Purification of Myosin from Bovine Tracheal Smooth Muscle, Filament Formation and Endogenous Association of Its Regulatory Complex
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Evolvement of the Sobieszek–Bremel Purification Approach for Smooth Muscle Myosin (from Gizzard to Airway Smooth Muscle)
3. Characterization of the Purified Myosin from Bovine Tracheal Smooth Muscle
3.1. Composition of Purified Bovine Tracheal Smooth Muscle Actomyosin
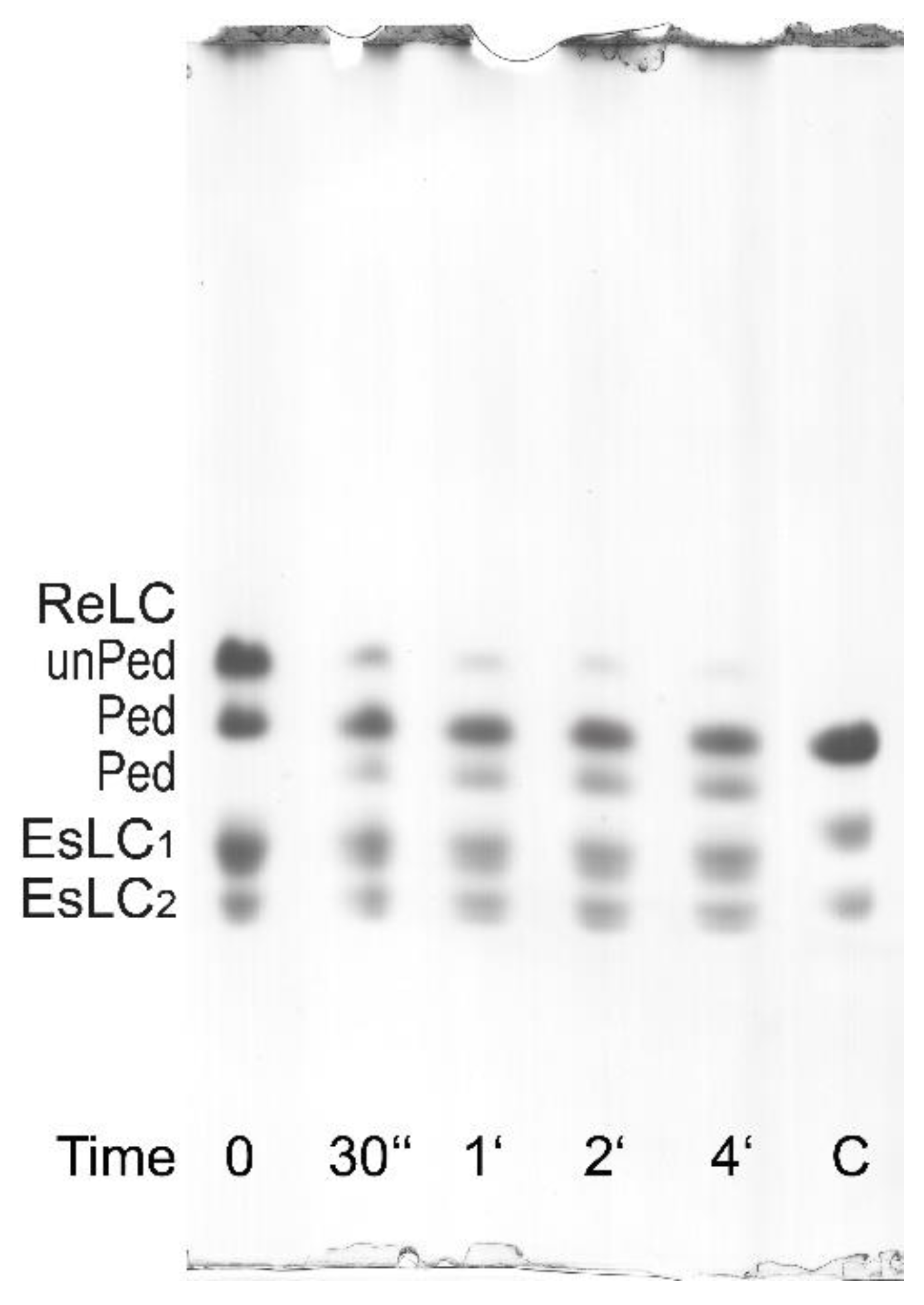
3.2. Regulatory Light Chain (ReLC) Phosphorylation of Purified Myosin
3.3. Formation of Filamentous Myosin by Dialysis
4. Myosin Filament Assembly and Copurification of the Regulatory Complex of Smooth Muscle
5. Quantification of the Endogenous Kinase Complex in Myosin
6. Removal of the Native-like Regulatory Complex from the Purified Smooth Muscle Myosin
6.1. Tropomyosin Removal from MYF and Filament Formation
6.2. Purification of CaM, MLCK, and MLCP
6.3. Removal of the Regulatory Complex from Myosin
7. Application in Asthma Research
8. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AA | ATPase Activity assay |
| am.sulf. | ammonium sulphate |
| ASM | airway smooth muscle |
| BW | Bis Wash (buffer) |
| CaM | calmodulin |
| CMY | crude myosin |
| KES | kinase extraction solution |
| LAMES | low ionic strength actomyosin extraction solution |
| ReLC | regulatory light chain |
| EsLC | essential light chain |
| LN2 | liquid nitrogen |
| MLCK | myosin light chain kinase |
| MLCP | myosin light chain phosphatase |
| MY | myosin |
| MYF | myofibril or myofibril-like preparation |
| o/n | overnight |
| SDS PAGE | sodium dodecyl sulfate polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis |
| UG PAGE | urea glycerol polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis |
| TM | tropomyosin |
| TL | telokin |
References
- Pratusevich, V.R.; Seow, C.Y.; Ford, L.E. Plasticity in canine ASM. J. Gen. Physiol. 1995, 105, 73–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuo, K.-H.; Herrera, A.M.; Wang, L.; Paré, P.D.; Ford, L.E.; Stephens, N.L.; Seow, C.Y. Structure-function correlation in airway smooth muscle adapted to different lengths. Am. J. Physiol. Physiol. 2003, 285, C384–C390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Chitano, P.; Seow, C.Y. Filament evanescence of myosin II and smooth muscle function. J. Gen. Physiol. 2021, 153, e202012781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lan, B.; Deng, L.; Donovan, G.M.; Chin, L.Y.M.; Syyong, H.T.; Wang, L.; Zhang, J.; Pascoe, C.; Norris, B.A.; Liu, J.C.