Identification of CD203c as a New Basophil-Specific Flow-Marker in Ph+ Chronic Myeloid Leukemia
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. CML Patients and Controls
2.2. Monoclonal Antibodies (mAb) and Other Reagents
2.3. Multi-Color Flow Cytometry
2.4. Purification of CML Basophils and Quantitative PCR (qPCR)
2.5. Incubation of Basophils with Anti-IgE Antibody or with Targeted Drugs
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. CD203c Is a Novel Biomarker of Blood Basophils in CML
3.2. CML Basophils Express Higher Baseline Levels of CD203c Than Normal Basophils
3.3. The Numbers of CD203c+ Cells and the Levels of CD203c on Basophils Decrease after Successful Treatment with Imatinib
3.4. CML Basophils Express CD203c Independent of BCR::ABL1 Kinase Activity
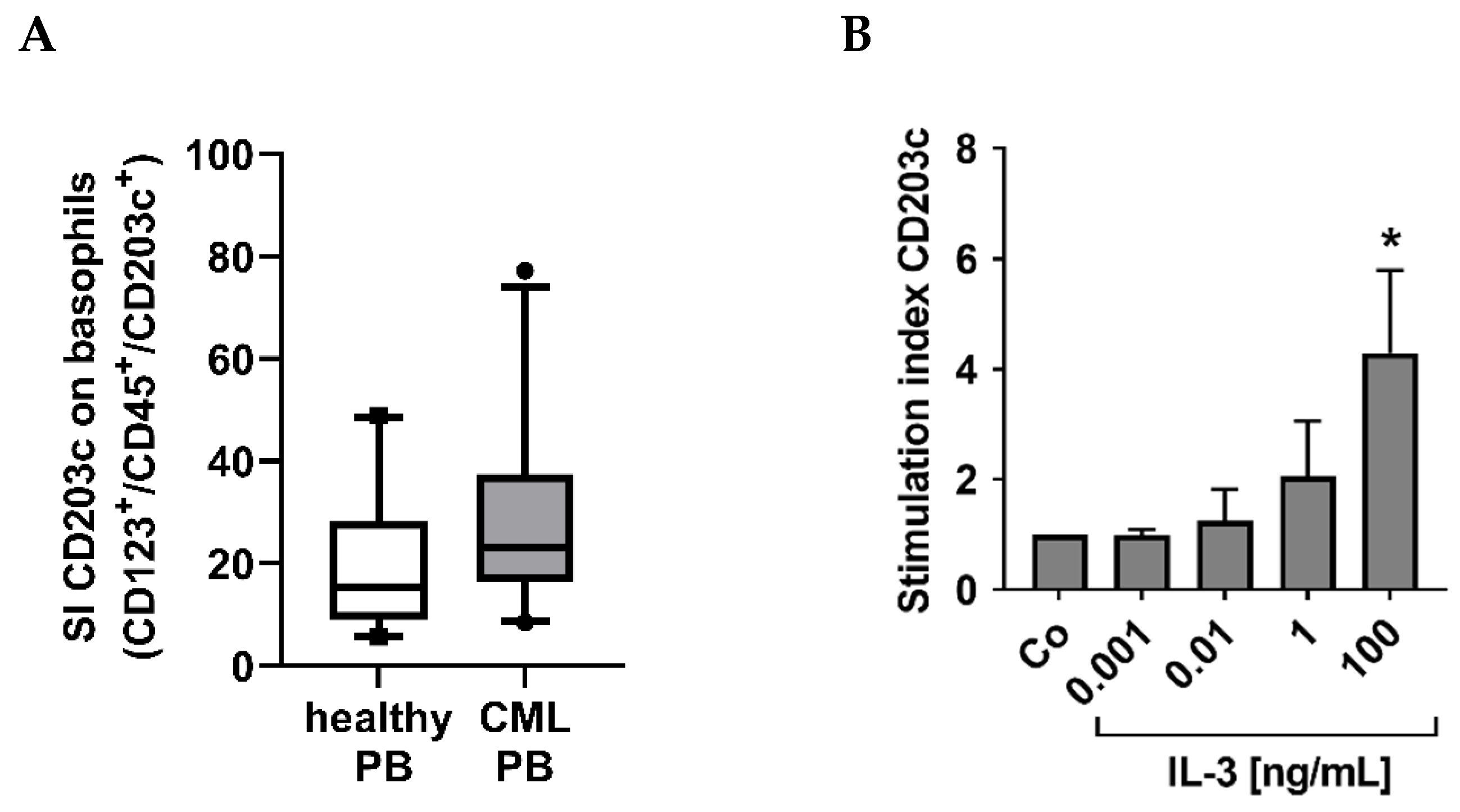
3.5. Cross-Linking of the IgE Receptor on Basophils Is Associated with an Increased Expression of CD203c on CML Basophils
3.6. The Numbers and Percentage of CD203c+ Cells at Diagnosis Correlate with the Risk Category Defined by the SOKAL and EUTOS Scores
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rowley, J.D. A new consistent chromosomal abnormality in chronic myelogenous leukaemia identified by quinacrine fluorescence and Giemsa staining. Nature 1973, 243, 290–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faderl, S.; Talpaz, M.; Estrov, Z.; O’Brien, S.; Kurzrock, R.; Kantarjian, H.M. The biology of chronic myeloid leukemia. N. Engl. J. Med. 1999, 341, 164–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Melo, J.V.; Barnes, D.J. Chronic myeloid leukaemia as a model of disease evolution in human cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2007, 7, 441–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giles, F.J.; Cortes, J.E.; Kantarjian, H.M.; O’Brien, S.M. Accelerated and blastic phases of chronic myelogenous leukemia. Hematol. Oncol. Clin. N. Am. 2004, 18, 753–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Druker, B.J.; Guilhot, F.; O’Brien, S.G.; Gathmann, I.; Kantarjian, H.; Gattermann, N.; Deininger, M.W.; Silver, R.T.; Goldman, J.M.; Stone, R.M.; et al. Five-year follow-up of patients receiving imatinib for chronic myeloid leukemia. N. Engl. J. Med. 2006, 355, 2408–2417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hochhaus, A.; Larson, R.A.; Guilhot, F.; Radich, J.P.; Branford, S.; Hughes, T.P.; Baccarani, M.; Deininger, M.W.; Cervantes, F.; Fujihara, S.; et al. Long-Term Outcomes of Imatinib Treatment for Chronic Myeloid Leukemia. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 376, 917–927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hehlmann, R.; Lauseker, M.; Saußele, S.; Pfirrmann, M.; Krause, S.; Kolb, H.J.; Neubauer, A.; Hossfeld, D.K.; Nerl, C.; Gratwohl, A.; et al. Assessment of imatinib as first-line treatment of chronic myeloid leukemia: 10-year survival results of the randomized CML study IV and impact of non-CML determinants. Leukemia 2017, 31, 2398–2406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, N.P. Advanced CML: Therapeutic options for patients in accelerated and blast phases. J. Natl. Compr. Cancer Netw. 2008, 6, S31–S36. [Google Scholar]
