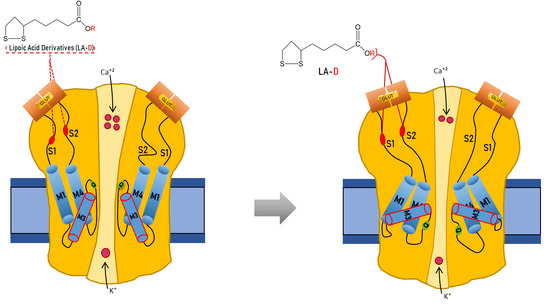
α-Lipoic Acid Derivatives as Allosteric Modulators for Targeting AMPA-Type Glutamate Receptors’ Gating Modules
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemistry
2.1.1. Purification
2.1.2. NMR Measurements
2.1.3. Assessment Nitric Oxide Release
2.1.4. Synthesis of α-Lipoic Acid Derivatives
2.2. Experimental Section
2.2.1. Characterization of Lipoic Acid
2.2.2. General Procedure Used for the Synthesis of Compounds LA1 and LA4
Synthesis of 1-Hydroxy-3-Lipo Ester (LA-PRO-OH) LA1
Synthesis of 1-Hydroxy-6-Lipoester (LA-HEX-OH) LA4
Synthesis of Compounds LA2 and LA3
2.3. Biological Activity
Whole-Cell Patch-Clamp Electrophysiology
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Modulation of Whole-Cell AMPA Receptor Currents by α-Lipoic Acid
3.2. α-LA Derivatives (LA1, LA2, LA3, and LA4) Reduced AMPA Receptor Activation While Enhancing the Deactivation of AMPA Receptor Subunits
3.3. Concentration-Dependent Inhibition of the Derivatives on AMPA-Type Receptors
3.4. α-LA and Its Derivatives Reduced AMPA Receptor Desensitization Rates (τw des)
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AMPA | α-amino-3-hydroxy-5-methyl-4-isoxazole propionic acid |
| α-LA | alpha-Lipoic acid |
| HEK293 | Human embryonic kidney 293 cells |
| AMPARs | α-amino-3-hydroxy-5-methyl-4-isoxazole propionic acid receptors |
| ATD | amino-terminal domain |
| LBD | ligand-binding domain |
| TMD | transmembrane domain |
| CTD | carboxyl-terminal domain |
| PAMs | positive allosteric modulators |
| NAMs | negative allosteric modulators |
| DCC | Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide |
| DCM | dichloromethane |
| NO | Nitric oxide |
| CC | column chromatography |
| FC | flash chromatography |
| LC-MS | liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry |
| DCU | Di cyclohexyl urea |
| CNS | central nervous system. |
References
- Collingridge, G.L.; Kehl, S.J.; McLennan, H. Excitatory amino acids in synaptic transmission in the Schaffer collateral-commissural pathway of the rat hippocampus. J. Physiol. 1983, 334, 33–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Traynelis, S.F.; Wollmuth, L.P.; McBain, C.J.; Menniti, F.S.; Vance, K.M.; Ogden, K.K.; Hansen, K.B.; Yuan, H.; Myers, S.J.; Dingledine, R. Glutamate receptor ion channels: Structure, regulation, and function. Pharmacol. Rev. 2010, 62, 405–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wenthold, R.J.; Petralia, R.S.; Niedzielski, A.S. Evidence for multiple AMPA receptor complexes in hippocampal CA1/CA2 neurons. J. Neurosci. 1996, 16, 1982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hansen, K.B.; Wollmuth, L.P.; Bowie, D.; Furukawa, H.; Menniti, F.S.; Sobolevsky, A.I.; Swanson, G.T.; Swanger, S.A.; Greger, I.H.; Nakagawa, T. Structure, Function, and Pharmacology of Glutamate Receptor Ion Channels. Pharmacol. Rev. 2021, 73, 298–487. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Y.; Chen, S.; Swensen, A.C.; Qian, W.-J.; Gouaux, E. Architecture and subunit arrangement of native AMPA receptors elucidated by cryo-EM. Science 2019, 364, 355–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bredt, D.S.; Nicoll, R.A. AMPA Receptor Trafficking at Excitatory Synapses. Neuron 2003, 40, 361–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greger, I.H.; Watson, J.F.; Cull-Candy, S.G. Structural and Functional Architecture of AMPA-Type Glutamate Receptors and Their Auxiliary Proteins. Neuron 2017, 94, 713–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sobolevsky, A.I.; Rosconi, M.P.; Gouaux, E. X-ray structure, symmetry and mechanism of an AMPA-subtype glutamate receptor. Nature 2009, 462, 745–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamalova, A.; Nakagawa, T. AMPA receptor structure and auxiliary subunits. J. Physiol. 2021, 599, 453–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charsouei, S.; Jabalameli, M.R.; Karimi-Moghadam, A. Molecular insights into the role of AMPA receptors in the synaptic plasticity, pathogenesis and treatment of epilepsy: Therapeutic potentials of perampanel and antisense oligonucleotide (ASO) technology. Acta Neurol. Belg. 2020, 120, 531–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robert, A.; Irizarry, S.N.; Hughes, T.; Howe, J.R. Subunit Interactions and AMPA Receptor Desensitization. J. Neurosci. 2001, 21, 5574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Eibl, C.; Weeks, A.M.; Riva, I.; Li, Y.