TGF-β1 Reduces Neutrophil Adhesion and Prevents Acute Vaso-Occlusive Processes in Sickle Cell Disease Mice
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Reagents
2.2. Animals
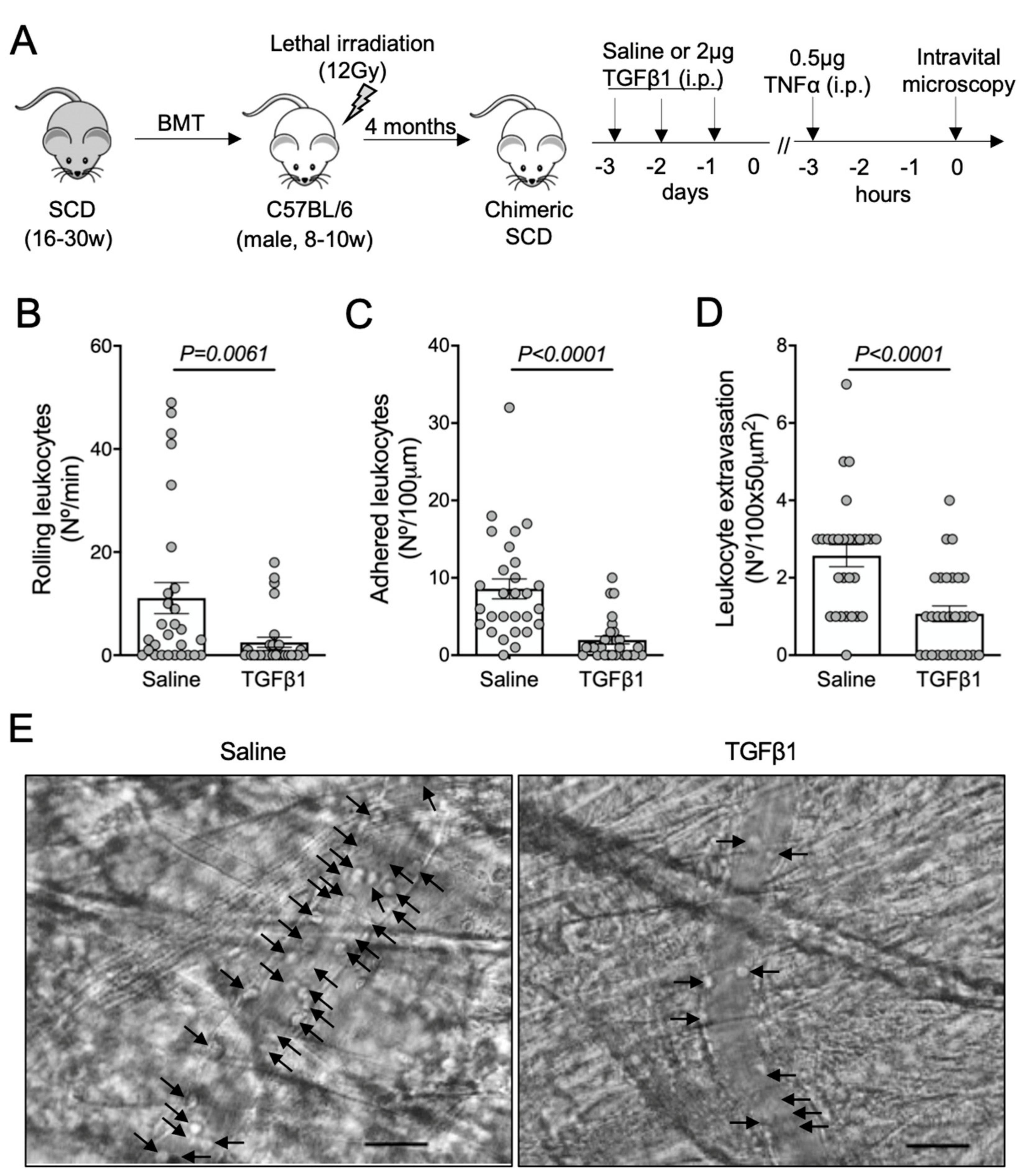
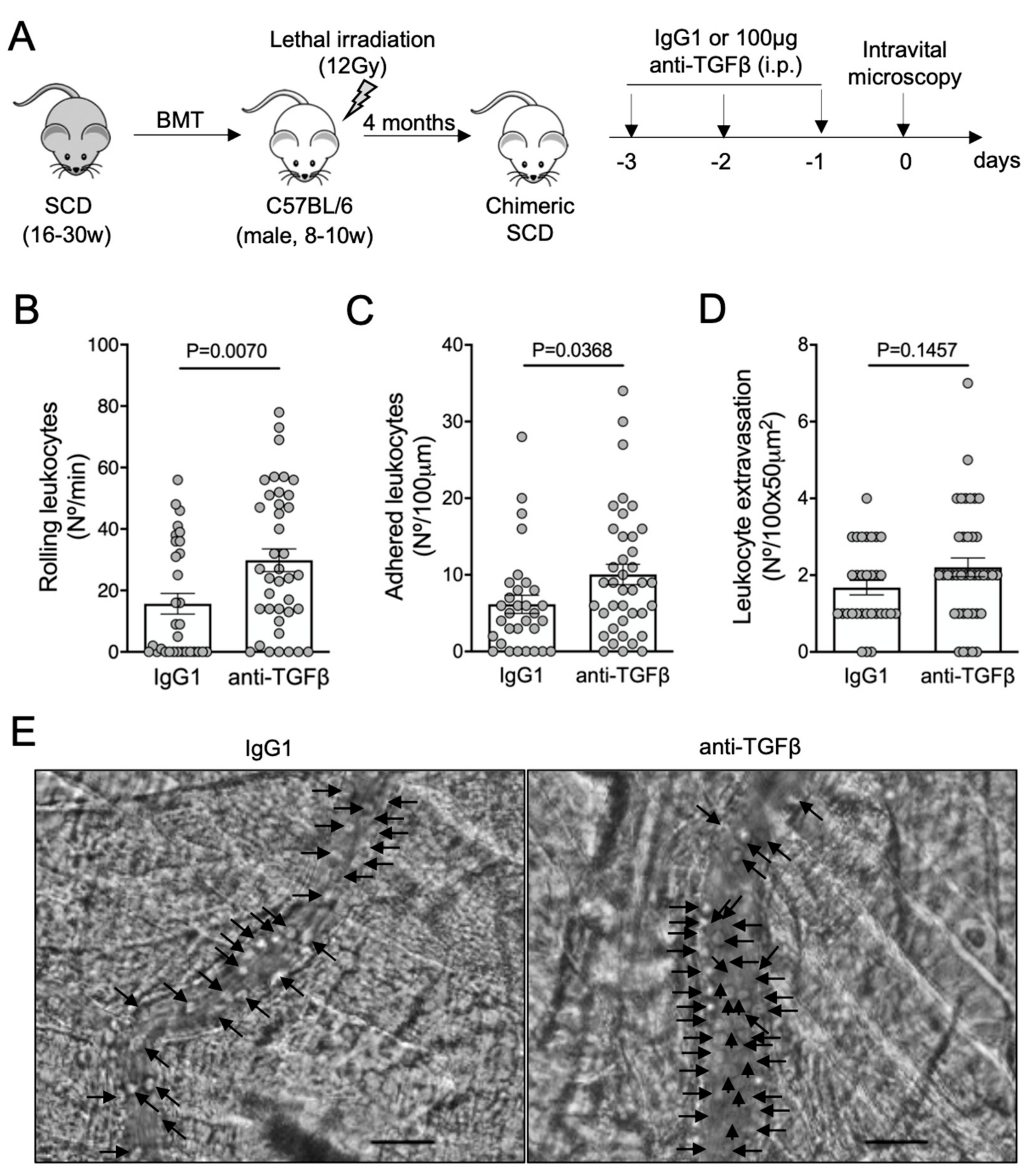
2.3. In Vivo Treatments
2.4. Intravital Microscopy
2.5. Human Samples
2.6. Human Neutrophil Isolation
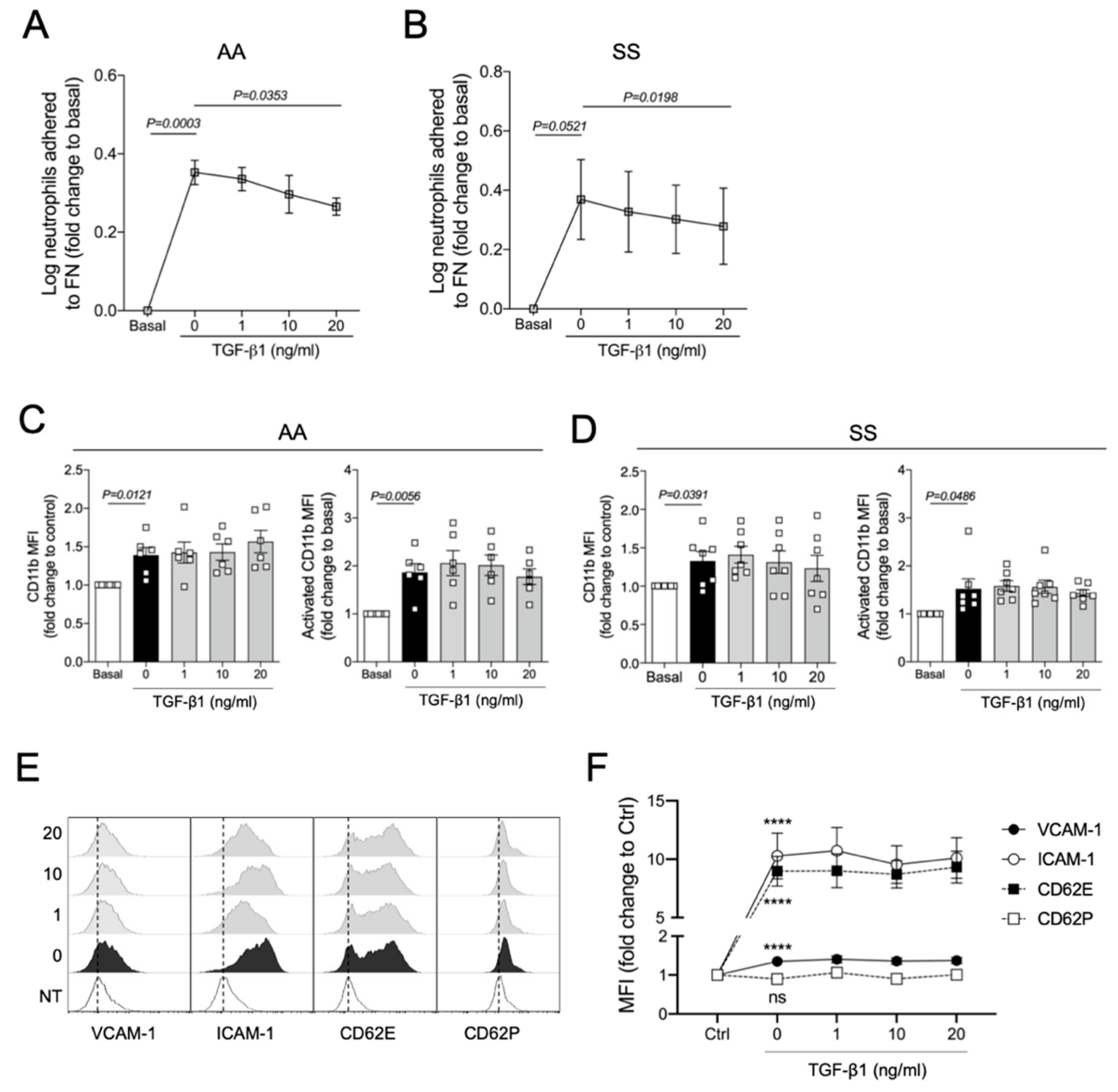
2.7. Static Adhesion Assay
2.8. Endothelial Cell Culture
2.9. Flow Cytometry
2.10. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. TGF-β1 Administration Prevents Vaso-Occlusive Episodes in SCD Mice
3.2. TGF-β1 Neutralization Exacerbates Vaso-Occlusion in SCD Mice
3.3. TGF-β1 Is Required for Microvascular Homeostasis in Healthy C57BL/6 Mice
3.4. TGF-β1 Reduces TNFα-Induced Adhesion of Human Neutrophils to Fibronectin In Vitro
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Massague, J. The transforming growth factor-beta family. Annu. Rev. Cell Biol. 1990, 6, 597–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morikawa, M.; Derynck, R.; Miyazono, K. TGF-beta and the TGF-beta Family: Context-Dependent Roles in Cell and Tissue Physiology. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2016, 8, a021873:1–a021873:26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Assoian, R.K.; Sporn, M.B. Type beta transforming growth factor in human platelets: Release during platelet degranulation and action on vascular smooth muscle cells. J. Cell Biol. 1986, 102, 1217–1223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Arjaans, M.; Oude Munnink, T.H.; Timmer-Bosscha, H.; Reiss, M.; Walenkamp, A.M.; Lub-de Hooge, M.N.; de Vries, E.G.; Schroder, C.P. Transforming growth factor (TGF)-beta expression and activation mechanisms as potential targets for anti-tumor therapy and tumor imaging. Pharmacol. Ther. 2012, 135, 123–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nolte, M.; Margadant, C. Controlling Immunity and Inflammation through Integrin-Dependent Regulation of TGF-beta. Trends Cell Biol. 2020, 30, 49–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larson, C.; Oronsky, B.; Carter, C.A.; Oronsky, A.; Knox, S.J.; Sher, D.; Reid, T.R. TGF-beta: A master immune regulator. Expert Opin. Ther. Targets 2020, 24, 427–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seoane, J.; Gomis, R.R. TGF-beta Family Signaling in Tumor Suppression and Cancer Progression. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2017, 9, 022277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Batlle, E.; Massague, J. Transforming Growth Factor-beta Signaling in Immunity and Cancer. Immunity 2019, 50, 924–940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres, L.S.; Okumura, J.V.; Silva, D.G.; Mimura, K.K.; Belini-Junior, E.; Oliveira, R.G.; Lobo, C.L.; Oliani, S.M.; Bonini-Domingos, C.R. Inflammation in Sickle Cell Disease: Differential and Down-Expressed Plasma Levels of Annexin A1 Protein. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0165833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres, L.S.; Teles, L.I.M.; Shaul, M.E.; Fridlender, Z.G.; Santos, I.; Leonardo, F.C.; de Melo Campos, P.; Benites, B.D.; Olalla Saad, S.T.; Costa, F.F.; et al. Accelerated low-density neutrophil transition in sickle cell anaemia may contribute to disease pathophysiology. Br. J. Haematol. 2021, 18009:1–18009:4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steinberg, M.H. Sickle cell anemia, the first molecular disease: Overview of molecular etiology, pathophysiology, and therapeutic approaches. Sci. World J. 2008, 8, 1295–1324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piel, F.B.; Steinberg, M.H.; Rees, D.C. Sickle Cell Disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 376, 1561–1573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Eaton, W.A.; Hofrichter, J. Sickle cell hemoglobin polymerization. Adv. Protein Chem. 1990, 40, 63–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bunn, H.F. Pathogenesis and treatment of sickle cell disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 1997, 337, 762–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ballas, S.K.; Marcolina, M.J. Hyperhemolysis during the evolution of uncomplicated acute painful episodes in