Understanding Intra- and Inter-Species Variability in Neural Stem Cells’ Biology Is Key to Their Successful Cryopreservation, Culture, and Propagation
Abstract
1. Introduction
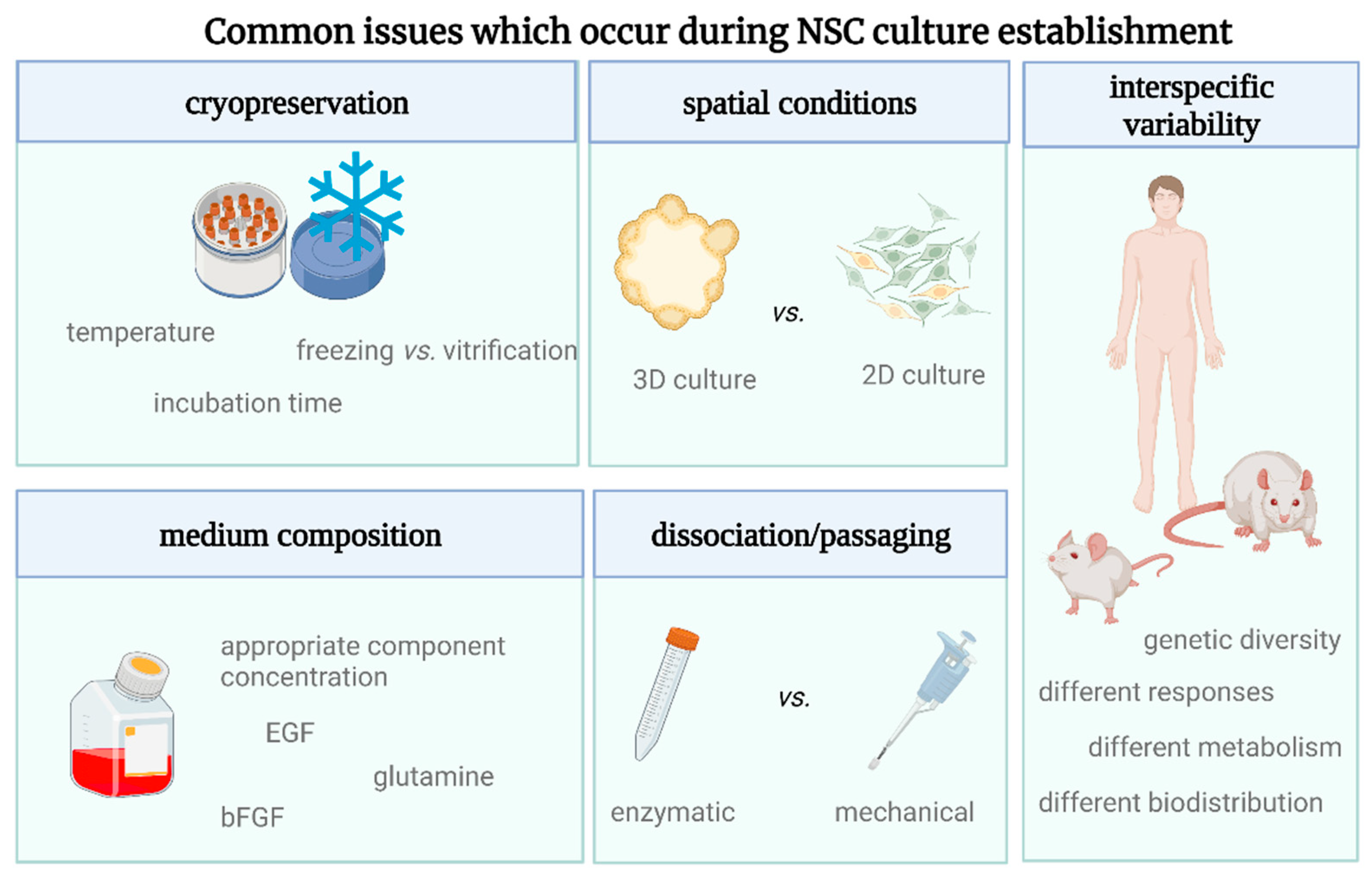
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. NSC Isolation
2.1.1. hNSCs’ Isolation
2.1.2. Mouse Neural Stem Cells (mNSCs) and Rat Neural Stem Cells (rNSCs) Isolation
2.2. Cell Culture
2.2.1. Thawing
2.2.2. Basic Culture
2.3. Live/Dead Assay
2.4. Proliferation Assay
2.5. Lactate Dehydrogenase Assay
2.6. Senescence Assay
2.7. Immunocytochemistry 2D
