Concussion: Beyond the Cascade
Abstract
1. Introduction
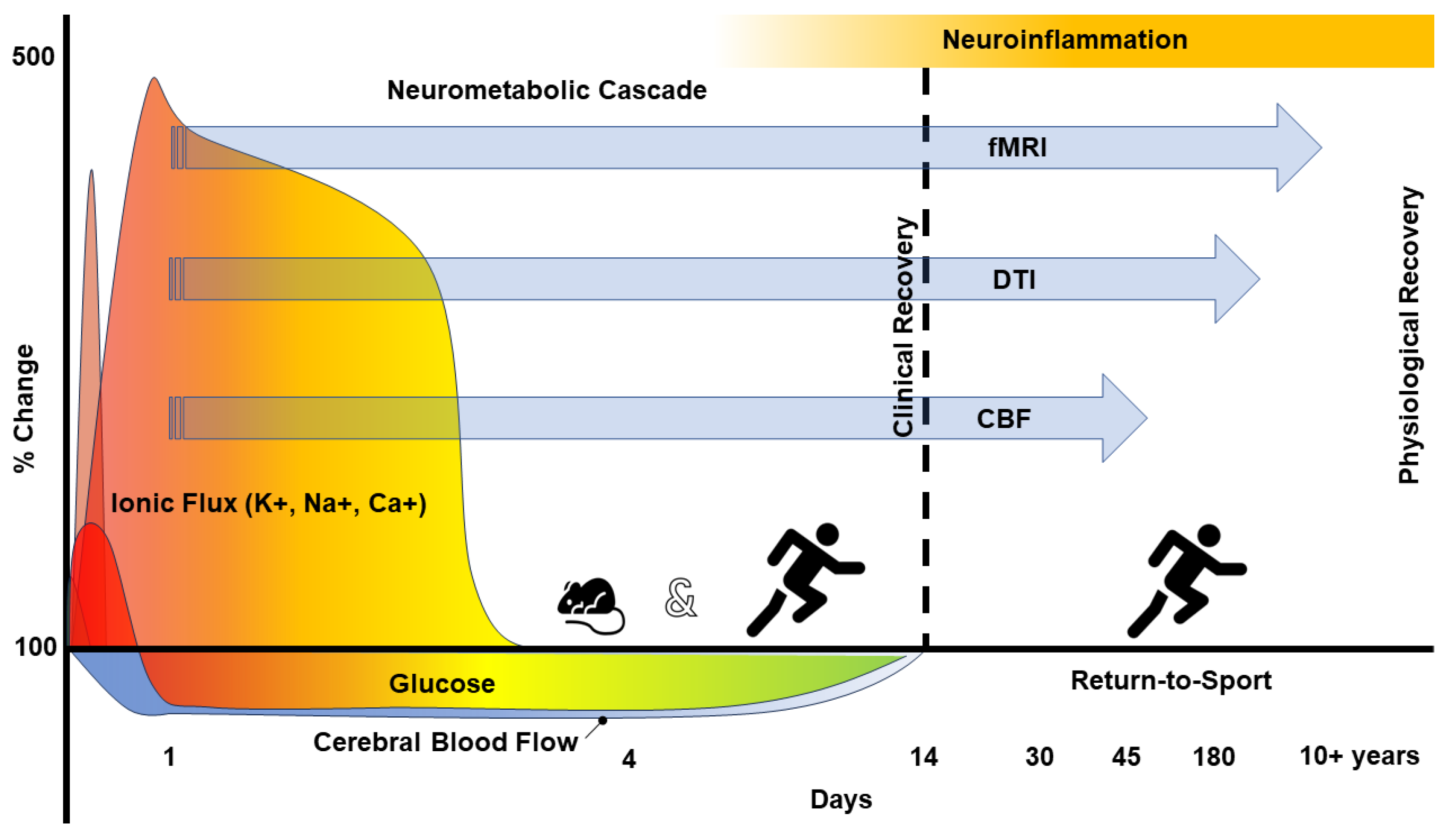
2. The Pathophysiology of Concussion
3. Neuroinflammation—Microglial Responsibility
4. Microglia in Neurological Disorders
5. Neuroinflammation Biomarker—TSPO
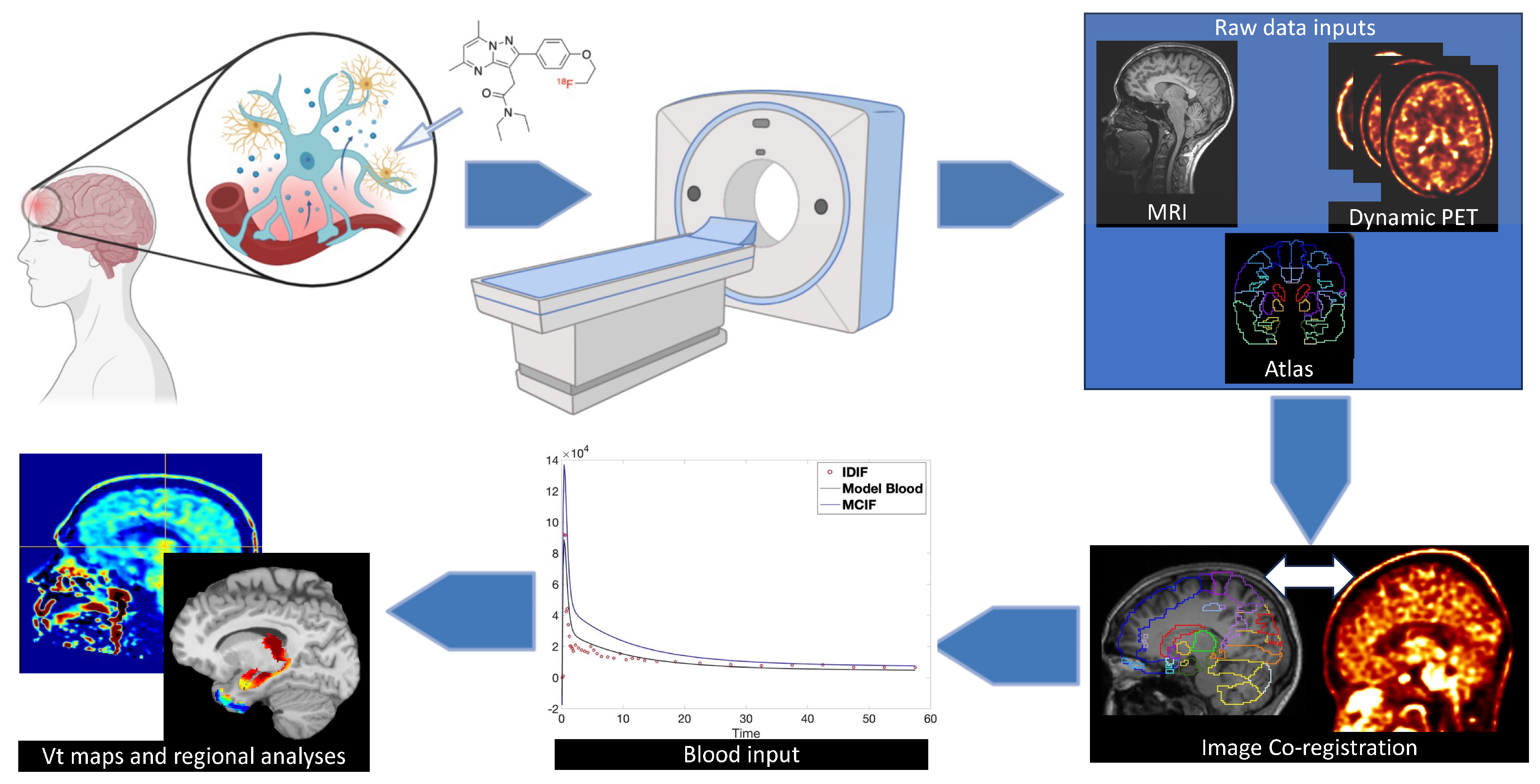
6. Imaging Neuroinflammation—(m)TBI
7. Analytical Concerns—Dynamic vs Static Imaging
8. Magnetic Resonance Imaging
9. Clinical Implications
10. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- McCrory, P.; Meeuwisse, W.; Dvorak, J.; Aubry, M.; Bailes, J.; Broglio, S.; Cantu, R.C.; Cassidy, D.; Echemendia, R.J.; Castellani, R.J.; et al. Consensus statement on concussion in sport-the 5(th) international conference on concussion in sport held in Berlin, October 2016. Br. J. Sports Med. 2017, 51, 838–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guskiewicz, K.M.; Marshall, S.W.; Bailes, J.; McCrea, M.; Cantu, R.C.; Randolph, C.; Jordan, B.D. Association between recurrent concussion and late-life cognitive impairment in retired professional football players. Neurosurgery 2005, 57, 719–726, discussion 719-726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Howell, D.R.; Beasley, M.; Vopat, L.; Meehan, W.P., 3rd. The Effect of Prior Concussion History on Dual-Task Gait following a Concussion. J. Neurotrauma 2017, 34, 838–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Beaumont, L.; Mongeon, D.; Tremblay, S.; Messier, J.; Prince, F.; Leclerc, S.; Lassonde, M.; Theoret, H. Persistent motor system abnormalities in formerly concussed athletes. J. Athl. Train. 2011, 46, 234–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerr, Z.Y.; Evenson, K.R.; Rosamond, W.D.; Mihalik, J.P.; Guskiewicz, K.M.; Marshall, S.W. Association between concussion and mental health in former collegiate athletes. Inj. Epidemiol. 2014, 1, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerr, Z.Y.; Marshall, S.W.; Harding, H.P.; Guskiewicz, K.M. Nine-year risk of depression diagnosis increases with increasing self-reported concussions in retired professional football players. Am. J. Sports Med. 2012, 40, 2206–2212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mucha, A.; Pardini, J.E.; Herring, S.A.; Murphy, J.; Elbin, R.J.; Bauer, R.M.; Schmidt, J.D.; Resch, J.E.; Broshek, D.K. Persisting symptoms after concussion: Considerations for active treatment. PM R J. Inj. Funct. Rehabil. 2023, 15, 663–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broglio, S.P.; McAllister, T.; Katz, B.P.; LaPradd, M.; Zhou, W.; McCrea, M.A.; Investigators, C.C. The Natural History of Sport-Related Concussion in Collegiate Athletes: Findings from the NCAA-DoD CARE Consortium. Sports Med. 2022, 52, 403–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Practice parameter: The management of concussion in sports (summary statement). Report of the Quality Standards Subcommittee. Neurology 1997, 48, 581–585. [CrossRef]
- Broglio, S.P.; Harezlak, J.; Katz, B.; Zhao, S.; McAllister, T.; McCrea, M.; Investigators, C.C. Acute Sport Concussion Assessment Optimization: A Prospective Assessment from the CARE Consortium. Sports Med. 2019, 49, 1977–1987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Resch, J.E.; Brown, C.N.; Schmidt, J.; Macciocchi, S.N.; Blueitt, D.; Cullum, C.M.; Ferrara, M.S. The sensitivity and specificity of clinical measures of sport concussion: Three tests are better than one. BMJ Open Sport Exerc. Med. 2016, 2, e000012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harmon, K.G.; Clugston, J.R.; Dec, K.; Hainline, B.; Herring, S.A.; Kane, S.; Kontos, A.P.; Leddy, J.J.; McCrea, M.A.; Poddar, S.K.; et al. American Medical Society for Sports Medicine Position Statement on Concussion in Sport. Clin. J. Sport. Med. 2019, 29, 87–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Churchill, N.W.; Hutchison, M.G.; Richards, D.; Leung, G.; Graham, S.J.; Schweizer, T.A. Neuroimaging of sport concussion: Persistent alterations in brain structure and function at medical clearance. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 8297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Nelson, L.D.; LaRoche, A.A.; Pfaller, A.Y.; Nencka, A.S.; Koch, K.M.; McCrea, M.A. Cerebral Blood Flow Alterations in Acute Sport-Related Concussion. J. Neurotrauma 2016, 33, 1227–1236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guskiewicz, K.M.; Register-Mihalik, J.; McCrory, P.; McCrea, M.; Johnston, K.; Makdissi, M.; Dvorak, J.; Davis, G.; Meeuwisse, W. Evidence-based approach to revising the SCAT2: Introducing the SCAT3. Br. J. Sports Med. 2013, 47, 289–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conti, M.; Bendriem, B. The new opportunities for high time resolution clinical TOF PET. Clin. Transl. Imaging 2019, 7, 139–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monk, S.H.; Legarreta, A.D.; Kirby, P.; Brett, B.L.; Yengo-Kahn, A.M.; Bhatia, A.; Solomon, G.S.; Zuckerman, S.L. Imaging findings after acute sport-related concussion in American football players: A systematic review. J. Clin. Neurosci. 2019, 61, 28–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Povlishock, J.T. Traumatically induced axonal injury: Pathogenesis and pathobiological implications. Brain Pathol. 1991, 2, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meier, T.B.; Huber, D.L.; Bohorquez-Montoya, L.; Nitta, M.E.; Savitz, J.; Teague, T.K.; Bazarian, J.J.; Hayes, R.L.; Nelson, L.D.; McCrea, M.A. A Prospective Study of Acute Blood-Based Biomarkers for Sport-Related Concussion. Ann. Neurol. 2020, 87, 907–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meier, T.B.; Nitta, M.E.; Teague, T.K.; Nelson, L.D.; McCrea, M.A.; Savitz, J. Prospective study of the effects of sport-related concussion on serum kynurenine pathway metabolites. Brain Behav. Immun. 