Sweat Proteomics in Cystic Fibrosis: Discovering Companion Biomarkers for Precision Medicine and Therapeutic Development
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
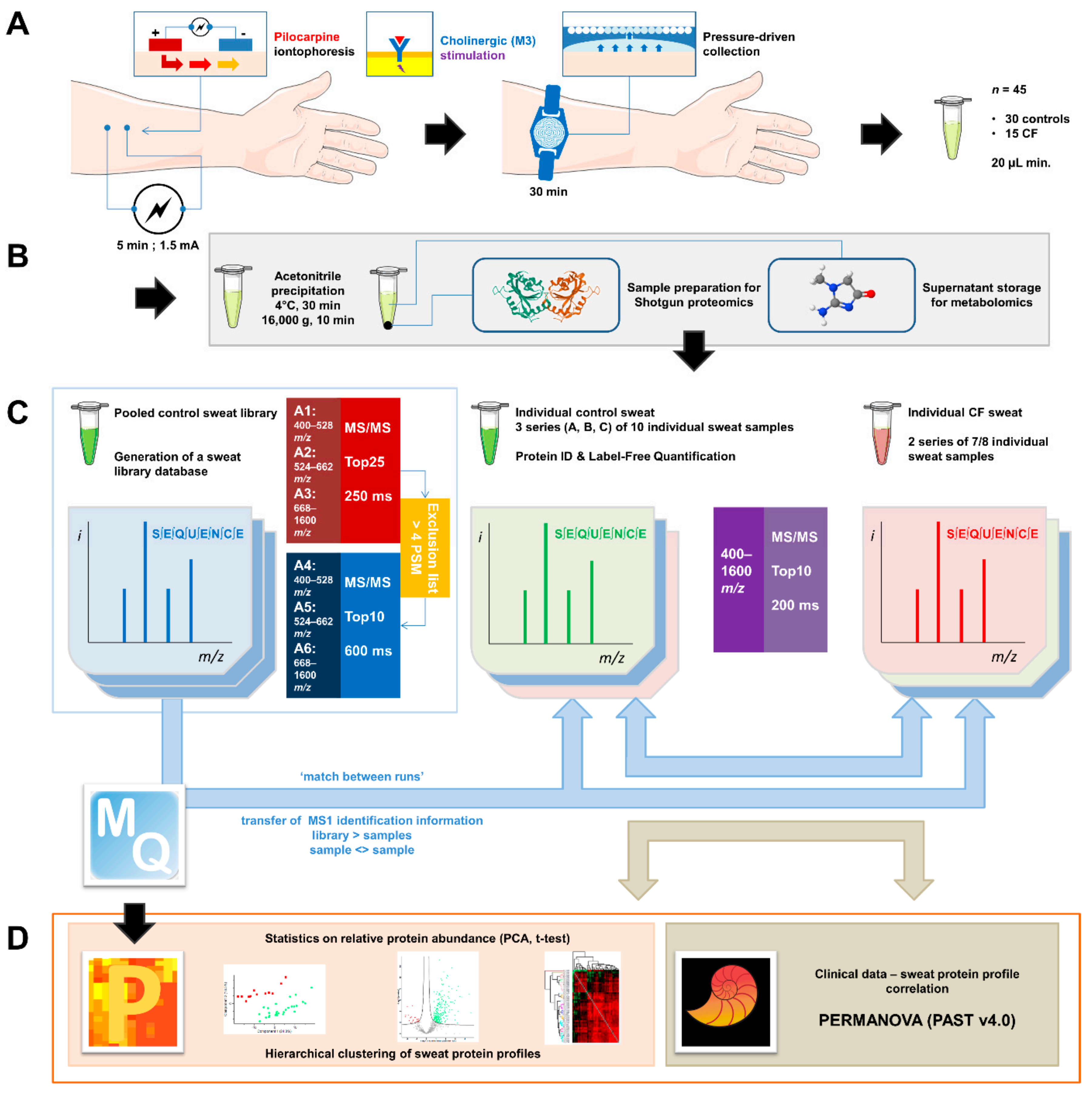
2.1. Sweat Collection
2.2. Sample Preparation for Shotgun Proteomics
2.3. Liquid Chromatography and Mass Spectrometry Data Acquisition
2.4. Bioinformatic Analysis
2.5. Characterization of Sweat Actin
2.6. Experimental Design and Statistical Rationale
3. Results
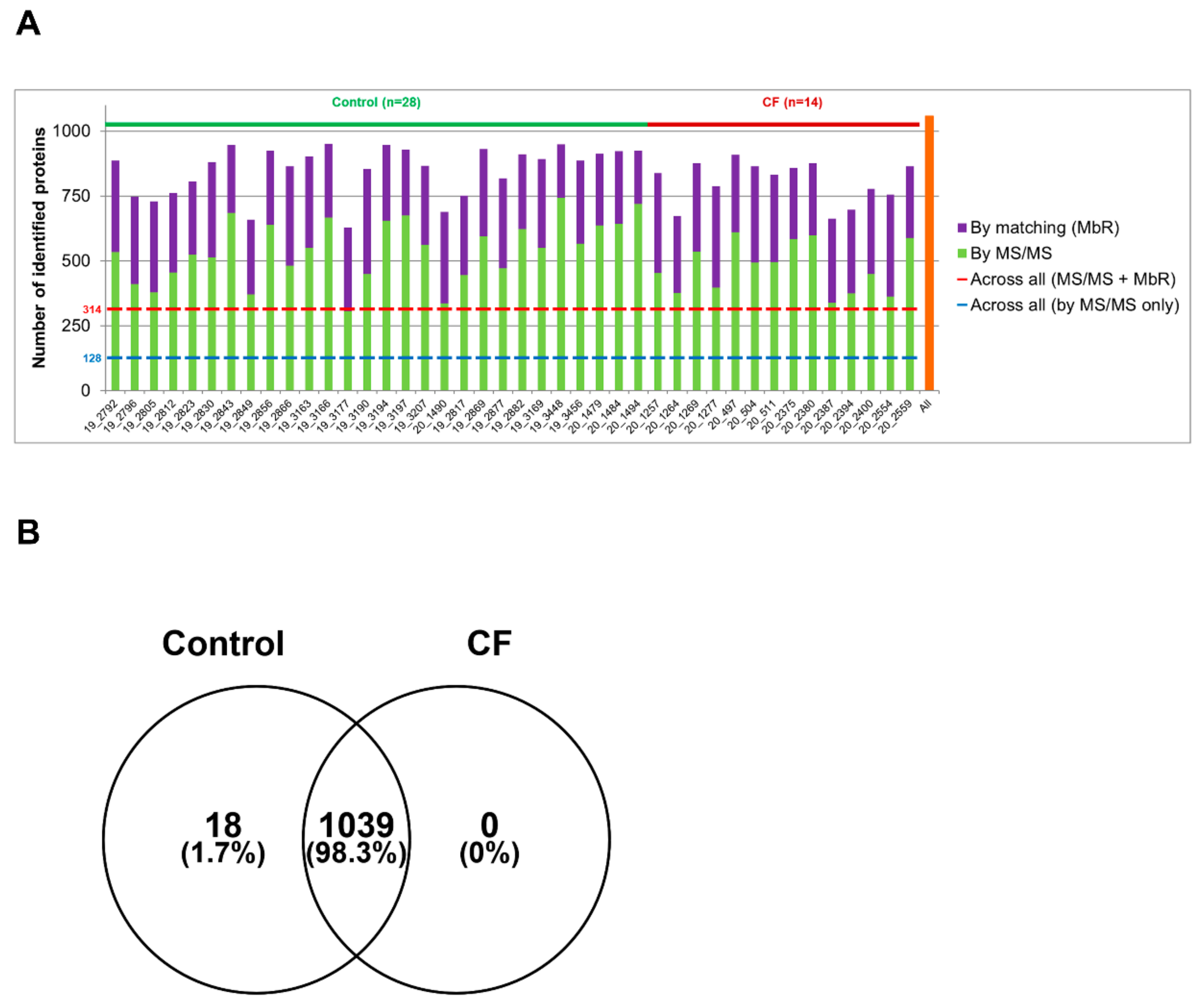
3.1. The Proteome of CF Sweat
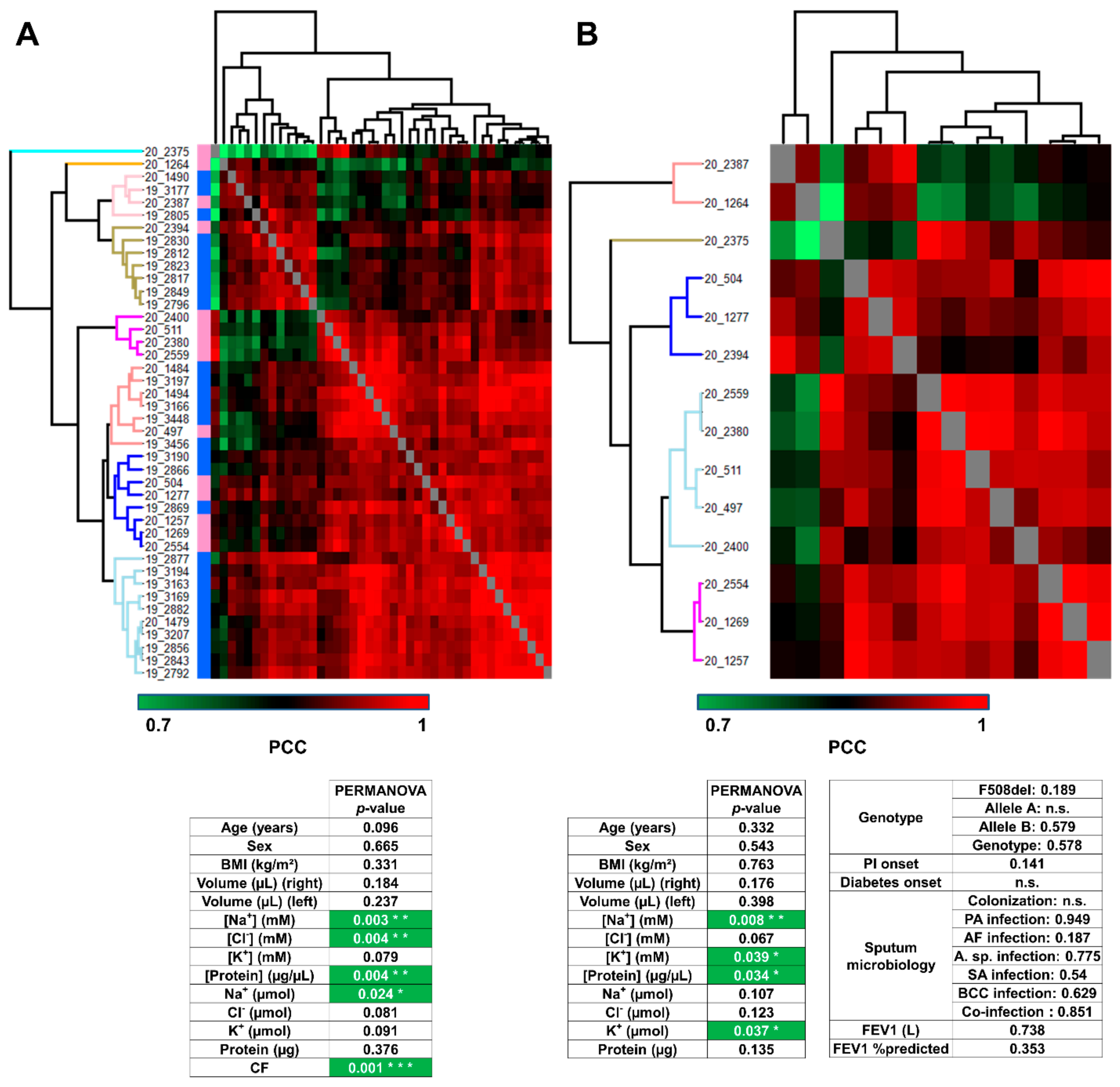
3.2. Analysis of Sweat Proteome Profiles
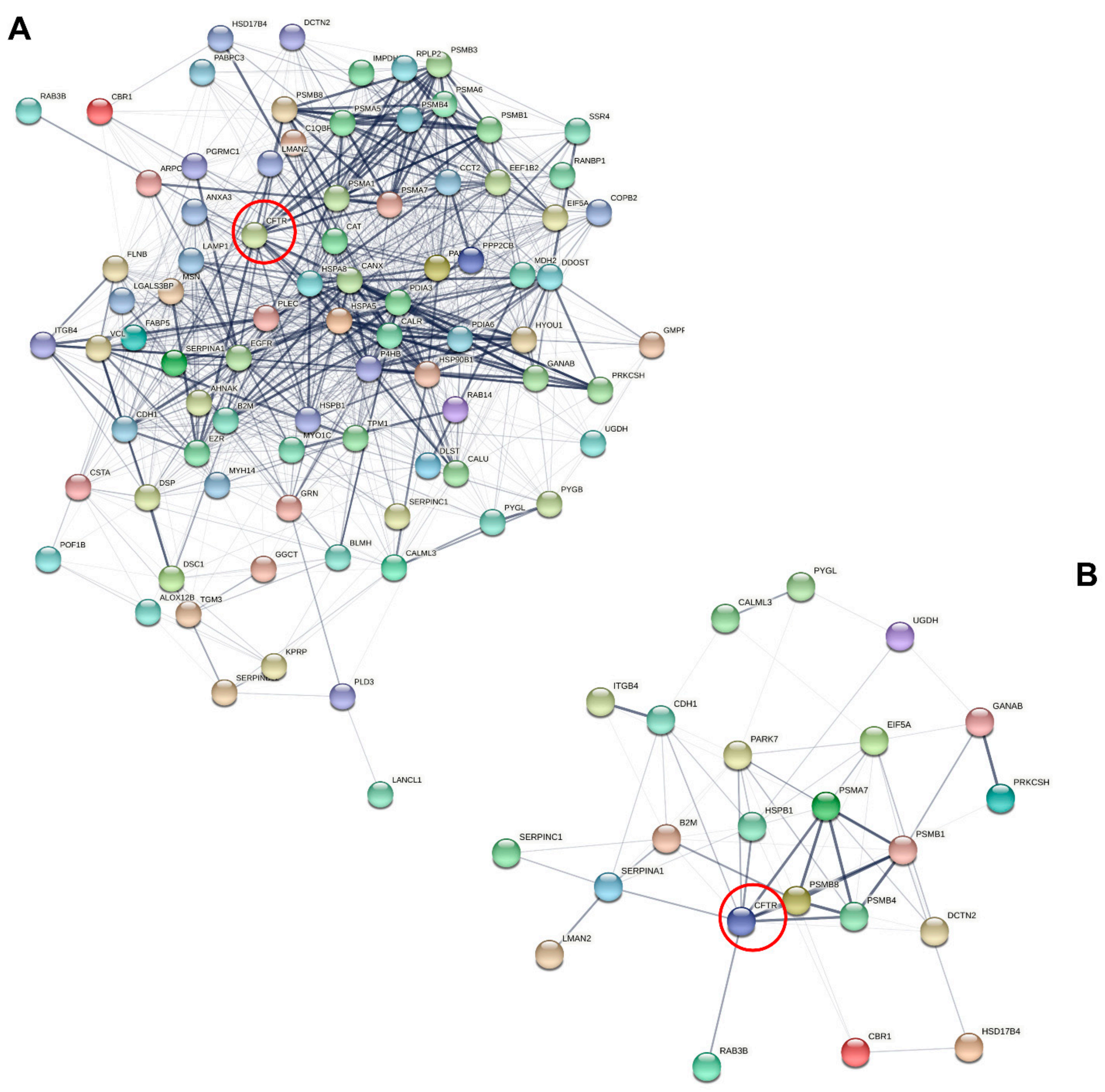
3.3. Characterization of Candidate CF Biomarkers
CF Biomarker Profiles Partially Reflect CF Severity Related to CFTR Genotype
3.4. Characterization of CF Severity Biomarkers
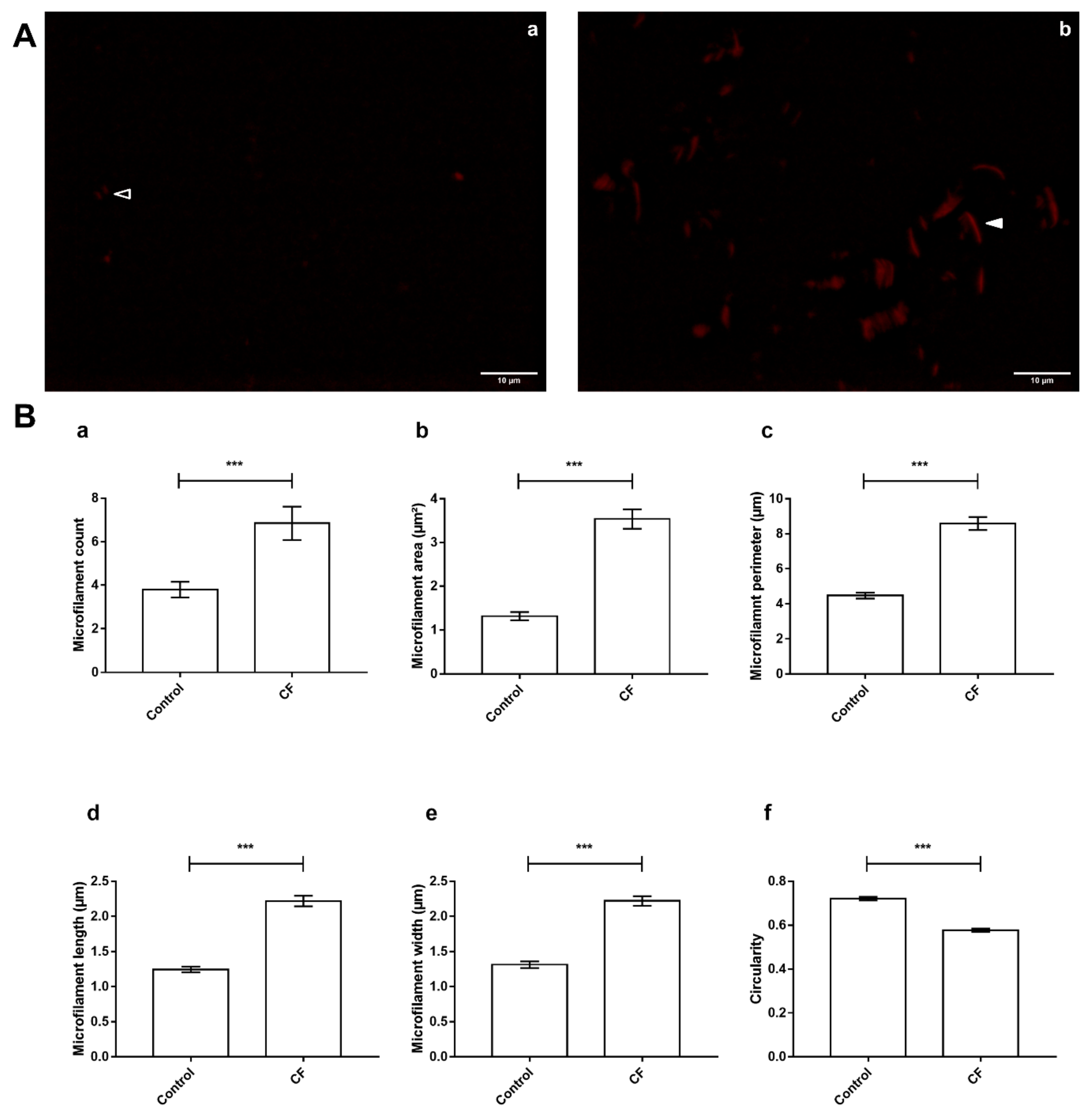
3.5. Actin Dynamics in CF Sweat
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ABP | Actin-Binding Proteins |
| ACT | Actin |
| ADH | Alcohol dehydrogenase 1 |
| ARPC | Actin-related protein complex 2/3 subunit |
| BMI | Body Mass Index |
| CF | Cystic Fibrosis |
| CFL | Cofilin-1 |
| DTT | Dithiothreitol |
| ER | Endoplasmic Reticulum |
| FDR | False Discovery Rate |
| FEV | Forced Expiratory Volume |
| IMD | IRSp53 and MIM (Missing In Metastases) homology Domain |
| LFQ | Label-Free Quantification |
| LYZ | Lysozyme C |
| MbR | Match between Runs |