2.8. Developing a New Procedure of Immunocytochemical Staining for Better hNSCs Neurosphere (3D) Immunofluorescent Visualization
2.9. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
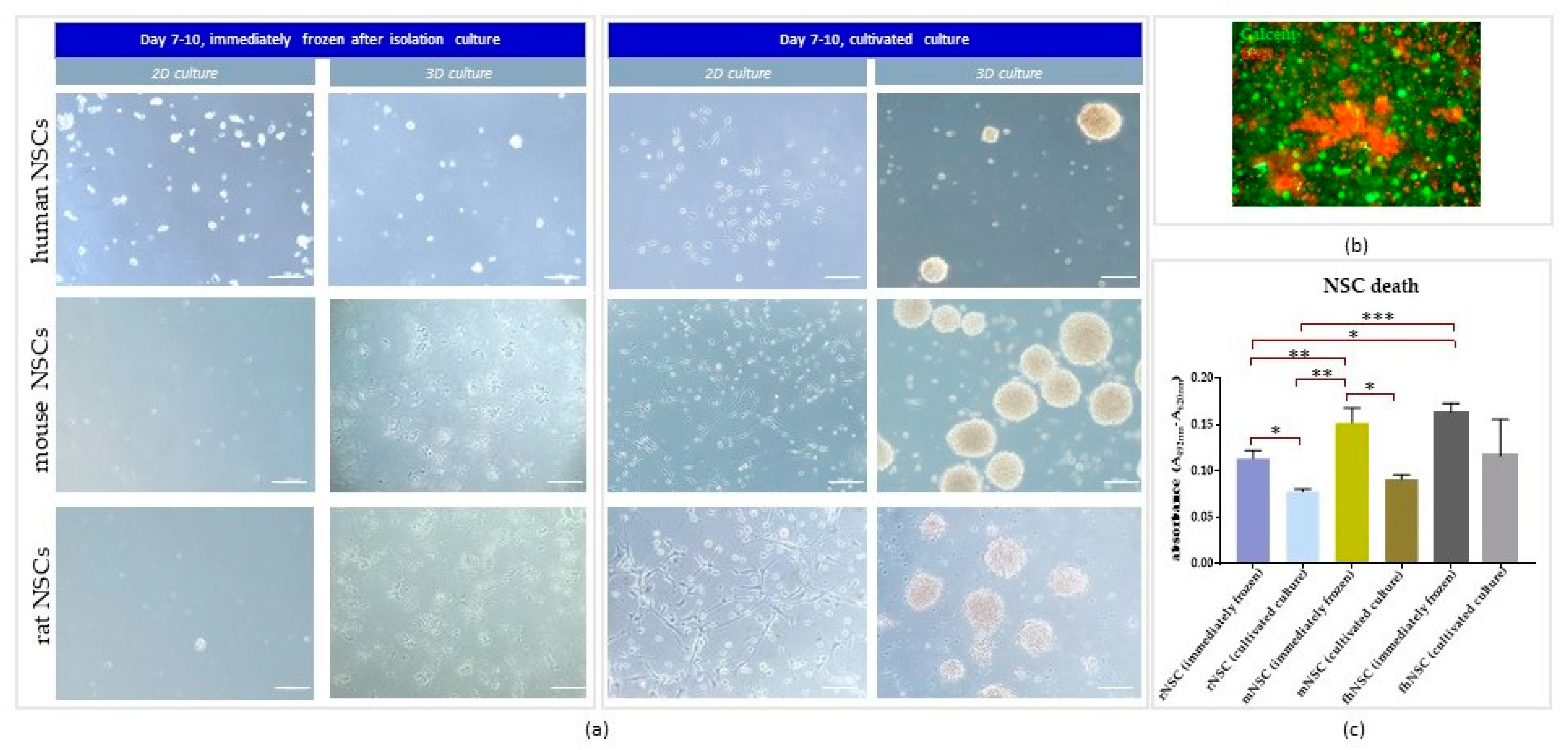
3.1. The Effect of Direct Cryopreservation on Human and Rodent NSCs’ Viability and Growth Potential
3.1.1. Intra-Species Variability
3.1.2. Inter-Species Variability
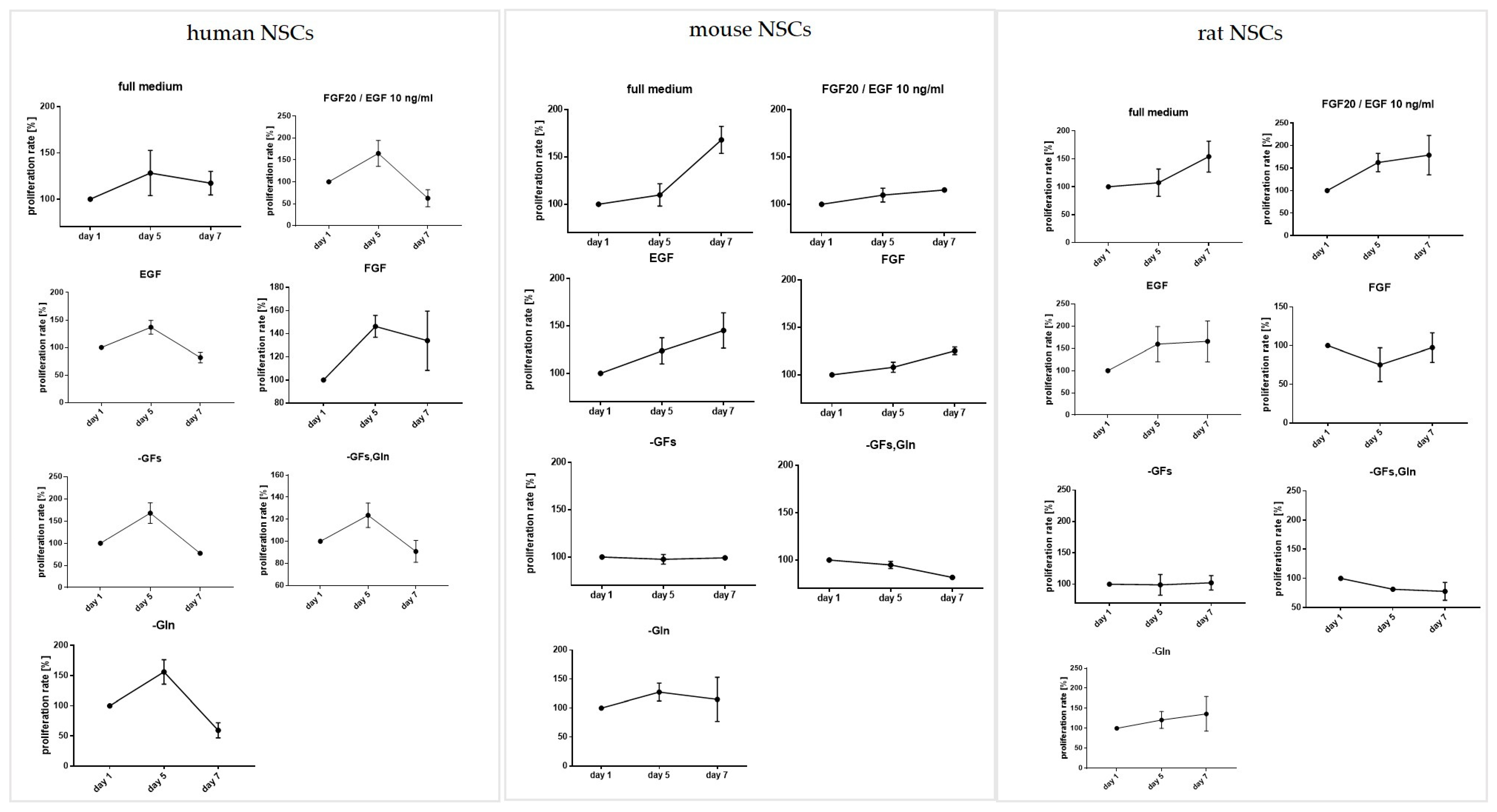
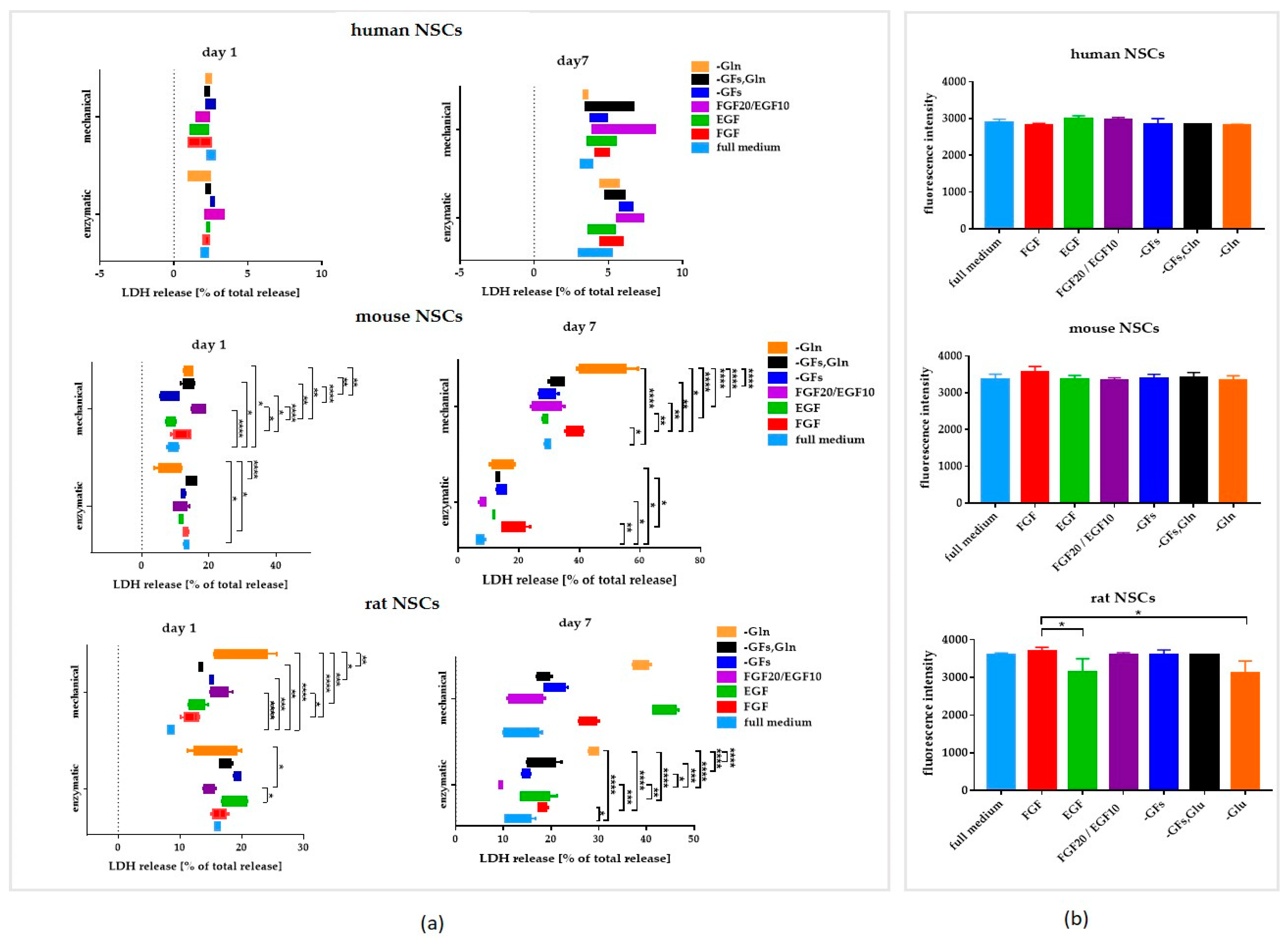
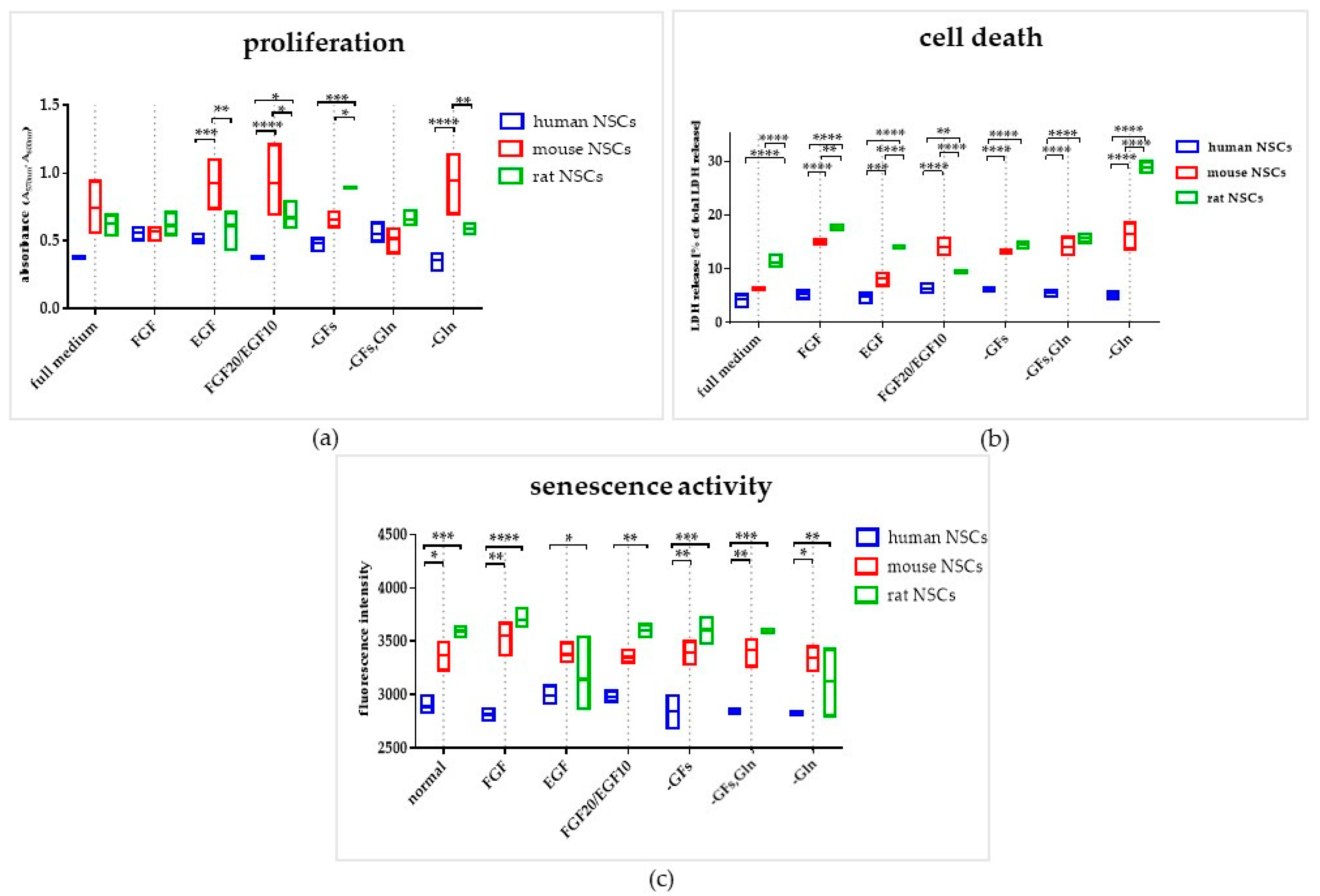
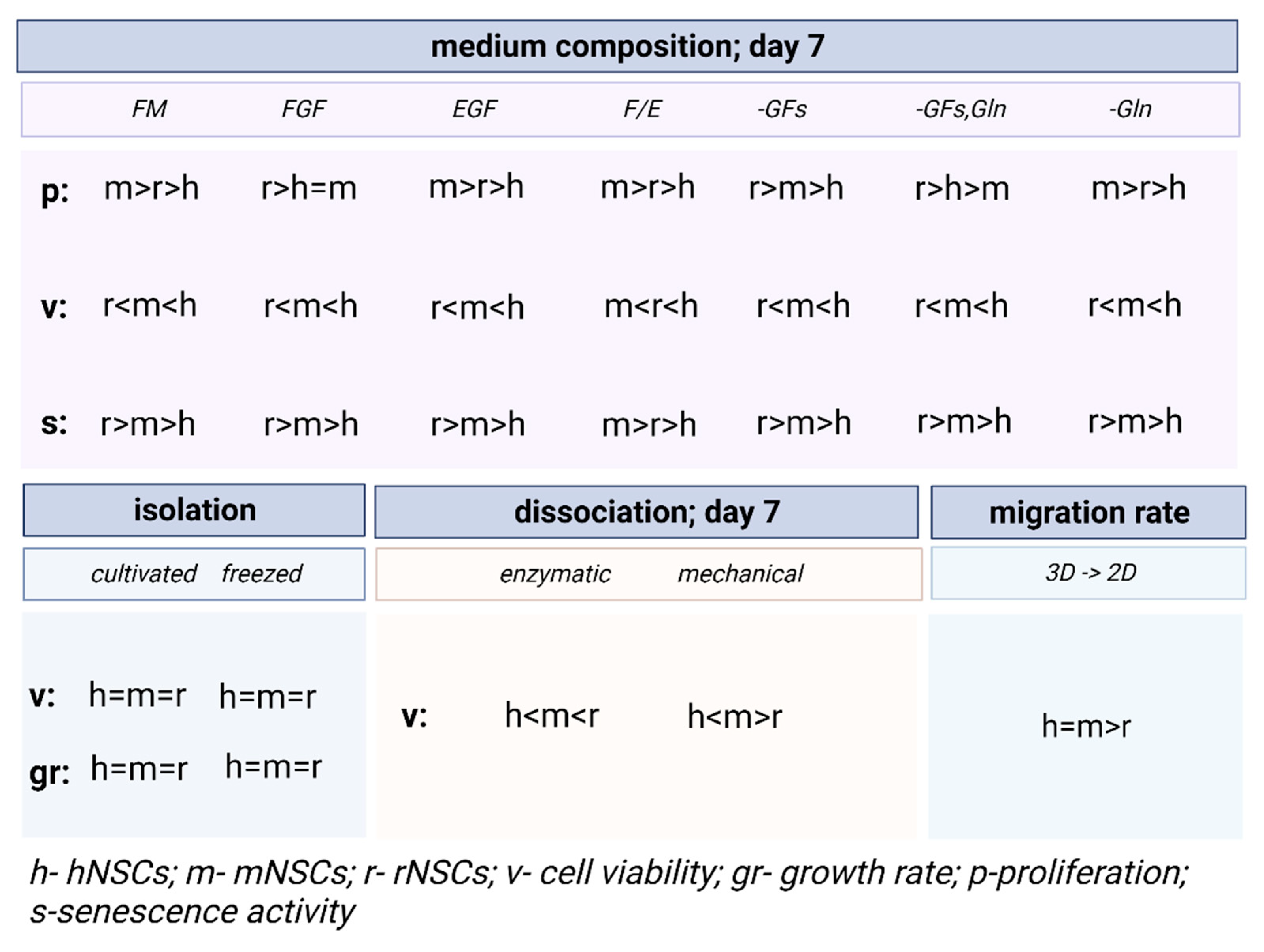