-Y.; et al. Force maintenance and myosin filament assembly regulated by Rho-kinase in airway smooth muscle. Am. J. Physiol. Cell. Mol. Physiol. 2015, 308, L1–L10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Chitano, P.; Seow, C.Y. Mechanopharmacology of Rho-kinase antagonism in airway smooth muscle and potential new therapy for asthma. Pharmacol. Res. 2020, 159, 104995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Chitano, P.; Paré, P.D.; Seow, C.Y. Upregulation of smooth muscle Rho-kinase protein expression in human asthma. Eur. Respir. J. 2019, 55, 1901785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapsali, T.; Permutt, S.; Laube, B.; Scichilone, N.; Togias, A. Potent bronchoprotective effect of deep inspiration and its absence in asthma. J. Appl. Physiol. 2000, 89, 711–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nadel, J.A.; Tierney, D.F. Effect of a previous deep inspiration on airway resistance in man. J. Appl. Physiol. 1961, 16, 717–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scichilone, N.; Kapsali, T.; Permutt, S.; Togias, A. Deep Inspiration-induced Bronchoprotection Is Stronger than Bronchodilation. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2000, 162, 910–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scichilone, N.; Pyrgos, G.; Kapsali, T.; Anderlind, C.; Brown, R.; Permutt, S.; Togias, A. Airways Hyperresponsiveness and the Effects of Lung Inflation. Int. Arch. Allergy Immunol. 2001, 124, 262–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skloot, G.; Togias, A. Bronchodilation and Bronchoprotection by Deep Inspiration and Their Relationship to Bronchial Hyperresponsiveness. Clin. Rev. Allergy Immunol. 2003, 24, 55–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ip, K.; Sobieszek, A.; Solomon, D.; Jiao, Y.; Paré, P.; Seow, C. Physical Integrity of Smooth Muscle Myosin Filaments is Enhanced by Phosphorylation of the Regulatory Myosin Light Chain. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2007, 20, 649–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rovner, A.S.; Fagnant, P.M.; Lowey, S.; Trybus, K.M. The carboxylterminal isoforms of smooth muscle myosin heavy chain determine thick filament assembly properties. J. Cell Biol. 2002, 156, 113–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kendrick-Jones, J.; Cande, W.Z.; Tooth, P.J.; Smith, R.C.; Scholey, J.M. Studies on the effect of phosphorylation of the 20,000Mr light chain of vertebrate smooth muscle myosin. J. Mol. Biol. 1983, 165, 139–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, H.; Onishi, H.; Takahashi, K.; Watanabe, S. Structure and Function of Chicken Gizzard Myosin1. J. Biochem. 