-J.; Plested, A.J.; Howe, J.R. Unitary Properties of AMPA Receptors with Reduced Desensitization. Biophys. J. 2017, 113, 2218–2235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O Trussell, L.; Thio, L.L.; Zorumski, C.F.; Fischbach, G.D. Rapid desensitization of glutamate receptors in vertebrate central neurons. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1988, 85, 2834–2838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dürr, K.L.; Chen, L.; Stein, R.A.; De Zorzi, R.; Folea, I.M.; Walz, T.; Mchaourab, H.S.; Gouaux, E. Structure and dynamics of AMPA receptor GluA2 in resting, pre-open, and desensitized states. Cell 2014, 158, 778–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Impagnatiello, F.; Oberto, A.; Longone, P.; Costa, E.; Guidotti, A. 7-Chloro-3-methyl-3,4-dihydro-2H-1,2,4-benzothiadiazine S,S-dioxide: A partial modulator of AMPA receptor desensitization devoid of neurotoxicity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1997, 94, 7053–7058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olney, J.W. Excitatory transmitter neurotoxicity. Neurobiol. Aging 1994, 15, 259–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanacora, G.; Zarate, C.A.; Krystal, J.H.; Manji, H.K. Targeting the glutamatergic system to develop novel, improved therapeutics for mood disorders. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2008, 7, 426–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dingledine, R.; Borges, K.; Bowie, D.; Traynelis, S.F. The glutamate receptor ion channels. Pharmacol. Rev. 1999, 51, 7–61. [Google Scholar]
- Rogawski, M.A. AMPA receptors as a molecular target in epilepsy therapy. Acta Neurol. Scand. 2013, 127, 9–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaradat, N.; Hawash, M.; Qneibi, M.; Shtayeh, T.; Sobuh, S.; Arar, M.; Bdir, S. The effect of novel negative allosteric 2,3-benzodiazepine on glutamate AMPA receptor and their cytotoxicity. J. Mol. Struct. 2022, 1261, 132936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Etsè, K.S.; Dorosz, J.; Christensen, K.M.; Thomas, J.-Y.; Pop, I.B.; Goffin, E.; Colson, T.; Lestage, P.; Danober, L.; Pirotte, B. Development of Thiochroman Dioxide Analogues of Benzothiadiazine Dioxides as New Positive Allosteric Modulators of α-Amino-3-hydroxy-5-methyl-4-isoxazolepropionic Acid (AMPA) Receptors. ACS Chem. Neurosci. 2021, 12, 2679–2692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patsalos, P.N. The clinical pharmacology profile of the new antiepileptic drug perampanel: A novel noncompetitive AMPA receptor antagonist. Epilepsia 2015, 56, 12–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruel, J.; Guitton, M.J.; Puel, J.-L. Negative Allosteric Modulation of AMPA-preferring Receptors by the Selective Isomer GYKI 53784 (LY303070), a Specific Non-competitive AMPA Antagonist. CNS Drug Rev. 2002, 8, 235–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rugg-Gunn, F. Adverse effects and safety profile of perampanel: A review of pooled data. Epilepsia 2014, 55, 13–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szénási, G.; Hársing, L.G. Pharmacology and prospective therapeutic usefulness of negative allosteric modulators of AMPA receptors. Drug Discov. Today: Ther. Strateg. 2004, 1, 69–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobi, E.; von Engelhardt, J. AMPA receptor complex constituents: Control of receptor assembly, membrane trafficking and subcellular localization. Mol. Cell. Neurosci. 2018, 91, 67–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kato, A.S.; Gill, M.B.; Yu, H.; Nisenbaum, E.S.; Bredt, D.S. TARPs differentially decorate AMPA receptors to specify neuropharmacology. Trends Neurosci. 2010, 33, 241–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malińska, D.; Winiarska, K.; Metabolizmu, Z.R.J.P.H.M.D. Kwas liponowy–charakterystyka i zastosowanie w terapii* Lipoic acid: Characteristics and therapeutic application. Postepy Hig. Med. Dosw. 2005, 59, 535–543. [Google Scholar]