2020, 87, 715–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stemper, B.D.; Pintar, F.A. Biomechanics of concussion. Prog. Neurol. Surg. 2014, 28, 14–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giza, C.C.; Hovda, D.A. The new neurometabolic cascade of concussion. Neurosurgery 2014, 75 (Suppl. S4), S24–S33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giza, C.C.; Hovda, D.A. The Neurometabolic Cascade of Concussion. J. Athl. Train. 2001, 36, 228–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nelson, L.D.; Guskiewicz, K.M.; Barr, W.B.; Hammeke, T.A.; Randolph, C.; Ahn, K.W.; Wang, Y.; McCrea, M.A. Age Differences in Recovery After Sport-Related Concussion: A Comparison of High School and Collegiate Athletes. J. Athl. Train. 2016, 51, 142–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papa, L.; Brophy, G.M.; Welch, R.D.; Lewis, L.M.; Braga, C.F.; Tan, C.N.; Ameli, N.J.; Lopez, M.A.; Haeussler, C.A.; Mendez Giordano, D.I.; et al. Time Course and Diagnostic Accuracy of Glial and Neuronal Blood Biomarkers GFAP and UCH-L1 in a Large Cohort of Trauma Patients With and Without Mild Traumatic Brain Injury. JAMA Neurol. 2016, 73, 551–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papa, L.; Mittal, M.K.; Ramirez, J.; Ramia, M.; Kirby, S.; Silvestri, S.; Giordano, P.; Weber, K.; Braga, C.F.; Tan, C.N.; et al. In Children and Youth with Mild and Moderate Traumatic Brain Injury, Glial Fibrillary Acidic Protein Out-Performs S100beta in Detecting Traumatic Intracranial Lesions on Computed Tomography. J. Neurotrauma 2016, 33, 58–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coughlin, J.M.; Wang, Y.; Minn, I.; Bienko, N.; Ambinder, E.B.; Xu, X.; Peters, M.E.; Dougherty, J.W.; Vranesic, M.; Koo, S.M.; et al. Imaging of Glial Cell Activation and White Matter Integrity in Brains of Active and Recently Retired National Football League Players. JAMA Neurol. 2017, 74, 67–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coughlin, J.M.; Wang, Y.; Munro, C.A.; Ma, S.; Yue, C.; Chen, S.; Airan, R.; Kim, P.K.; Adams, A.V.; Garcia, C.; et al. Neuroinflammation and brain atrophy in former NFL players: An in vivo multimodal imaging pilot study. Neurobiol. Dis. 2015, 74, 58–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebert, S.E.; Jensen, P.; Ozenne, B.; Armand, S.; Svarer, C.; Stenbaek, D.S.; Moeller, K.; Dyssegaard, A.; Thomsen, G.; Steinmetz, J.; et al. Molecular imaging of neuroinflammation in patients after mild traumatic brain injury: A longitudinal (123) I-CLINDE single photon emission computed tomography study. Eur. J. Neurol. 2019, 26, 1426–1432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meier, T.B.; Nelson, L.D.; Huber, D.L.; Bazarian, J.J.; Hayes, R.L.; McCrea, M.A. Prospective Assessment of Acute Blood Markers of Brain Injury in Sport-Related Concussion. J. Neurotrauma 2017, 34, 3134–3142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCrea, M.; Broglio, S.P.; McAllister, T.W.; Gill, J.; Giza, C.C.; Huber, D.L.; Harezlak, J.; Cameron, K.L.; Houston, M.N.; McGinty, G.; et al. Association of Blood Biomarkers With Acute Sport-Related Concussion in Collegiate Athletes: Findings From the NCAA and Department of Defense CARE Consortium. JAMA Netw. Open 2020, 3, e1919771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nitta, M.E.; Savitz, J.; Nelson, L.D.; Teague, T.K.; Hoelzle, J.B.; McCrea, M.A.; Meier, T.B. Acute elevation of serum inflammatory markers predicts symptom recovery after concussion. Neurology 2019, 93, e497–e507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Battista, A.P.; Churchill, N.; Rhind, S.G.; Richards, D.; Hutchison, M.G. Evidence of a distinct peripheral inflammatory profile in sport-related concussion. J. Neuroinflamm. 2019, 16, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Begum, G.; Reddy, R.; Yakoub, K.M.; Belli, A.; Davies, D.J.; Di Pietro, V. Differential Expression of Circulating Inflammatory Proteins Following Sport-Related Traumatic Brain Injury. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 1216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Echemendia, R.J.; Meeuwisse, W.; McCrory, P.; Davis, G.A.; Putukian, M.; Leddy, J.; Makdissi, M.; Sullivan, S.J.; Broglio, S.P.; Raftery, M.; et al. The Sport Concussion Assessment Tool 5th Edition (SCAT5). Br. J. Sports Med. 2017, 51, 848–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshino, A.; Hovda, D.A.; Kawamata, T.; Katayama, Y.; Becker, D.P. Dynamic changes in local cerebral glucose utilization following cerebral conclusion in rats: Evidence of a hyper- and subsequent hypometabolic state. Brain Res. 1991, 561, 106–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katayama, Y.; Becker, D.P.; Tamura, T.; Hovda, D.A. Massive increases in extracellular potassium and the indiscriminate release of glutamate following concussive brain injury. J. Neurosurg. 1990, 73, 889–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guskiewicz, K.M.; McCrea, M.; Marshall, S.W.; Cantu, R.C.; Randolph, C.; Barr, W.; Onate, J.A.; Kelly, J.P. Cumulative effects associated with recurrent concussion in collegiate football players: The NCAA Concussion Study. JAMA 2003, 290, 2549–2555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilbert, F.C.; Burdette, G.T.; Joyner, A.B.; Llewellyn, T.A.; Buckley, T.A. Association Between Concussion and Lower Extremity Injuries in Collegiate Athletes. Sports Health 2016, 8, 561–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Covassin, T.; Elbin, R.J.; Harris, W.; Parker, T.; Kontos, A. The Role of Age and Sex in Symptoms, Neurocognitive Performance, and Postural Stability in Athletes After Concussion. Am. J. Sports Med. 2012, 40, 1303–1312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Covassin, T.; Elbin, R.J.; Nakayama, Y. Tracking neurocognitive performance following concussion in high school athletes. Phys. Sportsmed. 