The Posttraumatic Increase of the Adhesion GPCR EMR2/ADGRE2 on Circulating Neutrophils Is Not Related to Injury Severity
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Ethics Statement and Clinical Study of Traumatized Patients
2.2. Blood Sample Preparation and Determination of Parameters
2.3. CFHR1 Genotype Assessment
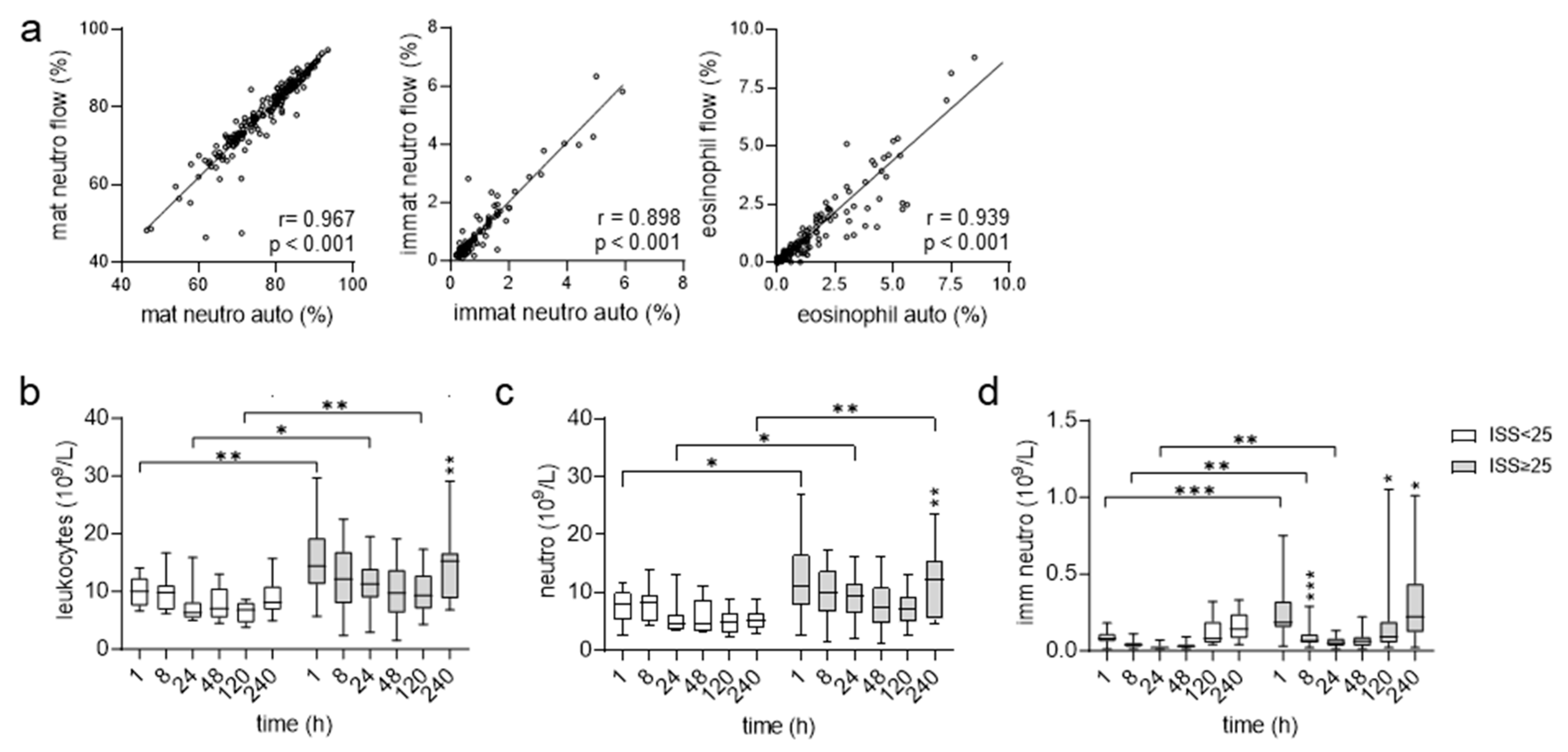
2.4. Flow Cytometric Analysis of Patients’ Leukocytes
2.5. Leukocytes and Neutrophils for In Vitro Experiments
2.6. In Vitro Experiments
2.7. ADGRE2 qRT-PCR Analysis
2.8. Statistics
3. Results
3.1. Higher Absolute Blood Counts for Neutrophils in Very Severely Injured Patients
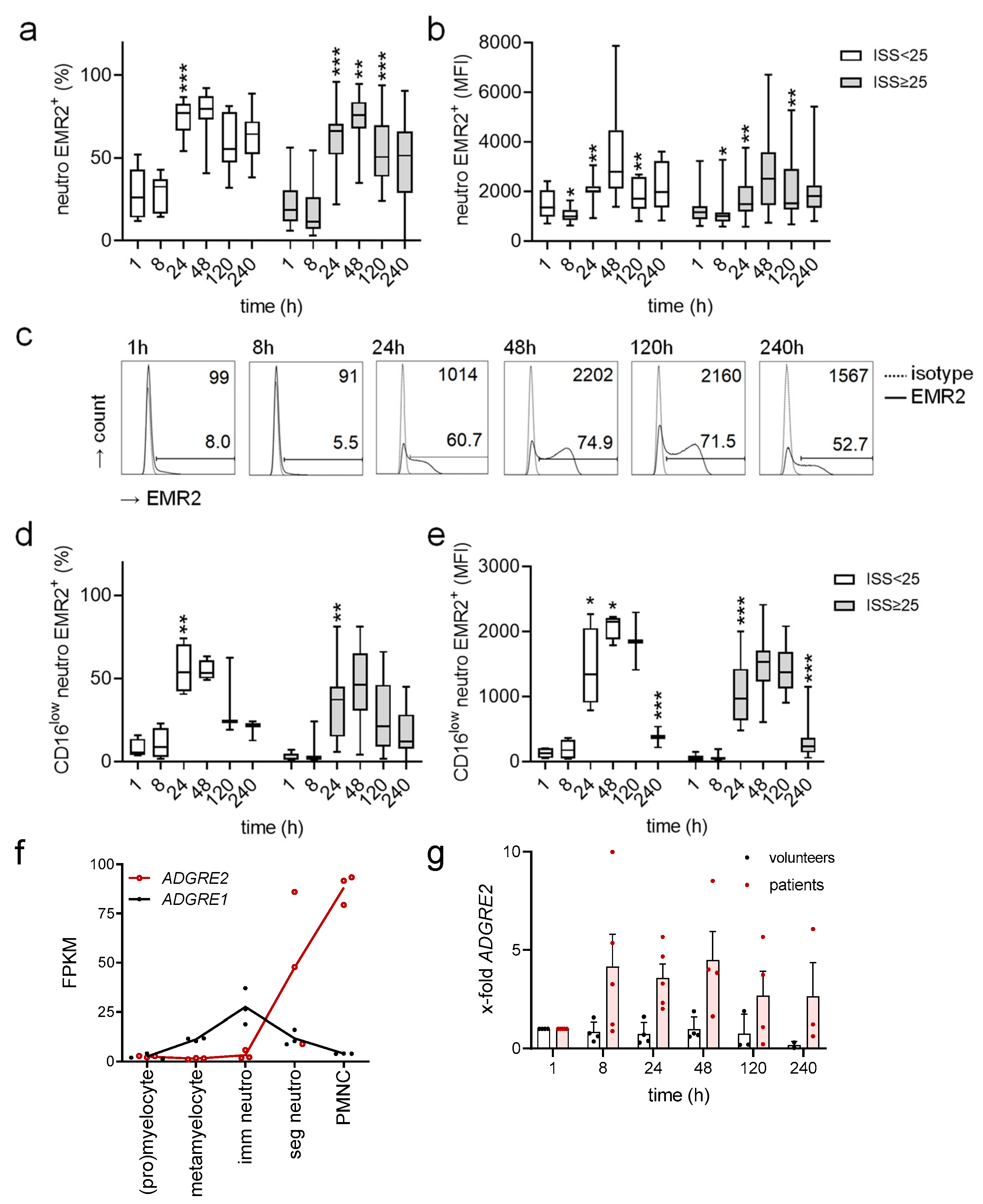
3.2. Uniform Posttraumatic Course of EMR2 Expression on Neutrophils in Injured Patients
3.3. Circulating EMR2+ Neutrophils Express Less CD62L and More CD11c Compared to EMR2−
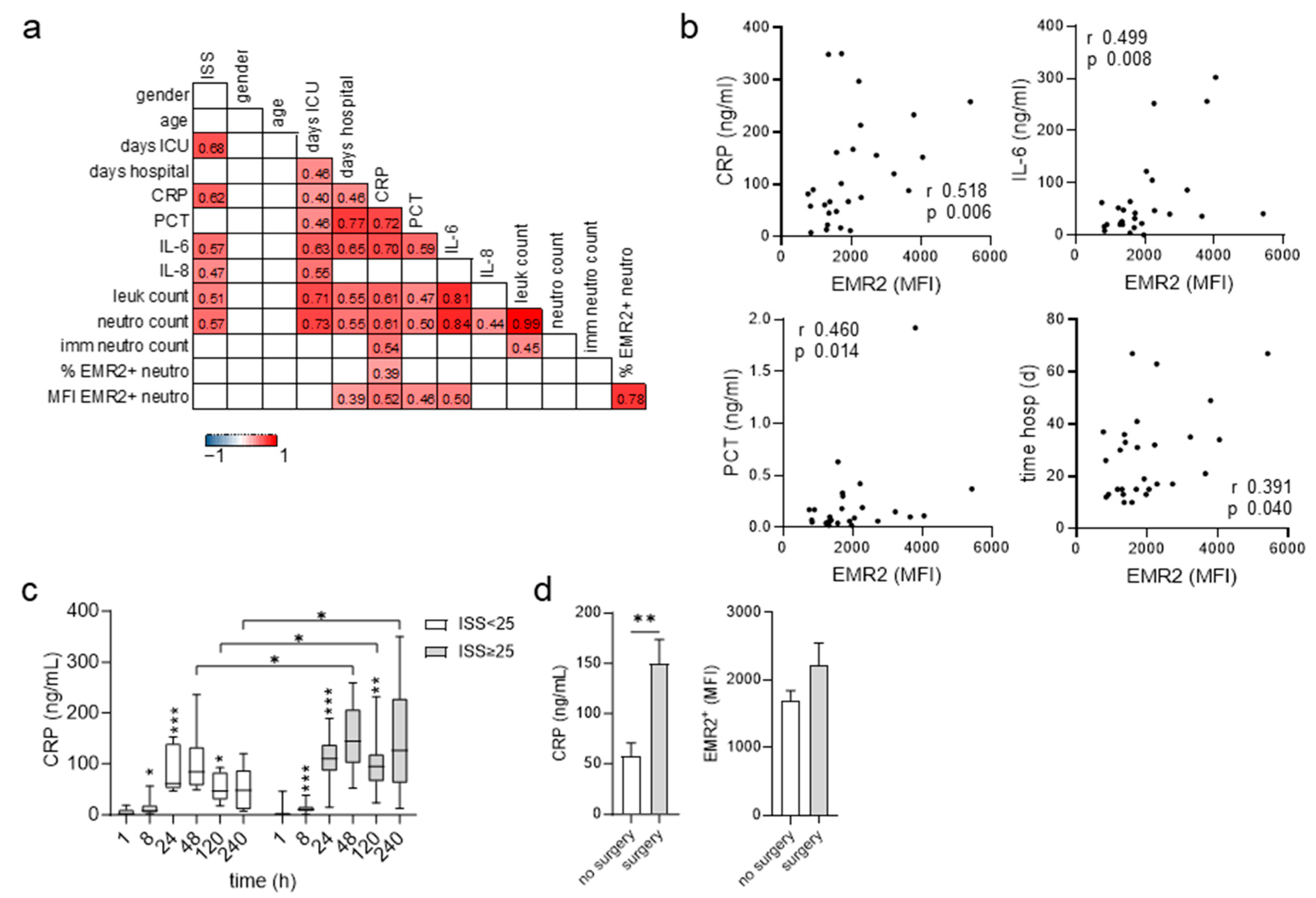
3.4. Posttraumatic Levels of EMR2 Expression on Neutrophils and C-Reactive Protein (CRP) Correlate
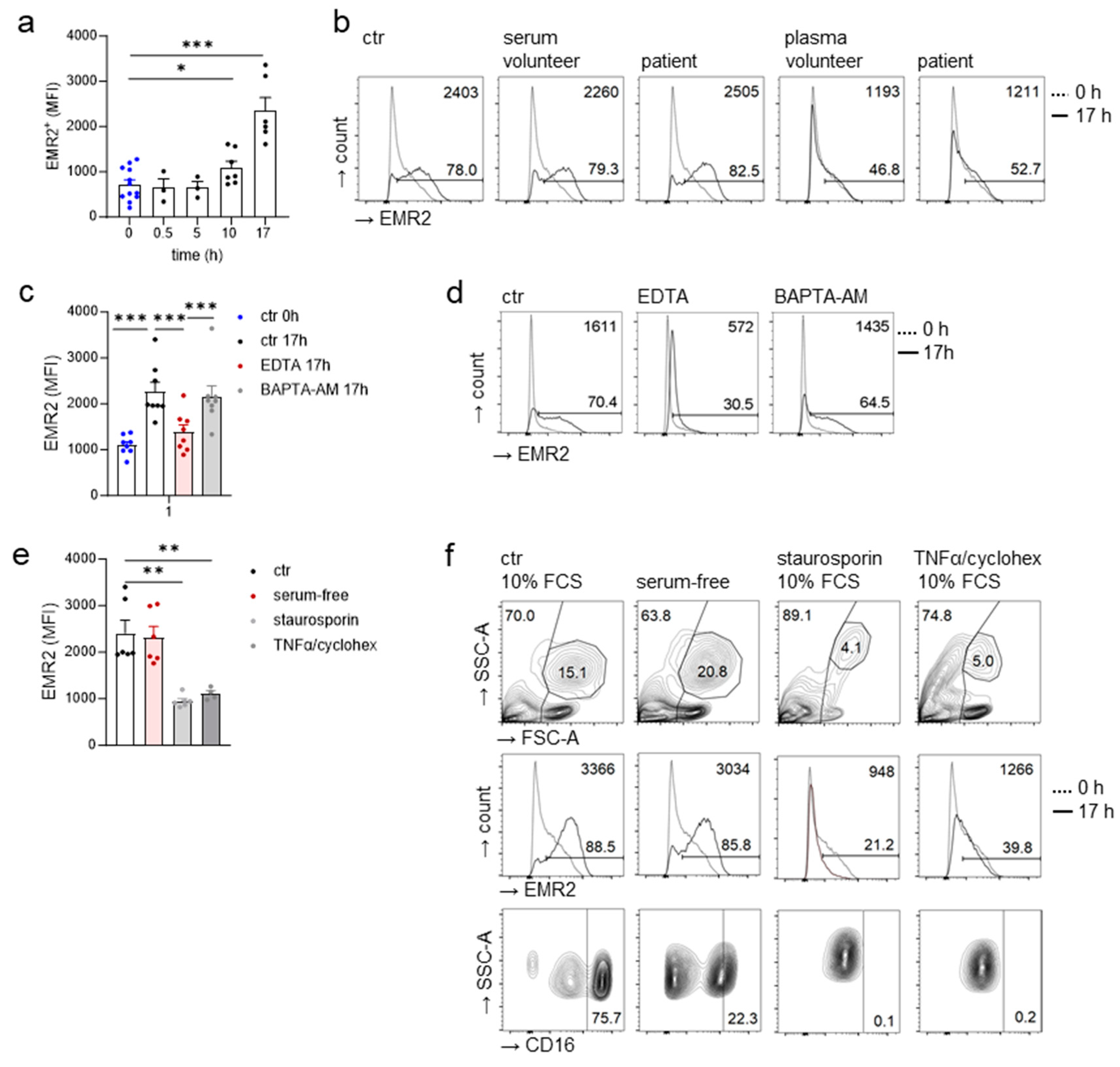
3.5. Extracellular Calcium-Dependent Increase in EMR2 Expression on Neutrophils In Vitro
3.6. Inflammatory Cytokines Do Not Regulate the Neutrophilic EMR2 Increase In Vitro
3.7. FHR1 Is Not Involved in Neutrophilic EMR2 Upregulation In Vitro
3.8. EMR2 Increased on Neutrophils Also in Serum-Free Cultures
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Correction Statement
References
- Lord, J.M.; Midwinter, M.J.; Chen, Y.-F.; Belli, A.; Brohi, K.; Kovacs, E.J.; Koenderman, L.; Kubes, P.; Lilford, R.J. The systemic immune response to trauma: An overview of pathophysiology and treatment. Lancet 2014, 384, 1455–1465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huber-Lang, M.; Lambris, J.D.; Ward, P.A. Innate immune responses to trauma. Nat. Immunol. 2018, 19, 327–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horner, E.; Lord, J.M.; Hazeldine, J. The immune suppressive properties of damage associated molecular patterns in the setting of sterile traumatic injury. Front Immunol. 2023, 14, 1239683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Relja, B.; Mörs, K.; Marzi, I. Danger signals in trauma. Eur. J. Trauma Emerg. Surg. 2018, 44, 301–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Finlay, L.D.; Conway Morris, A.; Deane, A.M.; Wood, A.J. Neutrophil kinetics and function after major trauma: A systematic review. World J. Crit. Care Med. 2021, 10, 260–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schioth, H.B.; Fredriksson, R. The GRAFS classification system of G-protein coupled receptors in comparative perspective. Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 2005, 142, 94–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexander, S.P.; Christopoulos, A.; Davenport, A.P.; Kelly, E.; Mathie, A.; Peters, J.A.; Veale, E.L.; Armstrong, J.F.; Faccenda, E.; Harding, S.D.; et al. The concise guide to pharmacology 2021/22: G protein-coupled receptors. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2021, 178 (Suppl. S1), S27–S156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamann, J.; Aust, G.; Arac, D.; Engel, F.B.; Formstone, C.; Frederiksson, R.; Hall, R.A.; Harty, B.L.; Kirchhoff, C.; Knapp, B.; et al. International Union of Basic and Clinical Pharmacology. XCI. Adhesion G protein-coupled receptors. Pharmacol. Rev. 2015, 67, 338–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nieberler, M.; Kittel, R.J.; Petrenko, A.G.; Lin, H.H.; Langenhan, T. Control of adhesion GPCR function through proteolytic processing. Handb. Exp. Pharmacol. 2016, 234, 83–109. [Google Scholar]
- Hamann, J.; Hsiao, C.C.; Lee, C.S.; Ravichandran, K.S.; Lin, H.H. Adhesion GPCRs as modulators of immune cell function. Handb. Exp. Pharmacol. 2016, 234, 329–350. [Google Scholar]
- Kwakkenbos, M.J.; Pouwels, W.; Matmati, M.; Stacey, M.; Lin, H.H.; Gordon, S.; van Lier, R.A.; Hamann, J. Expression of the largest CD97 and EMR2 isoforms on leukocytes facilitates a specific interaction with chondroitin sulfate on B cells. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2005, 77, 112–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwakkenbos, M.J.; Chang, G.W.; Lin, H.H.; Pouwels, W.; de Jong, E.C.; van Lier, R.A.; Gordon, S.; Hamann, J. The human EGF-TM7 family member EMR2 is a heterodimeric receptor expressed on myeloid cells. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2002, 71, 854–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, H.H.; Hsiao, C.C.; Pabst, C.; Hebert, J.; Schoneberg, T.; Hamann, J. Adhesion GPCRs in regulating immune responses and inflammation. Adv. Immunol. 2017, 136, 163–201. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Yona, S.; Lin, H.H.; Dri, P.; Davies, J.Q.; Hayhoe, R.P.; Lewis, S.M.; Heinsbroek, S.E.; Brown, K.A.; Perretti, M.; Hamann, J.; et al. Ligation of the adhesion-GPCR EMR2 regulates human neutrophil function. FASEB J. 2008, 22, 741–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.-Y.; Hwang, T.-L.; Lin, C.-Y.; Lin, T.-N.; Lai, H.-Y.; Tsai, W.-P.; Lin, H.