A New Gal in Town: A Systematic Review of the Role of Galanin and Its Receptors in Experimental Pain
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design
2.2. Search Strategies
2.3. Eligibility Criteria
2.4. Study Selection
2.5. Data Extraction, Management, and Synthesis
2.6. Quality Assessment
3. Results
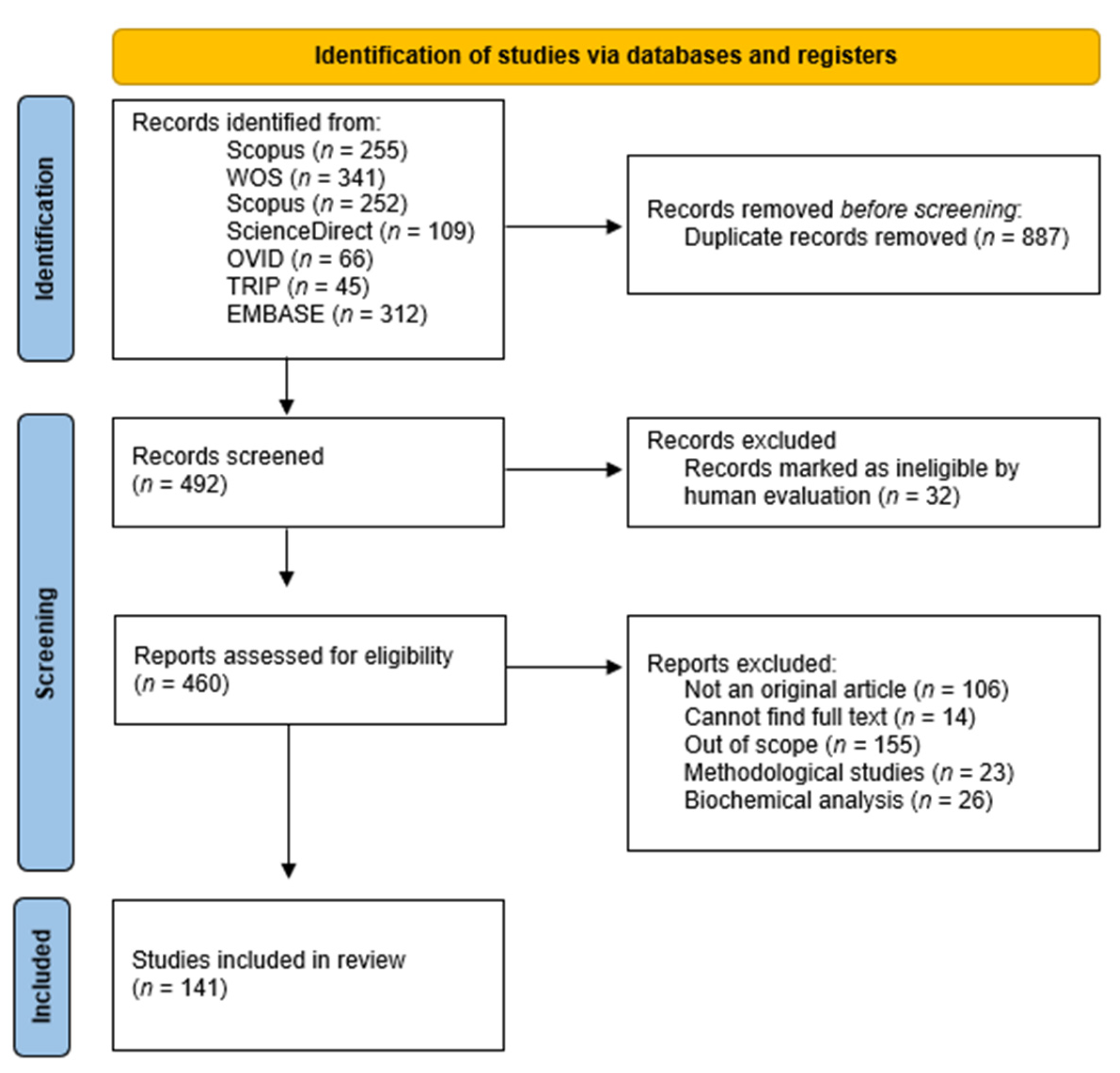
3.1. Search Results
3.2. Characteristics of the Included Studies
3.3. Assessment of Quality
4. The Role of Galanin in Pain Processing at the Spinal and Supraspinal Levels
5. Galanin Expression and Modulation in Chronic Pain Models
5.1. Endogenous Galanin
5.2. Primary Sensory Neurons and Dorsal Root Ganglia (DRG)
5.3. Spinal Dorsal Horn (SDH)
5.4. Supraspinal Galanin
6. Receptor Mechanisms Underlying the Varying Roles of Galanin
7. Other Mechanisms
8. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Treede, R.D.; Rief, W.; Barke, A.; Aziz, Q.; Bennett, M.I.; Benoliel, R.; Cohen, M.; Evers, S.; Finnerup, N.B.; First, M.B.; et al. A classification of chronic pain for ICD-11. Pain 2015, 156, 1003–1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Goldberg, D.S.; McGee, S.J. Pain as a global public health priority. BMC Public Health 2011, 11, 770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Breivik, H.; Collett, B.; Ventafridda, V.; Cohen, R.; Gallacher, D. Survey of chronic pain in Europe: Prevalence, impact on daily life, and treatment. Eur. J. Pain 2006, 10, 287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woolf, C.J. Central sensitization: Implications for the diagnosis and treatment of pain. Pain 2011, 152, 1–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bykov, Y.; Wagner, S.; Walter, O.; Döring, M.; Fischer, O.; Pospiech, D.; Köppl, T.; Altstädt, V. Synthesis of new DOPO conatining DIols based on diethanolamine. Heteroat. Chem. 2011, 6, 2873–2877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tatemoto, K.; Rökaeus, Å.; Jörnvall, H.; McDonald, T.J.; Mutt, V. Galanin—A novel biologically active peptide from porcine intestine. FEBS Lett. 1983, 164, 124–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Crawley, J.N. Galanin impairs cognitive abilities in rodents: Relevance to Alzheimer’s disease. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2008, 65, 1836–1841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Barson, J.R.; Morganstern, I.; Leibowitz, S.F. Galanin and consummatory behavior: Special relationship with dietary fat, alcohol and circulating lipids. EXS 2010, 102, 87–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, X.J.; Hökfelt, T.; Wiesenfeld-Hallin, Z. Galanin and spinal pain mechanisms: Where do we stand in 2008? Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2008, 65, 1813–1819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Ju, G.; Elde, R.; Hökfelt, T. Effect of peripheral nerve cut on neuropeptides in dorsal root ganglia and the spinal cord of monkey with special reference to galanin. J. Neurocytol. 1993, 22, 342–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melander, T.; Hökfelt, T.; Rökaeus, A. Distribution of galaninlike immunoreactivity in the rat central nervous system. J. Comp. Neurol. 1986, 248, 475–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skofitsch, G.; Jacobowitz, D.M. Galanin-like immunoreactivity in capsaicin sensitive sensory neurons and ganglia. Brain Res. Bull. 1985, 15, 191–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ch’ng, J.L.C.; Christofides, N.D.; Anand, P.; Gibson, S.J.; Allen, Y.S.; Su, H.C.; Tatemoto, K.; Morrison, J.F.B.; Polak, J.M.; Bloom, S.R. Distribution of galanin immunoreactivity in the central nervous system and the responses of galanin-containing neuronal pathways to injury. Neuroscience 1985, 16, 343–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, C.L.; Pasricha, P.J.; Hsieh, J.C.; Lu, R.H.; Lai, C.R.; Wu, L.L.; Chang, F.Y.; Lee, S.D. Changes of the neuropeptides content and gene expression in spinal cord and dorsal root ganglion after noxious colorectal distension. Regul. Pept. 2005, 131, 66–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Z.Q.; Shi, T.J.; Landry, M.; Hökfelt, T. Evidence for galanin receptors in primary sensory neurones and effect of axotomy and inflammation. Neuroreport 1997, 8, 237–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Yang, X.; Zhang, P.; Chen, X.; Liu, H.; Li, Z. Effects of exogenous galanin on neuropathic pain state and change of galanin and its receptors in DRG and SDH after sciatic nerve-pinch injury in rat. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e0037621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Moher, D.; Liberati, A.; Tetzlaff, J.; Altman, D.G. Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: The PRISMA statement. J. Clin. Epidemiol. 2009, 62, 1006–1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.J.; Farkas-Szallasi, T.; Lundberg, J.M.; Hökfelt, T.; Wiesenfeld-Hallin, Z.; Szallasi, A. Effects of the capsaicin analogue resiniferatoxin on spinal nociceptive mechanisms in the rat: Behavioral, electrophysiological and in situ hybridization studies. Brain Res. 1997, 752, 52–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blakeman, K.H.; Holmberg, K.; Hao, J.X.; Xu, X.J.; Kahl, U.; Lendahl, U.; Bartfai, T.; Wiesenfeld-Hallin, Z.; Hökfelt, T. Mice over-expressing galanin have elevated heat nociceptive threshold. Neuroreport 2001, 12, 423–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grass, S.; Crawley, J.N.; Xu, X.J.; Wiesenfeld-Hallin, Z. Reduced spinal cord sensitization to C-fibre stimulation in mice over-expressing galanin. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2003, 17, 1829–1832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alier, K.A.; Chen, Y.; Sollenberg, U.E.; Langel, Ü.; Smith, P.A. Selective stimulation of GalR1 and GalR2 in rat substantia gelatinosa reveals a cellular basis for the anti- and pro-nociceptive actions of galanin. Pain 2008, 137, 138–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yue, H.Y.; Fujita, T.; Kumamoto, E. Biphasic modulation by galanin of excitatory synaptic transmission in substantia gelatinosa neurons of adult rat spinal cord slices. J. Neurophysiol. 2011, 105, 2337–2349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Taylor, T.S.; Konda, P.; John, S.S.; Bulmer, D.C.; Hockley, J.R.F.; Smith, E.S.J. Galanin suppresses visceral afferent responses to noxious mechanical and inflammatory stimuli. Physiol. Rep. 2020, 8, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rezaei, K.; Xu, I.S.; Wu, W.P.; Shi, T.J.; Soomets, U.; Land, T.; Xu, X.J.; Wiesenfeld-Hallin, Z.; Hökfelt, T.; Bartfai, T.; et al. Intrathecal administration of PNA targeting galanin receptor reduces galanin-mediated inhibitory effect in the rat spinal cord. Neuroreport 2001, 12, 317–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Zhang, J.J.; Xu, S.L.; Yu, L.C. Antinociceptive effects induced by injection of the galanin receptor 1 agonist M617 into central nucleus of amygdala in rats. Neurosci. Lett. 2012, 526, 45–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, L.B.; Wang, Y.; Sun, X.X.; Liu, X.X.; Wang, Y.; Zhuang, W. Antinociceptive effects induced by intra-lateral habenula complex injection of the galanin receptor 1 agonist M617 in rats. Exp. Brain Res. 2016, 234, 493–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemons, L.L.; Wiley, R.G. Galanin receptor-expressing dorsal horn neurons: Role in nociception. Neuropeptides 2011, 45, 377–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hobson, S.A.; Holmes, F.E.; Kerr, N.C.H.; Pope, R.J.P.; Wynick, D. Mice deficient for galanin receptor 2 have decreased neurite outgrowth from adult sensory neurons and impaired pain-like behaviour. J. Neurochem. 