2010, 38, 87–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Churchill, N.W.; Hutchison, M.G.; Graham, S.J.; Schweizer, T.A. Mapping brain recovery after concussion: From acute injury to 1 year after medical clearance. Neurology 2019, 93, e1980–e1992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manley, G.; Gardner, A.J.; Schneider, K.J.; Guskiewicz, K.M.; Bailes, J.; Cantu, R.C.; Castellani, R.J.; Turner, M.; Jordan, B.D.; Randolph, C.; et al. A systematic review of potential long-term effects of sport-related concussion. Br. J. Sports Med. 2017, 51, 969–977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nimmerjahn, A.; Kirchhoff, F.; Helmchen, F. Resting microglial cells are highly dynamic surveillants of brain parenchyma in vivo. Science 2005, 308, 1314–1318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olah, M.; Biber, K.; Vinet, J.; Boddeke, H.W. Microglia phenotype diversity. CNS Neurol. Disord. Drug Targets 2011, 10, 108–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tronel, C.; Largeau, B.; Santiago Ribeiro, M.J.; Guilloteau, D.; Dupont, A.C.; Arlicot, N. Molecular Targets for PET Imaging of Activated Microglia: The Current Situation and Future Expectations. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawson, L.J.; Perry, V.H.; Dri, P.; Gordon, S. Heterogeneity in the distribution and morphology of microglia in the normal adult mouse brain. Neuroscience 1990, 39, 151–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mittelbronn, M.; Dietz, K.; Schluesener, H.J.; Meyermann, R. Local distribution of microglia in the normal adult human central nervous system differs by up to one order of magnitude. Acta Neuropathol. 2001, 101, 249–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savchenko, V.L.; McKanna, J.A.; Nikonenko, I.R.; Skibo, G.G. Microglia and astrocytes in the adult rat brain: Comparative immunocytochemical analysis demonstrates the efficacy of lipocortin 1 immunoreactivity. Neuroscience 2000, 96, 195–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.W.; Ahn, D.S.; Oh, Y.H.; Lee, S.; Kil, H.S.; Oh, S.J.; Lee, S.J.; Kim, J.S.; Ryu, J.S.; Moon, D.H.; et al. A new class of SN2 reactions catalyzed by protic solvents: Facile fluorination for isotopic labeling of diagnostic molecules. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2006, 128, 16394–16397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wyss-Coray, T.; Mucke, L. Inflammation in neurodegenerative disease—A double-edged sword. Neuron 2002, 35, 419–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sochocka, M.; Diniz, B.S.; Leszek, J. Inflammatory Response in the CNS: Friend or Foe? Mol. Neurobiol. 2017, 54, 8071–8089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Block, M.L.; Zecca, L.; Hong, J.S. Microglia-mediated neurotoxicity: Uncovering the molecular mechanisms. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2007, 8, 57–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanisch, U.K.; Kettenmann, H. Microglia: Active sensor and versatile effector cells in the normal and pathologic brain. Nat. Neurosci. 2007, 10, 1387–1394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Czeh, M.; Gressens, P.; Kaindl, A.M. The yin and yang of microglia. Dev. Neurosci. 2011, 33, 199–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ransohoff, R.M. A polarizing question: Do M1 and M2 microglia exist? Nat. Neurosci. 2016, 19, 987–991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morganti, J.M.; Riparip, L.K.; Rosi, S. Call Off the Dog(ma): M1/M2 Polarization Is Concurrent following Traumatic Brain Injury. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0148001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wake, H.; Moorhouse, A.J.; Jinno, S.; Kohsaka, S.; Nabekura, J. Resting microglia directly monitor the functional state of synapses in vivo and determine the fate of ischemic terminals. J. Neurosci. 2009, 29, 3974–3980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandrekar, S.; Jiang, Q.; Lee, C.Y.; Koenigsknecht-Talboo, J.; Holtzman, D.M.; Landreth, G.E. Microglia mediate the clearance of soluble Abeta through fluid phase macropinocytosis. J. Neurosci. 2009, 29, 4252–4262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graeber, M.B.; Streit, W.J. Microglia: Biology and pathology. Acta Neuropathol. 2010, 119, 89–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Werry, E.L.; Bright, F.M.; Piguet, O.; Ittner, L.M.; Halliday, G.M.; Hodges, J.R.; Kiernan, M.C.; Loy, C.T.; Kril, J.J.; Kassiou, M. Recent Developments in TSPO PET Imaging as A Biomarker of Neuroinflammation in Neurodegenerative Disorders. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 3161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaney, A.; Williams, S.R.; Boutin, H. In vivo molecular imaging of neuroinflammation in Alzheimer’s disease. J. Neurochem. 2019, 149, 438–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galovic, M.; Koepp, M. Advances of Molecular Imaging in Epilepsy. Curr. Neurol. Neurosci. Rep. 2016, 16, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, S.; Beja-Glasser, V.F.; Nfonoyim, B.M.; Frouin, A.; Li, S.; Ramakrishnan, S.; Merry, K.M.; Shi, Q.; Rosenthal, A.; Barres, B.A.; et al. Complement and microglia mediate early synapse loss in Alzheimer mouse models. Science 2016, 352, 712–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kopec, A.M.; Smith, C.J.; Ayre, N.R.; Sweat, S.C.; Bilbo, S.D. Microglial dopamine receptor elimination defines sex-specific nucleus accumbens development and social behavior in adolescent rats. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 3769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lafrenaye, A.D.; Todani, M.; Walker, S.A.; Povlishock, J.T. Microglia processes associate with diffusely injured axons following mild traumatic brain injury in the micro pig. J. Neuroinflamm. 