- Deininger, M.W. Diagnosing and managing advanced chronic myeloid leukemia. Am. Soc. Clin. Oncol. Educ. Book 2015, 35, 381–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hehlmann, R.; Saußele, S.; Voskanyan, A.; Silver, R.T. Management of CML-blast crisis. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Haematol. 2016, 29, 295–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denburg, J.A.; Wilson, W.E.; Bienenstock, J. Basophil production in myeloproliferative disorders: Increases during acute blastic transformation of chronic myeloid leukemia. Blood 1982, 60, 113–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kantarjian, H.M.; Dixon, D.; Keating, M.J.; Talpaz, M.; Walters, R.S.; McCredie, K.B.; Freireich, E.J. Characteristics of accelerated disease in chronic myelogenous leukemia. Cancer 1988, 61, 1441–1446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hasford, J.; Pfirrmann, M.; Hehlmann, R.; Allan, N.C.; Baccarani, M.; Kluin-Nelemans, J.C.; Alimena, G.; Steegmann, J.L.; Ansari, H. A new prognostic score for survival of patients with chronic myeloid leukemia treated with interferon alfa. Writing Committee for the Collaborative CML Prognostic Project Group. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 1998, 90, 850–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Steegmann, J.L.; Odriozola, J.; Rodriguez-Salvanés, F.; Giraldo, P.; García-Laraña, J.; Ferro, M.T.; Benítez, E.; Pérez-Pons, C.; Giralt, M.; Escribano, L.; et al. Stage, percentage of basophils at diagnosis, hematologic response within six months, cytogenetic response in the first year: The main prognostic variables affecting outcome in patients with chronic myeloid leukemia in chronic phase treated with interferon-alpha. Results of the CML89 trial of the Spanish Collaborative Group on interferon-alpha2a and CML. Haematologica 1999, 84, 978–987. [Google Scholar]
- Hasford, J.; Baccarani, M.; Hoffmann, V.; Guilhot, J.; Saussele, S.; Rosti, G.; Guilhot, F.; Porkka, K.; Ossenkoppele, G.; Lindoerfer, D.; et al. Predicting complete cytogenetic response and subsequent progression-free survival in 2060 patients with CML on imatinib treatment: The EUTOS score. Blood 2011, 118, 686–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Valent, P.; Agis, H.; Sperr, W.; Sillaber, C.; Horny, H.P. Diagnostic and prognostic value of new biochemical and immunohistochemical parameters in chronic myeloid leukemia. Leuk. Lymphoma 2008, 49, 635–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valent, P.; Horny, H.P.; Arock, M. The underestimated role of basophils in Ph+ chronic myeloid leukemia. Eur. J. Clin. Investig. 2018, 48, e13000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Agis, H.; Sperr, W.R.; Herndlhofer, S.; Semper, H.; Pirc-Danoewinata, H.; Haas, O.A.; Mannhalter, C.; Esterbauer, H.; Geissler, K.; Sillaber, C.; et al. Clinical and prognostic significance of histamine monitoring in patients with CML during treatment with imatinib (STI571). Ann. Oncol. 2007, 18, 1834–1841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sperr, W.R.; Pfeiffer, T.; Hoermann, G.; Herndlhofer, S.; Sillaber, C.; Mannhalter, C.; Kundi, M.; Valent, P. Serum-tryptase at diagnosis: A novel biomarker improving prognostication in Ph(+) CML. Am. J. Cancer Res. 2014, 5, 354–362. [Google Scholar]
