Biomarker-Targeted Therapies in Non–Small Cell Lung Cancer: Current Status and Perspectives
Abstract
:1. Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer
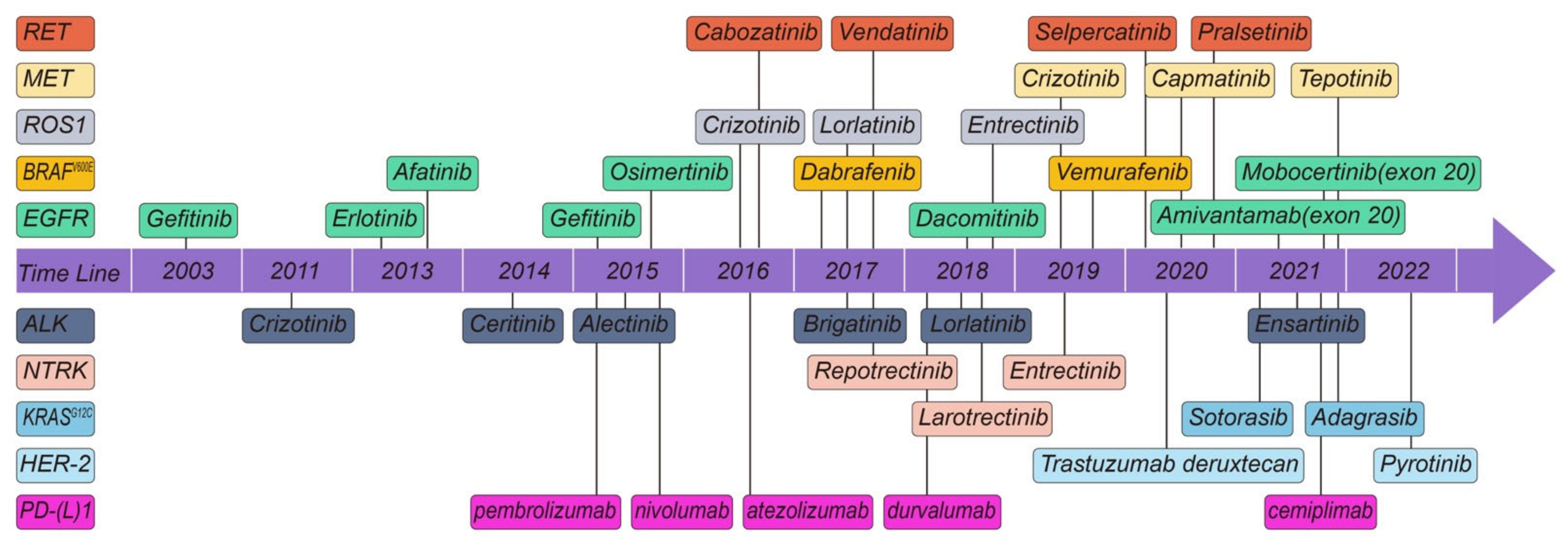
2. Molecular Targets
2.1. EGFR
2.1.1. EGFR p.L858R and EGFR Exon 19 Deletion
2.1.2. EGFR Exon 20 Insertion Mutations
2.1.3. Other EGFR Mutations
2.2. ALK
2.3. ROS1
2.4. BRAF
2.5. MET
2.6. RET
2.7. NTRK1
2.8. KRAS
2.9. HER2
3. Molecular Targets with Potential Therapeutics
3.1. NRG1
3.2. FGFR
4. Metabolic Targets
4.1. KEAP1-NFE2L2
4.2. STK11
5. Immune Targets
5.1. PD-1 and PD-L1
5.2. CTLA-4
6. Combined Immune-Therapies with Targets
6.1. STING
6.2. LAG3
6.3. TIGIT
7. Molecular Testing
8. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Siegel, R.L.; Miller, K.D.; Fuchs, H.E.; Jemal, A. Cancer statistics, 2022. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2022, 72, 7–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, M.; Meng, G.X.; Liu, X.W.; Ma, T.; Sun, G.; He, H. Deep-LC: A Novel Deep Learning Method of Identifying Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer-Related Genes. Front. Oncol. 2022, 12, 949546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soo, R.; Stone, E.; Cummings, K.; Jett, J.; Field, J.; Groen, H.; Mulshine, J.; Yatabe, Y.; Bubendorf, L.; Dacic, S.; et al. Scientific Advances in Thoracic Oncology 2016. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2017, 12, 1183–1209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Solito, S.; Marigo, I.; Pinton, L.; Damuzzo, V.; Mandruzzato, S.; Bronte, V. Myeloid-derived suppressor cell heterogeneity in human cancers. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2014, 1319, 47–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deb, D.; Moore, A.C.; Roy, U.B. The 2021 Global Lung Cancer Therapy Landscape. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2022, 17, 931–936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Comprehensive molecular profiling of lung adenocarcinoma. Nature 2014, 511, 543–550. [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- George, J.; Lim, J.; Jang, S.; Cun, Y.; OzRETić, L.; Kong, G.; Leenders, F.; Lu, X.; Fernández-Cuesta, L.; Bosco, G.; et al. Comprehensive genomic profiles of small cell lung cancer. Nature 2015, 524, 47–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ettinger, D.S.; Wood, D.E.; Aisner, D.L.; Akerley, W.; Bauman, J.R.; Bharat, A.; Bruno, D.S.; Chang, J.Y.; Chirieac, L.R.; D’Amico, T.A.; et al. NCCN Guidelines Insights: Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer, Version 2.2021. J. Natl. Compr. Canc. Netw. 2021, 19, 254–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Kung, H.-J.; Mack, P.C.; Gandara, D.R. Genotyping and genomic profiling of non-small-cell lung cancer: Implications for current and future therapies. J. Clin. Oncol. 2013, 31, 1039–1049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Qin, A.; Johnson, A.; Ross, J.S.; Miller, V.A.; Ali, S.M.; Schrock, A.B.; Gadgeel, S.M. Detection of Known and Novel FGFR Fusions in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer by Comprehensive Genomic Profiling. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2019, 14, 54–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, W.H.; Yang, J.C.H.; Mok, T.S.; Loong, H.H. Overview of current systemic management of EGFR-mutant NSCLC. Ann. Oncol. 2018, 29, i3–i9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rotow, J.; Bivona, T.G. Understanding and targeting resistance mechanisms in NSCLC. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2017, 17, 637–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshioka, H.; Shimokawa, M.; Seto, T.; Morita, S.; Yatabe, Y.; Okamoto, I.; Tsurutani, J.; Satouchi, M.; Hirashima, T.; Atagi, S.; et al. Final overall survival results of WJTOG3405, a randomized phase III trial comparing gefitinib versus cisplatin with docetaxel as the first-line treatment for patients with stage IIIB/IV or postoperative recurrent EGFR mutation-positive non-small-cell lung cancer. Ann. Oncol. 2019, 30, 1978–1984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhou, C.; Wu, Y.L.; Chen, G.; Feng, J.; Liu, X.Q.; Wang, C.; Zhang, S.; Wang, J.; Zhou, S.; Ren, S.; et al. Final overall survival results from a randomised, phase III study of erlotinib versus chemotherapy as first-line treatment of EGFR mutation-positive advanced non-small-cell lung cancer (OPTIMAL, CTONG-0802). Ann. Oncol. 2015, 26, 1877–1883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramalingam, S.S.; Vansteenkiste, J.; Planchard, D.; Cho, B.C.; Gray, J.E.; Ohe, Y.; Zhou, C.; Reungwetwattana, T.; Cheng, Y.; Chewaskulyong, B.; et al. Overall Survival with Osimertinib in Untreated, -Mutated Advanced NSCLC. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 382, 41–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paz-Ares, L.; Tan, E.H.; O’Byrne, K.; Zhang, L.; Hirsh, V.; Boyer, M.; Yang, J.C.H.; Mok, T.; Lee, K.H.; Lu, S.; et al. Afatinib versus gefitinib in patients with EGFR mutation-positive advanced non-small-cell lung cancer: Overall survival data from the phase IIb LUX-Lung 7 trial. Ann. Oncol. 2017, 28, 270–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Y.-L.; Cheng, Y.; Zhou, X.; Lee, K.H.; Nakagawa, K.; Niho, S.; Tsuji, F.; Linke, R.; Rosell, R.; Corral, J.; et al. Dacomitinib versus gefitinib as first-line treatment for patients with EGFR-mutation-positive non-small-cell lung cancer (ARCHER 1050): A randomised, open-label, phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2017, 18, 1454–1466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, Y.; Yun, C.-H.; Park, E.; Ercan, D.; Manuia, M.; Juarez, J.; Xu, C.; Rhee, K.; Chen, T.; Zhang, H.; et al. Overcoming EGFR(T790M) and EGFR(C797S) resistance with mutant-selective allosteric inhibitors. Nature 2016, 534, 129–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yu, H.A.; Pao, W. Targeted therapies: Afatinib—New therapy option for EGFR-mutant lung cancer. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2013, 10, 551–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, W.; Zhong, R.; He, J. Osimertinib in EGFR-Mutated Lung Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 384, 675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sequist, L.V.; Soria, J.-C.; Goldman, J.W.; Wakelee, H.A.; Gadgeel, S.M.; Varga, A.; Papadimitrakopoulou, V.; Solomon, B.J.; Oxnard, G.R.; Dziadziuszko, R.; et al. Rociletinib in EGFR-mutated non-small-cell lung cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 372, 1700–1709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mok, T.S.; Wu, Y.-L.; Ahn, M.-J.; Garassino, M.C.; Kim, H.R.; Ramalingam, S.S.; Shepherd, F.A.; He, Y.; Akamatsu, H.; Theelen, W.S.M.E.; et al. Osimertinib or Platinum-Pemetrexed in EGFR T790M-Positive Lung Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 376, 629–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ramalingam, S.S.; Yang, J.C.H.; Lee, C.K.; Kurata, T.; Kim, D.