3.2. The Influence of the Medium Composition (Growth Factors, Glutamine) on the Viability, Proliferation, and Senescence of Human and Rodent NSCs
- Full medium—the medium with 20 ng/mL of basic fibroblast growth factor (bFGF) and epidermal growth factor (EGF), which is a control for our experiments.
- FGF—standard medium, with bFGF as the only growth factor (without EGF).
- EGF—standard medium, with EGF as the only growth factor (without bFGF).
- FGF20/EGF10—standard medium, with 20 ng/mL of bFGF and 10 ng/mL of EGF.
- -GFs—standard medium without bFGF and EGF.
- -GFs, Gln—standard medium without bFGF, EGF, and glutamine.
- -Gln—standard medium without glutamine.
3.2.1. Intra-Species Variability in 2D
3.2.2. Inter-Species Variability in 2D
3.2.3. 3D Cells’ Response to Medium Conditions
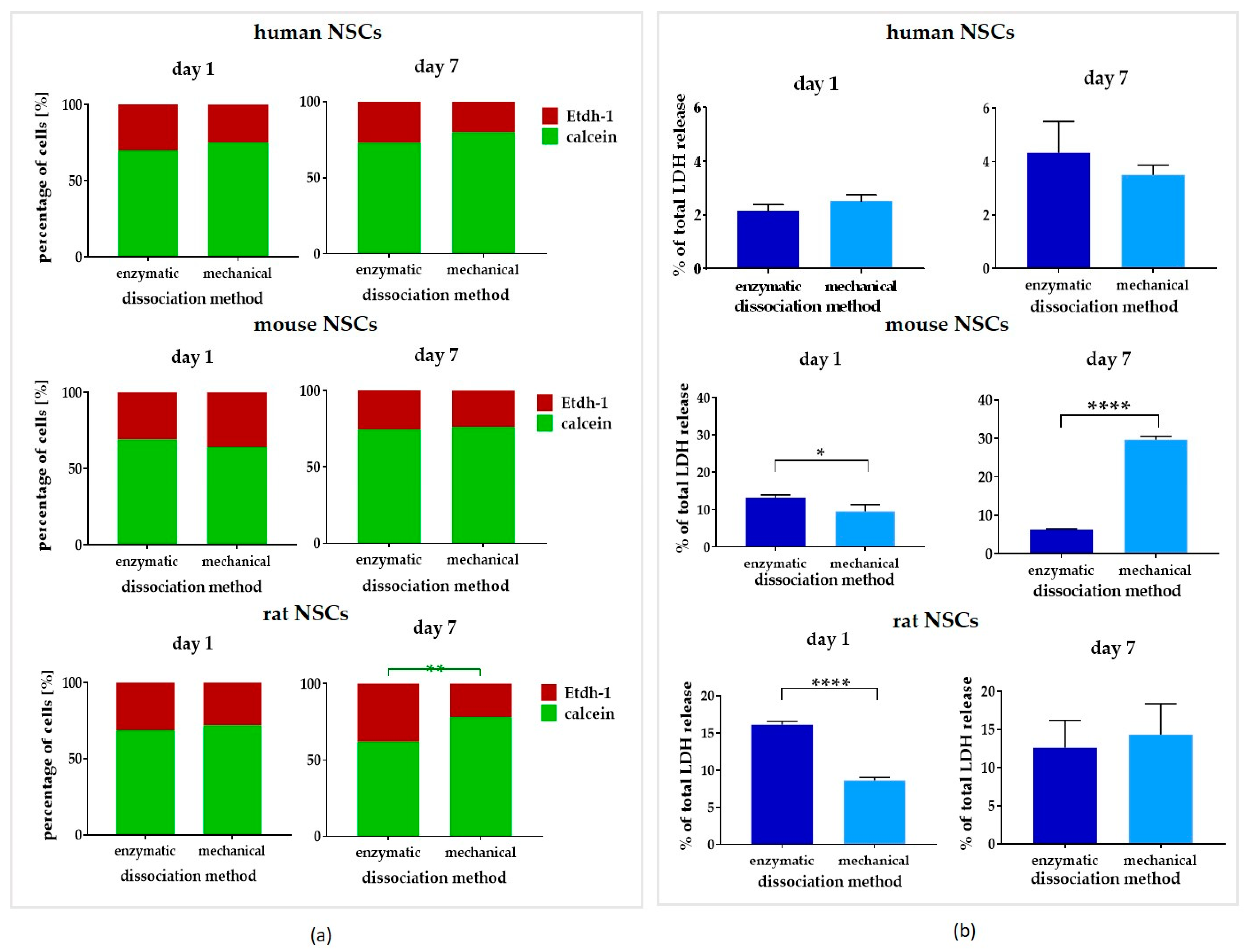
3.3. Comparison of Dissociation Methods—Enzymatic vs. Mechanical
3.3.1. Intra-Species Variability
3.3.2. Inter-Species Variability
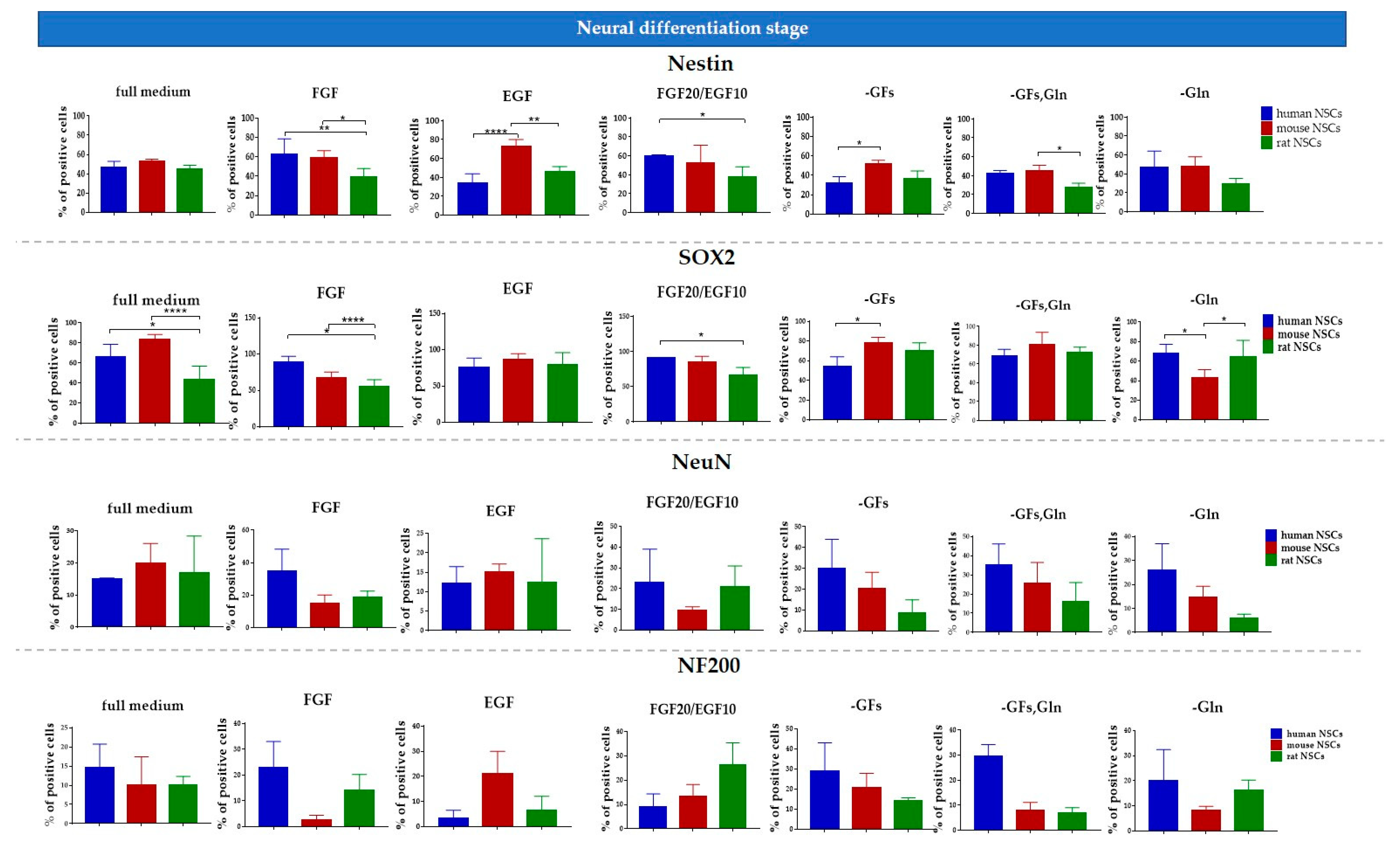
3.4. hNSCs’ Characteristics
3.4.1. Intra-Species Variability
3.4.2. Inter-Species Variability
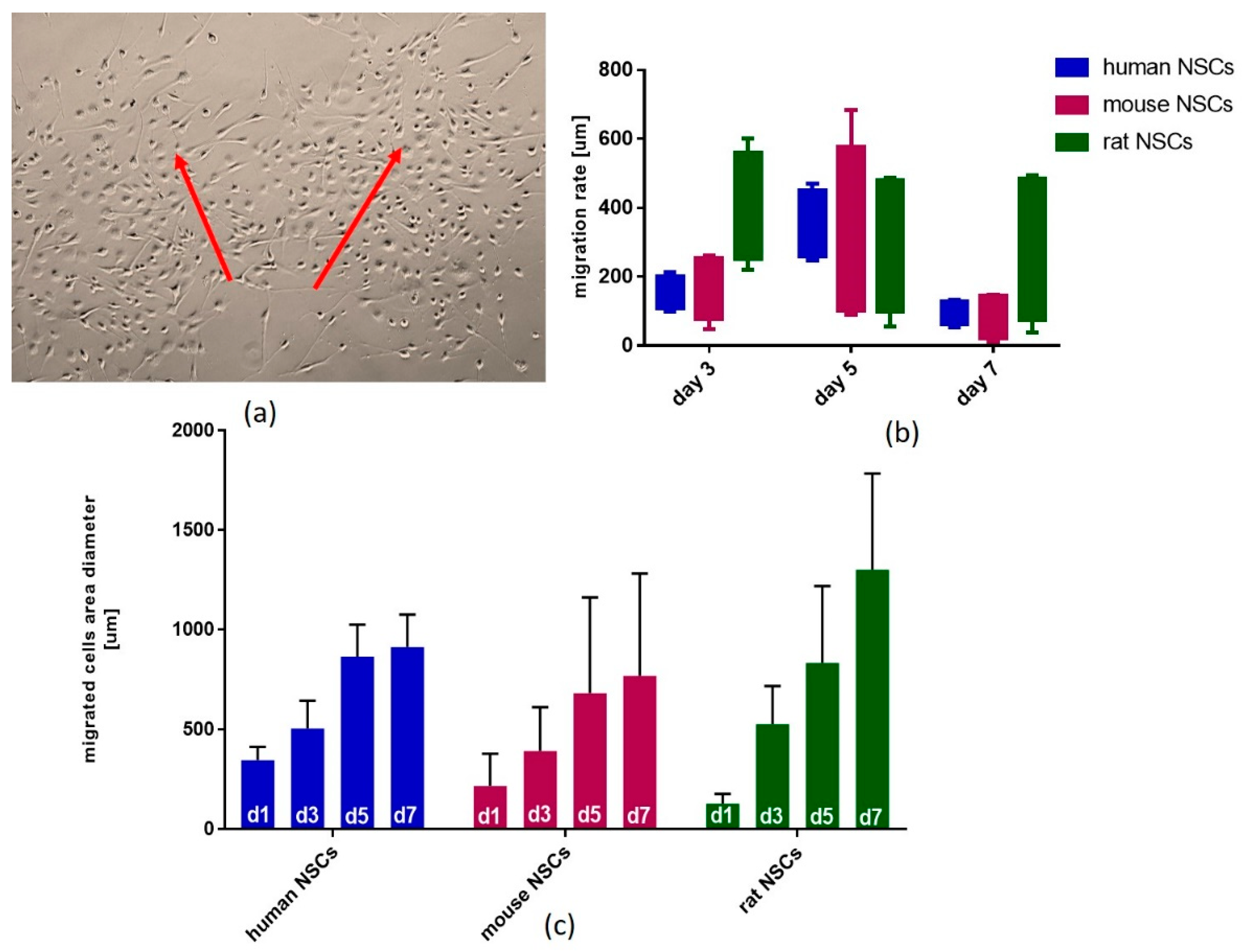
3.5. The Assessment of Migration of NSCs Grown as Neurospheres and Transferred to 2D Conditions
4. Discussion
4.1. The Effect of Direct Cryopreservation on Human and Rodent NSCs’ Viability and Growth Potential
4.2. The Influence of the Medium Composition (Growth Factors, Glutamine) on the Viability, Proliferation, and Senescence of Human and Rodent NSCs
4.3. The Influence of Dissociation Methods (Enzymatic and Mechanical) on the Viability, Proliferation, and Senescence of Human and Rodent NSCs
4.4. The Influence of Spatial Conditions (3D and 2D Culture) on the Viability, Proliferation, and Senescence of Human and Rodent NSCs
5. Conclusions
- Direct cultivation of NSCs before cryopreservation.