1978, 84, 1529–1542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trybus, K.M.; Huiatt, T.W.; Lowey, S. A bent monomeric conformation of myosin from smooth muscle. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1982, 79, 6151–6155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sobieszek, I.J.; Sobieszek, A. Myosin assembly of smooth muscle: From ribbons and side polarity to a row polar helical model. J. Muscle Res. Cell Motil. 2022, 43, 113–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sobieszek, A.; Bremel, R.D. Preparation and Properties of Vertebrate Smooth-Muscle Myofibrils and Actomyosin. JBIC J. Biol. Inorg. Chem. 1975, 55, 49–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Small, J.V.; Sobieszek, A. Ca-Regulation of Mammalian Smooth Muscle Actomyosin via a Kinase-Phosphatase-Dependent Phosphorylation and Dephosphorylation of the 20000-Mr Light Chain of Myosin. JBIC J. Biol. Inorg. Chem. 1977, 76, 521–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Small, J.V.; Sobieszek, A. The Contractile Apparatus of Smooth Muscle. Int. Rev. Cytol. 1980, 64, 241–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sobieszek, A. Vertebrate smooth muscle myosin Enzymatic and structural properties. In The Biochemis-try of Smooth Muscle; Stephens, N.L., Ed.; University Park Press: Baltimore, MD, USA, 1977; pp. 413–443. [Google Scholar]
- Sobieszek, A. Ca-Linked Phosphorylation of a Light Chain of Vertebrate Smooth-Muscle Myosin. JBIC J. Biol. Inorg. Chem. 1977, 73, 477–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sobieszek, A. Smooth Muscle Myosin: Molecule Conformation, Filament Assembly and Associated Regulatory Enzymes. In Airways Smooth Muscle: Biochemical Control of Contraction and Relaxation; Respiratory Pharmacology and Pharmacotherapy; Raeburn, D., Giembycz, M.A., Eds.; Birkhäuser: Basel, Switzerland, 1994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sobieszek, A.; Babiychuk, E.B.; Ortner, B.; Borkowski, J. Purification and Characterization of a Kinase-associated, Myofibrillar Smooth Muscle Myosin Light Chain Phosphatase Possessing a Calmodulin-targeting Subunit. J. Biol. Chem. 1997, 272, 7027–7033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sobieszek, A.; Borkowski, J.; Babiychuk, V.S. Purification and Characterization of a Smooth Muscle Myosin Light Chain Kinase-Phosphatase Complex. J. Biol. Chem. 1997, 272, 7034–7041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, F.; Haldeman, B.D.; John, O.A.; Brewer, P.D.; Wu, Y.