Inhibitory Fc-Gamma IIb Receptor Signaling Induced by Multivalent IgG-Fc Is Dependent on Sialylation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Generation of Tetra-Sialylated IVIg and Desialylated IVIg
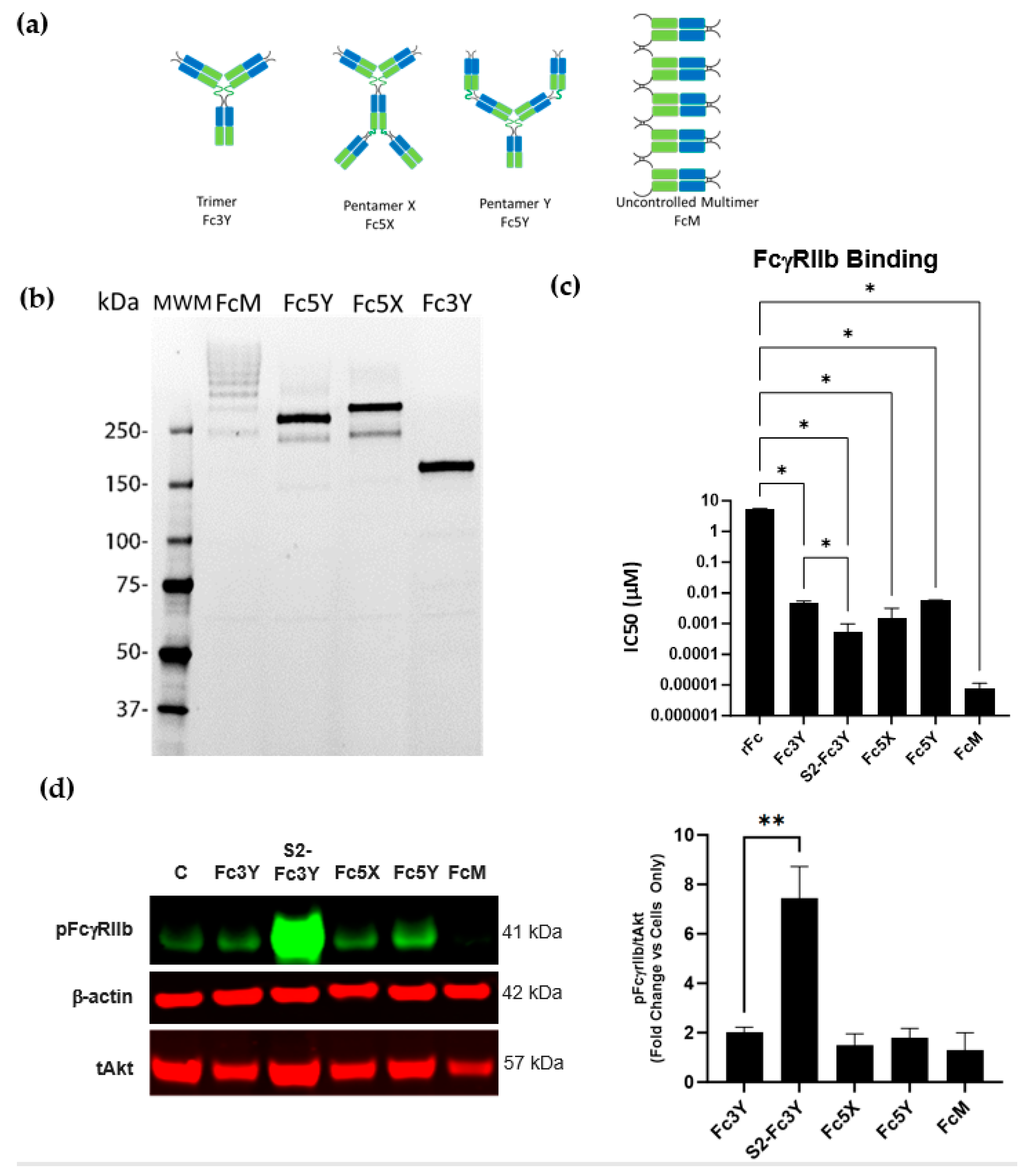
2.2. Generation of Multivalent Fc Molecules
2.3. Fc Glycosylation Analyses by Glycopeptide Liquid Chromatography–Mass Spectrometry (LC-MS/MS)
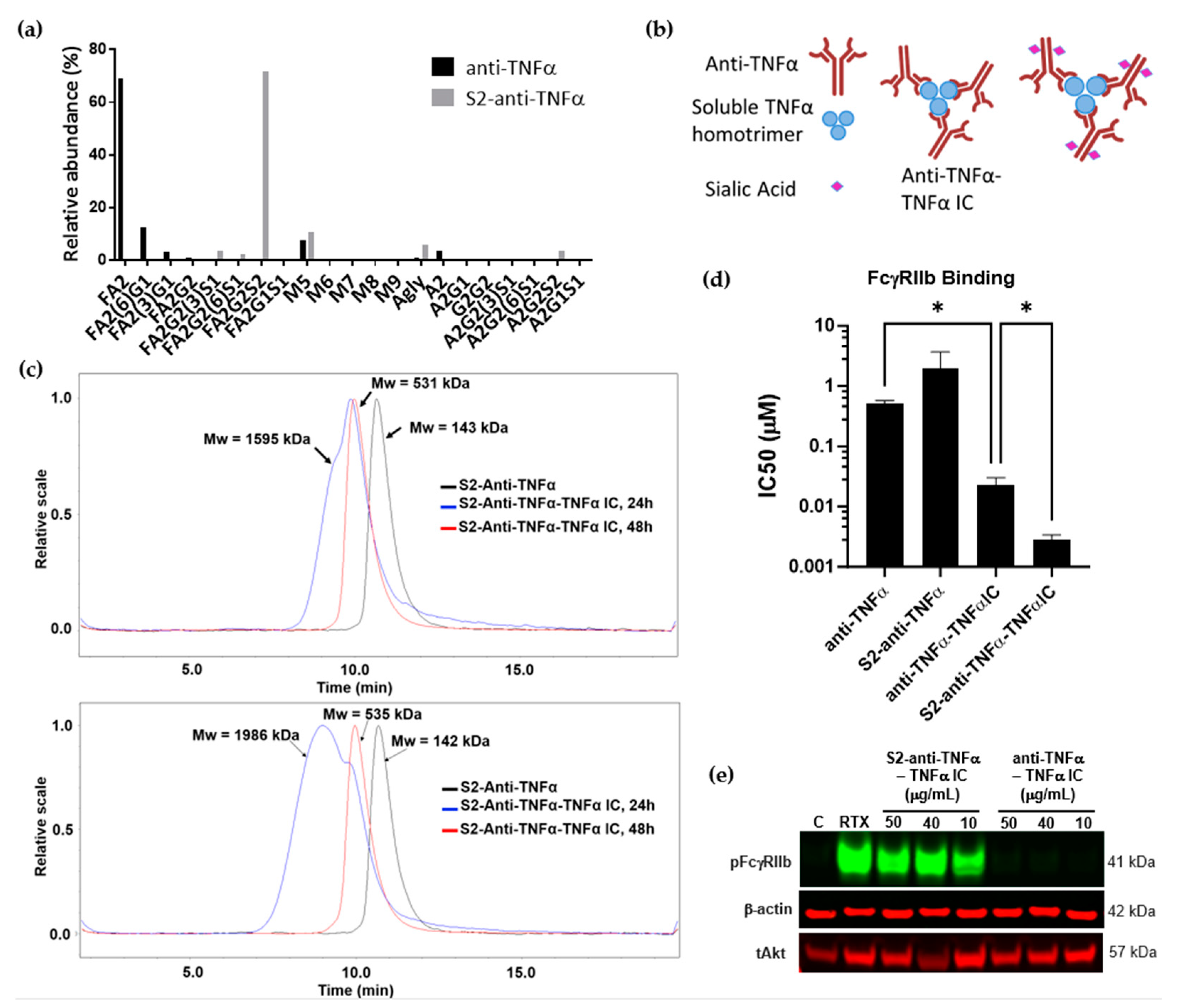
2.4. Measuring Complex Formation of TNFα-(S2) Anti-TNFα
2.5. Cell-Based FcγR Binding Measurements
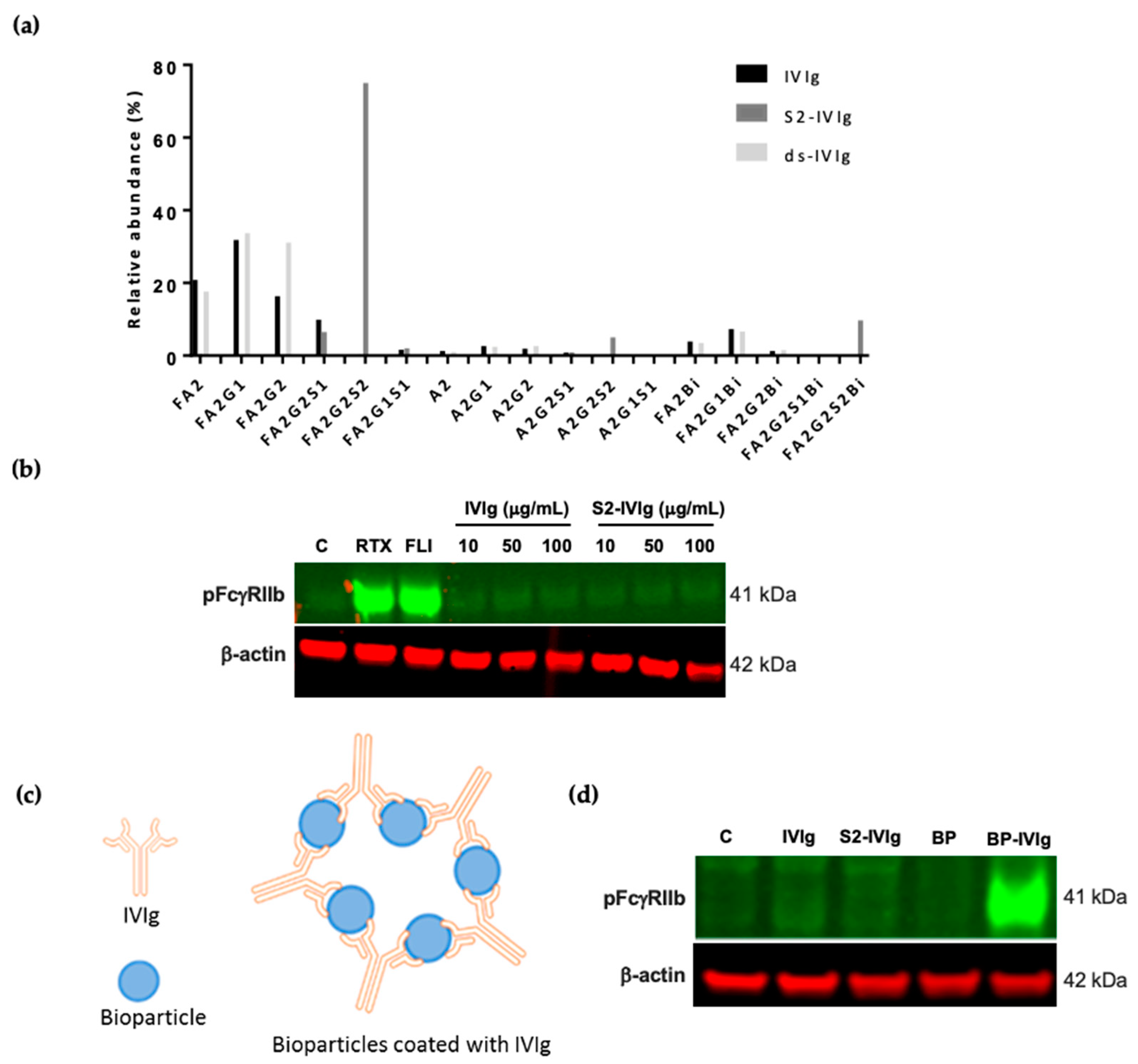
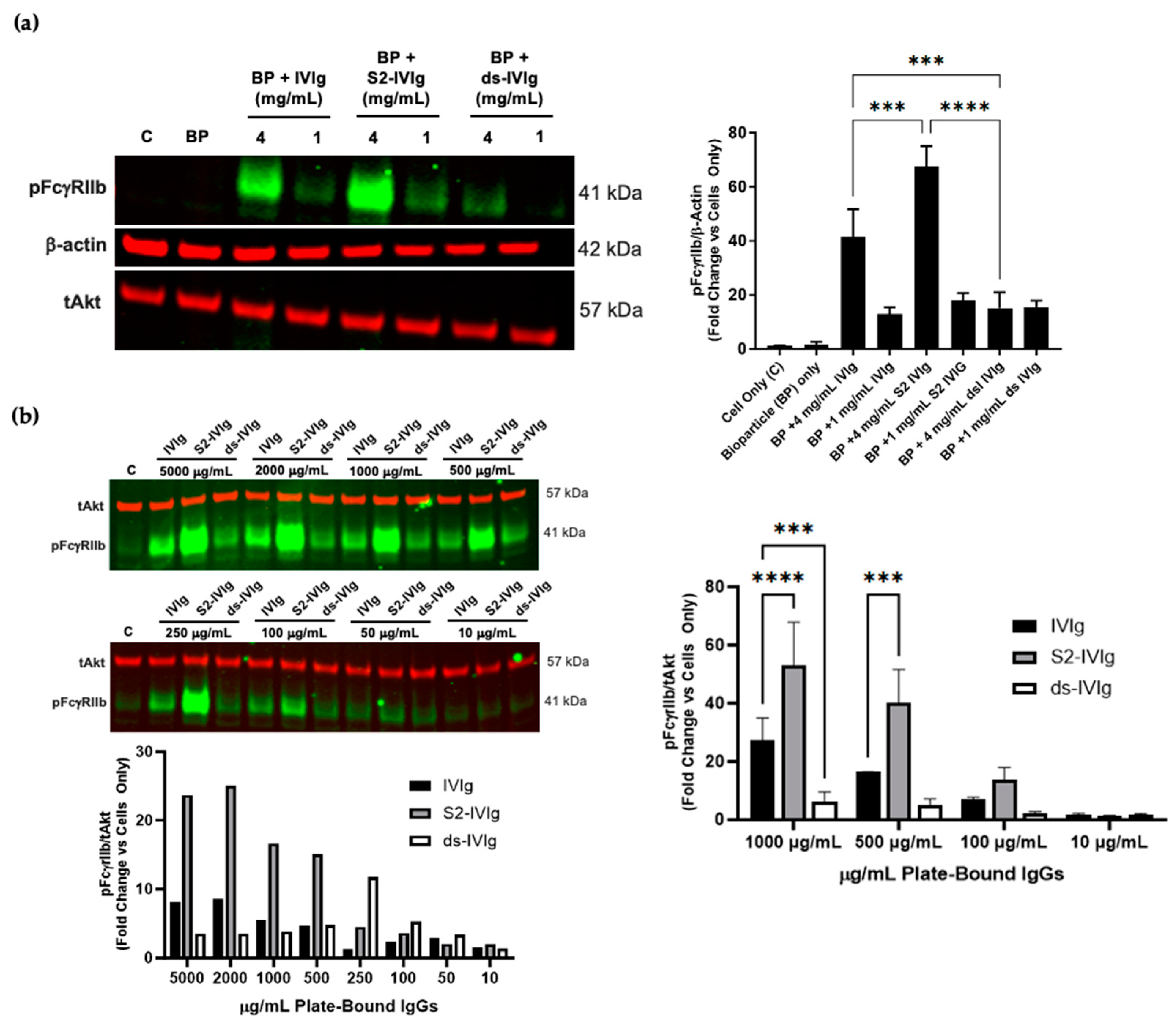
2.6. Staphylococcus aureus Bioparticle Coating with IVIg
2.7. Cell Treatments and Immunoblot Detection of Phosphorylated FcγRIIb in Daudi B Cell Lines
2.8. Flow Cytometry Analysis of Human PBMCs
2.9. Statistics
3. Results
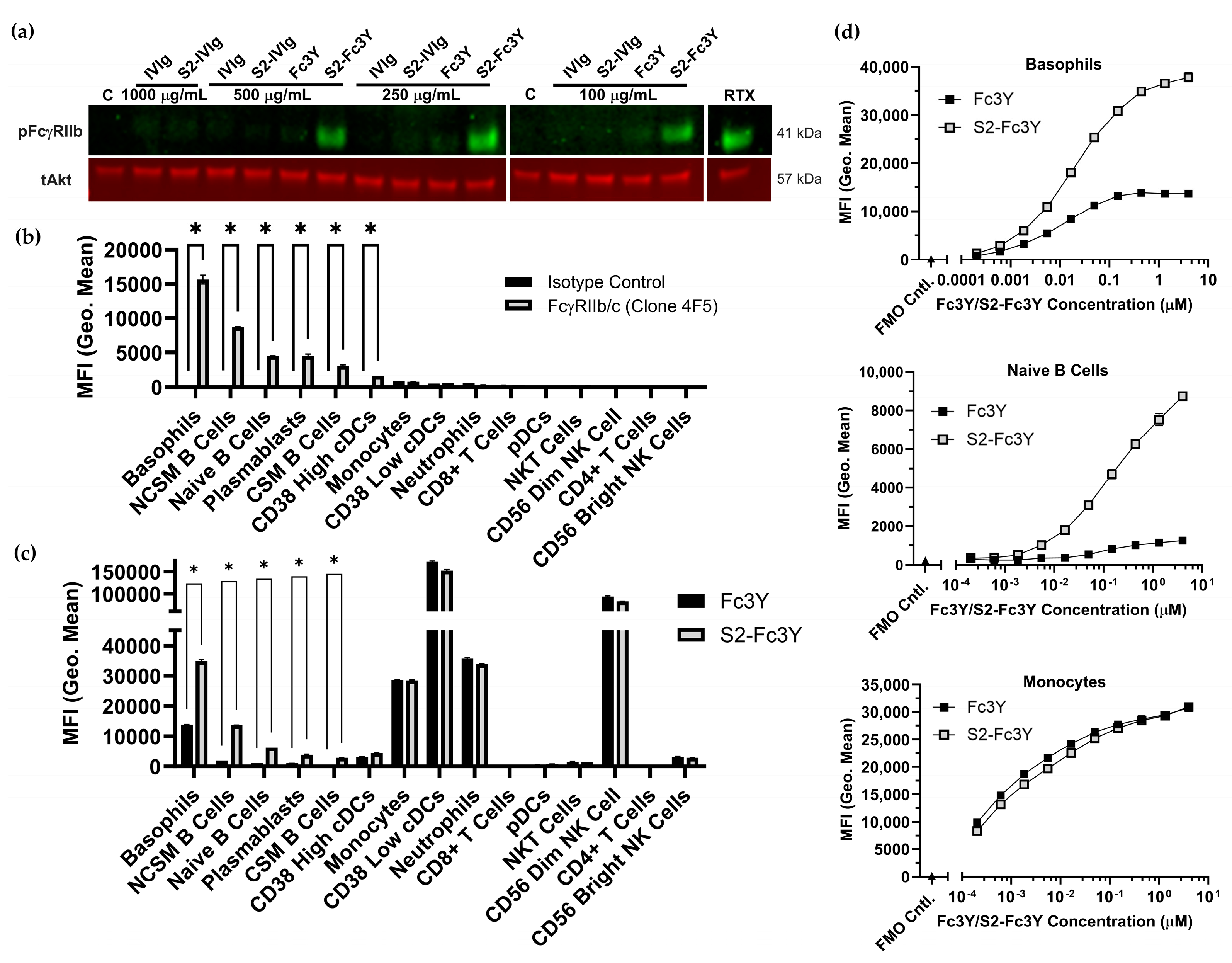
3.1. IVIg-Induced FcγRIIb Signaling in Human Immune Cells Is Dependent on Sialylation
3.2. IVIg-Induced FcγRIIb Signaling Is Sensitive to Sialylation Levels
3.3. TNFα/Anti-TNFα Immune Complexes Lead to FcγRIIb Signaling Only When Antibodies Are Sialylated
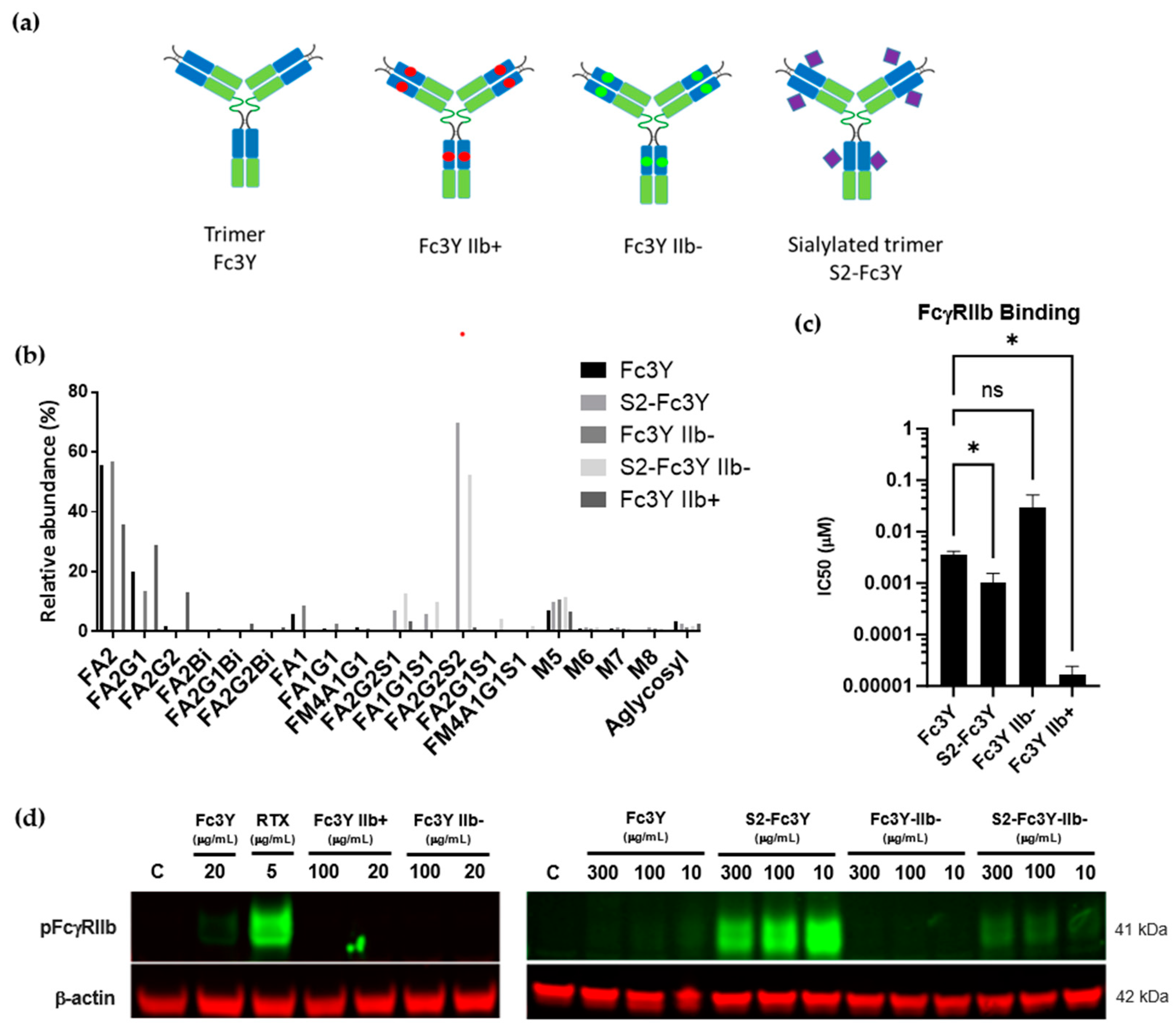
3.4. Increase in Fc Valency Significantly Impacts FcγRIIb Signaling Only in the Presence of Fc Sialylation
3.5. FcgRIIb Singaling in PBMCs Is Dependent on Fc Valency and Sialylation
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hogarth, P.M.; Pietersz, G.A. Fc receptor-targeted therapies for the treatment of inflammation, cancer and beyond. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2012, 11, 311–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nimmerjahn, F.; Ravetch, J.V. FcgammaRs in health and disease. Curr. Top. Microbiol. Immunol. 2011, 350, 105–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arnold, J.N.; Wormald, M.R.; Sim, R.B.; Rudd, P.M.; Dwek, R.A. The impact of glycosylation on the biological function and structure of human immunoglobulins. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2007, 25, 21–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwab, I.; Nimmerjahn, F. Intravenous immunoglobulin therapy: How does IgG modulate the immune system? Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2013, 13, 176–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mimura, Y.; Church, S.; Ghirlando, R.; Ashton, P.R.; Dong, S.; Goodall, M.; Lund, J.; Jefferis, R. The influence of glycosylation on the thermal stability and effector function expression of human IgG1-Fc: Properties of a series of truncated glycoforms. Mol. Immunol. 2000, 37, 697–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mimura, Y.; Sondermann, P.; Ghirlando, R.; Lund, J.; Young, S.P.; Goodall, M.; Jefferis, R. Role of oligosaccharide residues of IgG1-Fc in Fc gamma RIIb binding. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 45539–45547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jefferis, R.; Lund, J. Interaction sites on human IgG-Fc for FcgammaR: Current models. Immunol. Lett. 2002, 82, 57–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sondermann, P.; Kaiser, J.; Jacob, U. Molecular basis for immune complex recognition: A comparison of Fc-receptor structures. J. Mol. Biol. 2001, 309, 737–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nimmerjahn, F.; Ravetch, J.V. Fcgamma receptors: Old friends and new family members. Immunity 2006, 24, 19–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scallon, B.J.; Tam, S.H.; McCarthy, S.G.; Cai, A.N.; Raju, T.S. Higher levels of sialylated Fc glycans in immunoglobulin G molecules can adversely impact functionality. Mol. Immunol. 2007, 44, 1524–1534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaneko, Y.; Nimmerjahn, F.; Ravetch, J.V. Anti-inflammatory activity of immunoglobulin G resulting from Fc sialylation. Science 2006, 313, 670–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwab, I.; Mihai, S.; Seeling, M.; Kasperkiewicz, M.; Ludwig, R.J.; Nimmerjahn, F. Broad requirement for terminal sialic acid residues and FcgammaRIIB for the preventive and therapeutic activity of intravenous immunoglobulins in vivo. Eur. J. Immunol. 