-W.; John, T.; Nogami, N.; Ohe, Y.; Mann, H.; Rukazenkov, Y.; et al. Osimertinib As First-Line Treatment of EGFR Mutation-Positive Advanced Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2018, 36, 841–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yang, Z.; Yang, N.; Ou, Q.; Xiang, Y.; Jiang, T.; Wu, X.; Bao, H.; Tong, X.; Wang, X.; Shao, Y.W.; et al. Investigating Novel Resistance Mechanisms to Third-Generation EGFR Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor Osimertinib in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Patients. Clin. Cancer Res. 2018, 24, 3097–3107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- StarRETt, J.H.; Guernet, A.A.; Cuomo, M.E.; Poels, K.E.; van Alderwerelt van Rosenburgh, I.K.; Nagelberg, A.; Farnsworth, D.; Price, K.S.; Khan, H.; Ashtekar, K.D.; et al. Drug Sensitivity and Allele Specificity of First-Line Osimertinib Resistance Mutations. Cancer Res. 2020, 80, 2017–2030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, C.K.; Man, J.; Lord, S.; Cooper, W.; Links, M.; Gebski, V.; Herbst, R.S.; Gralla, R.J.; Mok, T.; Yang, J.C.-H. Clinical and Molecular Characteristics Associated with Survival Among Patients Treated with Checkpoint Inhibitors for Advanced Non-Small Cell Lung Carcinoma: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. JAMA Oncol. 2018, 4, 210–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrews Wright, N.M.; Goss, G.D. Third-generation epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitors for the treatment of non-small cell lung cancer. Transl. Lung Cancer Res. 2019, 8, S247–S264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meador, C.B.; Sequist, L.V.; Piotrowska, Z. Targeting Exon 20 Insertions in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: Recent Advances and Clinical Updates. Cancer Discov. 2021, 11, 2145–2157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Romero, D. Amivantamab is effective in NSCLC harbouring EGFR exon 20 insertions. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2021, 18, 604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choudhury, N.J.; Schoenfeld, A.J.; Flynn, J.; Falcon, C.J.; Rizvi, H.; Rudin, C.M.; Kris, M.G.; Arcila, M.E.; Heller, G.; Yu, H.A.; et al. Response to Standard Therapies and Comprehensive Genomic Analysis for Patients with Lung Adenocarcinoma with Exon 20 Insertions. Clin. Cancer Res. 2021, 27, 2920–2927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, J.H.; Lim, S.H.; An, H.J.; Kim, K.H.; Park, K.U.; Kang, E.J.; Choi, Y.H.; Ahn, M.S.; Lee, M.H.; Sun, J.-M.; et al. Osimertinib for Patients with Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer Harboring Uncommon EGFR Mutations: A Multicenter, Open-Label, Phase II Trial (KCSG-LU15-09). J. Clin. Oncol. 2020, 38, 488–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janning, M.; Süptitz, J.; Albers-Leischner, C.; Delpy, P.; Tufman, A.; Velthaus-Rusik, J.L.; Reck, M.; Jung, A.; Kauffmann-Guerrero, D.; Bonzheim, I.; et al. Treatment outcome of atypical EGFR mutations in the German National Network Genomic Medicine Lung Cancer (nNGM). Ann. Oncol. 2022, 33, 602–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soda, M.; Choi, Y.L.; Enomoto, M.; Takada, S.; Yamashita, Y.; Ishikawa, S.; Fujiwara, S.; Watanabe, H.; Kurashina, K.; Hatanaka, H.; et al. Identification of the transforming EML4-ALK fusion gene in non-small-cell lung cancer. Nature 2007, 448, 561–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Golding, B.; Luu, A.; Jones, R.; Viloria-Petit, A.M. The function and therapeutic targeting of anaplastic lymphoma kinase (ALK) in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). Mol. Cancer 2018, 17, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kris, M.G.; Johnson, B.E.; Berry, L.D.; Kwiatkowski, D.J.; Iafrate, A.J.; Wistuba, I.I.; Varella-Garcia, M.; Franklin, W.A.; Aronson, S.L.; Su, P.-F.; et al. Using multiplexed assays of oncogenic drivers in lung cancers to select targeted drugs. JAMA 2014, 311, 1998–2006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Katayama, R.; Lovly, C.M.; Shaw, A.T. Therapeutic targeting of anaplastic lymphoma kinase in lung cancer: A paradigm for precision cancer medicine. Clin. Cancer Res. 2015, 21, 2227–2235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shaw, A.T.; Yasothan, U.; Kirkpatrick, P. Crizotinib. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2011, 10, 897–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ceritinib gains FDA approval for lung cancer. Cancer Discov. 2014, 4, 753–754. [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Larkins, E.; Blumenthal, G.M.; Chen, H.; He, K.; Agarwal, R.; Gieser, G.; Stephens, O.; ZahALKa, E.; Ringgold, K.; Helms, W.; et al. FDA Approval: Alectinib for the Treatment of Metastatic, ALK-Positive Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Following Crizotinib. Clin. Cancer Res. 2016, 22, 5171–5176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- American Association for Cancer Research. Brigatinib Approved, but Treatment Role Uncertain. Cancer Discov. 2017, 7, OF3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solomon, B.J.; Besse, B.; Bauer, T.M.; Felip, E.; Soo, R.A.; Camidge, D.R.; Chiari, R.; Bearz, A.; Lin, C.-C.; Gadgeel, S.M.; et al. Lorlatinib in patients with ALK-positive non-small-cell lung cancer: Results from a global phase 2 study. Lancet Oncol. 2018, 19, 1654–1667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solomon, B.J.; Kim, D.-W.; Wu, Y.-L.; Nakagawa, K.; Mekhail, T.; Felip, E.; Cappuzzo, F.; Paolini, J.; Usari, T.; Tang, Y.; et al. Final Overall Survival Analysis From a Study Comparing First-Line Crizotinib Versus Chemotherapy in ALK-Mutation-Positive Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2018, 36, 2251–2258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Solomon, B.J.; Mok, T.; Kim, D.-W.; Wu, Y.-L.; Nakagawa, K.; Mekhail, T.; Felip, E.; Cappuzzo, F.; Paolini, J.; Usari, T.; et al. First-line crizotinib versus chemotherapy in ALK-positive lung cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2014, 371, 2167–2177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Soria, J.-C.; Tan, D.S.W.; Chiari, R.; Wu, Y.-L.; Paz-Ares, L.; Wolf, J.; Geater, S.L.; Orlov, S.; Cortinovis, D.; Yu, C.-J.; et al. First-line ceritinib versus platinum-based chemotherapy in advanced ALK-rearranged non-small-cell lung cancer (ASCEND-4): A randomised, open-label, phase 3 study. Lancet 2017, 389, 917–929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peters, S.; Camidge, D.R.; Shaw, A.T.; Gadgeel, S.; Ahn, J.S.; Kim, D.-W.; Ou, S.-H.I.; Pérol, M.; Dziadziuszko, R.; Rosell, R.; et al. Alectinib versus Crizotinib in Untreated ALK-Positive Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 377, 829–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camidge, D.R.; Kim, H.R.; Ahn, M.-J.; Yang, J.C.-H.; Han, J.-Y.; Lee, J.-S.; Hochmair, M.J.; Li, J.Y.-C.; Chang, G.-C.; Lee, K.H.; et al. Brigatinib versus Crizotinib in ALK-Positive Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 379, 2027–2039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaw, A.T.; Bauer, T.M.; de Marinis, F.; Felip, E.; Goto, Y.; Liu, G.; Mazieres, J.; Kim, D.-W.; Mok, T.; Polli, A.; et al. First-Line Lorlatinib or Crizotinib in Advanced -Positive Lung Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 383, 2018–2029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horn, L.; Wang, Z.; Wu, G.; Poddubskaya, E.; Mok, T.; Reck, M.; Wakelee, H.; Chiappori, A.A.; Lee, D.H.; Breder, V.; et al. Ensartinib vs Crizotinib for Patients with Anaplastic Lymphoma Kinase-Positive Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: A Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA Oncol. 2021, 7, 1617–1625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gainor, J.F.; Dardaei, L.; Yoda, S.; Friboulet, L.; Leshchiner, I.; Katayama, R.; Dagogo-Jack, I.; Gadgeel, S.; Schultz, K.; Singh, M.; et al. Molecular Mechanisms of Resistance to First- and Second-Generation ALK Inhibitors in ALK-Rearranged Lung Cancer. Cancer Discov. 