PCSK9 Inhibition: From Current Advances to Evolving Future
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Molecular Mechanism of PCSK9
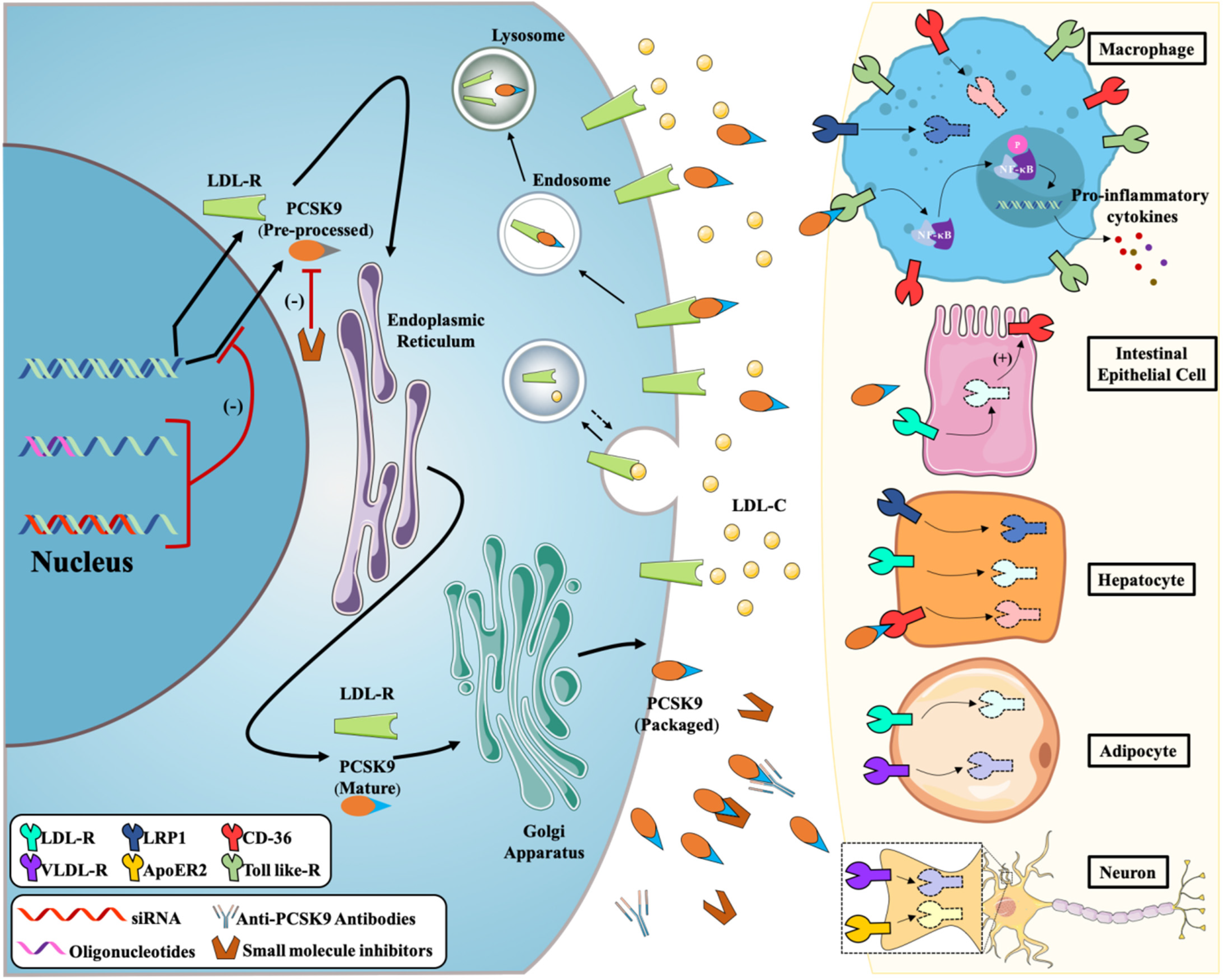
2.1. PCSK9 Increases Circulating LDL-C by Degrading LDL-R
2.2. PCSK9 Binds to TLR4 to Mediate the Inflammatory Response
2.3. PCSK9 Binds to CD36 to Promote Platelet Activation and Thrombosis
2.4. PCSK9 Binds to Lipid-Associated Receptors to Regulate Metabolism
3. Classification of PCSK9 Inhibitors
3.1. McAb Inhibitors
3.2. Nucleic Acid Drugs
3.3. Small-Molecule Drugs
3.4. Vaccine Drugs
3.5. CRISPR/Cas9-Targeted KO Drugs
4. Clinical Application of PCSK9 Inhibitors
4.1. Hyperlipidemia
4.2. Atherosclerosis
5. Potential Therapeutic Applications of PCSK9
5.1. Application of PCSK9 in the Treatment of Sepsis
5.2. Application of PCSK9 in Tumor Diagnosis and Treatment
5.3. Application of PCSK9 in Viral Infection
6. Summary and Outlook
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| Drugs | Title | Interventions | Conditions | Phase | Study Results |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Alirocumab | PCSK9 Inhibition in Patients with Symptomatic Intracranial Atherosclerosis | Alirocumab | Stroke Intracranial Atherosclerosis Intraplaque Hemorrhage | Early Phase 1 | No Results Available |
| Safety, Tolerability, and Bioeffects of Alirocumab in Non-treatment Seeking Heavy Drinkers | Alirocumab | Alcohol Associated Liver Disease Heavy Drinking Behavior | Phase 1 | No Results Available | |
| A Study of Alirocumab in Participants with ADH and GOFm of the PCSK9 Gene or LOFm of the Apo B Gene | Alirocumab | Hypercholesterolemia | Phase 2 | Has Results | |
| PCSK9 Inhibition After Heart Transplantation | alirocumab | Vasculopathy | Phase 2 | No Results Available | |
| Treatment of Severe Infection with Antihyperlipidemia Drug | Alirocumab | Sepsis Septic Shock | Phase 2 | No Results Available | |
| Open-Label Extension of Study R727-CL-1003 (NCT01266876) to Evaluate the Long-Term Safety and Efficacy of Alirocumab (REGN727) in Participants with HeFH | Alirocumab | Hypercholesterolemia HeFH | Phase 2 | Has Results | |
| Effect of PCSK9 Inhibition on Cardiovascular Risk in Treated HIV Infection (EPIC-HIV Study) | Alirocumab | Dyslipidemias Cardiovascular Diseases HIV Infections | Phase 3 | No Results Available | |
| PCSK 9 Inhibition as Secondary Prevention in Renal Transplant Patients | Evolocumab | Kidney Transplant Recipients with High Cardiovascular Risk Score | Phase 3 | No Results Available | |
| Treatment of Severe Infection with Antihyperlipidemia Drug | Alirocumab | Sepsis Septic Shock | Phase 3 | No Results Available | |
| Efficacy and Safety of Alirocumab (SAR236553/REGN727) Versus Placebo on Top of Lipid-Modifying Therapy in Patients with HeFH Not Adequately Controlled with Their Lipid-Modifying Therapy | Alirocumab | Hypercholesterolemia | Phase 3 | Has Results | |
| Vascular Effects of Alirocumab in Acute MI-Patients | Alirocumab | Coronary Vessel Coronary Circulation Atheroma; Myocardial | Phase 3 | No Results Available | |
| An Efficacy and Safety Study of Alirocumab in Children and Adolescents with HoFH | Alirocumab SAR236553 (REGN727) Atorvastatin Simvastatin Fluvastatin Pravastatin Lovastatin Rosuvastatin Ezetimibe | Hypercholesterolemia | Phase 3 | Has Results | |
| Impact of Early PCSK9 Inhibitor on Heart After Acute Myocardium Infarction | Alirocumab standard medications | Early PCSK9 Inhibitor on Ventricular Remodeling | Phase 4 | No Results Available | |
| Impact of Early PCSK9 Inhibitor Treatment on Heart After Acute Myocardium Infarction | alirocumab | Acute Myocardial Infarction | Phase 4 | No Results Available | |
| Impact of PCSK9 Inhibitors on Coronary Plaque Composition and Vulnerability Assessed by Optical Coherence Tomography | PCSK9 inhibitor plus statin standard statin therapy | Randomized Controlled Trials | Phase 4 | No Results Available | |
| Assessment of Atherosclerotic Plaque Characteristics Change by DCE-MRI with Alirocumab | Alirocumab | Atherosclerosis Hyperlipidemia | Phase 4 | No Results Available | |
| Alirocumab SAR236553 (REGN727) | Pharmacokinetic and Tolerability of Alirocumab SAR236553 (REGN727) in Patients with Hepatic Impairment and in Healthy Subjects | alirocumab SAR236553 (REGN727) | Hypercholesterolemia | Phase 1 | No Results Available |
| Pharmacokinetic of Alirocumab SAR236553 (REGN727) Administered Subcutaneously at 3 Different Injection Sites in Healthy Subjects | alirocumab SAR236553 (REGN727) | Hypercholesterolemia | Phase 1 | No Results Available | |
| Evolocumab | Cholesterol Disruption in Combination with FOLFIRINOX in Patients with Metastatic Pancreatic Adenocarcinoma | Evolocumab, Atorvastatin and Ezetimibe with FOLFIRINOX | Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma Pancreatic Cancer Pancreas Cancer Metastatic Cancer | Early Phase 1 | No Results Available |
| Study to Evaluate Pharmacokinetics and Pharmacodynamics of Evolocumab in rHGG | Evolocumab | Malignant Glioma Glioblastoma | Early Phase 1 | No Results Available | |
| PCSK9 Inhibitor Treatment for Patients with SPG5 | Evolocumab | Hereditary Spastic Paraplegia Type 5 | Phase 1 | No Results Available | |
| Evaluation of the Efficacy and Safety of Bempedoic Acid (ETC-1002) 180 mg when Added to PCSK9 Inhibitor Therapy | bempedoic acid 180 mg evolocumab | Hypercholesterolemia | Phase 2 | Has Results | |
| Impact of PCSK9 Inhibitors on Coronary Microvascular Dysfunction in Patients with Atherosclerotic Cardiovascular Disease Proved by Myocardial Ischemia and Needing Coronarography | Evolocumab | Atherosclerotic Cardiovascular Disease | Phase 2 | No Results Available | |
| Evolocumab for PCSK9 Lowering in Early Acute Sepsis (The PLEASE Study) | Evolocumab | Sepsis | Phase 2 | No Results Available | |
| Reduction of LDL-C with PCSK9 Inhibition in HeFH Disorder Study | Biological: Evolocumab | Hypercholesterolemia, Familial | Phase 2 | Has Results | |
| PCSK9 Inhibitor Treatment for Patients with SPG5 | evolocumab | Hereditary Spastic Paraplegia Type 5 | Phase 2 | No Results Available | |
| LAPLACE-TIMI 57: LDL-C Assessment with PCSK9 monoclonal Antibody Inhibition Combined with Statin therapy | Evolocumab | Hyperlipidemia | Phase 2 | Has Results | |
| Trial Assessing Long-Term Use of PCSK9 Inhibition in Subjects with Genetic LDL Disorders | Evolocumab | Severe Familial Hypercholesterolemia | Phase 2 | Has Results | |
| Monoclonal Antibody Against PCSK9 to Reduce Elevated LDL-C in Adults Currently Not Receiving Drug Therapy for Easing Lipid Levels | Evolocumab Ezetimibe | Hyperlipidemia | Phase 2 | Has Results | |
| Goal Achievement After Utilizing an Anti-PCSK9 Antibody in Statin Intolerant Subjects | Evolocumab Ezetimibe | Hyperlipidemia | Phase 2 | Has Results | |
| Trial Evaluating PCSK9 Antibody in Subjects with LDL Receptor Abnormalities | Evolocumab | HoFH | Phase 2 | Has Results | |
| Impact of PCSK9 Inhibition on Clinical Outcome in Patients During the Inflammatory Stage of the COVID-19 | Evolocumab Saline solution | SARS-CoV-2 Infection | Phase 3 | No Results Available | |
| Effects of PCSK9 Inhibition on Arterial Wall Inflammation in Patients with Elevated Lipoprotein(a) (Lp(a)) | Evolocumab Placebo | Subjects with Hyperlipidemia, Dyslipidemia | Phase 3 | Has Results | |
| Trial Assessing Long-Term Use of PCSK9 Inhibition in Subjects with Genetic LDL Disorders | Biological: Evolocumab | Severe Familial Hypercholesterolemia | Phase 3 | Has Results | |
| Trial Assessing Efficacy, Safety, and Tolerability of Proprotein Convertase Subtilisin/Kexin Type 9 (PCSK9) Inhibition in Pediatric Subjects with Genetic LDL Disorders | Evolocumab Placebo | Heterozygous Familial Hypercholesterolemia | Phase 3 | Has Results | |
| Evaluating PCSK9 Binding Antibody Influence on cognitive Health in High Cardiovascular Risk Subjects | Evolocumab Placebo Background Statin Therapy | Dyslipidemia | Phase 3 | Has Results | |
| Durable Effect of PCSK9 Antibody Compared with placebo Study | Evolocumab Placebo Atorvastatin Ezetimibe Other: Diet Only | Hypercholesterolemia | Phase 3 | Has Results | |
| Goal Achievement After Utilizing an Anti-PCSK9 Antibody in Statin Intolerant Subjects-4 | Evolocumab Ezetimibe | Hypercholesterolemia | Phase 3 | Has Results | |
| Effects on Lipoprotein Metabolism from PCSK9 Inhibition Utilizing a Monoclonal Antibody | Evolocumab Atorvastatin | Primary Hyperlipidemia and Mixed Dyslipidemia | Phase 3 | Has Results | |
| LDL-C Assessment with PCSK9 Monoclonal Antibody Inhibition Combined with Statin Therapy-2 | Evolocumab Ezetimibe Atorvastatin Rosuvastatin Simvastatin | Hyperlipidemia | Phase 3 | Has Results | |
| Goal Achievement After Utilizing an Anti-PCSK9 Antibody in Statin Intolerant Subjects-3 | Atorvastatin Ezetimibe Evolocumab | Hyperlipidemia | Phase 3 | Has Results | |
| Further Cardiovascular Outcomes Research with PCSK9 Inhibition in Subjects with Elevated Risk Open-label Extension | Evolocumab | Dyslipidemia | Phase 3 | No Results Available | |
| Goal Achievement After Utilizing an Anti-PCSK9 Antibody in Statin Intolerant Subjects -2 | Evolocumab Ezetimibe | Hyperlipidemia | Phase 3 | Has Results | |
| Further Cardiovascular Outcomes Research with PCSK9 Inhibition in Subjects with Elevated Risk | Evolocumab | Dyslipidemia | Phase 3 | Has Results | |
| Reduction of LDL-C with PCSK9 Inhibition in HeFH Disorder Study-2 | Evolocumab | Hyperlipidemia | Phase 3 | Has Results | |
| Global Assessment of Plaque regression with a PCSK9 antibody as Measured by IVUS | Evolocumab | Hypercholesterolemia | Phase 3 | Has Results | |
| Monoclonal Antibody Against PCSK9 to Reduce Elevated LDL-C in Subjects Currently Not Receiving Drug Therapy for Easing Lipid Levels-2 | Evolocumab Ezetimibe | Hyperlipidemia | Phase 3 | Has Results | |
