Gene Profiling of a 3D Psoriatic Skin Model Enriched in T Cells: Downregulation of PTPRM Promotes Keratinocyte Proliferation through Excessive ERK1/2 Signaling
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patients and Biopsies
2.2. Cell Culture and Media
2.3. T cell Culture and Polarization
2.4. Production of Tissue-Engineered Skin Substitutes
2.5. Histology and Immunofluorescence Analyses
2.6. Gene Expression Profiling
2.7. Bioinformatics and Statistical Analyses
2.8. Western Blot Analysis
2.9. Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA)
2.10. Electrophoretic Mobility-Shift Assay
2.11. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
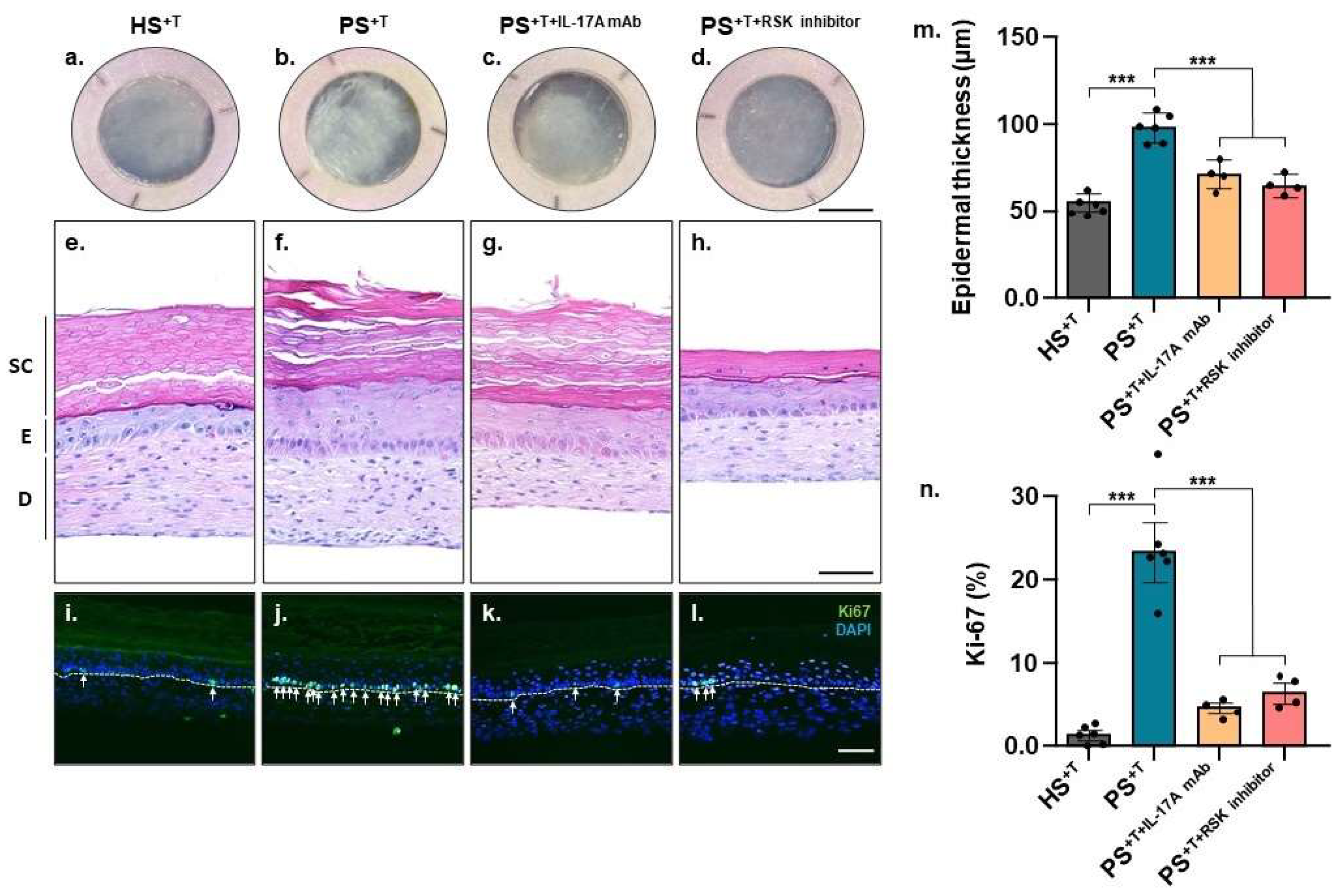
3.1. Skin Substitute Morphology
3.2. Differentially Expressed Genes between Healthy and Psoriatic Skin Substitutes
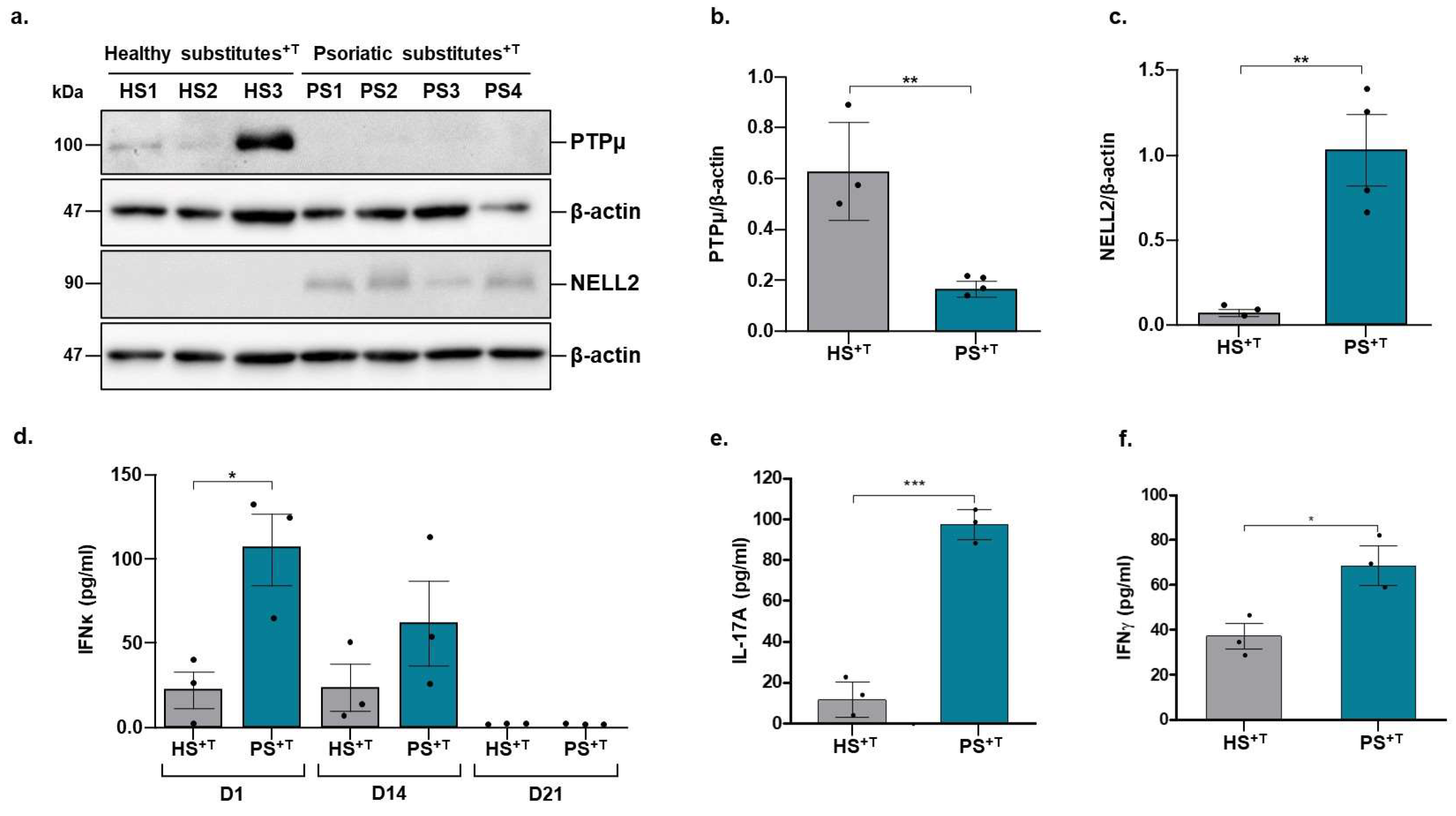
3.3. Validation of Deregulated Genes at the Proteomic Level
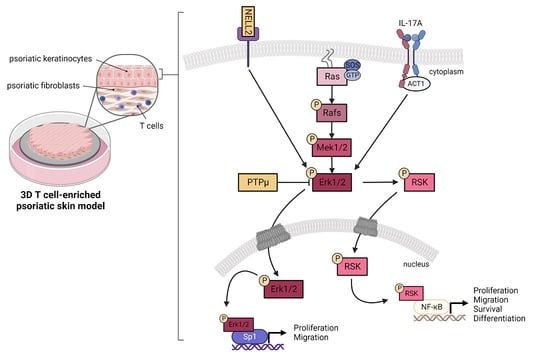
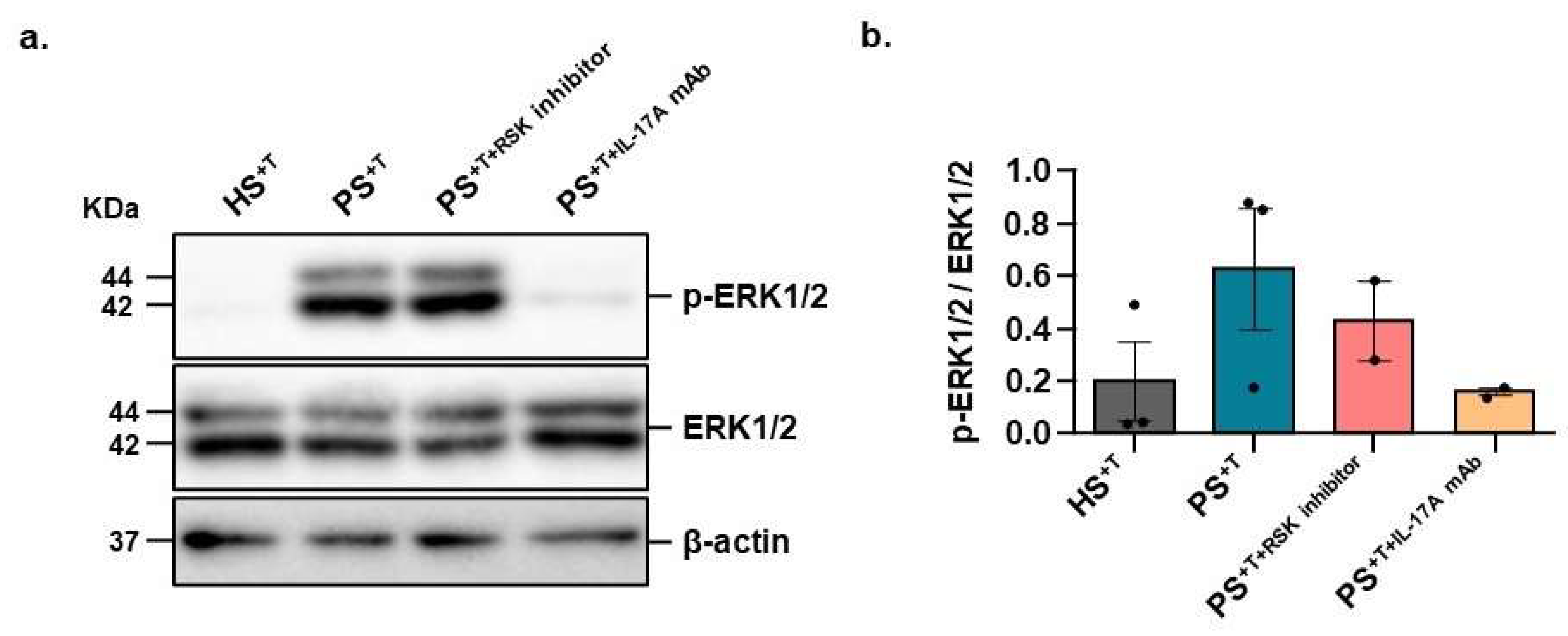
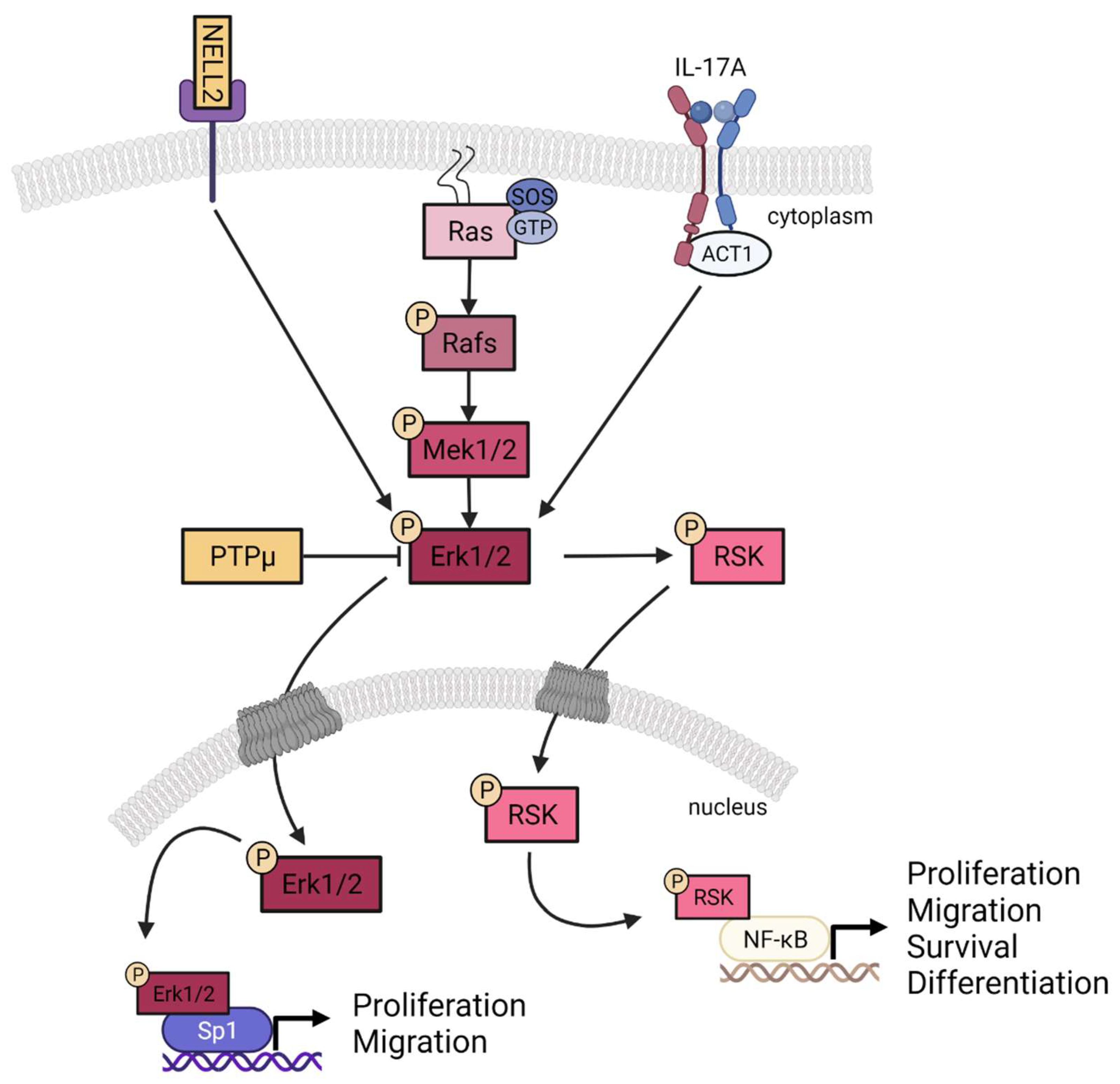
3.4. Contribution of NELL2 and PTPμ to the ERK1/2 Signaling Pathway in Psoriasis
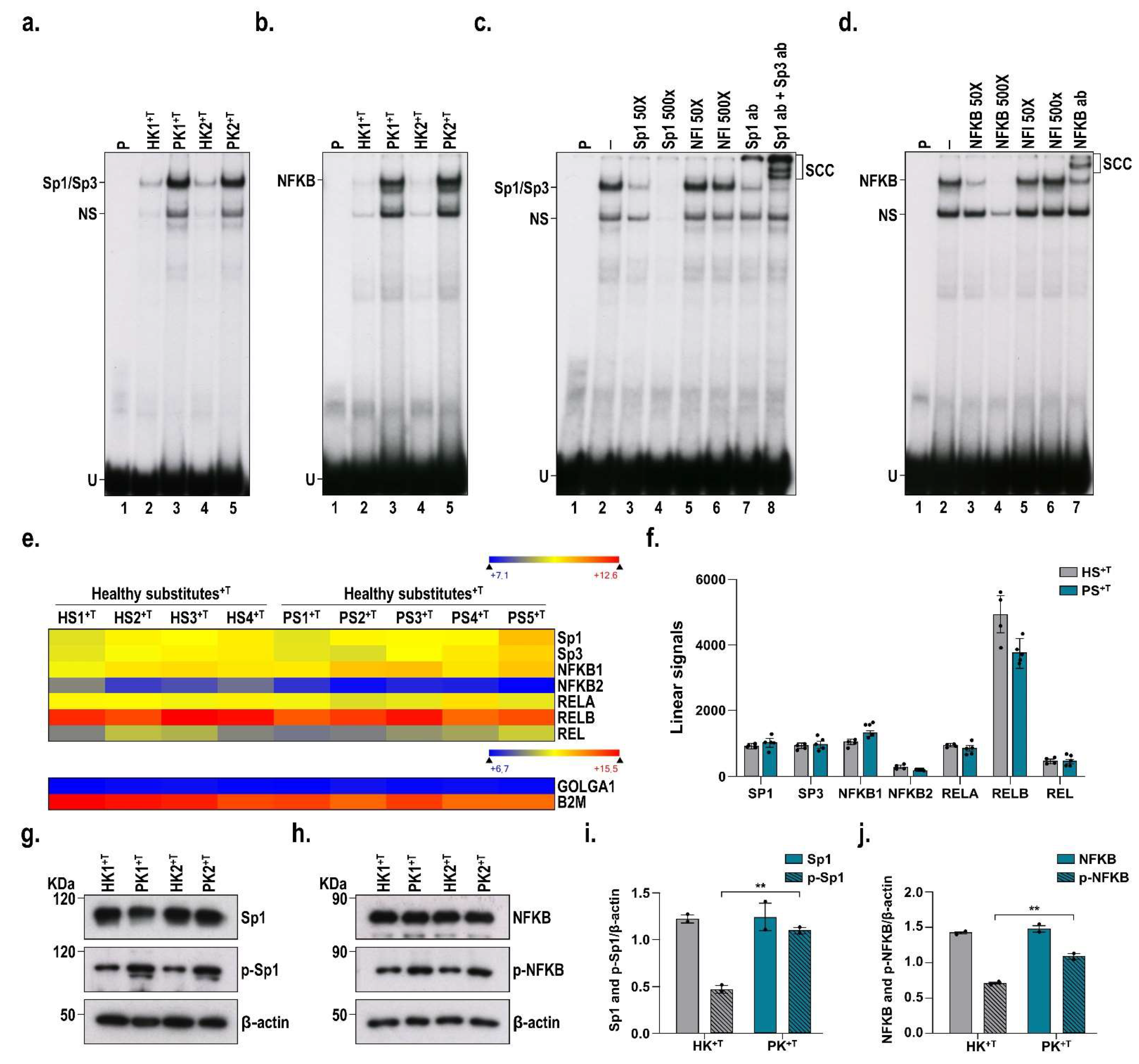
3.5. DNA-Binding Properties of Sp1 and NF-κB in Healthy and Psoriatic Keratinocytes Stimulated by T Cells
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lowes, M.A.; Suarez-Farinas, M.; Krueger, J.G. Immunology of psoriasis. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2014, 32, 227–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rioux, G.; Ridha, Z.; Simard, M.; Turgeon, F.; Guérin, S.L.; Pouliot, R. Transcriptome Profiling Analyses in Psoriasis: A Dynamic Contribution of Keratinocytes to the Pathogenesis. Genes 2020, 11, 1155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasquali, L.; Srivastava, A.; Meisgen, F.; Das Mahapatra, K.; Xia, P.; Xu Landen, N.; Pivarcsi, A.; Sonkoly, E. The Keratinocyte Transcriptome in Psoriasis: Pathways Related to Immune Responses, Cell Cycle and Keratinization. Acta Derm.-Venereol. 2019, 99, 196–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rioux, G.; Simard, M.; Morin, S.; Lorthois, I.; Guérin, S.L.; Pouliot, R. Development of a 3D psoriatic skin model optimized for infiltration of IL-17A producing T cells: Focus on the crosstalk between T cells and psoriatic keratinocytes. Acta Biomater. 2021, 136, 210–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, J.U.; Abaci, H.E.; Herron, L.; Guo, Z.; Sallee, B.; Pappalardo, A.; Jackow, J.; Wang, E.H.C.; Doucet, Y.; Christiano, A.M. Recapitulating T cell infiltration in 3D psoriatic skin models for patient-specific drug testing. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 4123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van den Bogaard, E.H.; Tjabringa, G.S.; Joosten, I.; Vonk-Bergers, M.; van Rijssen, E.; Tijssen, H.J.; Erkens, M.; Schalkwijk, J.; Koenen, H. Crosstalk between keratinocytes and T cells in a 3D microenvironment: A model to study inflammatory skin diseases. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2014, 134, 719–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rioux, G.; Pouliot-Berube, C.; Simard, M.; Benhassine, M.; Soucy, J.; Guerin, S.L.; Pouliot, R. The Tissue-Engineered Human Psoriatic Skin Substitute: A Valuable In Vitro Model to Identify Genes with Altered Expression in Lesional Psoriasis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 2923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pouliot-Berube, C.; Zaniolo, K.; Guerin, S.L.; Pouliot, R. Tissue-engineered human psoriatic skin supplemented with cytokines as an in vitro model to study plaque psoriasis. Regen. Med. 2016, 11, 545–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niehues, H.; van den Bogaard, E.H. Past, present and future of in vitro 3D reconstructed inflammatory skin models to study psoriasis. Exp. Dermatol. 2018, 27, 512–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, G.; Guerard, S.; Fortin, M.M.; Rusu, D.; Soucy, J.; Poubelle, P.E.; Pouliot, R. Pathological crosstalk in vitro between T lymphocytes and lesional keratinocytes in psoriasis: Necessity of direct cell-to-cell contact. Lab. Investig. J. Tech. Methods Pathol. 2012, 92, 1058–1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lorthois, I.; Simard, M.; Morin, S.; Pouliot, R. Infiltration of T Cells into a Three-Dimensional Psoriatic Skin Model Mimics Pathological Key Features. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 1670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guérard, S.; Allaeys, I.; Martin, G.; Pouliot, R.; Poubelle, P.E. Psoriatic keratinocytes prime neutrophils for an overproduction of superoxide anions. Arch. Dermatol. Res. 2013, 305, 879–889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosa Fortin, M.; Poubelle, P.E.; Soucy, J.; Pouliot, R. Cellular Interactions in Vitro: Psoriatic Keratinocytes Enhance T Lymphocyte Survival. Psoriasis Forum 2010, 16, 12–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eckert, R.L.; Efimova, T.; Dashti, S.R.; Balasubramanian, S.; Deucher, A.; Crish, J.F.; Sturniolo, M.; Bone, F. Keratinocyte survival, differentiation, and death: Many roads lead to mitogen-activated protein kinase. J. Investig. Dermatol. Symp. Proc. 2002, 7, 36–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Liu, H.T. MAPK signal pathways in the regulation of cell proliferation in mammalian cells. Cell Res. 2002, 12, 9–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, N.G.; Maller, J.L.; Tonks, N.K.; Sturgill, T.W. Requirement for integration of signals from two distinct phosphorylation pathways for activation of MAP kinase. Nature 1990, 343, 651–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, E.K.; Choi, E.J. Pathological roles of MAPK signaling pathways in human diseases. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2010, 1802, 396–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, Y.F.; Wang, B.J.; Cheng, H.T.; Kuo, L.H.; Wolfe, M.S. Tumor necrosis factor-alpha, interleukin-1beta, and interferon-gamma stimulate gamma-secretase-mediated cleavage of amyloid precursor protein through a JNK-dependent MAPK pathway. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 49523–49532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balmanno, K.; Cook, S.J. Tumour cell survival signalling by the ERK1/2 pathway. Cell Death Differ. 2009, 16, 368–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johansen, C.; Kragballe, K.; Westergaard, M.; Henningsen, J.; Kristiansen, K.; Iversen, L. The mitogen-activated protein kinases p38 and ERK1/2 are increased in lesional psoriatic skin. Br. J. Dermatol. 2005, 152, 37–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.J.; Li, C.Y.; Dai, H.Y.; Cai, D.X.; Wang, K.Y.; Xu, Y.H.; Chen, L.M.; Zhou, C.L. Expression and localization of the activated mitogen-activated protein kinase in lesional psoriatic skin. Exp. Mol. Pathol. 