2016, 6, 1118–1133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Song, Z.; Lian, S.; Mak, S.; Chow, M.Z.-Y.; Xu, C.; Wang, W.; Keung, H.Y.; Lu, C.; Kebede, F.T.; Gao, Y.; et al. Deep RNA Sequencing Revealed Fusion Junctional Heterogeneity May Predict Crizotinib Treatment Efficacy in ALK-Rearranged NSCLC. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2022, 17, 264–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noé, J.; Lovejoy, A.; Ou, S.-H.I.; Yaung, S.J.; Bordogna, W.; Klass, D.M.; Cummings, C.A.; Shaw, A.T. ALK Mutation Status Before and After Alectinib Treatment in Locally Advanced or Metastatic ALK-Positive NSCLC: Pooled Analysis of Two Prospective Trials. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2020, 15, 601–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, J.J.; Zhu, V.W.; Yoda, S.; Yeap, B.Y.; Schrock, A.B.; Dagogo-Jack, I.; Jessop, N.A.; Jiang, G.Y.; Le, L.P.; Gowen, K.; et al. Impact of EML4-ALK Variant on Resistance Mechanisms and Clinical Outcomes in ALK-Positive Lung Cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2018, 36, 1199–1206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shaw, A.T.; Solomon, B.J.; Besse, B.; Bauer, T.M.; Lin, C.-C.; Soo, R.A.; Riely, G.J.; Ou, S.-H.I.; Clancy, J.S.; Li, S.; et al. Resistance Mutations and Efficacy of Lorlatinib in Advanced Anaplastic Lymphoma Kinase-Positive Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2019, 37, 1370–1379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, S.; Zhou, Q.; Liu, X.; Du, Y.; Fan, Y.; Cheng, Y.; Fang, J.; Lu, Y.; Huang, C.; Zhou, J.; et al. Lorlatinib for Previously Treated ALK-Positive Advanced NSCLC: Primary Efficacy and Safety From a Phase 2 Study in People’s Republic of China. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2022, 17, 816–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Fan, Z.; Zhu, S.-J.; Huang, X.; Zhuang, Z.; Li, Y.; Deng, Z.; Gao, L.; Hong, X.; Zhang, T.; et al. A new ALK inhibitor overcomes resistance to first- and second-generation inhibitors in NSCLC. EMBO Mol. Med. 2022, 14, e14296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, X.; Xu, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Chu, L.; Yang, X.; Ni, J.; Li, Y.; Guo, T.; Zheng, Z.; et al. Neuroendocrine transformation from EGFR/ALK-wild type or TKI-naïve non-small cell lung cancer: An under-recognized phenomenon. Lung Cancer 2022, 169, 22–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camidge, D.R. Lorlatinib Should Not be Considered as the Preferred First-Line Option in Patients with Advanced ALK Rearranged NSCLC. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2021, 16, 528–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagasaka, M.; Ou, S.-H.I. Lorlatinib Should Be Considered as the Preferred First-Line Option in Patients with Advanced ALK-Rearranged NSCLC. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2021, 16, 532–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaw, A.T.; Friboulet, L.; Leshchiner, I.; Gainor, J.F.; Bergqvist, S.; Brooun, A.; Burke, B.J.; Deng, Y.-L.; Liu, W.; Dardaei, L.; et al. Resensitization to Crizotinib by the Lorlatinib ALK Resistance Mutation L1198F. N. Engl. J. Med. 2016, 374, 54–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Savic, S.; Rothschild, S.; Bubendorf, L. Lonely Driver ROS1. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2017, 12, 776–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaw, A.T.; Ou, S.H.; Bang, Y.J.; Camidge, D.R.; Solomon, B.J.; Salgia, R.; Riely, G.J.; Varella-Garcia, M.; Shapiro, G.I.; Costa, D.B.; et al. Crizotinib in ROS1-rearranged non-small-cell lung cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2014, 371, 1963–1971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rikova, K.; Guo, A.; Zeng, Q.; Possemato, A.; Yu, J.; Haack, H.; Nardone, J.; Lee, K.; Reeves, C.; Li, Y.; et al. Global survey of phosphotyrosine signaling identifies oncogenic kinases in lung cancer. Cell 2007, 131, 1190–1203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wu, Y.-L.; Yang, J.C.-H.; Kim, D.-W.; Lu, S.; Zhou, J.; Seto, T.; Yang, J.-J.; Yamamoto, N.; Ahn, M.-J.; Takahashi, T.; et al. Phase II Study of Crizotinib in East Asian Patients with ROS1-Positive Advanced Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2018, 36, 1405–1411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michels, S.; Massutí, B.; Schildhaus, H.-U.; Franklin, J.; Sebastian, M.; Felip, E.; Grohé, C.; Rodriguez-Abreu, D.; Abdulla, D.S.Y.; Bischoff, H.; et al. Safety and Efficacy of Crizotinib in Patients with Advanced or Metastatic ROS1-Rearranged Lung Cancer (EUCROSS): A European Phase II Clinical Trial. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2019, 14, 1266–1276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gainor, J.F.; Tseng, D.; Yoda, S.; Dagogo-Jack, I.; Friboulet, L.; Lin, J.J.; Hubbeling, H.G.; Dardaei, L.; Farago, A.F.; Schultz, K.R.; et al. Patterns of Metastatic Spread and Mechanisms of Resistance to Crizotinib in -Positive Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer. JCO Precis. Oncol. 2017, 1, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, S.M.; Kim, H.R.; Lee, J.-S.; Lee, K.H.; Lee, Y.-G.; Min, Y.J.; Cho, E.K.; Lee, S.S.; Kim, B.-S.; Choi, M.Y.; et al. Open-Label, Multicenter, Phase II Study of Ceritinib in Patients with Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer Harboring ROS1 Rearrangement. J. Clin. Oncol. 2017, 35, 2613–2618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Awad, M.M.; Engelman, J.A.; Shaw, A.T. Acquired resistance to crizotinib from a mutation in CD74-ROS1. N. Engl. J. Med. 2013, 369, 1173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Facchinetti, F.; Loriot, Y.; Kuo, M.-S.; Mahjoubi, L.; Lacroix, L.; Planchard, D.; Besse, B.; Farace, F.; Auger, N.; Remon, J.; et al. Crizotinib-Resistant ROS1 Mutations Reveal a Predictive Kinase Inhibitor Sensitivity Model for ROS1- and ALK-Rearranged Lung Cancers. Clin. Cancer Res. 2016, 22, 5983–5991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shaw, A.T.; Felip, E.; Bauer, T.M.; Besse, B.; Navarro, A.; Postel-Vinay, S.; Gainor, J.F.; Johnson, M.; Dietrich, J.; James, L.P.; et al. Lorlatinib in non-small-cell lung cancer with ALK or ROS1 rearrangement: An international, multicentre, open-label, single-arm first-in-man phase 1 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2017, 18, 1590–1599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menichincheri, M.; Ardini, E.; Magnaghi, P.; Avanzi, N.; Banfi, P.; Bossi, R.; Buffa, L.; Canevari, G.; Ceriani, L.; Colombo, M.; et al. Discovery of Entrectinib: A New 3-Aminoindazole As a Potent Anaplastic Lymphoma Kinase (ALK), c-ros Oncogene 1 Kinase (ROS1), and Pan-Tropomyosin Receptor Kinases (Pan-TRKs) inhibitor. J. Med. Chem. 2016, 59, 3392–3408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ardini, E.; Menichincheri, M.; Banfi, P.; Bosotti, R.; De Ponti, C.; Pulci, R.; Ballinari, D.; Ciomei, M.; Texido, G.; Degrassi, A.; et al. Entrectinib, a Pan-TRK, ROS1, and ALK Inhibitor with Activity in Multiple Molecularly Defined Cancer Indications. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2016, 15, 628–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Drilon, A.; Siena, S.; Dziadziuszko, R.; Barlesi, F.; Krebs, M.G.; Shaw, A.T.; de Braud, F.; Rolfo, C.; Ahn, M.-J.; Wolf, J.; et al. Entrectinib in ROS1 fusion-positive non-small-cell lung cancer: Integrated analysis of three phase 1–2 trials. Lancet Oncol. 