2015, 12, 186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cassidy, J.D.; Carroll, L.J.; Peloso, P.M.; Borg, J.; von Holst, H.; Holm, L.; Kraus, J.; Coronado, V.G.; Injury, W.H.O.C.C.T.F.o.M.T.B. Incidence, risk factors and prevention of mild traumatic brain injury: Results of the WHO Collaborating Centre Task Force on Mild Traumatic Brain Injury. J. Rehabil. Med. 2004, 36, 28–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weinstein, E.; Turner, M.; Kuzma, B.B.; Feuer, H. Second impact syndrome in football: New imaging and insights into a rare and devastating condition. J. Neurosurg. Pediatr. 2013, 11, 331–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marin, J.R.; Weaver, M.D.; Yealy, D.M.; Mannix, R.C. Trends in visits for traumatic brain injury to emergency departments in the United States. JAMA 2014, 311, 1917–1919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patricios, J.S.; Schneider, K.J.; Dvorak, J.; Ahmed, O.H.; Blauwet, C.; Cantu, R.C.; Davis, G.A.; Echemendia, R.J.; Makdissi, M.; McNamee, M.; et al. Consensus statement on concussion in sport: The 6th International Conference on Concussion in Sport-Amsterdam, October 2022. Br. J. Sports Med. 2023, 57, 695–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldstein, L.E.; Fisher, A.M.; Tagge, C.A.; Zhang, X.L.; Velisek, L.; Sullivan, J.A.; Upreti, C.; Kracht, J.M.; Ericsson, M.; Wojnarowicz, M.W.; et al. Chronic traumatic encephalopathy in blast-exposed military veterans and a blast neurotrauma mouse model. Sci. Transl. Med. 2012, 4, 134ra160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKee, A.C.; Cantu, R.C.; Nowinski, C.J.; Hedley-Whyte, E.T.; Gavett, B.E.; Budson, A.E.; Santini, V.E.; Lee, H.S.; Kubilus, C.A.; Stern, R.A. Chronic traumatic encephalopathy in athletes: Progressive tauopathy after repetitive head injury. J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol. 2009, 68, 709–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, V.E.; Stewart, J.E.; Begbie, F.D.; Trojanowski, J.Q.; Smith, D.H.; Stewart, W. Inflammation and white matter degeneration persist for years after a single traumatic brain injury. Brain 2013, 136 Pt 1, 28–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madathil, S.K.; Wilfred, B.S.; Urankar, S.E.; Yang, W.; Leung, L.Y.; Gilsdorf, J.S.; Shear, D.A. Early Microglial Activation Following Closed-Head Concussive Injury Is Dominated by Pro-Inflammatory M-1 Type. Front. Neurol. 2018, 9, 964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fairbairn, L.; Kapetanovic, R.; Sester, D.P.; Hume, D.A. The mononuclear phagocyte system of the pig as a model for understanding human innate immunity and disease. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2011, 89, 855–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wernersson, R.; Schierup, M.H.; Jorgensen, F.G.; Gorodkin, J.; Panitz, F.; Staerfeldt, H.H.; Christensen, O.F.; Mailund, T.; Hornshoj, H.; Klein, A.; et al. Pigs in sequence space: A 0.66X coverage pig genome survey based on shotgun sequencing. BMC Genom. 2005, 6, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukhin, A.G.; Papadopoulos, V.; Costa, E.; Krueger, K.E. Mitochondrial benzodiazepine receptors regulate steroid biosynthesis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1989, 86, 9813–9816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guilarte, T.R.; Loth, M.K.; Guariglia, S.R. TSPO Finds NOX2 in Microglia for Redox Homeostasis. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2016, 37, 334–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banati, R.B. Visualising microglial activation in vivo. Glia 2002, 40, 206–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Israel, I.; Ohsiek, A.; Al-Momani, E.; Albert-Weissenberger, C.; Stetter, C.; Mencl, S.; Buck, A.K.; Kleinschnitz, C.; Samnick, S.; Siren, A.L. Combined [(18)F]DPA-714 micro-positron emission tomography and autoradiography imaging of microglia activation after closed head injury in mice. J. Neuroinflamm. 2016, 13, 140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Fur, G.; Perrier, M.L.; Vaucher, N.; Imbault, F.; Flamier, A.; Benavides, J.; Uzan, A.; Renault, C.; Dubroeucq, M.C.; Gueremy, C. Peripheral benzodiazepine binding sites: Effect of PK 11195, 1-(2-chlorophenyl)-N-methyl-N-(1-methylpropyl)-3-isoquinolinecarboxamide. I. In vitro studies. Life Sci. 1983, 32, 1839–1847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chauveau, F.; Boutin, H.; Van Camp, N.; Dolle, F.; Tavitian, B. Nuclear imaging of neuroinflammation: A comprehensive review of [11C]PK11195 challengers. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2008, 35, 2304–2319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Endres, C.J.; Pomper, M.G.; James, M.; Uzuner, O.; Hammoud, D.A.; Watkins, C.C.; Reynolds, A.; Hilton, J.; Dannals, R.F.; Kassiou, M. Initial evaluation of 11C-DPA-713, a novel TSPO PET ligand, in humans. J. Nucl. Med. 2009, 50, 1276–1282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doorduin, J.; Klein, H.C.; Dierckx, R.A.; James, M.; Kassiou, M.; de Vries, E.F. [11C]-DPA-713 and [18F]-DPA-714 as new PET tracers for TSPO: A comparison with [11C]-(R)-PK11195 in a rat model of herpes encephalitis. Mol. Imaging Biol. 2009, 11, 386–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vignal, N.; Cisternino, S.; Rizzo-Padoin, N.; San, C.; Hontonnou, F.; Gele, T.; Decleves, X.; Sarda-Mantel, L.; Hosten, B. [(18)F]FEPPA a TSPO Radioligand: Optimized Radiosynthesis and Evaluation as a PET Radiotracer for Brain Inflammation in a Peripheral LPS-Injected Mouse Model. Molecules 2018, 23, 1375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Owen, D.R.; Gunn, R.N.; Rabiner, E.A.; Bennacef, I.; Fujita, M.; Kreisl, W.C.; Innis, R.B.; Pike, V.W.; Reynolds, R.; Matthews, P.M.; et al. Mixed-affinity binding in humans with 18-kDa translocator protein ligands. J. Nucl. Med. 2011, 52, 24–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mizrahi, R.; Rusjan, P.M.; Kennedy, J.; Pollock, B.; Mulsant, B.; Suridjan, I.; De Luca, V.; Wilson, A.A.; Houle, S. Translocator protein (18 kDa) polymorphism (rs6971) explains in-vivo brain binding affinity of the PET radioligand [(18)F]-FEPPA. J. Cereb. Blood Flow. Metab. 