Extracellular Ribosomal RNA Acts Synergistically with Toll-like Receptor 2 Agonists to Promote Inflammation
Abstract
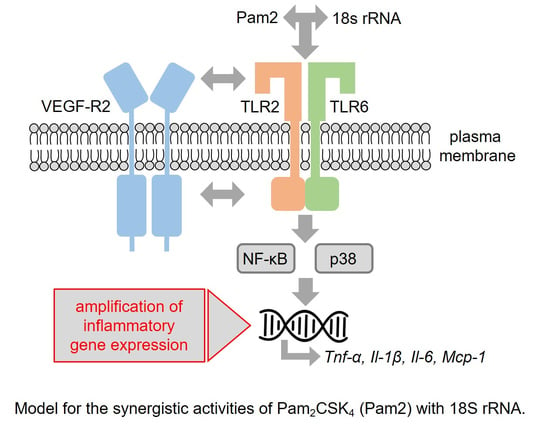
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cell Culture
2.2. Mice
2.3. Isolation and Quantification of RNA
2.4. In Vitro Transcription of Human 18S rRNA
2.5. Electrophoretic Mobility Shift Assay (EMSA)
2.6. TLR2 Fusion Protein
2.7. TLR2 Binding Assay
2.8. Quantitative Real-Time PCR
2.9. Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA)
2.10. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Synergistic Activity of 18S rRNA and Pam2 CSK4
3.2. Signaling Pathways Involved in 18S rRNA/Pam2 CSK4-Induced Activities
3.3. Synergistic Effects of 18S rRNA with Other TLR Ligands
3.4. Detection of 18S rRNA/Pam2 Complexes and Influence of 18S rRNA on Pam2 Binding to TLR2
3.5. Synergistic Activities of Different 18S rRNA Fragments Together with Pam2 CSK4
3.6. Synergistic Effects of 18S rRNA and Pam2 CSK4 In Vivo
3.7. Lack of Synergism between 18S rRNA and Pam2 CSK4 on Cytokine Induction in Endothelial Cells
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kawai, T.; Akira, S. Toll-like receptors and their crosstalk with other innate receptors in infection and immunity. Immunity 2011, 34, 637–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Takeda, K.; Kaisho, T.; Akira, S. Toll-like receptors. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2003, 21, 335–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akira, S.; Uematsu, S.; Takeuchi, O. Pathogen recognition and innate immunity. Cell 2006, 124, 783–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chen, N.; Zhou, M.; Dong, X.; Qu, J.; Gong, F.; Han, Y.; Qiu, Y.; Wang, J.; Liu, Y.; Wei, Y.; et al. Epidemiological and clinical characteristics of 99 cases of 2019 novel coronavirus pneumonia in Wuhan, China: A descriptive study. Lancet 2020, 395, 507–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fischer, S.; Cabrera-Fuentes, H.A.; Noll, T.; Preissner, K.T. Impact of extracellular RNA on endothelial barrier function. Cell Tissue Res. 2014, 355, 635–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischer, S.; Gerriets, T.; Wessels, C.; Walberer, M.; Kostin, S.; Stolz, E.; Zheleva, K.; Hocke, A.; Hippenstiel, S.; Preissner, K.T. Extracellular RNA mediates endothelial-cell permeability via vascular endothelial growth factor. Blood 2007, 110, 2457–2465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fischer, S.; Gesierich, S.; Griemert, B.; Schänzer, A.; Acker, T.; Augustin, H.G.; Olsson, A.-K.; Preissner, K.T. Extracellular RNA liberates Tumor-Necrosis-Factor-α to promote tumor cell trafficking and progression. Cancer Res. 2013, 73, 5080–5089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fischer, S.; Grantzow, T.; Pagel, J.-I.; Tschernatsch, M.; Sperandio, M.; Preissner, K.T.; Deindl, E. Extracellular RNA promotes leukocyte recruitment in the vascular system by mobilizing proinflammatory cytokines. Thromb. Haemost. 2012, 108, 730–741. [Google Scholar]
- Fischer, S.; Preissner, K.T. Extracellular nucleic acids as novel alarm signals in the vascular system: Mediators of defence and disease. Hämostaseologie 2013, 33, 37–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Preissner, K.T.; Fischer, S.; Deindl, E. Extracellular RNA as a Versatile DAMP and Alarm Signal That Influences Leukocyte Recruitment in Inflammation and Infection. Front. Cell. Dev. Biol. 2020, 8, 619221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Preissner, K.T.; Herwald, H. Extracellular nucleic acids in immunity and cardiovascular responses: Between alert and disease. Thromb. Haemost. 