-Y.; Ni, S.; Wilson, D.P.; Walsh, M.P.; Baker, J.E.; Cremo, C.R. Characterization of Tightly Associated Smooth Muscle Myosin–Myosin Light-Chain Kinase–Calmodulin Complexes. J. Mol. Biol. 2009, 390, 879–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sobieszek, A. Vectorial activation of smooth muscle myosin filaments and its modulation by telokin. Can. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 2005, 83, 899–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sobieszek, A. Gradient polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis in presence of sodium dodecyl sulfate: A practical approach to muscle contractile and regulatory proteins. Electrophoresis 1994, 15, 1014–1020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sobieszek, A.; Jertschin, P. Urea-glycerol-acrylamide gel electrophoresis of acidic low molecular weight muscle proteins: Rapid determination of myosin light chain phosphorylation in myosin, actomyosin and whole muscle samples. Electrophoresis 1986, 7, 417–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sparrow, M.P.; Maxwell, L.C.; Ruegg, J.C.; Bohr, D.F. Preparation and properties of a calcium ion-sensitive actomyosin from arteries. Am. J. Physiol. Content 1970, 219, 1366–1372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sobieszek, A.; Small, J. Myosin-linked calcium regulation in vertebrate smooth muscle. J. Mol. Biol. 1976, 102, 75–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.; Keller, T.C. Smitin, a novel smooth muscle titin–like protein, interacts with myosin filaments in vivo and in vitro. J. Cell Biol. 2002, 156, 101–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sobieszek, A. Smooth muscle myosin as a calmodulin binding protein. Affinity increase on filament assembly. J. Muscle Res. Cell Motil. 1990, 11, 114–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sobieszek, A.; Matusovsky, O.; Permyakova, T.V.; Sarg, B.; Lindner, H.; Shelud’Ko, N. Phosphorylation of myorod (catchin) by kinases tightly associated to molluscan and vertebrate smooth muscle myosins. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2006, 454, 197–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Persechini, A.; Hartshorne, D.J. Ordered phosphorylation of the two 20,000 molecular weight light chains of smooth muscle myosin. Biochemistry 1983, 22, 470–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikebe, M.; Komatsu, S.; Woodhead, J.L.; Mabuchi, K.; Ikebe, R.; Saito, J.; Craig, R.; Higashihara, M. The Tip of the Coiled-coil Rod Determines the Filament Formation of Smooth Muscle and Nonmuscle Myosin. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 30293–30300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sobieszek, A. Self-assembly of smooth muscle myosin filaments: Adaptation of filament length by telokin and Mg·ATP. Eur. Biophys. J. 2022, 51, 449–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sobieszek, A.; Andruchov, O.Y.; Grabarek, Z.; Kulikova, N.; Liebetrau, C.; Matusovsky, O.S. Modulation of myosin filament activation by telokin in smooth muscle: Liberation of myosin kinase and phosphatase from supramolecular complexes. Biophys. Chem. 2005, 113, 25–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sobieszek, A. Regulation of smooth muscle myosin light chain kinase: Allosteric effects and co-operative activation by calmodulin. J. Mol. Biol. 1991, 220, 947–957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sobieszek, A.; Strobl, A.; Ortner, B.; Babiychuk, E.B. Ca2+-calmodulin-dependent modification of smooth-muscle myosin light-chain kinase leading to its co-operative activation by calmodulin. Biochem. J. 1993, 295, 405–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filenko, A.; Danilova, V.; Sobieszek, A. Smooth muscle myosin light chain kinase, supramolecular organization, modulation of activity, and related conformational changes. Biophys. J. 1997, 73, 1593–1606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sobieszek, A. Calmodulin-Dependent Autophosphorylation of Smooth Muscle Myosin Light Chain Kinase: Intermolecular Reaction Mechanism via Dimerization of the Kinase and Potentiation of the Catalytic Activity Following Activation. Biochemistry 1995, 34, 11855–11863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sobieszek, A.; Sarg, B.; Lindner, H.; Seow, C.Y. Phosphorylation of caldesmon by myosin light chain kinase increases its binding affinity for phosphorylated myosin filaments. Biol. Chem. 2010, 391, 1091–1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cross, R.; Cross, K.; Sobieszek, A. ATP-linked monomer-polymer equilibrium of smooth muscle myosin: The free folded monomer traps ADP.Pi. EMBO J. 1986, 5, 2637–2641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sobieszek, A. Vectorial phosphorylation of filamentous smooth muscle myosin by calmodulin and myosin light chain kinase complex. J. Muscle Res. Cell Motil. 