| MPDS | MassPREP Digestion Standard |
| PCA | Principal Component Analysis |
| PCC | Pearson’s Correlation Coefficients |
| PERMANOVA | PERmutational Multivariate ANalysis Of Variance |
| PSM | Peptide-Spectrum Match |
| RP | Reverse Phase |
| TFA | TriFluoroacetic Acid |
| TRITC | TetramethylRhodamine IsoThioCyanate |
| UHPLC | Ultra High-Performance Liquid Chromatography |
| UPR | Unfolded Protein Response |
References
- Farrell, P.M.; Rosenstein, B.J.; White, T.B.; Accurso, F.J.; Castellani, C.; Cutting, G.R.; Durie, P.R.; LeGrys, V.A.; Massie, J.; Parad, R.B.; et al. Guidelines for Diagnosis of Cystic Fibrosis in Newborns through Older Adults: Cystic Fibrosis Foundation Consensus Report. J. Pediatr. 2008, 153, S4–S14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farrell, P.M.; White, T.B.; Ren, C.L.; Hempstead, S.E.; Accurso, F.; Derichs, N.; Howenstine, M.; McColley, S.A.; Rock, M.; Rosenfeld, M.; et al. Diagnosis of Cystic Fibrosis: Consensus Guidelines from the Cystic Fibrosis Foundation. J. Pediatr. 2017, 181, S4–S15.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cystic Fibrosis Mutation Database. Available online: http://www.genet.sickkids.on.ca/cftr/app (accessed on 6 January 2021).
- Bareil, C.; Thèze, C.; Béroud, C.; Hamroun, D.; Guittard, C.; René, C.; Paulet, D.; des Georges, M.; Claustres, M. UMD-CFTR: A Database Dedicated to CF and CFTR-Related Disorders. Hum. Mutat. 2010, 31, 1011–1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- The CFTR Mutations Database. Available online: http://www.umd.be/CFTR/ (accessed on 6 January 2021).
