Linking Adiposity to Interstitial Lung Disease: The Role of the Dysfunctional Adipocyte and Inflammation
Abstract
:1. Introduction
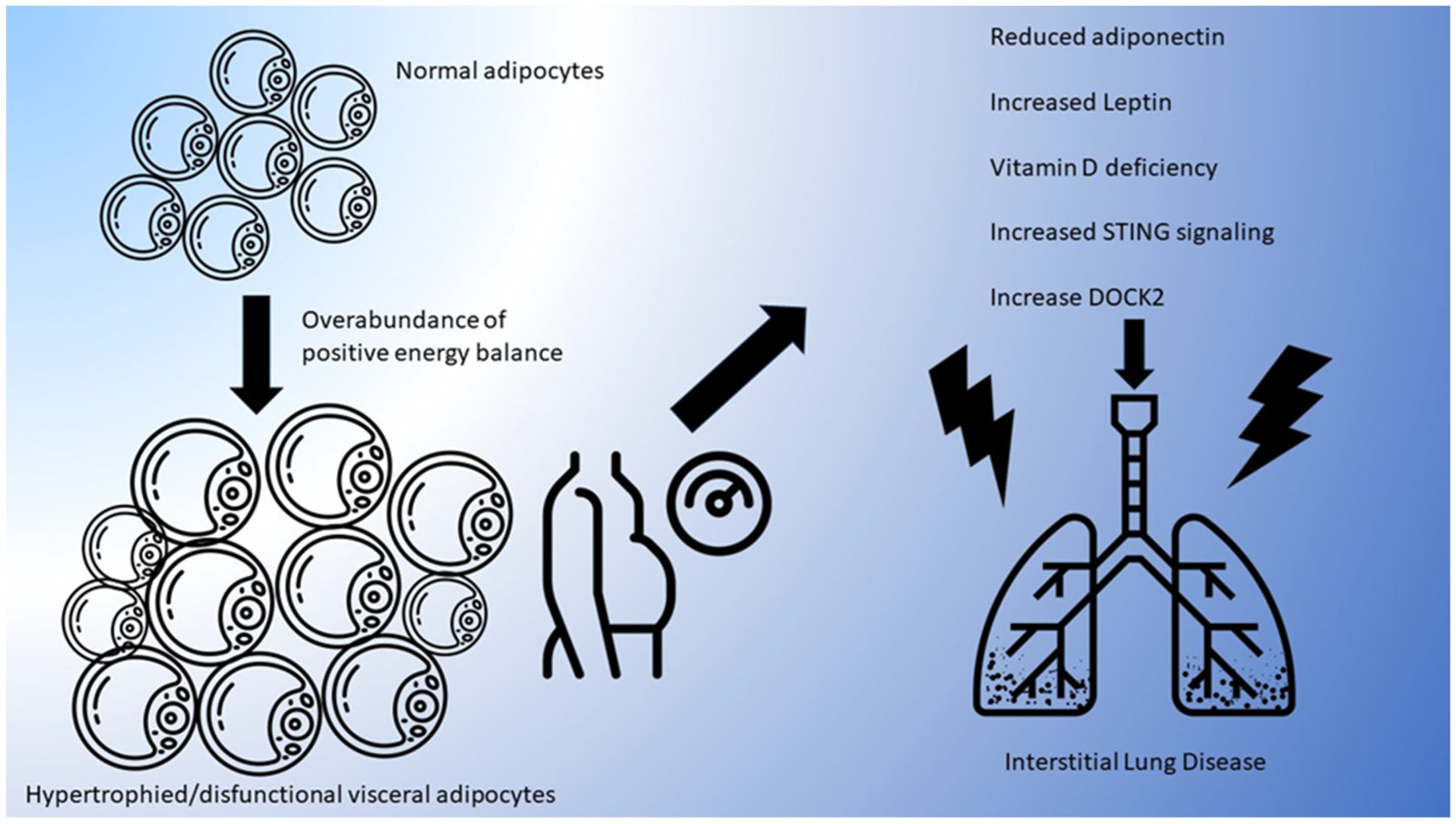
2. Adiposity and the Dysfunctional Adipocyte
3. Adiposity and ILD in Human Studies
3.1. Quantifying Adiposity
3.2. Adiposity Reduction and Clinical Outcomes in ILD
3.3. Adiposity and Underlying Systemic Rheumatic Diseases
4. Inflammation and ILD
4.1. Macrophages
4.2. T and B Lymphocytes
4.3. Eosinophils and Neutrophils
5. Potential Mechanistic Pathways Linking Adiposity with ILD
5.1. Adiponectin, Leptin, and Resistin and ILD Development
5.2. Adiposity-Induced Vitamin D Deficiency
5.3. DOCK2 Signaling
5.4. STING Signaling
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wallis, A.; Spinks, K. The Diagnosis and Management of Interstitial Lung Diseases. BMJ 2015, 350, h2072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luppi, F.; Sebastiani, M.; Salvarani, C.; Bendstrup, E.; Manfredi, A. Acute Exacerbation of Interstitial Lung Disease Associated with Rheumatic Disease. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2022, 18, 85–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zielinski, M.; Chwalba, A.; Jastrzebski, D.; Ziora, D. Adipokines in Interstitial Lung Diseases. Respir. Physiol. Neurobiol. 2023, 315, 104109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.S.; Anderson, M.R.; Podolanczuk, A.J.; Kawut, S.M.; Allison, M.A.; Raghu, G.; Hinckley-Stuckovsky, K.; Hoffman, E.A.; Tracy, R.P.; Barr, R.G.; et al. Associations of Serum Adipokines with Subclinical Interstitial Lung Disease Among Community-Dwelling Adults: The Multi-Ethnic Study of Atherosclerosis (MESA). Chest 2020, 157, 580–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cawley, J.; Biener, A.; Meyerhoefer, C.; Ding, Y.; Zvenyach, T.; Gabriel Smolarz, N.B.; Ramasamy, A. Direct Medical Costs of Obesity in the United States and the Most Populous States. J. Manag. Care Spec. Pharm. 2021, 27, 354–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guh, D.P.; Zhang, W.; Bansback, N.; Amarsi, Z.; Birmingham, C.L.; Anis, A.H. The Incidence of Co-Morbidities Related to Obesity and Overweight: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. BMC Public Health 2009, 9, 88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fox, C.S.; Massaro, J.M.; Hoffmann, U.; Pou, K.M.; Maurovich-Horvat, P.; Liu, C.Y.; Vasan, R.S.; Murabito, J.M.; Meigs, J.B.; Cupples, L.A.; et al. Abdominal Visceral and Subcutaneous Adipose Tissue Compartments: Association with Metabolic Risk Factors in the Framingham Heart Study. Circulation 2007, 116, 39–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scalia, R. The Microcirculation in Adipose Tissue Inflammation. Rev. Endocr. Metab. Disord. 2013, 14, 69–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frayn, K.N.; Karpe, F.; Fielding, B.A.; Macdonald, I.A.; Coppack, S.W. Integrative Physiology of Human Adipose Tissue. Int. J. Obes. 2003, 27, 875–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kershaw, E.E.; Flier, J.S. Adipose Tissue as an Endocrine Organ. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2004, 89, 2548–2556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Marken Lichtenbelt, W. Brown Adipose Tissue and the Regulation of Nonshivering Thermogenesis. Curr. Opin. Clin. Nutr. Metab. Care 2012, 15, 547–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marlatt, K.; Ravussin, E. Brown Adipose Tissue: An Update on Recent Findings. Curr Obes. Rep. 2017, 6, 389–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Vollenhoven, R.F.; Fleischmann, R.M.; Furst, D.E.; Lacey, S.; Lehane, P.B. Longterm Safety of Rituximab: Final Report of the Rheumatoid Arthritis Global Clinical Trial Program over 11 Years. J. Rheumatol. 