| Trial Evaluating PCSK9 Antibody in Subjects with LDL Receptor Abnormalities | Evolocumab | Homozygous Familial Hypercholesterolemia | Phase 3 | Has Results | |
| Effect of Evolocumab on Coronary Artery Plaque Volume and Composition by CCTA and Microcalcification by F18-NaF PET | Evolocumab 18F-NaF PET CCTA | Cardiovascular Disease Hyperlipidemia | Phase 3 | No Results Available | |
| Open Label Study to Evaluate Safety, Tolerability and Efficacy of Evolocumab (AMG 145) in Pediatric Subjects (10 to 17 Years of Age) with HeFH or HoFH. | evolocumab (AMG 145) | Familial Hypercholesterolemia | Phase 3 | No Results Available | |
| Evolocumab Compared to LDL-C Apheresis in Patients Receiving LDL-C Apheresis Prior to Study Enrollment | Evolocumab LDL-C Apheresis | Hypercholesterolemia | Phase 3 | Has Results | |
| Safety, Tolerability, and Efficacy on Low-Density Lipoprotein Cholesterol (LDL-C) of Evolocumab in Participants with Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV) and Hyperlipidemia/Mixed Dyslipidemia | Evolocumab Placebo | Subjects with Hyperlipidemia, Dyslipidemia and HIV Infection | Phase 3 | Has Results | |
| Effects of PCSK9 Inhibition by Evolocumab on Postprandial Lipid Metabolism in Type 2 Diabetes | Evolocumab | Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus | Phase 4 | No Results Available | |
| Multislice Computed Tomography Assessment of PCSK9 Inhibition on Coronary Perfusion | Evolocumab | Coronary Artery Disease | Phase 4 | No Results Available | |
| Expanded Combination of Evolocumab Plus Empagliflozin on Diabetes: EXCEED-BHS3 Trial | Evolocumab | Dyslipidemia Associated with Type II Diabetes Mellitus Diabetes Mellitus, Type 2 | Phase 4 | No Results Available | |
| Impact of Evolocumab on the Effects of Clopidogrel in Patients | Evolocumab | Atherosclerotic Cardiovascular Disease | Phase 4 | No Results Available | |
| Lipid Management in Renal Transplant Recipients Using Evolocumab. | Evolocumab Statins | Hyperlipidemias | Phase 4 | No Results Available | |
| Reducing Intracranial Atherosclerosis with Repatha | Repatha | Ischemic Stroke | Phase 4 | No Results Available | |
| Evinacumab (REGN1500) | Study of Evinacumab (REGN1500) in Participants with Persistent Hypercholesterolemia | Evinacumab | Hypercholesterolemia | Phase 2 | No Results Available |
| Alirocumab Evolocumab | Pharmacodynamic Biomarkers to Support Biosimilar Development: PCSK9 Inhibitors | Evolocumab Alirocumab | Healthy Subjects Pharmacokinetics Pharmacodynamics | Phase 1 | No Results Available |
| JS002 | A Single Dose Escalation Study of PCSK9 Inhibitor (JS002) in Health Subjects | JS002 Placebo | Hypercholesterolemia | Phase 1 | No Results Available |
|
AFFITOPE® AT04A AFFITOPE® AT06A | Study Assessing Safety, Immunogenicity, and LDLc-Lowering Activity of 2 PCSK9 Targeting AFFITOPE Vaccines in Healthy Subjects | AFFITOPE® AT04A + adjuvant AFFITOPE® AT06A + adjuvant | Hypercholesterolemia | Phase 1 | No Results Available |
| AK102 | A Study of PCSK9 Inhibitor AK102 in Healthy Subjects | AK102 | Hypercholesterolaemia | Phase 1 | No Results Available |
| A Study to Evaluate the Safety and Efficacy of the PCSK9 Inhibitor AK102 in Patients with HoFH | AK102 Statins Ezetimibe | HoFH | Phase 2 | No Results Available | |
| A Study of PCSK9 Inhibitor AK102 in Patients with HeFH | AK102 Placebo Statins and/or Ezetimibe | HeFH | Phase 2 | No Results Available | |
| A Phase II Study of PCSK9 Inhibitor AK102 in Patients with Hypercholesterolemia | AK102 Statins and/or Ezetimibe | Hypercholesterolemia | Phase 2 | No Results Available | |
| Bococizumab | B-HIVE Study | Bococizumab | Dyslipidemia Cardiovascular Disease | Phase 3 | Has Results |
| IBI306 | Single Ascending Dose Study of PCSK-9 Inhibitor (IBI306) in Healthy Subjects. | IBI306 | Hypercholesterolemia | Phase 1 | No Results Available |
| Multiple Ascending Dose Study of PCSK-9 Inhibitor (IBI306) in Chinese Patients with Hypercholesterolemia | IBI306 | Hypercholesterolemia | Phase 2 | No Results Available | |
| A Study to Evaluate Safety and Efficacy of IBI306, a PCSK9 Monoclonal Antibody in Chinese Subjects with HoFH | IBI306 | HoFH | Phase 2 | No Results Available | |
| Application of PCSK9 Inhibitors in Patients with HeFH | Protein convertase subtilisin/kexin type 9 inhibitor | Efficacy and Safety Heterozygous Familial Hypercholesterolemia | Phase 3 | No Results Available | |
| A Study to Evaluate Safety and Efficacy of IBI306, a PCSK9 Monoclonal Antibody in Chinese Subjects with HoFH | IBI306 | Homozygous Familial Hypercholesterolemia | Phase 3 | No Results Available | |
| A Study of IBI306 in Participants with Hypercholesterolemia | IBI306 | Hypercholesterolemia | Phase 3 | No Results Available | |
| LIB003 | Study to Evaluate Efficacy and Safety of LIB003 in Patients on Lipid-Lowering Therapy Needing Additional LDL-C Reduction | LIB003 | LDL Cholesterol | Phase 2 | No Results Available |
| Long-term Efficacy and Safety of OLE LIB003 in HoFH, HeFH, and High-risk CVD Patients Requiring Further LDL-C Reduction | Lerodalcibep | Cardiovascular Disease with Mention of Arteriosclerosis Elevated Cholesterol Familial Hypercholesterolemia | Phase 3 | No Results Available | |
| Study of Long-Term Efficacy and Safety of LIB003 in cardiovascular disease or High Risk for cardiovascular disease Patients Needing Further LDL-C Reduction | Lerodalcibep | Cardiovascular Risk Factor Cardiovascular Diseases Cardiovascular Stroke Hypercholesterolemia | Phase 3 | No Results Available | |
| Study to Assess the Efficacy and Safety of LIB003 in HeFH Patients on Oral Lipid Therapy Needing Further LDL-C Reduction | Lerodalcibep | Heterozygous Familial Hypercholesterolemia | Phase 3 | No Results Available | |
| LIB003 evolocumab | Phase 3 Study to Evaluate the Efficacy and Safety of LIB003 with Evolocumab in HoFH | LIB003 Evolocumab | Homozygous Familial Hypercholesterolemia | Phase 3 | No Results Available |
| LIB003 Evolocumab alirocumab | Trial to Evaluate Efficacy and Safety of LIB003, Evolocumab and Alirocumab in High-risk cardiovascular disease Patients | Lerodalcibep Evolocumab Alirocumab | Hypercholesterolemia Cardiovascular Diseases | Phase 3 | No Results Available |
| PF-04950615 (RN316) | A Multiple Dose Study Of PF-04950615 (RN316) In Subjects on Maximum Doses of Statins | PF-04950615 (RN316) | Hypercholesterolemia Dyslipidemia | Phase 2 | Has Results |
| Lerodalcibep | Study of Efficacy and Safety of LIB003 in Patient with cardiovascular disease on Statins Requiring Additional LDL-C Reduction | Lerodalcibep | Cardiovascular Diseases Hyper-LDL-cholesterolemia | Phase 3 | No Results Available |
| LGT209 | Safety, Tolerability, PK, and PD of LGT209 in Healthy Volunteers and Patients with Hypercholesterolemia | LGT209 Placebo | Hypercholesterolemia | Phase 1 | No Results Available |
| Safety, Pharmacokinetics, and Pharmacodynamics of LGT209 in Healthy Volunteers with Elevated Cholesterol in Hypercholesterolemic Patients Treated with Statins | LGT209 50 mg LGT209 300 mg Placebo Statins (atorvastatin or simvastatin) | Hypercholesterolemia LDL Cholesterol | Phase 1 | No Results Available | |
| siRNA Inclisiran | A Study of Inclisiran in Participants with Renal Impairment Compared to Participants with Normal Renal Function (ORION-7) | Inclisiran | Renal Impairment | Phase 1 | No Results Available |
| An Extension Trial of Inclisiran Compared to Evolocumab in Participants with Cardiovascular Disease and High Cholesterol | Inclisiran Evolocumab | Atherosclerotic Cardiovascular Disease Symptomatic Atherosclerosis Type 2 Diabetes Familial Hypercholesterolemia | Phase 2 | No Results Available | |
| A Randomized Trial Assessing the Effects of Inclisiran on Clinical Outcomes Among People with Cardiovascular Disease | Inclisiran Placebo | Atherosclerotic Cardiovascular Disease | Phase 3 | No Results Available | |
| Trial to Assess the Effect of Long-Term Dosing of Inclisiran in Subjects with High CV Risk and Elevated LDL-C | Inclisiran Sodium | ASCVD Elevated Cholesterol Heterozygous Familial Hypercholesterolemia Homozygous Familial Hypercholesterolemia | Phase 3 | No Results Available | |
| Inclisiran for Subjects with ASCVD or ASCVD-Risk Equivalents and Elevated Low-density Lipoprotein Cholesterol | Inclisiran Sodium Placebo | ASCVD Risk Factor, Cardiovascular Elevated Cholesterol | Phase 3 | Has Results | |
| Inclisiran for Participants with Atherosclerotic Cardiovascular Disease and Elevated Low-density Lipoprotein Cholesterol | Inclisiran Sodium Placebo | ASCVD Elevated Cholesterol | Phase 3 | Has Results | |
| Trial to Evaluate the Effect of Inclisiran Treatment on Low-Density Lipoprotein Cholesterol (LDL-C) in Subjects with HeFH | Inclisiran Placebo | Heterozygous Familial Hypercholesterolemia Elevated Cholesterol | Phase 3 | Has Results | |
| A Study of Inclisiran in Participants with HoFH | Inclisiran for injection Placebo | Homozygous Familial Hypercholesterolemia | Phase 3 | No Results Available | |
| RNA ALN-PCSSC | A Study of ALN-PCSSC in Participants with HoFH | ALN-PCSSC Standard of Care | HoFH | Phase 2 | Has Results |
| Trial to Evaluate the Effect of ALN-PCSSC Treatment on Low Density Lipoprotein Cholesterol (LDL-C) | ALN-PCSSC Normal | Atherosclerotic Cardiovascular Disease Familial Hypercholesterolemia Diabetes | Phase 2 | Has Results | |
| CIVI 007 | Phase 2a Study to Assess CIVI 007 in Patients on a Background of Statin Therapy | CIVI 007 | Hypercholesterolemia | Phase 2 | No Results Available |
| PCSK9 AZD8233 | A Study of AZD8233 in Participants with Dyslipidemia. | Part A: Placebo Part A: AZD8233 Part B: Placebo Part B: AZD8233 | Dyslipidemia | Phase 1 | No Results Available |
| A Study of AZD8233 in Participants with Dyslipidemia | AZD8233 Placebo | Dyslipidemia | Phase 2 | No Results Available | |
