Myosteatosis in Cirrhosis: A Review of Diagnosis, Pathophysiological Mechanisms and Potential Interventions
Abstract
1. Introduction
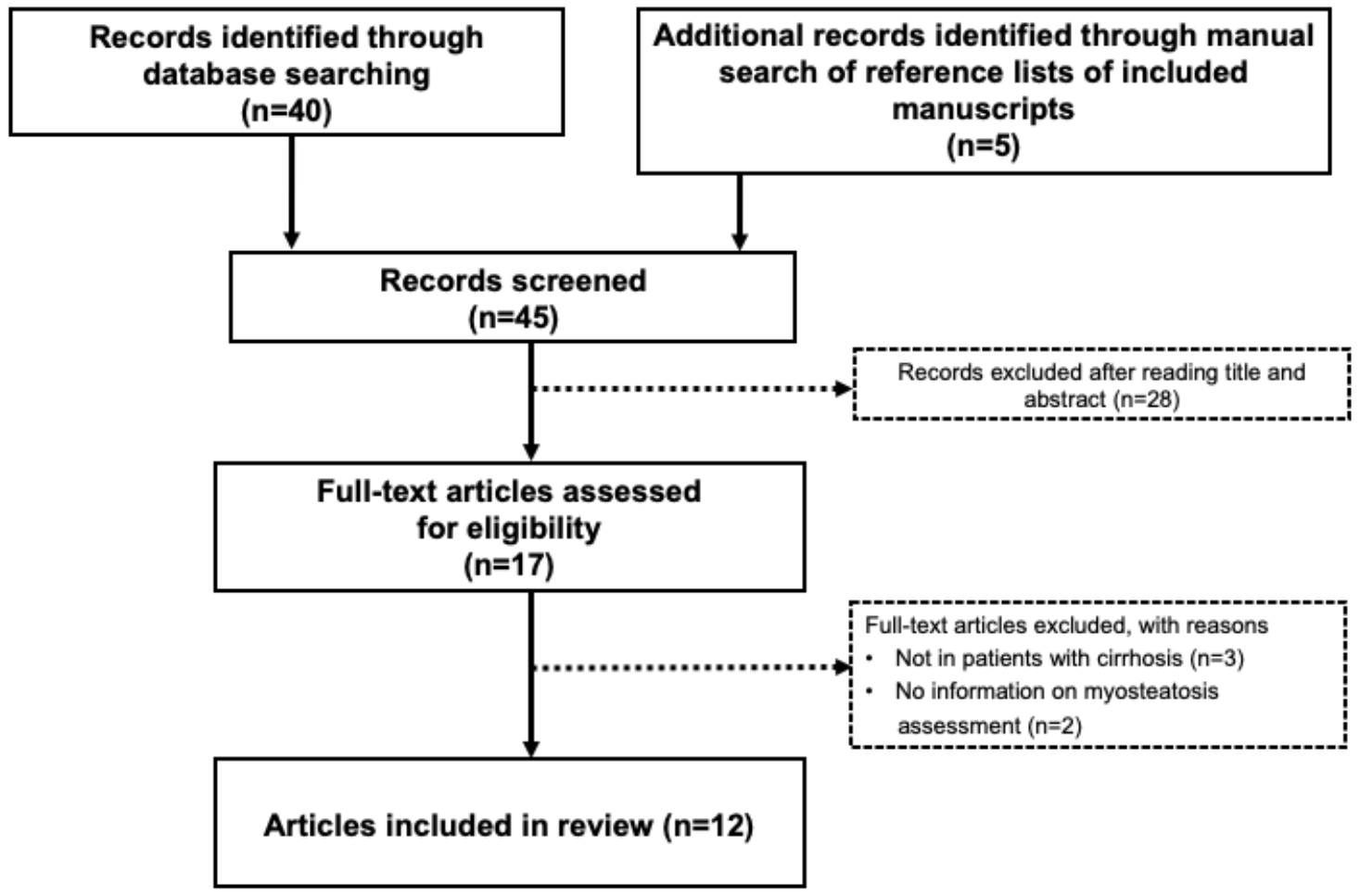
2. Search Strategy
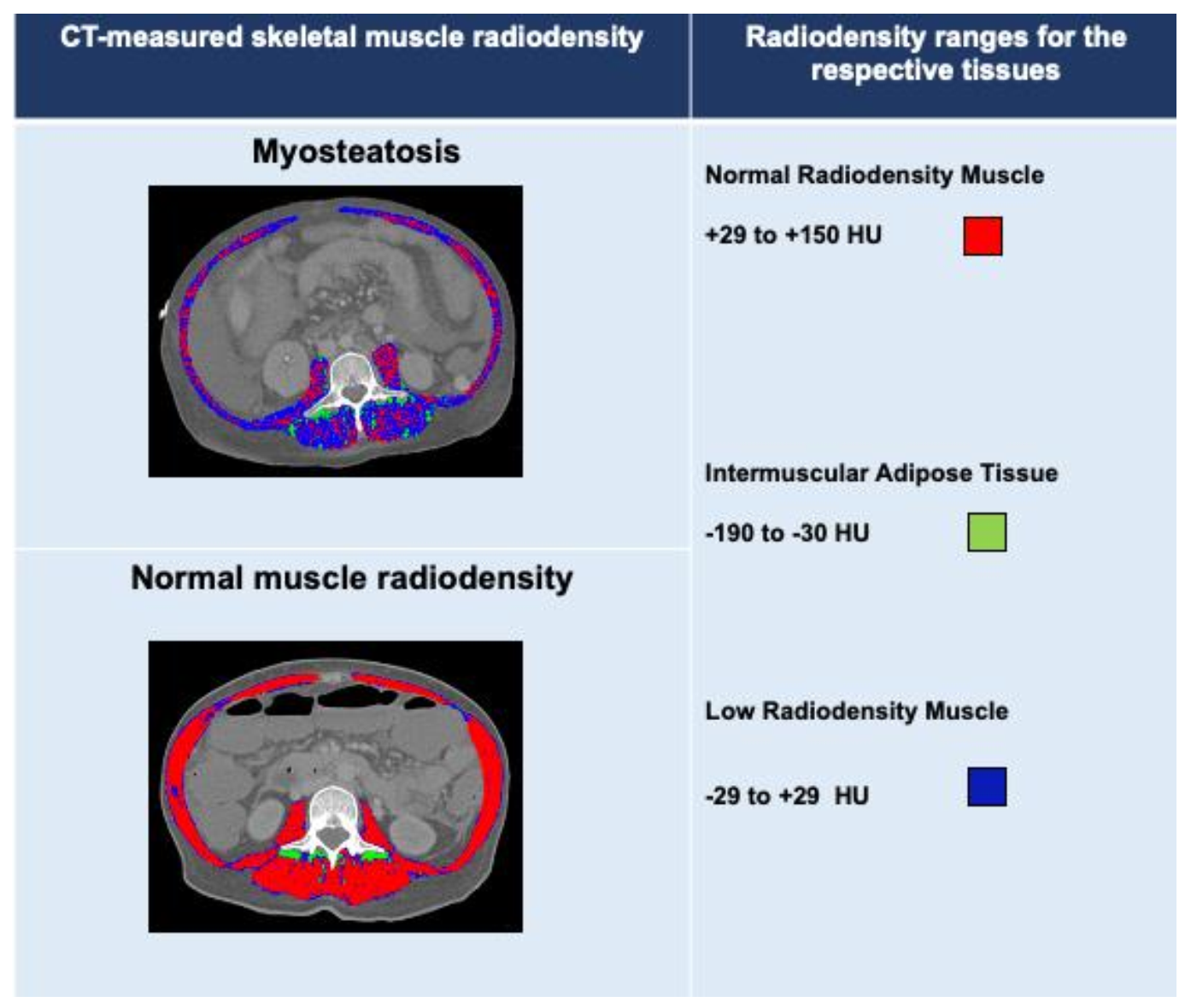
3. Diagnosing Myosteatosis
4. Clinical Significance of Myosteatosis
| Author/ Year | Study Population | Cutoff for Myosteatosis | Prevalence of Myosteatosis | Outcome Associated with Myosteatosis |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Montano-Loza et al., 2016 [19] | 678 patients with cirrhosis evaluated for LT | L3 muscle radiodensity <41 HU in patients with a BMI up to 24.9 and <33 in those with a BMI ≥25 kg/m2 | 52% | Myosteatosis was an independent predictor of long-term mortality. |
| Bhanji et al., 2018 [16] | 675 patients with cirrhosis evaluated for LT | L3 muscle radiodensity <41 HU in patients with a BMI up to 24.9 and <33 in those with a BMI ≥25 kg/m2 | 52% | Myosteatosis was identified in 70% of patients with overt hepatic encephalopathy and was an independent predictor of both hepatic encephalopathy and mortality. |
| Kalafateli et al., 2018 [21] | 98 consecutive patients with cirrhosis | Average psoas muscle radiodensity at the level of the fourth to fifth lumbar vertebrae below 43.14 HU | 20% | Myosteatosis was associated with a higher risk of 12-month mortality after adjusting for age, sex and Child–Pugh score. |
| Tachi et al., 2018 [15] | 362 patients with chronic liver disease | L3 muscle radiodensity <41 HU in patients with a BMI up to 24.9 and <33 in those with a BMI ≥25 kg/m2 | 82% | Myosteatosis, low BMI, low alanine aminotransferase and female sex were predictors of sarcopenia in patients with chronic liver disease. |
| Nardelli et al., 2019 [28] | 64 patients with cirrhosis who were administered a test to detectminimal hepatic encephalopathy | L3 muscle radiodensity <41 HU in patients with a BMI up to 24.9 and <33 in those with a BMI ≥25 kg/m2 | 38% | Myosteatosis was associated with the presence of minimal hepatic encephalopathy and the development of overt hepatic encephalopathy. |
| Lattanzi et al., 2019 [31] | 249 patients with cirrhosis evaluated for LT | L3 muscle radiodensity <41 HU in patients with a BMI up to 24.9 and <33 in those with a BMI ≥25 kg/m2 | 54% | MELD–Sarco–Myo–HE score was developed, which improved MELD accuracy in predicting 3- and 6-month mortality. |
| Czigany et al., 2020 [32] | 225 consecutive recipients of orthotopic LT | L3 muscle radiodensity <41 HU in patients with a BMI up to 24.9 and <33 in those with a BMI ≥25 kg/m2 | 44% | Higher mortality and complication rates over the first 3 months, length of intensive care unit and hospital stay and procedural costs in patients with myosteatosis, with no differences in long-term graft and patient survival between groups. |
| Shenvi et al., 2020 [27] | 180 recipients of LT | Preoperative fat fraction of MRI <0.8 | 16% | Myosteatosis was associated with increased length of hospital stay post-LT. |
| Meister et al., 2021 [22] | 264 consecutive recipients who underwent deceased donor orthotopic LT | L3 muscle radiodensity <26.6 HU in female and <28.6 HU in male patients | 25% | Applied cutoffs identified patients at risk for inferior short- but not long-term graft and patient outcomes after LT. |