- Bühring, H.J.; Simmons, P.J.; Pudney, M.; Müller, R.; Jarrossay, D.; van Agthoven, A.; Willheim, M.; Brugger, W.; Valent, P.; Kanz, L. The monoclonal antibody 97A6 defines a novel surface antigen expressed on human basophils and their multipotent and unipotent progenitors. Blood 1999, 94, 2343–2356. [Google Scholar]
- Bühring, H.J.; Seiffert, M.; Giesert, C.; Marxer, A.; Kanz, L.; Valent, P.; Sano, K. The basophil activation marker defined by antibody 97A6 is identical to the ectonucleotide pyrophosphatase/phosphodiesterase 3. Blood 2001, 97, 3303–3305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ghannadan, M.; Hauswirth, A.W.; Schernthaner, G.H.; Müller, M.R.; Klepetko, W.; Schatzl, G.; Sperr, W.R.; Bühring, H.J.; Valent, P. Detection of novel CD antigens on the surface of human mast cells and basophils. Int. Arch. Allergy Immunol. 2002, 127, 299–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hauswirth, A.W.; Natter, S.; Ghannadan, M.; Majlesi, Y.; Schernthaner, G.H.; Sperr, W.R.; Bühring, H.J.; Valenta, R.; Valent, P. Recombinant allergens promote expression of CD203c on basophils in sensitized individuals. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2002, 110, 102–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buehring, H.J.; Streble, A.; Valent, P. The basophil-specific ectoenzyme E-NPP3 (CD203c) as a marker for cell activation and allergy diagnosis. Int. Arch. Allergy Immunol. 2004, 133, 317–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hauswirth, A.W.; Escribano, L.; Prados, A.; Nuñez, R.; Mirkina, I.; Kneidinger, M.; Florian, S.; Sonneck, K.; Vales, A.; Schernthaner, G.H.; et al. CD203c is overexpressed on neoplastic mast cells in systemic mastocytosis and is upregulated upon IgE receptor cross-linking. Int. J. Immunopathol. Pharmacol. 2008, 21, 797–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cerny-Reiterer, S.; Ghanim, V.; Hoermann, G.; Aichberger, K.J.; Herrmann, H.; Muellauer, L.; Repa, A.; Sillaber, C.; Walls, A.F.; Mayerhofer, M.; et al. Identification of basophils as a major source of hepatocyte growth factor in chronic myeloid leukemia: A novel mechanism of BCR-ABL1-independent disease progression. Neoplasia 2012, 14, 572–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Valent, P.; Sotlar, K.; Blatt, K.; Hartmann, K.; Reiter, A.; Sadovnik, I.; Sperr, W.R.; Bettelheim, P.; Akin, C.; Bauer, K.; et al. Proposed diagnostic criteria and classification of basophilic leukemias and related disorders. Leukemia 2017, 31, 788–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sperr, W.R.; El-Samahi, A.; Kundi, M.; Girschikofsky, M.; Winkler, S.; Lutz, D.; Endler, G.; Rumpold, H.; Agis, H.; Sillaber, C.; et al. Elevated tryptase levels selectively cluster in myeloid neoplasms: A novel diagnostic approach and screen marker in clinical haematology. Eur. J. Clin. Investig. 