2014, 44, 1444–1453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Washburn, N.; Schwab, I.; Ortiz, D.; Bhatnagar, N.; Lansing, J.C.; Medeiros, A.; Tyler, S.; Mekala, D.; Cochran, E.; Sarvaiya, H.; et al. Controlled tetra-Fc sialylation of IVIg results in a drug candidate with consistent enhanced anti-inflammatory activity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, E1297–E1306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tackenberg, B.; Jelcic, I.; Baerenwaldt, A.; Oertel, W.H.; Sommer, N.; Nimmerjahn, F.; Lunemann, J.D. Impaired inhibitory Fcgamma receptor IIB expression on B cells in chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 4788–4792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anthony, R.M.; Kobayashi, T.; Wermeling, F.; Ravetch, J.V. Intravenous gammaglobulin suppresses inflammation through a novel T(H)2 pathway. Nature 2011, 475, 110–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anthony, R.M.; Nimmerjahn, F.; Ashline, D.J.; Reinhold, V.N.; Paulson, J.C.; Ravetch, J.V. Recapitulation of IVIG anti-inflammatory activity with a recombinant IgG Fc. Science 2008, 320, 373–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruhns, P.; Samuelsson, A.; Pollard, J.W.; Ravetch, J.V. Colony-stimulating factor-1-dependent macrophages are responsible for IVIG protection in antibody-induced autoimmune disease. Immunity 2003, 18, 573–581. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, H.S.; Sun, D.S.; Lien, T.S.; Chang, H.H. Dendritic cells modulate platelet activity in IVIg-mediated amelioration of ITP in mice. Blood 2010, 116, 5002–5009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Samuelsson, A.; Towers, T.L.; Ravetch, J.V. Anti-inflammatory activity of IVIG mediated