Combined Pulmonary Fibrosis and Emphysema: When Scylla and Charybdis Ally
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Definition, Symptoms and Prevalence
3. Pathophysiology
3.1. Pulmonary Function Tests and Blood Gas Analysis
3.2. Radiographic Features
3.2.1. Emphysema Appearance in Computed Tomography
- emphysema lesions of the upper zones distant to fibrotic lesions of the bases;
- progressive transition with diffuse emphysema (centrilobular and/or bullous) and zone of transition between bullae and honeycombing;
- paraseptal emphysema with predominant subpleural bullae of enlarging size at the bases.
3.2.2. Fibrotic Changes in Computed Tomography
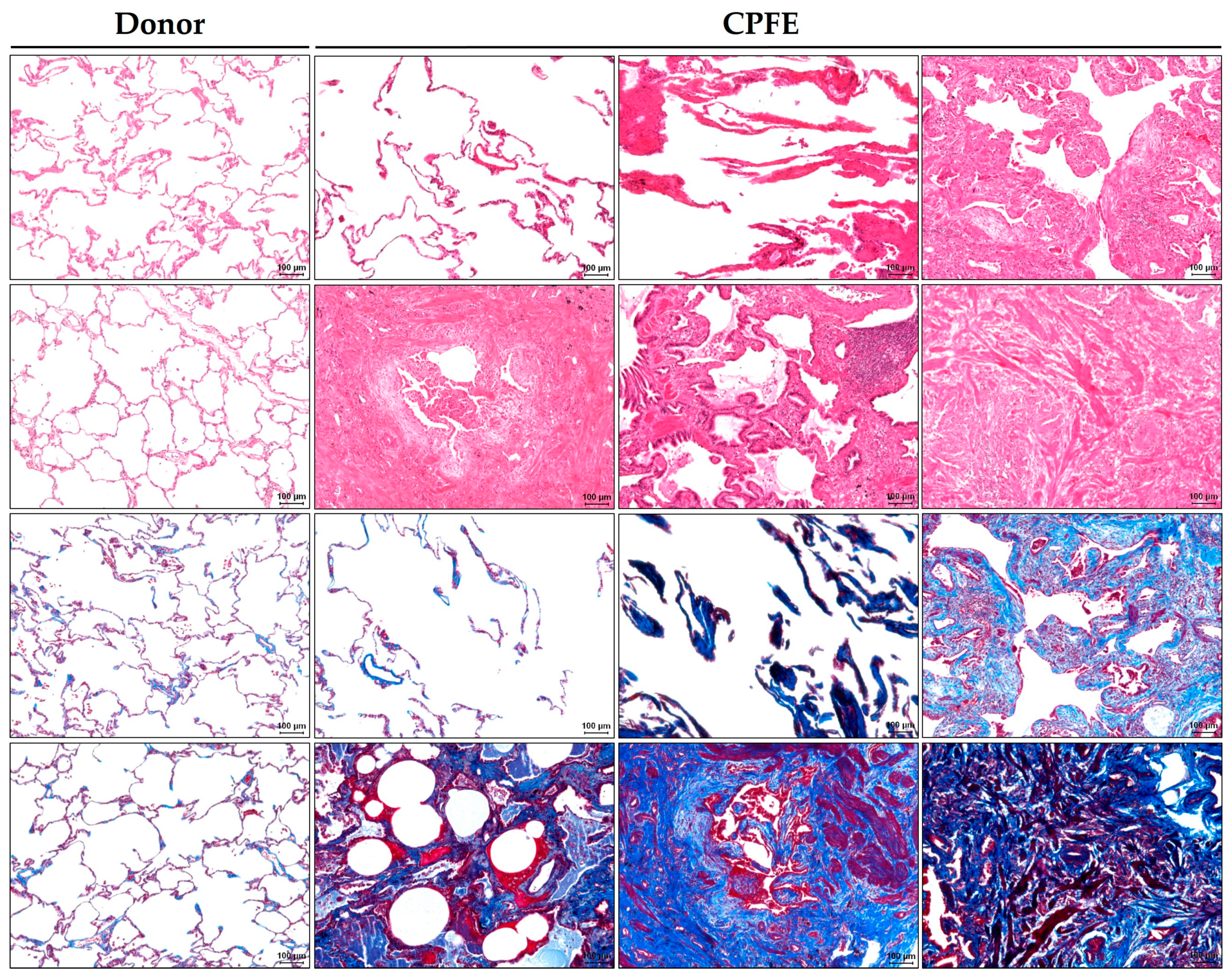
3.3. Histopathology
3.3.1. Emphysematous Changes in Histopathology
3.3.2. Fibrotic Changes in Histopathology
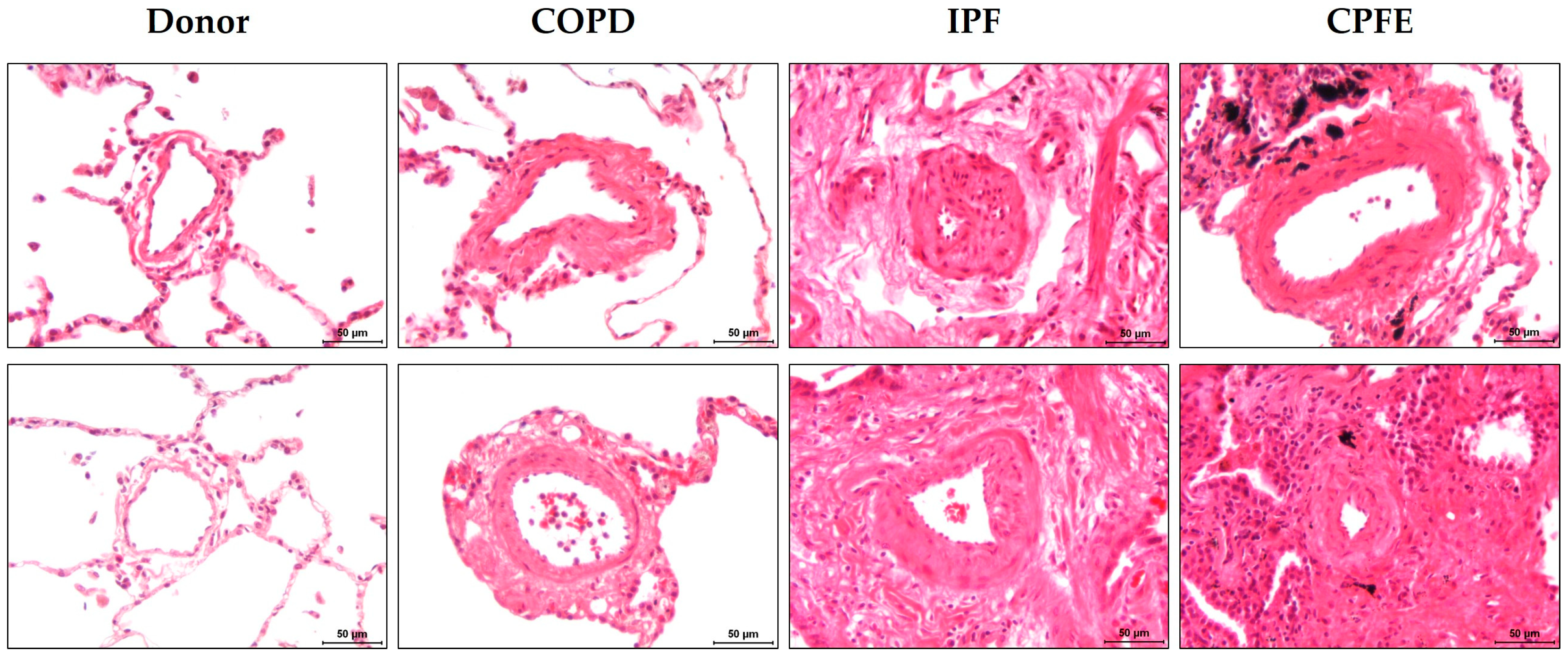
3.3.3. Pulmonary Vasculopathy
3.4. Inflammatory Cells and Mediators
3.5. Comorbidities
4. Pathogenesis
4.1. Smoking and Occupational Exposures
4.2. Connective Tissue Diseases and Other Autoimmune Disorders
4.3. Genetic Factors
5. Animal Models of CPFE
5.1. Combined Cigarette Smoke Exposure and Bleomycin Lung Injury in Mice