- Proper concentration of growth factors (bFGF and EGF) in the medium, which we estimated at 20 ng/mL for both bFGF and EGF.
- Presence of glutamine in the medium.
- Enzymatic method of neurosphere dissociation.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| NSCs | neural stem cells |
| hNSCs | human neural stem cells |
| rNSCs | rat neural stem cells |
| mNSCs | mouse neural stem cells |
| LDH | lactate dehydrogenase |
| HBSS | Hanks’ Balanced Salt Solution |
| DMSO | dimethyl sulfoxide |
| CNS | central nervous system |
| bFGF | basic fibroblast growth factor |
| EGF | epidermal growth factor |
| NGF | nerve growth factor |
| BDNF | brain-derived neurotrophic factor |
| VEGF | vascular endothelial growth factor |
| IGF | insulin-like growth factor |
References
- Lippert, T.; Gelineau, L.; Napoli, E.; Borlongan, C.V. Harnessing neural stem cells for treating psychiatric symptoms associated with fetal alcohol spectrum disorder and epilepsy. Prog. Neuro-Psychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 2018, 80, 10–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beattie, R.; Hippenmeyer, S. Mechanisms of radial glia progenitor cell lineage progression. FEBS Lett. 2017, 591, 3993–4008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rakic, P. Evolution of the neocortex: A perspective from developmental biology. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2009, 10, 724–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, Y.; Shin, S.; Jha, B.S.; Liu, Q.; Sheng, J.; Li, F.; Zhan, M.; Davis, J.; Bharti, K.; Zeng, X.; et al. Efficient and Rapid Derivation of Primitive Neural Stem Cells and Generation of Brain Subtype Neurons from Human Pluripotent Stem Cells. STEM CELLS Transl. Med. 2013, 2, 862–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrari, D.; Gelati, M.; Profico, D.C.; Vescovi, A.L. Human Fetal Neural Stem Cells for Neurodegenerative Disease Treatment. Results Probl. Cell Differ. 2018, 66, 307–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pluchino, S.; Zanotti, L.; Deleidi, M.; Martino, G. Neural stem cells and their use as therapeutic tool in neurological disorders. Brain Res. 2005, 48, 211–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, T.; Yuan, Z.; Weng, J.; Pei, D.; Du, X.; He, C.; Lai, P. Challenges and advances in clinical applications of mesenchymal stromal cells. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2021, 14, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitrecic, D.; Nicaise, C.; Klimaschewski, L.; Gajovic, S.; Bohl, D.; Pochet, R. Genetically modified stem cells for the treatment of neurological diseases. Front. Biosci. 2012, E4, 1170–1181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitrečić, D. Current Advances in Intravascular Administration of Stem Cells for Neurological Diseases: A New Dose of Rejuvenation Injected. Rejuvenation Res. 2011, 14, 553–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hribljan, V.; Salamon, I.; Đemaili, A.; Alić, I.; Mitrečić, D. Transplantation of neural stem cells in the mouse model of ischemic brain stroke and expression of genes involved in programmed cell death. Croat. Med. J. 2018, 59, 203–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martino, G.; Pluchino, S. The therapeutic potential of neural stem cells. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2006, 7, 395–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Willis, C.M.; Nicaise, A.M.; Peruzzotti-Jametti, L.; Pluchino, S. The Neural Stem Cell Secretome and Its Role in Brain Repair; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2020; Volume 1729, p. 146615. [Google Scholar]
- Kaminska, A.; Radoszkiewicz, K.; Rybkowska, P.; Wedzinska, A.; Sarnowska, A. Interaction of Neural Stem Cells (NSCs) and Mesenchymal Stem Cells (MSCs) as a Promising Approach in Brain Study and Nerve Regeneration. Cells 2022, 11, 1464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marei, H.E.; Casalbore, P.; Althani, A.; Coccè, V.; Cenciarelli, C.; Alessandri, G.; Brini, A.T.; Parati, E.; Bondiolotti, G.; Pessina, A. Human Olfactory Bulb Neural Stem Cells (Hu-OBNSCs) Can Be Loaded with Paclitaxel and Used to Inhibit Glioblastoma Cell Growth. Pharmaceutics 2019, 11, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rezk, S.; Lashen, S.; El-Adl, M.; Elshopakey, G.E.; Elghareeb, M.M.; Hendam, B.M.; Caceci, T.; Cenciarelli, C.; Marei, H.E. Effects of Rosemary Oil (Rosmarinus officinalis) supplementation on the fate of the transplanted human olfactory bulb neural stem cells against ibotenic acid-induced neurotoxicity (Alzheimer model) in rat. Metab. Brain Dis. 2022, 37, 973–988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.; Zhang, L. Neural stem cell therapies and hypoxic-ischemic brain injury. Prog. Neurobiol. 2018, 173, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuazon, J.P.; Castelli, V.; Lee, J.-Y.; Desideri, G.B.; Stuppia, L.; Cimini, A.M.; Borlongan, C.V. Neural Stem Cells. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2019, 1201, 79–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, Q.; Liao, L.-Y.; Lau, B.W.-M.; Sánchez-Vidaña, D.I. Exogenous neural stem cell transplantation for cerebral ischemia. Neural Regen. Res. 2019, 14, 1129–1137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrari, D.; Binda, E.; De Filippis, L.; Vescovi, A.L. Isolation of Neural Stem Cells from Neural Tissues Using the Neurosphere Technique. Curr. Protoc. Stem Cell Biol. 2010, 15, 2D.6.1–2D.6.18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vescovi, A.L.; Parati, E.A.; Gritti, A.; Poulinb, P.; Ferrariob, M.; Wankec, E.; Schoellera, P.F.; Cova, L.; Panliliob, M.A.; Colombod, A.; et al. Isolation and Cloning of Multipotential Stem Cells from the Embryonic Human CNS and Establishment of Transplantable Human Neural Stem Cell Lines by Epigenetic Stimulation. Exp. Neurol. 1999, 156, 71–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gelati, M.; Profico, D.; Projetti-Pensi, M.; Muzi, G.; Sgaravizzi, G.; Vescovi, A.L. Culturing and Expansion of “Clinical Grade” Precursors Cells from the Fetal Human Central Nervous System. Methods Mol. Biol. 2013, 1059, 65–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, D.-H.; Eve, D.J.; Sanberg, P.R.; Musso, J.; Bachstetter, A.D.; Wolfson, A.; Schlunk, A.; Baradez, M.