2006, 99, 1000–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hua, X.Y.; Hayes, C.S.; Hofer, A.; Fitzsimmons, B.; Kilk, K.; Langel, Ü.; Bartfai, T.; Yaksh, T.L. Galanin Acts at GalR1 Receptors in Spinal Antinociception: Synergy with Morphine and AP-5. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2004, 308, 574–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wiesenfeld-Hallin, Z.; Xu, X.J.; Villar, M.J.; Hökfelt, T. Intrathecal galanin potentiates the spinal analgesic effect of morphine: Electrophysiological and behavioural studies. Neurosci. Lett. 1990, 109, 217–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reimann, W.; Englberger, W.; Friderichs, E.; Selve, N.; Wilffert, B. Spinal antinociception by morphine in rats is antagonised by galanin receptor antagonists. Naunyn-Schmiedebergs Arch. Pharmacol. 1994, 350, 380–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, D.; Ye, H.H.; Yu, L.C.; Lundeberg, T. Intra-periaqueductal grey injection of galanin increases the nociceptive response latency in rats, an effect reversed by naloxone. Brain Res. 1999, 834, 152–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zubrzycka, M.; Janecka, A. Interactions of galanin with endomorphin-2, vasopressin and oxytocin in nociceptive modulation of the trigemino-hypoglossal reflex in rats. Physiol. Res. 2008, 57, 769–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, W.Y.; Liu, Z.; Liu, D.; Yu, L.C. Antinociceptive effects of galanin in the central nucleus of amygdala of rats, an involvement of opioid receptors. Brain Res. 2010, 1320, 16–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hulse, R.P. Identification of mechano-sensitive C fibre sensitization and contribution to nerve injury-induced mechanical hyperalgesia. Eur. J. Pain 2016, 20, 615–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Post, C.; Alari, L.; Hokfelt, T. Intrathecal galanin increases the latency in the tail-flick and hot-plate tests in mouse. Acta Physiol. Scand. 1988, 132, 583–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuraishi, Y.; Kawabata, S.; Matsumoto, T.; Nakamura, A.; Fujita, H.; Satoh, M. Involvement of substance P in hyperalgesia induced by intrathecal galanin. Neurosci. Res. 1991, 11, 276–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiesenfeld-Hallin, Z.; Xu, X.-J.; Hao, J.-X.; Hokfelt, T. The behavioural effects of intrathecal galanin on tests of thermal and mechanical nociception in the rat. Acta Physiol. Scand. 1993, 147, 457–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.J.; Wiesenfeld-Hallin, Z.; Hökfelt, T. Intrathecal galanin blocks the prolonged increase in spinal cord flexor reflex excitability induced by conditioning stimulation of unmyelinated muscle afferents in the rat. Brain Res. 1991, 541, 350–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, I.S.; Grass, S.; Xu, X.J.; Wiesenfeld-Hallin, Z. On the role of galanin in mediating spinal flexor reflex excitability in inflammation. Neuroscience 1998, 85, 827–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grass, S.; Jacoby, A.S.; Iismaa, T.P.; Crawley, J.N.; Xu, X.J.; Wiesenfeld-Hallin, Z. Flexor reflex excitability in mice lacking galanin receptor galanin-R1. Neurosci. Lett. 2003, 345, 153–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Przewłocka, B.; Machelska, H.; Rekowski, P.; Kupryszewski, G.; Przewłocki, R. Intracerebroventricular galanin and N-terminal galanin fragment enhance the morphine-induced analgesia in the rat. J. Neural Transm. 1995, 102, 229–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, X.; Yu, L.C. Alternation of galanin in nociceptive modulation in the central nervous system of rats during morphine tolerance: A behavioral and immunohistochemical study. Brain Res. 2006, 1086, 85–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, L.B.; Wang, X.B.; Jiao, S.; Wu, X.; Yu, L.C. Antinociceptive effects of intracerebroventricular injection of the galanin receptor 1 agonist M 617 in rats. Neurosci. Lett. 2011, 491, 174–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, J.; Fu, L.B.; Yu, L.C. Involvement of protein kinase C in the galanin-induced antinociception in the brain of rats. Neurosci. Lett. 2011, 497, 60–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zubrzycka, M.; Janecka, A. Effect of galanin on substance P- and vasoactive intestinal polypeptide-induced nociceptive trigemino-hypoglossal reflex in rats. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 2007, 58, 479–486. [Google Scholar]
- Kong, Q.; Yu, L.C. Antinociceptive effects induced by intra-periaqueductal grey injection of the galanin receptor 1 agonist M617 in rats with morphine tolerance. Neurosci. Lett. 2013, 550, 125–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.Y.; Zhang, Y.M.; Zhang, M.L.; Yu, L.C. Involvement of galanin receptor 2 and CaMKII in galanin-induced antinociception in periaqueductal grey of rats. Neurosci. Lett. 2015, 604, 124–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.G.; Yu, L.C. Interactions of galanin and opioids in nociceptive modulation in the arcuate nucleus of hypothalamus in rats. Regul. Pept. 2005, 124, 37–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.G.; Gu, X.L.; Yu, L.C. The neural pathway of galanin in the hypothalamic arcuate nucleus of rats: Activation of beta-endorphinergic neurons projecting to periaqueductal gray matter. J. Neurosci. Res. 2007, 85, 2400–2406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.D.; Barde, S.; Yang, T.; Lei, B.; Eriksson, L.I.; Mathew, J.P.; Andreska, T.; Akassoglou, K.; Harkany, T.; Hökfelt, T.G.M.; et al. Orthopedic surgery modulates neuropeptides and BDNF expression at the spinal and hippocampal levels. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, E6686–E6695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Holmes, F.E.; Kerr, N.; Chen, Y.J.; Vanderplank, P.; McArdle, C.A.; Wynick, D. Targeted disruption of the orphan receptor Gpr151 does not alter pain-related behaviour despite a strong induction in dorsal root ganglion expression in a model of neuropathic pain. Mol. Cell. Neurosci. 