- Levy, H.; Farrell, P.M. New Challenges in the Diagnosis and Management of Cystic Fibrosis. J. Pediatr. 2015, 166, 1337–1341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vermeulen, F.; Lebecque, P.; De Boeck, K.; Leal, T. Biological Variability of the Sweat Chloride in Diagnostic Sweat Tests: A Retrospective Analysis. J. Cyst. Fibros. 2017, 16, 30–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vij, N. Prognosis-Based Early Intervention Strategies to Resolve Exacerbation and Progressive Lung Function Decline in Cystic Fibrosis. JPM 2021, 11, 96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muhlebach, M.S.; Clancy, J.; Heltshe, S.L.; Ziady, A.; Kelley, T.; Accurso, F.; Pilewski, J.; Mayer-Hamblett, N.; Joseloff, E.; Sagel, S.D. Biomarkers for Cystic Fibrosis Drug Development. J. Cyst. Fibros. 2016, 15, 714–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayer-Hamblett, N.; VanDevanter, D.R. Accelerated Approval or Risk Reduction? How Response Biomarkers Advance Therapeutics through Clinical Trials in Cystic Fibrosis. Trends Mol. Med. 2020, 26, 1068–1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, R.; Baines, A.; Khan, U.; Wagner, B.D.; Sagel, S.D. Evaluation of Airway and Circulating Inflammatory Biomarkers for Cystic Fibrosis Drug Development. J. Cyst. Fibros. 