2015, 42, 1761–1766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghaben, A.L.; Scherer, P.E. Adipogenesis and Metabolic Health. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2019, 20, 242–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hotamisligil, G.S. Inflammation and Metabolic Disorders. Insight Rev.—Nat. 2006, 444, 860–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawai, T.; Autieri, M.V.; Scalia, R. Adipose Tissue Inflammation and Metabolic Dysfunction in Obesity. Am. J. Physiol.—Cell Physiol. 2021, 320, C375–C391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sacks, H.; Symonds, M.E. Anatomical Locations of Human Brown Adipose Tissue: Functional Relevance and Implications in Obesity and Type 2 Diabetes. Diabetes 2013, 62, 1783–1790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bartelt, A.; Heeren, J. Adipose Tissue Browning and Metabolic Health. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2014, 10, 24–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rutkowski, J.M.; Stern, J.H.; Scherer, P.E. The Cell Biology of Fat Expansion. J. Cell Biol. 2015, 208, 501–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santillana, N.; Astudillo-Guerrero, C.; D’Espessailles, A.; Cruz, G. White Adipose Tissue Dysfunction: Pathophysiology and Emergent Measurements. Nutrients 2023, 15, 1722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iacobini, C.; Pugliese, G.; Fantauzzi, C.; Federici, M. Metabolically Healthy versus Metabolically Unhealthy Obesity. Metabolism 2019, 92, 51–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ibrahim, M.M. Subcutaneous and Visceral Adipose Tissue: Structural and Functional Differences. Obes. Rev. 2010, 11, 11–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Longo, M.; Zatterale, F.; Naderi, J.; Parrillo, L.; Formisano, P.; Raciti, G.A.; Beguinot, F.; Miele, C. Adipose Tissue Dysfunction as Determinant of Obesity-Associated Metabolic Complications. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 2358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, M.; Hu, T.; Zhang, S.; Zhou, L. Associations of Different Adipose Tissue Depots with Insulin Resistance: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Observational Studies. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 18495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okada-Iwabu, M.; Yamauchi, T.; Iwabu, M.; Honma, T.; Hamagami, K.I.; Matsuda, K.; Yamaguchi, M.; Tanabe, H.; Kimura-Someya, T.; Shirouzu, M.; et al. A Small-Molecule AdipoR Agonist for Type 2 Diabetes and Short Life in Obesity. Nature 2013, 503, 493–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiernan, K.; MacIver, N.J. The Role of the Adipokine Leptin in Immune Cell Function in Health and Disease. Front. Immunol. 2021, 11, 622468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fasshauer, M.; Blüher, M. Adipokines in Health and Disease. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2015, 36, 461–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masschelin, P.M.; Cox, A.R.; Chernis, N.; Hartig, S.M. The Impact of Oxidative Stress on Adipose Tissue Energy Balance. Front. Physiol. 2020, 10, 1638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Yan, X.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, J.; Liu, B.; Yu, S.; Fu, J.; Liu, Y.; Su, J. Macrophage Polarization Mediated by Mitochondrial Dysfunction Induces Adipose Tissue Inflammation in Obesity. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 9252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kronzer, V.L.; Huang, W.; Dellaripa, P.F.; Huang, S.; Feathers, V.; Lu, B.; Iannaccone, C.K.; Gill, R.R.; Hatabu, H.; Nishino, M.; et al. Lifestyle and Clinical Risk Factors for Incident Rheumatoid Arthritis-Associated Interstitial Lung Disease. J. Rheumatol. 