Integrins and Actions of Androgen in Breast Cancer
Abstract
:1. Introduction
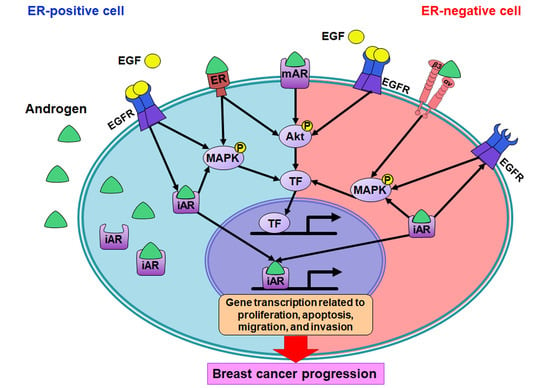
2. Androgen-Induced Signal Transduction in Breast Cancer Cells
3. Integrin-Related Signals in Breast Cancers
4. Interaction between Androgen and Integrins
5. Androgen, Integrin αvβ3, and PD-L1 Expression in Cancer Cells
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- Yin, L.; Duan, J.J.; Bian, X.W.; Yu, S.C. Triple-negative breast cancer molecular subtyping and treatment progress. Breast Cancer Res. 2020, 22, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.; Spezia, M.; Huang, S.; Yuan, C.; Zeng, Z.; Zhang, L.; Ji, X.; Liu, W.; Huang, B.; Luo, W.; et al. Breast cancer development and progression: Risk factors, cancer stem cells, signaling pathways, genomics, and molecular pathogenesis. Genes Dis. 2018, 5, 77–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levin, E.R. Membrane oestrogen receptor alpha signalling to cell functions. J. Physiol. 2009, 587, 5019–5023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Birrell, S.N.; Bentel, J.M.; Hickey, T.E.; Ricciardelli, C.; Weger, M.A.; Horsfall, D.J.; Tilley, W.D. Androgens induce divergent proliferative responses in human breast cancer cell lines. J. Steroid. Biochem. Mol. Biol. 1995, 52, 459–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, M.; Shi, H. Sex Hormones and Their Receptors Regulate Liver Energy Homeostasis. Int. J. Endocrinol. 2015, 2015, 294278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Collignon, J.; Lousberg, L.; Schroeder, H.; Jerusalem, G. Triple-negative breast cancer: Treatment challenges and solutions. Breast Cancer (Dove Med. Press.) 2016, 8, 93–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szelei, J.; Jimenez, J.; Soto, A.M.; Luizzi, M.F.; Sonnenschein, C. Androgen-induced inhibition of proliferation in human breast cancer MCF7 cells transfected with androgen receptor. Endocrinology 1997, 138, 1406–1412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greeve, M.A.; Allan, R.K.; Harvey, J.M.; Bentel, J.M. Inhibition of MCF-7 breast cancer cell proliferation by 5alpha-dihydrotestosterone; a role for p21(Cip1/Waf1). J. Mol. Endocrinol. 2004, 32, 793–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, H.Y.; Sun, M.; Lin, C.; Tang, H.Y.; London, D.; Shih, A.; Davis, F.B.; Davis, P.J. Androgen-induced human breast cancer cell proliferation is mediated by discrete mechanisms in estrogen receptor-alpha-positive and -negative breast cancer cells. J. Steroid. Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2009, 113, 182–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chin, Y.T.; Yang, S.H.; Chang, T.C.; Changou, C.A.; Lai, H.Y.; Fu, E.; HuangFu, W.C.; Davis, P.J.; Lin, H.Y.; Liu, L.F. Mechanisms of dihydrotestosterone action on resveratrol-induced anti-proliferation in breast cancer cells with different ERα status. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 35866–35879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alkaabi, D.; Arafat, K.; Sulaiman, S.; Al-Azawi, A.M.; Attoub, S. PD-1 Independent Role of PD-L1 in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer Progression. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 6420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Labrie, F.; Luu-The, V.; Martel, C.; Chernomoretz, A.; Calvo, E.; Morissette, J.; Labrie, C. Dehydroepiandrosterone (DHEA) is an anabolic steroid like dihydrotestosterone (DHT), the most potent natural androgen, and tetrahydrogestrinone (THG). J. Steroid. Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2006, 100, 52–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lonergan, P.E.; Tindall, D.J. Androgen receptor signaling in prostate cancer development and progression. J. Carcinog. 2011, 10, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanamura, T.; Christenson, J.L.; O’Neill, K.I.; Rosas, E.; Spoelstra, N.S.; Williams, M.M.; Richer, J.K. Secreted indicators of androgen receptor activity in breast cancer pre-clinical models. Breast Cancer Res. 2021, 23, 102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Yan, F.; Lei, X.; Wei, D.; Lu, H.; Zhu, Z.; Xiang, A.; Ye, Z.; Wang, L.; Zheng, W.; et al. Androgen receptor-mediated upregulation of quaking affects androgen receptor-related prostate cancer development and anti-androgen receptor therapy. Mol. Med. Rep. 2018, 17, 8203–8211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Zhou, D.; Chen, S. SGK3 is an androgen-inducible kinase promoting prostate cancer cell proliferation through activation of p70 S6 kinase and up-regulation of cyclin D1. Mol. Endocrinol. 