through the inhibitory Fc receptor. Science 2001, 291, 484–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hurez, V.; Kaveri, S.V.; Mouhoub, A.; Dietrich, G.; Mani, J.C.; Klatzmann, D.; Kazatchkine, M.D. Anti-CD4 activity of normal human immunoglobulin G for therapeutic use. (Intravenous immunoglobulin, IVIg). Ther. Immunol. 1994, 1, 269–277. [Google Scholar]
- Lamoureux, J.; Aubin, E.; Lemieux, R. Autoimmune complexes in human serum in presence of therapeutic amounts of intravenous immunoglobulins. Blood 2003, 101, 1660–1662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamoureux, J.; Aubin, E.; Lemieux, R. Autoantibodies purified from therapeutic preparations of intravenous immunoglobulins (IVIg) induce the formation of autoimmune complexes in normal human serum: A role in the in vivo mechanisms of action of IVIg? Int. Immunol. 2004, 16, 929–936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Svenson, M.; Hansen, M.B.; Ross, C.; Diamant, M.; Rieneck, K.; Nielsen, H.; Bendtzen, K. Antibody to granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor is a dominant anti-cytokine activity in human IgG preparations. Blood 1998, 91, 2054–2061. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Jerzak, M.; Rechberger, T.; Gorski, A. Intravenous immunoglobulin therapy influences T cell adhesion to extracellular matrix in women with a history of recurrent spontaneous abortions. Am. J. Reprod. Immunol. 2000, 44, 336–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rossi, F.; Kazatchkine, M.D. Antiidiotypes against autoantibodies in pooled normal human polyspecific Ig. J. Immunol. 1989, 143, 4104–4109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takei, S.; Arora, Y.K.; Walker, S.M. Intravenous immunoglobulin contains specific antibodies inhibitory to activation of T cells by staphylococcal toxin superantigens [see comment]. J. Clin. Investig. 