2017, 117, 1272–1282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zernecke, A.; Preissner, K.T. Extracellular ribonucleic acids (RNA) enter the stage in cardiovascular disease. Circ. Res. 2016, 118, 469–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elsemüller, A.K.; Tomalla, V.; Gärtner, U.; Troidl, K.; Jeratsch, S.; Graumann, J.; Baal, N.; Hackstein, H.; Lasch, M.; Deindl, E.; et al. Characterization of mast cell-derived rRNA-containing microvesicles and their inflammatory impact on endothelial cells. FASEB J. 2019, 33, 5457–5467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fischer, S.; Nasyrov, E.; Brosien, M.; Preissner, K.T.; Marti, H.H.; Kunze, R. Self-extracellular RNA promotes pro-inflammatory response of astrocytes to exogenous and endogenous danger signals. J. Neuroinflamm. 2021, 18, 252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cabrera-Fuentes, H.A.; Ruiz-Meana, M.; Simsekyilmaz, S.; Kostin, S.; Inserte, J.; Saffarzadeh, M.; Galuska, S.P.; Vijayan, V.; Barba, I.; Barreto, G.; et al. RNase1 prevents the damaging interplay between extracellular RNA and tumour necrosis factor-alpha in cardiac ischaemia/reperfusion injury. Thromb. Haemost. 2014, 112, 1110–1119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palazzo, A.F.; Lee, E.S. Non-coding RNA: What is functional and what is junk? Front. Genet. 2015, 6, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cabrera-Fuentes, H.A.; Lopez, M.L.; McCurdy, S.; Fischer, S.; Meiler, S.; Baumer, Y.; Galuska, S.P.; Preissner, K.T.; Boisvert, W.A. Regulation of monocyte/macrophage polarisation by extracellular RNA. Thromb. Haemost. 2015, 113, 473–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Noll, F.; Behnke, J.; Leiting, S.; Troidl, K.; Alves, G.T.; Muller-Redetzky, H.; Preissner, K.T.; Fischer, S. Self-extracellular RNA acts in synergy with exogenous danger signals to promote inflammation. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0190002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Troidl, K.; Schubert, C.; Vlacil, A.K.; Chennupati, R.; Koch, S.; Schütt, J.; Oberoi, R.; Schaper, W.; Schmitz-Rixen, T.; Schieffer, B.; et al. The Lipopeptide MALP-2 Promotes Collateral Growth. Cells 2020, 9, 997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mühlradt, P.F.; Kiess, M.; Meyer, H.; Süssmuth, R.; Jung, G. Isolation, structure elucidation, and synthesis of a macrophage stimulatory lipopeptide from Mycoplasma fermentans acting at picomolar concentration. J. Exp. Med. 1997, 185, 1951–1958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rutz, M.; Metzger, J.; Gellert, T.; Luppa, P.; Lipford, G.B.; Wagner, H.; Bauer, S. Toll-like receptor 9 binds single-stranded CpG-DNA in a sequence- and pH-dependent manner. Eur. J. Immunol. 2004, 34, 2541–2550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fischer, S.; Nishio, M.; Peters, S.C.; Tschernatsch, M.; Walberer, M.; Weidemann, S.; Heidenreich, R.; Couraud, P.O.; Weksler, B.B.; Romero, I.A.; et al. Signaling mechanism of extracellular RNA in endothelial cells. FASEB J. 2009, 23, 2100–2109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fong, T.A.; Shawver, L.K.; Sun, L.; Tang, C.; App, H.; Powell, T.J.; Kim, Y.H.; Schreck, R.; Wang, X.; Risau, W.; et al. SU5416 is a potent and selective inhibitor of the vascular endothelial growth factor receptor (Flk-1/KDR) that inhibits tyrosine kinase catalysis, tumor vascularization, and growth of multiple tumor types. Cancer Res. 1999, 59, 99–106. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hayden, M.S.; Ghosh, S. Shared principles in NF-kappaB signaling. Cell 2008, 132, 344–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Uematsu, S.; Akira, S. Toll-like receptors and innate immunity. J. Mol. Med. 2006, 84, 712–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- West, A.P.; Koblansky, A.A.; Ghosh, S. Recognition and signaling by toll-like receptors. Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol. 2006, 22, 409–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Black, R.A.; Rauch, C.T.; Kozlosky, C.J.; Peschon, J.J.; Slack, J.L.; Wolfson, M.F.; Castner, B.J.; Stocking, K.L.; Reddy, P.; Srinivasan, S.; et al. A metalloproteinase disintegrin that releases tumor-necrosis factor-alpha from cells. Nature 1997, 385, 729–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozinsky, A.; Underhill, D.M.; Fontenot, J.D.; Hajjar, A.M.; Smith, K.D.; Wilson, C.B.; Schroeder, L.; Aderem, A. The repertoire for pattern recognition of pathogens by the innate immune system is defined by cooperation between toll-like receptors. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2000, 97, 13766–13771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kang, J.Y.; Nan, X.; Jin, M.S.; Youn, S.J.; Ryu, Y.H.; Mah, S.; Han, S.H.; Lee, H.; Paik, S.G.; Lee, J.O. Recognition of lipopeptide patterns by Toll-like receptor 2-Toll-like receptor 6 heterodimer. Immunity 2009, 31, 873–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Buwitt-Beckmann, U.; Heine, H.; Wiesmüller, K.H.; Jung, G.; Brock, R.; Akira, S.; Ulmer, A.J. Toll-like receptor 6-independent signaling by diacylated lipopeptides. Europ. J. Immunol. 2005, 35, 282–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buwitt-Beckmann, U.; Heine, H.; Wiesmüller, K.H.; Jung, G.; Brock, R.; Akira, S.; Ulmer, A.J. TLR1- and TLR6-independent recognition of bacterial lipopeptides. J. Biol. Chem. 2006, 281, 9049–9057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jimenez-Dalmaroni, M.J.; Xiao, N.; Corper, A.L.; Verdino, P.; Ainge, G.D.; Larsen, D.S.; Painter, G.F.; Rudd, P.M.; Dwek, R.A.; Hoebe, K.; et al. Soluble CD36 ectodomain binds negatively charged diacylglycerol ligands and acts as a co-receptor for TLR2. PLoS ONE 2009, 4, e7411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marre, M.L.; Petnicki-Ocwieja, T.; DeFrancesco, A.S.; Darcy, C.T.; Hu, L.T. Human integrin α(3)β(1) regulates TLR2 recognition of lipopeptides from endosomal compartments. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e12871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hajishengallis, G.; Wang, M.; Liang, S.; Triantafilou, M.; Triantafilou, K. Pathogen induction of CXCR4/TLR2 cross-talk impairs host defense function. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 13532–13537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Van Bergenhenegouwen, J.; Plantinga, T.S.; Joosten, L.A.; Netea, M.G.; Folkerts, G.; Kraneveld, A.D.; Garssen, J.; Vos, A.P. TLR2 & Co: A critical analysis of the complex interactions between TLR2 and coreceptors. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2013, 94, 885–902. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.; Zhou, J.; Ma, D.; Lu, X.; Ming, S.; Shan, G.; Zhang, X.; Hou, J.; Chen, Z.; Zuo, D. Mannan binding lectin attenuates double-stranded RNA-mediated TLR3 activation and innate immunity. FEBS Lett. 2014, 588, 866–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bagchi, A.; Herrup, E.A.; Warren, H.S.; Trigilio, J.; Shin, H.S.; Valentine, C.; Hellman, J. MyD88-dependent and MyD88-independent pathways in synergy, priming, and tolerance between TLR agonists. J. Immunol. 2007, 178, 1164–1171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bohnenkamp, H.R.; Papazisis, K.T.; Burchell, J.M.; Taylor-Papadimitriou, J. Synergism of Toll-like receptor-induced interleukin-12p70 secretion by monocyte-derived dendritic cells is mediated through p38 MAPK and lowers the threshold of T-helper cell type 1 responses. Cell Immunol. 2007, 247, 72–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, M.S.; Lee, J.O. Structures of TLR-ligand complexes. Curr. Opin. Immunol. 2008, 20, 414–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mäkelä, S.M.; Strengell, M.; Pietilä, T.E.; Osterlund, P.; Julkunen, I. Multiple signaling pathways contribute to synergistic TLR ligand-dependent cytokine gene expression in human monocyte-derived macrophages and dendritic cells. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2009, 85, 664–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Napolitani, G.; Rinaldi, A.; Bertoni, F.; Sallusto, F.; Lanzavecchia, A. Selected Toll-like receptor agonist combinations synergistically trigger a T helper type 1-polarizing program in dendritic cells. Nat. Immunol. 2005, 6, 769–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lien, E.; Sellati, T.J.; Yoshimura, A.; Flo, T.H.; Rawadi, G.; Finberg, R.W.; Carroll, J.D.; Espevik, T.; Ingalls, R.R.; Radolf, J.D.; et al. Toll-like receptor 2 functions as a pattern recognition receptor for diverse bacterial products. J. Biol. Chem. 1999, 274, 33419–33425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nishiguchi, M.; Matsumoto, M.; Takao, T.; Hoshino, M.; Shimonishi, Y.; Tsuji, S.; Begum, N.A.; Takeuchi, O.; Akira, S.; Toyoshima, K.; et al. Mycoplasma fermentans lipoprotein M161Ag-induced cell activation is mediated by Toll-like receptor 2: Role of N-terminal hydrophobic portion in its multiple functions. J. Immunol. 2001, 166, 2610–2616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Georgieva, E.; Leber, S.L.; Wex, C.; Garbers, C. Perturbation of the actin cytoskeleton in human hepatoma cells influences Interleukin-6 (IL-6) signaling, but not soluble IL-6 receptor generation or NF-κB activation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 7171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayden, M.S.; Ghosh, S. Regulation of NF-κB by TNF family cytokines. Sem. Immunol. 2014, 26, 253–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schroder, K.; Tschopp, J. The inflammasomes. Cell 2010, 140, 821–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yanai, H.; Ban, T.; Wang, Z.; Choi, M.K.; Kawamura, T.; Negishi, H.; Nakasato, M.; Lu, Y.; Hangai, S.; Koshiba, R.; et al. HMGB proteins function as universal sentinels for nucleic-acid-mediated innate immune responses. Nature 2009, 462, 99–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Youn, J.H.; Oh, Y.J.; Kim, E.S.; Choi, J.Y.; Shin, J.-S. High mobility group box 1 protein binding to lipopolysaccharide facilitates transfer of lipopolysaccharide to CD14 and enhances lipopolysaccharide-mediated TNF-alpha production in monocytes. J. Immunol. 2008, 180, 5067–5074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Samy, R.P.; Lim, L.H. DAMPs and influenza virus infection in ageing. Ageing Res. Rev. 2015, 24, 83–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]











Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Grote, K.; Nicolai, M.; Schubert, U.; Schieffer, B.; Troidl, C.; Preissner, K.T.; Bauer, S.; Fischer, S. Extracellular Ribosomal RNA Acts Synergistically with Toll-like Receptor 2 Agonists to Promote Inflammation. Cells 2022, 11, 1440. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells11091440
Grote K, Nicolai M, Schubert U, Schieffer B, Troidl C, Preissner KT, Bauer S, Fischer S. Extracellular Ribosomal RNA Acts Synergistically with Toll-like Receptor 2 Agonists to Promote Inflammation. Cells. 2022; 11(9):1440. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells11091440
Chicago/Turabian StyleGrote, Karsten, Marina Nicolai, Uwe Schubert, Bernhard Schieffer, Christian Troidl, Klaus T. Preissner, Stefan Bauer, and Silvia Fischer. 2022. "Extracellular Ribosomal RNA Acts Synergistically with Toll-like Receptor 2 Agonists to Promote Inflammation" Cells 11, no. 9: 1440. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells11091440
APA StyleGrote, K., Nicolai, M., Schubert, U., Schieffer, B., Troidl, C., Preissner, K. T., Bauer, S., & Fischer, S. (2022). Extracellular Ribosomal RNA Acts Synergistically with Toll-like Receptor 2 Agonists to Promote Inflammation. Cells, 11(9), 1440. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells11091440