2014, 28, 935–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Acharya, S.; Anand, S.; Khan, M.A.; Zubair, H.; Srivastava, S.K.; Singh, S.; Singh, A.P. Biphasic transcriptional and posttranscriptional regulation of MYB by androgen signaling mediates its growth control in prostate cancer. J. Biol. Chem. 2023, 299, 102725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agoff, S.N.; Swanson, P.E.; Linden, H.; Hawes, S.E.; Lawton, T.J. Androgen receptor expression in estrogen receptor-negative breast cancer. Immunohistochemical, clinical, and prognostic associations. Am. J. Clin. Pathol. 2003, 120, 725–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, S.; Yousefi, H.; Savage, I.V.; Okpechi, S.C.; Wright, M.K.; Matossian, M.D.; Collins-Burow, B.M.; Burow, M.E.; Alahari, S.K. Ceritinib is a novel triple negative breast cancer therapeutic agent. Mol. Cancer 2022, 21, 138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farmer, P.; Bonnefoi, H.; Becette, V.; Tubiana-Hulin, M.; Fumoleau, P.; Larsimont, D.; Macgrogan, G.; Bergh, J.; Cameron, D.; Goldstein, D.; et al. Identification of molecular apocrine breast tumours by microarray analysis. Oncogene 2005, 24, 4660–4671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doane, A.S.; Danso, M.; Lal, P.; Donaton, M.; Zhang, L.; Hudis, C.; Gerald, W.L. An estrogen receptor-negative breast cancer subset characterized by a hormonally regulated transcriptional program and response to androgen. Oncogene 2006, 25, 3994–4008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pietri, E.; Conteduca, V.; Andreis, D.; Massa, I.; Melegari, E.; Sarti, S.; Cecconetto, L.; Schirone, A.; Bravaccini, S.; Serra, P.; et al. Androgen receptor signaling pathways as a target for breast cancer treatment. Endocr. Relat. Cancer 2016, 23, R485–R498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lehmann, B.D.; Bauer, J.A.; Chen, X.; Sanders, M.E.; Chakravarthy, A.B.; Shyr, Y.; Pietenpol, J.A. Identification of human triple-negative breast cancer subtypes and preclinical models for selection of targeted therapies. J. Clin. Investig. 2011, 121, 2750–2767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ho, Y.; Li, Z.L.; Shih, Y.J.; Chen, Y.R.; Wang, K.; Whang-Peng, J.; Lin, H.Y.; Davis, P.J. Integrin αvβ3 in the Mediating Effects of Dihydrotestosterone and Resveratrol on Breast Cancer Cell Proliferation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 2906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Papakonstanti, E.A.; Kampa, M.; Castanas, E.; Stournaras, C. A rapid, nongenomic, signaling pathway regulates the actin reorganization induced by activation of membrane testosterone receptors. Mol. Endocrinol. 2003, 17, 870–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Liu, L.; Hou, J.; Wen, D.; Yan, C.; Pu, J.; Ouyang, J.; Pan, H. Rapid membrane effect of testosterone in LNCaP cells. Urol. Int. 2008, 81, 353–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kallergi, G.; Agelaki, S.; Markomanolaki, H.; Georgoulias, V.; Stournaras, C. Activation of FAK/PI3K/Rac1 signaling controls actin reorganization and inhibits cell motility in human cancer cells. Cell Physiol. Biochem. 2007, 20, 977–986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.; Honisch, S.; Liu, G.; Schmidt, S.; Pantelakos, S.; Alkahtani, S.; Toulany, M.; Lang, F.; Stournaras, C. Inhibition of SGK1 enhances mAR-induced apoptosis in MCF-7 breast cancer cells. Cancer Biol. Ther. 2015, 16, 52–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Du, J.; Hu, Z.; Liu, J.; Tian, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Wang, L.; Gu, L. Activation of Rac1-PI3K/Akt is required for epidermal growth factor-induced PAK1 activation and cell migration in MDA-MB-231 breast cancer cells. J. Biomed. Res. 2011, 25, 237–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Meng, J.; Wang, Z.Y. A switch role of Src in the biphasic EGF signaling of ER-negative breast cancer cells. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e41613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moerkens, M.; Zhang, Y.; Wester, L.; van de Water, B.; Meerman, J.H. Epidermal growth factor receptor signalling in human breast cancer cells operates parallel to estrogen receptor α signalling and results in tamoxifen insensitive proliferation. BMC Cancer 2014, 14, 283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, T.; Zhu, Q.; Li, X.; Zhu, G.; Deng, S.; Wang, Y.; Ni, L.; Chen, X.; Zhang, Y.; Xia, T.; et al. Protease Nexin I is a feedback regulator of EGF/PKC/MAPK/EGR1 signaling in breast cancer cells metastasis and stemness. Cell Death Dis. 2019, 10, 649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naderi, A.; Hughes-Davies, L. A functionally significant cross-talk between androgen receptor and ErbB2 pathways in estrogen receptor negative breast cancer. Neoplasia 2008, 10, 542–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vranic, S.; Tawfik, O.; Palazzo, J.; Bilalovic, N.; Eyzaguirre, E.; Lee, L.M.; Adegboyega, P.; Hagenkord, J.; Gatalica, Z. EGFR and HER-2/neu expression in invasive apocrine carcinoma of the breast. Mod. Pathol. 