| A Study of AZD8233 in Participants with Dyslipidemia. | Part A: Placebo Part A: AZD8233 Part B: Placebo Part B: AZD8233 | Dyslipidemia | No Results Available | ||
| PCSK9 SPC5001 | Multiple Ascending Dose Study of SPC5001 in Treatment of Healthy Subjects and Subjects with FH | SPC5001 Saline 0.9% | Hypercholesterolemia | Phase 1 | No Results Available |
| EPC | PCSK9 Inhibitors in the Progression of Aortic Stenosis | PCSK9 Inhibitor [EPC] Placebos | Aortic Valve Stenosis | Phase 2 | No Results Available |
| Fish oil | Comparison of EPA and DHA-Rich Fish Oils on Lipoprotein Metabolism in Adults | EPA-rich fish oil DHA-rich fish oil | Lipoprotein Metabolism PCSK9 Proteomics | Phase 2 | Has Results |
| Drugs | Title | Interventions | Conditions | Phase | Study Results |
| Alirocumab | PCSK9 Inhibition in Patients with Symptomatic Intracranial Atherosclerosis | Alirocumab | Stroke Intracranial Atherosclerosis Intraplaque Hemorrhage | Early Phase 1 | No Results Available |
| Safety, Tolerability, and Bioeffects of Alirocumab in Non-treatment Seeking Heavy Drinkers | Alirocumab | Alcohol Associated Liver Disease Heavy Drinking Behavior | Phase 1 | No Results Available | |
| A Study of Alirocumab in Participants with ADH and GOFm of the PCSK9 Gene or LOFm of the Apo B Gene | Alirocumab | Hypercholesterolemia | Phase 2 | Has Results | |
| PCSK9 Inhibition After Heart Transplantation | alirocumab | Vasculopathy | Phase 2 | No Results Available | |
| Treatment of Severe Infection with Antihyperlipidemia Drug | Alirocumab | Sepsis Septic Shock | Phase 2 | No Results Available | |
| Open-Label Extension of Study R727-CL-1003 (NCT01266876) to Evaluate the Long-Term Safety and Efficacy of Alirocumab (REGN727) in Participants with HeFH | Alirocumab | Hypercholesterolemia HeFH | Phase 2 | Has Results | |
| Effect of PCSK9 Inhibition on Cardiovascular Risk in Treated HIV Infection (EPIC-HIV Study) | Alirocumab | Dyslipidemias Cardiovascular DiseasesHIV Infections | Phase 3 | No Results Available | |
| PCSK 9 Inhibition as Secondary Prevention in Renal Transplant Patients | Evolocumab | Kidney Transplant Recipients with High Cardiovascular Risk Score | Phase 3 | No Results Available | |
| Treatment of Severe Infection with Antihyperlipidemia Drug | Alirocumab | Sepsis Septic Shock | Phase 3 | No Results Available | |
| Efficacy and Safety of Alirocumab (SAR236553/REGN727) Versus Placebo on Top of Lipid-Modifying Therapy in Patients with HeFH Not Adequately Controlled with Their Lipid-Modifying Therapy | Alirocumab | Hypercholesterolemia | Phase 3 | Has Results | |
| Vascular Effects of Alirocumab in Acute MI-Patients | Alirocumab | Coronary Vessel Coronary Circulation Atheroma; Myocardial | Phase 3 | No Results Available | |
| An Efficacy and Safety Study of Alirocumab in Children and Adolescents with HoFH | Alirocumab SAR236553 (REGN727) Atorvastatin Simvastatin Fluvastatin Pravastatin Lovastatin Rosuvastatin Ezetimibe | Hypercholesterolemia | Phase 3 | Has Results | |
| Impact of Early PCSK9 Inhibitor on Heart After Acute Myocardium Infarction | Alirocumab standard medications | Early PCSK9 Inhibitor on Ventricular Remodeling | Phase 4 | No Results Available | |
| Impact of Early PCSK9 Inhibitor Treatment on Heart After Acute Myocardium Infarction | alirocumab | Acute Myocardial Infarction | Phase 4 | No Results Available | |
| Impact of PCSK9 Inhibitors on Coronary Plaque Composition and Vulnerability Assessed by Optical Coherence Tomography | PCSK9 inhibitor plus statin standard statin therapy | Randomized Controlled Trials | Phase 4 | No Results Available | |
| Assessment of Atherosclerotic Plaque Characteristics Change by DCE-MRI with Alirocumab | Alirocumab | Atherosclerosis Hyperlipidemia | Phase 4 | No Results Available | |
| Alirocumab SAR236553 (REGN727) | Pharmacokinetic and Tolerability of Alirocumab SAR236553 (REGN727) in Patients with Hepatic Impairment and in Healthy Subjects | alirocumab SAR236553 (REGN727) | Hypercholesterolemia | Phase 1 | No Results Available |
| Pharmacokinetic of Alirocumab SAR236553 (REGN727) Administered Subcutaneously at 3 Different Injection Sites in Healthy Subjects | alirocumab SAR236553 (REGN727) | Hypercholesterolemia | Phase 1 | No Results Available | |
| Evolocumab | Cholesterol Disruption in Combination with FOLFIRINOX in Patients with Metastatic Pancreatic Adenocarcinoma | Evolocumab, Atorvastatin and Ezetimibe with FOLFIRINOX | Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma Pancreatic Cancer Pancreas Cancer Metastatic Cancer | Early Phase 1 | No Results Available |
| Study to Evaluate Pharmacokinetics and Pharmacodynamics of Evolocumab in rHGG | Evolocumab | Malignant Glioma Glioblastoma | Early Phase 1 | No Results Available | |
| PCSK9 Inhibitor Treatment for Patients with SPG5 | Evolocumab | Hereditary Spastic Paraplegia Type 5 | Phase 1 | No Results Available | |
| Evaluation of the Efficacy and Safety of Bempedoic Acid (ETC-1002) 180 mg when Added to PCSK9 Inhibitor Therapy | bempedoic acid 180 mg evolocumab | Hypercholesterolemia | Phase 2 | Has Results | |
| Impact of PCSK9 Inhibitors on Coronary Microvascular Dysfunction in Patients with Atherosclerotic Cardiovascular Disease Proved by Myocardial Ischemia and Needing Coronarography | Evolocumab | Atherosclerotic Cardiovascular Disease | Phase 2 | No Results Available | |
| Evolocumab for PCSK9 Lowering in Early Acute Sepsis (The PLEASE Study) | Evolocumab | Sepsis | Phase 2 | No Results Available | |
| Reduction of LDL-C with PCSK9 Inhibition in HeFH Disorder Study | Biological: Evolocumab | Hypercholesterolemia, Familial | Phase 2 | Has Results | |
| PCSK9 Inhibitor Treatment for Patients with SPG5 | evolocumab | Hereditary Spastic Paraplegia Type 5 | Phase 2 | No Results Available | |
| LAPLACE-TIMI 57: LDL-C Assessment with PCSK9 monoclonal Antibody Inhibition Combined with Statin therapy | Evolocumab | Hyperlipidemia | Phase 2 | Has Results | |
| Trial Assessing Long-Term Use of PCSK9 Inhibition in Subjects with Genetic LDL Disorders | Evolocumab | Severe Familial Hypercholesterolemia | Phase 2 | Has Results | |
| Monoclonal Antibody Against PCSK9 to Reduce Elevated LDL-C in Adults Currently Not Receiving Drug Therapy for Easing Lipid Levels | Evolocumab Ezetimibe | Hyperlipidemia | Phase 2 | Has Results | |
| Goal Achievement After Utilizing an Anti-PCSK9 Antibody in Statin Intolerant Subjects | Evolocumab Ezetimibe | Hyperlipidemia | Phase 2 | Has Results | |
| Trial Evaluating PCSK9 Antibody in Subjects with LDL Receptor Abnormalities | Evolocumab | HoFH | Phase 2 | Has Results | |
| Impact of PCSK9 Inhibition on Clinical Outcome in Patients During the Inflammatory Stage of the COVID-19 | Evolocumab Saline solution | SARS-CoV-2 Infection | Phase 3 | No Results Available | |
| Effects of PCSK9 Inhibition on Arterial Wall Inflammation in Patients with Elevated Lipoprotein(a) (Lp(a)) | Evolocumab Placebo | Subjects with Hyperlipidemia, Dyslipidemia | Phase 3 | Has Results | |
| Trial Assessing Long-Term Use of PCSK9 Inhibition in Subjects with Genetic LDL Disorders | Biological: Evolocumab | Severe Familial Hypercholesterolemia | Phase 3 | Has Results | |
| Trial Assessing Efficacy, Safety, and Tolerability of Proprotein Convertase Subtilisin/Kexin Type 9 (PCSK9) Inhibition in Pediatric Subjects with Genetic LDL Disorders | Evolocumab Placebo | Heterozygous Familial Hypercholesterolemia | Phase 3 | Has Results | |
| Evaluating PCSK9 Binding Antibody Influence on cognitive Health in High Cardiovascular Risk Subjects | Evolocumab Placebo Background Statin Therapy | Dyslipidemia | Phase 3 | Has Results | |
| Durable Effect of PCSK9 Antibody Compared with placebo Study | Evolocumab Placebo Atorvastatin Ezetimibe Other: Diet Only | Hypercholesterolemia | Phase 3 | Has Results | |
| Goal Achievement After Utilizing an Anti-PCSK9 Antibody in Statin Intolerant Subjects-4 | Evolocumab Ezetimibe | Hypercholesterolemia | Phase 3 | Has Results | |
| Effects on Lipoprotein Metabolism from PCSK9 Inhibition Utilizing a Monoclonal Antibody | Evolocumab Atorvastatin | Primary Hyperlipidemia and Mixed Dyslipidemia | Phase 3 | Has Results | |
| LDL-C Assessment with PCSK9 Monoclonal Antibody Inhibition Combined with Statin Therapy-2 | Evolocumab Ezetimibe Atorvastatin Rosuvastatin Simvastatin | Hyperlipidemia | Phase 3 | Has Results | |
| Goal Achievement After Utilizing an Anti-PCSK9 Antibody in Statin Intolerant Subjects-3 | Atorvastatin Ezetimibe Evolocumab | Hyperlipidemia | Phase 3 | Has Results | |
| Further Cardiovascular Outcomes Research with PCSK9 Inhibition in Subjects with Elevated Risk Open-label Extension | Evolocumab | Dyslipidemia | Phase 3 | No Results Available | |
| Goal Achievement After Utilizing an Anti-PCSK9 Antibody in Statin Intolerant Subjects -2 | Evolocumab Ezetimibe | Hyperlipidemia | Phase 3 | Has Results | |
| Further Cardiovascular Outcomes Research with PCSK9 Inhibition in Subjects with Elevated Risk | Evolocumab | Dyslipidemia | Phase 3 | Has Results | |
| Reduction of LDL-C with PCSK9 Inhibition in HeFH Disorder Study-2 | Evolocumab | Hyperlipidemia | Phase 3 | Has Results | |
| Global Assessment of Plaque regression with a PCSK9 antibody as Measured by IVUS | Evolocumab | Hypercholesterolemia | Phase 3 | Has Results | |
| Monoclonal Antibody Against PCSK9 to Reduce Elevated LDL-C in Subjects Currently Not Receiving Drug Therapy for Easing Lipid Levels-2 | Evolocumab Ezetimibe | Hyperlipidemia | Phase 3 | Has Results | |
| Trial Evaluating PCSK9 Antibody in Subjects with LDL Receptor Abnormalities | Evolocumab | Homozygous Familial Hypercholesterolemia | Phase 3 | Has Results | |
| Effect of Evolocumab on Coronary Artery Plaque Volume and Composition by CCTA and Microcalcification by F18-NaF PET | Evolocumab 18F-NaF PET CCTA | Cardiovascular Disease Hyperlipidemia | Phase 3 | No Results Available | |
