PRP8-Induced CircMaml2 Facilitates the Healing of the Intestinal Mucosa via Recruiting PTBP1 and Regulating Sec62
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cell Lines
2.2. RNase R Treatment
2.3. RNA Extraction, gDNA Extraction, and qRT-PCR Analysis
2.4. Nucleic Acid Electrophoresis
2.5. Experimental Animals and Establishment of the Burn Model
2.6. H&E Staining
2.7. Adenovirus Infection
2.8. Colony Formation Assays
2.9. Cell Counting Kit-8 (CCK-8) Assays
2.10. Edu Assays
2.11. Wound Healing Assays
2.12. Transwell Assays
2.13. RNA Isolation of Nuclear and Cytoplasmic Fractions
2.14. Pull-Down Assay and MS Analysis
2.15. RNA Immunoprecipitation (RIP)
2.16. Western Blot Analysis
2.17. Lentivirus Transfection
2.18. Assessment of Endogenous RNA Degradation
2.19. Transfection of siRNA and miRNA Mimic
2.20. Dual-Luciferase Reporter Assay
2.21. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
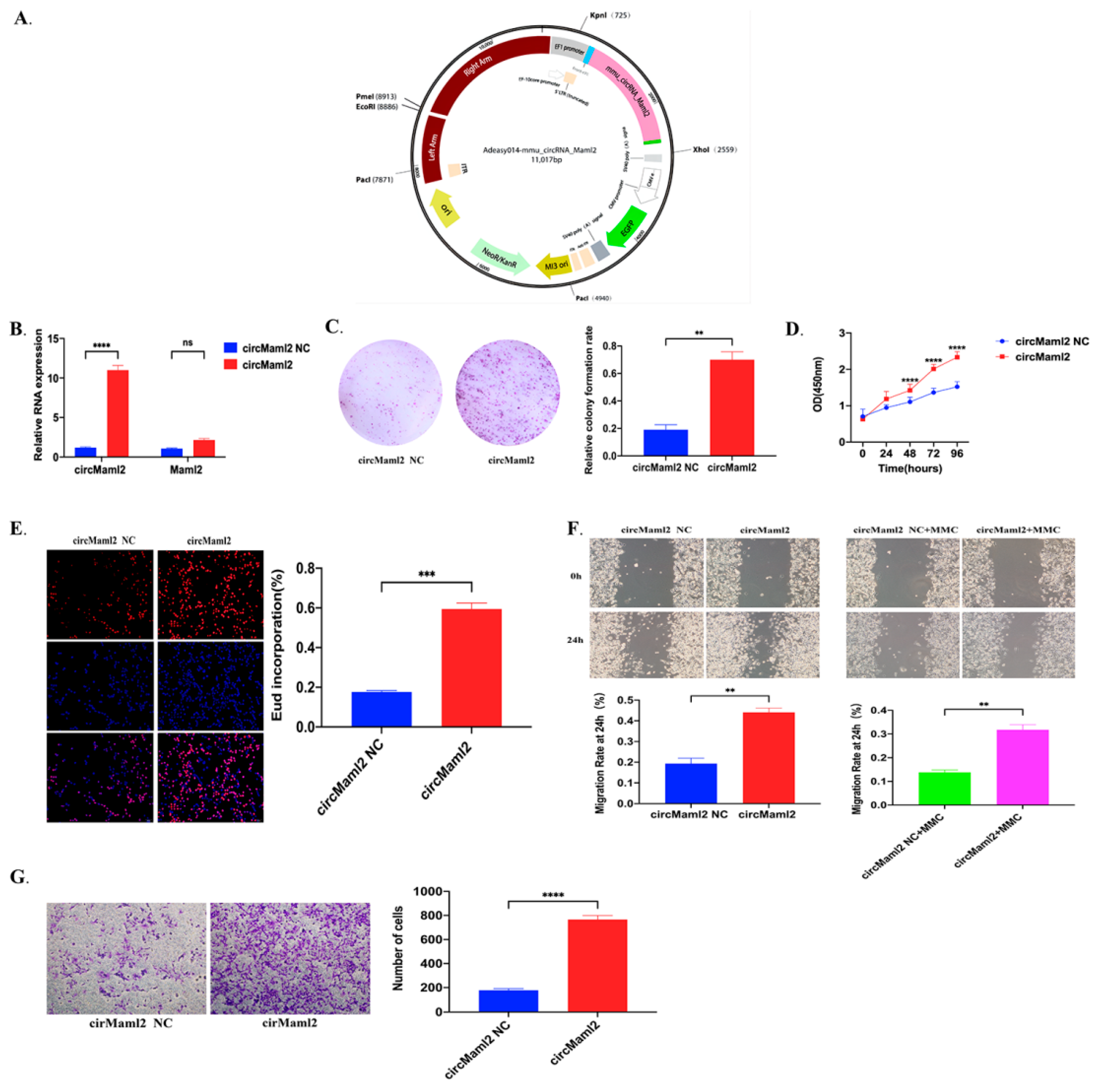
3.1. CircMaml2 Upregulation Promotes the Migration and Proliferation of MC38 Cells
3.2. CircMaml2 Directly Interacts with the RBP PTBP1
3.3. CircMaml2 Enhances PTBP1 to Upregulate Ebf1 Expression

3.4. CircMaml2 Promotes the Migration and Proliferation of MC38 Cells by Acting on PTBP1-Ebf1
3.5. CircMaml2 Sponges miR-683
3.6. CircMaml2 Rescues the Inhibition of miR-683
3.7. PRP8 Induces the Biogenesis of CircMaml2
3.8. CircMaml2 Can Promote the Repair of Intestinal Mucosal Injury in Burned Mice
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Li, X.; Hammer, A.M.; Rendon, J.L.; Choudhry, M.A. Intestine immune homeostasis after alcohol and burn injury. Shock 2015, 43, 540–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Deitch, E.A. Multiple organ failure. Pathophysiology and potential future therapy. Ann. Surg. 1992, 216, 117–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Magnotti, L.J.; Deitch, E.A. Burns, bacterial translocation, gut barrier function, and failure. J. Burn Care Rehabil. 2005, 26, 383–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.F.; Zhang, F.; Lineaweaver, W.C. History and Advancement of Burn Treatments. Ann. Plast. Surg. 2017, 78, S2–S8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, A.W.; Dewey, W.S.; King, B.T. Rehabilitation of Burn Injuries: An Update. Phys. Med. Rehabil. Clin. N. Am. 2019, 30, 111–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, A.; Imran, J.; Madni, T.; Wolf, S.E. Nutrition and metabolism in burn patients. Burn. Trauma 2017, 5, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, C.; Li, Y.; Zhuang, M.; Zhu, B.; Zhang, W.; Yan, H.; Zhang, P.; Li, D.; Yang, J.; Sun, Y. Long noncoding RNA H19 act as a competing endogenous RNA of Let-7g to facilitate IEC-6 cell migration and proliferation via regulating EGF. J. Cell. Physiol. 2021, 236, 2881–2892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanger, H.L.; Klotz, G.; Riesner, D.; Gross, H.J.; Kleinschmidt, A.K. Viroids are single-stranded covalently closed circular RNA molecules existing as highly base-paired rod-like structures. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1976, 73, 3852–3856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Caba, L.; Florea, L.; Gug, C.; Dimitriu, D.C.; Gorduza, E.V. Circular RNA-Is the Circle Perfect? Biomolecules 2021, 11, 1755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, S.; Yang, X.; Li, X.; Wang, J.; Gao, Y.; Shang, R.; Sun, W.; Dou, K.; Li, H. Circular RNA: A new star of noncoding RNAs. Cancer Lett. 2015, 365, 141–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verduci, L.; Tarcitano, E.; Strano, S.; Yarden, Y.; Blandino, G. CircRNAs: Role in human diseases and potential use as biomarkers. Cell Death Dis. 2021, 12, 468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Memczak, S.; Jens, M.; Elefsinioti, A.; Torti, F.; Krueger, J.; Rybak, A.; Maier, L.; Mackowiak, S.D.; Gregersen, L.H.; Munschauer, M.; et al. Circular RNAs are a large class of animal RNAs with regulatory potency. Nature 2013, 495, 333–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Xu, Q.; Huang, Z.-J.; Mao, N.; Lin, Z.-T.; Cheng, L.; Sun, B.; Wang, G. CircRNAs: A new target for the diagnosis and treatment of digestive system neoplasms. Cell Death Dis. 2021, 12, 205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lei, B.; Tian, Z.; Fan, W.; Ni, B. Circular RNA: A novel biomarker and therapeutic target for human cancers. Int. J. Med. Sci. 2019, 16, 292–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, J.; Huang, C.; Zou, Y.; Ye, J.; Yu, J.; Gui, Y. CircTLK1 promotes the proliferation and metastasis of renal cell carcinoma by sponging miR-136-5p. Mol. Cancer 2020, 19, 103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Wang, S.; Wang, H.; Cao, J.; Huang, X.; Chen, Z.; Xu, P.; Sun, G.; Xu, J.; Lv, J.; et al. Circular RNA circNRIP1 acts as a microRNA-149-5p sponge to promote gastric cancer progression via the AKT1/mTOR pathway. Mol. Cancer 2019, 18, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Barbato, C. MicroRNA-Mediated Silencing Pathways in the Nervous System and Neurological Diseases. Cells 2022, 11, 2375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, G.; Liang, M.; Liu, H.; Huang, J.; Li, P.; Wang, C.; Zhang, Y.; Lin, Y.; Jiang, X. CircRNA hsa_circRNA_104348 promotes hepatocellular carcinoma progression through modulating miR-187-3p/RTKN2 axis and activating Wnt/β-catenin pathway. Cell Death Dis. 2020, 11, 1065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Zhao, X.; Wang, Y.; Ren, F.; Sun, D.; Yan, Y.; Kong, X.; Bu, J.; Liu, M.; Xu, S. circRNA-002178 act as a ceRNA to promote PDL1/PD1 expression in lung adenocarcinoma. Cell Death Dis. 2020, 11, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, Z.L.; Li, B.; Luo, Y.-X.; Lin, Q.; Liu, S.-R.; Zhang, X.-Q.; Zhou, H.; Yang, J.-H.; Qu, L.-H. Comprehensive Genomic Characterization of RNA-Binding Proteins across Human Cancers. Cell Rep. 2018, 22, 286–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, W.W.; Zhang, C.; Yang, W.; Yong, T.; Awan, F.M.; Yang, B.B. Identifying and Characterizing circRNA-Protein Interaction. Theranostics 2017, 7, 4183–4191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gerstberger, S.; Hafner, M.; Tuschl, T. A census of human RNA-binding proteins. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2014, 15, 829–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lunde, B.M.; Moore, C.; Varani, G. RNA-binding proteins: Modular design for efficient function. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2007, 8, 479–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, C.; Zhou, X.; Geng, X.