2010, 23, 644–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chia, K.; O’Brien, M.; Brown, M.; Lim, E. Targeting the Androgen Receptor in Breast Cancer. Curr. Oncol. Rep. 2015, 17, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castoria, G.; Giovannelli, P.; Di Donato, M.; Hayashi, R.; Arra, C.; Appella, E.; Auricchio, F.; Migliaccio, A. Targeting androgen receptor/Src complex impairs the aggressive phenotype of human fibrosarcoma cells. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e76899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Migliaccio, A.; Castoria, G.; Di Domenico, M.; Ciociola, A.; Lombardi, M.; De Falco, A.; Nanayakkara, M.; Bottero, D.; De Stasio, R.; Varricchio, L.; et al. Crosstalk between EGFR and extranuclear steroid receptors. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2006, 1089, 194–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulkoyluoglu, E.; Madak-Erdogan, Z. Nuclear and extranuclear-initiated estrogen receptor signaling crosstalk and endocrine resistance in breast cancer. Steroids 2016, 114, 41–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuentes, N.; Silveyra, P. Estrogen receptor signaling mechanisms. Adv. Protein Chem. Struct. Biol. 2019, 116, 135–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Migliaccio, A.; Castoria, G.; Di Domenico, M.; de Falco, A.; Bilancio, A.; Lombardi, M.; Barone, M.V.; Ametrano, D.; Zannini, M.S.; Abbondanza, C.; et al. Steroid-induced androgen receptor-oestradiol receptor beta-Src complex triggers prostate cancer cell proliferation. Embo. J. 2000, 19, 5406–5417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giovannelli, P.; Di Donato, M.; Auricchio, F.; Castoria, G.; Migliaccio, A. Androgens Induce Invasiveness of Triple Negative Breast Cancer Cells Through AR/Src/PI3-K Complex Assembly. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 4490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mattila, M.M.; Tarkkonen, K.M.; Seppänen, J.A.; Ruohola, J.K.; Valve, E.M.; Härkönen, P.L. Androgen and fibroblast growth factor 8 (FGF8) downregulation of thrombospondin 1 (TSP1) in mouse breast cancer cells. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2006, 253, 36–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borgenström, M.; Tienhaara, A.; Spillmann, D.; Salmivirta, M.; Jalkanen, M. Testosterone-induced growth of S115 mouse mammary tumor cells is dependent on heparan sulfate. Exp. Cell Res. 2001, 264, 307–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, A.M.; O’Connell, M.J.; Miyamoto, H.; Huang, J.; Yao, J.L.; Messing, E.M.; Reeder, J.E. Androgenic dependence of exophytic tumor growth in a transgenic mouse model of bladder cancer: A role for thrombospondin-1. BMC Urol. 2008, 8, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hickey, T.E.; Selth, L.A.; Chia, K.M.; Laven-Law, G.; Milioli, H.H.; Roden, D.; Jindal, S.; Hui, M.; Finlay-Schultz, J.; Ebrahimie, E.; et al. The androgen receptor is a tumor suppressor in estrogen receptor-positive breast cancer. Nat. Med. 2021, 27, 310–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, L.; Gao, H.; Yu, J.; Zhang, H.; Nguyen, T.T.L.; Gu, Y.; Passow, M.R.; Carter, J.M.; Qin, B.; Boughey, J.C.; et al. Pharmacological Targeting of Androgen Receptor Elicits Context-Specific Effects in Estrogen Receptor-Positive Breast Cancer. Cancer Res. 2023, 83, 456–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shih, Y.W.; Chien, S.T.; Chen, P.S.; Lee, J.H.; Wu, S.H.; Yin, L.T. Alpha-mangostin suppresses phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate-induced MMP-2/MMP-9 expressions via alphavbeta3 integrin/FAK/ERK and NF-kappaB signaling pathway in human lung adenocarcinoma A549 cells. Cell Biochem. Biophys. 