2017, 78, 35–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rydh-Rinder, M.; Holmberg, K.; Elfvin, L.G.; Wiesenfeld-Hallin, Z.; Hökfelt, T. Effects of peripheral axotomy on neuropeptides and nitric oxide synthase in dorsal root ganglia and spinal cord of the guinea pig: An immunohistochemical study. Brain Res. 1996, 707, 180–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, R.R.; Zhang, Q.; Pettersson, R.F.; Hökfelt, T. aFGF, bFGF and NGF differentially regulate neuropeptide expression in dorsal root ganglia after axotomy and induce autotomy. Regul. Pept. 1996, 66, 179–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corness, J.; Shi, T.J.; Xu, Z.Q.; Brulet, P.; Hökfelt, T. Influence of leukemia inhibitory factor on galanin/GMAP and neuropeptide Y expression in mouse primary sensory neurons after axotomy. Exp. Brain Res. 1996, 112, 79–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, W.; Bisby, M.A. Differential expression of galanin immunoreactivities in the primary sensory neurons following partial and complete sciatic nerve injuries. Neuroscience 1997, 79, 1183–1195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, T.J.; Zhang, X.; Berge, O.G.; Erickson, J.C.; Palmiter, R.D.; Hökfelt, T. Effect of peripheral axotomy on dorsal root ganglion neuron phenotype and autotomy behaviour in neuropeptide Y-deficient mice. Regul. Pept. 1998, 75–76, 161–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukuoka, T.; Tokunaga, A.; Kondo, E.; Miki, K.; Tachibana, T.; Noguchi, K. Change in mRNAs for neuropeptides and the GABA(A) receptor in dorsal root ganglion neurons in a rat experimental neuropathic pain model. Pain 1998, 78, 13–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macdonald, R.; Bingham, S.; Bond, B.C.; Parsons, A.A.; Philpott, K.L. Determination of changes in mRNA expression in a rat model of neuropathic pain by TaqmanTM quantitative RT-PCR. Mol. Brain Res. 2001, 90, 48–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.H.; Lu, Y.J.; Bao, L.; Zhang, X. Peripheral nerve injury induces reorganization of galanin-containing afferents in the superficial dorsal horn of monkey spinal cord. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2007, 25, 1087–1096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nahin, R.L.; Ren, K.; De León, M.; Ruda, M. Primary sensory neurons exhibit altered gene expression in a rat model of neuropathic pain. Pain 1994, 58, 95–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson-Gerwing, T.D.; Verge, V.M.K. Neurotrophin-3 attenuates galanin expression in the chronic constriction injury model of neuropathic pain. Neuroscience 2006, 141, 2075–2085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reinhold, A.K.; Batti, L.; Bilbao, D.; Buness, A.; Rittner, H.L.; Heppenstall, P.A. Differential transcriptional profiling of damaged and intact adjacent dorsal root ganglia neurons in neuropathic pain differential transcriptional profiling of damaged and intact adjacent dorsal root ganglia neurons in neuropathic pain. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0123342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barajon, I.; Bersani, M.; Quartu, M.; Del Fiacco, M.; Cavaletti, G.; Holst, J.J.; Tredici, G. Neuropeptides and morphological changes in cisplatin-induced dorsal root ganglion neuronopathy. Exp. Neurol. 1996, 138, 93–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coronel, M.F.; Brumovsky, P.R.; Hökfelt, T.; Villar, M.J. Differential galanin upregulation in dorsal root ganglia and spinal cord after graded single ligature nerve constriction of the rat sciatic nerve. J. Chem. Neuroanat. 2008, 35, 94–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coronel, M.F.; Musolino, P.L.; Brumovsky, P.R.; Hökfelt, T.; Villar, M.J. Bone marrow stromal cells attenuate injury-induced changes in galanin, NPY and NPY Y1-receptor expression after a sciatic nerve constriction. Neuropeptides 2009, 43, 125–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.P.; Fu, E.S.; Sagen, J.; Levitt, R.C.; Candiotti, K.A.; Bethea, J.R.; Brambilla, R. Glial NF-kappa B inhibition alters neuropeptide expression after sciatic nerve injury in mice. Brain Res. 2011, 1385, 38–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Long, A.; Bongenhielm, U.; Boissonade, F.M.; Fried, K.; Robinson, P.P. Neuropeptide immunereactivity in ligature-induced neuromas of the inferior alveolar nerve in the ferret. Brain Res. 1998, 791, 263–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bird, E.V.; Long, A.; Boissonade, F.M.; Fried, K.; Robinson, P.P. Neuropeptide expression following constriction or section of the inferior alveolar nerve in the ferret. J. Peripher. Nerv. Syst. 2002, 7, 168–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Yajima, T.; Wang, M.; Shen, J.F.; Ichikawa, H.; Sato, T. Effects of trigeminal nerve injury on the expression of galanin and its receptors in the rat trigeminal ganglion. Neuropeptides 2020, 84, 102098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sten Shi, T.J.; Cui, J.G.; Meyerson, B.A.; Linderoth, B.; Hökfelt, T. Regulation of galanin and neuropeptide Y in dorsal root ganglia and dorsal horn in rat mononeuropathic models: Possible relation to tactile hypersensitivity. Neuroscience 1999, 93, 741–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Guo, W.; Ossipov, M.H.; Vanderah, T.W.; Porreca, F.; Lai, J. Glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor normalizes neurochemical changes in injured dorsal root ganglion neurons and prevents the expression of experimental neuropathic pain. Neuroscience 2003, 121, 815–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peters, C.M.; Ghilardi, J.R.; Keyser, C.P.; Kubota, K.; Lindsay, T.H.; Luger, N.M.; Mach, D.B.; Schwei, M.J.; Sevcik, M.A.; Mantyh, P.W. Tumor-induced injury of primary afferent sensory nerve fibers in bone cancer pain. Exp. Neurol. 2005, 193, 85–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garry, E.M.; Delaney, A.; Anderson, H.A.; Sirinathsinghji, E.C.; Clapp, R.H.; Martin, W.J.; Kinchington, P.R.; Krah, D.L.; Abbadie, C.; Fleetwood-Walker, S.M. Varicella zoster virus induces neuropathic changes in rat dorsal root ganglia and behavioral reflex sensitisation that is attenuated by gabapentin or sodium channel blocking drugs. Pain 2005, 118, 97–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hulse, R.; Wynick, D.; Donaldson, L.F. Characterization of a novel neuropathic pain model in mice. Neuroreport 2008, 19, 825–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.F.; Zhang, D.D.; Liao, J.C.; Xiao, L.; Wang, Q.; Qiu, W. Galanin and its receptor system promote the repair of injured sciatic nerves in diabetic rats. Neural Regen. Res. 2016, 11, 1517–1526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boateng, E.K.; Novejarque, A.; Pheby, T.; Rice, A.S.C.; Huang, W. Heterogeneous responses of dorsal root ganglion neurons in neuropathies induced by peripheral nerve trauma and the antiretroviral drug stavudine. Eur. J. Pain 2015, 19, 236–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chen, S.H.; Lue, J.H.; Hsiao, Y.J.; Lai, S.M.; Wang, H.Y.; Lin, C.T.; Chen, Y.C.; Tsai, Y.J. Elevated galanin receptor type 2 primarily contributes to mechanical hypersensitivity after median nerve injury. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0199512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calzà, L.; Pozza, M.; Arletti, R.; Manzini, E.; Hökfelt, T. Long-lasting regulation of galanin, opioid, and other peptides in dorsal root ganglia and spinal cord during experimental polyarthritis. Exp. Neurol. 2000, 164, 333–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, J.; Gao, T.; Shi, T.; Xiang, Q.; Xu, X.; Wiesenfeld-Hallin, Z.; Hökfelt, T.; Svensson, C.I. Phenotypic changes in dorsal root ganglion and spinal cord in the collagen antibody-induced arthritis mouse model. J. Comp. Neurol. 2015, 523, 1505–1528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hope, P.J.; Lang, C.W.; Grubb, B.D.; Duggan, A.W. Release of immunoreactive galanin in the spinal cord of rats with ankle inflammation: Studies with antibody microprobes. Neuroscience 1994, 60, 801–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.X.; Brumovsky, P.; Schmidt, R.; Brown, W.; Payza, K.; Hodzic, L.; Pou, C.; Godbout, C.; Hökfelt, T. Receptor subtype-specific pronociceptive and analgesic actions of galanin in the spinal cord: Selective actions via Galr1 and Galr2 receptors. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2001, 98, 9960–9964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Carlton, S.M.; Coggeshall, R.E. Stereological analysis of galanin and CGRP synapses in the dorsal horn of neuropathic primates. Brain Res. 1996, 711, 16–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colvin, L.A.; Duggan, A.W. Primary afferent-evoked release of immunoreactive galanin in the spinal cord of the neuropathic rat. Br. J. Anaesth. 1998, 81, 436–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, W.; Bisby, M.A. Ultrastructural localization of increased neuropeptide immunoreactivity in the axons and cells of the gracile nucleus following chronic constriction injury of the sciatic nerve. Neuroscience 1999, 93, 335–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coronel, M.F.; Villar, M.J.; Brumovsky, P.R.; González, S.L. Spinal neuropeptide expression and neuropathic behavior in the acute and chronic phases after spinal cord injury: Effects of progesterone administration. Peptides 2017, 88, 189–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munglani, R.; Harrison, S.M.; Smith, G.D.; Bountra, C.; Birch, P.J.; Elliot, P.J.; Hunt, S.P. Neuropeptide changes persist in spinal cord despite resolving hyperalgesia in a rat model of mononeuropathy. Brain Res. 1996, 743, 102–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calzà, L.; Pozza, M.; Zanni, M.; Manzini, C.U.; Manzini, E.; Hökfelt, T. Peptide plasticity in primary sensory neurons and spinal cord during adjuvant-induced arthritis in the rat: An immunocytochemical and in situ hybridization study. Neuroscience 1997, 82, 575–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imbe, H.; Abe, T.; Okamoto, K.; Sato, M.; Ito, H.; Kumabe, S.; Senba, E. Increase of galanin-like immunoreactivity in rat hypothalamic arcuate neurons after peripheral nerve injury. Neurosci. Lett. 2004, 368, 102–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishii, H.; Nomura, M.; Aono, H.; Fujimoto, N.; Matsumoto, T. Up-regulation of galanin and corticotropin-releasing hormone mRNAs in the key hypothalamic and amygdaloid nuclei in a mouse model of visceral pain. Regul. Pept. 2007, 141, 105–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amorim, D.; David-Pereira, A.; Marques, P.; Puga, S.; Rebelo, P.; Costa, P.; Pertovaara, A.; Almeida, A.; Pinto-Ribeiro, F. A role of supraspinal galanin in behavioural hyperalgesia in the rat. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e113077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Gao, Y.; Li, C.Y.; Dong, W.; Li, M.N.; Liu, Y.N.; Dong, Y.; Xu, S.L. Galanin plays a role in antinociception via binding to galanin receptors in the nucleus accumbens of rats with neuropathic pain. Neurosci. Lett. 2019, 706, 93–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernandez-Zafra, T.; Gao, T.; Jurczak, A.; Sandor, K.; Hore, Z.; Agalave, N.M.; Su, J.; Estelius, J.; Lampa, J.; Hokfelt, T.; et al. Exploring the transcriptome of resident spinal microglia after collagen antibody-induced arthritis. Pain 2019, 160, 224–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pope, R.J.P.; Holmes, F.E.; Kerr, N.C.; Wynick, D. Characterisation of the nociceptive phenotype of suppressible galanin over-expressing transgenic mice. Mol. Pain 2010, 6, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hygge-Blakeman, K.; Brumovsky, P.; Hao, J.X.; Xu, X.J.; Hökfelt, T.; Crawley, J.N.; Wiesenfeld-Hallin, Z. Galanin over-expression decreases the development of neuropathic pain-like behaviors in mice after partial sciatic nerve injury. Brain Res. 2004, 1025, 152–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holmberg, K.; Kuteeva, E.; Brumovsky, P.; Kahl, U.; Karlström, H.; Lucas, G.A.; Rodriguez, J.; Westerblad, H.; Hilke, S.; Theodorsson, E.; et al. Generation and phenotypic characterization of a galanin over-expressing mouse. Neuroscience 2005, 133, 59–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wiesenfeld-Hallin, Z.; Xu, X.J.; Villar, M.J.; Hökfelt, T. The effect of intrathecal galanin on the flexor reflex in rat: Increased depression after sciatic nerve section. Neurosci. Lett. 1989, 105, 149–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satoh, M.; Kuraishi, Y.; Kawamura, M. Effects of intrathecal antibodies to substance P, calcitonin gene-related peptide and galanin on repeated cold stress-induced hyperalgesia: Comparison with carrageenan-induced hyperalgesia. Pain 1992, 49, 273–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiesenfeld-Hallin, Z.; Xu, X.J.; Langel, U.; Bedecs, K.; Hokfelt, T.; Bartfai, T. Galanin-mediated control of pain: Enhanced role after nerve injury. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1992, 89, 3334–3337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Verge, V.M.K.; Xu, X.J.; Langel, Ü.; Hökfelt, T.; Wiesenfeld-Hallin, Z.; Bartfai, T. Evidence for endogenous inhibition of autotomy by galanin in the rat after sciatic nerve section: Demonstrated by chronic intrathecal infusion of a high affinity galanin receptor antagonist. Neurosci. Lett. 1993, 149, 193–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hulse, R.P.; Donaldson, L.F.; Wynick, D. Differential roles of galanin on mechanical and cooling responses at the primary afferent nociceptor. Mol. Pain 2012, 8, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jimenez-Andrade, J.M.; Zhou, S.; Du, J.; Yamani, A.; Grady, J.J.; Castañeda-Hernandez, G.; Carlton, S.M. Pro-nociceptive role of peripheral galanin in inflammatory pain. Pain 2004, 110, 10–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jimenez-Andrade, J.M.; Zhou, S.; Yamani, A.; Valencia De Ita, S.; Castañeda-Hernandez, G.; Carlton, S.M. Mechanism by which peripheral galanin increases acute inflammatory pain. Brain Res. 2005, 1056, 113–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jimenez-Andrade, J.M.; Lundström, L.; Sollenberg, U.E.; Langel, Ü.; Castañeda-Hernandez, G.; Carlton, S.M. Activation of peripheral galanin receptors: Differential effects on nociception. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 2006, 85, 273–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lundeberg, T.; Meister, B.; Björkstrand, E.; Uvnäs-Moberg, K. Oxytocin modulates the effects of galanin in carrageenan-induced hyperalgesia in rats. Brain Res. 1993, 608, 181–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, L.; Wiesenfeld-Hallin, Z. The effects of pretreatment with tachykinin antagonists and galanin on the development of spinal cord hyperexcitability following sciatic nerve section in the rat. Neuropeptides 1995, 28, 161–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerr, B.J.; Cafferty, W.B.J.; Gupta, Y.K.; Bacon, A.; Wynick, D.; McMahon, S.B.; Thompson, S.W.N. Galanin knockout mice reveal nociceptive deficits following peripheral nerve injury. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2000, 12, 793–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hao, J.X. Intrathecal galanin alleviates allodynia-like behaviour in rats after partial peripheral nerve injury. Eur. J. Neurosci. 1999, 11, 427–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.X.; Hökfelt, T. Effect of intrathecal galanin and its putative antagonist M35 on pain behavior in a neuropathic pain model. Brain Res. 2000, 886, 67–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, S.L.; Zhang, Y.P.; Lundeberg, T.; Yu, L.C. Effects of galanin on wide-dynamic range neuron activity in the spinal dorsal horn of rats with sciatic nerve ligation. Regul. Pept. 2000, 95, 19–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, P.; McLachlan, E.M. Long-term changes in the distribution of galanin in dorsal root ganglia after sciatic or spinal nerve transection in rats. Neuroscience 2001, 103, 1059–1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flatters, S.J.L.; Fox, A.J.; Dickenson, A.H. Nerve injury induces plasticity that results in spinal inhibitory effects of galanin. Pain 2002, 98, 249–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flatters, S.J.L.; Fox, A.J.; Dickenson, A.H. In vivo and in vitro effects of peripheral galanin on nociceptive transmission in naive and neuropathic states. Neuroscience 2003, 116, 1005–1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, W.; Gao, L.; Sapra, A.; Yu, L.C. Antinociceptive role of galanin in the spinal cord of rats with inflammation, an involvement of opioid systems. Regul. Pept. 2005, 132, 85–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, S.J.; Chang, J.W.; Won, R.; Cha, M.H.; Nam, T.S.; Lee, H.J.; Lee, B.H. Modulation of neuropathic pain by galanin and neuropeptide y at the level of the medulla in rats. Int. J. Neurosci. 2009, 119, 1941–1955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, X.; Liu, Z.; Liu, H.; Yang, X.; Li, Z. The effects of galanin on neuropathic pain in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2012, 680, 28–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hulse, R.P.; Wynick, D.; Donaldson, L.F. Activation of the galanin receptor 2 in the periphery reverses nerve injury-induced allodynia. Mol. Pain 2011, 7, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sten Shi, T.J.; Zhang, X.; Holmberg, K.; Xu, Z.Q.D.; Hökfelt, T. Expression and regulation of galanin-R2 receptors in rat primary sensory neurons: Effect of axotomy and inflammation. Neurosci. Lett. 1997, 237, 57–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Botz, B.; Kemény, Á.; Brunner, S.M.; Locker, F.; Csepregi, J.; Mócsai, A.; Pintér, E.; McDougall, J.J.; Kofler, B.; Helyes, Z. Lack of Galanin 3 Receptor Aggravates Murine Autoimmune Arthritis. J. Mol. Neurosci. 2016, 59, 260–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wu, S.; Marie Lutz, B.; Miao, X.; Liang, L.; Mo, K.; Chang, Y.J.; Du, P.; Soteropoulos, P.; Tian, B.; Kaufman, A.G.; et al. Dorsal root ganglion transcriptome analysis following peripheral nerve injury in mice. Mol. Pain 2016, 12, 1744806916629048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Blakeman, K.H.; Hao, J.X.; Xu, X.J.; Jacoby, A.S.; Shine, J.; Crawley, J.N.; Iismaa, T.; Wiesenfeld-Hallin, Z. Hyperalgesia and increased neuropathic pain-like response in mice lacking galanin receptor 1 receptors. Neuroscience 2003, 117, 221–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malkmus, S.; Lu, X.; Bartfai, T.; Yaksh, T.L.; Hua, X.Y. Increased hyperalgesia after tissue injury and faster recovery of allodynia after nerve injury in the GalR1 knockout mice. Neuropeptides 2005, 39, 217–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Gao, Y.; Li, C.Y.; Dong, W.; Dong, Y.; Li, M.N.; Liu, Y.N.; Xu, S.L. Galanin receptor 1 plays an antinociceptive effect via inhibiting PKA activation in the nucleus accumbens of rats with neuropathic pain. Physiol. Res. 2019, 68, 511–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyu, C.; Xia, S.; Lyu, G.W.; Dun, X.P.; Zheng, K.; Su, J.; Barde, S.; Xu, Z.Q.D.; Hökfelt, T.; Shi, T.J.S. A preliminary study on DRGs and spinal cord of a galanin receptor 2-EGFP transgenic mouse. Neuropeptides 2020, 79, 102000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, T.J.S.; Hua, X.Y.; Lu, X.; Malkmus, S.; Kinney, J.; Holmberg, K.; Wirz, S.; Ceccatelli, S.; Yaksh, T.; Bartfai, T.; et al. Sensory neuronal phenotype in galanin receptor 2 knockout mice: Focus on dorsal root ganglion neurone development and pain behaviour. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2006, 23, 627–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brumovsky, P.; Mennicken, F.; O’Donnell, D.; Hökfelt, T. Differential distribution and regulation of galanin receptors- 1 and -2 in the rat lumbar spinal cord. Brain Res. 2006, 1085, 111–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metcalf, C.S.; Klein, B.D.; McDougle, D.R.; Zhang, L.; Smith, M.D.; Bulaj, G.; White, H.S. Analgesic properties of a peripherally acting and GalR2 receptor—Preferring galanin analog in inflammatory, neuropathic, and acute pain models. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2015, 352, 185–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Duan, H.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, X.M.; Xu, H.H.; Shu, J.; Xu, S.L. Antinociceptive roles of galanin receptor 1 in nucleus accumbens of rats in a model of neuropathic pain. J. Neurosci. Res. 2015, 93, 1542–1551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, Y.; Li, C.Y.; Zhang, X.M.; Liu, Y.N.; Yang, S.; Li, M.N.; Xu, S.L. The activation of galanin receptor 2 plays an antinociceptive effect in nucleus accumbens of rats with neuropathic pain. J. Physiol. Sci. 2021, 71, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Zhang, X.; Li, C.; Liu, Y.; Yang, S.; Xu, S. Galanin Receptor 2 Is Involved in Galanin-Induced Analgesic Effect by Activating PKC and CaMKII in the Nucleus Accumbens of Inflammatory Pain Rats. Front. Neurosci. 