2012, 32, 968–972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Owen, D.R.; Howell, O.W.; Tang, S.P.; Wells, L.A.; Bennacef, I.; Bergstrom, M.; Gunn, R.N.; Rabiner, E.A.; Wilkins, M.R.; Reynolds, R.; et al. Two binding sites for [3H]PBR28 in human brain: Implications for TSPO PET imaging of neuroinflammation. J. Cereb. Blood Flow. Metab. 2010, 30, 1608–1618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Owen, D.R.; Yeo, A.J.; Gunn, R.N.; Song, K.; Wadsworth, G.; Lewis, A.; Rhodes, C.; Pulford, D.J.; Bennacef, I.; Parker, C.A.; et al. An 18-kDa translocator protein (TSPO) polymorphism explains differences in binding affinity of the PET radioligand PBR28. J. Cereb. Blood Flow. Metab. 2012, 32, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colasanti, A.; Guo, Q.; Muhlert, N.; Giannetti, P.; Onega, M.; Newbould, R.D.; Ciccarelli, O.; Rison, S.; Thomas, C.; Nicholas, R.; et al. In Vivo Assessment of Brain White Matter Inflammation in Multiple Sclerosis with (18)F-PBR111 PET. J. Nucl. Med. 2014, 55, 1112–1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ratai, E.M.; Alshikho, M.J.; Zurcher, N.R.; Loggia, M.L.; Cebulla, C.L.; Cernasov, P.; Reynolds, B.; Fish, J.; Seth, R.; Babu, S.; et al. Integrated imaging of [(11)C]-PBR28 PET, MR diffusion and magnetic resonance spectroscopy (1)H-MRS in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Neuroimage Clin. 2018, 20, 357–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kreisl, W.C.; Lyoo, C.H.; McGwier, M.; Snow, J.; Jenko, K.J.; Kimura, N.; Corona, W.; Morse, C.L.; Zoghbi, S.S.; Pike, V.W.; et al. In vivo radioligand binding to translocator protein correlates with severity of Alzheimer’s disease. Brain 2013, 136 Pt 7, 2228–2238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rojas, C.; Stathis, M.; Coughlin, J.M.; Pomper, M.; Slusher, B.S. The Low-Affinity Binding of Second Generation Radiotracers Targeting TSPO is Associated with a Unique Allosteric Binding Site. J. Neuroimmune Pharmacol. 2018, 13, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nutma, E.; Gebro, E.; Marzin, M.C.; van der Valk, P.; Matthews, P.M.; Owen, D.R.; Amor, S. Activated microglia do not increase 18 kDa translocator protein (TSPO) expression in the multiple sclerosis brain. Glia 2021, 69, 2447–2458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nutma, E.; Stephenson, J.A.; Gorter, R.P.; de Bruin, J.; Boucherie, D.M.; Donat, C.K.; Breur, M.; van der Valk, P.; Matthews, P.M.; Owen, D.R.; et al. A quantitative neuropathological assessment of translocator protein expression in multiple sclerosis. Brain 2019, 142, 3440–3455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaunzner, U.W.; Kang, Y.; Zhang, S.; Morris, E.; Yao, Y.; Pandya, S.; Hurtado Rua, S.M.; Park, C.; Gillen, K.M.; Nguyen, T.D.; et al. Quantitative susceptibility mapping identifies inflammation in a subset of chronic multiple sclerosis lesions. Brain 2019, 142, 133–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Territo, P.R.; Meyer, J.A.; Peters, J.S.; Riley, A.A.; McCarthy, B.P.; Gao, M.; Wang, M.; Green, M.A.; Zheng, Q.H.; Hutchins, G.D. Characterization of (11)C-GSK1482160 for Targeting the P2X7 Receptor as a Biomarker for Neuroinflammation. J. Nucl. Med. 2017, 58, 458–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beaino, W.; Janssen, B.; Kooij, G.; van der Pol, S.M.A.; van Het Hof, B.; van Horssen, J.; Windhorst, A.D.; de Vries, H.E. Purinergic receptors P2Y12R and P2X7R: Potential targets for PET imaging of microglia phenotypes in multiple sclerosis. J. Neuroinflamm. 2017, 14, 259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lebedev, A.; Jiao, J.; Lee, J.; Yang, F.; Allison, N.; Herschman, H.; Sadeghi, S. Radiochemistry on electrodes: Synthesis of an 18F-labelled and in vivo stable COX-2 inhibitor. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0176606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.J.; Shrestha, S.S.; Cortes, M.; Singh, P.; Morse, C.; Liow, J.S.; Gladding, R.L.; Brouwer, C.; Henry, K.; Gallagher, E.; et al. Evaluation of Two Potent and Selective PET Radioligands to Image COX-1 and COX-2 in Rhesus Monkeys. J. Nucl. Med. 2018, 59, 1907–1912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horti, A.G.; Naik, R.; Foss, C.A.; Minn, I.; Misheneva, V.; Du, Y.; Wang, Y.; Mathews, W.B.; Wu, Y.; Hall, A.; et al. PET imaging of microglia by targeting macrophage colony-stimulating factor 1 receptor (CSF1R). Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 1686–1691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Masel, B.E.; DeWitt, D.S. Traumatic brain injury: A disease process, not an event. J. Neurotrauma 2010, 27, 1529–1540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Donat, C.K.; Gaber, K.; Meixensberger, J.; Brust, P.; Pinborg, L.H.; Hansen, H.H.; Mikkelsen, J.D. Changes in Binding of [(123)I]CLINDE, a High-Affinity Translocator Protein 18 kDa (TSPO) Selective Radioligand in a Rat Model of Traumatic Brain Injury. Neuromol. Med. 2016, 18, 158–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwarzmaier, S.M.; Plesnila, N. Contributions of the immune system to the pathophysiology of traumatic brain injury—Evidence by intravital microscopy. Front. Cell Neurosci. 2014, 8, 358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giunta, B.; Obregon, D.; Velisetty, R.; Sanberg, P.R.; Borlongan, C.V.; Tan, J. The immunology of traumatic brain injury: A prime target for Alzheimer’s disease prevention. J. Neuroinflamm. 