| Open Label Study to Evaluate Safety, Tolerability and Efficacy of Evolocumab (AMG 145) in Pediatric Subjects (10 to 17 Years of Age) with HeFH or HoFH. | evolocumab (AMG 145) | Familial Hypercholesterolemia | Phase 3 | No Results Available | |
| Evolocumab Compared to LDL-C Apheresis in Patients Receiving LDL-C Apheresis Prior to Study Enrollment | Evolocumab LDL-C Apheresis | Hypercholesterolemia | Phase 3 | Has Results | |
| Safety, Tolerability, and Efficacy on Low-Density Lipoprotein Cholesterol (LDL-C) of Evolocumab in Participants with Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV) and Hyperlipidemia/Mixed Dyslipidemia | Evolocumab Placebo | Subjects with Hyperlipidemia, Dyslipidemiaand HIV Infection | Phase 3 | Has Results | |
| Effects of PCSK9 Inhibition by Evolocumab on Postprandial Lipid Metabolism in Type 2 Diabetes | Evolocumab | Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus | Phase 4 | No Results Available | |
| Multislice Computed Tomography Assessment of PCSK9 Inhibition on Coronary Perfusion | Evolocumab | Coronary Artery Disease | Phase 4 | No Results Available | |
| Expanded Combination of Evolocumab Plus Empagliflozin on Diabetes: EXCEED-BHS3 Trial | Evolocumab | Dyslipidemia Associated with Type II Diabetes Mellitus Diabetes Mellitus, Type 2 | Phase 4 | No Results Available | |
| Impact of Evolocumab on the Effects of Clopidogrel in Patients | Evolocumab | Atherosclerotic Cardiovascular Disease | Phase 4 | No Results Available | |
| Lipid Management in Renal Transplant Recipients Using Evolocumab. | Evolocumab Statins | Hyperlipidemias | Phase 4 | No Results Available | |
| Reducing Intracranial Atherosclerosis with Repatha | Repatha | Ischemic Stroke | Phase 4 | No Results Available | |
| Evinacumab (REGN1500) | Study of Evinacumab (REGN1500) in Participants with Persistent Hypercholesterolemia | Evinacumab | Hypercholesterolemia | Phase 2 | No Results Available |
| Alirocumab Evolocumab | Pharmacodynamic Biomarkers to Support Biosimilar Development: PCSK9 Inhibitors | Evolocumab Alirocumab | Healthy Subjects Pharmacokinetics Pharmacodynamics | Phase 1 | No Results Available |
| JS002 | A Single Dose Escalation Study of PCSK9 Inhibitor (JS002) in Health Subjects | JS002 Placebo | Hypercholesterolemia | Phase 1 | No Results Available |
| AFFITOPE® AT04A AFFITOPE® AT06A | Study Assessing Safety, Immunogenicity, and LDLc-Lowering Activity of 2 PCSK9 Targeting AFFITOPE Vaccines in Healthy Subjects | AFFITOPE® AT04A + adjuvant AFFITOPE® AT06A + adjuvant | Hypercholesterolemia | Phase 1 | No Results Available |
| AK102 | A Study of PCSK9 Inhibitor AK102 in Healthy Subjects | AK102 | Hypercholesterolaemia | Phase 1 | No Results Available |
| A Study to Evaluate the Safety and Efficacy of the PCSK9 Inhibitor AK102 in Patients with HoFH | AK102 Statins Ezetimibe | HoFH | Phase 2 | No Results Available | |
| A Study of PCSK9 Inhibitor AK102 in Patients with HeFH | AK102 Placebo Statins and/or Ezetimibe | HeFH | Phase 2 | No Results Available | |
| A Phase II Study of PCSK9 Inhibitor AK102 in Patients with Hypercholesterolemia | AK102 Statins and/or Ezetimibe | Hypercholesterolemia | Phase 2 | No Results Available | |
| Bococizumab | B-HIVE Study | Bococizumab | Dyslipidemia Cardiovascular Disease | Phase 3 | Has Results |
| IBI306 | Single Ascending Dose Study of PCSK-9 Inhibitor (IBI306) in Healthy Subjects. | IBI306 | Hypercholesterolemia | Phase 1 | No Results Available |
| Multiple Ascending Dose Study of PCSK-9 Inhibitor (IBI306) in Chinese Patients with Hypercholesterolemia | IBI306 | Hypercholesterolemia | Phase 2 | No Results Available | |
| A Study to Evaluate Safety and Efficacy of IBI306, a PCSK9 Monoclonal Antibody in Chinese Subjects with HoFH | IBI306 | HoFH | Phase 2 | No Results Available | |
| Application of PCSK9 Inhibitors in Patients with HeFH | Protein convertase subtilisin/kexin type 9 inhibitor | Efficacy and Safety Heterozygous Familial Hypercholesterolemia | Phase 3 | No Results Available | |
| A Study to Evaluate Safety and Efficacy of IBI306, a PCSK9 Monoclonal Antibody in Chinese Subjects with HoFH | IBI306 | Homozygous Familial Hypercholesterolemia | Phase 3 | No Results Available | |
| A Study of IBI306 in Participants with Hypercholesterolemia | IBI306 | Hypercholesterolemia | Phase 3 | No Results Available | |
| LIB003 | Study to Evaluate Efficacy and Safety of LIB003 in Patients on Lipid-Lowering Therapy Needing Additional LDL-C Reduction | LIB003 | LDL Cholesterol | Phase 2 | No Results Available |
| Long-term Efficacy and Safety of OLE LIB003 in HoFH, HeFH, and High-risk CVD Patients Requiring Further LDL-C Reduction | Lerodalcibep | Cardiovascular Disease with Mention of Arteriosclerosis Elevated Cholesterol Familial Hypercholesterolemia | Phase 3 | No Results Available | |
| Study of Long-Term Efficacy and Safety of LIB003 in cardiovascular disease or High Risk for cardiovascular disease Patients Needing Further LDL-C Reduction | Lerodalcibep | Cardiovascular Risk Factor Cardiovascular Diseases Cardiovascular Stroke Hypercholesterolemia | Phase 3 | No Results Available | |
| Study to Assess the Efficacy and Safety of LIB003 in HeFH Patients on Oral Lipid Therapy Needing Further LDL-C Reduction | Lerodalcibep | Heterozygous Familial Hypercholesterolemia | Phase 3 | No Results Available | |
| LIB003 evolocumab | Phase 3 Study to Evaluate the Efficacy and Safety of LIB003 with Evolocumab in HoFH | LIB003 Evolocumab | Homozygous Familial Hypercholesterolemia | Phase 3 | No Results Available |
| LIB003 Evolocumab alirocumab | Trial to Evaluate Efficacy and Safety of LIB003, Evolocumab and Alirocumab in High-risk cardiovascular disease Patients | Lerodalcibep Evolocumab Alirocumab | Hypercholesterolemia Cardiovascular Diseases | Phase 3 | No Results Available |
| PF-04950615 (RN316) | A Multiple Dose Study Of PF-04950615 (RN316) In Subjects on Maximum Doses of Statins | PF-04950615 (RN316) | Hypercholesterolemia Dyslipidemia | Phase 2 | Has Results |
| Lerodalcibep | Study of Efficacy and Safety of LIB003 in Patient with cardiovascular disease on Statins Requiring Additional LDL-C Reduction | Lerodalcibep | Cardiovascular DiseasesHyper-LDL-cholesterolemia | Phase 3 | No Results Available |
| LGT209 | Safety, Tolerability, PK, and PD of LGT209 in Healthy Volunteers and Patients with Hypercholesterolemia | LGT209 Placebo | Hypercholesterolemia | Phase 1 | No Results Available |
| Safety, Pharmacokinetics, and Pharmacodynamics of LGT209 in Healthy Volunteers with Elevated Cholesterol in Hypercholesterolemic Patients Treated with Statins | LGT209 50 mg LGT209 300 mg Placebo Statins (atorvastatin or simvastatin) | Hypercholesterolemia LDL Cholesterol | Phase 1 | No Results Available | |
| siRNA Inclisiran | A Study of Inclisiran in Participants with Renal Impairment Compared to Participants with Normal Renal Function (ORION-7) | Inclisiran | Renal Impairment | Phase 1 | No Results Available |
| An Extension Trial of Inclisiran Compared to Evolocumab in Participants with Cardiovascular Disease and High Cholesterol | Inclisiran Evolocumab | Atherosclerotic Cardiovascular Disease Symptomatic Atherosclerosis Type 2 Diabetes Familial Hypercholesterolemia | Phase 2 | No Results Available | |
| A Randomized Trial Assessing the Effects of Inclisiran on Clinical Outcomes Among People with Cardiovascular Disease | Inclisiran Placebo | Atherosclerotic Cardiovascular Disease | Phase 3 | No Results Available | |
| Trial to Assess the Effect of Long-Term Dosing of Inclisiran in Subjects with High CV Risk and Elevated LDL-C | Inclisiran Sodium | ASCVD Elevated Cholesterol Heterozygous Familial Hypercholesterolemia Homozygous Familial Hypercholesterolemia | Phase 3 | No Results Available | |
| Inclisiran for Subjects with ASCVD or ASCVD-Risk Equivalents and Elevated Low-density Lipoprotein Cholesterol | Inclisiran Sodium Placebo | ASCVD Risk Factor, Cardiovascular Elevated Cholesterol | Phase 3 | Has Results | |
| Inclisiran for Participants with Atherosclerotic Cardiovascular Disease and Elevated Low-density Lipoprotein Cholesterol | Inclisiran Sodium Placebo | ASCVD Elevated Cholesterol | Phase 3 | Has Results | |
| Trial to Evaluate the Effect of Inclisiran Treatment on Low-Density Lipoprotein Cholesterol (LDL-C) in Subjects with HeFH | Inclisiran Placebo | Heterozygous Familial Hypercholesterolemia Elevated Cholesterol | Phase 3 | Has Results | |
| A Study of Inclisiran in Participants with HoFH | Inclisiran for injection Placebo | Homozygous Familial Hypercholesterolemia | Phase 3 | No Results Available | |
| RNA ALN-PCSSC | A Study of ALN-PCSSC in Participants with HoFH | ALN-PCSSC Standard of Care | HoFH | Phase 2 | Has Results |
| Trial to Evaluate the Effect of ALN-PCSSC Treatment on Low Density Lipoprotein Cholesterol (LDL-C) | ALN-PCSSC Normal | Atherosclerotic Cardiovascular Disease Familial Hypercholesterolemia Diabetes | Phase 2 | Has Results | |
| CIVI 007 | Phase 2a Study to Assess CIVI 007 in Patients on a Background of Statin Therapy | CIVI 007 | Hypercholesterolemia | Phase 2 | No Results Available |
| PCSK9 AZD8233 | A Study of AZD8233 in Participants with Dyslipidemia. | Part A: Placebo Part A: AZD8233 Part B: Placebo Part B: AZD8233 | Dyslipidemia | Phase 1 | No Results Available |
| A Study of AZD8233 in Participants with Dyslipidemia | AZD8233 Placebo | Dyslipidemia | Phase 2 | No Results Available | |
| A Study of AZD8233 in Participants with Dyslipidemia. | Part A: Placebo Part A: AZD8233 Part B: Placebo Part B: AZD8233 | Dyslipidemia | No Results Available | ||
| PCSK9 SPC5001 | Multiple Ascending Dose Study of SPC5001 in Treatment of Healthy Subjects and Subjects with FH | SPC5001 Saline 0.9% | Hypercholesterolemia | Phase 1 | No Results Available |