-H. EMR2 receptor ligation modulates cytokine secretion profiles and cell survival of lipopolysaccharide-treated neutrophils. Chang Gung Med. J. 2011, 34, 468–477. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Irmscher, S.; Brix, S.R.; Zipfel, S.L.H.; Halder, L.D.; Mutluturk, S.; Wulf, S.; Girdauskas, E.; Reichenspurner, H.; Stahl, R.A.K.; Jungnickel, B.; et al. Serum FHR1 binding to necrotic-type cells activates monocytic inflammasome and marks necrotic sites in vasculopathies. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 2961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- I, K.-Y.; Tseng, W.-Y.; Wang, W.-C.; Gordon, S.; Ng, K.-F.; Lin, H.-H. Stimulation of vibratory urticaria-associated Adhesion-GPCR, EMR2/ADGRE2, triggers the NLRP3 inflammasome activation signal in human monocytes. Front Immunol. 2020, 11, 602016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bedoui, S.; Herold, M.J.; Strasser, A. Emerging connectivity of programmed cell death pathways and its physiological implications. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2020, 21, 678–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, S.M.; Treacher, D.F.; Edgeworth, J.; Mahalingam, G.; Brown, C.S.; Mare, T.A.; Stacey, M.; Beale, R.; Brown, K.A. Expression of CD11c and EMR2 on neutrophils: Potential diagnostic biomarkers for sepsis and systemic inflammation. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2015, 182, 184–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- VanDerHeyden, N.; Cox, T.B. Trauma scoring. In Current Therapy of Trauma and Surgical Critical Care; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Loftis, K.L.; Price, J.P.; Gillich, P.J.; Cookman, K.J.; Brammer, A.L.; St Germain, T.; Barnes, J.; Graymire, V.; Nayduch, D.A.; Read-Allsopp, C.; et al. Development of an expert based ICD-9-CM and ICD-10-CM map to AIS 2005 update 2008. Traffic Inj. Prev. 2016, 17 (Suppl. S1), 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hefele, F.; Ditsch, A.; Krysiak, N.; Caldwell, C.C.; Biberthaler, P.; van Griensven, M.; Huber-Wagner, S.; Hanschen, M. Trauma induces interleukin-17A expression on Th17 cells and CD4+ regulatory T cells as well as platelet dysfunction. Front Immunol. 2019, 10, 2389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janicova, A.; Becker, N.; Xu, B.; Simic, M.; Noack, L.; Wagner, N.; Müller, A.J.; Bertrand, J.; Marzi, I.; Relja, B. Severe traumatic injury induces phenotypic and functional changes of neutrophils and monocytes. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 4139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bongers, S.H.; Chen, N.; van Grinsven, E.; van Staveren, S.; Hassani, M.; Spijkerman, R.; Hesselink, L.; Lo Tam Loi, A.T.; van Aalst, C.; Leijte, G.P.; et al. Kinetics of neutrophil subsets in acute, subacute, and chronic Inflammation. Front Immunol. 2021, 12, 674079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dransfield, I.; Buckle, A.M.; Savill, J.S.; McDowall, A.; Haslett, C.; Hogg, N. Neutrophil apoptosis is associated with a reduction in CD16 (Fc gamma RIII) expression. J. Immunol. 1994, 153, 1254–1263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hundhammer, T.; Gruber, M.; Wittmann, S. Paralytic impact of centrifugation on human neutrophils. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 2896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carneiro-Goetten, J.O.L.; Rodrigues, B.S.; Nogoceke, R.A.; do Nascimento, T.G.; Moreno-Amaral, A.N.; Stuelp-Campelo, P.M.; Elifio-Esposito, S. Neutrophils activated by BJcuL, a C-type lectin isolated from Bothrops jararacussu venom, decrease the invasion potential of neuroblastoma SK-N-SH cells in vitro. J. Venom. Anim. Toxins Incl. Trop. Dis. 2020, 26, e20190073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beyer, C.; Stearns, N.A.; Giessl, A.; Distler, J.H.W.; Schett, G.; Pisetsky, D.S. The extracellular release of DNA and HMGB1 from Jurkat T cells during in vitro necrotic cell death. Innate Immun. 2012, 18, 727–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, D.C.; Cornwell, E.E. 3.; Phillips, J.; Paradise, J.; Campbell, K. Early leukocytosis in trauma patients: What difference does it make? Curr. Surg. 2003, 60, 632–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoogendijk, A.J.; Pourfarzad, F.; Aarts, C.E.M.; Tool, A.T.J.; Hiemstra, I.H.; Grassi, L.; Frontini, M.; Meijer, A.B.; van den Biggelaar, M.; Kuijpers, T.W. Dynamic transcriptome-proteome correlation networks reveal human myeloid differentiation and neutrophil-specific programming. Cell Rep. 2019, 29, 2505–2519.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, G.W.; Davies, J.Q.; Stacey, M.; Yona, S.; Bowdish, D.M.; Hamann, J.; Chen, T.C.; Lin, C.Y.; Gordon, S.; Lin, H.H. CD312, the human adhesion-GPCR EMR2, is differentially expressed during differentiation, maturation, and activation of myeloid cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2007, 353, 133–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.-H.; Jeng, W.-J.; Ho, Y.-P.; Teng, W.; Hsieh, Y.-C.; Chen, W.-T.; Chen, Y.