2012, 9, 185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maxwell, W.L.; MacKinnon, M.A.; Stewart, J.E.; Graham, D.I. Stereology of cerebral cortex after traumatic brain injury matched to the Glasgow outcome score. Brain 2010, 133 Pt 1, 139–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramlackhansingh, A.F.; Brooks, D.J.; Greenwood, R.J.; Bose, S.K.; Turkheimer, F.E.; Kinnunen, K.M.; Gentleman, S.; Heckemann, R.A.; Gunanayagam, K.; Gelosa, G.; et al. Inflammation after trauma: Microglial activation and traumatic brain injury. Ann. Neurol. 2011, 70, 374–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schiff, N.D.; Giacino, J.T.; Kalmar, K.; Victor, J.D.; Baker, K.; Gerber, M.; Fritz, B.; Eisenberg, B.; Biondi, T.; O’Connor, J.; et al. Behavioural improvements with thalamic stimulation after severe traumatic brain injury. Nature 2007, 448, 600–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Folkersma, H.; Boellaard, R.; Yaqub, M.; Kloet, R.W.; Windhorst, A.D.; Lammertsma, A.A.; Vandertop, W.P.; van Berckel, B.N. Widespread and prolonged increase in (R)-(11)C-PK11195 binding after traumatic brain injury. J. Nucl. Med. 2011, 52, 1235–1239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donat, C.K.; Scott, G.; Gentleman, S.M.; Sastre, M. Microglial Activation in Traumatic Brain Injury. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2017, 9, 208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghadery, C.; Best, L.A.; Pavese, N.; Tai, Y.F.; Strafella, A.P. PET Evaluation of Microglial Activation in Non-neurodegenerative Brain Diseases. Curr. Neurol. Neurosci. Rep. 2019, 19, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neumann, K.D.; Seshadri, S.; Thompson, X.D.; Druzgal, T.J.; Massey, J.C.; Newman, B.; Reyes, J.; Simpson, S.R.; McCauley, K.S.; Patrie, J.; et al. Microglial Activation Persists Beyond Clinical Recovery Following Sport Concussion in Collegiate Athletes. Front. Neurol. 2023, 14, 1127708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garcia-Panach, J.; Lull, N.; Lull, J.J.; Ferri, J.; Martinez, C.; Sopena, P.; Robles, M.; Chirivella, J.; Noe, E. A voxel-based analysis of FDG-PET in traumatic brain injury: Regional metabolism and relationship between the thalamus and cortical areas. J. Neurotrauma 2011, 28, 1707–1717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kato, T.; Nakayama, N.; Yasokawa, Y.; Okumura, A.; Shinoda, J.; Iwama, T. Statistical image analysis of cerebral glucose metabolism in patients with cognitive impairment following diffuse traumatic brain injury. J. Neurotrauma 2007, 24, 919–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gross, H.; Kling, A.; Henry, G.; Herndon, C.; Lavretsky, H. Local cerebral glucose metabolism in patients with long-term behavioral and cognitive deficits following mild traumatic brain injury. J. Neuropsychiatry Clin. Neurosci. 1996, 8, 324–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peskind, E.R.; Petrie, E.C.; Cross, D.J.; Pagulayan, K.; McCraw, K.; Hoff, D.; Hart, K.; Yu, C.E.; Raskind, M.A.; Cook, D.G.; et al. Cerebrocerebellar hypometabolism associated with repetitive blast exposure mild traumatic brain injury in 12 Iraq war Veterans with persistent post-concussive symptoms. Neuroimage 2011, 54 (Suppl. S1), S76–S82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bremner, J.D.; Innis, R.B.; Salomon, R.M.; Staib, L.H.; Ng, C.K.; Miller, H.L.; Bronen, R.A.; Krystal, J.H.; Duncan, J.; Rich, D.; et al. Positron emission tomography measurement of cerebral metabolic correlates of tryptophan depletion-induced depressive relapse. Arch. Gen. Psychiatry 1997, 54, 364–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molina, M.E.; Isoardi, R.; Prado, M.N.; Bentolila, S. Basal cerebral glucose distribution in long-term post-traumatic stress disorder. World J. Biol. Psychiatry 2010, 11 Pt 2, 493–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrie, E.C.; Cross, D.J.; Yarnykh, V.L.; Richards, T.; Martin, N.M.; Pagulayan, K.; Hoff, D.; Hart, K.; Mayer, C.; Tarabochia, M.; et al. Neuroimaging, behavioral, and psychological sequelae of repetitive combined blast/impact mild traumatic brain injury in Iraq and Afghanistan war veterans. J. Neurotrauma 2014, 31, 425–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byrnes, K.R.; Wilson, C.M.; Brabazon, F.; von Leden, R.; Jurgens, J.S.; Oakes, T.R.; Selwyn, R.G. FDG-PET imaging in mild traumatic brain injury: A critical review. Front. Neuroenerg. 2014, 5, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leiva-Salinas, C.; Schiff, D.; Flors, L.; Patrie, J.T.; Rehm, P.K. FDG PET/MR Imaging Coregistration Helps Predict Survival in Patients with Glioblastoma and Radiologic Progression after Standard of Care Treatment. Radiology 2017, 283, 508–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quigg, M.; Kundu, B. Dynamic FDG-PET demonstration of functional brain abnormalities. Ann. Clin. Transl. Neurol. 2022, 9, 1487–1497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coughlin, J.M.; Yang, T.; Rebman, A.W.; Bechtold, K.T.; Du, Y.; Mathews, W.B.; Lesniak, W.G.; Mihm, E.A.; Frey, S.M.; Marshall, E.S.; et al. Imaging glial activation in patients with post-treatment Lyme disease symptoms: A pilot study using [(11)C]DPA-713 PET. J. Neuroinflammation 2018, 15, 346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cumming, P.; Burgher, B.; Patkar, O.; Breakspear, M.; Vasdev, N.; Thomas, P.; Liu, G.J.; Banati, R. Sifting through the surfeit of neuroinflammation tracers. J. Cereb. Blood Flow. Metab. 2018, 38, 204–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kundu, B.K.; Antkowiack, P.; Shi, W. Dynamic FDG PET imaging of the brain in a mouse model of dystonia; p. 1554.