2021, 48, 656–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cotton, C.; Alton, P.; Hughes, D.M.; Zhao, S.S. Genetic Liability to Gastro-Esophageal Reflux Disease, Obesity, and Risk of Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. Respir. Investig. 2023, 61, 335–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, Y.; Feng, C.; Tang, H.; Deng, P.; Li, Y.; Wang, J.; Zhu, S.; Zhu, L. Management of BMI Is a Potential New Approach for the Prevention of Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. Front. Genet. 2022, 13, 821029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alakhras, M.; Decker, P.A.; Nadrous, H.F.; Collazo-Clavell, M.; Ryu, J.H. Body Mass Index and Mortality in Patients with Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. Chest 2007, 131, 1448–1453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sangani, R.G.; Ghio, A.J.; Mujahid, H.; Patel, Z.; Catherman, K.; Wen, S.; Parker, J.E. Outcomes of Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis Improve with Obesity: A Rural Appalachian Experience. South. Med. J. 2021, 114, 424–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashwell, M.; Gibson, S. Waist-to-Height Ratio as an Indicator of “Early Health Risk”: Simpler and More Predictive than Using a “matrix” Based on BMI and Waist Circumference. BMJ Open 2016, 6, e010159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janssen, I.; Katzmarzyk, P.T.; Ross, R. Waist Circumference and Not Body Mass Index Explains Obesity-Related Health Risk. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2004, 79, 379–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guasch-Ferré, M.; Bulló, M.; Martínez-González, M.Á.; Corella, D.; Estruch, R.; Covas, M.-I.; Arós, F.; Wärnberg, J.; Fiol, M.; Lapetra, J.; et al. Waist-to-Height Ratio and Cardiovascular Risk Factors in Elderly Individuals at High Cardiovascular Risk. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e43275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brambilla, P.; Bedogni, G.; Heo, M.; Pietrobelli, A. Waist Circumference-to-Height Ratio Predicts Adiposity Better than Body Mass Index in Children and Adolescents. Int. J. Obes. 2013, 37, 943–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, H.J.; Friedrich, N.; Klotsche, J.; Pieper, L.; Nauck, M.; John, U.; Dörr, M.; Felix, S.; Lehnert, H.; Pittrow, D.; et al. The Predictive Value of Different Measures of Obesity for Incident Cardiovascular Events and Mortality. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2010, 95, 1777–1785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hata, A.; Schiebler, M.L.; Lynch, D.A.; Hatabu, H. Interstitial Lung Abnormalities: State of the Art. Radiology 2021, 301, 19–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, M.R.; Kim, J.S.; Allison, M.; Giles, J.T.; Hoffman, E.A.; Ding, J.; Barr, R.G.; Podolanczuk, A. Adiposity and Interstitial Lung Abnormalities in Community-Dwelling Adults: The MESA Cohort Study. Chest 2021, 160, 582–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Comes, A.; Wong, A.W.; Fisher, J.H.; Morisset, J.; Johannson, K.A.; Farrand, E.; Fell, C.D.; Kolb, M.; Manganas, H.; Cox, G.; et al. Association of BMI and Change in Weight with Mortality in Patients with Fibrotic Interstitial Lung Disease. Chest 2022, 161, 1320–1329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clamon, G.; Byrne, M.M.; Talbert, E.E. Inflammation as a Therapeutic Target in Cancer Cachexia. Cancers 2022, 14, 5262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, Y.; Yoshimura, K.; Enomoto, Y.; Yasui, H.; Hozumi, H.; Karayama, M.; Furuhashi, K.; Enomoto, N.; Fujisawa, T.; Nakamura, Y.; et al. Distinct Profile and Prognostic Impact of Body Composition Changes in Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis and Idiopathic Pleuroparenchymal Fibroelastosis. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 14074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ardila-Gatas, J.; Sharma, G.; Nor Hanipah, Z.; Tu, C.; Brethauer, S.A.; Aminian, A.; Tolle, L.; Schauer, P.R. Bariatric Surgery in Patients with Interstitial Lung Disease. Surg. Endosc. 2019, 33, 1952–1958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sekine, A.; Wasamoto, S.; Hagiwara, E.; Yamakawa, H.; Ikeda, S.; Okabayashi, H.; Oda, T.; Okuda, R.; Kitamura, H.; Baba, T.; et al. Beneficial Impact of Weight Loss on Respiratory Function in Interstitial Lung Disease Patients with Obesity. Respir. Investig. 2021, 59, 247–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dixon, A.E.; Peters, U. The Effect of Obesity on Lung Function. Expert Rev. Respir. Med. 2018, 12, 755–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehari, A.; Afreen, S.; Ngwa, J.; Setse, R.; Thomas, A.N.; Poddar, V.; Davis, W.; Polk, O.D.; Hassan, S.; Thomas, A. V Obesity and Pulmonary Function in African Americans. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0140610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamaguchi, K.; Fukushima, Y.; Yamaguchi, A.; Itai, M.; Shin, Y.; Uno, S.; Muto, S.; Kouno, S.; Tsurumaki, H.; Yatomi, M.; et al. Influence of Obesity in Interstitial Lung Disease Associated with Anti-Aminoacyl-TRNA Synthetase Antibodies. Respir. Med. 2022, 193, 106741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnold, D.T.; Donald, C.; Lyon, M.; Hamilton, F.W.; Morley, A.J.; Attwood, M.; Dipper, A.; Barratt, S.L. Krebs von Den Lungen 6 (KL-6) as a Marker for Disease Severity and Persistent Radiological Abnormalities Following COVID-19 Infection at 12 Weeks. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0249607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M.M.; Balmert, L.C.; Marangoni, R.G.; Carns, M.; Hinchcliff, M.; Korman, B.D.; Varga, J. Circulating CTRP9 Is Associated with Severity of Systemic Sclerosis-Associated Interstitial Lung Disease. Arthritis Care Res. 2023, 75, 152–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nieva-Vazquez, A.; Pérez-Fuentes, R.; Torres-Rasgado, E.; López-López, J.G.; Romero, J.R. Serum Resistin Levels Are Associated with Adiposity and Insulin Sensitivity in Obese Hispanic Subjects. Metab. Syndr. Relat. Disord. 2014, 12, 143–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sawicka, K.; Michalska-Jakubus, M.; Kowal, M.; Potembska, E.; Krasowska, D. Resistin: A Possible Biomarker of Organ Involvement in Systemic Sclerosis Patients? Clin. Exp. Rheumatol. 2017, 35 (Suppl. S1), 144–150. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ye, L.; Zuo, Y.; Chen, F.; Xu, Y.; Zhang, P.; Yang, H.; Lin, S.; Peng, Q.; Wang, G.; Shu, X. Resistin Expression Is Associated with Interstitial Lung Disease in Dermatomyositis. Front. Med. 2022, 9, 903887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- American Thoracic Society (ATS); The European Respiratory Society (ERS). American Thoracic Society; European Respiratory Society American Thoracic Society/European Respiratory Society. International Multidisciplinary Consensus Classification of the Idiopathic Interstitial Pneumonias. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2002, 165, 277–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maher, T.M.; Nambiar, A.M.; Wells, A.U. The Role of Precision Medicine in Interstitial Lung Disease. Eur. Respir. J. 2022, 60, 2102146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, E.S. Lung Extracellular Matrix and Fibroblast Function. Ann. Am. Thorac. Soc. 2015, 12 (Suppl. S1), S30–S33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, E.B. The Complex Role of Adipokines in Obesity, Inflammation, and Autoimmunity. Clin. Sci. 2021, 135, 731–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Sunil, C.; Qian, G. Obesity and the Development of Lung Fibrosis. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 812166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, S.; Alexander, M.; Misharin, A.V.; Budinger, G.R.S. The Role of Macrophages in the Resolution of Inflammation. J. Clin. Investig. 2019, 129, 2619–2628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weisberg, S.P.; McCann, D.; Desai, M.; Rosenbaum, M.; Leibel, R.L.; Ferrante, A.W. Obesity Is Associated with Macrophage Accumulation in Adipose Tissue. J. Clin. Investig. 2003, 112, 1796–1808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruggiero, A.D.; Key, C.C.C.; Kavanagh, K. Adipose Tissue Macrophage Polarization in Healthy and Unhealthy Obesity. Front. Nutr. 2021, 8, 625331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, J.; Wu, D.; Qiu, Y. Adipose Tissue Macrophage in Obesity-Associated Metabolic Diseases. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 977485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruiz-Ojeda, F.J.; Méndez-Gutiérrez, A.; Aguilera, C.M.; Plaza-Díaz, J. Extracellular Matrix Remodeling of Adipose Tissue in Obesity and Metabolic Diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 4888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ogawa, T.; Shichino, S.; Ueha, S.; Matsushima, K. Macrophages in Lung Fibrosis. Int. Immunol. 2021, 33, 665–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Adwi, Y.; Westra, J.; van Goor, H.; Burgess, J.K.; Denton, C.P.; Mulder, D.J. Macrophages as Determinants and Regulators of Fibrosis in Systemic Sclerosis. Rheumatology 2023, 62, 535–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Wang, Y.; Wu, G.; Xiong, W.; Gu, W.; Wang, C.-Y. Macrophages: Friend or Foe in Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis? Respir. Res. 2018, 19, 170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Misharin, A.V.; Morales-Nebreda, L.; Reyfman, P.A.; Cuda, C.M.; Walter, J.M.; McQuattie-Pimentel, A.C.; Chen, C.-I.; Anekalla, K.R.; Joshi, N.; Williams, K.J.N.; et al. Monocyte-Derived Alveolar Macrophages Drive Lung Fibrosis and Persist in the Lung over the Life Span. J. Exp. Med. 2017, 214, 2387–2404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCubbrey, A.L.; Barthel, L.; Mohning, M.P.; Redente, E.F.; Mould, K.J.; Thomas, S.M.; Leach, S.M.; Danhorn, T.; Gibbings, S.L.; Jakubzick, C.V.; et al. Deletion of C-FLIP from CD11bhi Macrophages Prevents Development of Bleomycin-Induced Lung Fibrosis. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2018, 58, 66–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joshi, N.; Watanabe, S.; Verma, R.; Jablonski, R.P.; Chen, C.-I.; Cheresh, P.; Markov, N.S.; Reyfman, P.A.; McQuattie-Pimentel, A.C.; Sichizya, L.; et al. A Spatially Restricted Fibrotic Niche in Pulmonary Fibrosis Is Sustained by M-CSF/M-CSFR Signalling in Monocyte-Derived Alveolar Macrophages. Eur. Respir. J. 2020, 55, 1900646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, P.K.; Anderson, K.C.; McManus, S.A.; Tu, T.-H.; King, E.M.; Mould, K.J.; Redente, E.F.; Henson, P.M.; Janssen, W.J.; McCubbrey, A.L. Single-Cell RNA Sequencing Reveals Unique Monocyte-Derived Interstitial Macrophage Subsets during Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Acute Lung Inflammation. Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell. Mol. Physiol. 