- He, M.; Wu, Y.; Hong, M.; Yun, Z.; Li, T.; Jiang, Y. α-Lipoic acid treatment alleviates postharvest pericarp browning of litchi fruit by regulating antioxidant ability and energy metabolism. Postharvest Biol. Technol. 2021, 180, 111629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seifar, F.; Khalili, M.; Khaledyan, H.; Moghadam, S.A.; Izadi, A.; Azimi, A.; Shakouri, S.K. α-Lipoic acid, functional fatty acid, as a novel therapeutic alternative for central nervous system diseases: A review. Nutr. Neurosci. 2019, 22, 306–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.; Karunakaran, U.; Jeoung, N.H.; Jeon, J.-H.; Lee, I.-K. Physiological effect and therapeutic application of alpha lipoic acid. Curr. Med. Chem. 2014, 21, 3636–3645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, U.; Jialal, I. Retracted: Alpha-lipoic acid supplementation and diabetes. Nutr. Rev. 2008, 66, 646–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lodge, J.K.; Packer, L. 9—Natural Sources of Lipoic Acid in Plant and Animal Tissues. In Antioxidant Food Supplements in Human Health; Packer, L., Hiramatsu, M., Yoshikawa, T., Eds.; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 1999; pp. 121–134. [Google Scholar]
- Rochette, L.; Ghibu, S.; Richard, C.; Zeller, M.; Cottin, Y.; Vergely, C. Direct and indirect antioxidant properties of α-lipoic acid and therapeutic potential. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2013, 57, 114–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leu, J.-G.; Lin, C.-Y.; Jian, J.-H.; Shih, C.-Y.; Liang, Y.-J. Epigallocatechin-3-gallate combined with alpha lipoic acid attenuates high glucose-induced receptor for advanced glycation end products (RAGE) expression in human embryonic kidney cells. An. Acad Bras. Cienc. 2013, 85, 745–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sabharwal, A.K.; May, J.M. Alpha-Lipoic acid and ascorbate prevent LDL oxidation and oxidant stress in endothelial cells. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 2008, 309, 125–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schreibelt, G.; Musters, R.J.P.; Reijerkerk, A.; de Groot, L.R.; van der Pol, S.M.A.; Hendrikx, E.M.L.; Döpp, E.D.; Dijkstra, C.D.; Drukarch, B.; de Vries, H.E. Lipoic Acid Affects Cellular Migration into the Central Nervous System and Stabilizes Blood-Brain Barrier Integrity. J. Immunol. 2006, 177, 2630–2637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qneibi, M.; Hamed, O.; Natsheh, A.R.; Fares, O.; Jaradat, N.; Emwas, N.; Al-Kerm, R. Inhibition and assessment of the biophysical gating properties of GluA2 and GluA2/A3 AMPA receptors using curcumin derivatives. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0221132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qneibi, M.; Hamed, O.; Fares, O.; Jaradat, N.; Natsheh, A.-R.; AbuHasan, Q.; Emwas, N.; Al-Kerm, R.; Al-Kerm, R. The inhibitory role of curcumin derivatives on AMPA receptor subunits and their effect on the gating biophysical properties. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2019, 136, 104951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qneibi, M.; Jaradat, N.; Hawash, M.; Olgac, A.; Emwas, N. Ortho versus Meta Chlorophenyl-2,3-Benzodiazepine Analogues: Synthesis, Molecular Modeling, and Biological Activity as AMPAR Antagonists. ACS Omega 2020, 5, 3588–3595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qneibi, M.; Hamed, O.; Jaradat, N.; Hawash, M.; Al-Kerm, R.; Al-Kerm, R.; Sobuh, S.; Tarazi, S. The AMPA receptor biophysical gating properties and binding site: Focus on novel curcumin-based diazepines as non-competitive antagonists. Bioorganic Chem. 2021, 116, 105406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narangoda, C.; Sakipov, S.N.; Kurnikova, M.G. AMPA Receptor Noncompetitive Inhibitors Occupy a Promiscuous Binding Site. ACS Chem. Neurosci. 2019, 10, 4511–4521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]







Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Qneibi, M.; Nassar, S.; Bdir, S.; Hidmi, A. α-Lipoic Acid Derivatives as Allosteric Modulators for Targeting AMPA-Type Glutamate Receptors’ Gating Modules. Cells 2022, 11, 3608. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells11223608
Qneibi M, Nassar S, Bdir S, Hidmi A. α-Lipoic Acid Derivatives as Allosteric Modulators for Targeting AMPA-Type Glutamate Receptors’ Gating Modules. Cells. 2022; 11(22):3608. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells11223608
Chicago/Turabian StyleQneibi, Mohammad, Safa’ Nassar, Sosana Bdir, and Adel Hidmi. 2022. "α-Lipoic Acid Derivatives as Allosteric Modulators for Targeting AMPA-Type Glutamate Receptors’ Gating Modules" Cells 11, no. 22: 3608. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells11223608
APA StyleQneibi, M., Nassar, S., Bdir, S., & Hidmi, A. (2022). α-Lipoic Acid Derivatives as Allosteric Modulators for Targeting AMPA-Type Glutamate Receptors’ Gating Modules. Cells, 11(22), 3608. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells11223608