2020, 21, 261–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roskoski, R. Allosteric MEK1/2 inhibitors including cobimetanib and trametinib in the treatment of cutaneous melanomas. Pharmacol. Res. 2017, 117, 20–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hyman, D.; Puzanov, I.; Subbiah, V.; Faris, J.; Chau, I.; Blay, J.; Wolf, J.; Raje, N.; Diamond, E.; Hollebecque, A.; et al. Vemurafenib in Multiple Nonmelanoma Cancers with BRAF V600 Mutations. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 373, 726–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Planchard, D.; Kim, T.; Mazieres, J.; Quoix, E.; Riely, G.; Barlesi, F.; Souquet, P.; Smit, E.; Groen, H.; Kelly, R.; et al. Dabrafenib in patients with BRAF(V600E)-positive advanced non-small-cell lung cancer: A single-arm, multicentre, open-label, phase 2 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2016, 17, 642–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Planchard, D.; Smit, E.; Groen, H.; Mazieres, J.; Besse, B.; Helland, Å.; Giannone, V.; D’Amelio, A.; Zhang, P.; Mookerjee, B.; et al. Dabrafenib plus trametinib in patients with previously untreated BRAF-mutant Metastatic non-small-cell lung cancer: An open-label, phase 2 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2017, 18, 1307–1316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Odogwu, L.; Mathieu, L.; Blumenthal, G.; Larkins, E.; Goldberg, K.B.; Griffin, N.; Bijwaard, K.; Lee, E.Y.; Philip, R.; Jiang, X.; et al. FDA Approval Summary: Dabrafenib and Trametinib for the Treatment of Metastatic Non-Small Cell Lung Cancers Harboring Mutations. Oncologist 2018, 23, 740–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mazieres, J.; Cropet, C.; Montané, L.; Barlesi, F.; Souquet, P.J.; Quantin, X.; Dubos-Arvis, C.; Otto, J.; Favier, L.; Avrillon, V.; et al. Vemurafenib in non-small-cell lung cancer patients with BRAF and BRAF mutations. Ann. Oncol. 2020, 31, 289–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Eder, J.P.; Vande Woude, G.F.; Boerner, S.A.; LoRusso, P.M. Novel therapeutic inhibitors of the c-MET signaling pathway in cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2009, 15, 2207–2214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schrock, A.B.; Frampton, G.M.; Suh, J.; Chalmers, Z.R.; Rosenzweig, M.; Erlich, R.L.; Halmos, B.; Goldman, J.; Forde, P.; Leuenberger, K.; et al. Characterization of 298 Patients with Lung Cancer Harboring MET Exon 14 Skipping Alterations. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2016, 11, 1493–1502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vansteenkiste, J.F.; Van De Kerkhove, C.; Wauters, E.; Van Mol, P. Capmatinib for the treatment of non-small cell lung cancer. Expert Rev. Anticancer Ther. 2019, 19, 659–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wolf, J.; Seto, T.; Han, J.-Y.; Reguart, N.; Garon, E.B.; Groen, H.J.M.; Tan, D.S.W.; Hida, T.; de Jonge, M.; Orlov, S.V.; et al. Capmatinib in Exon 14-Mutated or -Amplified Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 383, 944–957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paik, P.K.; Felip, E.; Veillon, R.; Sakai, H.; Cortot, A.B.; Garassino, M.C.; Mazieres, J.; Viteri, S.; Senellart, H.; Van Meerbeeck, J.; et al. Tepotinib in Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer with Exon 14 Skipping Mutations. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 383, 931–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heist, R.S.; Sequist, L.V.; Borger, D.; Gainor, J.F.; Arellano, R.S.; Le, L.P.; Dias-Santagata, D.; Clark, J.W.; Engelman, J.A.; Shaw, A.T.; et al. Acquired Resistance to Crizotinib in NSCLC with MET Exon 14 Skipping. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2016, 11, 1242–1245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fujino, T.; Kobayashi, Y.; Suda, K.; Koga, T.; Nishino, M.; Ohara, S.; Chiba, M.; Shimoji, M.; Tomizawa, K.; Takemoto, T.; et al. Sensitivity and Resistance of MET Exon 14 Mutations in Lung Cancer to Eight MET Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors In Vitro. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2019, 14, 1753–1765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suzawa, K.; Offin, M.; Lu, D.; Kurzatkowski, C.; Vojnic, M.; Smith, R.S.; Sabari, J.K.; Tai, H.; Mattar, M.; Khodos, I.; et al. Activation of KRAS Mediates Resistance to Targeted Therapy in MET Exon 14-mutant Non-small Cell Lung Cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2019, 25, 1248–1260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Guo, R.; Offin, M.; Brannon, A.R.; Chang, J.; Chow, A.; Delasos, L.; Girshman, J.; Wilkins, O.; McCarthy, C.G.; Makhnin, A.; et al. Exon 14-altered Lung Cancers and MET Inhibitor Resistance. Clin. Cancer Res. 2021, 27, 799–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gautschi, O.; Milia, J.; Filleron, T.; Wolf, J.; Carbone, D.P.; Owen, D.; Camidge, R.; Narayanan, V.; Doebele, R.C.; Besse, B.; et al. Targeting RET in Patients with RET-Rearranged Lung Cancers: Results From the Global, Multicenter RET Registry. J. Clin. Oncol. 2017, 35, 1403–1410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Drilon, A.; Rekhtman, N.; Arcila, M.; Wang, L.; Ni, A.; Albano, M.; Van Voorthuysen, M.; Somwar, R.; Smith, R.S.; Montecalvo, J.; et al. Cabozantinib in patients with advanced RET-rearranged non-small-cell lung cancer: An open-label, single-centre, phase 2, single-arm trial. Lancet Oncol. 2016, 17, 1653–1660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, S.H.; Lee, J.K.; Ahn, M.J.; Kim, D.W.; Sun, J.M.; Keam, B.; Kim, T.M.; Heo, D.S.; Ahn, J.S.; Choi, Y.L.; et al. Vandetanib in pretreated patients with advanced non-small cell lung cancer-harboring RET rearrangement: A phase II clinical trial. Ann. Oncol. 2017, 28, 292–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drilon, A.; Oxnard, G.R.; Tan, D.S.W.; Loong, H.H.F.; Johnson, M.; Gainor, J.; McCoach, C.E.; Gautschi, O.; Besse, B.; Cho, B.C.; et al. Efficacy of Selpercatinib in Fusion-Positive Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 383, 813–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gainor, J.F.; Curigliano, G.; Kim, D.-W.; Lee, D.H.; Besse, B.; Baik, C.S.; Doebele, R.C.; Cassier, P.A.; Lopes, G.; Tan, D.S.W.; et al. Pralsetinib for RET fusion-positive non-small-cell lung cancer (ARROW): A multi-cohort, open-label, phase 1/2 study. Lancet Oncol. 2021, 22, 959–969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Indo, Y.; Tsuruta, M.; Hayashida, Y.; Karim, M.A.; Ohta, K.; Kawano, T.; Mitsubuchi, H.; Tonoki, H.; Awaya, Y.; Matsuda, I. Mutations in the TRKA/NGF receptor gene in patients with congenital insensitivity to pain with anhidrosis. Nat. Genet. 1996, 13, 485–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hofman, P. Next-Generation Sequencing with Liquid Biopsies from Treatment-Naïve Non-Small Cell Lung Carcinoma Patients. Cancers 2021, 13, 2049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drilon, A.; Laetsch, T.W.; Kummar, S.; DuBois, S.G.; Lassen, U.N.; DeMETri, G.D.; Nathenson, M.; Doebele, R.C.; Farago, A.F.; Pappo, A.S.; et al. Efficacy of Larotrectinib in TRK Fusion-Positive Cancers in Adults and Children. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 378, 731–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doebele, R.C.; Drilon, A.; Paz-Ares, L.; Siena, S.; Shaw, A.T.; Farago, A.F.; Blakely, C.M.; Seto, T.; Cho, B.C.; Tosi, D.; et al. Entrectinib in patients with advanced or Metastatic NTRK fusion-positive solid tumours: Integrated analysis of three phase 1–2 trials. Lancet Oncol. 