2023, 324, L536–L549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, P.; Li, S.; Chen, H. Macrophages in Lung Injury, Repair, and Fibrosis. Cells 2021, 10, 436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kreuter, M.; Lee, J.S.; Tzouvelekis, A.; Oldham, J.M.; Molyneaux, P.L.; Weycker, D.; Atwood, M.; Kirchgaessler, K.-U.; Maher, T.M. Monocyte Count as a Prognostic Biomarker in Patients with Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2021, 204, 74–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trombetta, A.C.; Soldano, S.; Contini, P.; Tomatis, V.; Ruaro, B.; Paolino, S.; Brizzolara, R.; Montagna, P.; Sulli, A.; Pizzorni, C.; et al. A Circulating Cell Population Showing Both M1 and M2 Monocyte/Macrophage Surface Markers Characterizes Systemic Sclerosis Patients with Lung Involvement. Respir. Res. 2018, 19, 186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhandari, R.; Ball, M.S.; Martyanov, V.; Popovich, D.; Schaafsma, E.; Han, S.; ElTanbouly, M.; Orzechowski, N.M.; Carns, M.; Arroyo, E.; et al. Profibrotic Activation of Human Macrophages in Systemic Sclerosis. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2020, 72, 1160–1169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McDowell, S.A.C.; Milette, S.; Doré, S.; Yu, M.W.; Sorin, M.; Wilson, L.; Desharnais, L.; Cristea, A.; Varol, O.; Atallah, A.; et al. Obesity Alters Monocyte Developmental Trajectories to Enhance Metastasis. J. Exp. Med. 2023, 220, e20220509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krinninger, P.; Ensenauer, R.; Ehlers, K.; Rauh, K.; Stoll, J.; Krauss-Etschmann, S.; Hauner, H.; Laumen, H. Peripheral Monocytes of Obese Women Display Increased Chemokine Receptor Expression and Migration Capacity. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2014, 99, 2500–2509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsukuda, T.K.; Ohnishi, H.; Fujimoto, M.; Nakatani, Y.; Takamatsu, K.; Naka, T.; Yokoyama, A. Lung CCR6−CXCR3− Type 2 Helper T Cells as an Indicator of Progressive Fibrosing Interstitial Lung Diseases. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 19577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matarese, G. The Link between Obesity and Autoimmunity. Science 2023, 379, 1298–1300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.; Chung, H.; Lee, J.E.; Kim, J.; Hwang, J.; Chung, Y. Immunologic Aspects of Dyslipidemia: A Critical Regulator of Adaptive Immunity and Immune Disorders. J. Lipid Atheroscler. 2021, 10, 184–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moog, M.T.; Hinze, C.; Bormann, T.; Aschenbrenner, F.; Knudsen, L.; DeLuca, D.S.; Jonigk, D.; Neubert, L.; Welte, T.; Gauldie, J.; et al. B Cells Are Not Involved in the Regulation of Adenoviral TGF-Β1- or Bleomycin-Induced Lung Fibrosis in Mice. J. Immunol. 2022, 208, 1259–1271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atkins, S.R.; Turesson, C.; Myers, J.L.; Tazelaar, H.D.; Ryu, J.H.; Matteson, E.L.; Bongartz, T. Morphologic and Quantitative Assessment of CD20+ B Cell Infiltrates in Rheumatoid Arthritis-Associated Nonspecific Interstitial Pneumonia and Usual Interstitial Pneumonia. Arthritis Rheum. 2006, 54, 635–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rangel-Moreno, J.; Hartson, L.; Navarro, C.; Gaxiola, M.; Selman, M.; Randall, T.D. Inducible Bronchus-Associated Lymphoid Tissue (IBALT) in Patients with Pulmonary Complications of Rheumatoid Arthritis. J. Clin. Investig. 2006, 116, 3183–3194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ali, M.F.; Egan, A.M.; Shaughnessy, G.F.; Anderson, D.K.; Kottom, T.J.; Dasari, H.; Van Keulen, V.P.; Aubry, M.-C.; Yi, E.S.; Limper, A.H.; et al. Antifibrotics Modify B-Cell-Induced Fibroblast Migration and Activation in Patients with Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2021, 64, 722–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oleinika, K.; Slisere, B.; Catalán, D.; Rosser, E.C. B Cell Contribution to Immunometabolic Dysfunction and Impaired Immune Responses in Obesity. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2022, 210, 263–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frasca, D.; Ferracci, F.; Diaz, A.; Romero, M.; Lechner, S.; Blomberg, B.B. Obesity Decreases B Cell Responses in Young and Elderly Individuals. Obesity 2016, 24, 615–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jenks, S.A.; Cashman, K.S.; Zumaquero, E.; Marigorta, U.M.; Patel, A.V.; Wang, X.; Tomar, D.; Woodruff, M.C.; Simon, Z.; Bugrovsky, R.; et al. Distinct Effector B Cells Induced by Unregulated Toll-like Receptor 7 Contribute to Pathogenic Responses in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. Immunity 2018, 49, 725–739.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agrawal, S.; Gollapudi, S.; Su, H.; Gupta, S. Leptin Activates Human B Cells to Secrete TNF-α, IL-6, and IL-10 via JAK2/STAT3 and P38MAPK/ERK1/2 Signaling Pathway. J. Clin. Immunol. 2011, 31, 472–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, C.K.; Cheung, P.F.Y.; Lam, C.W.K. Leptin-Mediated Cytokine Release and Migration of Eosinophils: Implications for Immunopathophysiology of Allergic Inflammation. Eur. J. Immunol. 2007, 37, 2337–2348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cottin, V. Eosinophilic Lung Diseases. Clin. Chest Med. 2016, 37, 535–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haley, S.; Shah, D.; Romero, F.; Summer, R. Scleroderma-Related Lung Disease: Are Adipokines Involved Pathogenically? Curr. Rheumatol. Rep. 2013, 15, 381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Summer, R.; Little, F.F.; Ouchi, N.; Takemura, Y.; Aprahamian, T.; Dwyer, D.; Fitzsimmons, K.; Suki, B.; Parameswaran, H.; Fine, A.; et al. Alveolar Macrophage Activation and an Emphysema-like Phenotype in Adiponectin-Deficient Mice. Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell. Mol. Physiol. 2008, 294, L1035–L1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jain, M.; Budinger, G.R.S.; Lo, A.; Urich, D.; Rivera, S.E.; Ghosh, A.K.; Gonzalez, A.; Chiarella, S.E.; Marks, K.; Donnelly, H.K.; et al. Leptin Promotes Fibroproliferative Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome by Inhibiting Peroxisome Proliferator-Activated Receptor-γ. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2011, 183, 1490–1498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, Q.; Johns, R.A. Resistin Family Proteins in Pulmonary Diseases. Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell. Mol. Physiol. 2020, 319, L422–L434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, H.; Chung, S.I.; Park, H.J.; Oh, E.Y.; Kim, S.-R.; Park, K.H.; Lee, J.-H.; Park, J.-W. Obesity-Induced Vitamin D Deficiency Contributes to Lung Fibrosis and Airway Hyperresponsiveness. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2021, 64, 357–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, L.; Zhang, L.; Li, C.; Gai, Z.; Li, Y. Vitamin D and Vitamin D Receptor: New Insights in the Treatment of Hypertension. Curr. Protein Pept. Sci. 2019, 20, 984–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uhal, B.D.; Li, X.; Piasecki, C.C.; Molina-Molina, M. Angiotensin Signalling in Pulmonary Fibrosis. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2012, 44, 465–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; Tan, X.; Yu, B.; Sun, W.; Wang, H.; Hu, H.; Du, Y.; He, R.; Gao, R.; Peng, Q.; et al. DOCK2 Regulates Antifungal Immunity by Regulating RAC GTPase Activity. Cell. Mol. Immunol. 2022, 19, 602–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Li, F.; Xu, Z.; Yin, A.; Yin, H.; Li, C.; Chen, S.