2009, 39, 914–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valent, P.; Sperr, W.R.; Sotlar, K.; Reiter, A.; Akin, C.; Gotlib, J.; Horny, H.P.; Arock, M. The serum tryptase test: An emerging robust biomarker in clinical hematology. Exp. Rev. Hematol. 2014, 7, 683–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hauswirth, A.W.; Sonneck, K.; Florian, S.M.; Krauth, M.T.; Bohm, A.; Sperr, W.R.; Valenta, R.; Schernthaner, G.H.; Printz, D.; Fritsch, G.; et al. Interleukin-3 promotes the expression of E-NPP3/CD203C on human blood basophils in healthy subjects and in patients with birch pollen allergy. Int. J. Immunopathol. Pharmacol. 2007, 20, 267–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smiljkovic, D.; Herrmann, H.; Sadovnik, I.; Gamperl, S.; Berger, D.; Stefanzl, G.; Eisenwort, G.; Hoermann, G.; Kopanja, S.; Dorofeeva, Y.; et al. Expression and Regulation of Siglec-6 (CD327) on Human Mast Cells and Basophils. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2022; in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bosma, T.J.; Kennedy, M.A.; Bodger, M.P.; Hollings, P.E.; Fitzgerald, P.H. Basophils exhibit rearrangement of the bcr gene in Philadelphia chromosome-positive chronic myeloid leukemia. Leukemia 1988, 2, 141–143. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bodger, M.P.; Morris, C.M.; Kennedy, M.A.; Bowen, J.A.; Hilton, J.M.; Fitzgerald, P.H. Basophils (Bsp-1+) derive from the leukemic clone in human myeloid leukemias involving the chromosome breakpoint 9q34. Blood 1989, 73, 777–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Vardiman, J.W.; Melo, J.; Baccarani, M.; Thiele, J. Chronic myelogenous leukemia, BCR/ABL1 positive. In WHO Classification of Tumours of Haematopoietic and Lymphoid Tissues, 4th ed.; Swerdlow, S.H., Campo, E., Harris, N.L., Eds.; IARC Press: Lyon, France, 2008; pp. 32–37. [Google Scholar]
- Sokal, J.E.; Cox, E.B.; Baccarani, M.; Tura, S.; Gomez, G.A.; Robertson, J.E.; Tso, C.Y.; Braun, T.J.; Clarkson, B.D.; Cervantes, F.; et al. Prognostic discrimination in “good-risk” chronic granulocytic leukemia. Blood 1984, 63, 789–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baccarani, M.; Saglio, G.; Goldman, J.; Hochhaus, A.; Simonsson, B.; Appelbaum, F.; Apperley, J.; Cervantes, F.; Cortes, J.; Deininger, M.; et al. European LeukemiaNet. Evolving concepts in the management of chronic myeloid leukemia: Recommendations from an expert panel on behalf of the European LeukemiaNet. Blood 2006, 108, 1809–1820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Baccarani, M.; Cortes, J.; Pane, F.; Niederwieser, D.; Saglio, G.; Apperley, J.; Cervantes, F.; Deininger, M.; Gratwohl, A.; Guilhot, F.; et al. European LeukemiaNet. Chronic myeloid leukemia: An update of concepts and management recommendations of European LeukemiaNet. J. Clin. Oncol. 2009, 27, 6041–6051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Martinelli, G.; Iacobucci, I.; Soverini, S.; Cilloni, D.; Saglio, G.; Pane, F.; Baccarani, M. Monitoring minimal residual disease and controlling drug resistance in chronic myeloid leukaemia patients in treatment with imatinib as a guide to clinical management. Hematol. Oncol. 