2007, 83, 413–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pagès, G.; Lenormand, P.; L’Allemain, G.; Chambard, J.C.; Meloche, S.; Pouysségur, J. Mitogen-activated protein kinases p42mapk and p44mapk are required for fibroblast proliferation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1993, 90, 8319–8323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Germain, L.; Rouabhia, M.; Guignard, R.; Carrier, L.; Bouvard, V.; Auger, F.A. Improvement of human keratinocyte isolation and culture using thermolysin. Burn. J. Int. Soc. Burn. Inj. 1993, 19, 99–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manel, N.; Unutmaz, D.; Littman, D.R. The differentiation of human T(H)-17 cells requires transforming growth factor-beta and induction of the nuclear receptor RORgammat. Nat. Immunol. 2008, 9, 641–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Acosta-Rodriguez, E.V.; Napolitani, G.; Lanzavecchia, A.; Sallusto, F. Interleukins 1beta and 6 but not transforming growth factor-beta are essential for the differentiation of interleukin 17-producing human T helper cells. Nat. Immunol. 2007, 8, 942–949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, J.; Yamane, H.; Paul, W.E. Differentiation of effector CD4 T cell populations (*). Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2010, 28, 445–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jean, J.; Lapointe, M.; Soucy, J.; Pouliot, R. Development of an in vitro psoriatic skin model by tissue engineering. J. Dermatol. Sci. 2009, 53, 19–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Couture, C.; Zaniolo, K.; Carrier, P.; Lake, J.; Patenaude, J.; Germain, L.; Guérin, S.L. The tissue-engineered human cornea as a model to study expression of matrix metalloproteinases during corneal wound healing. Biomaterials 2016, 78, 86–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krämer, A.; Green, J.; Pollard, J., Jr.; Tugendreich, S. Causal analysis approaches in Ingenuity Pathway Analysis. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 523–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le-Bel, G.; Cortez Ghio, S.; Larouche, D.; Germain, L.; Guérin, S.L. Qualitatively Monitoring Binding and Expression of the Transcription Factors Sp1 and NFI as a Useful Tool to Evaluate the Quality of Primary Cultured Epithelial Stem Cells in Tissue Reconstruction. Methods Mol. Biol. 2019, 1879, 43–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gudjonsson, J.E.; Ding, J.; Johnston, A.; Tejasvi, T.; Guzman, A.M.; Nair, R.P.; Voorhees, J.J.; Abecasis, G.R.; Elder, J.T. Assessment of the psoriatic transcriptome in a large sample: Additional regulated genes and comparisons with in vitro models. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2010, 130, 1829–1840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Tsoi, L.C.; Swindell, W.R.; Gudjonsson, J.E.; Tejasvi, T.; Johnston, A.; Ding, J.; Stuart, P.E.; Xing, X.; Kochkodan, J.J.; et al. Transcriptome analysis of psoriasis in a large case-control sample: RNA-seq provides insights into disease mechanisms. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2014, 134, 1828–1838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simard, M.; Rioux, G.; Morin, S.; Martin, C.; Guérin, S.L.; Flamand, N.; Julien, P.; Fradette, J.; Pouliot, R. Investigation of Omega-3 Polyunsaturated Fatty Acid Biological Activity in a Tissue-Engineered Skin Model Involving Psoriatic Cells. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2021, 141, 2391–2401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morin, A.; Simard, M.; Rioux, G.; Grenier, A.; Morin, S.; Pouliot, R. Application of an In Vitro Psoriatic Skin Model to Study Cutaneous Metabolization of Tazarotene. Processes 2019, 7, 871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morin, S.; Simard, M.; Rioux, G.; Julien, P.; Pouliot, R. Alpha-Linolenic Acid Modulates T Cell Incorporation in a 3D Tissue-Engineered Psoriatic Skin Model. Cells 2022, 11, 1513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simard, M.; Grenier, A.; Rioux, G.; Tremblay, A.; Blais, I.; Flamand, N.; Pouliot, R. Remodeling of the Dermal Extracellular Matrix in a Tissue-Engineered Psoriatic Skin Model by n-3 Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Liu, L.; Bian, C.; Diao, Q.; Nisar, M.F.; Jiang, X.; Bartsch, J.W.; Zhong, M.; Hu, X.; Zhong, J.L. MicroRNA let-7b inhibits keratinocyte differentiation by targeting IL-6 mediated ERK signaling in psoriasis. Cell Commun. Signal. CCS 2018, 16, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lories, R.J.; Derese, I.; Luyten, F.P.; de Vlam, K. Activation of nuclear factor kappa B and mitogen activated protein kinases in psoriatic arthritis before and after etanercept treatment. Clin. Exp. Rheumatol. 2008, 26, 96–102. [Google Scholar]
- Takahashi, H.; Ibe, M.; Nakamura, S.; Ishida-Yamamoto, A.; Hashimoto, Y.; Iizuka, H. Extracellular regulated kinase and c-Jun N-terminal kinase are activated in psoriatic involved epidermis. J. Dermatol. Sci. 2002, 30, 94–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haase, I.; Hobbs, R.M.; Romero, M.R.; Broad, S.; Watt, F.M. A role for mitogen-activated protein kinase activation by integrins in the pathogenesis of psoriasis. J. Clin. Investig. 2001, 108, 527–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Yu, P.; Liu, M.; Deng, Y.; Dong, Y.; Liu, Q.; Zhang, J.; Wu, T. ERK inhibitor JSI287 alleviates imiquimod-induced mice skin lesions by ERK/IL-17 signaling pathway. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2019, 66, 236–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cochaud, S.; Giustiniani, J.; Thomas, C.; Laprevotte, E.; Garbar, C.; Savoye, A.M.; Curé, H.; Mascaux, C.; Alberici, G.; Bonnefoy, N.; et al. IL-17A is produced by breast cancer TILs and promotes chemoresistance and proliferation through ERK1/2. Sci. Rep. 2013, 3, 3456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swaidani, S.; Liu, C.; Zhao, J.; Bulek, K.; Li, X. TRAF Regulation of IL-17 Cytokine Signaling. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 1293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awane, M.; Andres, P.G.; Li, D.J.; Reinecker, H.C. NF-kappa B-inducing kinase is a common mediator of IL-17-, TNF-alpha-, and IL-1 beta-induced chemokine promoter activation in intestinal epithelial cells. J. Immunol. 1999, 162, 5337–5344. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sebkova, L.; Pellicanò, A.; Monteleone, G.; Grazioli, B.; Guarnieri, G.; Imeneo, M.; Pallone, F.; Luzza, F. Extracellular signal-regulated protein kinase mediates interleukin 17 (IL-17)-induced IL-8 secretion in Helicobacter pylori-infected human gastric epithelial cells. Infect. Immun. 