-Y. DOCK2 Deficiency Mitigates HFD-Induced Obesity by Reducing Adipose Tissue Inflammation and Increasing Energy Expenditure. J. Lipid Res. 2017, 58, 1777–1784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, G.; Adeyanju, O.; Sunil, C.; Huang, S.K.; Chen, S.-Y.; Tucker, T.A.; Idell, S.; Guo, X. Dedicator of Cytokinesis 2 (DOCK2) Deficiency Attenuates Lung Injury Associated with Chronic High-Fat and High-Fructose Diet-Induced Obesity. Am. J. Pathol. 2022, 192, 226–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Adeyanju, O.; Sunil, C.; Mandlem, V.; Olajuyin, A.; Huang, S.; Chen, S.-Y.; Idell, S.; Tucker, T.A.; Qian, G. DOCK2 Contributes to Pulmonary Fibrosis by Promoting Lung Fibroblast to Myofibroblast Transition. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 2022, 323, C133–C144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qi, Y.; Wu, Z.; Chen, D.; Zhu, L.; Yang, Y. A Role of STING Signaling in Obesity-Induced Lung Inflammation. Int. J. Obes. 2023, 47, 325–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bai, J.; Cervantes, C.; Liu, J.; He, S.; Zhou, H.; Zhang, B.; Cai, H.; Yin, D.; Hu, D.; Li, Z.; et al. DsbA-L Prevents Obesity-Induced Inflammation and Insulin Resistance by Suppressing the MtDNA Release-Activated CGAS-CGAMP-STING Pathway. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, 12196–12201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Proposed Adiposity-Related Disruptions Tied to ILD Development | Adiposity Influence on Mediator | Mediator Pathogenicity for ILD | Downstream Effects of Adiposity on Pathway |
|---|---|---|---|
| Adiponectin | Levels fall | Protective | Increased TNF-α and MMP-12 from less adiponectin |
| Leptin | Levels rise | Pathogenic | Increased inflammatory cytokines and profibrotic gene expression from more leptin |
| Resistin | Unclear effect on levels | Pathogenic | Increased inflammatory cytokines + Th2-mediated lung inflammation from more resistin Decreased Myofibroblast apoptosis from more resistin |
| Vitamin D | Levels fall | Protective | Increased TGFβ and renin from less vitamin D |
| STING pathway | Levels rise | Pathogenic | Increased TNF-α, IL-6, and IFNβ from more STING signaling |
| DOCK2 | Levels rise | Pathogenic | Increased TGFβ effects, myofibroblast transformation, and inflammatory cytokines from increased DOCK2 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Macklin, M.; Thompson, C.; Kawano-Dourado, L.; Bauer Ventura, I.; Weschenfelder, C.; Trostchansky, A.; Marcadenti, A.; Tighe, R.M. Linking Adiposity to Interstitial Lung Disease: The Role of the Dysfunctional Adipocyte and Inflammation. Cells 2023, 12, 2206. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells12182206
Macklin M, Thompson C, Kawano-Dourado L, Bauer Ventura I, Weschenfelder C, Trostchansky A, Marcadenti A, Tighe RM. Linking Adiposity to Interstitial Lung Disease: The Role of the Dysfunctional Adipocyte and Inflammation. Cells. 2023; 12(18):2206. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells12182206
Chicago/Turabian StyleMacklin, Michael, Chelsea Thompson, Leticia Kawano-Dourado, Iazsmin Bauer Ventura, Camila Weschenfelder, Andrés Trostchansky, Aline Marcadenti, and Robert M. Tighe. 2023. "Linking Adiposity to Interstitial Lung Disease: The Role of the Dysfunctional Adipocyte and Inflammation" Cells 12, no. 18: 2206. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells12182206
APA StyleMacklin, M., Thompson, C., Kawano-Dourado, L., Bauer Ventura, I., Weschenfelder, C., Trostchansky, A., Marcadenti, A., & Tighe, R. M. (2023). Linking Adiposity to Interstitial Lung Disease: The Role of the Dysfunctional Adipocyte and Inflammation. Cells, 12(18), 2206. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells12182206