- Lavisse, S.; Garcia-Lorenzo, D.; Peyronneau, M.A.; Bodini, B.; Thiriez, C.; Kuhnast, B.; Comtat, C.; Remy, P.; Stankoff, B.; Bottlaender, M. Optimized Quantification of Translocator Protein Radioligand (1)(8)F-DPA-714 Uptake in the Brain of Genotyped Healthy Volunteers. J. Nucl. Med. 2015, 56, 1048–1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Golla, S.S.; Boellaard, R.; Oikonen, V.; Hoffmann, A.; van Berckel, B.N.; Windhorst, A.D.; Virta, J.; Haaparanta-Solin, M.; Luoto, P.; Savisto, N.; et al. Quantification of [18F]DPA-714 binding in the human brain: Initial studies in healthy controls and Alzheimer’s disease patients. J. Cereb. Blood Flow. Metab. 2015, 35, 766–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Golla, S.S.; Boellaard, R.; Oikonen, V.; Hoffmann, A.; van Berckel, B.N.; Windhorst, A.D.; Virta, J.; Te Beek, E.T.; Groeneveld, G.J.; Haaparanta-Solin, M.; et al. Parametric Binding Images of the TSPO Ligand 18F-DPA-714. J. Nucl. Med. 2016, 57, 1543–1547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hagens, M.H.J.; Golla, S.V.; Wijburg, M.T.; Yaqub, M.; Heijtel, D.; Steenwijk, M.D.; Schober, P.; Breve, J.J.P.; Schuit, R.C.; Reekie, T.A.; et al. In vivo assessment of neuroinflammation in progressive multiple sclerosis: A proof of concept study with [(18)F]DPA714 PET. J. Neuroinflamm. 2018, 15, 314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laforest, R.; Sharp, T.L.; Engelbach, J.A.; Fettig, N.M.; Herrero, P.; Kim, J.; Lewis, J.S.; Rowland, D.J.; Tai, Y.C.; Welch, M.J. Measurement of input functions in rodents: Challenges and solutions. Nucl. Med. Biol. 2005, 32, 679–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Locke, L.W.; Berr, S.S.; Kundu, B.K. Image-derived input function from cardiac gated maximum a posteriori reconstructed PET images in mice. Mol. Imaging Biol. 2011, 13, 342–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Huang, Q.; Massey, J.C.; Minczuk, K.; Li, J.; Kundu, B.K. Non-invasive determination of blood input function to compute rate of myocardial glucose uptake from dynamic FDG PET images of rat heart in vivo: Comparative study between the inferior vena cava and the left ventricular blood pool with spill over and partial volume corrections. Phys. Med. Biol. 2019, 64, 165010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhong, M.; Kundu, B.K. Optimization of a Model Corrected Blood Input Function from Dynamic FDG-PET Images of Small Animal Heart In Vivo. IEEE Trans. Nucl. Sci. 2013, 60, 3417–3422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Logan, J.; Fowler, J.S.; Volkow, N.D.; Wolf, A.P.; Dewey, S.L.; Schlyer, D.J.; MacGregor, R.R.; Hitzemann, R.; Bendriem, B.; Gatley, S.J.; et al. Graphical analysis of reversible radioligand binding from time-activity measurements applied to [N-11C-methyl]-(-)-cocaine PET studies in human subjects. J. Cereb. Blood Flow. Metab. 1990, 10, 740–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lammertsma, A.A.; Hume, S.P. Simplified reference tissue model for PET receptor studies. Neuroimage 1996, 4 Pt 1, 153–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDonald, B.C.; Saykin, A.J.; McAllister, T.W. Functional MRI of mild traumatic brain injury (mTBI): Progress and perspectives from the first decade of studies. Brain Imaging Behav. 2012, 6, 193–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eierud, C.; Craddock, R.C.; Fletcher, S.; Aulakh, M.; King-Casas, B.; Kuehl, D.; LaConte, S.M. Neuroimaging after mild traumatic brain injury: Review and meta-analysis. Neuroimage Clin. 2014, 4, 283–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayer, A.R.; Kaushal, M.; Dodd, A.B.; Hanlon, F.M.; Shaff, N.A.; Mannix, R.; Master, C.L.; Leddy, J.J.; Stephenson, D.; Wertz, C.J.; et al. Advanced biomarkers of pediatric mild traumatic brain injury: Progress and perils. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2018, 94, 149–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayer, A.R.; Bellgowan, P.S.; Hanlon, F.M. Functional magnetic resonance imaging of mild traumatic brain injury. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2015, 49, 8–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenbaum, S.B.; Lipton, M.L. Embracing chaos: The scope and importance of clinical and pathological heterogeneity in mTBI. Brain Imaging Behav. 2012, 6, 255–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogawa, S.; Lee, T.M.; Kay, A.R.; Tank, D.W. Brain magnetic resonance imaging with contrast dependent on blood oxygenation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1990, 87, 9868–9872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bandettini, P.A. Neuronal or hemodynamic? Grappling with the functional MRI signal. Brain Connect. 2014, 4, 487–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hillman, E.M. Coupling mechanism and significance of the BOLD signal: A status report. Annu. Rev. Neurosci. 2014, 37, 161–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buckner, R.L. Event-related fMRI and the hemodynamic response. Hum. Brain Mapp. 1998, 6, 373–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prichard, J.W.; Grossman, R.I. New reasons for early use of MRI in stroke. Neurology 1999, 52, 1733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arfanakis, K.; Haughton, V.M.; Carew, J.D.; Rogers, B.P.; Dempsey, R.J.; Meyerand, M.E. Diffusion tensor MR imaging in diffuse axonal injury. Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2002, 23, 794–802. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- O’Phelan, K.H.; Otoshi, C.K.; Ernst, T.; Chang, L. Common Patterns of Regional Brain Injury Detectable by Diffusion Tensor Imaging in Otherwise Normal-Appearing White Matter in Patients with Early Moderate to Severe Traumatic Brain Injury. J. Neurotrauma 2018, 35, 739–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, D.H.; Meaney, D.F. Axonal Damage in Traumatic Brain Injury. Progress Clin. Neurosci. 2000, 6, 483–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, J.; Hayward, K.S.; Brown, K.E.; Zwicker, J.G.; Ponsford, J.; van Donkelaar, P.; Babul, S.; Boyd, L.A. Imaging in pediatric concussion: A systematic review. Pediatrics 2018, 141, e20173406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khong, E.; Odenwald, N.; Hashim, E.; Cusimano, M.D. Diffusion tensor imaging findings in post-concussion syndrome patients after mild traumatic brain injury: A systematic review. Front. Neurol. 2016, 7, 156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niogi, S.N.; Mukherjee, P. Diffusion tensor imaging of mild traumatic brain injury. J. Head Trauma Rehabil. 2010, 25, 241–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pierpaoli, C.; Barnett, A.; Pajevic, S.; Chen, R.; Penix, L.; Virta, A.; Basser, P. Water diffusion changes in Wallerian degeneration and their dependence on white matter architecture. Neuroimage 2001, 13, 1174–1185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wheeler-Kingshott, C.A.; Cercignani, M. About “axial” and “radial” diffusivities. Magn. Reson. Med. 2009, 61, 1255–1260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dodd, A.B.; Epstein, K.; Ling, J.M.; Mayer, A.R. Diffusion tensor imaging findings in semi-acute mild traumatic brain injury. J. Neurotrauma 2014, 31, 1235–1248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lipton, M.L.; Kim, N.; Park, Y.K.; Hulkower, M.B.; Gardin, T.M.; Shifteh, K.; Kim, M.; Zimmerman, M.E.; Lipton, R.B.; Branch, C.A. Robust detection of traumatic axonal injury in indi- vidual mild traumatic brain injury patients: Intersubject variation, change over time and bidirectional changes in anisotropy. Brain Imaging Behav. 