2020, 21, 271–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drilon, A.; Nagasubramanian, R.; Blake, J.F.; Ku, N.; Tuch, B.B.; Ebata, K.; Smith, S.; Lauriault, V.; Kolakowski, G.R.; Brandhuber, B.J.; et al. A Next-Generation TRK Kinase Inhibitor Overcomes Acquired Resistance to Prior TRK Kinase Inhibition in Patients with TRK Fusion-Positive Solid Tumors. Cancer Discov. 2017, 7, 963–972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Drilon, A.; Ou, S.-H.I.; Cho, B.C.; Kim, D.-W.; Lee, J.; Lin, J.J.; Zhu, V.W.; Ahn, M.-J.; Camidge, D.R.; Nguyen, J.; et al. Repotrectinib (TPX-0005) Is a Next-Generation ROS1/TRK/ALK Inhibitor That Potently Inhibits ROS1/TRK/ALK Solvent- Front Mutations. Cancer Discov. 2018, 8, 1227–1236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kim, D.; Xue, J.Y.; Lito, P. Targeting KRAS(G12C): From Inhibitory Mechanism to Modulation of Antitumor Effects in Patients. Cell 2020, 183, 850–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salgia, R.; Pharaon, R.; Mambetsariev, I.; Nam, A.; Sattler, M. The improbable targeted therapy: KRAS as an emerging target in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). Cell Rep. Med. 2021, 2, 100186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skoulidis, F.; Li, B.T.; Dy, G.K.; Price, T.J.; Falchook, G.S.; Wolf, J.; Italiano, A.; Schuler, M.; Borghaei, H.; Barlesi, F.; et al. Sotorasib for Lung Cancers with p.G12C Mutation. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 384, 2371–2381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riely, G.J.; Ou, S.H.I.; Rybkin, I.; Spira, A.; Papadopoulos, K.; Sabari, J.K.; Johnson, M.; Heist, R.S.; Bazhenova, L.; Barve, M.; et al. 99O_PR KRYSTAL-1: Activity and preliminary pharmacodynamic (PD) analysis of adagrasib (MRTX849) in patients (Pts) with advanced non–small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) harboring KRASG12C mutation. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2021, 16, S751–S752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stephens, P.; Hunter, C.; Bignell, G.; Edkins, S.; Davies, H.; Teague, J.; Stevens, C.; O’Meara, S.; Smith, R.; Parker, A.; et al. Lung cancer: Intragenic ERBB2 kinase mutations in tumours. Nature 2004, 431, 525–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.T.; Shen, R.; Buonocore, D.; Olah, Z.T.; Ni, A.; Ginsberg, M.S.; Ulaner, G.A.; Offin, M.; Feldman, D.; Hembrough, T.; et al. Ado-Trastuzumab Emtansine for Patients with HER2-Mutant Lung Cancers: Results From a Phase II Basket Trial. J. Clin. Oncol. 2018, 36, 2532–2537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peters, S.; Stahel, R.; Bubendorf, L.; Bonomi, P.; Villegas, A.; Kowalski, D.M.; Baik, C.S.; Isla, D.; Carpeno, J.D.C.; Garrido, P.; et al. Trastuzumab Emtansine (T-DM1) in Patients with Previously Treated HER2-Overexpressing Metastatic Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: Efficacy, Safety, and Biomarkers. Clin. Cancer Res. 2019, 25, 64–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Song, Z.; Li, Y.; Chen, S.; Ying, S.; Xu, S.; Huang, J.; Wu, D.; Lv, D.; Bei, T.; Liu, S.; et al. Efficacy and safety of pyrotinib in advanced lung adenocarcinoma with HER2 mutations: A multicenter, single-arm, phase II trial. BMC Med. 2022, 20, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smit, E.F.; Nakagawa, K.; Nagasaka, M.; Felip, E.; Goto, Y.; Li, B.T.; Pacheco, J.M.; Murakami, H.; Barlesi, F.; Saltos, A.N.; et al. Trastuzumab deruxtecan (T-DXd; DS-8201) in patients with HER2-mutated Metastatic non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC): Interim results of DESTINY-Lung01. J. Clin. Oncol. 2020, 38, 9504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.T.; Smit, E.F.; Goto, Y.; Nakagawa, K.; Udagawa, H.; Mazières, J.; Nagasaka, M.; Bazhenova, L.; Saltos, A.N.; Felip, E.; et al. Trastuzumab Deruxtecan in -Mutant Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2022, 386, 241–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandez-Cuesta, L.; Plenker, D.; Osada, H.; Sun, R.; Menon, R.; Leenders, F.; Ortiz-Cuaran, S.; Peifer, M.; Bos, M.; Daßler, J.; et al. CD74-NRG1 fusions in lung adenocarcinoma. Cancer Discov. 2014, 4, 415–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Drilon, A.; Somwar, R.; Mangatt, B.P.; Edgren, H.; Desmeules, P.; Ruusulehto, A.; Smith, R.S.; Delasos, L.; Vojnic, M.; Plodkowski, A.J.; et al. Response to ERBB3-Directed Targeted Therapy in -Rearranged Cancers. Cancer Discov. 2018, 8, 686–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Estrada-Bernal, A.; Le, A.T.; Doak, A.E.; Tirunagaru, V.G.; Silva, S.; Bull, M.R.; Smaill, J.B.; Patterson, A.V.; Kim, C.; Liu, S.V.; et al. Tarloxotinib Is a Hypoxia-Activated Pan-HER Kinase Inhibitor Active Against a Broad Range of HER-Family Oncogenes. Clin. Cancer Res. 2021, 27, 1463–1475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zarczynska, I.; Gorska-Arcisz, M.; Cortez, A.J.; Kujawa, K.A.; Wilk, A.M.; Skladanowski, A.C.; Stanczak, A.; Skupinska, M.; Wieczorek, M.; Lisowska, K.M.; et al. p38 Mediates Resistance to FGFR Inhibition in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Cells 2021, 10, 3363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DeNicola, G.M.; KarRETh, F.A.; Humpton, T.J.; Gopinathan, A.; Wei, C.; Frese, K.; Mangal, D.; Yu, K.H.; Yeo, C.J.; Calhoun, E.S.; et al. Oncogene-induced Nrf2 transcription promotes ROS detoxification and tumorigenesis. Nature 2011, 475, 106–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Satoh, H.; Moriguchi, T.; Saigusa, D.; Baird, L.; Yu, L.; Rokutan, H.; Igarashi, K.; Ebina, M.; Shibata, T.; Yamamoto, M. NRF2 Intensifies Host Defense Systems to Prevent Lung Carcinogenesis, but After Tumor Initiation Accelerates Malignant Cell Growth. Cancer Res. 2016, 76, 3088–3096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Binkley, M.S.; Jeon, Y.-J.; Nesselbush, M.; Moding, E.J.; Nabet, B.Y.; Almanza, D.; Kunder, C.; Stehr, H.; Yoo, C.H.; Rhee, S.; et al. Mutations Predict Lung Cancer Radiation Resistance That Can Be Targeted by Glutaminase Inhibition. Cancer Discov. 2020, 10, 1826–1841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.A.; Suzawa, K.; Jordan, E.; Zehir, A.; Ni, A.; Kim, R.; Kris, M.G.; Hellmann, M.D.; Li, B.T.; Somwar, R.; et al. Concurrent Alterations in EGFR-Mutant Lung Cancers Associated with Resistance to EGFR Kinase Inhibitors and Characterization of MTOR as a Mediator of Resistance. Clin. Cancer Res. 2018, 24, 3108–3118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shibata, T.; Saito, S.; Kokubu, A.; Suzuki, T.; Yamamoto, M.; Hirohashi, S. Global downstream pathway analysis reveals a dependence of oncogenic NF-E2-related factor 2 mutation on the mTOR growth signaling pathway. Cancer Res. 2010, 70, 9095–9105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Paik, P.K.; Ahn, L.S.H.; Ginsberg, M.S.; Plodkowski, A.J.; Kim, R.; Doyle, L.A.; Rudin, C.M. Targeting NFE2L2/KEAP1 mutations in advanced NSCLC with the TORC1/2 inhibitor TAK-228. J. Clin. Oncol. 