| EPC | PCSK9 Inhibitors in the Progression of Aortic Stenosis | PCSK9 Inhibitor [EPC] Placebos | Aortic Valve Stenosis | Phase 2 | No Results Available |
| Fish oil | Comparison of EPA and DHA-Rich Fish Oils on Lipoprotein Metabolism in Adults | EPA-rich fish oil DHA-rich fish oil | Lipoprotein Metabolism PCSK9 Proteomics | Phase 2 | Has Results |
References
- Seidah, N.G.; Benjannet, S.; Wickham, L.; Marcinkiewicz, J.; Jasmin, S.B.; Stifani, S.; Basak, A.; Prat, A.; Chretien, M. The secretory proprotein convertase neural apoptosis-regulated convertase 1 (NARC-1): Liver regeneration and neuronal differentiation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 928–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yurtseven, E.; Ural, D.; Baysal, K.; Tokgözoğlu, L. An Update on the Role of PCSK9 in Atherosclerosis. J. Atheroscler. Thromb. 2020, 27, 909–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seidah, N.; Awan, Z.; Chrétien, M.; Mbikay, M. PCSK9: A key modulator of cardiovascular health. Circ. Res. 2014, 114, 1022–1036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lo Surdo, P.; Bottomley, M.; Calzetta, A.; Settembre, E.; Cirillo, A.; Pandit, S.; Ni, Y.; Hubbard, B.; Sitlani, A.; Carfí, A. Mechanistic implications for LDL receptor degradation from the PCSK9/LDLR structure at neutral pH. EMBO Rep. 2011, 12, 1300–1305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Denis, M.; Marcinkiewicz, J.; Zaid, A.; Gauthier, D.; Poirier, S.; Lazure, C.; Seidah, N.; Prat, A. Gene inactivation of proprotein convertase subtilisin/kexin type 9 reduces atherosclerosis in mice. Circulation 2012, 125, 894–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leander, K.; Mälarstig, A.; Van’t Hooft, F.; Hyde, C.; Hellénius, M.; Troutt, J.; Konrad, R.; Öhrvik, J.; Hamsten, A.; de Faire, U. Circulating Proprotein Convertase Subtilisin/Kexin Type 9 (PCSK9) Predicts Future Risk of Cardiovascular Events Independently of Established Risk Factors. Circulation 2016, 133, 1230–1239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, J.; Oemrawsingh, R.; Garcia-Garcia, H.; Boersma, E.; van Geuns, R.; Serruys, P.; Kardys, I.; Akkerhuis, K. PCSK9 in relation to coronary plaque inflammation: Results of the ATHEROREMO-IVUS study. Atherosclerosis 2016, 248, 117–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stein, E.A.; Mellis, S.; Yancopoulos, G.D.; Stahl, N.; Logan, D.; Smith, W.B.; Lisbon, E.; Gutierrez, M.; Webb, C.; Wu, R.; et al. Effect of a monoclonal antibody to PCSK9 on LDL cholesterol. N. Engl. J. Med. 2012, 366, 1108–1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Z.; Peng, J.; Ren, Z.; Yang, J.; Li, T.; Li, T.; Wang, Z.; Wei, D.; Liu, L.; Zheng, X.; et al. New role of PCSK9 in atherosclerotic inflammation promotion involving the TLR4/NF-κB pathway. Atherosclerosis 2017, 262, 113–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giunzioni, I.; Tavori, H.; Covarrubias, R.; Major, A.; Ding, L.; Zhang, Y.; DeVay, R.; Hong, L.; Fan, D.; Predazzi, I.; et al. Local effects of human PCSK9 on the atherosclerotic lesion. J. Pathol. 2016, 238, 52–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tavori, H.; Giunzioni, I.; Predazzi, I.; Plubell, D.; Shivinsky, A.; Miles, J.; Devay, R.; Liang, H.; Rashid, S.; Linton, M.; et al. Human PCSK9 promotes hepatic lipogenesis and atherosclerosis development via apoE- and LDLR-mediated mechanisms. Cardiovasc. Res. 2016, 110, 268–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferri, N.; Tibolla, G.; Pirillo, A.; Cipollone, F.; Mezzetti, A.; Pacia, S.; Corsini, A.; Catapano, A.L. Proprotein convertase subtilisin kexin type 9 (PCSK9) secreted by cultured smooth muscle cells reduces macrophages LDLR levels. Atherosclerosis 2012, 220, 381–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamamoto, T.; Lu, C.; Ryan, R.O. A two-step binding model of PCSK9 interaction with the low density lipoprotein receptor. J. Biol. Chem. 2011, 286, 5464–5470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, Z.; Liu, S.; Wang, X.; Deng, X.; Fan, Y.; Sun, C.; Wang, Y.; Mehta, J. Hemodynamic shear stress via ROS modulates PCSK9 expression in human vascular endothelial and smooth muscle cells and along the mouse aorta. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2015, 22, 760–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, Z.; Liu, S.; Wang, X.; Deng, X.; Fan, Y.; Shahanawaz, J.; Shmookler Reis, R.; Varughese, K.; Sawamura, T.; Mehta, J. Cross-talk between LOX-1 and PCSK9 in vascular tissues. Cardiovasc. Res. 2015, 107, 556–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grune, J.; Meyborg, H.; Bezhaeva, T.; Kappert, K.; Hillmeister, P.; Kintscher, U.; Pieske, B.; Stawowy, P. PCSK9 regulates the chemokine receptor CCR2 on monocytes. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2017, 485, 312–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Deng, X.; Zhang, P.; Wang, X.; Fan, Y.; Zhou, S.; Mu, S.; Mehta, J.L.; Ding, Z. Blood flow patterns regulate PCSK9 secretion via MyD88-mediated pro-inflammatory cytokines. Cardiovasc. Res. 2020, 116, 1721–1732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cammisotto, V.; Pastori, D.; Nocella, C.; Bartimoccia, S.; Castellani, V.; Marchese, C.; Scavalli, A.S.; Ettorre, E.; Viceconte, N.; Violi, F.; et al. PCSK9 Regulates Nox2-Mediated Platelet Activation via CD36 Receptor in Patients with Atrial Fibrillation. Antioxidants 2020, 9, 296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, Z.; Hu, L.; Zhang, J.; Yang, W.; Liu, X.; Jia, D.; Yao, Z.; Chang, L.; Pan, G.; Zhong, H.; et al. PCSK9 (Proprotein Convertase Subtilisin/Kexin 9) Enhances Platelet Activation, Thrombosis, and Myocardial Infarct Expansion by Binding to Platelet CD36. Circulation 2021, 143, 45–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walley, K.R.; Thain, K.R.; Russell, J.A.; Reilly, M.P.; Meyer, N.J.; Ferguson, J.F.; Christie, J.D.; Nakada, T.A.; Fjell, C.D.; Thair, S.A.; et al. PCSK9 is a critical regulator of the innate immune response and septic shock outcome. Sci. Transl. Med. 2014, 6, 258ra143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, X.; Bao, X.; Hu, M.; Chang, H.; Jiao, M.; Cheng, J.; Xie, L.; Huang, Q.; Li, F.; Li, C. Inhibition of PCSK9 potentiates immune checkpoint therapy for cancer. Nature 2020, 588, 693–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caron, J.; Pène, V.; Tolosa, L.; Villaret, M.; Luce, E.; Fourrier, A.; Heslan, J.; Saheb, S.; Bruckert, E.; Gómez-Lechón, M.; et al. Low-density lipoprotein receptor-deficient hepatocytes differentiated from induced pluripotent stem cells allow familial hypercholesterolemia modeling, CRISPR/Cas-mediated genetic correction, and productive hepatitis C virus infection. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2019, 10, 221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gan, E.S.; Tan, H.C.; Le, D.H.T.; Huynh, T.T.; Wills, B.; Seidah, N.G.; Ooi, E.E.; Yacoub, S. Dengue virus induces PCSK9 expression to alter antiviral responses and disease outcomes. J. Clin. Investig. 2020, 130, 5223–5234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cawley, N.X.; Lyons, A.T.; Abebe, D.; Wassif, C.A.; Porter, F.D. Evaluation of the Potential Role of Proprotein Convertase Subtilisin/Kexin Type 9 (PCSK9) in Niemann-Pick Disease, Type C1. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 2430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khoshnejad, M.; Patel, A.; Wojtak, K.; Kudchodkar, S.B.; Humeau, L.; Lyssenko, N.N.; Rader, D.J.; Muthumani, K.; Weiner, D.B. Development of Novel DNA-Encoded PCSK9 Monoclonal Antibodies as Lipid-Lowering Therapeutics. Mol. Ther. J. Am. Soc. Gene Ther. 2019, 27, 188–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, J.; Wang, S. Comparative Effectiveness of Inclisiran 100, 300, and 500 mg in a Population with Hyperlipidemia: A Network Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. Am. J. Cardiovasc. Drugs 2018, 18, 271–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosenson, R.S.; Hegele, R.A.; Fazio, S.; Cannon, C.P. The Evolving Future of PCSK9 Inhibitors. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2018, 72, 314–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabatine, M.S.; Giugliano, R.P.; Keech, A.C.; Honarpour, N.; Wiviott, S.D.; Murphy, S.A.; Kuder, J.F.; Wang, H.; Liu, T.; Wasserman, S.M.; et al. Evolocumab and Clinical Outcomes in Patients with Cardiovascular Disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 376, 1713–1722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwartz, G.G.; Bessac, L.; Berdan, L.G.; Bhatt, D.L.; Bittner, V.; Diaz, R.; Goodman, S.G.; Hanotin, C.; Harrington, R.A.; Jukema, J.W.; et al. Effect of alirocumab, a monoclonal antibody to PCSK9, on long-term cardiovascular outcomes following acute coronary syndromes: Rationale and design of the ODYSSEY outcomes trial. Am. Heart J. 2014, 168, 682–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giugliano, R.P.; Mach, F.; Zavitz, K.; Kurtz, C.; Im, K.; Kanevsky, E.; Schneider, J.; Wang, H.; Keech, A.; Pedersen, T.R.; et al. Cognitive Function in a Randomized Trial of Evolocumab. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 377, 633–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benjannet, S.; Rhainds, D.; Essalmani, R.; Mayne, J.; Wickham, L.; Jin, W.; Asselin, M.C.; Hamelin, J.; Varret, M.; Allard, D.; et al. NARC-1/PCSK9 and its natural mutants: Zymogen cleavage and effects on the low density lipoprotein (LDL) receptor and LDL cholesterol. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 48865–48875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ray, K.K.; Wright, R.S.; Kallend, D.; Koenig, W.; Leiter, L.A.; Raal, F.J.; Bisch, J.A.; Richardson, T.; Jaros, M.; Wijngaard, P.L.J.; et al. Two Phase 3 Trials of Inclisiran in Patients with Elevated LDL Cholesterol. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 382, 1507–1519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwartz, G.G.; Steg, P.G.; Szarek, M.; Bhatt, D.L.; Bittner, V.A.; Diaz, R.; Edelberg, J.M.; Goodman, S.G.; Hanotin, C.; Harrington, R.A.; et al. Alirocumab and Cardiovascular Outcomes after Acute Coronary Syndrome. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 379, 2097–2107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palmer-Smith, H.; Basak, A. Regulatory effects of peptides from the pro and catalytic domains of proprotein convertase subtilisin/kexin 9 (PCSK9) on low-density lipoprotein receptor (LDL-R). Curr. Med. Chem. 2010, 17, 2168–2182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, M.; Ahmed, S. Emerging role of proprotein convertase subtilisin/kexin type-9 (PCSK-9) in inflammation and diseases. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2019, 370, 170–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gitt, A.K.; Lautsch, D.; Ferrières, J.; Ferrari, G.D.; Vyas, A.; Baxter, C.; Bash, L.D.; Ashton, V.; Horack, M.; Almahmeed, W. Cholesterol target value attainment and lipid-lowering therapy in patients with stable or acute coronary heart disease: Results from the Dyslipidemia International Study II. Atherosclerosis 2017, 266, 158–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dicembrini, I.; Giannini, S.; Ragghianti, B.; Mannucci, E.; Monami, M. Effects of PCSK9 inhibitors on LDL cholesterol, cardiovascular morbidity and all-cause mortality: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. J. Endocrinol. Investig. 2019, 42, 1029–1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Chen, W.; Lu, M.; Wang, Y. Association Between Circulating Proprotein Convertase Subtilisin/Kexin Type 9 and Major Adverse Cardiovascular Events, Stroke, and All-Cause Mortality: Systemic Review and Meta-Analysis. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2021, 8, 617249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, J.C.; Boerwinkle, E.; Mosley, T.H.; Hobbs, H.H. Sequence Variations in PCSK9, Low LDL, and Protection against Coronary Heart Disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2006, 354, 1264–1272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scalise, V.; Sanguinetti, C.; Neri, T.; Cianchetti, S.; Lai, M.; Carnicelli, V.; Celi, A.; Pedrinelli, R. PCSK9 Induces Tissue Factor Expression by Activation of TLR4/NFkB Signaling. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 12640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Zeng, Y.; Hu, Z.; Liang, H. PCSK9 promotes the secretion of pro-inflammatory cytokines by macrophages to aggravate H/R-induced cardiomyocyte injury via activating NF-κB signalling. Gen. Physiol. Biophys. 2020, 39, 123–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cammisotto, V.; Baratta, F.; Castellani, V.; Bartimoccia, S.; Nocella, C.; D’Erasmo, L.; Cocomello, N.; Barale, C.; Scicali, R.; Di Pino, A.; et al. Proprotein Convertase Subtilisin Kexin Type 9 Inhibitors Reduce Platelet Activation Modulating ox-LDL Pathways. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 7193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kassassir, H.; Siewiera, K.; Sychowski, R.; Watała, C. Can the antiplatelet effects of cangrelor be reliably studied in mice under in vivo and in vitro conditions using flow cytometry? Pharmacol. Rep. 2013, 65, 870–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gurbel, P.; Jeong, Y.; Navarese, E.; Tantry, U. Platelet-Mediated Thrombosis: From Bench to Bedside. Circ. Res. 2016, 118, 1380–1391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demers, A.; Samami, S.; Lauzier, B.; Des Rosiers, C.; Ngo Sock, E.; Ong, H.; Mayer, G. PCSK9 Induces CD36 Degradation and Affects Long-Chain Fatty Acid Uptake and Triglyceride Metabolism in Adipocytes and in Mouse Liver. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2015, 35, 2517–2525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poirier, S.; Mayer, G.; Benjannet, S.; Bergeron, E.; Marcinkiewicz, J.; Nassoury, N.; Mayer, H.; Nimpf, J.; Prat, A.; Seidah, N. The proprotein convertase PCSK9 induces the degradation of low density lipoprotein receptor (LDLR) and its closest family members VLDLR and ApoER2. J. Biol. Chem. 2008, 283, 2363–2372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kysenius, K.; Muggalla, P.; Mätlik, K.; Arumäe, U.; Huttunen, H. PCSK9 regulates neuronal apoptosis by adjusting ApoER2 levels and signaling. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. CMLS 2012, 69, 1903–1916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benn, M.; Nordestgaard, B.G.; Frikke-Schmidt, R.; Tybjaerg-Hansen, A. Low LDL cholesterol, PCSK9 and HMGCR genetic variation, and risk of Alzheimer’s disease and Parkinson’s disease: Mendelian randomisation study. BMJ 2017, 357, j1648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Visser, M.E.; Witztum, J.L.; Stroes, E.S.; Kastelein, J.J. Antisense oligonucleotides for the treatment of dyslipidaemia. Eur. Heart J. 2012, 33, 1451–1458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ray, K.K.; Landmesser, U.; Leiter, L.A.; Kallend, D.; Dufour, R.; Karakas, M.; Hall, T.; Troquay, R.P.; Turner, T.; Visseren, F.L.; et al. Inclisiran in Patients at High Cardiovascular Risk with Elevated LDL Cholesterol. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 376, 1430–1440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, X.; Raghavan, A.; Chen, T.; Qiao, L.; Zhang, Y.; Ding, Q.; Musunuru, K. CRISPR-Cas9 Targeting of PCSK9 in Human Hepatocytes in vivo-Brief Report. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2016, 36, 783–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitchell, T.; Chao, G.; Sitkoff, D.; Lo, F.; Monshizadegan, H.; Meyers, D.; Low, S.; Russo, K.; DiBella, R.; Denhez, F.; et al. Pharmacologic profile of the Adnectin BMS-962476, a small protein biologic alternative to PCSK9 antibodies for low-density lipoprotein lowering. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2014, 350, 412–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Momtazi-Borojeni, A.A.; Jaafari, M.R.; Banach, M.; Gorabi, A.M.; Sahraei, H.; Sahebkar, A. Pre-Clinical Evaluation of the Nanoliposomal antiPCSK9 Vaccine in Healthy Non-Human Primates. Vaccines 2021, 9, 749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robinson, J.G.; Farnier, M.; Krempf, M.; Bergeron, J.; Luc, G.; Averna, M.; Stroes, E.S.; Langslet, G.; Raal, F.J.; El Shahawy, M.; et al. Efficacy and safety of alirocumab in reducing lipids and cardiovascular events. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 372, 1489–1499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Safaeian, L.; Mirian, M.; Bahrizadeh, S. Evolocumab, a PCSK9 inhibitor, protects human endothelial cells against H2O2-induced oxidative stress. Arch. Physiol. Biochem. 2020, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raal, F.J.; Kallend, D.; Ray, K.K.; Turner, T.; Koenig, W.; Wright, R.S.; Wijngaard, P.L.J.; Curcio, D.; Jaros, M.J.; Leiter, L.A.; et al. Inclisiran for the Treatment of Heterozygous Familial Hypercholesterolemia. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 382, 1520–1530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gennemark, P.; Walter, K.; Clemmensen, N.; Rekic, D.; Nilsson, C.A.M.; Knochel, J.; Holtta, M.; Wernevik, L.; Rosengren, B.; Kakol-Palm, D.; et al. An oral antisense oligonucleotide for PCSK9 inhibition. Sci. Transl. Med. 2021, 13, eabe9117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, N.; Fan, L.; Dong, Y.; Xu, X.; Yu, C.; Chen, J.; Ren, J. New PCSK9 inhibitor miR-552-3p reduces LDL-C via enhancing LDLR in high fat diet-fed mice. Pharmacol. Res. 2021, 167, 105562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rekić, D.; Azarov, I.; Knöchel, J.; Sokolov, V.; Nilsson, C.; Wernevik, L.; Han, D.; Rydén-Bergsten, T.; Ebrahimi, A.; Dota, C.; et al. AZD8233 antisense oligonucleotide targeting PCSK9 does not prolong QT interval. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Momtazi-Borojeni, A.A.; Jaafari, M.R.; Afshar, M.; Banach, M.; Sahebkar, A. PCSK9 immunization using nanoliposomes: Preventive efficacy against hypercholesterolemia and atherosclerosis. Arch. Med. Sci. 2021, 17, 1365–1377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ly, K.; Saavedra, Y.G.; Canuel, M.; Routhier, S.; Desjardins, R.; Hamelin, J.; Mayne, J.; Lazure, C.; Seidah, N.G.; Day, R. Annexin A2 reduces PCSK9 protein levels via a translational mechanism and interacts with the M1 and M2 domains of PCSK9. J. Biol. Chem. 2014, 289, 17732–17746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Chen, X.; Zhang, X.; Su, C.; Yang, M.; He, W.; Du, Y.; Si, S.; Wang, L.; Hong, B. A small-molecule inhibitor of PCSK9 transcription ameliorates atherosclerosis through the modulation of FoxO1/3 and HNF1alpha. EBioMedicine 2020, 52, 102650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Eigenbrot, C.; Zhou, L.; Shia, S.; Li, W.; Quan, C.; Tom, J.; Moran, P.; Di Lello, P.; Skelton, N.J.; et al. Identification of a small peptide that inhibits PCSK9 protein binding to the low density lipoprotein receptor. J. Biol. Chem. 2014, 289, 942–955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, Z.; Wang, X.; Liu, S.; Shahanawaz, J.; Theus, S.; Fan, Y.; Deng, X.; Zhou, S.; Mehta, J.L. PCSK9 expression in the ischaemic heart and its relationship to infarct size, cardiac function, and development of autophagy. Cardiovasc. Res. 2018, 114, 1738–1751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Available online: https://www.merck.com (accessed on 5 August 2022).