-O.; Sinden, J.D.; Gemma, C. Increased Neuronal Proliferation in the Dentate Gyrus of Aged Rats Following Neural Stem Cell Implantation. Stem Cells Dev. 2010, 19, 175–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.-H.; Lee, J.-E.; Kim, S.U.; Cho, K.-G. Stereological Analysis on Migration of Human Neural Stem Cells in the Brain of Rats Bearing Glioma. Neurosurgery 2010, 66, 333–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reynolds, B.A.; Weiss, S. Generation of Neurons and Astrocytes from Isolated Cells of the Adult Mammalian Central Nervous System. Science 1992, 255, 1707–1710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deleyrolle, L.P.; Reynolds, B.A. Isolation, Expansion, and Differentiation of Adult Mammalian Neural Stem and Progenitor Cells Using the Neurosphere Assay. Methods Mol. Biol. 2009, 549, 91–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soares, R.; Ribeiro, F.F.; Lourenço, D.M.; Rodrigues, R.S.; Moreira, J.B.; Sebastião, A.M.; Morais, V.A.; Xapelli, S. Isolation and Expansion of Neurospheres from Postnatal (P1−3) Mouse Neurogenic Niches. JoVE J. Vis. Exp. 2020, e60822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azari, H.; Sharififar, S.; Rahman, M.; Ansari, S.; Reynolds, B.A. Establishing Embryonic Mouse Neural Stem Cell Culture Using the Neurosphere Assay. J. Vis. Exp. 2011, e2457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azari, H.; Louis, S.A.; Sharififar, S.; Vedam-Mai, V.; Reynolds, B.A. Neural-Colony Forming Cell Assay: An Assay To Discriminate Bona Fide Neural Stem Cells from Neural Progenitor Cells. J. Vis. Exp. 2011, e2639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reynolds, B.A.; Rietze, R.L. Neural stem cells and neurospheres—re-evaluating the relationship. Nat. Methods 2005, 2, 333–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campos, L.S.; Decker, L.; Taylor, V.; Skarnes, W. Notch, Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor, and β1-Integrin Pathways Are Coordinated in Neural Stem Cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2006, 281, 5300–5309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lathia, J.D.; Mattson, M.P.; Cheng, A. Notch: From neural development to neurological disorders. J. Neurochem. 2008, 107, 1471–1481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kilpatrick, T.; Bartlett, P. Cloned multipotential precursors from the mouse cerebrum require FGF-2, whereas glial restricted precursors are stimulated with either FGF-2 or EGF. J. Neurosci. 1995, 15, 3653–3661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tropepe, V.; Sibilia, M.; Cirunacd, B.G.; Rossantced, J.; Wagner, E.F.; Van Der Kooy, D. Distinct Neural Stem Cells Proliferate in Response to EGF and FGF in the Developing Mouse Telencephalon. Dev. Biol. 1999, 208, 166–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arsenijevic, Y.; Weiss, S.; Schneider, B.; Aebischer, P. Insulin-Like Growth Factor-I Is Necessary for Neural Stem Cell Proliferation and Demonstrates Distinct Actions of Epidermal Growth Factor and Fibroblast Growth Factor-2. J. Neurosci. 2001, 21, 7194–7202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Louis, S.A.; Mak, C.K.H.; Reynolds, B.A. Methods to Culture, Differentiate, and Characterize Neural Stem Cells from the Adult and Embryonic Mouse Central Nervous System. Methods Mol. Biol. 2013, 946, 479–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ciccolini, F.; Svendsen, C.N. Fibroblast Growth Factor 2 (FGF-2) Promotes Acquisition of Epidermal Growth Factor (EGF) Responsiveness in Mouse Striatal Precursor Cells: Identification of Neural Precursors Responding to both EGF and FGF-2. J. Neurosci. 1998, 18, 7869–7880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeBerardinis, R.J.; Mancuso, A.; Daikhin, E.; Nissim, I.; Yudkoff, M.; Wehrli, S.; Thompson, C.B. Beyond aerobic glycolysis: Transformed cells can engage in glutamine metabolism that exceeds the requirement for protein and nucleotide synthesis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 19345–19350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, C.S.; Ding, X.; Allmeroth, K.; Denzel, M.S.; Eming, S.A.; Wickströ, S.A. Glutamine Metabolism Controls Stem Cell Fate Reversibility and Long-Term Maintenance in the Hair Follicle. Cell Metab. 2020, 32, 629–642.e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicklin, P.; Bergman, P.; Zhang, B.; Triantafellow, E.; Wang, H.; Nyfeler, B.; Yang, H.; Hild, M.; Kung, C.; Wilson, C.; et al. Bidirectional Transport of Amino Acids Regulates mTOR and Autophagy. Cell 2009, 136, 521–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Son, J.; Lyssiotis, C.A.; Ying, H.; Wang, X.; Hua, S.; Ligorio, M.; Perera, R.M.; Ferrone, C.R.; Mullarky, E.; Shyh-Chang, N.; et al. Glutamine supports pancreatic cancer growth through a KRAS-regulated metabolic pathway. Nature 2013, 496, 101–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeo, H.; Lyssiotis, C.; Zhang, Y.; Ying, H.; Asara, J.M.; Cantley, L.C.; Paik, J.-H. FoxO3 coordinates metabolic pathways to maintain redox balance in neural stem cells. EMBO J. 2013, 32, 2589–2602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ryu, J.M.; Lee, S.H.; Seong, J.K.; Han, H.J. Glutamine contributes to maintenance of mouse embryonic stem cell self-renewal through PKC-dependent downregulation of HDAC1 and DNMT1/3a. Cell Cycle 2015, 14, 3292–3305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pagin, M.; Pernebrink, M.; Giubbolini, S.; Barone, C.; Sambruni, G.; Zhu, Y.; Chiara, M.; Ottolenghi, S.; Pavesi, G.; Wei, C.-L.; et al. Sox2 Controls Neural Stem Cell Self-Renewal Through a Fos-Centered Gene Regulatory Network. Stem. Cells 2021, 39, 1107–1119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wachs, F.-P.; Couillard-Despres, S.; Engelhardt, M.; Wilhelm, D.; Ploetz, S.; Vroemen, M.; Kaesbauer, J.; Uyanik, G.; Klucken, J.; Karl, C.; et al. High Efficacy of Clonal Growth and Expansion of Adult Neural Stem Cells. Lab. Investig. 2003, 83, 949–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gil-Perotín, S.; Duran-Moreno, M.; Cebrián-Silla, A.; Ramírez, M.; García-Belda, P.; García-Verdugo, J.M. Adult Neural Stem Cells from the Subventricular Zone: A Review of the Neurosphere Assay. Anat. Rec. 2013, 296, 1435–1452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, H.; Yang, H.; Liu, L.; Li, X.; Pan, B.; Fu, Z.; Chu, T.; Liu, J.; Kang, Y.; Ning, G.; et al. A modified protocol for the isolation, culture, and cryopreservation of rat embryonic neural stem cells. Exp. Ther. Med. 2020, 20, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, T.; Li, C.; Zhang, C.