2004, 72, 5019–5026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, Q.; Yang, H.; Liu, E.; Wang, H. P38/ERK MAPK signaling pathways are involved in the regulation of filaggrin and involucrin by IL-17. Mol. Med. Rep. 2017, 16, 8863–8867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, X.; Yang, J.; Yang, X.; Wei, Y.; Zhu, L.; Gao, D.; Li, M. IL-17A induces endothelial inflammation in systemic sclerosis via the ERK signaling pathway. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e85032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahman, M.S.; Yamasaki, A.; Yang, J.; Shan, L.; Halayko, A.J.; Gounni, A.S. IL-17A induces eotaxin-1/CC chemokine ligand 11 expression in human airway smooth muscle cells: Role of MAPK (Erk1/2, JNK, and p38) pathways. J. Immunol. 2006, 177, 4064–4071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lowes, M.A.; Russell, C.B.; Martin, D.A.; Towne, J.E.; Krueger, J.G. The IL-23/T17 pathogenic axis in psoriasis is amplified by keratinocyte responses. Trends Immunol. 2013, 34, 174–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blauvelt, A. T-helper 17 cells in psoriatic plaques and additional genetic links between IL-23 and psoriasis. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2008, 128, 1064–1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blauvelt, A. Safety of secukinumab in the treatment of psoriasis. Expert Opin. Drug. Saf. 2016, 15, 1413–1420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Arul, N.; Cho, Y.Y. A Rising Cancer Prevention Target of RSK2 in Human Skin Cancer. Front. Oncol. 2013, 3, 201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, J.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, Y.; Gao, L.; Tong, X.; Xie, Y.; Hu, Q.; Chen, C.; Ding, S.; et al. RPL22 Overexpression Promotes Psoriasis-Like Lesion by Inducing Keratinocytes Abnormal Biological Behavior. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 699900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wrone-Smith, T.; Mitra, R.S.; Thompson, C.B.; Jasty, R.; Castle, V.P.; Nickoloff, B.J. Keratinocytes derived from psoriatic plaques are resistant to apoptosis compared with normal skin. Am. J. Pathol. 1997, 151, 1321–1329. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Soulsby, M.; Bennett, A.M. Physiological signaling specificity by protein tyrosine phosphatases. Physiology 2009, 24, 281–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Starr, I.; Seiffert-Sinha, K.; Sinha, A.A.; Gokcumen, O. Evolutionary context of psoriatic immune skin response. Evol. Med. Public Health 2021, 9, 474–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Becka, S.; Zhang, P.; Craig, S.E.; Lodowski, D.T.; Wang, Z.; Brady-Kalnay, S.M. Characterization of the adhesive properties of the type IIb subfamily receptor protein tyrosine phosphatases. Cell Commun. Adhes. 2010, 17, 34–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brady-Kalnay, S.M.; Flint, A.J.; Tonks, N.K. Homophilic binding of PTP mu, a receptor-type protein tyrosine phosphatase, can mediate cell-cell aggregation. J. Cell Biol. 1993, 122, 961–972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, P.H.; Ye, L.; Mason, M.D.; Jiang, W.G. Protein tyrosine phosphatase µ (PTP µ or PTPRM), a negative regulator of proliferation and invasion of breast cancer cells, is associated with disease prognosis. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e50183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sui, X.F.; Kiser, T.D.; Hyun, S.W.; Angelini, D.J.; Del Vecchio, R.L.; Young, B.A.; Hasday, J.D.; Romer, L.H.; Passaniti, A.; Tonks, N.K.; et al. Receptor protein tyrosine phosphatase micro regulates the paracellular pathway in human lung microvascular endothelia. Am. J. Pathol. 2005, 166, 1247–1258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, H.; Tsuji, H.; Minami-Hori, M.; Miyauchi, Y.; Iizuka, H. Defective barrier function accompanied by structural changes of psoriatic stratum corneum. J. Dermatol. 2014, 41, 144–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orsmond, A.; Bereza-Malcolm, L.; Lynch, T.; March, L.; Xue, M. Skin Barrier Dysregulation in Psoriasis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 10841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montero-Vilchez, T.; Segura-Fernández-Nogueras, M.V.; Pérez-Rodríguez, I.; Soler-Gongora, M.; Martinez-Lopez, A.; Fernández-González, A.; Molina-Leyva, A.; Arias-Santiago, S. Skin Barrier Function in Psoriasis and Atopic Dermatitis: Transepidermal Water Loss and Temperature as Useful Tools to Assess Disease Severity. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brady-Kalnay, S.M.; Mourton, T.; Nixon, J.P.; Pietz, G.E.; Kinch, M.; Chen, H.; Brackenbury, R.; Rimm, D.L.; Del Vecchio, R.L.; Tonks, N.K. Dynamic interaction of PTPmu with multiple cadherins in vivo. J. Cell Biol. 1998, 141, 287–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, E.; Cook, P.W.; Parkos, C.A.; Park, Y.K.; Pittelkow, M.R.; Coffey, R.J. Amphiregulin causes functional downregulation of adherens junctions in psoriasis. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2005, 124, 1134–1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikoma, A.; Steinhoff, M.; Ständer, S.; Yosipovitch, G.; Schmelz, M. The neurobiology of itch. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2006, 7, 535–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; He, Y. The Role of Nociceptive Neurons in the Pathogenesis of Psoriasis. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 1984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farber, E.M.; Lanigan, S.W.; Boer, J. The role of cutaneous sensory nerves in the maintenance of psoriasis. Int. J. Dermatol. 1990, 29, 418–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joseph, T.; Kurian, J.; Warwick, D.J.; Friedmann, P.S. Unilateral remission of psoriasis following traumatic nerve palsy. Br. J. Dermatol. 2005, 152, 185–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raychaudhuri, S.P.; Farber, E.M. Are sensory nerves essential for the development of psoriatic lesions? J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 1993, 28, 488–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, T.H.; Nakamura, M.; Farahnik, B.; Abrouk, M.; Lee, K.; Singh, R.; Gevorgyan, A.; Koo, J.; Bhutani, T. The Role of the Nervous System in the Pathophysiology of Psoriasis: A Review of Cases of Psoriasis Remission or Improvement Following Denervation Injury. Am. J. Clin. Dermatol. 2016, 17, 257–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taneda, K.; Tominaga, M.; Negi, O.; Tengara, S.; Kamo, A.; Ogawa, H.; Takamori, K. Evaluation of epidermal nerve density and opioid receptor levels in psoriatic itch. Br. J. Dermatol. 