- A Study of the Efficacy and Safety of MK-0616 (Oral PCSK9 Inhibitor) in Adults with Hypercholesterolemia (MK-0616-008). Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/record/NCT05261126?intr=MK-0616&draw=2&rank=2 (accessed on 5 August 2022).
- Ridker, P.M.; Revkin, J.; Amarenco, P.; Brunell, R.; Curto, M.; Civeira, F.; Flather, M.; Glynn, R.J.; Gregoire, J.; Jukema, J.W.; et al. Cardiovascular Efficacy and Safety of Bococizumab in High-Risk Patients. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 376, 1527–1539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raal, F.J.; Stein, E.A.; Dufour, R.; Turner, T.; Civeira, F.; Burgess, L.; Langslet, G.; Scott, R.; Olsson, A.G.; Sullivan, D.; et al. PCSK9 inhibition with evolocumab (AMG 145) in heterozygous familial hypercholesterolaemia (RUTHERFORD-2): A randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Lancet 2015, 385, 331–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ray, K.K.; Colhoun, H.M.; Szarek, M.; Baccara-Dinet, M.; Bhatt, D.L.; Bittner, V.A.; Budaj, A.J.; Diaz, R.; Goodman, S.G.; Hanotin, C.; et al. Effects of alirocumab on cardiovascular and metabolic outcomes after acute coronary syndrome in patients with or without diabetes: A prespecified analysis of the ODYSSEY OUTCOMES randomised controlled trial. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2019, 7, 618–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raal, F.J.; Chilton, R.; Ranjith, N.; Rambiritch, V.; Leisegang, R.F.; Ebrahim, I.O.; Tonder, A.V.; Shunmoogam, N.; Bouharati, C.; Musa, M.G.; et al. PCSK9 Inhibitors: From Nature’s Lessons to Clinical Utility. Endocr. Metab. Immune Disord. Drug Targets 2020, 20, 840–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahamad, S.; Mathew, S.; Khan, W.A.; Mohanan, K. Development of small-molecule PCSK9 inhibitors for the treatment of hypercholesterolemia. Drug Discov. Today 2022, 27, 1332–1349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahebkar, A.; Momtazi-Borojeni, A.A.; Banach, M. PCSK9 vaccine: So near, yet so far! Eur. Heart J. 2021, 42, 4007–4010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Momtazi-Borojeni, A.A.; Jaafari, M.R.; Badiee, A.; Sahebkar, A. Long-term generation of antiPCSK9 antibody using a nanoliposome-based vaccine delivery system. Atherosclerosis 2019, 283, 69–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Momtazi-Borojeni, A.A.; Jaafari, M.R.; Badiee, A.; Banach, M.; Sahebkar, A. Therapeutic effect of nanoliposomal PCSK9 vaccine in a mouse model of atherosclerosis. BMC Med. 2019, 17, 223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chadwick, A.C.; Musunuru, K. Treatment of Dyslipidemia Using CRISPR/Cas9 Genome Editing. Curr. Atheroscler. Rep. 2017, 19, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Q.; Su, J.; Liu, Y.; Jin, X.; Zhong, X.; Mo, L.; Wang, Q.; Deng, H.; Yang, Y. In vivo PCSK9 gene editing using an all-in-one self-cleavage AAV-CRISPR system. Mol. Ther.-Methods Clin. Dev. 2021, 20, 652–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, Q.; Strong, A.; Patel, K.M.; Ng, S.L.; Gosis, B.S.; Regan, S.N.; Cowan, C.A.; Rader, D.J.; Musunuru, K. Permanent alteration of PCSK9 with in vivo CRISPR-Cas9 genome editing. Circ. Res. 2014, 115, 488–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rothgangl, T.; Dennis, M.K.; Lin, P.J.C.; Oka, R.; Witzigmann, D.; Villiger, L.; Qi, W.; Hruzova, M.; Kissling, L.; Lenggenhager, D.; et al. In vivo adenine base editing of PCSK9 in macaques reduces LDL cholesterol levels. Nat. Biotechnol. 2021, 39, 949–957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- A Study of VERVE-101 in Patients with Familial Hypercholesterolemia and Cardiovascular Disease. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT05398029?cond=Verve-101&draw=2&rank=1 (accessed on 1 August 2022).
- Association, C.M. Guidelines for primary diagnosis and treatment of dyslipidemia (2019). Chin. J. Gen. Pract. 2019, 018, 417–421. [Google Scholar]
- Koren, M.J.; Giugliano, R.P.; Raal, F.J.; Sullivan, D.; Bolognese, M.; Langslet, G.; Civeira, F.; Somaratne, R.; Nelson, P.; Liu, T.; et al. Efficacy and safety of longer-term administration of evolocumab (AMG 145) in patients with hypercholesterolemia: 52-week results from the Open-Label Study of Long-Term Evaluation Against LDL-C (OSLER) randomized trial. Circulation 2014, 129, 234–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, G.; Qian, Y.W.; Kowala, M.C.; Konrad, R.J. Further LDL cholesterol lowering through targeting PCSK9 for coronary artery disease. Endocr. Metab. Immune Disord. Drug Targets 2008, 8, 238–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blom, D.J.; Hala, T.; Bolognese, M.; Lillestol, M.J.; Toth, P.D.; Burgess, L.; Ceska, R.; Roth, E.; Koren, M.J.; Ballantyne, C.M.; et al. A 52-week placebo-controlled trial of evolocumab in hyperlipidemia. N. Engl. J. Med. 2014, 370, 1809–1819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, J.; Tao, J.; Xi, L.; Wang, Z.; Liu, L. PCSK9 mediates the oxidative low-density lipoprotein-induced pyroptosis of vascular endothelial cells via the UQCRC1/ROS pathway. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2021, 47, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nicholls, S.J.; Puri, R.; Anderson, T.; Ballantyne, C.M.; Cho, L.; Kastelein, J.J.; Koenig, W.; Somaratne, R.; Kassahun, H.; Yang, J.; et al. Effect of Evolocumab on Progression of Coronary Disease in Statin-Treated Patients: The GLAGOV Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA 2016, 316, 2373–2384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toscano, A.; Cinquegrani, M.; Scuruchi, M.; Di Pino, A.; Piro, S.; Ferrara, V.; Morace, C.; Lo Gullo, A.; Imbalzano, E.; Purrello, F.; et al. PCSK9 Plasma Levels Are Associated with Mechanical Vascular Impairment in Familial Hypercholesterolemia Subjects without a History of Atherosclerotic Cardiovascular Disease: Results of Six-Month Add-On PCSK9 Inhibitor Therapy. Biomolecules 2022, 12, 562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palee, S.; McSweeney, C.M.; Maneechote, C.; Moisescu, D.M.; Jaiwongkam, T.; Kerdphoo, S.; Chattipakorn, S.C.; Chattipakorn, N. PCSK9 inhibitor improves cardiac function and reduces infarct size in rats with ischaemia/reperfusion injury: Benefits beyond lipid-lowering effects. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2019, 23, 7310–7319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grin, P.M.; Dwivedi, D.J.; Chathely, K.M.; Trigatti, B.L.; Prat, A.; Seidah, N.G.; Liaw, P.C.; Fox-Robichaud, A.E. Low-density lipoprotein (LDL)-dependent uptake of Gram-positive lipoteichoic acid and Gram-negative lipopolysaccharide occurs through LDL receptor. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 10496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyd, J.H.; Fjell, C.D.; Russell, J.A.; Sirounis, D.; Cirstea, M.S.; Walley, K.R. Increased Plasma PCSK9 Levels Are Associated with Reduced Endotoxin Clearance and the Development of Acute Organ Failures during Sepsis. J. Innate Immun. 2016, 8, 211–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walley, K.R. Role of lipoproteins and proprotein convertase subtilisin/kexin type 9 in endotoxin clearance in sepsis. Curr. Opin. Crit. Care 2016, 22, 464–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dwivedi, D.J.; Grin, P.M.; Khan, M.; Prat, A.; Zhou, J.; Fox-Robichaud, A.E.; Seidah, N.G.; Liaw, P.C. Differential Expression of PCSK9 Modulates Infection, Inflammation, and Coagulation in a Murine Model of Sepsis. Shock 2016, 46, 672–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Y.; Wu, W.; Sun, S.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, Z. PCSK9: A Potential Therapeutic Target for Sepsis. J. Immunol. Res. 2020, 2020, 2687692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leung, A.K.K.; Genga, K.R.; Topchiy, E.; Cirstea, M.; Shimada, T.; Fjell, C.; Russell, J.A.; Boyd, J.H.; Walley, K.R. Reduced Proprotein convertase subtilisin/kexin 9 (PCSK9) function increases lipoteichoic acid clearance and improves outcomes in Gram positive septic shock patients. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 10588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaler, C.R.; Joshua, C.; Rudak, P.T.; Arash, M.; Szabo, P.A.; Tun-Abraham, M.E.; Jamie, R.; Corbett, A.J.; James, M.C.; Mccormick, J.K. MAIT cells launch a rapid, robust and distinct hyperinflammatory response to bacterial superantigens and quickly acquire an anergic phenotype that impedes their cognate antimicrobial function: Defining a novel mechanism of superantigen-induced immunopathol. PLoS Biol. 2017, 15, e2001930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laudanski, K. Humanized Mice as a Tool to Study Sepsis—More Than Meets the Eye. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 2403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atreya, M.R.; Whitacre, B.E.; Cvijanovich, N.Z.; Bigham, M.T.; Thomas, N.J.; Schwarz, A.J.; Weiss, S.L.; Fitzgerald, J.C.; Allen, G.L.; Lutfi, R.; et al. Proprotein Convertase Subtilisin/Kexin Type 9 Loss-of-Function Is Detrimental to the Juvenile Host with Septic Shock. Crit. Care Med. 2020, 48, 1513–1520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vecchié, A.; Bonaventura, A.; Meessen, J.; Novelli, D.; Minetti, S.; Elia, E.; Ferrara, D.; Ansaldo, A.M.; Scaravilli, V.; Villa, S.; et al. PCSK9 is associated with mortality in patients with septic shock: Data from the ALBIOS study. J. Intern. Med. 2021, 289, 179–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Innocenti, F.; Gori, A.M.; Giusti, B.; Tozzi, C.; Donnini, C.; Meo, F.; Giacomelli, I.; Ralli, M.L.; Sereni, A.; Sticchi, E.; et al. Plasma PCSK9 levels and sepsis severity: An early assessment in the emergency department. Clin. Exp. Med. 2021, 21, 101–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rannikko, J.; Jacome Sanz, D.; Ortutay, Z.; Seiskari, T.; Aittoniemi, J.; Huttunen, R.; Syrjänen, J.; Pesu, M. Reduced plasma PCSK9 response in patients with bacteraemia is associated with mortality. J. Intern. Med. 2019, 286, 553–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molina, S.; Castet, V.; Fournier-Wirth, C.; Pichard-Garcia, L.; Avner, R.; Harats, D.; Roitelman, J.; Barbaras, R.; Graber, P.; Ghersa, P.; et al. The low-density lipoprotein receptor plays a role in the infection of primary human hepatocytes by hepatitis C virus. J. Hepatol. 