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, J.; Wang, Y.; Jing, J.; Zhou, X.; Pan, W. Circular RNA hsa_circ_0006401 promotes proliferation and metastasis in colorectal carcinoma. Cell Death Dis. 2021, 12, 443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prats, A.C.; David, F.; Diallo, L.H.; Roussel, E.; Tatin, F.; Garmy-Susini, B.; Lacazette, E. Circular RNA, the Key for Translation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 8591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.; Yan, H.; Deng, Y.; Lou, J.; Zhang, P.; Cui, Q.; Sun, H.; Tang, H.; Sun, Y.; Yang, J.; et al. Expression profile and bioinformatics analysis of circular RNA in intestinal mucosal injury and repair after severe burns. Cell Biol. Int. 2020, 44, 2570–2587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Liao, Y.; Lou, J.; Zhuang, M.; Yan, H.; Li, Q.; Deng, Y.; Xu, X.; Wen, D.; Sun, Y. CircRNA_Maml2 promotes the proliferation and migration of intestinal epithelial cells after severe burns by regulating the miR-93-3p/FZD7/Wnt/β-catenin pathway. Burn. Trauma 2022, 10, tkac009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeschke, M.G.; Van Baar, M.E.; Choudhry, M.A.; Chung, K.K.; Gibran, N.S.; Logsetty, S. Burn injury. Nat. Rev. Dis. Prim. 2020, 6, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Zhuang, M.; Zhu, B.; Li, Y.; Zhang, W.; Yan, H.; Zhang, P.; Li, D.; Yang, J.; Sun, Y.; et al. Epidermal growth factor regulation by autophagy-mediated lncRNA H19 in murine intestinal tract after severe burn. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2020, 24, 5878–5887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhuang, M.; Deng, Y.; Zhang, W.; Zhu, B.; Yan, H.; Lou, J.; Zhang, P.; Cui, Q.; Tang, H.; Sun, H.; et al. LncRNA Bmp1 promotes the healing of intestinal mucosal lesions via the miR-128-3p/PHF6/PI3K/AKT pathway. Cell Death Dis. 2021, 12, 595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Liu, T.; Wang, X.; He, A. Circles reshaping the RNA world: From waste to treasure. Mol. Cancer 2017, 16, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Salzman, J. Circular RNA Expression: Its Potential Regulation and Function. Trends Genet. 2016, 32, 309–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chen, W.; Zhang, B.; Chang, X. Emerging roles of circular RNAs in osteoporosis. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2021, 25, 9089–9101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.L. The expanding regulatory mechanisms and cellular functions of circular RNAs. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2020, 21, 475–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, L.D.; Zhang, J. Circular RNAs: An emerging type of RNA in cancer. Int. J. Immunopathol. Pharmacol. 2017, 30, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhang, H.D.; Jiang, L.H.; Sun, D.W.; Hou, J.C.; Ji, Z.L. CircRNA: A novel type of biomarker for cancer. Breast Cancer 2018, 25, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, W.Y.; Cai, Z.-R.; Liu, J.; Wang, D.-S.; Ju, H.-Q.; Xu, R.