1993, 91, 602–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teeling, J.L.; Jansen-Hendriks, T.; Kuijpers, T.W.; de Haas, M.; van de Winkel, J.G.; Hack, C.E.; Bleeker, W.K. Therapeutic efficacy of intravenous immunoglobulin preparations depends on the immunoglobulin G dimers: Studies in experimental immune thrombocytopenia. Blood 2001, 98, 1095–1099. [Google Scholar]
- Zhuang, Q.; Mazer, B. Inhibition of IgE production in vitro by intact and fragmented intravenous immunoglobulin. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2001, 108, 229–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kao, D.; Danzer, H.; Collin, M.; Gross, A.; Eichler, J.; Stambuk, J.; Lauc, G.; Lux, A.; Nimmerjahn, F. A Monosaccharide Residue Is Sufficient to Maintain Mouse and Human IgG Subclass Activity and Directs IgG Effector Functions to Cellular Fc Receptors. Cell Rep. 2015, 13, 2376–2385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lux, A.; Yu, X.; Scanlan, C.N.; Nimmerjahn, F. Impact of immune complex size and glycosylation on IgG binding to human FcgammaRs. J. Immunol. 2013, 190, 4315–4323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, S.H.; Vaughan, A.T.; Ashton-Key, M.; Williams, E.L.; Dixon, S.V.; Chan, H.T.; Beers, S.A.; French, R.R.; Cox, K.L.; Davies, A.J.; et al. Fc gamma receptor IIb on target B cells promotes rituximab internalization and reduces clinical efficacy. Blood 2011, 118, 2530–2540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siragam, V.; Brinc, D.; Crow, A.R.; Song, S.; Freedman, J.; Lazarus, A.H. Can antibodies with specificity for soluble antigens mimic the therapeutic effects of intravenous IgG in the treatment of autoimmune disease? J. Clin. Investig. 2005, 115, 155–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santora, L.C.; Kaymakcalan, Z.; Sakorafas, P.; Krull, I.S.; Grant, K. Characterization of noncovalent complexes of recombinant human monoclonal antibody and antigen using cation exchange, size exclusion chromatography, and BIAcore. Anal. Biochem. 