2007, 46, 411–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abifadel, M.; Varret, M.; Rabès, J.P.; Allard, D.; Ouguerram, K.; Devillers, M.; Cruaud, C.; Benjannet, S.; Wickham, L.; Erlich, D.; et al. Mutations in PCSK9 cause autosomal dominant hypercholesterolemia. Nat. Genet. 2003, 34, 154–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruz, P.; Mo, H.; Mcconathy, W.J.; Nirupama, S.; Lacko, A.G. The role of cholesterol metabolism and cholesterol transport in carcinogenesis: A review of scientific findings, relevant to future cancer therapeutics. Front. Pharmacol. 2013, 4, 119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharya, A.; Chowdhury, A.; Chaudhury, K.; Shukla, P.C. Proprotein convertase subtilisin/kexin type 9 (PCSK9): A potential multifaceted player in cancer. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Rev. Cancer 2021, 1876, 188581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, J.; Cai, T.; Zheng, X.; Ren, Y.; Qi, J.; Lu, X.; Chen, H.; Lin, H.; Chen, Z.; Liu, M.; et al. Potentiating CD8+ T cell antitumor activity by inhibiting PCSK9 to promote LDLR-mediated TCR recycling and signaling. Protein Cell 2021, 12, 240–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, M.S.; Goldstein, J.L. The SREBP pathway: Regulation of cholesterol metabolism by proteolysis of a membrane-bound transcription factor. Cell 1997, 89, 331–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ridker, P.M.; Rose, L.M.; Kastelein, J.J.P.; Santos, R.D.; Wei, C.; Revkin, J.; Yunis, C.; Tardif, J.C.; Shear, C.L.; Studies of PCSK9 Inhibition and the Reduction of vascular Events (SPIRE) Investigators. Cardiovascular event reduction with PCSK9 inhibition among 1578 patients with familial hypercholesterolemia: Results from the SPIRE randomized trials of bococizumab. J. Clin. Lipidol. 2018, 12, 958–965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nicholls, S.J.; Kataoka, Y.; Nissen, S.E.; Prati, F.; Windecker, S.; Puri, R.; Hucko, T.; Aradi, D.; Herrman, J.R.; Hermanides, R.S.; et al. Effect of Evolocumab on Coronary Plaque Phenotype and Burden in Statin-Treated Patients Following Myocardial Infarction. JACC Cardiovasc. Imaging 2022, 15, 1308–1321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Donoghue, M.L.; Fazio, S.; Giugliano, R.P.; Stroes, E.S.G.; Kanevsky, E.; Gouni-Berthold, I.; Im, K.; Lira Pineda, A.; Wasserman, S.M.; Češka, R.; et al. Lipoprotein(a), PCSK9 Inhibition, and Cardiovascular Risk. Circulation 2019, 139, 1483–1492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marston, N.A.; Gurmu, Y.; Melloni, G.E.M.; Bonaca, M.; Gencer, B.; Sever, P.S.; Pedersen, T.R.; Keech, A.C.; Roselli, C.; Lubitz, S.A.; et al. The Effect of PCSK9 (Proprotein Convertase Subtilisin/Kexin Type 9) Inhibition on the Risk of Venous Thromboembolism. Circulation 2020, 141, 1600–1607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergmark, B.A.; O’Donoghue, M.L.; Murphy, S.A.; Kuder, J.F.; Ezhov, M.V.; Ceška, R.; Gouni-Berthold, I.; Jensen, H.K.; Tokgozoglu, S.L.; Mach, F.; et al. An Exploratory Analysis of Proprotein Convertase Subtilisin/Kexin Type 9 Inhibition and Aortic Stenosis in the FOURIER Trial. JAMA Cardiol. 2020, 5, 709–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nowak, C.; Arnlov, J. A Mendelian randomization study of the effects of blood lipids on breast cancer risk. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 3957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seidah, N.G. The PCSK9 discovery, an inactive protease with varied functions in hypercholesterolemia, viral infections, and cancer. J. Lipid Res. 2021, 62, 100130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raal, F.J.; Honarpour, N.; Blom, D.J.; Hovingh, G.K.; Xu, F.; Scott, R.; Wasserman, S.M.; Stein, E.A.; Investigators, T. Inhibition of PCSK9 with evolocumab in homozygous familial hypercholesterolaemia (TESLA Part B): A randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Lancet 2015, 385, 341–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartgers, M.L.; Defesche, J.C.; Langslet, G.; Hopkins, P.N.; Kastelein, J.J.; Baccara-Dinet, M.T.; Seiz, W.; Hamon, S.; Banerjee, P.; Stefanutti, C. Alirocumab efficacy in patients with double heterozygous, compound heterozygous, or homozygous familial hypercholesterolemia. J. Clin. Lipidol. 2018, 12, 390–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ference, B.A.; Robinson, J.G.; Brook, R.D.; Catapano, A.L.; Chapman, M.J.; Neff, D.R.; Voros, S.; Giugliano, R.P.; Smith, G.D.; Fazio, S.; et al. Variation in PCSK9 and HMGCR and Risk of Cardiovascular Disease and Diabetes. N. Engl. J. Med. 2016, 375, 2144–2153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Musunuru, K.; Chadwick, A.C.; Mizoguchi, T.; Garcia, S.P.; DeNizio, J.E.; Reiss, C.W.; Wang, K.; Iyer, S.; Dutta, C.; Clendaniel, V.; et al. In vivo CRISPR base editing of PCSK9 durably lowers cholesterol in primates. Nature 2021, 593, 429–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| State | Drug | Strategies | Application | Security | Mechanism | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Marketed drugs | Alirocumab | Monoclonal antibody | Cardiovascular disease and primary hyperlipidemia, including HeFH and HoFH | Safe, efficient, with occasional adverse reactions | PCSK9 binds to LDL-R on the surface of liver cells, promoting the degradation of LDL-R in the liver and reducing LDL-C levels. | [27,54] |
| Evolocumab | Monoclonal antibody | Cardiovascular disease and primary hyperlipidemia, including HeFH and HoFH | Safe, efficient, with occasional adverse reactions | PCSK9 binds LDL-R, degrades LDL-R, and removes LDL-C. | [27,55] | |
| Inclisiran | siRNA | Adults with HeFH or clinical ASCVD in patients who require additional lowering of LDL-C | Safe, with occasional injection site adverse reactions | Inclisiran interferes with PCSK9 in liver cells by RNA, increases the circulation and expression of LDL-C receptors on the surface of liver cells, the uptake of LDL-C, and the reduction of LDL-C. | [26,56] | |
| Drugs under development | AZD8233 | ASO | Hyperlipidemia | Still in clinical trial | It is designed to target PCSK9 mRNA, thereby inhibiting the intracellular protein translation and synthesis of PCSK9 protein. Targets endogenous liver Pcsk9 expression with a GalNAc-ASO approach to ablate circulating PCSK9, induce hepatic LDL-R expression, and thereby reduce plasma total and LDL-C concentrations. | [57] |
| MiR-552-3p | ASO | Hyperlipidemia | To be tested | MiR-552-3p can bind to the 3′ untranslated region (3′-UTR) of PCSK9 to inhibit translation and interact with the promoter of PCSK9 to suppress transcription and increase the LDL-R protein level, promote LDL-C uptake, and lower serum LDL-C. | [58] | |
| BMS-962476 | Antibody-like protein | Hypercholesterolemia | The experimental data are not sufficient | BMS-962476 blocks PCSK9 biologic activity by preventing binding and cointernalization with LDL-R during endocytosis, resulting in interruption of the subsequent sorting/degradation steps and increased receptor recycling and LDL uptake. | [52] | |
| L-IFPTA vaccine | Vaccine | Hypercholesterolemia and As | Long-lasting, durable, and safe | L-IFPTA vaccine-induced functional antibodies can specifically bind to circulating PCSK9, inhibit its interaction with LDL-R and thereby increase the expression of LDL-R on the surface of liver cells, leading to significant reductions in TC and (V)LDL-C. | [59,60] | |
| Annexin A2 | Polypeptide | Hyperlipidemia | To be tested | Annexin A2 interacts with the M1 and M2 Domains of PCSK9; the function of PCSK9 induced LDL-R was blocked, and PCSK9 was inhibited. | [57,61] | |
| 7030B-C5 | Small molecule | Cardiovascular disease | To be tested | HNF1 α and FoxO3 regulate transcription to inhibit PCSK9 expression and increase HepG2 cell-mediated total LDL-R protein and its uptake of LDL-C. | [62] | |
| Pep2-8 | Polypeptide | Cardiovascular disease | To be tested | Neutralize the activity of PCSK9 and realize the functional recovery of cellular LDL receptors. | [63,64] | |
| MK-0616 | Hypercholesterolemia | Still in clinical trial | Mk-0616 interferes with the binding of LDL-C to LDL-R and causes the liver to express more LDL-R, thereby reducing plasma LDL-C levels. | [65,66] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, C.; Chen, J.; Chen, H.; Zhang, T.; He, D.; Luo, Q.; Chi, J.; Hong, Z.; Liao, Y.; Zhang, S.; et al. PCSK9 Inhibition: From Current Advances to Evolving Future. Cells 2022, 11, 2972. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells11192972
Liu C, Chen J, Chen H, Zhang T, He D, Luo Q, Chi J, Hong Z, Liao Y, Zhang S, et al. PCSK9 Inhibition: From Current Advances to Evolving Future. Cells. 2022; 11(19):2972. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells11192972
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Chunping, Jing Chen, Huiqi Chen, Tong Zhang, Dongyue He, Qiyuan Luo, Jiaxin Chi, Zebin Hong, Yizhong Liao, Shihui Zhang, and et al. 2022. "PCSK9 Inhibition: From Current Advances to Evolving Future" Cells 11, no. 19: 2972. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells11192972
APA StyleLiu, C., Chen, J., Chen, H., Zhang, T., He, D., Luo, Q., Chi, J., Hong, Z., Liao, Y., Zhang, S., Wu, Q., Cen, H., Chen, G., Li, J., & Wang, L. (2022). PCSK9 Inhibition: From Current Advances to Evolving Future. Cells, 11(19), 2972. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells11192972



.png)