| Bot et al., 2021 [25] | 261 patients listed for LT | Lowest quartile of muscle radiodensity at the level of L3 (<34.0 HU) | 25% | Higher risk of waitlist mortality in patients with myosteatosis (HR of 9.12 (HR 8.88, 95% CI: 1.95–40.41, p = 0.005). No association between intramuscular adipose tissue content and wait-list mortality in multivariate sensitivity analysis. |
| Feng et al., 2021 [24] | 202 hospitalized patients with cirrhosis | L3 radiodensity of the multifidus muscles normalized to the radiodensity of subcutaneous adipose tissue (>−0.44 in male and >−0.37 in female patients) | 19% | Higher incidence of myosteatosis in frail male patient (62.5 vs. 15.8%, p = 0.001). |
| Irwin et al., 2021 [34] | 106 LT recipients | L3 muscle radiodensity <41 HU in patients with a BMI up to 24.9 and <33 in those with a BMI ≥25 kg/m2 | 72% | Myosteatosis was associated with a higher risk of post-LT adverse outcomes, including mortality and allograft failure at 1 year, as well as longer hospital and intensive care unit stays. |
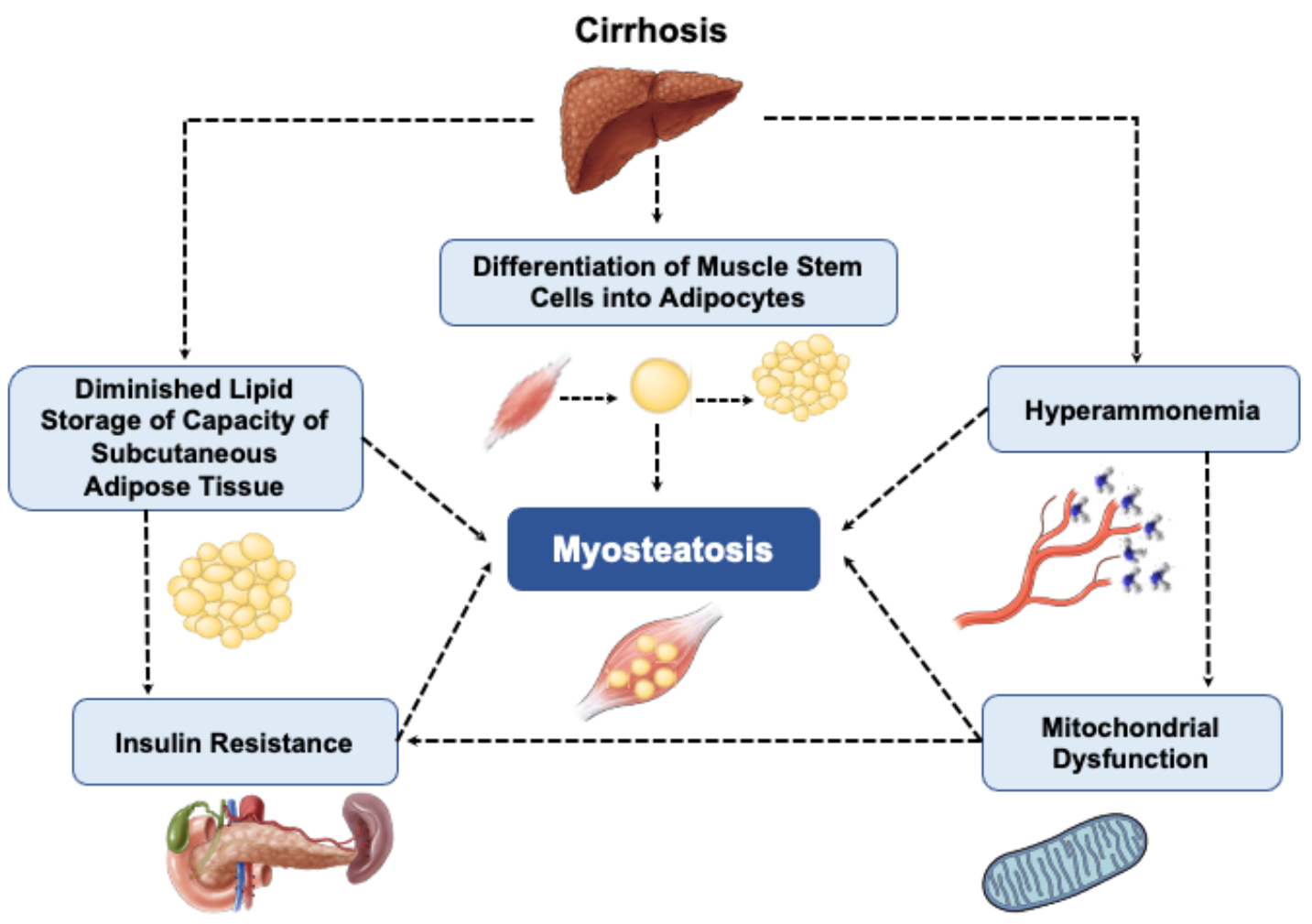
5. Mechanisms of Myosteatosis in Cirrhosis
6. Potential Pharmaceutical Targets Based on Pathogenic Pathways
6.1. Ammonia-Lowering Treatments
6.2. Long-Chain n-3 Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids
7. Considerations for Future Research Trial Designs
8. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ebadi, M.; Bhanji, R.A.; Tandon, P.; Mazurak, V.; Baracos, V.E.; Montano-Loza, A.J. Review article: Prognostic significance of body composition abnormalities in patients with cirrhosis. Aliment. Pharm. 2020, 52, 600–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ebadi, M.; Montano-Loza, A.J. Clinical relevance of skeletal muscle abnormalities in patients with cirrhosis. Dig. Liver Dis. 2019, 51, 1493–1499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carey, E.J.; Lai, J.C.; Sonnenday, C.; Tapper, E.B.; Tandon, P.; Duarte-Rojo, A.; Dunn, M.A.; Tsien, C.; Kallwitz, E.R.; Ng, V.; et al. A North American Expert Opinion Statement on Sarcopenia in Liver Transplantation. Hepatology 2019, 70, 1816–1829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naimo, M.A.; Varanoske, A.N.; Hughes, J.M.; Pasiakos, S.M. Skeletal Muscle Quality: A Biomarker for Assessing Physical Performance Capabilities in Young Populations. Front. Physiol. 2021, 12, 706699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gumucio, J.P.; Qasawa, A.H.; Ferrara, P.J.; Malik, A.N.; Funai, K.; McDonagh, B.; Mendias, C.L. Reduced mitochondrial lipid oxidation leads to fat accumulation in myosteatosis. FASEB J. Off. Publ. Fed. Am. Soc. Exp. Biol. 2019, 33, 7863–7881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Correa-de-Araujo, R.; Harris-Love, M.O.; Miljkovic, I.; Fragala, M.S.; Anthony, B.W.; Manini, T.M. The Need for Standardized Assessment of Muscle Quality in Skeletal Muscle Function Deficit and Other Aging-Related Muscle Dysfunctions: A Symposium Report. Front. Physiol. 2017, 8, 87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogawa, M.; Lester, R.; Akima, H.; Gorgey, A.S. Quantification of intermuscular and intramuscular adipose tissue using magnetic resonance imaging after neurodegenerative disorders. Neural Regen. Res. 2017, 12, 2100–2105. [Google Scholar]
