Y.; Yu, Z.H.; Chen, L.; Walls, C.D.; Zhang, S.; Wu, L.; Zhang, Z.Y. Mechanistic insights explain the transforming potential of the T507K substitution in the protein-tyrosine phosphatase SHP2. J. Biol. Chem. 2020, 295, 6187–6201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cunnick, J.M.; Dorsey, J.F.; Munoz-Antonia, T.; Mei, L.; Wu, J. Requirement of SHP2 binding to Grb2-associated binder-1 for mitogen-activated protein kinase activation in response to lysophosphatidic acid and epidermal growth factor. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 13842–13848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Oxnard, G.R.; Hu, Y.; Mileham, K.F.; Husain, H.; Costa, D.B.; Tracy, P.; Feeney, N.; Sholl, L.M.; Dahlberg, S.E.; Redig, A.J.; et al. Assessment of Resistance Mechanisms and Clinical Implications in Patients with EGFR T790M-Positive Lung Cancer and Acquired Resistance to Osimertinib. JAMA Oncol. 2018, 4, 1527–1534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Roper, N.; Brown, A.L.; Wei, J.S.; Pack, S.; Trindade, C.; Kim, C.; Restifo, O.; Gao, S.; Sindiri, S.; Mehrabadi, F.; et al. Clonal Evolution and Heterogeneity of Osimertinib Acquired Resistance Mechanisms in EGFR Mutant Lung Cancer. Cell Rep. Med. 2020, 1, 100007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortiz-Cuaran, S.; Scheffler, M.; Plenker, D.; Dahmen, L.; Scheel, A.H.; Fernandez-Cuesta, L.; Meder, L.; Lovly, C.M.; Persigehl, T.; Merkelbach-Bruse, S.; et al. Heterogeneous Mechanisms of Primary and Acquired Resistance to Third-Generation EGFR Inhibitors. Clin. Cancer Res. 2016, 22, 4837–4847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shi, P.; Oh, Y.T.; Deng, L.; Zhang, G.; Qian, G.; Zhang, S.; Ren, H.; Wu, G.; Legendre, B., Jr.; Anderson, E.; et al. Overcoming Acquired Resistance to AZD9291, A Third-Generation EGFR Inhibitor, through Modulation of MEK/ERK-Dependent Bim and Mcl-1 Degradation. Clin. Cancer Res. 2017, 23, 6567–6579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Costa, D.B.; Halmos, B.; Kumar, A.; Schumer, S.T.; Huberman, M.S.; Boggon, T.J.; Tenen, D.G.; Kobayashi, S. BIM mediates EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitor-induced apoptosis in lung cancers with oncogenic EGFR mutations. PLoS Med. 2007, 4, 1669–1679, discussion 1680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gong, Y.; Somwar, R.; Politi, K.; Balak, M.; Chmielecki, J.; Jiang, X.; Pao, W. Induction of BIM is essential for apoptosis triggered by EGFR kinase inhibitors in mutant EGFR-dependent lung adenocarcinomas. PLoS Med. 2007, 4, e294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newsom-Davis, T.; Prieske, S.; Walczak, H. Is TRAIL the holy grail of cancer therapy? Apoptosis 2009, 14, 607–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Zhu, H.; Xu, C.J.; Yuan, J. Cleavage of BID by caspase 8 mediates the mitochondrial damage in the Fas pathway of apoptosis. Cell 1998, 94, 491–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shi, P.; Zhang, S.; Zhu, L.; Qian, G.; Ren, H.; Ramalingam, S.S.; Chen, M.; Sun, S.Y. The Third-Generation EGFR Inhibitor, Osimertinib, Promotes c-FLIP Degradation, Enhancing Apoptosis Including TRAIL-Induced Apoptosis in NSCLC Cells with Activating EGFR Mutations. Transl. Oncol. 2019, 12, 705–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bentires-Alj, M.; Paez, J.G.; David, F.S.; Keilhack, H.; Halmos, B.; Naoki, K.; Maris, J.M.; Richardson, A.; Bardelli, A.; Sugarbaker, D.J.; et al. Activating mutations of the noonan syndrome-associated SHP2/PTPN11 gene in human solid tumors and adult acute myelogenous leukemia. Cancer Res. 2004, 64, 8816–8820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Miyamoto, D.; Miyamoto, M.; Takahashi, A.; Yomogita, Y.; Higashi, H.; Kondo, S.; Hatakeyama, M. Isolation of a distinct class of gain-of-function SHP-2 mutants with oncogenic RAS-like transforming activity from solid tumors. Oncogene 2008, 27, 3508–3515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brennan, C.W.; Verhaak, R.G.; McKenna, A.; Campos, B.; Noushmehr, H.; Salama, S.R.; Zheng, S.; Chakravarty, D.; Sanborn, J.Z.; Berman, S.H.; et al. The somatic genomic landscape of glioblastoma. Cell 2013, 155, 462–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, H.; Neel, B.G. The “Gab” in signal transduction. Trends Cell Biol. 2003, 13, 122–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cunnick, J.M.; Meng, S.; Ren, Y.; Desponts, C.; Wang, H.G.; Djeu, J.Y.; Wu, J. Regulation of the mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling pathway by SHP2. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 9498–9504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- LaMarche, M.J.; Acker, M.; Argintaru, A.; Bauer, D.; Boisclair, J.; Chan, H.; Chen, C.H.; Chen, Y.N.; Chen, Z.; Deng, Z.; et al. Identification of TNO155, an Allosteric SHP2 Inhibitor for the Treatment of Cancer. J. Med. Chem. 2020, 63, 13578–13594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nishihara, S.; Yamaoka, T.; Ishikawa, F.; Ohmori, T.; Ando, K.; Kusumoto, S.; Kishino, Y.; Manabe, R.; Hasebe, Y.; Sagara, H.; et al. Diverse Mechanisms of Resistance against Osimertinib, a Third-Generation EGFR-TKI, in Lung Adenocarcinoma Cells with an EGFR-Activating Mutation. Cells 2022, 11, 2201. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells11142201
Nishihara S, Yamaoka T, Ishikawa F, Ohmori T, Ando K, Kusumoto S, Kishino Y, Manabe R, Hasebe Y, Sagara H, et al. Diverse Mechanisms of Resistance against Osimertinib, a Third-Generation EGFR-TKI, in Lung Adenocarcinoma Cells with an EGFR-Activating Mutation. Cells. 2022; 11(14):2201. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells11142201
Chicago/Turabian StyleNishihara, Shigetoshi, Toshimitsu Yamaoka, Fumihiro Ishikawa, Tohru Ohmori, Koichi Ando, Sojiro Kusumoto, Yasunari Kishino, Ryo Manabe, Yuki Hasebe, Hironori Sagara, and et al. 2022. "Diverse Mechanisms of Resistance against Osimertinib, a Third-Generation EGFR-TKI, in Lung Adenocarcinoma Cells with an EGFR-Activating Mutation" Cells 11, no. 14: 2201. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells11142201
APA StyleNishihara, S., Yamaoka, T., Ishikawa, F., Ohmori, T., Ando, K., Kusumoto, S., Kishino, Y., Manabe, R., Hasebe, Y., Sagara, H., Yoshida, H., & Tsurutani, J. (2022). Diverse Mechanisms of Resistance against Osimertinib, a Third-Generation EGFR-TKI, in Lung Adenocarcinoma Cells with an EGFR-Activating Mutation. Cells, 11(14), 2201. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells11142201