2021, 14, 1466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.Y.; Huo, M.L.; Wu, X.Y.; Huang, Y.Q.; Wang, L.; Zhang, X.; Jiang, Y.M.; Zhang, M.L.; Wang, L.L.; Yu, L.C. Involvement of galanin and galanin receptor 1 in nociceptive modulation in the central nucleus of amygdala in normal and neuropathic rats. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 15317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sun, Y.G.; Li, J.; Yang, B.N.; Yu, L.C. Antinociceptive effects of galanin in the rat tuberomammillary nucleus and the plasticity of galanin receptor 1 during hyperalgesia. J. Neurosci. Res. 2004, 77, 718–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.L.; Wang, H.B.; Fu, F.H.; Yu, L.C. Involvement of galanin and galanin receptor 2 in nociceptive modulation in anterior cingulate cortex of normal rats and rats with mononeuropathy. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 45930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, D.; Lundeberg, T.; Yu, L.C. Antinociceptive role of galanin in periaqueductal grey of rats with experimentally induced mononeuropathy. Neuroscience 2000, 96, 767–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.G.; Gu, X.L.; Lundeberg, T.; Yu, L.C. An antinociceptive role of galanin in the arcuate nucleus of hypothalamus in intact rats and rats with inflammation. Pain 2003, 106, 143–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, X.L.; Sun, Y.G.; Yu, L.C. Involvement of galanin in nociceptive regulation in the arcuate nucleus of hypothalamus in rats with mononeuropathy. Behav. Brain Res. 2007, 179, 331–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Li, X.H.; Li, Y.; Qian, R.; Li, J.; Xu, S.L. Involvements of galanin and its receptors in antinociception in nucleus accumbens of rats with inflammatory pain. Neurosci. Res. 2015, 97, 20–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, M.L.; Fu, F.H.; Yu, L.C. Antinociception induced by galanin in anterior cingulate cortex in rats with acute inflammation. Neurosci. Lett. 2017, 638, 156–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, K.; Xu, Y.; Yang, H.; Shu, H.H.; Xiang, H.B.; Tian, Y.K. Subarachnoid transplantation of immortalized galanin-over-expressing astrocytes attenuates chronic neuropathic pain. Eur. J. Pain 2010, 14, 595–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.P.; Lundeberg, T.; Yu, L.C. Interactions of galanin and morphine in the spinal antinociception in rats with mononeuropathy. Brain Res. 2000, 852, 485–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.P.; Yu, L.C.; Lundeberg, T. An interaction of opioids and galanin in dorsal horn of the spinal cord in mononeuropathic rats. Regul. Pept. 2000, 86, 89–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerr, B.J.; Gupta, Y.; Pope, R.; Thompson, S.W.N.; Wynick, D.; McMahon, S.B. Endogenous galanin potentiates spinal nociceptive processing following inflammation. Pain 2001, 93, 267–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, R.R.; Zhang, Q.; Bedecs, K.; Arvidsson, J.; Zhang, X.; Xu, X.J.; Wiesenfeld- Hallin, Z.; Bartfai, T.; Hokfelt, T. Galanin antisense oligonucleotides reduce galanin levels in dorsal root ganglia and induce autotomy in rats after axotomy. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1994, 91, 12540–12543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Heppelmann, B.; Just, S.; Pawlak, M. Galanin influences the mechanosensitivity of sensory endings in the rat knee joint. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2000, 12, 1567–1572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Honore, P.; Rogers, S.D.; Schwei, M.J.; Salak-Johnson, J.L.; Luger, N.M.; Sabino, M.C.; Clohisy, D.R.; Mantyh, P.W. Murine models of inflammatory, neuropathic and cancer pain each generates a unique set of neurochemical changes in the spinal cord and sensory neurons. Neuroscience 2000, 98, 585–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, W.; Bisby, M.A. Increase of galanin mRNA in lumbar dorsal root ganglion neurons of adult rats after partial sciatic nerve ligation. Neurosci. Lett. 1999, 262, 195–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hofmann, H.A.; De Vry, J.; Siegling, A.; Spreyer, P.; Denzer, D. Pharmacological sensitivity and gene expression analysis of the tibial nerve injury model of neuropathic pain. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2003, 470, 17–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wallace, V.C.J.; Blackbeard, J.; Pheby, T.; Segerdahl, A.R.; Davies, M.; Hasnie, F.; Hall, S.; McMahon, S.B.; Rice, A.S.C. Pharmacological, behavioural and mechanistic analysis of HIV-1 gp120 induced painful neuropathy. Pain 2007, 133, 47–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bao, L.; Wang, H.F.; Cai, H.J.; Tong, Y.G.; Jin, S.X.; Lu, Y.J.; Grant, G.; Hökfelt, T.; Zhang, X. Peripheral axotomy induces only very limited sprouting of coarse myelinated afferents into inner lamina II of rat spinal cord. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2002, 16, 175–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, L.C.; Lundeberg, S.; An, H.; Wang, F.X.; Lundeberg, T. Effects of intrathecal galanin on nociceptive responses in rats with mononeuropathy. Life Sci. 1999, 64, 1145–1153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sundström, E.; Melander, T. Effects of galanin on 5-HT neurons in the rat CNS. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 1988, 146, 327–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Webling, K.E.B.; Runesson, J.; Bartfai, T.; Langel, Ü. Galanin receptors and ligands. Front. Endocrinol. 2012, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lang, R.; Gundlach, A.L.; Kofler, B. The galanin peptide family: Receptor pharmacology, pleiotropic biological actions, and implications in health and disease. Pharmacol. Ther. 2007, 115, 177–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gustafson, E.L.; Smith, K.E.; Durkin, M.M.; Gerald, C.; Branchek, T.A. Distribution of a rat galanin receptor mRNA in rat brain. Neuroreport 1996, 7, 953–957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lundström, L.; Sollenberg, U.; Brewer, A.; Kouya, P.F.; Zheng, K.; Xu, X.J.; Sheng, X.; Robinson, J.K.; Wiesenfeld-Hallin, Z.; Xu, Z.Q.; et al. A galanin receptor subtype 1 specific agonist. Int. J. Pept. Res. Ther. 2005, 11, 17–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Donnell, D.; Ahmad, S.; Wahlestedt, C.; Walker, P. Expression of the novel galanin receptor subtype GALR2 in the adult rat CNS: Distinct distribution from GALR. J. Comp. Neurol. 1999, 409, 469–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borroto-Escuela, D.O.; Pita-Rodriguez, M.; Fores-Pons, R.; Barbancho, M.A.; Fuxe, K.; Narváez, M. Galanin and neuropeptide Y interactions elicit antidepressant activity linked to neuronal precursor cells of the dentate gyrus in the ventral hippocampus. J. Cell. Physiol. 