2021, 20, 50–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raiszadeh, M.M.; Ross, M.M.; Russo, P.S.; Schaepper, M.A.; Zhou, W.; Deng, J.; Ng, D.; Dickson, A.; Dickson, C.; Strom, M.; et al. Proteomic Analysis of Eccrine Sweat: Implications for the Discovery of Schizophrenia Biomarker Proteins. J. Proteome Res. 2012, 11, 2127–2139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adewole, O.O.; Erhabor, G.E.; Adewole, T.O.; Ojo, A.O.; Oshokoya, H.; Wolfe, L.M.; Prenni, J.E. Proteomic Profiling of Eccrine Sweat Reveals Its Potential as a Diagnostic Biofluid for Active Tuberculosis. Prot. Clin. Appl. 2016, 10, 547–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harshman, S.W.; Pitsch, R.L.; Smith, Z.K.; O’Connor, M.L.; Geier, B.A.; Qualley, A.V.; Schaeublin, N.M.; Fischer, M.V.; Eckerle, J.J.; Strang, A.J.; et al. The Proteomic and Metabolomic Characterization of Exercise-Induced Sweat for Human Performance Monitoring: A Pilot Investigation. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0203133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katchman, B.A.; Zhu, M.; Blain Christen, J.; Anderson, K.S. Eccrine Sweat as a Biofluid for Profiling Immune Biomarkers. PROTEOMICS-Clin. Appl. 2018, 12, 1800010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- C34: Sweat Sample Collection & Chloride Analysis—CLSI. Available online: https://clsi.org/standards/products/clinical-chemistry-and-toxicology/documents/c34/ (accessed on 7 May 2021).