2019, 37, 9085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romero, R.; Sayin, V.I.; Davidson, S.M.; Bauer, M.R.; Singh, S.X.; LeBoeuf, S.E.; Karakousi, T.R.; Ellis, D.C.; Bhutkar, A.; Sánchez-Rivera, F.J.; et al. KEAP1 loss promotes KRAS-driven lung cancer and results in dependence on glutaminolysis. Nat. Med. 2017, 23, 1362–1368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Krishnamurthy, N.; Goodman, A.M.; Barkauskas, D.A.; Kurzrock, R. STK11 alterations in the pan-cancer setting: Prognostic and therapeutic implications. Eur. J. Cancer 2021, 148, 215–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roosan, M.R.; Mambetsariev, I.; Pharaon, R.; Fricke, J.; Husain, H.; Reckamp, K.L.; Koczywas, M.; Massarelli, E.; Bild, A.H.; Salgia, R. Usefulness of Circulating Tumor DNA in Identifying Somatic Mutations and Tracking Tumor Evolution in Patients with Non-small Cell Lung Cancer. Chest 2021, 160, 1095–1107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skoulidis, F.; Goldberg, M.E.; Greenawalt, D.M.; Hellmann, M.D.; Awad, M.M.; Gainor, J.F.; Schrock, A.B.; Hartmaier, R.J.; Trabucco, S.E.; Gay, L.; et al. Mutations and PD-1 Inhibitor Resistance in -Mutant Lung Adenocarcinoma. Cancer Discov. 2018, 8, 822–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Papillon-Cavanagh, S.; Doshi, P.; Dobrin, R.; Szustakowski, J.; Walsh, A.M. and mutations as prognostic biomarkers in an observational real-world lung adenocarcinoma cohort. ESMO Open 2020, 5, e000706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ishida, Y.; Agata, Y.; Shibahara, K.; Honjo, T. Induced expression of PD-1, a novel member of the immunoglobulin gene superfamily, upon programmed cell death. EMBO J. 1992, 11, 3887–3895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, C.Y.; Huang, J.A.; Chen, Y.; Chen, C.; Zhang, X.G. High expression of PD-L1 in lung cancer may contribute to poor prognosis and tumor cells immune escape through suppressing tumor infiltrating dendritic cells maturation. Med. Oncol. 2011, 28, 682–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khanna, P.; Blais, N.; Gaudreau, P.-O.; Corrales-Rodriguez, L. Immunotherapy Comes of Age in Lung Cancer. Clin. Lung Cancer 2017, 18, 13–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borghaei, H.; Paz-Ares, L.; Horn, L.; Spigel, D.R.; Steins, M.; Ready, N.E.; Chow, L.Q.; Vokes, E.E.; Felip, E.; Holgado, E.; et al. Nivolumab versus Docetaxel in Advanced Nonsquamous Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 373, 1627–1639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brahmer, J.; Reckamp, K.L.; Baas, P.; Crinò, L.; Eberhardt, W.E.E.; Poddubskaya, E.; Antonia, S.; Pluzanski, A.; Vokes, E.E.; Holgado, E.; et al. Nivolumab versus Docetaxel in Advanced Squamous-Cell Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 373, 123–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Carbone, D.P.; Reck, M.; Paz-Ares, L.; Creelan, B.; Horn, L.; Steins, M.; Felip, E.; van den Heuvel, M.M.; Ciuleanu, T.-E.; Badin, F.; et al. First-Line Nivolumab in Stage IV or Recurrent Non–Small-Cell Lung Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 376, 2415–2426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garon, E.B.; Hellmann, M.D.; Rizvi, N.A.; Carcereny, E.; Leighl, N.B.; Ahn, M.-J.; Eder, J.P.; Balmanoukian, A.S.; Aggarwal, C.; Horn, L.; et al. Five-Year Overall Survival for Patients with Advanced Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer Treated with Pembrolizumab: Results From the Phase I KEYNOTE-001 Study. J. Clin. Oncol. 2019, 37, 2518–2527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reck, M.; Rodríguez-Abreu, D.; Robinson, A.G.; Hui, R.; Csőszi, T.; Fülöp, A.; Gottfried, M.; Peled, N.; Tafreshi, A.; Cuffe, S.; et al. Five-Year Outcomes with Pembrolizumab Versus Chemotherapy for Metastatic Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer with PD-L1 Tumor Proportion Score ≥ 50. J. Clin. Oncol. 2021, 39, 2339–2349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mok, T.S.K.; Wu, Y.-L.; Kudaba, I.; Kowalski, D.M.; Cho, B.C.; Turna, H.Z.; Castro, G.; Srimuninnimit, V.; Laktionov, K.K.; Bondarenko, I.; et al. Pembrolizumab versus chemotherapy for previously untreated, PD-L1-expressing, locally advanced or Metastatic non-small-cell lung cancer (KEYNOTE-042): A randomised, open-label, controlled, phase 3 trial. Lancet 2019, 393, 1819–1830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fehrenbacher, L.; Spira, A.; Ballinger, M.; Kowanetz, M.; Vansteenkiste, J.; Mazieres, J.; Park, K.; Smith, D.; Artal-Cortes, A.; Lewanski, C.; et al. Atezolizumab versus docetaxel for patients with previously treated non-small-cell lung cancer (POPLAR): A multicentre, open-label, phase 2 randomised controlled trial. Lancet 2016, 387, 1837–1846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rittmeyer, A.; Barlesi, F.; Waterkamp, D.; Park, K.; Ciardiello, F.; von Pawel, J.; Gadgeel, S.M.; Hida, T.; Kowalski, D.M.; Dols, M.C.; et al. Atezolizumab versus docetaxel in patients with previously treated non-small-cell lung cancer (OAK): A phase 3, open-label, multicentre randomised controlled trial. Lancet 2017, 389, 255–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herbst, R.S.; Giaccone, G.; de Marinis, F.; Reinmuth, N.; Vergnenegre, A.; Barrios, C.H.; Morise, M.; Felip, E.; Andric, Z.; Geater, S.; et al. Atezolizumab for First-Line Treatment of PD-L1-Selected Patients with NSCLC. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 383, 1328–1339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verschraegen, C.F.; Jerusalem, G.; McClay, E.F.; Iannotti, N.; Redfern, C.H.; Bennouna, J.; Chen, F.L.; Kelly, K.; Mehnert, J.; Morris, J.C.; et al. Efficacy and safety of first-line avelumab in patients with advanced non-small cell lung cancer: Results from a phase Ib cohort of the JAVELIN Solid Tumor study. J. Immunother. Cancer 2020, 8, e001064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barlesi, F.; Vansteenkiste, J.; Spigel, D.; Ishii, H.; Garassino, M.; de Marinis, F.; Özgüroğlu, M.; Szczesna, A.; Polychronis, A.; Uslu, R.; et al. Avelumab versus docetaxel in patients with platinum-treated advanced non-small-cell lung cancer (JAVELIN Lung 200): An open-label, randomised, phase 3 study. Lancet Oncol. 2018, 19, 1468–1479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, K.; Özgüroğlu, M.; Vansteenkiste, J.; Spigel, D.; Yang, J.C.H.; Ishii, H.; Garassino, M.; de Marinis, F.; Szczesna, A.; Polychronis, A.; et al. Avelumab Versus Docetaxel in Patients with Platinum-Treated Advanced NSCLC: 2-Year Follow-Up From the JAVELIN Lung 200 Phase 3 Trial. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2021, 16, 1369–1378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antonia, S.J.; Villegas, A.; Daniel, D.; Vicente, D.; Murakami, S.; Hui, R.; Yokoi, T.; Chiappori, A.; Lee, K.H.; de Wit, M.; et al. Durvalumab after Chemoradiotherapy in Stage III Non–Small-Cell Lung Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 377, 1919–1929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Antonia, S.J.; Villegas, A.; Daniel, D.; Vicente, D.; Murakami, S.; Hui, R.; Kurata, T.; Chiappori, A.; Lee, K.H.; de Wit, M.; et al. Overall Survival with Durvalumab after Chemoradiotherapy in Stage III NSCLC. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 379, 2342–2350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gray, J.E.; Villegas, A.; Daniel, D.; Vicente, D.; Murakami, S.; Hui, R.; Kurata, T.; Chiappori, A.; Lee, K.H.; Cho, B.C.; et al. Three-Year Overall Survival with Durvalumab after Chemoradiotherapy in Stage III NSCLC-Update from PACIFIC. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2020, 15, 288–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Paz-Ares, L.; Spira, A.; Raben, D.; Planchard, D.; Cho, B.C.; Özgüroğlu, M.; Daniel, D.; Villegas, A.; Vicente, D.; Hui, R.; et al. Outcomes with durvalumab by tumour PD-L1 expression in unresectable, stage III non-small-cell lung cancer in the PACIFIC trial. Ann. Oncol. 