-H. Circular RNA: Metabolism, functions and interactions with proteins. Mol. Cancer 2020, 19, 172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, A.; Zheng, H.; Wu, Z.; Chen, M.; Huang, Y. Circular RNA-protein interactions: Functions, mechanisms, and identification. Theranostics 2020, 10, 3503–3517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janga, S.C.; Mittal, N. Construction, structure and dynamics of post-transcriptional regulatory network directed by RNA-binding proteins. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2011, 722, 103–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Dong, F.; Mao, Y. Control of CNS functions by RNA-binding proteins in neurological diseases. Curr. Pharmacol. Rep. 2018, 4, 301–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, W.; Zhou, B.-L.; Rong, L.-J.; Ye, L.; Xu, H.-J.; Zhou, Y.; Yan, X.-J.; Liu, W.-D.; Zhu, B.; Wang, L.; et al. Roles of PTBP1 in alternative splicing, glycolysis, and oncogensis. J. Zhejiang Univ. Sci. B 2020, 21, 122–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, Q.; Cavallaro, G.; Parisi, F.; Milioto, S.; Fakhrullin, R.; Lazzara, G. Ssc-MiR-21-5p and Ssc-MiR-615 Regulates the Proliferation and Apoptosis of Leydig Cells by Targeting SOX5. Cells 2022, 11, 2253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheung, H.C.; Hai, T.; Zhu, W.; Baggerly, K.A.; Tsavachidis, S.; Krahe, R.; Cote, G.J. Splicing factors PTBP1 and PTBP2 promote proliferation and migration of glioma cell lines. Brain 2009, 132, 2277–2288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Coelho, M.B.; Ascher, D.B.; Gooding, C.; Lang, E.; Maude, H.; Turner, D.; Llorian, M.; Pires, D.E.; Attig, J.; Smith, C.W. Functional interactions between polypyrimidine tract binding protein and PRI peptide ligand containing proteins. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 2016, 44, 1058–1065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Han, F.; Liu, W.; Shi, X. PTBP1 promotes tumorigenesis by regulating apoptosis and cell cycle in colon cancer. Bull. Cancer 2018, 105, 1193–1201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dhandapani, M.C.; Venkatesan, V.; Pricilla, C. MicroRNAs in childhood nephrotic syndrome. J. Cell. Physiol. 2021, 236, 7186–7210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linxweiler, M.; Schick, B.; Zimmermann, R. Let’s talk about Secs: Sec61, Sec62 and Sec63 in signal transduction, oncology and personalized medicine. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2017, 2, 17002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Du, J.; Zhao, Z.; Zhao, H.; Liu, D.; Liu, H.; Chen, J.; Cheng, B.; Zhai, X.; Yin, Z.; Zhang, Y.; et al. Sec62 promotes early recurrence of hepatocellular carcinoma through activating integrinα/CAV1 signalling. Oncogenesis 2019, 8, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Conn, S.J.; Pillman, K.A.; Toubia, J.; Conn, V.M.; Salmanidis, M.; Phillips, C.A.; Roslan, S.; Schreiber, A.W.; Gregory, P.A.; Goodall, G.J. The RNA binding protein quaking regulates formation of circRNAs. Cell 2015, 160, 1125–1134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, X.; Liu, C.-X.; Xue, W.; Zhang, Y.; Jiang, S.; Yin, Q.-F.; Wei, J.; Yao, R.W.; Yang, L.; Chen, L.-L. Coordinated circRNA Biogenesis and Function with NF90/NF110 in Viral Infection. Mol. Cell 2017, 67, 214–227.e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bachmayr-Heyda, A.; Reiner, A.T.; Auer, K.; Sukhbaatar, N.; Aust, S.; Bachleitner-Hofmann, T.; Mesteri, I.; Grunt, T.W.; Zeillinger, R.; Pils, D. Correlation of circular RNA abundance with proliferation--exemplified with colorectal and ovarian cancer, idiopathic lung fibrosis, and normal human tissues. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 8057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zeng, L.; Liu, Y.; Sun, H.; Li, S.; Wang, S.; Shu, L.; Liu, N.; Yin, S.; et al. Amphibian-derived peptide homodimer OA-GL17d promotes skin wound regeneration through the miR-663a/TGF-β1/Smad axis. Burn. Trauma 2022, 10, tkac032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]






| Genes | Primers (5′-3′) |
|---|---|
| CircMaml2 | Forward: GGGTCAGCAGAGCCAGAGGAG; Reverse: GAGAGCCTGAAGTGCCTTGTGTC |
| Maml2 | Forward: GAGCCTGGTAATGACGACTGGATG; Reverse: GAGCCTGCGGATCATCTTCCTTC |
| PTBP1 | Forward: AGCCAGCCTTCACTAGACCAGAC; Reverse: CAGCAGCAGCAGCAGCAGAC |
| Ebf1 | Forward: AGAAGACAGCAGGTCCACATCCTC; Reverse: ACTTGTAATGTGCGGCTGCCTTC |
| Gpc6 | Forward: GGAGTCACCCAAAGTCCCAC; Reverse: AGAGATACAGGGCCGAGTCC |
| Lpp | Forward: TGGATGCTTGCGGTCTCATTCAC; Reverse: CAGAGCCACAATGCGGACAGTC |
| Auts2 | Forward: CGAAGACGACCCGAAAGCAGAC; Reverse: AGGCACGGCAGATGTAGGAGAG |
| Smyd3 | Forward: GATGCCAACATACGAGCCTCCTAAG; Reverse: TACAGAAGGTCCACACAGCAAACAC |
| Dock1 | Forward: CGAAGACGACCCGAAAGCAGAC; Reverse: AGGCACGGCAGATGTAGGAGAG |
| St6galnac3 | Forward: TTTATTCTGCTCTTCGTTGT; Reverse: TGCTCTGAGGATTCTCTGGT |
| miR-683 | Forward: TGCCCACTCTACCCATTGATTGC |
| Sec62 | Forward: GATGAGGAGGATGACGACAAAGATGG; Reverse: ATGACCGCCTTTCTCTGGATTGAAC |
| Klhdc8a | Forward: GGGCAGTTGTGTAGGAAGGAAGC; Reverse: AGGTCAGGAGAAGGTGGCAGAAG |
| Smurf1 | Forward: CGATGAGGAGAGGAGAGCCAGAC; Reverse: GCAGAGCCTTGAAGCCTTGGAG |
| PRP8 | Forward: CGAGTCTGGCTGTTCTTTATGC; Reverse: ATGTACGGACCGTCCTTTAAGTAG |
| GAPDH | Forward: TTCAACGGCACAGTCAAG; Reverse: CACCCCATTTGATGTTAGTG |
| U6 | Forward: CCTGCTTCGGCAGCACA |
| Score | Histologic Characteristic(s) |
|---|---|
| 1 | Only lost the tip of the villus. |
| 2 | 50% villus loss |
| 3 | The entire villus disappeared, but the crypts were preserved. |
| 4 | Completely lost the epithelium. |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Deng, Y.; Xu, X.; Meng, F.; Lou, J.; Liao, Y.; Li, Q.; Zhuang, M.; Sun, Y. PRP8-Induced CircMaml2 Facilitates the Healing of the Intestinal Mucosa via Recruiting PTBP1 and Regulating Sec62. Cells 2022, 11, 3460. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells11213460
Deng Y, Xu X, Meng F, Lou J, Liao Y, Li Q, Zhuang M, Sun Y. PRP8-Induced CircMaml2 Facilitates the Healing of the Intestinal Mucosa via Recruiting PTBP1 and Regulating Sec62. Cells. 2022; 11(21):3460. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells11213460
Chicago/Turabian StyleDeng, Yuequ, Xiaoqing Xu, Fanze Meng, Jiaqi Lou, Yu Liao, Qi Li, Mengmeng Zhuang, and Yong Sun. 2022. "PRP8-Induced CircMaml2 Facilitates the Healing of the Intestinal Mucosa via Recruiting PTBP1 and Regulating Sec62" Cells 11, no. 21: 3460. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells11213460
APA StyleDeng, Y., Xu, X., Meng, F., Lou, J., Liao, Y., Li, Q., Zhuang, M., & Sun, Y. (2022). PRP8-Induced CircMaml2 Facilitates the Healing of the Intestinal Mucosa via Recruiting PTBP1 and Regulating Sec62. Cells, 11(21), 3460. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells11213460