2021, 236, 3565–3578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narváez, M.; Millón, C.; Borroto-Escuela, D.; Flores-Burgess, A.; Santín, L.; Parrado, C.; Gago, B.; Puigcerver, A.; Fuxe, K.; Narváez, J.A.; et al. Galanin receptor 2-neuropeptide Y Y1 receptor interactions in the amygdala lead to increased anxiolytic actions. Brain Struct. Funct. 2015, 220, 2289–2301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mennicken, F.; Hoffert, C.; Pelletier, M.; Ahmad, S.; O’Donnell, D. Restricted distribution of galanin receptor 3 (GalR3) mRNA in the adult rat central nervous system. J. Chem. Neuroanat. 2002, 24, 257–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Nicholas, A.P.; Hökfelt, T. Ultrastructural studies on peptides in the dorsal horn of the rat spinal cord-II. Co-existence of galanin with other peptides in local neurons. Neuroscience 1995, 64, 875–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stevens, C.W.; Kajander, K.C.; Bennett, G.J.; Seybold, V.S. Bilateral and differential changes in spinal mu, delta and kappa opioid binding in rats with a painful, unilateral neuropathy. Pain 1991, 46, 315–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Mechanism | Effects |
|---|---|
| Endogenous Galanin | Increase in sensory neurons after administration of resiniferatoxin, an ultrapotent capsaicin analog [18] |
| Galanin Overexpression | Antinociceptive effect on thermal and mechanical sensitivity [19] |
| Reduced facilitation of the nociceptive flexor reflex [20] | |
| Galanin Receptors | GalR1 receptors are located predominantly post-synaptically whereas GalR2 receptors may be localised both pre- and post-synaptically in the spinal cord [21] |
| Galanin at lower concentrations activates GalR2/R3, whereas galanin at higher concentrations also activates GalR1 [22] | |
| GalR1 activation, but not GalR2/3 activation, suppresses mechanical sensitivity [23] | |
| Inactivation of GalR1 attenuates the antinociceptive effect of galanin [24] | |
| GalR1 is an antinociceptive target in the central nucleus of the amygdala [25,26] | |
| Selective destruction of GalR1-expressing superficial dorsal horn neurons produces heat hypoalgesia [27] | |
| The absence of GalR2 induces the loss of a subset of sensory neurons (likely nociceptors) [28] | |
| Interaction with Opioids | Potentiates the analgesic effect of morphine [29,30,31] |
| Interaction between galanin and opioids [32] | |
| Galanin exerts its antinociceptive effects through the µ-opioid receptor [33] | |
| Both µ- and δ-opioid receptors are involved in galanin-induced antinociception [34] | |
| Local Administration to Peripheral Nerves | Administration of galanin to the saphenous nerve truck inhibits axonal excitability (antinociceptive effect) [35] |
| Administration of galanin to the lumbar splanchnic nerve reduces mechanical sensitivity (antinociceptive effect) [23] | |
| Intrathecal Galanin | Antinociceptive effect on thermal and mechanical sensitivity [31,36,37,38] |
| Antinociceptive effect on formalin-induced nociception [29] | |
| No effect on flexor reflex [30] | |
| Reduced facilitation of the nociceptive flexor reflex [24,39,40] | |
| Antinociceptive effect mediated by activation of spinal GalR1, but not GalR2 receptors [29] | |
| Antinociceptive effect mediated by activation of GalR2/3 receptors [41] | |
| Supraspinal Galanin | Intracerebroventricular administration of galanin: - no effect on mechanical and thermal sensitivity after administration of N-terminal galanin fragment [42] - antinociceptive effect on thermal and mechanical sensitivity [43,44,45] - reduced facilitation of the nociceptive trigemino-hypoglossal reflex [33,46] |
| Galanin administration to the periaqueductal grey (PAG) has an antinociceptive effect on thermal and mechanical sensitivity [32,47,48] Activation of GalR1 induces antinociception in rats with morphine tolerance [47] GalR2 antagonist administration (M871) attenuates the antinociceptive effects of galanin [48] | |
| Galanin administration to the arcuate nucleus of the hypothalamus (ARC)—decreases thermal and mechanical sensitivity [49,50] | |
| Galanin administration to the central nucleus of the amygdala (AMY)—decreases thermal and mechanical sensitivity [25,34] | |
| Galanin administration to the lateral habenula complex (LHb)—decreases thermal and mechanical sensitivity [26] |
| Mechanism | Effects |
|---|---|
| Galanin Levels—DRG | Increased in DRG neurons in animal models of neuropathic pain: sciatic nerve axotomy [10,15,51,52,53,54,55,56,57,58,59,60] chronic constriction injury of the sciatic nerve [56,61,62,63] cisplatin-induced neuropathy [64,65,66,67] alveolar nerve axotomy [68,69,70] photochemically induced sciatic nerve injury [71] spinal nerve ligation [72] sarcoma-induced cancer pain [73] varicella zoster virus-induced neuropathy [74] partial saphenous nerve ligation injury [75] sciatic nerve pinch [16,76] tibial nerve injury [77] median nerve chronic constriction injury [78] |
| Increased in DRG neurons in animal models of inflammatory pain: CFA induced arthritis, especially at time-course points with high inflammation and severe joint destruction [79] collagen antibody-induced arthritis [80] | |
| Galanin Levels—Spinal | Increased in the spinal cord in animal models of neuropathic pain: flexion of inflamed ankles [81] sciatic nerve axotomy [53,56,82] spinal nerve ligation [72,83] chronic constriction injury of the sciatic nerve [56,67,84,85] noxious colorectal distension [14] sciatic nerve pinch [16] streptozotocin-induced diabetes [76] spinal cord injury [86] |
| Decreased in the spinal cord in animal models of neuropathic pain: cisplatin-induced neuropathy [64] chronic constriction injury of the sciatic nerve [87] | |
| Decreased in the spinal cord at the onset of Freud’s adjuvant-induced inflammation, which gradually increases [88] | |
| Galanin Levels—Supraspinal | Increased in the ARC after: spared nerve injury [89] visceral pain induced by cyclophosphamide (CP) [90] |
| Increase in the RVM and the dorsal raphe nucleus in monoarthritis [91] | |
| Increased in the NAc after chronic constriction injury of the sciatic nerve [92] | |
| Effect of Galanin Knockout or Overexpression | Decreased in the spinal cord at the onset of Freud’s adjuvant-induced inflammation, which gradually increases [88] |
| No change in spinal galanin levels after collagen antibody-induced arthritis [93] | |
| Galanin suppression increases allodynic responses after sciatic nerve axotomy [94] | |
| Galanin overexpression decreases thermal/mechanical hyperalgesia after sciatic nerve injury [94,95] | |
| Galanin over-expressing animals displayed increased levels of galanin in the DRG and their corresponding nerve terminals after sciatic nerve axotomy [96] | |
| Role of Endogenous Galanin | Galanin had a biphasic effect on the flexor reflex in rats with intact nerves, including facilitation, followed by depression, in a dose-dependent manner [97] |