2001, 22, 505–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sobieszek, A.; Small, J. Regulation of the actin-myosin interaction in vertebrate smooth muscle: Activation via a myosin light-chain kinase and the effect of tropomyosin. J. Mol. Biol. 1977, 112, 559–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Paré, P.D.; Seow, C.Y. Effects of length oscillation on the subsequent force development in swine tracheal smooth muscle. J. Appl. Physiol. 2000, 88, 2246–2250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuo, K.-H.; Wang, L.; Paré, P.D.; Ford, L.E.; Seow, C.Y. Myosin thick filament lability induced by mechanical strain in airway smooth muscle. J. Appl. Physiol. 2001, 90, 1811–1816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skloot, G.; Permutt, S.; Togias, A. Airway hyperresponsiveness in asthma: A problem of limited smooth muscle relaxation with inspiration. J. Clin. Investig. 1995, 96, 2393–2403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malmberg, P.; Larsson, K.; Sundblad, B.; Zhiping, W. Importance of the Time Interval Between FEV1, Measurements in a Methacholine Provocation Test. Chest 1993, 104, 680–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fish, J.E.; Peterman, V.I.; Cugell, D.W. Effect of deep inspiration on airway conductance in subjects with allergic rhinitis and allergic asthma. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 1977, 60, 41–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chin, L.Y.; Bossé, Y.; Pascoe, C.; Hackett, T.L.; Seow, C.Y.; Paré, P.D. Mechanical properties of asthmatic airway smooth muscle. Eur. Respir. J. 2012, 40, 45–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koziol-White, C.J.; Yoo, E.J.; Cao, G.; Zhang, J.; Papanikolaou, E.; Pushkarsky, I.; Andrews, A.; E Himes, B.; Damoiseaux, R.D.; Liggett, S.B.; et al. Inhibition of PI3K promotes dilation of human small airways in a rho kinase-dependent manner. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2016, 173, 2726–2738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, H.; Rao, K.; Halayko, A.J.; Liu, X.; Stephens, N.L. Ragweed Sensitization—Induced Increase of Myosin Light Chain Kinase Content in Canine Airway Smooth Muscle. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 1992, 7, 567–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rao, K.; Jiang, H.; Halayko, A.J.; Pan, N.; Kepron, W.; Stephens, N.L. Increased ATPase Activity and Myosin Light Chain Kinase (MLCK) Content in Airway Smooth Muscle from Sensitized Dogs. Regul. Smooth Muscle Contract. 