- Hausman, G.J.; Basu, U.; Du, M.; Fernyhough-Culver, M.; Dodson, M.V. Intermuscular and intramuscular adipose tissues: Bad vs. good adipose tissues. Adipocyte 2014, 3, 242–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linge, J.; Petersson, M.; Forsgren, M.F.; Sanyal, A.J.; Dahlqvist Leinhard, O. Adverse muscle composition predicts all-cause mortality in the UK Biobank imaging study. J. Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle 2021, 12, 1513–1526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Correa-de-Araujo, R.; Addison, O.; Miljkovic, I.; Goodpaster, B.H.; Bergman, B.C.; Clark, R.V.; Elena, J.W.; Esser, K.A.; Ferrucci, L.; Harris-Love, M.O.; et al. Myosteatosis in the Context of Skeletal Muscle Function Deficit: An Interdisciplinary Workshop at the National Institute on Aging. Front. Physiol. 2020, 11, 963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aubrey, J.; Esfandiari, N.; Baracos, V.E.; Buteau, F.A.; Frenette, J.; Putman, C.T.; Mazurak, V.C. Measurement of skeletal muscle radiation attenuation and basis of its biological variation. Acta Physiol. 2014, 210, 489–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heymsfield, S.B.; Wang, Z.; Baumgartner, R.N.; Ross, R. Human body composition: Advances in models and methods. Annu Rev. Nutr 1997, 17, 527–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitsiopoulos, N.; Baumgartner, R.N.; Heymsfield, S.B.; Lyons, W.; Gallagher, D.; Ross, R. Cadaver validation of skeletal muscle measurement by magnetic resonance imaging and computerized tomography. J. Appl. Physiol. 1998, 85, 115–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Kan, G.A.; Cameron Chumlea, W.; Gillette-Guyonet, S.; Houles, M.; Dupuy, C.; Rolland, Y.; Vellas, B. Clinical trials on sarcopenia: Methodological issues regarding phase 3 trials. Clin. Geriatr. Med. 2011, 27, 471–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tachi, Y.; Kozuka, A.; Hirai, T.; Ishizu, Y.; Honda, T.; Kuzuya, T.; Hayashi, K.; Ishigami, M.; Goto, H. Impact of myosteatosis on skeletal muscle volume loss in patients with chronic liver disease. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2018, 33, 1659–1666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhanji, R.A.; Moctezuma-Velazquez, C.; Duarte-Rojo, A.; Ebadi, M.; Ghosh, S.; Rose, C.; Montano-Loza, A.J. Myosteatosis and sarcopenia are associated with hepatic encephalopathy in patients with cirrhosis. Hepatol. Int. 2018, 12, 377–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, H.; Kim, D.W.; Ko, Y.; Ha, J.; Shin, Y.B.; Lee, J.; Sung, Y.S.; Kim, K.W. Updated systematic review and meta-analysis on diagnostic issues and the prognostic impact of myosteatosis: A new paradigm beyond sarcopenia. Ageing Res. Rev. 2021, 70, 101398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, L.; Birdsell, L.; Macdonald, N.; Reiman, T.; Clandinin, M.T.; McCargar, L.J.; Murphy, R.; Ghosh, S.; Sawyer, M.B.; Baracos, V.E. Cancer cachexia in the age of obesity: Skeletal muscle depletion is a powerful prognostic factor, independent of body mass index. J. Clin. Oncol. Off. J. Am. Soc. Clin. Oncol. 2013, 31, 1539–1547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montano-Loza, A.J.; Angulo, P.; Meza-Junco, J.; Prado, C.M.; Sawyer, M.B.; Beaumont, C.; Esfandiari, N.; Ma, M.; Baracos, V.E. Sarcopenic obesity and myosteatosis are associated with higher mortality in patients with cirrhosis. J. Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle 2016, 7, 126–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lundsgaard, A.M.; Kiens, B. Gender differences in skeletal muscle substrate metabolism-molecular mechanisms and insulin sensitivity. Front. Endocrinol. 2014, 5, 195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalafateli, M.; Karatzas, A.; Tsiaoussis, G.; Koutroumpakis, E.; Tselekouni, P.; Koukias, N.; Konstantakis, C.; Assimakopoulos, S.; Gogos, C.; Thomopoulos, K.; et al. Muscle fat infiltration assessed by total psoas density on computed tomography predicts mortality in cirrhosis. Ann. Gastroenterol. 2018, 31, 491–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meister, F.A.; Bednarsch, J.; Amygdalos, I.; Boecker, J.; Strnad, P.; Bruners, P.; Lang, S.A.; Ulmer, T.F.; Heij, L.; Santana, D.A.M.; et al. Various myosteatosis selection criteria and their value in the assessment of short- and long-term outcomes following liver transplantation. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 13368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebadi, M.; Wang, C.W.; Lai, J.C.; Dasarathy, S.; Kappus, M.R.; Dunn, M.A.; Carey, E.J.; Montano-Loza, A.J. From the Fitness LE, Exercise in Liver Transplantation C: Poor performance of psoas muscle index for identification of patients with higher waitlist mortality risk in cirrhosis. J. Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle 2018, 9, 1053–1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, H.; Wang, X.; Mao, L.; Yu, Z.; Cui, B.; Lin, L.; Hui, Y.; Zhao, X.; Xu, X.; Fan, X.; et al. Relationship between sarcopenia/myosteatosis and frailty in hospitalized patients with cirrhosis: A sex-stratified analysis. Ther. Adv. Chronic Dis. 2021, 12, 20406223211026996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bot, D.; Droop, A.; Lucassen, C.J.; van Veen, M.E.; van Vugt, J.L.A.; Shahbazi Feshtali, S.; Leistra, E.; Tushuizen, M.E.; van Hoek, B. Both muscle quantity and quality are predictors of waiting list mortality in patients with end-stage liver disease. Clin. Nutr. ESPEN 2021, 42, 272–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshizumi, T.; Nakamura, T.; Yamane, M.; Islam, A.H.; Menju, M.; Yamasaki, K.; Arai, T.; Kotani, K.; Funahashi, T.; Yamashita, S.; et al. Abdominal fat: Standardized technique for measurement at CT. Radiology 1999, 211, 283–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shenvi, S.D.; Taber, D.J.; Hardie, A.D.; Botstein, J.O.; McGillicuddy, J.W. Assessment of magnetic resonance imaging derived fat fraction as a sensitive and reliable predictor of myosteatosis in liver transplant recipients. HPB 2020, 22, 102–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nardelli, S.; Lattanzi, B.; Merli, M.; Farcomeni, A.; Gioia, S.; Ridola, L.; Riggio, O. Muscle alterations are associated with minimal and overt hepatic encephalopathy in patients with liver cirrhosis. Hepatology 2019, 70, 1704–1713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gioia, S.; Merli, M.; Nardelli, S.; Lattanzi, B.; Pitocchi, F.; Ridola, L.; Riggio, O. The modification of quantity and quality of muscle mass improves the cognitive impairment after TIPS. Liver Int. Off. J. Int. Assoc. Study Liver 2019, 39, 871–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jahangiri, Y.; Pathak, P.; Tomozawa, Y.; Li, L.; Schlansky, B.L.; Farsad, K. Muscle Gain after Transjugular Intrahepatic Portosystemic Shunt Creation: Time Course and Prognostic Implications for Survival in Cirrhosis. J. Vasc. Interv. Radiol. 