| Intrathecal injections of antibodies against galanin inhibited carrageenan-induced hyperalgesia [98] | |
| M35 administration has a facilitatory effect on flexor reflex excitability, which was potentiated after nerve axotomy [99] | |
| M35 administration enhances autotomy behaviour after sciatic nerve axotomy [100] | |
| Intra-arterial infusion of galanin inhibits acetone and menthol responses in the naive rodent and following models of neuropathic (partial sciatic nerve injury) and inflammatory pain (carrageenan) [101] | |
| Intraplantar administration of galanin at low doses increases capsaicin-evoked nociceptive behaviours [102,103,104] | |
| Intrathecal Administration of Galanin | Reduces carrageenan-induced inflammation and hyperalgesia [105] |
| Reduced facilitation of the nociceptive flexor reflex after sciatic nerve axotomy [106] | |
| Low doses of galanin have a pronociceptive effect on mechanical and cold allodynia after chronic constriction injury of the sciatic nerve [107] | |
| Antinociceptive effect on mechanical/thermal hyperalgesia after: photochemically-induced sciatic nerve injury [108] chronic constriction injury of the sciatic nerve [109,110] kaolin/carrageenan-induced arthritis [111] spinal nerve ligation [112,113] carrageenan-induced inflammation [114] spared nerve injury [115] sciatic nerve-pinch injury [16,76] streptozotocin-induced diabetes [76,116] | |
| Altered the responses of mechano-nociceptive C-fibre afferents in a dose-dependent manner in both naive and nerve-injured animals, with low concentrations facilitating and high markedly inhibiting mechano-nociceptor activity [117] | |
| Role of Galanin Receptors | Decreased expression of GalR1 after in DRG and spinal cord neurons: carrageenan-induced inflammation [118] sciatic nerve axotomy [118,119] streptozotocin-induced diabetes [76,116] spinal nerve ligation [120] sciatic nerve pinch injury [76] |
| GalR1 knockout animals display increased mechanical and thermal hypersensitivity after sciatic nerve injury [121] | |
| GalR1 knockout mice have no differences concerning acute nociception but showed a modest tendency towards increased hyperalgesia after tissue injury and inflammation [122] | |
| Activation of GalR1 reduces CAP-induced inflammatory pain, while the opposite is observed after activation of GalR2 [104] | |
| The modulatory effects of galanin on cooling are independent of GalR2 and GalR3 activation but mediated by activation of GalR1 [101]. | |
| Activation of GalR1, but not GalR2, attenuated diabetic neuropathic pain [116] | |
| GalR1 activation results in the inhibition of the PKA and induces antinociceptive effects after chronic constriction injury of the sciatic nerve [123] | |
| Increased expression of GalR2 in DRG and spinal cord neurons after: carrageenan-induced inflammation [118] sciatic nerve pinch injury [76] median nerve chronic constriction injury [78] spared nerve injury [124] | |
| Decreased expression of GalR2 in DRG and spinal cord neurons after: sciatic nerve axotomy [118,119] streptozotocin-induced diabetes [76,116] spinal cord injury [86] alveolar nerve axotomy [70] | |
| Lack of the GalR2 results in a considerable developmental loss of DRG neurons after spinal nerve injury [125] and sciatic nerve axotomy [126] | |
| Activation of GalR2 has an antinociceptive effect after nerve injury and inflammation [127] | |
| A low dose of galanin has a pronociceptive role at the spinal cord level, which is mediated by GalR2 receptors whereas the antiallodynic effect of high-dose galanin on neuropathic pain is mediated by the GalR1 receptors [107] | |
| Increased expression of GalR1 and GalR2 in the NAc after: carrageenan-induced inflammation [128] chronic constriction injury of the sciatic nerve [128,129] | |
| GalR2 activation in the NAc induces CAMKII and PKC after carrageenan-induced inflammation [130] | |
| Increased expression of GalR1 in the CeA after chronic constriction injury of the sciatic nerve [131] | |
| Increased expression of GalR1 in the TM after chronic constriction injury of the sciatic nerve [132] | |
| GalR2 is involved in the galanin-induced antinociception in the ACC [119,133] | |
| GalR3 does not mediate mechanical hyperalgesia in autoimmune arthritis [119] | |
| Supraspinal Administration of Galanin | Galanin administration to the PAG decreases mechanical and thermal hyperalgesia after chronic constriction injury of the sciatic nerve [134] |
| Galanin administration to the ARC decreases mechanical and thermal hyperalgesia after: carrageenan-induced inflammation [135] sciatic nerve ligation [136] | |
| Galanin administration to the TM decreases mechanical and thermal hyperalgesia after carrageenan-induced inflammation and chronic constriction injury of the sciatic nerve [132] | |
| Galanin administration of galanin to the dorsomedial hypothalamic nucleus is pronociceptive in awake healthy and kaolin/carrageenan-arthritic animals [91] | |
| Galanin administration to the NAc decreases mechanical and thermal hyperalgesia after: carrageenan-induced inflammation [137] chronic constriction injury of the sciatic nerve [92,128] | |
| Administration of M35 in the NAc attenuated the antinociceptive effects of galanin after chronic constriction injury of the sciatic nerve [123] | |
| Galanin administration to the ACC decreases mechanical/thermal hyperalgesia after: carrageenan-induced inflammation [138] chronic constriction injury of the sciatic nerve [133] | |
| Galanin administration to the CeA decreases mechanical/thermal hyperalgesia after chronic constriction injury of the sciatic nerve [131] | |
| Subarachnoid transplantation of immortalised galanin-over-expressing astrocytes has an antinociceptive effect after spared nerve injury [139] | |
| Interaction with opioids | Galanin acts synergically with opioids to inhibit the nociceptive information transmission in animal models of chronic constriction injury of the sciatic nerve [134,140,141] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fonseca-Rodrigues, D.; Almeida, A.; Pinto-Ribeiro, F. A New Gal in Town: A Systematic Review of the Role of Galanin and Its Receptors in Experimental Pain. Cells 2022, 11, 839. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells11050839
Fonseca-Rodrigues D, Almeida A, Pinto-Ribeiro F. A New Gal in Town: A Systematic Review of the Role of Galanin and Its Receptors in Experimental Pain. Cells. 2022; 11(5):839. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells11050839
Chicago/Turabian StyleFonseca-Rodrigues, Diana, Armando Almeida, and Filipa Pinto-Ribeiro. 2022. "A New Gal in Town: A Systematic Review of the Role of Galanin and Its Receptors in Experimental Pain" Cells 11, no. 5: 839. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells11050839
APA StyleFonseca-Rodrigues, D., Almeida, A., & Pinto-Ribeiro, F. (2022). A New Gal in Town: A Systematic Review of the Role of Galanin and Its Receptors in Experimental Pain. Cells, 11(5), 839. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells11050839