2012, 6, 329–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McAllister, T.W.; Ford, J.C.; Ji, S.; Beckwith, J.G.; Flashman, L.A.; Paulsen, K.; Greenwald, R.M. Maximum principal strain and strain rate associated with concussion diagnosis correlates with changes in corpus callosum white matter indices. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 2012, 40, 127–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rutgers, D.R.; Fillard, P.; Paradot, G.; Tadie, M.; Lasjaunias, P.; Ducreux, D. Diffusion tensor imaging characteristics of the corpus callosum in mild, moderate, and severe traumatic brain injury. Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2008, 29, 1730–1735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Johnson, B.; Pennell, D.; Ray, W.; Sebastianelli, W.; Slobounov, S. Are functional deficits in concussed individuals consistent with white matter structural alterations: Combined FMRI & DTI study. Exp. Brain Res. 2010, 204, 57–70. [Google Scholar]
- Maugans, T.A.; Farley, C.; Altaye, M.; Leach, J.; Cecil, K.M. Pediatric sports-related concussion produces cerebral blood flow alterations. Pediatrics 2012, 129, 28–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Messe, A.; Caplain, S.; Paradot, G.; Garrigue, D.; Mineo, J.F.; Soto Ares, G.; Ducreux, D.; Vignaud, F.; Rozec, G.; Desal, H.; et al. Diffusion tensor imaging and white matter lesions at the subacute stage in mild traumatic brain injury with persistent neurobehavioral impairment. Human. Brain Mapping 2011, 32, 999–1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lange, R.T.; Iverson, G.L.; Brubacher, J.R.; Madler, B.; Heran, M.K. Diffusion tensor imaging findings are not strongly associated with postconcussional disorder 2 months following mild traumatic brain injury. J. Head Trauma Rehabil. 2012, 27, 188–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polak, P.; Leddy, J.J.; Dwyer, M.G.; Willer, B.; Zivadinov, R. Diffusion tensor imaging alterations in patients with postconcussion syndrome undergoing exercise treatment: A pilot longitudinal study. J. Head Trauma Rehabil. 2015, 30, 32–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levin, H.S.; Wilde, E.; Troyanskaya, M.; Petersen, N.J.; Schiebel, R.; Newsome, M.; Radaideh, M.; Wu, T.; Yallampalli, R.; Chu, Z.; et al. Diffusion tensor imaging of mild to moderate blast-related traumatic brain injury and its sequelae. J. Neurotrauma 2010, 27, 683–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilde, E.A.; McCauley, S.R.; Hunter, J.V.; Bigler, E.D.; Chu, Z.; Wang, Z.J.; Hanten, G.R.; Troyanskaya, M.; Yallampalli, R.; Li, X.; et al. Diffusion tensor imaging of acute mild traumatic brain injury in adolscents. Neurology 2008, 70, 948–955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayer, A.R.; Ling, J.M.; Yang, Z.; Pena, A.; Yeo, R.A.; Klimaj, S. Diffusion abnormalities in pediatric mild traumatic brain injury. J. Neurotrauma 2012, 32, 17961–17969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Beek, L.; Ghesquiere, P.; Lagae, L.; De Smedt, B. Mathematical difficulties and white matter abnormalities in subacute pediatric mild traumatic brain injury. J. Neurotrauma 2015, 32, 1567–1578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsushita, M.; Hosoda, K.; Naitoh, Y.; Yamashita, H.; Kohmura, E. Utility of diffusion tensor imaging in the acute stage of mild to moderate traumatic brain injury for detecting white matter lesions and predicting long-term cognitive function in adults. J. Neurotrauma 2011, 115, 130–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naess-Schmidt, E.T.; Blicher, J.U.; Eskildsen, S.F.; Tietze, A.; Hansen, B.; Stubbs, P.W.; Jespersen, S.; Ostergaard, L.; Nielsen, J.F. Microstructural changes in the thalamus after mild traumatic brain injury: A longitudinal diffusion and mean kurtosis tensor MRI study. Brain Inj. 2017, 31, 230–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borich, M.; Makan, N.; Boyd, L.; Virji-Babul, N. Combining whole-brain voxel-wise analysis with in vivo tracto- graphy of diffusion behavior after sports-related concussion in ado- lescents: A preliminary report. J. Neurotrauma 2013, 30, 1243–1249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grossman, E.J.; Jensen, J.H.; Babb, J.S.; Chen, Q.; Tabesh, A.; Fieremans, E.; Xia, D.; Inglese, M.; Grossman, R.I. Cognitive impairment in mild traumatic brain injury: A longitudinal diffusional kurtosis and perfusion imaging study. Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2013, 34, 951–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henry, L.C.; Tremblay, J.; Tremblay, S.; Lee, A.; Brun, C.; Lepore, N.; Theoret, H.; Ellemberg, D.; Lassonde, M. Acute and chronic changes in diffusivity measures after sports concussion. J. Neurotrauma 2011, 28, 2049–2059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albrecht, D.S.; Granziera, C.; Hooker, J.M.; Loggia, M.L. In vivo imaging of human neuroinflammation. ACS Chem. Neurosci. 2016, 7, 470–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosenblum, D.J.; Walton, S.R.; Erdman, N.K.; Broshek, D.K.; Hart, J.M.; Resch, J.E. If Not Now, When? An Absence of Neurocognitive and Postural Stability Deficits in Collegiate Athletes with One or More Concussions. J. Neurotrauma 2020, 37, 1211–1220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McPherson, A.L.; Nagai, T.; Webster, K.E.; Hewett, T.E. Musculoskeletal Injury Risk After Sport-Related Concussion: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Am. J. Sports Med. 2019, 47, 1754–1762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stamm, J.M.; Bourlas, A.P.; Baugh, C.M.; Fritts, N.G.; Daneshvar, D.H.; Martin, B.M.; McClean, M.D.; Tripodis, Y.; Stern, R.A. Age of first exposure to football and later-life cognitive impairment in former NFL players. Neurology 2015, 84, 1114–1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stern, R.A.; Riley, D.O.; Daneshvar, D.H.; Nowinski, C.J.; Cantu, R.C.; McKee, A.C. Long-term consequences of repetitive brain trauma: Chronic traumatic encephalopathy. PM R J. Inj. Funct. Rehabil. 2011, 3 (Suppl. S2), S460–S467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Neumann, K.D.; Broshek, D.K.; Newman, B.T.; Druzgal, T.J.; Kundu, B.K.; Resch, J.E. Concussion: Beyond the Cascade. Cells 2023, 12, 2128. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells12172128
Neumann KD, Broshek DK, Newman BT, Druzgal TJ, Kundu BK, Resch JE. Concussion: Beyond the Cascade. Cells. 2023; 12(17):2128. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells12172128
Chicago/Turabian StyleNeumann, Kiel D., Donna K. Broshek, Benjamin T. Newman, T. Jason Druzgal, Bijoy K. Kundu, and Jacob E. Resch. 2023. "Concussion: Beyond the Cascade" Cells 12, no. 17: 2128. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells12172128
APA StyleNeumann, K. D., Broshek, D. K., Newman, B. T., Druzgal, T. J., Kundu, B. K., & Resch, J. E. (2023). Concussion: Beyond the Cascade. Cells, 12(17), 2128. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells12172128