-C.; Lin, H.-H.; Sheen, I.-S.; Lin, C.-Y. Increased EMR2 expression on neutrophils correlates with disease severity and predicts overall mortality in cirrhotic patients. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 38250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kishimoto, T.K.; Jutila, M.A.; Berg, E.L.; Butcher, E.C. Neutrophil Mac-1 and MEL-14 adhesion proteins inversely regulated by chemotactic factors. Science 1989, 245, 1238–1241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rajab, I.M.; Hart, P.C.; Potempa, L.A. How C-reactive protein structural isoforms with distinctive bioactivities affect disease progression. Front Immunol. 2020, 11, 2126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shakespeare, P.G.; Ball, A.J.; Spurr, E.D. Serum protein changes after abdominal surgery. Ann. Clin. Biochem. 1989, 26, 49–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, D.; Namas, R.A.; Vodovotz, Y.; Peitzman, A.B.; Simmons, R.L.; Yuan, H.; Mi, Q.; Billiar, T.R. Unsupervised clustering analysis based on MODS severity identifies four distinct organ dysfunction patterns in severely injured blunt trauma patients. Front Med. 2020, 7, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonaroti, J.; Billiar, I.; Moheimani, H.; Wu, J.; Namas, R.; Li, S.; Kar, U.K.; Vodovotz, Y.; Neal, M.D.; Sperry, J.L.; et al. Plasma proteomics reveals early, broad release of chemokine, cytokine, TNF, and interferon mediators following trauma with delayed increases in a subset of chemokines and cytokines in patients that remain critically ill. Front Immunol. 2022, 13, 1038086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eklund, C.M. Proinflammatory cytokines in CRP baseline regulation. Adv. Clin. Chem. 2009, 48, 111–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyden, S.E.; Desai, A.; Cruse, G.; Young, M.L.; Bolan, H.C.; Scott, L.M.; Eisch, A.R.; Long, R.D.; Lee, C.C.; Satorius, C.L.; et al. Vibratory urticaria associated with a missense variant in ADGRE2. N. Engl. J Med. 2016, 374, 656–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skerka, C.; Pradel, G.; Halder, L.D.; Zipfel, P.F.; Zipfel, S.L.H.; Strauß, O. Factor H-related protein 1: A complement regulatory protein and guardian of necrotic-type surfaces. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2021, 178, 2823–2831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holmes, L.V.; Strain, L.; Staniforth, S.J.; Moore, I.; Marchbank, K.; Kavanagh, D.; Goodship, J.A.; Cordell, H.J.; Goodship, T.H.J. Determining the population frequency of the CFHR3/CFHR1 deletion at 1q32. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e60352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, T.; Liu, L.; Jiang, W.; Zhou, R. DAMP-sensing receptors in sterile inflammation and inflammatory diseases. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2020, 20, 95–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- I, K.-Y.; Huang, Y.-S.; Hu, C.-H.; Tseng, W.-Y.; Cheng, C.-H.; Stacey, M.; Gordon, S.; Chang, G.-W.; Lin, H.-H. Activation of Adhesion GPCR EMR2/ADGRE2 induces macrophage differentiation and inflammatory responses via Gα(16)/Akt/MAPK/NF-κB signaling pathways. Front Immunol. 2017, 8, 373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Preissner, K.T.; Koyama, T.; Müller, D.; Tschopp, J.; Müller-Berghaus, G. Domain structure of the endothelial cell receptor thrombomodulin as deduced from modulation of its anticoagulant functions. Evidence for a glycosaminoglycan-dependent secondary binding site for thrombin. J. Biol. Chem. 1990, 265, 4915–4922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarrazin, S.; Lyon, M.; Deakin, J.A.; Guerrini, M.; Lassalle, P.; Delehedde, M.; Lortat-Jacob, H. Characterization and binding activity of the chondroitin/dermatan sulfate chain from Endocan, a soluble endothelial proteoglycan. Glycobiology 2010, 20, 1380–1388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DiMicco, M.A.; Patwari, P.; Siparsky, P.N.; Kumar, S.; Pratta, M.A.; Lark, M.W.; Kim, Y.-J.; Grodzinsky, A.J. Mechanisms and kinetics of glycosaminoglycan release following in vitro cartilage injury. Arthritis Rheum. 2004, 50, 840–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LaRivière, W.B.; Liao, S.; McMurtry, S.A.; Oshima, K.; Han, X.; Zhang, F.; Yan, S.; Haeger, S.M.; Ransom, M.; Bastarache, J.A.; et al. Alveolar heparan sulfate shedding impedes recovery from bleomycin-induced lung injury. Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell. Mol. Physiol. 2020, 318, L1198–L1210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stacey, M.; Chang, G.W.; Davies, J.Q.; Kwakkenbos, M.J.; Sanderson, R.D.; Hamann, J.; Gordon, S.; Lin, H.H. The epidermal growth factor-like domains of the human EMR2 receptor mediate cell attachment through chondroitin sulphate glycosaminoglycans. Blood 2003, 102, 2916–2924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burzava, A.L.S.; Jasieniak, M.; Cockshell, M.P.; Bonder, C.S.; Harding, F.J.; Griesser, H.J.; Voelcker, N.H. Affinity binding of EMR2 expressing