1991, 304, 369–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chitano, P.; Voynow, J.A.; Pozzato, V.; Msc, V.C.; Burch, L.H.; Wang, L.; Murphy, T.M. Ontogenesis of myosin light chain kinase mRNA and protein content in guinea pig tracheal smooth muscle. Pediatr. Pulmonol. 2004, 38, 456–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ammit, A.J.; Armour, C.L.; Black, J.L. Smooth-Muscle Myosin Light-Chain Kinase Content Is Increased in Human Sensitized Airways. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2000, 161, 257–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Léguillette, R.; Laviolette, M.; Bergeron, C.; Zitouni, N.; Kogut, P.; Solway, J.; Kachmar, L.; Hamid, Q.; Lauzon, A.-M. Myosin, Transgelin, and Myosin Light Chain Kinase. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2009, 179, 194–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

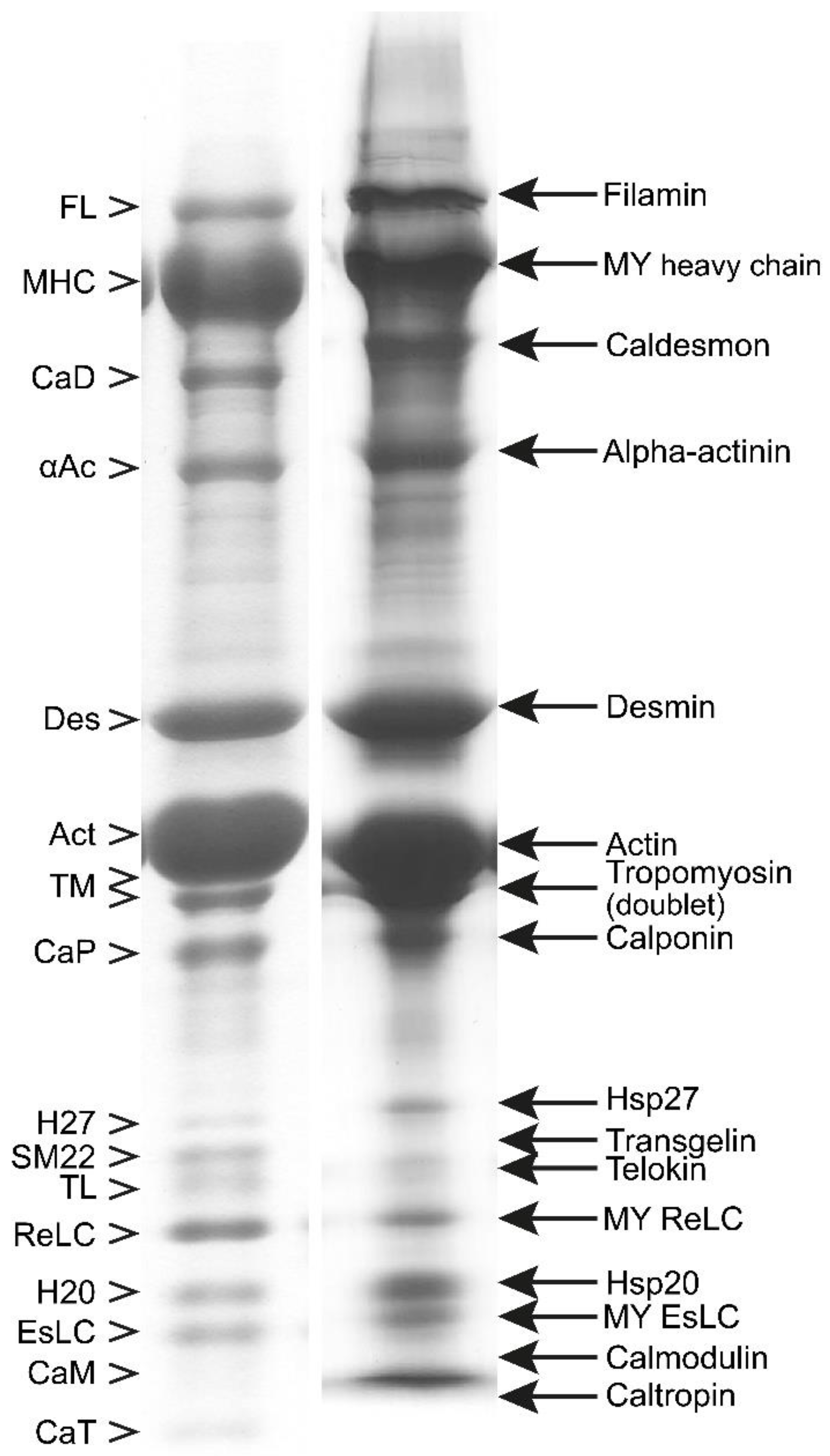
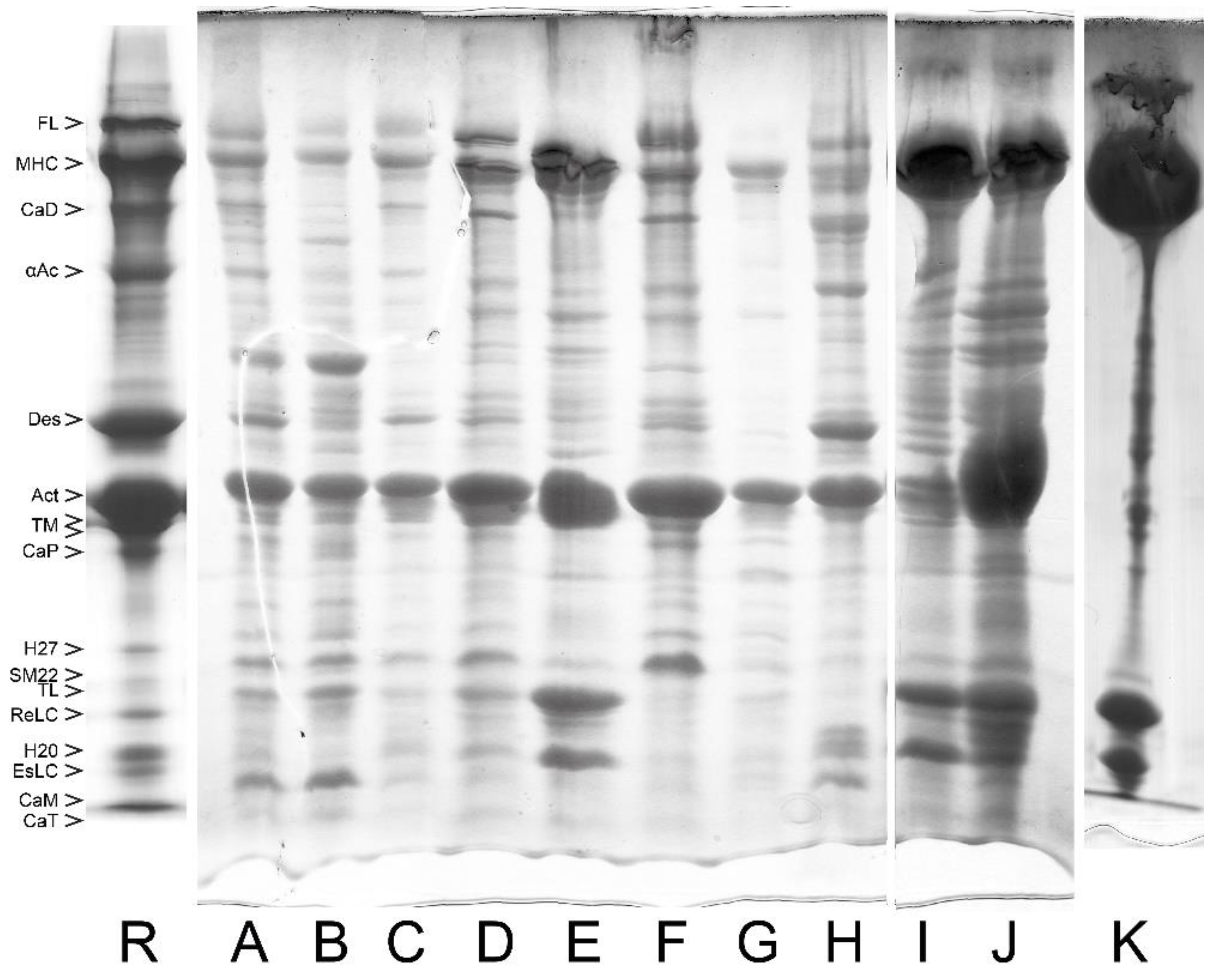

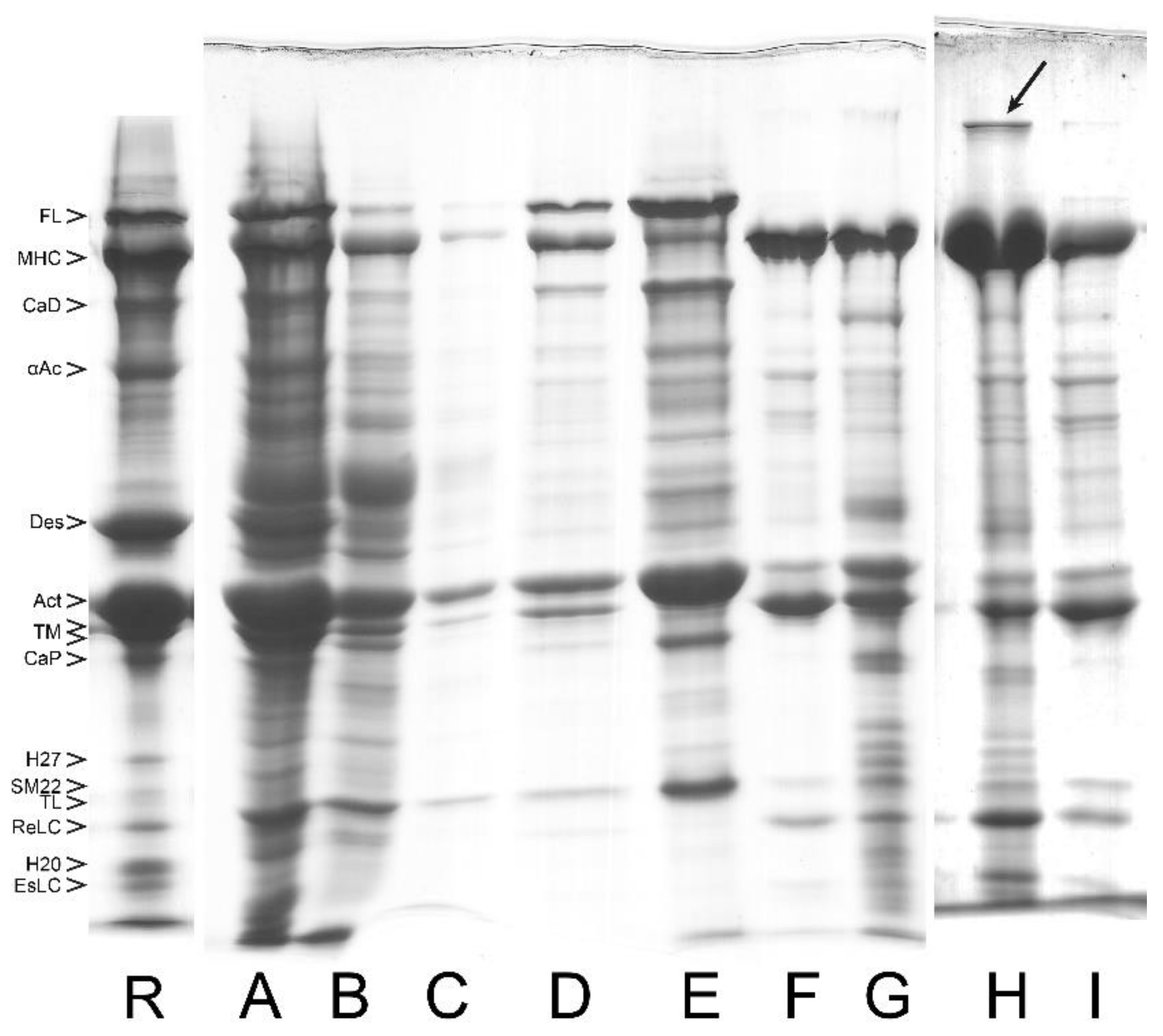
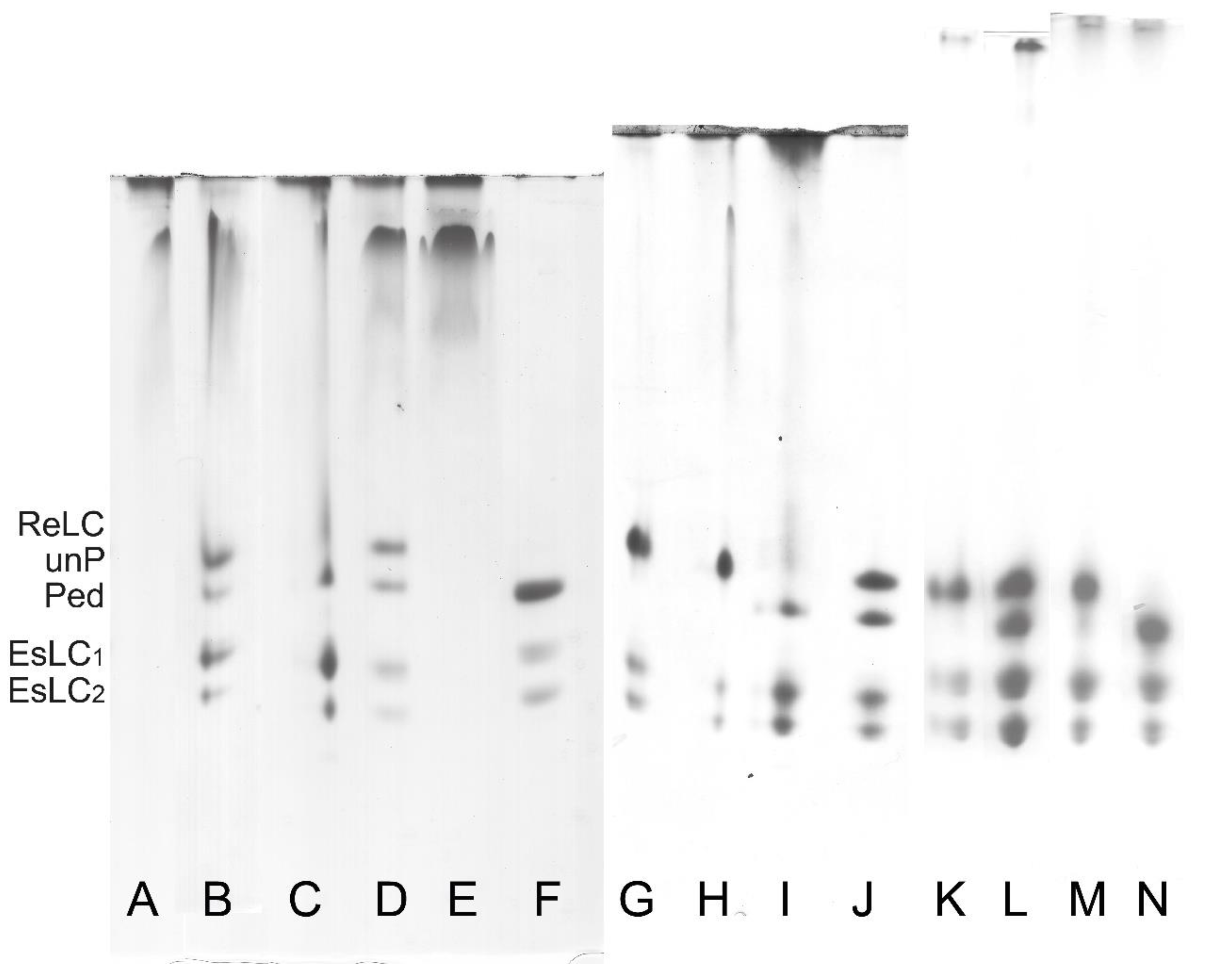

| References | Source | To Obtain Myofibril (MYF) | To Obtain Actomyosin | To Remove Tropomyosin | To Obtain Pure Smooth Muscle Myosin | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mincing | Homogenization | More homogenization | Am.Sulf. Precipitation | Actin Removal and Further Purification | ||
| Sobieszek and Bremel 1975 [18] Sobieszek 1977 [22] | Chicken or turkey gizzard. | Twice with 1.2 mm holed meat grinder; this step determines the size of the fibril bundles. | “Washing buffer”: KCl (60 mM), cysteine (1 mM), MgCl2 (1 mM), imidazole (20 mM), and streptomycin (100 mg/L), pH 6.9 at 4 °C, Triton X-100 0.3–0.5%. Homogenization for 20 s with a Sorvall Omnimixer. Two passes with a Teflon-glass homogenizer. Centrifugation (12,000× g 10–15 min). | ATP (10 mM), EDTA (1 mM), KCl (60 mM), cysteine (1 mM), MgCl2 (1 mM), imidazole (40 mM), and streptomycin (100 mg/L), pH 7.1 at 4 °C. Centrifugation (12,000× g 30 min). Filtration through glass wool. | Am.sulf. (25% saturation). Centrifugation 12,000× g 45 min. Redissolvation of pellet in a solution containing KCl (60 mM), cysteine (1 mM), and imidazole (20 mM) pH 7.0. | Centrifugation at 40,000× g 16 h to yield crude myosin fraction. Precipitation with 35–40 mM of either CaCl2 or MgCl2. Redissolvation and dialyzation against 0.3–0.6 M KCl to remove Ca2+. Dilution to 60 mM KCl in the presence of ATP (1 mM) and EDTA (1 mM) pH 7.0. Dialyzation overnight against a medium containing 0.6M KCl, EGTA (1 mM), imidazole (20 mM), pH 7.0, and centrifugation at 105,000× g 2.5 h. |
| Sobieszek and Small 1976 [31] | Chicken or turkey gizzard. | Same as above. | Same as above. | Mg2+ precipitation (pH 6.8). | Same as above. | Same as above. |