patients with sickle cell anemia. Transfusion 2006, 46, 105–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bensinger, T.A.; Gillette, P.N. Hemolysis in sickle cell disease. Arch. Intern. Med. 1974, 133, 624–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kato, G.J.; Steinberg, M.H.; Gladwin, M.T. Intravascular hemolysis and the pathophysiology of sickle cell disease. J. Clin. Investig. 2017, 127, 750–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hebbel, R.P. Ischemia-reperfusion injury in sickle cell anemia: Relationship to acute chest syndrome, endothelial dysfunction, arterial vasculopathy, and inflammatory pain. Hematol. Oncol. Clin. N. Am. 2014, 28, 181–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frenette, P.S. Sickle cell vaso-occlusion: Multistep and multicellular paradigm. Curr. Opin. Hematol. 2002, 9, 101–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiang, E.Y.; Hidalgo, A.; Chang, J.; Frenette, P.S. Imaging receptor microdomains on leukocyte subsets in live mice. Nat. Methods 2007, 4, 219–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turhan, A.; Weiss, L.A.; Mohandas, N.; Coller, B.S.; Frenette, P.S. Primary role for adherent leukocytes in sickle cell vascular occlusion: A new paradigm. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 99, 3047–3051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hidalgo, A.; Chang, J.; Jang, J.E.; Peired, A.J.; Chiang, E.Y.; Frenette, P.S. Heterotypic interactions enabled by polarized neutrophil microdomains mediate thromboinflammatory injury. Nat. Med. 2009, 15, 384–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Platt, O.S.; Brambilla, D.J.; Rosse, W.F.; Milner, P.F.; Castro, O.; Steinberg, M.H.; Klug, P.P. Mortality in sickle cell disease. Life expectancy and risk factors for early death. N. Engl. J. Med. 1994, 330, 1639–1644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Platt, O.S. Sickle cell anemia as an inflammatory disease. J. Clin. Investig. 