- Tyanova, S.; Temu, T.; Cox, J. The MaxQuant Computational Platform for Mass Spectrometry-Based Shotgun Proteomics. Nat. Protoc. 2016, 11, 2301–2319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tyanova, S.; Temu, T.; Sinitcyn, P.; Carlson, A.; Hein, M.Y.; Geiger, T.; Mann, M.; Cox, J. The Perseus Computational Platform for Comprehensive Analysis of (Prote)Omics Data. Nat. Methods 2016, 13, 731–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Past: Paleontological Statistics Software Package for Education and Data Analysis. Available online: https://palaeo-electronica.org/2001_1/past/issue1_01.htm (accessed on 6 January 2021).
- Wiśniewski, J.R.; Hein, M.Y.; Cox, J.; Mann, M. A “Proteomic Ruler” for Protein Copy Number and Concentration Estimation without Spike-in Standards. Mol. Cell. Proteomics 2014, 13, 3497–3506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapur, J.N.; Sahoo, P.K.; Wong, A.K.C. A New Method for Gray-Level Picture Thresholding Using the Entropy of the Histogram. Comput. Vis. Graph. Image Process. 1985, 29, 273–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burat, B.; Reynaerts, A.; Baiwir, D.; Fléron, M.; Eppe, G.; Leal, T.; Mazzucchelli, G. Characterization of the Human Eccrine Sweat Proteome—A Focus on the Biological Variability of Individual Sweat Protein Profiles. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 10871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pankow, S.; Bamberger, C.; Calzolari, D.; Martínez-Bartolomé, S.; Lavallée-Adam, M.; Balch, W.E.; Yates, J.R. ∆F508 CFTR Interactome Remodelling Promotes Rescue of Cystic Fibrosis. Nature 2015, 528, 510–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Preumont, V.; Hermans, M.P.; Lebecque, P.; Buysschaert, M. Glucose Homeostasis and Genotype-Phenotype Interplay in Cystic Fibrosis Patients with CFTR Gene F508 Mutation. Diabetes Care 2007, 30, 1187–1192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Veit, G.; Oliver, K.; Apaja, P.M.; Perdomo, D.; Bidaud-Meynard, A.; Lin, S.-T.; Guo, J.; Icyuz, M.; Sorscher, E.J.; Hartman, J.L.; et al. Ribosomal Stalk Protein Silencing Partially Corrects the ΔF508-CFTR Functional Expression Defect. PLoS Biol. 2016, 14, e1002462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zucollo, A.; Martiarena, J.; Luna, C.; Pivetta, O.; Villagra, A.; Catanzaro, O. The Kallikrein-Kinin System of Sweat in Normal and Cystic Fibrosis Subjects. Agents Actions Suppl. 1992, 38 Pt 3, 493–498. [Google Scholar]
- Rao, G.J.S.; Posner, L.A.; Nadler, H.L. Deficiency of Kallikrein Activity in Plasma of Patients with Cystic Fibrosis. Science 1972, 177, 610–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, K.Y.H.; Applegarth, D.A.; George, A.; Davidson, F. Plasma Arginine Esterase Activity in Cystic Fibrosis of the Pancreas. Clin. Chim. Acta 1977, 74, 71–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thelin, W.R.; Chen, Y.; Gentzsch, M.; Kreda, S.M.; Sallee, J.L.; Scarlett, C.O.; Borchers, C.H.; Jacobson, K.; Stutts, M.J.; Milgram, S.L. Direct Interaction with Filamins Modulates the Stability and Plasma Membrane Expression of CFTR. J. Clin. Investig. 2007, 117, 364–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peters-Hall, J.R.; Brown, K.J.; Pillai, D.K.; Tomney, A.; Garvin, L.M.; Wu, X.; Rose, M.C. Quantitative Proteomics Reveals an Altered Cystic Fibrosis In Vitro Bronchial Epithelial Secretome. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2015, 53, 22–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rauniyar, N.; Gupta, V.; Balch, W.E.; Yates, J.R. Quantitative Proteomic Profiling Reveals Differentially Regulated Proteins in Cystic Fibrosis Cells. J. Proteome Res. 2014, 13, 4668–4675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Puglia, M.; Landi, C.; Gagliardi, A.; Breslin, L.; Armini, A.; Brunetti, J.; Pini, A.; Bianchi, L.; Bini, L. The Proteome Speciation of an Immortalized Cystic Fibrosis Cell Line: New Perspectives on the Pathophysiology of the Disease. J. Proteomics 2018, 170, 28–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roxo-Rosa, M.; da Costa, G.; Luider, T.M.; Scholte, B.J.; Coelho, A.V.; Amaral, M.D.; Penque, D. Proteomic Analysis of Nasal Cells from Cystic Fibrosis Patients and Non-Cystic Fibrosis Control Individuals: Search for Novel Biomarkers of Cystic Fibrosis Lung Disease. Proteomics 2006, 6, 2314–2325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benabdelkamel, H.; Alamri, H.; Okla, M.; Masood, A.; Abdel Jabar, M.; Alanazi, I.O.; Alfadda, A.A.; Nizami, I.; Dasouki, M.; Abdel Rahman, A.M. Serum-Based Proteomics Profiling in Adult Patients with Cystic Fibrosis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 7415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gauthier, S.; Pranke, I.; Jung, V.; Martignetti, L.; Stoven, V.; Nguyen-Khoa, T.; Semeraro, M.; Hinzpeter, A.; Edelman, A.; Guerrera, I.C.; et al. Urinary Exosomes of Patients with