2011, 165, 277–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Song, Y.; Zhu, L.; Wang, X.; Yang, B.; Lu, P.; Chen, Q.; Bin, L.; Deng, L. Interferon Kappa Is Up-Regulated in Psoriasis and It Up-Regulates Psoriasis-Associated Cytokines in vivo. Clin. Cosmet. Investig. Dermatol. 2019, 12, 865–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gharaee-Kermani, M.; Estadt, S.N.; Tsoi, L.C.; Wolf-Fortune, S.J.; Liu, J.; Xing, X.; Theros, J.; Reed, T.J.; Lowe, L.; Gruszka, D.; et al. IFN-κ Is a Rheostat for Development of Psoriasiform Inflammation. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2021, 142, 155–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scarponi, C.; Nardelli, B.; Lafleur, D.W.; Moore, P.A.; Madonna, S.; De Pità, O.; Girolomoni, G.; Albanesi, C. Analysis of IFN-kappa expression in pathologic skin conditions: Downregulation in psoriasis and atopic dermatitis. J. Interferon Cytokine Res. Off. J. Int. Soc. Interferon Cytokine Res. 2006, 26, 133–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarkar, M.K.; Hile, G.A.; Tsoi, L.C.; Xing, X.; Liu, J.; Liang, Y.; Berthier, C.C.; Swindell, W.R.; Patrick, M.T.; Shao, S.; et al. Photosensitivity and type I IFN responses in cutaneous lupus are driven by epidermal-derived interferon kappa. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2018, 77, 1653–1664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ueyama, A.; Yamamoto, M.; Tsujii, K.; Furue, Y.; Imura, C.; Shichijo, M.; Yasui, K. Mechanism of pathogenesis of imiquimod-induced skin inflammation in the mouse: A role for interferon-alpha in dendritic cell activation by imiquimod. J. Dermatol. 2014, 41, 135–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wohn, C.; Ober-Blöbaum, J.L.; Haak, S.; Pantelyushin, S.; Cheong, C.; Zahner, S.P.; Onderwater, S.; Kant, M.; Weighardt, H.; Holzmann, B.; et al. Langerin(neg) conventional dendritic cells produce IL-23 to drive psoriatic plaque formation in mice. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 10723–10728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van der Fits, L.; van der Wel, L.I.; Laman, J.D.; Prens, E.P.; Verschuren, M.C. In psoriasis lesional skin the type I interferon signaling pathway is activated, whereas interferon-alpha sensitivity is unaltered. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2004, 122, 51–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.-j. Type1 Interferons Potential Initiating Factors Linking Skin Wounds With Psoriasis Pathogenesis. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 1440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Platanias, L.C. Mechanisms of type-I- and type-II-interferon-mediated signalling. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2005, 5, 375–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mallone, R.; Mannering, S.I.; Brooks-Worrell, B.M.; Durinovic-Bello, I.; Cilio, C.M.; Wong, F.S.; Schloot, N.C. Isolation and preservation of peripheral blood mononuclear cells for analysis of islet antigen-reactive T cell responses: Position statement of the T-Cell Workshop Committee of the Immunology of Diabetes Society. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2011, 163, 33–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eding, C.B.; Enerbäck, C. Involved and Uninvolved Psoriatic Keratinocytes Display a Resistance to Apoptosis that may Contribute to Epidermal Thickness. Acta Derm.-Venereol. 