2000, 106, 337–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almeida, C.B.; Scheiermann, C.; Jang, J.E.; Prophete, C.; Costa, F.F.; Conran, N.; Frenette, P.S. Hydroxyurea and a cGMP-amplifying agent have immediate benefits on acute vaso-occlusive events in sickle cell disease mice. Blood 2012, 120, 2879–2888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ando, T.; Hatsushika, K.; Wako, M.; Ohba, T.; Koyama, K.; Ohnuma, Y.; Katoh, R.; Ogawa, H.; Okumura, K.; Luo, J.; et al. Orally administered TGF-beta is biologically active in the intestinal mucosa and enhances oral tolerance. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2007, 120, 916–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okamoto, A.; Kawamura, T.; Kanbe, K.; Kanamaru, Y.; Ogawa, H.; Okumura, K.; Nakao, A. Suppression of serum IgE response and systemic anaphylaxis in a food allergy model by orally administered high-dose TGF-beta. Int. Immunol. 2005, 17, 705–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Moses, H.L.; Roberts, A.B.; Derynck, R. The Discovery and Early Days of TGF-beta: A Historical Perspective. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2016, a021865:1–a021865:28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Derynck, R.; Jarrett, J.A.; Chen, E.Y.; Goeddel, D.V. The murine transforming growth factor-beta precursor. J. Biol. Chem. 1986, 261, 4377–4379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- English, D.; Andersen, B.R. Single-step separation of red blood cells. Granulocytes and mononuclear leukocytes on discontinuous density gradients of Ficoll-Hypaque. J. Immunol. Methods 1974, 5, 249–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Assis, A.; Conran, N.; Canalli, A.A.; Lorand-Metze, I.; Saad, S.T.; Costa, F.F. Effect of cytokines and chemokines on sickle neutrophil adhesion to fibronectin. Acta Haematol. 2005, 113, 130–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meyer, A.; Wang, W.; Qu, J.; Croft, L.; Degen, J.L.; Coller, B.S.; Ahamed, J. Platelet TGF-beta1 contributions to plasma TGF-beta1, cardiac fibrosis, and systolic dysfunction in a mouse model of pressure overload. Blood 2012, 119, 1064–1074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yaswen, L.; Kulkarni, A.B.; Fredrickson, T.; Mittleman, B.; Schiffman, R.; Payne, S.; Longenecker, G.; Mozes, E.; Karlsson, S. Autoimmune