2020, 31, 798–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faivre-Finn, C.; Vicente, D.; Kurata, T.; Planchard, D.; Paz-Ares, L.; Vansteenkiste, J.F.; Spigel, D.R.; Garassino, M.C.; Reck, M.; Senan, S.; et al. Four-Year Survival with Durvalumab After Chemoradiotherapy in Stage III NSCLC-an Update from the PACIFIC Trial. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2021, 16, 860–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spigel, D.R.; Faivre-Finn, C.; Gray, J.E.; Vicente, D.; Planchard, D.; Paz-Ares, L.; Vansteenkiste, J.F.; Garassino, M.C.; Hui, R.; Quantin, X.; et al. Five-Year Survival Outcomes From the PACIFIC Trial: Durvalumab After Chemoradiotherapy in Stage III Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2022, 40, 1301–1311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sezer, A.; Kilickap, S.; Gümüş, M.; Bondarenko, I.; Özgüroğlu, M.; Gogishvili, M.; Turk, H.M.; Cicin, I.; Bentsion, D.; Gladkov, O.; et al. Cemiplimab monotherapy for first-line treatment of advanced non-small-cell lung cancer with PD-L1 of at least 50%: A multicentre, open-label, global, phase 3, randomised, controlled trial. Lancet 2021, 397, 592–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.-Y.; Wu, Y.-L. Tislelizumab: An investigational anti-PD-1 antibody for the treatment of advanced non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). Expert Opin. Investig. Drugs 2020, 29, 1355–1364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciciola, P.; Cascetta, P.; Bianco, C.; Formisano, L.; Bianco, R. Combining Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors with Anti-Angiogenic Agents. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, S.; Qin, C.; Hu, H.; Liu, T.; He, Y.; Guo, H.; Yan, H.; Zhang, J.; Tang, S.; Zhou, H. Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: Progress, Challenges, and Prospects. Cells 2022, 11, 320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WALKer, L.S.K.; Sansom, D.M. The emerging role of CTLA4 as a cell-extrinsic regulator of T cell responses. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2011, 11, 852–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlino, M.S.; Larkin, J.; Long, G.V. Immune checkpoint inhibitors in melanoma. Lancet 2021, 398, 1002–1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.; Menon, H.; Verma, V.; Guo, C.; Ramapriyan, R.; Barsoumian, H.; Younes, A.; Hu, Y.; Wasley, M.; Cortez, M.A.; et al. Response and outcomes after anti-CTLA4 versus anti-PD1 combined with stereotactic body radiation therapy for Metastatic non-small cell lung cancer: RETrospective analysis of two single-institution prospective trials. J. Immunother. Cancer 2020, 8, e000492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hellmann, M.D.; Paz-Ares, L.; Bernabe Caro, R.; Zurawski, B.; Kim, S.-W.; Carcereny Costa, E.; Park, K.; Alexandru, A.; Lupinacci, L.; de la Mora Jimenez, E.; et al. Nivolumab plus Ipilimumab in Advanced Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2019, 381, 2020–2031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paz-Ares, L.G.; Ramalingam, S.S.; Ciuleanu, T.-E.; Lee, J.-S.; Urban, L.; Caro, R.B.; Park, K.; Sakai, H.; Ohe, Y.; Nishio, M.; et al. First-Line Nivolumab Plus Ipilimumab in Advanced NSCLC: 4-Year Outcomes From the Randomized, Open-Label, Phase 3 CheckMate 227 Part 1 Trial. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2022, 17, 289–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Antonia, S.; Goldberg, S.B.; Balmanoukian, A.; Chaft, J.E.; Sanborn, R.E.; Gupta, A.; Narwal, R.; Steele, K.; Gu, Y.; Karakunnel, J.J.; et al. Safety and antitumour activity of durvalumab plus tremelimumab in non-small cell lung cancer: A multicentre, phase 1b study. Lancet Oncol. 2016, 17, 299–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rizvi, N.A.; Cho, B.C.; Reinmuth, N.; Lee, K.H.; Luft, A.; Ahn, M.-J.; van den Heuvel, M.M.; Cobo, M.; Vicente, D.; Smolin, A.; et al. Durvalumab with or without Tremelimumab vs Standard Chemotherapy in First-line Treatment of Metastatic Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: The MYSTIC Phase 3 Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA Oncol. 2020, 6, 661–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Barber, G.N. STING: Infection, inflammation and cancer. Nat. Rev. Immunol 2015, 15, 760–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sen, T.; Rodriguez, B.L.; Chen, L.; Corte, C.M.D.; Morikawa, N.; Fujimoto, J.; Cristea, S.; Nguyen, T.; Diao, L.; Li, L.; et al. Targeting DNA Damage Response Promotes Antitumor Immunity through STING-Mediated T-cell Activation in Small Cell Lung Cancer. Cancer Discov. 2019, 9, 646–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Della Corte, C.M.; Sen, T.; Gay, C.M.; Ramkumar, K.; Diao, L.; Cardnell, R.J.; Rodriguez, B.L.; Stewart, C.A.; Papadimitrakopoulou, V.A.; Gibson, L.; et al. STING Pathway Expression Identifies NSCLC with an Immune-Responsive Phenotype. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2020, 15, 777–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raaby Gammelgaard, K.; Sandfeld-Paulsen, B.; Godsk, S.H.; Demuth, C.; Meldgaard, P.; Sorensen, B.S.; Jakobsen, M.R. cGAS-STING pathway expression as a prognostic tool in NSCLC. Transl. Lung Cancer Res. 2021, 10, 340–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Sanmamed, M.F.; Datar, I.; Su, T.T.; Ji, L.; Sun, J.; Chen, L.; Chen, Y.; Zhu, G.; Yin, W.; et al. Fibrinogen-like Protein 1 Is a Major Immune Inhibitory Ligand of LAG-3. Cell 2019, 176, 334–347.e12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puhr, H.C.; Ilhan-Mutlu, A. New emerging targets in cancer immunotherapy: The role of LAG3. ESMO Open 2019, 4, e000482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhou, J.; Yu, X.; Hou, L.; Zhao, J.; Zhou, F.; Chu, X.; Wu, Y.; Zhou, C.; Su, C. Epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitor remodels tumor microenvironment by upregulating LAG-3 in advanced non-small-cell lung cancer. Lung Cancer 2021, 153, 143–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, D.S.; Schoffski, P.; Calvo, A.; Sarantopoulos, J.; Ochoa De Olza, M.; Carvajal, R.D.; Prawira, A.; Kyi, C.; Esaki, T.; Akerley, W.L. Phase I/II study of LAG525±spartalizumab (PDR001) in patients (pts) with advanced malignancies. J Clin. Oncol. 2018, 36, 3012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nemunaitis, J.; Nemunaitis, M.; Senzer, N.; Snitz, P.; Bedell, C.; Kumar, P.; Pappen, B.; Maples, P.; Shawler, D.; Fakhrai, H. Phase II trial of Belagenpumatucel-L, a TGF-β2 antisense gene modified allogeneic tumor vaccine in advanced non small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) patients. Cancer Gene Ther. 2009, 16, 620–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Harjunpää, H.; Guillerey, C. TIGIT as an emerging immune checkpoint. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2020, 200, 108–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cho, B.C.; Abreu, D.R.; Hussein, M.; Cobo, M.; Patel, A.J.; Secen, N.; Lee, K.H.; Massuti, B.; HiRET, S.; Yang, J.C.H.; et al. Tiragolumab plus atezolizumab versus placebo plus atezolizumab as a first-line treatment for PD-L1-selected non-small-cell lung cancer (CITYSCAPE): Primary and follow-up analyses of a randomised, double-blind, phase 2 study. Lancet Oncol. 