2017, 97, 788–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, T.; Zhang, L.; Joo, D.; Sun, S.C. NF-κB signaling in inflammation. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2017, 2, 17023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Briggs, M.R.; Kadonaga, J.T.; Bell, S.P.; Tjian, R. Purification and biochemical characterization of the promoter-specific transcription factor, Sp1. Science 1986, 234, 47–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Connor, L.; Gilmour, J.; Bonifer, C. The Role of the Ubiquitously Expressed Transcription Factor Sp1 in Tissue-specific Transcriptional Regulation and in Disease. Yale J. Biol. Med. 2016, 89, 513–525. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lizzul, P.F.; Aphale, A.; Malaviya, R.; Sun, Y.; Masud, S.; Dombrovskiy, V.; Gottlieb, A.B. Differential expression of phosphorylated NF-kappaB/RelA in normal and psoriatic epidermis and downregulation of NF-kappaB in response to treatment with etanercept. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2005, 124, 1275–1283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldminz, A.M.; Au, S.C.; Kim, N.; Gottlieb, A.B.; Lizzul, P.F. NF-κB: An essential transcription factor in psoriasis. J. Dermatol. Sci. 2013, 69, 89–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seidel, P.; Merfort, I.; Hughes, J.M.; Oliver, B.G.; Tamm, M.; Roth, M. Dimethylfumarate inhibits NF-{kappa}B function at multiple levels to limit airway smooth muscle cell cytokine secretion. Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell. Mol. Physiol. 2009, 297, L326–L339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gesser, B.; Rasmussen, M.K.; Raaby, L.; Rosada, C.; Johansen, C.; Kjellerup, R.B.; Kragballe, K.; Iversen, L. Dimethylfumarate inhibits MIF-induced proliferation of keratinocytes by inhibiting MSK1 and RSK1 activation and by inducing nuclear p-c-Jun (S63) and p-p53 (S15) expression. Inflamm. Res. Off. J. Eur. Histamine Res. Soc. 2011, 60, 643–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masson-Gadais, B.; Fugère, C.; Paquet, C.; Leclerc, S.; Lefort, N.R.; Germain, L.; Guérin, S.L. The feeder layer-mediated extended lifetime of cultured human skin keratinocytes is associated with altered levels of the transcription factors Sp1 and Sp3. J. Cell. Physiol. 2006, 206, 831–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rioux, G.; Turgeon, F.; Le-Bel, G.; Grenier, C.; Guérin, S.L.; Pouliot, R. Gene Profiling of a 3D Psoriatic Skin Model Enriched in T Cells: Downregulation of PTPRM Promotes Keratinocyte Proliferation through Excessive ERK1/2 Signaling. Cells 2022, 11, 2904. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells11182904
Rioux G, Turgeon F, Le-Bel G, Grenier C, Guérin SL, Pouliot R. Gene Profiling of a 3D Psoriatic Skin Model Enriched in T Cells: Downregulation of PTPRM Promotes Keratinocyte Proliferation through Excessive ERK1/2 Signaling. Cells. 2022; 11(18):2904. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells11182904
Chicago/Turabian StyleRioux, Geneviève, Florence Turgeon, Gaëtan Le-Bel, Camille Grenier, Sylvain L. Guérin, and Roxane Pouliot. 2022. "Gene Profiling of a 3D Psoriatic Skin Model Enriched in T Cells: Downregulation of PTPRM Promotes Keratinocyte Proliferation through Excessive ERK1/2 Signaling" Cells 11, no. 18: 2904. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells11182904