manifestations in the transforming growth factor-beta 1 knockout mouse. Blood 1996, 87, 1439–1445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shull, M.M.; Ormsby, I.; Kier, A.B.; Pawlowski, S.; Diebold, R.J.; Yin, M.; Allen, R.; Sidman, C.; Proetzel, G.; Calvin, D.; et al. Targeted disruption of the mouse transforming growth factor-beta 1 gene results in multifocal inflammatory disease. Nature 1992, 359, 693–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monteleone, G.; Kumberova, A.; Croft, N.M.; McKenzie, C.; Steer, H.W.; MacDonald, T.T. Blocking Smad7 restores TGF-beta1 signaling in chronic inflammatory bowel disease. J. Clin. Investig. 2001, 108, 601–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lard, L.R.; Mul, F.P.; de Haas, M.; Roos, D.; Duits, A.J. Neutrophil activation in sickle cell disease. J. Leukoc. Biol. 1999, 66, 411–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lum, A.F.; Wun, T.; Staunton, D.; Simon, S.I. Inflammatory potential of neutrophils detected in sickle cell disease. Am. J. Hematol. 2004, 76, 126–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Xu, C.; Manwani, D.; Frenette, P.S. Neutrophils, platelets, and inflammatory pathways at the nexus of sickle cell disease pathophysiology. Blood 2016, 127, 801–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shen, L.; Smith, J.M.; Shen, Z.; Eriksson, M.; Sentman, C.; Wira, C.R. Inhibition of human neutrophil degranulation by transforming growth factor-beta1. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2007, 149, 155–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gamble, J.R.; Vadas, M.A. Endothelial adhesiveness for blood neutrophils is inhibited by transforming growth factor-beta. Science 1988, 242, 97–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, W.B.; Noack, L.; Khew-Goodall, Y.; Isenmann, S.; Vadas, M.A.; Gamble, J.R. Transforming growth factor-beta 1 inhibits the production of IL-8 and the transmigration of neutrophils through activated endothelium. J. Immunol. 1996, 157, 360–368. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Gamble, J.R.; Khew-Goodall, Y.; Vadas, M.A. Transforming growth factor-beta inhibits E-selectin expression on human endothelial cells. J. Immunol. 1993, 150, 4494–4503. [Google Scholar]