2010, 58, 31–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujita, M.; Ieguchi, K.; Cedano-Prieto, D.M.; Fong, A.; Wilkerson, C.; Chen, J.Q.; Wu, M.; Lo, S.H.; Cheung, A.T.; Wilson, M.D.; et al. An integrin binding-defective mutant of insulin-like growth factor-1 (R36E/R37E IGF1) acts as a dominant-negative antagonist of the IGF1 receptor (IGF1R) and suppresses tumorigenesis but still binds to IGF1R. J. Biol. Chem. 2013, 288, 19593–19603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rapraeger, A.C. Synstatin: A selective inhibitor of the syndecan-1-coupled IGF1R-αvβ3 integrin complex in tumorigenesis and angiogenesis. FEBS J. 2013, 280, 2207–2215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, P.J.; Mousa, S.A.; Lin, H.Y. Nongenomic Actions of Thyroid Hormone: The Integrin Component. Physiol. Rev. 2021, 101, 319–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Humphries, M.J. Integrin structure. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 2000, 28, 311–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hynes, R.O. Integrins: Bidirectional, allosteric signaling machines. Cell 2002, 110, 673–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takada, Y.; Ye, X.; Simon, S. The integrins. Genome Biol. 2007, 8, 215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yousefi, H.; Vatanmakanian, M.; Mahdiannasser, M.; Mashouri, L.; Alahari, N.V.; Monjezi, M.R.; Ilbeigi, S.; Alahari, S.K. Understanding the role of integrins in breast cancer invasion, metastasis, angiogenesis, and drug resistance. Oncogene 2021, 40, 1043–1063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ganguly, K.K.; Pal, S.; Moulik, S.; Chatterjee, A. Integrins and metastasis. Cell Adh. Migr. 2013, 7, 251–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindberg, K.; Ström, A.; Lock, J.G.; Gustafsson, J.A.; Haldosén, L.A.; Helguero, L.A. Expression of estrogen receptor beta increases integrin alpha1 and integrin beta1 levels and enhances adhesion of breast cancer cells. J. Cell Physiol. 2010, 222, 156–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wafai, R.; Williams, E.D.; de Souza, E.; Simpson, P.T.; McCart Reed, A.E.; Kutasovic, J.R.; Waltham, M.; Snell, C.E.; Blick, T.; Thompson, E.W.; et al. Integrin alpha-2 and beta-1 expression increases through multiple generations of the EDW01 patient-derived xenograft model of breast cancer-insight into their role in epithelial mesenchymal transition in vivo gained from an in vitro model system. Breast Cancer Res. 2020, 22, 136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Sun, L.; Li, H.; Ai, L.; Ma, Q.; Qiao, X.; Yang, J.; Zhang, H.; Ou, X.; Wang, Y.; et al. Binding blockade between TLN1 and integrin β1 represses triple-negative breast cancer. Elife 2022, 11, e68481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miskin, R.P.; Warren, J.S.A.; Ndoye, A.; Wu, L.; Lamar, J.M.; DiPersio, C.M. Integrin α3β1 Promotes Invasive and Metastatic Properties of Breast Cancer Cells through Induction of the Brn-2 Transcription Factor. Cancers 2021, 13, 480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.X.; Dang, X.T.T.; Vu, L.T.; Lim, C.M.H.; Yeo, E.Y.M.; Lam, B.W.S.; Leong, S.M.; Omar, N.; Putti, T.C.; Yeh, Y.C.; et al. αvβ1 integrin is enriched in extracellular vesicles of metastatic breast cancer cells: A mechanism mediated by galectin-3. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2022, 11, e12234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carter, R.Z.; Micocci, K.C.; Natoli, A.; Redvers, R.P.; Paquet-Fifield, S.; Martin, A.C.; Denoyer, D.; Ling, X.; Kim, S.H.; Tomasin, R.; et al. Tumour but not stromal expression of β3 integrin is essential, and is required early, for spontaneous dissemination of bone-metastatic breast cancer. J. Pathol. 2015, 235, 760–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Drabsch, Y.; Pujuguet, P.; Ren, J.; van Laar, T.; Zhang, L.; van Dam, H.; Clément-Lacroix, P.; Ten Dijke, P. Genetic depletion and pharmacological targeting of αv integrin in breast cancer cells impairs metastasis in zebrafish and mouse xenograft models. Breast Cancer Res. 2015, 17, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lowell, C.A.; Mayadas, T.N. Overview: Studying integrins in vivo. Methods Mol. Biol. 2012, 757, 369–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takayama, S.; Ishii, S.; Ikeda, T.; Masamura, S.; Doi, M.; Kitajima, M. The relationship between bone metastasis from human breast cancer and integrin alpha(v)beta3 expression. Anticancer Res. 2005, 25, 79–83. [Google Scholar]