| Small and Sobieszek 1977 [19] | Pig stomach. | Same as Sobieszek and Small 1976 [31]. | As above for gizzard, except pH 6.8 and addition of 250 µM of the PMSF inhibitor and 2–3 passes in the Glenco 300 mL size Teflon-glass tight homogenizer. | Same as Sobieszek and Small 1976 [31], except pH 6.9, CaCl2 (2–20 mM). | Same as Sobieszek and Small 1976 [31]. | Same as above for gizzard, but for pig stomach and bovine tracheal smooth muscle purifications, it was important to add also Pefabloc S C protease inhibitor (0.1 µM final) to the dissolved CMY just before the o/n dialysis. |
| Sobieszek 1994a [23], Ip et al. 2007 [12] | Bovine trachea. | Dissected muscle pulverized in LN2. | “Bis Wash buffer (BW)” (in mM: 40 KCl, 2 MgCl2, 10 imidazole, 0.5 DTT, 0.5% Triton X-100, and 10 Tris base) pH 6.6 at 4 °C. Centrifugation 39,100× g 30 min. | Pellet homogenization in “LAMES” (in mM: 90 KCl, 2 EDTA, 2 EGTA, 7.5 Na2ATP, 1 DTT, and 40 imidazole) pH 7.2 at 4 °C. | Am.sulf (40–60% saturation). | ATP replenishment and an excess of MgCl2 (50 mM). Am. sulf. (40% saturation, then 60% saturation). Pellet dissolvation in BW and dialyzation against 50% BW overnight then full BW for an additional 3 h. Centrifugation at 29,325× g 30 min at 4 °C and the pellet resuspension in BW. |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, L.; Sobieszek, I.J.; Seow, C.Y.; Sobieszek, A. Purification of Myosin from Bovine Tracheal Smooth Muscle, Filament Formation and Endogenous Association of Its Regulatory Complex. Cells 2023, 12, 514. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells12030514
Wang L, Sobieszek IJ, Seow CY, Sobieszek A. Purification of Myosin from Bovine Tracheal Smooth Muscle, Filament Formation and Endogenous Association of Its Regulatory Complex. Cells. 2023; 12(3):514. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells12030514
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Lu, Isabel J. Sobieszek, Chun Y. Seow, and Apolinary Sobieszek. 2023. "Purification of Myosin from Bovine Tracheal Smooth Muscle, Filament Formation and Endogenous Association of Its Regulatory Complex" Cells 12, no. 3: 514. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells12030514
APA StyleWang, L., Sobieszek, I. J., Seow, C. Y., & Sobieszek, A. (2023). Purification of Myosin from Bovine Tracheal Smooth Muscle, Filament Formation and Endogenous Association of Its Regulatory Complex. Cells, 12(3), 514. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells12030514