Cystic Fibrosis Unravel CFTR-Related Renal Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 6625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bamburg, J.R.; Harris, H.E.; Weeds, A.G. Partial Purification and Characterization of an Actin Depolymerizing Factor from Brain. FEBS Lett. 1980, 121, 178–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernstein, B.W.; Bamburg, J.R. ADF/Cofilin: A Functional Node in Cell Biology. Trends Cell Biol. 2010, 20, 187–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanellos, G.; Frame, M.C. Cellular Functions of the ADF/Cofilin Family at a Glance. J. Cell Sci. 2016, 129, 3211–3218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vantroys, M.; Huyck, L.; Leyman, S.; Dhaese, S.; Vandekerkhove, J.; Ampe, C. Ins and Outs of ADF/Cofilin Activity and Regulation. Eur. J. Cell Biol. 2008, 87, 649–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeoh, S.; Pope, B.; Mannherz, H.G.; Weeds, A. Determining the Differences in Actin Binding by Human ADF and Cofilin1. J. Mol. Biol. 2002, 315, 911–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andrianantoandro, E.; Pollard, T.D. Mechanism of Actin Filament Turnover by Severing and Nucleation at Different Concentrations of ADF/Cofilin. Mol. Cell 2006, 24, 13–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frantz, C.; Barreiro, G.; Dominguez, L.; Chen, X.; Eddy, R.; Condeelis, J.; Kelly, M.J.S.; Jacobson, M.P.; Barber, D.L. Cofilin Is a PH Sensor for Actin Free Barbed End Formation: Role of Phosphoinositide Binding. J. Cell Biol. 2008, 183, 865–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, K.; Kang, W.H.; Saga, K.; Sato, K.T. Biology of Sweat Glands and Their Disorders. I. Normal Sweat Gland Function. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 1989, 20, 537–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emrich, H.M.; Stoll, E.; Friolet, B.; Colombo, J.P.; Richterich, R.; Rossi, E. Sweat Composition in Relation to Rate of Sweating in Patients with Cystic Fibrosis of the Pancreas. Pediatr. Res. 1968, 2, 464–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuhn, T.B.; Bamburg, J.R. Tropomyosin and ADF/Cofilin as Collaborators and Competitors. In Tropomyosin; Gunning, P., Ed.; Advances in Experimental Medicine and Biology; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2008; Volume 644, pp. 232–249. ISBN 978-0-387-85765-7. [Google Scholar]
- Ono, S.; Ono, K. Tropomyosin Inhibits ADF/Cofilin-Dependent Actin Filament Dynamics. J. Cell Biol. 2002, 156, 1065–1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taoka, M.; Ichimura, T.; Wakamiya-Tsuruta, A.; Kubota, Y.; Araki, T.; Obinata, T.; Isobe, T. V-1, a Protein Expressed Transiently during Murine Cerebellar Development, Regulates Actin Polymerization via Interaction with Capping Protein. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 5864–5870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamagishi, A.; Masuda, M.; Ohki, T.; Onishi, H.; Mochizuki, N. A Novel Actin Bundling/Filopodium-Forming Domain Conserved in Insulin Receptor Tyrosine Kinase Substrate P53 and Missing in Metastasis Protein. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 14929–14936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Millard, T.H.; Bompard, G.; Heung, M.Y.; Dafforn, T.R.; Scott, D.J.; Machesky, L.M.; Fütterer, K. Structural Basis of Filopodia Formation Induced by the IRSp53/MIM Homology Domain of Human IRSp53. EMBO J. 2005, 24, 240–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosslenbroich, V.; Dai, L.; Baader, S.L.; Noegel, A.A.; Gieselmann, V.; Kappler, J. Collapsin Response Mediator Protein-4 Regulates F-Actin Bundling. Exp. Cell Res. 2005, 310, 434–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanders, L.K.; Xian, W.; Guaqueta, C.; Strohman, M.J.; Vrasich, C.R.; Luijten, E.; Wong, G.C.L. Control of Electrostatic Interactions between F-Actin and Genetically Modified Lysozyme in Aqueous Media. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 15994–15999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sol, A.; Blotnick, E.; Bachrach, G.; Muhlrad, A. LL-37 Induces Polymerization and Bundling of Actin and Affects Actin Structure. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e50078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Muhlrad, A.; Grintsevich, E.E.; Reisler, E. Polycation Induced Actin Bundles. Biophys. Chem. 2011, 155, 45–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Vasconcellos, C.; Allen, P.; Wohl, M.; Drazen, J.; Janmey, P.; Stossel, T. Reduction in Viscosity of Cystic Fibrosis Sputum in Vitro by Gelsolin. Science 1994, 263, 969–971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schultz, A.; Puvvadi, R.; Borisov, S.M.; Shaw, N.C.; Klimant, I.; Berry, L.J.; Montgomery, S.T.; Nguyen, T.; Kreda, S.M.; Kicic, A.; et al. Airway Surface Liquid PH Is Not Acidic in Children with Cystic Fibrosis. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 1409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hill, D.B.; Long, R.F.; Kissner, W.J.; Atieh, E.; Garbarine, I.C.; Markovetz, M.R.; Fontana, N.C.; Christy, M.; Habibpour, M.; Tarran, R.; et al. Pathological Mucus and Impaired Mucus Clearance in Cystic Fibrosis Patients Result from Increased Concentration, Not Altered PH. Eur. Respir. J. 2018, 52, 1801297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shibuya, Y.; Wills, P.J.; Cole, P.J. Effect of Osmolality on Mucociliary Transportability and Rheology of Cystic Fibrosis and Bronchiectasis Sputum. Respirology 2003, 8, 181–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murakami, M.; Ohtake, T.; Dorschner, R.A.; Gallo, R.L.; Schittek, B.; Garbe, C. Cathelicidin Anti-Microbial Peptide Expression in Sweat, an Innate Defense System for the Skin. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2002, 119, 1090–1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiner, D.J.; Bucki, R.; Janmey, P.A. The Antimicrobial Activity of the Cathelicidin LL37 Is Inhibited by F-Actin Bundles and Restored by Gelsolin. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2003, 28, 738–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schittek, B.; Hipfel, R.; Sauer, B.; Bauer, J.; Kalbacher, H.; Stevanovic, S.; Schirle, M.; Schroeder, K.; Blin, N.; Meier, F.; et al. Dermcidin: A Novel Human Antibiotic Peptide Secreted by Sweat Glands. Nat. Immunol. 2001, 2, 1133–1137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baechle, D.; Flad, T.; Cansier, A.; Steffen, H.; Schittek, B.; Tolson, J.; Herrmann, T.; Dihazi, H.; Beck, A.; Mueller, G.A.; et al. Cathepsin D Is Present in Human Eccrine Sweat and Involved in the Postsecretory Processing of the Antimicrobial Peptide DCD-1L. J. Biol. Chem. 2006, 281, 5406–5415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Csősz, É.; Emri, G.; Kalló, G.; Tsaprailis, G.; Tőzsér, J. Highly Abundant Defense Proteins in Human Sweat as Revealed by Targeted Proteomics and Label-Free Quantification Mass Spectrometry. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2015, 29, 2024–2031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Sample IDs | Age (Years) | Sex | BMI (kg/m2) | Collected Volume (µL) (Right Arm) | Collected Volume (µL) (Left Arm) | [Na+] (mM) | [Cl−] (mM) | [K+] (mM) | [Protein] (µg/µL) | Na+ (µmol) | Cl− (µmol) | K+ (µmol) | Protein (µg) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 19_2792 | 36 | M | 22.7 | 62.1 | 87.8 | 56 | 26 | 8 | 0.488 | 3.48 | 1.61 | 0.50 | 42.85 | Control (n = 28) |
| 19_2796 | 29 | M | 31.6 | 48.1 | 42.4 | 23 | 4 | 10 | 0.557 | 1.11 | 0.19 | 0.48 | 23.62 | |
| 19_2805 | 28 | M | 30.0 | 98.9 | 97.5 | 59 | 24 | 7 | 0.340 | 5.84 | 2.37 | 0.69 | 33.15 | |
| 19_2812 | 40 | M | 25.5 | 89.6 | 96.5 | 39 | 18 | 8 | 0.432 | 3.49 | 1.61 | 0.72 | 41.69 | |
| 19_2866 | 74 | M | 21.3 | 56.9 | 64.2 | 37 | 12 | 12 | 0.551 | 2.11 | 0.68 | 0.68 | 35.37 | |
| 19_2823 | 31 | F | 19.8 | 71.8 | 89.8 | 32 | 10 | 10 | 0.262 | 2.30 | 0.72 | 0.72 | 23.53 | |
| 19_2830 | 30 | F | 23.1 | 94.0 | 77.9 | 32 | 11 | 8 | 0.462 | 3.01 | 1.03 | 0.75 | 35.99 | |
| 19_2843 | 24 | F | 18.2 | 63.5 | 64.1 | 65 | 36 | 10 | 0.472 | 4.13 | 2.29 | 0.64 | 30.26 | |
| 19_2849 | 27 | F | 20.5 | 97.7 | 84.6 | 22 | 10 | 8 | 0.432 | 2.15 | 0.98 | 0.78 | 36.55 | |
| 19_2856 | 29 | F | 18.7 | 79.7 | 70.4 | 28 | 6 | 8 | 0.422 | 2.23 | 0.48 | 0.64 | 29.71 | |
| 19_3163 | 32 | F | 19.4 | 44.8 | 30.1 | 30 | 12 | 9 | 0.785 | 1.34 | 0.54 | 0.40 | 23.63 | |
| 19_3166 | 26 | F | 18.9 | 57.2 | 64.0 | 44 | 22 | 10 | 0.494 | 2.52 | 1.26 | 0.57 | 31.62 | |
| 20_1490 | 39 | F | 21.3 | 40.1 | 43.5 | 26 | 12 | 8 | 0.371 | 1.04 | 0.48 | 0.32 | 16.14 | |
| 19_3177 | 28 | M | 23.1 | 35.9 | 27.0 | 51 | 30 | 8 | 0.475 | 1.83 | 1.08 | 0.29 | 12.83 | |
| 19_3190 | 29 | M | 24.5 | 98.6 | 80.7 | 55 | 28 | 6 | 0.406 | 5.42 | 2.76 | 0.59 | 32.76 | |
| 19_3194 | 41 | M | 24.1 | 34.4 | 42.7 | 36 | 8 | 9 | 0.736 | 1.24 | 0.28 | 0.31 | 31.43 | |
| 19_3197 | 36 | M | 22.5 | 27.5 | 82.7 | 91 | 44 | 8 | 0.504 | 2.50 | 1.21 | 0.22 | 41.68 | |
| 19_3207 | 28 | M | 23.8 | 84.9 | 93.2 | 45 | 22 | 7 | 0.364 | 3.82 | 1.87 | 0.59 | 33.92 | |
| 20_1494 | 29 | F | 20.9 | 61.3 | 64.4 | 54 | 30 | 12 | 0.441 | 3.31 | 1.84 | 0.74 | 28.40 | |
| 19_2869 | 28 | F | 17.7 | 57.1 | 45.9 | 67 | 10 | 24 | 0.646 | 3.83 | 0.57 | 1.37 | 29.65 | |
| 19_2877 | 33 | F | 22.3 | 102.7 | 83.7 | 35 | 12 | 7 | 0.350 | 3.59 | 1.23 | 0.72 | 29.30 | |
| 19_2882 | 24 | F | 20.6 | 57.2 | 53.6 | 29 | 10 | 6 | 0.377 | 1.66 | 0.57 | 0.34 | 20.21 | |
| 19_3169 | 57 | F | 19.2 | 35.6 | 29.9 | 58 | 24 | 8 | 0.661 | 2.06 | 0.85 | 0.28 | 19.76 | |
| 20_1479 | 25 | M | 24.5 | 56.4 | 72.6 | 69 | 38 | 7 | 0.336 | 3.89 | 2.14 | 0.39 | 24.39 | |
| 20_1484 | 24 | M | 23.6 | 99.0 | 93.4 | 49 | 20 | 8 | 0.622 | 4.85 | 1.98 | 0.79 | 58.09 | |
| 19_2817 | 26 | M | 20.8 | 47.4 | 40.4 | 73 | 44 | 9 | 0.314 | 3.46 | 2.09 | 0.43 | 12.69 | |