2006, 24, 196–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hughes, T.; Deininger, M.; Hochhaus, A.; Branford, S.; Radich, J.; Kaeda, J.; Baccarani, M.; Cortes, J.; Cross, N.C.; Druker, B.J.; et al. Monitoring CML patients responding to treatment with tyrosine kinase inhibitors: Review and recommendations for harmonizing current methodology for detecting BCR-ABL transcripts and kinase domain mutations and for expressing results. Blood 2006, 108, 28–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Müller, M.C.; Cross, N.C.; Erben, P.; Schenk, T.; Hanfstein, B.; Ernst, T.; Hehlmann, R.; Branford, S.; Saglio, G.; Hochhaus, A. Harmonization of molecular monitoring of CML therapy in Europe. Leukemia 2009, 23, 1957–1963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Herrmann, H.; Cerny-Reiterer, S.; Gleixner, K.V.; Blatt, K.; Herndlhofer, S.; Rabitsch, W.; Jäger, E.; Mitterbauer-Hohendanner, G.; Streubel, B.; Selzer, E.; et al. CD34(+)/CD38(−) stem cells in chronic myeloid leukemia express Siglec-3 (CD33) and are responsive to the CD33-targeting drug gemtuzumab/ozogamicin. Haematologica 2012, 97, 219–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]








| Normal PB | Control BM | CML PB | CML BM | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Basophils CD45+/CD123+/CD203c+/CD14− | ++ | ++ | ++ | ++ |
| T cells CD45+/CD3+/CD19− | − | − | − | − |
| B cells CD45+/CD19+/CD3− | − | − | − | − |
| Monocytes CD45+/CD14+/CD123− | − | − | − | − |
| NK cells CD45+/CD56+/CD3− | − | − | − | − |
| Neutrophils CD45+/CD16+ | − | − | − | − |
| Eosinophils CD45+/SSChigh | − | − | − | − |
| Mast cells CD45+/CD117+/CD34− | n.a. | +/− ** | n.a. | +/− |
| Stem/progenitor cells CD34+/CD45+ | n.a. | − * | n.a. | − * |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sadovnik, I.; Ivanov, D.; Smiljkovic, D.; Stefanzl, G.; Degenfeld-Schonburg, L.; Herndlhofer, S.; Eisenwort, G.; Hauswirth, A.W.; Sliwa, T.; Keil, F.; et al. Identification of CD203c as a New Basophil-Specific Flow-Marker in Ph+ Chronic Myeloid Leukemia. Cells 2023, 12, 3. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells12010003
Sadovnik I, Ivanov D, Smiljkovic D, Stefanzl G, Degenfeld-Schonburg L, Herndlhofer S, Eisenwort G, Hauswirth AW, Sliwa T, Keil F, et al. Identification of CD203c as a New Basophil-Specific Flow-Marker in Ph+ Chronic Myeloid Leukemia. Cells. 2023; 12(1):3. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells12010003
Chicago/Turabian StyleSadovnik, Irina, Daniel Ivanov, Dubravka Smiljkovic, Gabriele Stefanzl, Lina Degenfeld-Schonburg, Susanne Herndlhofer, Gregor Eisenwort, Alexander W. Hauswirth, Thamer Sliwa, Felix Keil, and et al. 2023. "Identification of CD203c as a New Basophil-Specific Flow-Marker in Ph+ Chronic Myeloid Leukemia" Cells 12, no. 1: 3. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells12010003
APA StyleSadovnik, I., Ivanov, D., Smiljkovic, D., Stefanzl, G., Degenfeld-Schonburg, L., Herndlhofer, S., Eisenwort, G., Hauswirth, A. W., Sliwa, T., Keil, F., Sperr, W. R., & Valent, P. (2023). Identification of CD203c as a New Basophil-Specific Flow-Marker in Ph+ Chronic Myeloid Leukemia. Cells, 12(1), 3. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells12010003