cells by surface-grafted chondroitin sulfate B. Biomacromolecules 2017, 18, 1697–1704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, D.; Tosello-Trampont, A.C.; Elliott, M.R.; Lu, M.; Haney, L.B.; Ma, Z.; Klibanov, A.L.; Mandell, J.W.; Ravichandran, K.S. BAI1 is an engulfment receptor for apoptotic cells upstream of the ELMO/Dock180/Rac module. Nature 2007, 450, 430–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Billings, E.A.; Lee, C.S.; Owen, K.A.; D’Souza, R.S.; Ravichandran, K.S.; Casanova, J.E. The adhesion GPCR BAI1 mediates macrophage ROS production and microbicidal activity against Gram-negative bacteria. Sci. Signal. 2016, 9, ra14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsiao, C.-C.; van der Poel, M.; van Ham, T.J.; Hamann, J. Macrophages do not express the phagocytic receptor BAI1/ADGRB1. Front Immunol. 2019, 10, 962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goretti Riça, I.; Joughin, B.A.; Teke, M.E.; Emmons, T.R.; Griffith, A.M.; Cahill, L.A.; Banner-Goodspeed, V.M.; Robson, S.C.; Hernandez, J.M.; Segal, B.H.; et al. Neutrophil heterogeneity and emergence of a distinct population of CD11b/CD18-activated low-density neutrophils after trauma. J. Trauma Acute Care Surg. 2023, 94, 187–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pillay, J.; Kamp, V.M.; van Hoffen, E.; Visser, T.; Tak, T.; Lammers, J.-W.; Ulfman, L.H.; Leenen, L.P.; Pickkers, P.; Koenderman, L. A subset of neutrophils in human systemic inflammation inhibits T cell responses through Mac-1. J. Clin. Invest. 2012, 122, 327–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Visser, T.; Hietbrink, F.; Groeneveld, K.M.; Koenderman, L.; Leenen, L.P.H. Isolated blunt chest injury leads to transient activation of circulating neutrophils. Eur. J. Trauma Emerg. Surg. 2011, 37, 177–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| ISS < 25 | ISS ≥ 25 | p-Value * | |
|---|---|---|---|
| patients (n) | 9 | 25 | |
| ISS | 17 (10.5–18.0) | 38 (30.5–44.0) | <0.001 |
| age (years) | 65.0 (39.0–74.0) | 53.0 (32.5–68.0) | 0.355 |
| sex, female (n) | 2 | 8 | 0.673 |
| days at ICU (n) | 2.0 (1.5–3.34) | 11.0 (5.0–15.5) | <0.001 |
| days in hospital (n) | 15.0 (11.0–28.0) | 19.0 (13.0–35.5) | 0.335 |
| death in hospital (n) | 2 | 2 | 0.489 |
| surgery between 1–8 h (n) | 5 | 21 | 0.216 |
| SOFA score # at 24 h | 1.0 (0–3.0) | 6.0 (2.0–10) | 0.003 |
| Serum/ Plasma (10%) | Stimulus/Condition | To Examine | Effect of Neutrophilic EMR2 # |
|---|---|---|---|
| FCS | - | control # | |