2001, 299, 119–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beneduce, C.; Kurtagic, E.; Bosques, C.J. Anti-inflammatory Activity of IgG-Fc. Curr. Top. Microbiol. Immunol. 2019, 423, 35–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nimmerjahn, F.; Vidarsson, G.; Cragg, M.S. Effect of posttranslational modifications and subclass on IgG activity: From immunity to immunotherapy. Nat. Immunol. 2023, 24, 1244–1255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pincetic, A.; Bournazos, S.; DiLillo, D.J.; Maamary, J.; Wang, T.T.; Dahan, R.; Fiebiger, B.M.; Ravetch, J.V. Type I and type II Fc receptors regulate innate and adaptive immunity. Nat. Immunol. 2014, 15, 707–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maenaka, K.; van der Merwe, P.A.; Stuart, D.I.; Jones, E.Y.; Sondermann, P. The human low affinity Fcgamma receptors IIa, IIb, and III bind IgG with fast kinetics and distinct thermodynamic properties. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 44898–44904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boruchov, A.M.; Heller, G.; Veri, M.C.; Bonvini, E.; Ravetch, J.V.; Young, J.W. Activating and inhibitory IgG Fc receptors on human DCs mediate opposing functions. J. Clin. Investig. 2005, 115, 2914–2923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, S.Y.; Vostiar, I.; Karki, S.; Moore, G.L.; Lazar, G.A.; Pong, E.; Joyce, P.F.; Szymkowski, D.E.; Desjarlais, J.R. Inhibition of B cell receptor-mediated activation of primary human B cells by coengagement of CD19 and FcgammaRIIb with Fc-engineered antibodies. Mol. Immunol. 2008, 45, 3926–3933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heyman, B. Feedback regulation by IgG antibodies. Immunol. Lett. 2003, 88, 157–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiener, P.A.; Lioubin, M.N.; Rohrschneider, L.R.; Ledbetter, J.A.; Nadler, S.G.; Diegel, M.L. Co-ligation of the antigen and Fc receptors gives rise to the selective modulation of