2019, 30, 866–872.e864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lattanzi, B.; Nardelli, S.; Pigliacelli, A.; Di Cola, S.; Farcomeni, A.; D’Ambrosio, D.; Gioia, S.; Ginanni Corradini, S.; Lucidi, C.; Mennini, G.; et al. The additive value of sarcopenia, myosteatosis and hepatic encephalopathy in the predictivity of model for end-stage liver disease. Dig. Liver Dis. 2019, 51, 1508–1512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Czigany, Z.; Kramp, W.; Bednarsch, J.; van der Kroft, G.; Boecker, J.; Strnad, P.; Zimmermann, M.; Koek, G.; Neumann, U.P.; Lurje, G. Myosteatosis to predict inferior perioperative outcome in patients undergoing orthotopic liver transplantation. Am. J. Transplant. 2020, 20, 493–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Czigany, Z.; Kramp, W.; Lurje, I.; Miller, H.; Bednarsch, J.; Lang, S.A.; Ulmer, T.F.; Bruners, P.; Strnad, P.; Trautwein, C.; et al. The role of recipient myosteatosis in graft and patient survival after deceased donor liver transplantation. J. Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle 2021, 12, 358–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Irwin, N.E.A.; Fabian, J.; Hari, K.R.; Lorentz, L.; Mahomed, A.; Botha, J.F. Myosteatosis, the More Significant Predictor of Outcome: An Analysis of the Impact of Myosteatosis, Sarcopenia, and Sarcopenic Obesity on Liver Transplant Outcomes in Johannesburg, South Africa. Exp. Clin. Transplant. 2021, 19, 948–955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, N.; Takahashi, H.; Yee, G.M.; Kitajima, Y.; Katagiri, S.; Kojima, M.; Anzai, K.; Eguchi, Y.; Hamilton, J.A. Influence of muscle fiber type composition on early fat accumulation under high-fat diet challenge. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0182430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wietek, B.M.; Machann, J.; Mader, I.; Thamer, C.; Haring, H.U.; Claussen, C.D.; Stumvoll, M.; Schick, F. Muscle type dependent increase in intramyocellular lipids during prolonged fasting of human subjects: A proton MRS study. Horm. Metab. Res. 2004, 36, 639–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beha, A.; Juretschke, H.P.; Kuhlmann, J.; Neumann-Haefelin, C.; Belz, U.; Gerl, M.; Kramer, W.; Roden, M.; Herling, A.W. Muscle type-specific fatty acid metabolism in insulin resistance: An integrated in vivo study in Zucker diabetic fatty rats. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2006, 290, E989–E997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Mastrocola, R.; Collino, M.; Nigro, D.; Chiazza, F.; D’Antona, G.; Aragno, M.; Minetto, M.A. Accumulation of advanced glycation end-products and activation of the SCAP/SREBP Lipogenetic pathway occur in diet-induced obese mouse skeletal muscle. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0119587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zamboni, M.; Gattazzo, S.; Rossi, A.P. Myosteatosis: A relevant, yet poorly explored element of sarcopenia. Eur. Geriatr. Med. 2019, 10, 5–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perkisas, S.; De Cock, A.M.; Verhoeven, V.; Vandewoude, M. Intramuscular Adipose Tissue and the Functional Components of Sarcopenia in Hospitalized Geriatric Patients. Geriatrics 2017, 2, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collino, M.; Mastrocola, R.; Nigro, D.; Chiazza, F.; Aragno, M.; D’Antona, G.; Minetto, M.A. Variability in myosteatosis and insulin resistance induced by high-fat diet in mouse skeletal muscles. BioMed Res. Int. 2014, 2014, 569623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Leary, M.F.; Wallace, G.R.; Davis, E.T.; Murphy, D.P.; Nicholson, T.; Bennett, A.J.; Tsintzas, K.; Jones, S.W. Obese subcutaneous adipose tissue impairs human myogenesis, particularly in old skeletal muscle, via resistin-mediated activation of NFkappaB. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 15360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, W.; Feng, J.; Jiang, D.; Zhou, X.; Jiang, Q.; Cai, M.; Wang, X.; Shan, T.; Wang, Y. AMPK regulates lipid accumulation in skeletal muscle cells through FTO-dependent demethylation of N(6)-methyladenosine. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 41606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, H.; Dridi, S.; Huang, Y.; Baum, J.I. Leucine decreases intramyocellular lipid deposition in an mTORC1-independent manner in palmitate-treated C2C12 myotubes. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2020, 318, E152–E163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davuluri, G.; Allawy, A.; Thapaliya, S.; Rennison, J.H.; Singh, D.; Kumar, A.; Sandlers, Y.; Van Wagoner, D.R.; Flask, C.A.; Hoppel, C.; et al. Hyperammonaemia-induced skeletal muscle mitochondrial dysfunction results in cataplerosis and oxidative stress. J. Physiol. 2016, 594, 7341–7360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stretch, C.; Aubin, J.M.; Mickiewicz, B.; Leugner, D.; Al-Manasra, T.; Tobola, E.; Salazar, S.; Sutherland, F.R.; Ball, C.G.; Dixon, E.; et al. Sarcopenia and myosteatosis are accompanied by distinct biological profiles in patients with pancreatic and periampullary adenocarcinomas. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0196235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brehm, A.; Krssak, M.; Schmid, A.I.; Nowotny, P.; Waldhausl, W.; Roden, M. Increased lipid availability impairs insulin-stimulated ATP synthesis in human skeletal muscle. Diabetes 2006, 55, 136–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jana, B.A.; Chintamaneni, P.K.; Krishnamurthy, P.T.; Wadhwani, A.; Mohankumar, S.K. Cytosolic lipid excess-induced mitochondrial dysfunction is the cause or effect of high fat diet-induced skeletal muscle insulin resistance: A molecular insight. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2019, 46, 957–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nachit, M.; De Rudder, M.; Thissen, J.P.; Schakman, O.; Bouzin, C.; Horsmans, Y.; Vande Velde, G.; Leclercq, I.A. Myosteatosis rather than sarcopenia associates with non-alcoholic steatohepatitis in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease preclinical models. J. Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle 2021, 12, 144–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nachit, M.; Lanthier, N.; Rodriguez, J.; Neyrinck, A.M.; Cani, P.D.; Bindels, L.B.; Hiel, S.; Pachikian, B.D.; Trefois, P.; Thissen, J.P.; et al. A dynamic association between myosteatosis and liver stiffness: Results from a prospective interventional study in obese patients. JHEP Rep. 2021, 3, 100323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biltz, N.K.; Collins, K.H.; Shen, K.C.; Schwartz, K.; Harris, C.A.; Meyer, G.A. Infiltration of intramuscular adipose tissue impairs skeletal muscle contraction. J. Physiol. 2020, 598, 2669–2683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zoico, E.; Rossi, A.; Di Francesco, V.; Sepe, A.; Olioso, D.; Pizzini, F.; Fantin, F.; Bosello, O.; Cominacini, L.; Harris, T.B.; et al. Adipose tissue infiltration in skeletal muscle of healthy elderly men: Relationships with body composition, insulin resistance, and inflammation at the systemic and tissue level. J. Gerontol. A Biol. Sci. Med. Sci. 2010, 65, 295–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morales, P.E.; Bucarey, J.L.; Espinosa, A. Muscle Lipid Metabolism: Role of Lipid Droplets and Perilipins. J. Diabetes Res. 2017, 2017, 1789395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.Y.; van de Wall, E.; Laplante, M.; Azzara, A.; Trujillo, M.E.; Hofmann, S.M.; Schraw, T.; Durand, J.L.; Li, H.; Li, G.; et al. Obesity-associated improvements in metabolic profile through expansion of adipose tissue. J. Clin. Investig. 2007, 117, 2621–2637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tardif, N.; Salles, J.; Guillet, C.; Tordjman, J.; Reggio, S.; Landrier, J.F.; Giraudet, C.; Patrac, V.; Bertrand-Michel, J.; Migne, C.; et al. Muscle ectopic fat deposition contributes to anabolic resistance in obese sarcopenic old rats through eIF2alpha activation. Aging Cell 2014, 13, 1001–1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miljkovic, I.; Zmuda, J.M. Epidemiology of myosteatosis. Curr. Opin. Clin. Nutr. Metab. Care 2010, 13, 260–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muto, Y.; Sato, S.; Watanabe, A.; Moriwaki, H.; Suzuki, K.; Kato, A.; Kato, M.; Nakamura, T.; Higuchi, K.; Nishiguchi, S.; et al. Effects of oral branched-chain amino acid granules on event-free survival in patients with liver cirrhosis. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. Off. Clin. Pract. J. Am. Gastroenterol. Assoc. 2005, 3, 705–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Davuluri, G.; Silva, R.N.E.; Engelen, M.; Ten Have, G.A.M.; Prayson, R.; Deutz, N.E.P.; Dasarathy, S. Ammonia lowering reverses sarcopenia of cirrhosis by restoring skeletal muscle proteostasis. Hepatology 2017, 65, 2045–2058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davuluri, G.; Krokowski, D.; Guan, B.J.; Kumar, A.; Thapaliya, S.; Singh, D.; Hatzoglou, M.; Dasarathy, S. Metabolic adaptation of skeletal muscle to hyperammonemia drives the beneficial effects of l-leucine in cirrhosis. J. Hepatol. 2016, 65, 929–937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malaguarnera, M.; Vacante, M.; Giordano, M.; Pennisi, G.; Bella, R.; Rampello, L.; Malaguarnera, M.; Li Volti, G.; Galvano, F. Oral acetyl-L-carnitine therapy reduces fatigue in overt hepatic encephalopathy: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2011, 93, 799–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herbst, E.A.; Paglialunga, S.; Gerling, C.; Whitfield, J.; Mukai, K.; Chabowski, A.; Heigenhauser, G.J.; Spriet, L.L.; Holloway, G.P. Omega-3 supplementation alters mitochondrial membrane composition and respiration kinetics in human skeletal muscle. J. Physiol. 