-Y.; Zhao, J. Effect of accutase or trypsin dissociation on the apoptosis of human striatum-derived neural stem cells. Zhongguo Yi Xue Ke Xue Yuan Xue Bao 2015, 37, 185–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, K.; Liu, T.-Q.; Dai, M.-S.; Ge, D.; Li, X.-Q.; Ma, X.-H.; Cui, Z.-F. Comparison of different culture modes for long-term expansion of neural stem cells. Cytotechnology 2006, 52, 209–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sen, A.; Kallos, M.S.; Behie, L.A. New Tissue Dissociation Protocol for Scaled-up Production of Neural Stem Cells in Suspension Bioreactors. Tissue Eng. 2004, 10, 904–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azari, H.; Rahman, M.; Sharififar, S.; Reynolds, B.A. Isolation and Expansion of the Adult Mouse Neural Stem Cells Using the Neurosphere Assay. JoVE J. Vis. Exp. 2010, 45, e2393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martín-Ibáñez, R.; Guardia, I.; Pardo, M.; Herranz, C.; Zietlow, R.; Vinh, N.-N.; Rosser, A.; Canals, J.M. Insights in spatio-temporal characterization of human fetal neural stem cells. Exp. Neurol. 2017, 291, 20–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, T.; Wang, X.; Xie, S.; Zhang, D.; Wang, X.; Li, B.; Ma, W.; Xin, H. A comparison of proliferative capacity and passaging potential between neural stem and progenitor cells in adherent and neurosphere cultures. Int. J. Dev. Neurosci. 2011, 29, 723–731. Available online: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/21664447/ (accessed on 31 March 2020). [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gritti, A.; Frölichsthal-Schoeller, P.; Galli, R.; Parati, E.A.; Cova, L.; Pagano, S.F.; Bjornson, C.R.; Vescovi, A.L. Epidermal and Fibroblast Growth Factors Behave as Mitogenic Regulators for a Single Multipotent Stem Cell-Like Population from the Subventricular Region of the Adult Mouse Forebrain. J. Neurosci. 1999, 19, 3287–3297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanai, N.; Tramontin, A.D.; Quiñones-Hinojosa, A.; Barbaro, N.M.; Gupta, N.; Kunwar, S.; Lawton, M.T.; McDermott, M.W.; Parsa, A.T.; García-Verdugo, J.M.; et al. Unique astrocyte ribbon in adult human brain contains neural stem cells but lacks chain migration. Nature 2004, 427, 740–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gritti, A.; Parati, E.; Cova, L.; Frolichsthal, P.; Galli, R.; Wanke, E.; Faravelli, L.; Morassutti, D.; Roisen, F.; Nickel, D.; et al. Multipotential stem cells from the adult mouse brain proliferate and self-renew in response to basic fibroblast growth factor. J. Neurosci. 1996, 16, 1091–1100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryder, E.F.; Snyder, E.Y.; Cepko, C.L. Establishment and characterization of multipotent neural cell lines using retrovirus vector-mediated oncogene transfer. J. Neurobiol. 1990, 21, 356–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Filippis, L.; Lamorte, G.; Snyder, E.Y.; Malgaroli, A.; Vescovi, A.L. A Novel, Immortal, and Multipotent Human Neural Stem Cell Line Generating Functional Neurons and Oligodendrocytes. STEM CELLS 2007, 25, 2312–2321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grochowski, C.; Radzikowska, E.; Maciejewski, R. Neural stem cell therapy—Brief review. Clin. Neurol. Neurosurg. 2018, 173, 8–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Bhattacharyya, A. Human Models Are Needed for Studying Human Neurodevelopmental Disorders. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2018, 103, 829–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







| 2D Culture | 3D Culture | |
| Medium composition | DMEM/F12 (Gibco, Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA) GlutaMAX® (1%, Gibco) Penicillin/streptomycin (1%, Gibco) Heparin (0.1%, Sigma-Aldrich, Saint Louis, MO, USA) N2 supplement ® (1%, Gibco) B27 supplement® (2%, Gibco) EGF (20 ng/mL, Gibco) bFGF (20 ng/mL, Gibco) | |
| Coating | poli-L-lysine + laminin | The non-adhesive coating on NunclonSphera® plates and t75 flasks (Nunc, Thermo Scientific™) |
| Seeding density | 40,000 cells/cm2 | 1 × 104 cells/cm2 |
| Antibody | Catalog Number | Source | Isotype | Dilution | Manufacturer |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| anti-Nestin | SAB4200347 | Rabbit polyclonal | IgG | 1:500 | Sigma-Aldrich |
| anti-NeuN | MAB377 | Mouse monoclonal | IgM | 1:50 | Millipore |
| anti-NF200 | N0142 | Mouse monoclonal | IgG1 | 1:800 | Sigma-Aldrich |
| anti-SOX2 | SAB5700644 | Rabbit polyclonal | IgG | 1:150 | Sigma-Aldrich |
| Antibody | Fluorochrome | Catalog Number | Isotype | Dilution | Manufacturer |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Alexa Fluor Goat (anti-rabbit) | Alexa 488 | A11034 | IgG | 1:1000 | Life Technologies |
| Alexa FluorGoat (anti-mouse) | Alexa 546 | A21123 | IgG1 | 1:1000 | Life Technologies |
| Alexa FluorGoat (anti-mouse) | Alexa 546 | A21045 | IgM | 1:1000 | Life Technologies |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Radoszkiewicz, K.; Jezierska-Woźniak, K.; Waśniewski, T.; Sarnowska, A. Understanding Intra- and Inter-Species Variability in Neural Stem Cells’ Biology Is Key to Their Successful Cryopreservation, Culture, and Propagation. Cells 2023, 12, 488. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells12030488
Radoszkiewicz K, Jezierska-Woźniak K, Waśniewski T, Sarnowska A. Understanding Intra- and Inter-Species Variability in Neural Stem Cells’ Biology Is Key to Their Successful Cryopreservation, Culture, and Propagation. Cells. 2023; 12(3):488. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells12030488
Chicago/Turabian StyleRadoszkiewicz, Klaudia, Katarzyna Jezierska-Woźniak, Tomasz Waśniewski, and Anna Sarnowska. 2023. "Understanding Intra- and Inter-Species Variability in Neural Stem Cells’ Biology Is Key to Their Successful Cryopreservation, Culture, and Propagation" Cells 12, no. 3: 488. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells12030488
APA StyleRadoszkiewicz, K., Jezierska-Woźniak, K., Waśniewski, T., & Sarnowska, A. (2023). Understanding Intra- and Inter-Species Variability in Neural Stem Cells’ Biology Is Key to Their Successful Cryopreservation, Culture, and Propagation. Cells, 12(3), 488. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells12030488