intracellular signaling in B cells. Regulation of the association of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase and inositol 5′-phosphatase with the antigen receptor complex. J. Biol. Chem. 1997, 272, 3838–3844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ono, M.; Okada, H.; Bolland, S.; Yanagi, S.; Kurosaki, T.; Ravetch, J.V. Deletion of SHIP or SHP-1 reveals two distinct pathways for inhibitory signaling. Cell 1997, 90, 293–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiang, Z.; Cutler, A.J.; Brownlie, R.J.; Fairfax, K.; Lawlor, K.E.; Severinson, E.; Walker, E.U.; Manz, R.A.; Tarlinton, D.M.; Smith, K.G. FcgammaRIIb controls bone marrow plasma cell persistence and apoptosis. Nat. Immunol. 2007, 8, 419–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pearse, R.N.; Kawabe, T.; Bolland, S.; Guinamard, R.; Kurosaki, T.; Ravetch, J.V. SHIP recruitment attenuates Fc gamma RIIB-induced B cell apoptosis. Immunity 1999, 10, 753–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rieth, N.; Carle, A.; Muller, M.A.; ter Meer, D.; Direnberger, C.; Pohl, T.; Sondermann, P. Characterization of SM201, an anti-hFcgammaRIIB antibody not interfering with ligand binding that mediates immune complex dependent inhibition of B cells. Immunol. Lett. 2014, 160, 145–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akilesh, S.; Petkova, S.; Sproule, T.J.; Shaffer, D.J.; Christianson, G.J.; Roopenian, D. The MHC class I-like Fc receptor promotes humorally mediated autoimmune disease. J. Clin. Investig. 2004, 113, 1328–1333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crow, A.R.; Song, S.; Freedman, J.; Helgason, C.D.; Humphries, R.K.; Siminovitch, K.A.; Lazarus, A.H. IVIg-mediated amelioration of murine ITP via FcgammaRIIB is independent of SHIP1, SHP-1, and Btk activity. Blood 2003, 102, 558–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mihaylova, N.; Voynova, E.; Tchorbanov, A.; Dolashka-Angelova, P.; Bayry, J.; Devreese, B.; Kaveri, S.; Vassilev, T. Simultaneous engagement of FcgammaIIb and CD22 inhibitory receptors silences targeted B cells and suppresses autoimmune disease activity. Mol. Immunol. 