2014, 592, 1341–1352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Almasud, A.A.; Giles, K.H.; Miklavcic, J.J.; Martins, K.J.B.; Baracos, V.E.; Putman, C.T.; Guan, L.L.; Mazurak, V.C. Fish oil mitigates myosteatosis and improves chemotherapy efficacy in a preclinical model of colon cancer. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0183576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mourtzakis, M.; Prado, C.M.; Lieffers, J.R.; Reiman, T.; McCargar, L.J.; Baracos, V.E. A practical and precise approach to quantification of body composition in cancer patients using computed tomography images acquired during routine care. Appl. Physiol. Nutr. Metab. 2008, 33, 997–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Kan, G.A.; Andre, E.; Bischoff Ferrari, H.A.; Boirie, Y.; Onder, G.; Pahor, M.; Ritz, P.; Rolland, Y.; Sampaio, C.; Studenski, S.; et al. Carla Task Force on Sarcopenia: Propositions for clinical trials. J. Nutr. Health Aging 2009, 13, 700–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Czobor, P.; Skolnick, P. The secrets of a successful clinical trial: Compliance, compliance, and compliance. Mol. Interv. 2011, 11, 107–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakpal, T.V. Sample size estimation in clinical trial. Perspect. Clin. Res. 2010, 1, 67–69. [Google Scholar]
- van Vugt, J.L.A.; Coebergh van den Braak, R.R.J.; Schippers, H.J.W.; Veen, K.M.; Levolger, S.; de Bruin, R.W.F.; Koek, M.; Niessen, W.J.; IJzermansa, J.N.M.; Willemsen, F. Contrast-enhancement influences skeletal muscle density, but not skeletal muscle mass, measurements on computed tomography. Clin. Nutr. 2018, 37, 1707–1714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ebadi, M.; Tsien, C.; Bhanji, R.A.; Dunichand-Hoedl, A.R.; Rider, E.; Motamedrad, M.; Mazurak, V.C.; Baracos, V.; Montano-Loza, A.J. Myosteatosis in Cirrhosis: A Review of Diagnosis, Pathophysiological Mechanisms and Potential Interventions. Cells 2022, 11, 1216. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells11071216
Ebadi M, Tsien C, Bhanji RA, Dunichand-Hoedl AR, Rider E, Motamedrad M, Mazurak VC, Baracos V, Montano-Loza AJ. Myosteatosis in Cirrhosis: A Review of Diagnosis, Pathophysiological Mechanisms and Potential Interventions. Cells. 2022; 11(7):1216. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells11071216
Chicago/Turabian StyleEbadi, Maryam, Cynthia Tsien, Rahima A. Bhanji, Abha R. Dunichand-Hoedl, Elora Rider, Maryam Motamedrad, Vera C. Mazurak, Vickie Baracos, and Aldo J. Montano-Loza. 2022. "Myosteatosis in Cirrhosis: A Review of Diagnosis, Pathophysiological Mechanisms and Potential Interventions" Cells 11, no. 7: 1216. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells11071216
APA StyleEbadi, M., Tsien, C., Bhanji, R. A., Dunichand-Hoedl, A. R., Rider, E., Motamedrad, M., Mazurak, V. C., Baracos, V., & Montano-Loza, A. J. (2022). Myosteatosis in Cirrhosis: A Review of Diagnosis, Pathophysiological Mechanisms and Potential Interventions. Cells, 11(7), 1216. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells11071216