- Goumans, M.J.; Liu, Z.; ten Dijke, P. TGF-beta signaling in vascular biology and dysfunction. Cell Res. 2009, 19, 116–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Goumans, M.J.; Ten Dijke, P. TGF-beta Signaling in Control of Cardiovascular Function. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2018, 10, a022210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gough, N.R.; Xiang, X.; Mishra, L. TGF-beta Signaling in Liver, Pancreas, and Gastrointestinal Diseases and Cancer. Gastroenterology 2021, 161, 434–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Torres, L.S.; Chweih, H.; Fabris, F.C.Z.; Gotardo, E.M.F.; Leonardo, F.C.; Saad, S.T.O.; Costa, F.F.; Conran, N. TGF-β1 Reduces Neutrophil Adhesion and Prevents Acute Vaso-Occlusive Processes in Sickle Cell Disease Mice. Cells 2022, 11, 1200. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells11071200
Torres LS, Chweih H, Fabris FCZ, Gotardo EMF, Leonardo FC, Saad STO, Costa FF, Conran N. TGF-β1 Reduces Neutrophil Adhesion and Prevents Acute Vaso-Occlusive Processes in Sickle Cell Disease Mice. Cells. 2022; 11(7):1200. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells11071200
Chicago/Turabian StyleTorres, Lidiane S., Hanan Chweih, Fernanda C. Z. Fabris, Erica M. F. Gotardo, Flávia C. Leonardo, Sara T. Olalla Saad, Fernando F. Costa, and Nicola Conran. 2022. "TGF-β1 Reduces Neutrophil Adhesion and Prevents Acute Vaso-Occlusive Processes in Sickle Cell Disease Mice" Cells 11, no. 7: 1200. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells11071200
APA StyleTorres, L. S., Chweih, H., Fabris, F. C. Z., Gotardo, E. M. F., Leonardo, F. C., Saad, S. T. O., Costa, F. F., & Conran, N. (2022). TGF-β1 Reduces Neutrophil Adhesion and Prevents Acute Vaso-Occlusive Processes in Sickle Cell Disease Mice. Cells, 11(7), 1200. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells11071200