| 19_3448 | 30 | M | 20.6 | 91.2 | 74.0 | 50 | 22 | 10 | 0.448 | 4.56 | 2.01 | 0.91 | 33.15 | |
| 19_3456 | 31 | M | 22.6 | 101.5 | 99.5 | 69 | 40 | 5 | 0.198 | 7.00 | 4.06 | 0.51 | 19.70 | |
| 20_497 | 36 | M | 24.7 | 98.5 | 92.1 | 122 | 106 | 14 | 0.492 | 12.02 | 10.44 | 1.38 | 45.31 | CF (n = 14) |
| 20_504 | 32 | M | 26.8 | 74.6 | 85.8 | 106 | 100 | 17 | 0.424 | 7.91 | 7.46 | 1.27 | 36.38 | |
| 20_511 | 57 | M | 25.3 | 72.0 | 34.6 | 75 | 56 | 9 | 0.472 | 5.40 | 4.03 | 0.65 | 16.33 | |
| 20_1257 | 43 | M | 25.4 | 55.3 | 71.4 | 130 | 102 | 9 | 0.208 | 7.19 | 5.64 | 0.50 | 14.85 | |
| 20_1264 | 31 | M | 20.9 | 54.0 | 30.2 | 103 | 92 | 14 | 1.315 | 5.56 | 4.97 | 0.76 | 39.71 | |
| 20_1269 | 55 | M | 20.5 | 59.9 | 53.1 | 151 | 114 | 8 | 0.237 | 9.04 | 6.83 | 0.48 | 12.58 | |
| 20_1277 | 23 | F | 20.8 | 103.4 | 102.7 | 106 | 102 | 13 | 0.414 | 10.96 | 10.55 | 1.34 | 42.52 | |
| 20_2375 | 46 | F | 21.6 | 14.1 | 43.2 | 67 | 61 | 13 | 1.060 | 0.94 | 0.86 | 0.18 | 45.79 | |
| 20_2380 | 35 | M | 18.5 | 62.9 | 90.3 | 109 | 84 | 14 | 0.489 | 6.86 | 5.28 | 0.88 | 44.16 | |
| 20_2387 | 47 | F | 27.9 | 64.8 | 71.3 | 72 | 68 | 10 | 0.512 | 4.67 | 4.41 | 0.65 | 36.51 | |
| 20_2394 | 30 | M | 25.0 | 77.4 | 75.2 | 110 | 100 | 16 | 0.515 | 8.51 | 7.74 | 1.24 | 38.73 | |
| 20_2400 | 63 | F | 19.7 | 52.2 | 55.3 | 98 | 82 | 15 | 0.404 | 5.12 | 4.28 | 0.78 | 22.34 | |
| 20_2554 | 21 | M | 23.7 | 89.9 | 103.4 | 142 | 108 | 9 | 0.287 | 12.77 | 9.71 | 0.81 | 29.68 | |
| 20_2559 | 54 | M | 19.8 | 18.6 | 47.6 | 123 | 94 | 15 | 0.504 | 2.29 | 1.75 | 0.28 | 23.99 | |
| Mean | 33 | 13 F 15 M | 22.2 | 67.7 | 67.7 | 47 | 21 | 9 | 0.462 | 3.13 | 1.39 | 0.58 | 29.72 | |
| Median | 29 | 21.8 | 61.7 | 71.5 | 47 | 21 | 8 | 0.445 | 3.16 | 1.22 | 0.59 | 29.98 | ||
| SD | 11 | 3.2 | 24.2 | 22.7 | 18 | 12 | 3 | 0.137 | 1.49 | 0.89 | 0.24 | 9.87 | ||
| SEM | 2 | 0.6 | 4.6 | 4.3 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 0.026 | 0.28 | 0.17 | 0.05 | 1.87 | ||
| Mean | 41 | 4 F 10 M | 22.9 | 64.1 | 68.3 | 108 | 91 | 13 | 0.524 | 7.09 | 6.00 | 0.80 | 32.06 | |
| Median | 40 | 22.7 | 63.9 | 71.4 | 108 | 97 | 14 | 0.481 | 7.02 | 5.46 | 0.77 | 36.44 | ||
| SD | 13 | 3.0 | 25.8 | 24.6 | 25 | 18 | 3 | 0.303 | 3.44 | 2.98 | 0.39 | 11.93 | ||
| SEM | 4 | 0.8 | 6.9 | 6.6 | 7 | 5 | 1 | 0.081 | 0.92 | 0.80 | 0.10 | 3.19 | ||
| t-test p-value | 0.034 * | 0.503 | 0.662 | 0.941 | <0.001 *** | <0.001 *** | 0.001 ** | 0.368 | <0.001 *** | <0.001 *** | 0.033 * | 0.502 |
| Sample IDs | Genotype | Pancreatic Insufficiency Onset | Diabetes Onset | Sputum Microbiology | FEV1 %Predicted |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 20_497 | F508del/Y913S | NO | NO | PA/MSSA | 44.0 |
| 20_504 | F508del/F508del | YES | NO | mucoid PA | 46.4 |
| 20_511 | F508del/ND | NO | NO | mucoid PA/AF | 83.0 |
| 20_1257 | F508del/F508del | YES | NO | PA/A. sp. | 39.0 |
| 20_1264 | F508del/306insA | YES | NO | PA/A. sp. | 63.3 |
| 20_1269 | F508del/F508del | YES | YES | PA | 60.0 |
| 20_1277 | F508del/1717- 1G- > A | YES | NO | - | 101.0 |
| 20_2375 | F508del/1002-113-110delGAAT | NO | NO | AF/MSSA | 127.0 |
| 20_2380 | F508del/F508del | YES | NO | PA/AF/MSSA | 70.0 |
| 20_2387 | F508del/P574H | NO | NO | PA | 73.0 |
| 20_2394 | F508del/2184insA | YES | NO | BCC/MRSA | 42.0 |
| 20_2400 | 1717-3T- > G/1717-3T- > G | NO | NO | - | 94.0 |
| 20_2554 | F508del/F508del | YES | NO | intermittent PA | 103.0 |
| 20_2559 | F508del/F508del | YES | YES | A. sp./MRSA | 59.0 |
| Mean | 71.8 | ||||
| Median | 66.7 | ||||
| SD | 26.7 | ||||
| SEM | 7.1 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Burat, B.; Reynaerts, A.; Baiwir, D.; Fléron, M.; Gohy, S.; Eppe, G.; Leal, T.; Mazzucchelli, G. Sweat Proteomics in Cystic Fibrosis: Discovering Companion Biomarkers for Precision Medicine and Therapeutic Development. Cells 2022, 11, 2358. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells11152358
Burat B, Reynaerts A, Baiwir D, Fléron M, Gohy S, Eppe G, Leal T, Mazzucchelli G. Sweat Proteomics in Cystic Fibrosis: Discovering Companion Biomarkers for Precision Medicine and Therapeutic Development. Cells. 2022; 11(15):2358. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells11152358
Chicago/Turabian StyleBurat, Bastien, Audrey Reynaerts, Dominique Baiwir, Maximilien Fléron, Sophie Gohy, Gauthier Eppe, Teresinha Leal, and Gabriel Mazzucchelli. 2022. "Sweat Proteomics in Cystic Fibrosis: Discovering Companion Biomarkers for Precision Medicine and Therapeutic Development" Cells 11, no. 15: 2358. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells11152358
APA StyleBurat, B., Reynaerts, A., Baiwir, D., Fléron, M., Gohy, S., Eppe, G., Leal, T., & Mazzucchelli, G. (2022). Sweat Proteomics in Cystic Fibrosis: Discovering Companion Biomarkers for Precision Medicine and Therapeutic Development. Cells, 11(15), 2358. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells11152358