| human serum | uninjured volunteers, patients 24 h after trauma | stimuli present in patient’s sera | - |
| human plasma | uninjured volunteer, patient 24 h after trauma | stimuli present in patient’s plasma | inhibition compared to serum |
| FCS | 1 mM EDTA | extracellular Ca2+ chelator | inhibition |
| FCS | 10 μM BAPTA-AM | intracellular Ca2+ chelator | - |
| FCS | rh IL-1b, IL-6, IL-8, IL-17b; CCL2 (MCP1), TNFα | role of cytokines upregulated after trauma and/or inducing hepatic CRP | - |
| FCS | 1 mM LPS | PAMP | - |
| FCS | force | mechanotransduction | - |
| inactivated FCS | - | complement | - |
| FCS/human serum | necrotic cells | DAMP | - |
| FCS/human serum | immobilized FHR1 | FHR1 | - |
| FCS/human serum | immobilized FHR1 + necrotic cells | FHR1 + DAMP | - |
| - | serum withdrawal | growth factors in serum | - |
| - | serum withdrawal + 20 mM Z-VAD-FMK | role of caspases | - |
| FCS | 1 μM staurosporin | induction intrinsic apoptosis | no EMR2 increase, death neutrophils |
| FCS | 5 ng/mL TNFα/ 10 µg/mL cycloheximide | induction extrinsic apoptosis | no EMR2 increase, death neutrophils |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zheng, L.; Rang, M.; Fuchs, C.; Keß, A.; Wunsch, M.; Hentschel, J.; Hsiao, C.-C.; Kleber, C.; Osterhoff, G.; Aust, G. The Posttraumatic Increase of the Adhesion GPCR EMR2/ADGRE2 on Circulating Neutrophils Is Not Related to Injury Severity. Cells 2023, 12, 2657. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells12222657
Zheng L, Rang M, Fuchs C, Keß A, Wunsch M, Hentschel J, Hsiao C-C, Kleber C, Osterhoff G, Aust G. The Posttraumatic Increase of the Adhesion GPCR EMR2/ADGRE2 on Circulating Neutrophils Is Not Related to Injury Severity. Cells. 2023; 12(22):2657. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells12222657
Chicago/Turabian StyleZheng, Leyu, Moujie Rang, Carolin Fuchs, Annette Keß, Mandy Wunsch, Julia Hentschel, Cheng-Chih Hsiao, Christian Kleber, Georg Osterhoff, and Gabriela Aust. 2023. "The Posttraumatic Increase of the Adhesion GPCR EMR2/ADGRE2 on Circulating Neutrophils Is Not Related to Injury Severity" Cells 12, no. 22: 2657. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells12222657
APA StyleZheng, L., Rang, M., Fuchs, C., Keß, A., Wunsch, M., Hentschel, J., Hsiao, C.-C., Kleber, C., Osterhoff, G., & Aust, G. (2023). The Posttraumatic Increase of the Adhesion GPCR EMR2/ADGRE2 on Circulating Neutrophils Is Not Related to Injury Severity. Cells, 12(22), 2657. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells12222657