2022, 23, 781–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalemkerian, G.P.; Narula, N.; Kennedy, E.B.; Biermann, W.A.; Donington, J.; Leighl, N.B.; Lew, M.; Pantelas, J.; Ramalingam, S.S.; Reck, M.; et al. Molecular Testing Guideline for the Selection of Patients with Lung Cancer for Treatment with Targeted Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors: American Society of Clinical Oncology Endorsement of the College of American Pathologists/International Association for the Study of Lung Cancer/Association for Molecular Pathology Clinical Practice Guideline Update. J. Clin. Oncol. 2018, 36, 911–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rolfo, C.; Mack, P.C.; Scagliotti, G.V.; Baas, P.; Barlesi, F.; Bivona, T.G.; Herbst, R.S.; Mok, T.S.; Peled, N.; Pirker, R.; et al. Liquid Biopsy for Advanced Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer (NSCLC): A Statement Paper from the IASLC. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2018, 13, 1248–1268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Layfield, L.J.; Hammer, R.D.; White, S.K.; Furtado, L.V.; Schmidt, R.L. Molecular Testing Strategies for Pulmonary Adenocarcinoma: An Optimal Approach with Cost Analysis. Arch. Pathol. Lab. Med. 2019, 143, 628–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tan, A.C.; Lai, G.G.Y.; Tan, G.S.; Poon, S.Y.; Doble, B.; Lim, T.H.; Aung, Z.W.; Takano, A.; Tan, W.L.; Ang, M.-K.; et al. Utility of incorporating next-generation sequencing (NGS) in an Asian non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) population: Incremental yield of actionable alterations and cost-effectiveness analysis. Lung Cancer 2020, 139, 207–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drilon, A.; Wang, L.; Arcila, M.E.; Balasubramanian, S.; Greenbowe, J.R.; Ross, J.S.; Stephens, P.; Lipson, D.; Miller, V.A.; Kris, M.G.; et al. Broad, Hybrid Capture-Based Next-Generation Sequencing Identifies Actionable Genomic Alterations in Lung Adenocarcinomas Otherwise Negative for Such Alterations by Other Genomic Testing Approaches. Clin. Cancer Res. 2015, 21, 3631–3639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Han, J.-Y.; Kim, S.H.; Lee, Y.-S.; Lee, S.-Y.; Hwang, J.-A.; Kim, J.Y.; Yoon, S.J.; Lee, G.K. Comparison of targeted next-generation sequencing with conventional sequencing for predicting the responsiveness to epidermal growth factor receptor-tyrosine kinase inhibitor (EGFR-TKI) therapy in never-smokers with lung adenocarcinoma. Lung Cancer 2014, 85, 161–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tuononen, K.; Mäki-Nevala, S.; Sarhadi, V.K.; Wirtanen, A.; Rönty, M.; Salmenkivi, K.; Andrews, J.M.; Telaranta-Keerie, A.I.; Hannula, S.; Lagström, S.; et al. Comparison of targeted next-generation sequencing (NGS) and real-time PCR in the detection of EGFR, KRAS, and BRAF mutations on formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded tumor material of non-small cell lung carcinoma-superiority of NGS. Genes Chromosom. Cancer 2013, 52, 503–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davies, K.D.; Lomboy, A.; Lawrence, C.A.; Yourshaw, M.; Bocsi, G.T.; Camidge, D.R.; Aisner, D.L. DNA-Based versus RNA-Based Detection of MET Exon 14 Skipping Events in Lung Cancer. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2019, 14, 737–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tan, A.C.; Seet, A.O.L.; Lai, G.G.Y.; Lim, T.H.; Lim, A.S.T.; Tan, G.S.; Takano, A.; Tai, D.W.M.; Tan, T.J.Y.; Lam, J.Y.C.; et al. Molecular Characterization and Clinical Outcomes in RET-Rearranged NSCLC. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2020, 15, 1928–1934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roskoski, R. Properties of FDA-approved small molecule protein kinase inhibitors: A 2022 update. Pharmacol. Res. 2022, 175, 106037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cooper, A.J.; Sequist, L.V.; Lin, J.J. Third-generation EGFR and ALK inhibitors: Mechanisms of resistance and management. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2022, 19, 499–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Passaro, A.; Brahmer, J.; Antonia, S.; Mok, T.; Peters, S. Managing Resistance to Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors in Lung Cancer: Treatment and Novel Strategies. J. Clin. Oncol. 2022, 40, 598–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garon, E.B.; Spira, A.I.; Johnson, M.; Bazhenova, L.; Leach, J.; Cummings, A.L.; Candia, A.; Coffman, R.L.; Janatpour, M.J.; Janssen, R.; et al. A Phase Ib Open-Label, Multicenter Study of Inhaled DV281, a TLR9 Agonist, in Combination with Nivolumab in Patients with Advanced or Metastatic Non-small Cell Lung Cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2021, 27, 4566–4573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otsuka, T.; Nishida, S.; Shibahara, T.; Temizoz, B.; Hamaguchi, M.; Shiroyama, T.; Kimura, K.; Miyake, K.; Hirata, H.; Mizuno, Y.; et al. CpG ODN (K3)-toll-like receptor 9 agonist-induces Th1-type immune response and enhances cytotoxic activity in advanced lung cancer patients: A phase I study. BMC Cancer 2022, 22, 744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gillette, M.A.; Satpathy, S.; Cao, S.; Dhanasekaran, S.M.; Vasaikar, S.V.; Krug, K.; Petralia, F.; Li, Y.; Liang, W.-W.; Reva, B.; et al. Proteogenomic Characterization Reveals Therapeutic Vulnerabilities in Lung Adenocarcinoma. Cell 2020, 182, 200–225.e35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Drugs | Trails | Comparator | ORR, % | PFS, HR | OS, HR | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gefitinib | WJTOG-3405 | Cisplatin plus docetaxel | 62.1 vs. 32.2 | 0.489 | 1.252 | [13] |
| Erlotinib | OPTIMAL | Carboplatin plus gemcitabine | 83 vs. 36 | 0.16 | 1.19 | [14] |
| Afatinib | LUX-Lung-7 | Gefitinib | 72.5 vs. 56 | 0.73 | 0.86 | [16] |
| Osimertinib | FLAURA | Erlotinib or gefitinib | 80 vs. 76 | 0.46 | 0.80 | [15] |
| Dacomitinib | ARCHER-1050 | Gefitinib | 75 vs. 72 | 0.59 | 0.760 | [17] |
| Drugs | Trails | Comparator | ORR, % | PFS, HR | OS, HR | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Crizotinib | PROFILE-1014 | Platinum plus pemetrexed | 74 vs. 45 | 0.45 | 0.76 | [42] |
| Ceritinib | ASCEND-4 | Platinum plus pemetrexed | 72.5 vs. 26.7 | 0.55 | 0.73 | [44] |
| Alectinib | ALEX | Crizotinib | 82.9 vs. 75.5 | 0.5 | 0.67 | [45] |
| Brigatinib | ALTA-1L | Crizotinib | 71 vs. 60 | 0.49 | 0.92 | [46] |
| Lorlatinib | CROWN | Crizotinib | 76 vs. 58 | 0.28 | 0.72 | [47] |
| Ensartinib | eXalt3 | Crizotinib | 75 vs. 67 | 0.52 | 0.88 | [48] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Guo, H.; Zhang, J.; Qin, C.; Yan, H.; Liu, T.; Hu, H.; Tang, S.; Tang, S.; Zhou, H. Biomarker-Targeted Therapies in Non–Small Cell Lung Cancer: Current Status and Perspectives. Cells 2022, 11, 3200. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells11203200
Guo H, Zhang J, Qin C, Yan H, Liu T, Hu H, Tang S, Tang S, Zhou H. Biomarker-Targeted Therapies in Non–Small Cell Lung Cancer: Current Status and Perspectives. Cells. 2022; 11(20):3200. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells11203200
Chicago/Turabian StyleGuo, Haiyang, Jun Zhang, Chao Qin, Hang Yan, Tao Liu, Haiyang Hu, Shengjie Tang, Shoujun Tang, and Haining Zhou. 2022. "Biomarker-Targeted Therapies in Non–Small Cell Lung Cancer: Current Status and Perspectives" Cells 11, no. 20: 3200. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells11203200
APA StyleGuo, H., Zhang, J., Qin, C., Yan, H., Liu, T., Hu, H., Tang, S., Tang, S., & Zhou, H. (2022). Biomarker-Targeted Therapies in Non–Small Cell Lung Cancer: Current Status and Perspectives. Cells, 11(20), 3200. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells11203200