- Brooks, P.C.; Strömblad, S.; Klemke, R.; Visscher, D.; Sarkar, F.H.; Cheresh, D.A. Antiintegrin alpha v beta 3 blocks human breast cancer growth and angiogenesis in human skin. J. Clin. Investig. 1995, 96, 1815–1822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weis, S.M.; Cheresh, D.A. αV integrins in angiogenesis and cancer. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 2011, 1, a006478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, S.D.; Reynolds, L.E.; Kostourou, V.; Reynolds, A.R.; da Silva, R.G.; Tavora, B.; Baker, M.; Marshall, J.F.; Hodivala-Dilke, K.M. Alphav beta3 integrin limits the contribution of neuropilin-1 to vascular endothelial growth factor-induced angiogenesis. J. Biol. Chem. 2009, 284, 33966–33981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, J.P.; Stehle, T.; Zhang, R.; Joachimiak, A.; Frech, M.; Goodman, S.L.; Arnaout, M.A. Crystal structure of the extracellular segment of integrin alpha Vbeta3 in complex with an Arg-Gly-Asp ligand. Science 2002, 296, 151–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hensley, P.J.; Desiniotis, A.; Wang, C.; Stromberg, A.; Chen, C.S.; Kyprianou, N. Novel pharmacologic targeting of tight junctions and focal adhesions in prostate cancer cells. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e86238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.F.; Yang, Y.N.; Chu, H.R.; Huang, T.Y.; Wang, S.H.; Chen, H.Y.; Li, Z.L.; Yang, Y.S.H.; Lin, H.Y.; Hercbergs, A.; et al. Role of Integrin αvβ3 in Doxycycline-Induced Anti-Proliferation in Breast Cancer Cells. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2022, 10, 829788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.; Son, S.; Ko, Y.; Shin, I. CTGF regulates cell proliferation, migration, and glucose metabolism through activation of FAK signaling in triple-negative breast cancer. Oncogene 2021, 40, 2667–2681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bai, M.; Dong, Y.; Huang, H.; Fu, H.; Duan, Y.; Wang, Q.; Du, L. Tumour targeted contrast enhanced ultrasound imaging dual-modal microbubbles for diagnosis and treatment of triple negative breast cancer. RSC Adv. 2019, 9, 5682–5691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhong, P.; Gu, X.; Cheng, R.; Deng, C.; Meng, F.; Zhong, Z. α(v)β(3) integrin-targeted micellar mertansine prodrug effectively inhibits triple-negative breast cancer in vivo. Int. J. Nanomed. 2017, 12, 7913–7921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lan, K.C.; Wei, K.T.; Lin, P.W.; Lin, C.C.; Won, P.L.; Liu, Y.F.; Chen, Y.J.; Cheng, B.H.; Chu, T.G.; Chen, J.F.; et al. Targeted activation of androgen receptor signaling in the periosteum improves bone fracture repair. Cell Death Dis. 2022, 13, 123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jang, Y.G.; Go, R.E.; Hwang, K.A.; Choi, K.C. Resveratrol inhibits DHT-induced progression of prostate cancer cell line through interfering with the AR and CXCR4 pathway. J. Steroid. Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2019, 192, 105406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siech, C.; Rutz, J.; Maxeiner, S.; Grein, T.; Sonnenburg, M.; Tsaur, I.; Chun, F.K.; Blaheta, R.A. Insulin-like Growth Factor-1 Influences Prostate Cancer Cell Growth and Invasion through an Integrin α3, α5, αV, and β1 Dependent Mechanism. Cancers 2022, 14, 363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, W.L.; Jeng, L.B.; Lai, H.C.; Liao, P.Y.; Chang, C. Androgen receptor enhances cell adhesion and decreases cell migration via modulating β1-integrin-AKT signaling in hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Cancer Lett. 2014, 351, 64–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuzio, P.; Lucarelli, G.; Perlino, E.; Battaglia, M.; Bettocchi, C.; Selvaggi, F.P.; Ditonno, P. Androgen deprivation therapy regulation of beta1C integrin expression in prostate cancer. Oncol. Rep. 2009, 22, 327–335. [Google Scholar]
- Ziaee, S.; Chung, L.W. Induction of integrin α2 in a highly bone metastatic human prostate cancer cell line: Roles of RANKL and AR under three-dimensional suspension culture. Mol. Cancer 2014, 13, 208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evangelou, A.; Letarte, M.; Marks, A.; Brown, T.J. Androgen modulation of adhesion and antiadhesion molecules in PC-3 prostate cancer cells expressing androgen receptor. Endocrinology 2002, 143, 3897–3904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirtti, T.; Nylund, C.; Lehtonen, J.; Hiekkanen, H.; Nissinen, L.; Kallajoki, M.; Alanen, K.; Gullberg, D.; Heino, J. Regulation of prostate cell collagen receptors by malignant transformation. Int. J. Cancer 2006, 118, 889–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, R.; Hensley, P.J.; Li, J.; Zhang, Y.; Stark, T.W.; Heller, A.; Qian, H.; Shi, J.; Liu, Z.; Huang, J.A.; et al. Integrin-associated CD151 is a suppressor of prostate cancer progression. Am. J. Transl. Res. 2020, 12, 1428–1442. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sayeed, A.; Fedele, C.; Trerotola, M.; Ganguly, K.K.; Languino, L.R. IGF-IR promotes prostate cancer growth by stabilizing α5β1 integrin protein levels. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e76513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nollet, E.A.; Cardo-Vila, M.; Ganguly, S.S.; Tran, J.D.; Schulz, V.V.; Cress, A.; Corey, E.; Miranti, C.K. Androgen receptor-induced integrin α6β1 and Bnip3 promote survival and resistance to PI3K inhibitors in castration-resistant prostate cancer. Oncogene 2020, 39, 5390–5404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonaccorsi, L.; Carloni, V.; Muratori, M.; Salvadori, A.; Giannini, A.; Carini, M.; Serio, M.; Forti, G.; Baldi, E. Androgen receptor expression in prostate carcinoma cells suppresses alpha6beta4 integrin-mediated invasive phenotype. Endocrinology 2000, 141, 3172–3182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, H.; Wang, T.; Li, J.; Fedele, C.; Liu, Q.; Zhang, J.; Jiang, Z.; Jain, D.; Iozzo, R.V.; Violette, S.M.; et al. αvβ6 Integrin Promotes Castrate-Resistant Prostate Cancer through JNK1-Mediated Activation of Androgen Receptor. Cancer Res. 2016, 76, 5163–5174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dutta, A.; Li, J.; Lu, H.; Akech, J.; Pratap, J.; Wang, T.; Zerlanko, B.J.; FitzGerald, T.J.; Jiang, Z.; Birbe, R.; et al. Integrin αvβ6 promotes an osteolytic program in cancer cells by upregulating MMP2. Cancer Res. 2014, 74, 1598–1608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De, S.; Razorenova, O.; McCabe, N.P.; O’Toole, T.; Qin, J.; Byzova, T.V. VEGF-integrin interplay controls tumor growth and vascularization. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 7589–7594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quaglia, F.; Krishn, S.R.; Sossey-Alaoui, K.; Rana, P.S.; Pluskota, E.; Park, P.H.; Shields, C.D.; Lin, S.; McCue, P.; Kossenkov, A.V.; et al. The NOGO receptor NgR2, a novel αVβ3 integrin effector, induces neuroendocrine differentiation in prostate cancer. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 18879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quaglia, F.; Krishn, S.R.; Wang, Y.; Goodrich, D.W.; McCue, P.; Kossenkov, A.V.; Mandigo, A.C.; Knudsen, K.E.; Weinreb, P.H.; Corey, E.; et al. Differential expression of αVβ3 and αVβ6 integrins in prostate cancer progression. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0244985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishn, S.R.; Garcia, V.; Naranjo, N.M.; Quaglia, F.; Shields, C.D.; Harris, M.A.; Kossenkov, A.V.; Liu, Q.; Corey, E.; Altieri, D.C.; et al. Small extracellular vesicle-mediated ITGB6 siRNA delivery downregulates the αVβ6 integrin and inhibits adhesion and migration of recipient prostate cancer cells. Cancer Biol. Ther. 2022, 23, 173–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toth, R.K.; Tran, J.D.; Muldong, M.T.; Nollet, E.A.; Schulz, V.V.; Jensen, C.C.; Hazlehurst, L.A.; Corey, E.; Durden, D.; Jamieson, C.; et al. Hypoxia-induced PIM kinase and laminin-activated integrin α6 mediate resistance to PI3K inhibitors in bone-metastatic CRPC. Am. J. Clin. Exp. Urol. 2019, 7, 297–312. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Q.; Kohli, M.; Bergen, H.R., 3rd; Cheville, J.C.; Karnes, R.J.; Cao, H.; Young, C.Y.; Tindall, D.J.; McNiven, M.A.; Donkena, K.V. Preclinical evaluation of the supercritical extract of azadirachta indica (neem) leaves in vitro and in vivo on inhibition of prostate cancer tumor growth. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2014, 13, 1067–1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kallergi, G.; Mavroudis, D.; Georgoulias, V.; Stournaras, C. Phosphorylation of FAK, PI-3K, and impaired actin organization in CK-positive micrometastatic breast cancer cells. Mol. Med. 2007, 13, 79–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hecker, T.P.; Grammer, J.R.; Gillespie, G.Y.; Stewart, J., Jr.; Gladson, C.L. Focal adhesion kinase enhances signaling through the Shc/extracellular signal-regulated kinase pathway in anaplastic astrocytoma tumor biopsy samples. Cancer Res. 2002, 62, 2699–2707. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Rajendran, M.; Thomes, P.; Zhang, L.; Veeramani, S.; Lin, M.F. p66Shc--a longevity redox protein in human prostate cancer progression and metastasis: p66Shc in cancer progression and metastasis. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2010, 29, 207–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Veeramani, S.; Yuan, T.C.; Lin, F.F.; Lin, M.F. Mitochondrial redox signaling by p66Shc is involved in regulating androgenic growth stimulation of human prostate cancer cells. Oncogene 2008, 27, 5057–5068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, S.; Kumar, S.; Rajendran, M.; Alam, S.M.; Lin, F.F.; Cheng, P.W.; Lin, M.F. Steroids up-regulate p66Shc longevity protein in growth regulation by inhibiting its ubiquitination. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e15942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, K.; Chen, Y.F.; Yang, Y.S.H.; Huang, H.M.; Lee, S.Y.; Shih, Y.J.; Li, Z.L.; Whang-Peng, J.; Lin, H.Y.; Davis, P.J. The power of heteronemin in cancers. J. Biomed. Sci. 2022, 29, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, P.J.; Mousa, S.A.; Cody, V.; Tang, H.Y.; Lin, H.Y. Small molecule hormone or hormone-like ligands of integrin αVβ3: Implications for cancer cell behavior. Horm. Cancer 2013, 4, 335–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schütz, F.; Stefanovic, S.; Mayer, L.; von Au, A.; Domschke, C.; Sohn, C. PD-1/PD-L1 Pathway in Breast Cancer. Oncol. Res. Treat. 2017, 40, 294–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hudson, K.; Cross, N.; Jordan-Mahy, N.; Leyland, R. The Extrinsic and Intrinsic Roles of PD-L1 and Its Receptor PD-1: Implications for Immunotherapy Treatment. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 568931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tung, N.; Garber, J.E.; Hacker, M.R.; Torous, V.; Freeman, G.J.; Poles, E.; Rodig, S.; Alexander, B.; Lee, L.; Collins, L.C.; et al. Prevalence and predictors of androgen receptor and programmed death-ligand 1 in BRCA1-associated and sporadic triple-negative breast cancer. NPJ Breast Cancer 2016, 2, 16002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatterjee, S.; Chatterjee, A.; Jana, S.; Dey, S.; Roy, H.; Das, M.K.; Alam, J.; Adhikary, A.; Chowdhury, A.; Biswas, A.; et al. Transforming growth factor beta orchestrates PD-L1 enrichment in tumor-derived exosomes and mediates CD8 T-cell dysfunction regulating early phosphorylation of TCR signalome in breast cancer. Carcinogenesis 2021, 42, 38–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, W.; Hua, Y.; Qiu, H.; Hao, J.; Zou, K.; Li, Z.; Hu, S.; Guo, P.; Chen, M.; Sui, S.; et al. PD-L1 promotes tumor growth and progression by activating WIP and β-catenin signaling pathways and predicts poor prognosis in lung cancer. Cell Death Dis. 2020, 11, 506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, T.Y.; Chang, T.C.; Chin, Y.T.; Pan, Y.S.; Chang, W.J.; Liu, F.C.; Hastuti, E.D.; Chiu, S.J.; Wang, S.H.; Changou, C.A.; et al. NDAT Targets PI3K-Mediated PD-L1 Upregulation to Reduce Proliferation in Gefitinib-Resistant Colorectal Cancer. Cells 2020, 9, 1830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lotfinejad, P.; Kazemi, T.; Safaei, S.; Amini, M.; Roshani Asl, E.; Baghbani, E.; Sandoghchian Shotorbani, S.; Jadidi Niaragh, F.; Derakhshani, A.; Abdoli Shadbad, M.; et al. PD-L1 silencing inhibits triple-negative breast cancer development and upregulates T-cell-induced pro-inflammatory cytokines. Biomed. Pharm. 2021, 138, 111436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soliman, H.; Khalil, F.; Antonia, S. PD-L1 expression is increased in a subset of basal type breast cancer cells. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e88557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mittendorf, E.A.; Philips, A.V.; Meric-Bernstam, F.; Qiao, N.; Wu, Y.; Harrington, S.; Su, X.; Wang, Y.; Gonzalez-Angulo, A.M.; Akcakanat, A.; et al. PD-L1 expression in triple-negative breast cancer. Cancer Immunol. Res. 2014, 2, 361–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, P.; Jin, X.; Fan, Z.; Wang, Z.; Yue, S.; Wu, C.; Chen, S.; Wu, Y.; Chen, M.; Gu, D.; et al. Super-enhancer receives signals from the extracellular matrix to induce PD-L1-mediated immune evasion via integrin/BRAF/TAK1/ERK/ETV4 signaling. Cancer Biol. Med. 2021, 19, 669–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malenica, I.; Adam, J.; Corgnac, S.; Mezquita, L.; Auclin, E.; Damei, I.; Grynszpan, L.; Gros, G.; de Montpréville, V.; Planchard, D.; et al. Integrin-α(V)-mediated activation of TGF-β regulates anti-tumour CD8 T cell immunity and response to PD-1 blockade. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 5209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanamura, T.; Kitano, S.; Kagamu, H.; Yamashita, M.; Terao, M.; Okamura, T.; Kumaki, N.; Hozumi, K.; Iwamoto, T.; Honda, C.; et al. Expression of hormone receptors is associated with specific immunological profiles of the breast cancer microenvironment. Breast Cancer Res. 2023, 25, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gevensleben, H.; Dietrich, D.; Golletz, C.; Steiner, S.; Jung, M.; Thiesler, T.; Majores, M.; Stein, J.; Uhl, B.; Müller, S.; et al. The Immune Checkpoint Regulator PD-L1 Is Highly Expressed in Aggressive Primary Prostate Cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2016, 22, 1969–1977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meng, Y.; Wu, H.; Yao, Y.; Li, R. The expression of programmed death-ligand 1 in patients with invasive breast cancer. Gland. Surg. 2020, 9, 2106–2115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chartier, S.; Brochard, C.; Martinat, C.; Coussy, F.; Feron, J.G.; Kirova, Y.; Cottu, P.; Marchiò, C.; Vincent-Salomon, A. TROP2, androgen receptor, and PD-L1 status in histological subtypes of high-grade metaplastic breast carcinomas. Histopathology 2023, 82, 664–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, F.F.; Sun, H.M.; Fang, R.P.; Zhang, L.; Shi, H.; Wang, X.; Fu, X.L.; Li, X.M.; Shi, X.H.; Wu, Y.; et al. The modulation of PD-L1 induced by the oncogenic HBXIP for breast cancer growth. Acta Pharm. Sin. 2022, 43, 429–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Receptor | Cancer Type | Functions | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| AR | Prostate cancer | 1. To form a ligand–AR complex and to control gene expression 2. To stimulate the proliferation of prostate cancer cells | [12] |
| ERα | ER-positive breast cancer | To stimulate the proliferation of ER-positive breast cancer cells | [9] |
| Integrin αv | Prostate cancer | To regulate tumor cell migration and growth | [13] |
| Integrin β1 | Hepatocellular carcinoma | To induce cell adhesion through PI3K/AKT signaling pathway | [14] |
| Integrin β1C | Prostate cancer | To be correlated with prostate cancer progression | [15] |
| Integrin α2 | Prostate cancer | To regulate metastasis mediated by adhesion to ColI through RANKL/RANK signaling | [16] |
| Integrin α2β1 | Periosteum-derived progenitor cells | To involve cancer cell migration | [17] |
| Prostate cancer | To regulate cancer progression | [18] | |
| To be controlled its expression by AR | [19] | ||
| Integrin α3 | Prostate cancer | To regulate tumor cell growth | [13] |
| Integrin α3β1 | Prostate cancer | To repress cell proliferation and EMT in prostate cancer by CD151 | [20] |
| Integrin α5β1 | Prostate cancer | To promote prostate cancer growth | [21] |
| Integrin α6β1 | Prostate cancer | To promote the survival of CRPC cells selectively on laminin through the induction of autophagy and mitophagy | [22] |
| Integrin α6β4 | Prostate cancer | To be involved in invasion | [23] |
| To promote the survival of cancer cells | [24] | ||
| To repress cell proliferation and EMT by CD151 | [20] | ||
| To promote an osteolytic program in cancer cells by upregulating MMP2 | [25] | ||
| Integrin αvβ3 | ER-negative breast cancer | To stimulate proliferation of ER-negative breast cancer cells | [10] |
| Breast cancer | To regulate cell proliferation | [9] | |
| Prostate cancer | To regulate cell proliferation through the p66Shc/VEGF pathway | [26] | |
| To induce neuroendocrine differentiation through NOGO receptor NgR2 | [27] | ||
| Neuroendocrine prostate cancer | To promote cancer metastasis | [28] | |
| Integrin αvβ6 | Prostate cancer | To promote an osteolytic program in cancer cells by upregulating MMP2 | [25] |
| To induce cell adhesion and migration | [29] | ||
| Castration-resistant prostate cancer | To promote cancer cell survival | [24] | |
| To promote survival and resistance to PI3K inhibition | [30] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tsai, C.-C.; Yang, Y.-C.S.H.; Chen, Y.-F.; Huang, L.-Y.; Yang, Y.-N.; Lee, S.-Y.; Wang, W.-L.; Lee, H.-L.; Whang-Peng, J.; Lin, H.-Y.; et al. Integrins and Actions of Androgen in Breast Cancer. Cells 2023, 12, 2126. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells12172126
Tsai C-C, Yang Y-CSH, Chen Y-F, Huang L-Y, Yang Y-N, Lee S-Y, Wang W-L, Lee H-L, Whang-Peng J, Lin H-Y, et al. Integrins and Actions of Androgen in Breast Cancer. Cells. 2023; 12(17):2126. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells12172126
Chicago/Turabian StyleTsai, Chung-Che, Yu-Chen S. H. Yang, Yi-Fong Chen, Lin-Yi Huang, Yung-Ning Yang, Sheng-Yang Lee, Wen-Long Wang, Hsin-Lun Lee, Jacqueline Whang-Peng, Hung-Yun Lin, and et al. 2023. "Integrins and Actions of Androgen in Breast Cancer" Cells 12, no. 17: 2126. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells12172126
APA StyleTsai, C. -C., Yang, Y. -C. S. H., Chen, Y. -F., Huang, L. -Y., Yang, Y. -N., Lee, S. -Y., Wang, W. -L., Lee, H. -L., Whang-Peng, J., Lin, H. -Y., & Wang, K. (2023). Integrins and Actions of Androgen in Breast Cancer. Cells, 12(17), 2126. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells12172126