2009, 47, 123–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seeling, M.; Pohnl, M.; Kara, S.; Horstmann, N.; Riemer, C.; Wohner, M.; Liang, C.; Bruckner, C.; Eiring, P.; Werner, A.; et al. Immunoglobulin G-dependent inhibition of inflammatory bone remodeling requires pattern recognition receptor Dectin-1. Immunity 2023, 56, 1046–1063.e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Beneduce, C.; Nguyen, S.; Washburn, N.; Schaeck, J.; Meccariello, R.; Holte, K.; Ortiz, D.; Manning, A.M.; Bosques, C.J.; Kurtagic, E. Inhibitory Fc-Gamma IIb Receptor Signaling Induced by Multivalent IgG-Fc Is Dependent on Sialylation. Cells 2023, 12, 2130. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells12172130
Beneduce C, Nguyen S, Washburn N, Schaeck J, Meccariello R, Holte K, Ortiz D, Manning AM, Bosques CJ, Kurtagic E. Inhibitory Fc-Gamma IIb Receptor Signaling Induced by Multivalent IgG-Fc Is Dependent on Sialylation. Cells. 2023; 12(17):2130. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells12172130
Chicago/Turabian StyleBeneduce, Christopher, Stephanie Nguyen, Nathaniel Washburn, John Schaeck, Robin Meccariello, Kimberly Holte, Daniel Ortiz, Anthony M. Manning, Carlos J. Bosques, and Elma Kurtagic. 2023. "Inhibitory Fc-Gamma IIb Receptor Signaling Induced by Multivalent IgG-Fc Is Dependent on Sialylation" Cells 12, no. 17: 2130. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells12172130
APA StyleBeneduce, C., Nguyen, S., Washburn, N., Schaeck, J., Meccariello, R., Holte, K., Ortiz, D., Manning, A. M., Bosques, C. J., & Kurtagic, E. (2023). Inhibitory Fc-Gamma IIb Receptor Signaling Induced by Multivalent IgG-Fc Is Dependent on Sialylation. Cells, 12(17), 2130. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells12172130