5.2. Transgenic Mouse Models with Co-Existing Emphysema and Fibrosis
5.3. Combined Emphysema and Fibrosis in Other Animal Species
6. Management and Prognosis
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| CPFE | Combined pulmonary fibrosis and emphysema |
| CT | Computed tomography |
| IPF | Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis |
| COPD | Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease |
| CTD | Connective tissue disease |
| ILD | Interstitial lung disease |
| RA | Rheumatoid arthritis |
| SSc | Systemic sclerosis |
| TLC | Total lung capacity |
| RV | Residual volume |
| FVC | Forced vital capacity |
| FEV1 | Forced expiratory volume in 1 s |
| DLCO | Carbon monoxide diffusion capacity |
| KCO | Carbon monoxide transfer coefficient |
| HRCT | High resolution CT |
| UIP | Usual interstitial pneumonia |
| fNSIP | Fibrotic nonspecific interstitial pneumonia |
| DIP | Desquamative interstitial pneumonia |
| RB | Respiratory bronchiolitis |
| cHP | Chronic hypersensitivity pneumonitis |
| fILD | Fibrosing ILD |
| SRIF | Smoking-related interstitial pneumonitis |
| LCH | Langerhans cell histiocytosis |
| PH | Pulmonary hypertension |
| AEF | Airspace enlargement with fibrosis |
| BAL | Bronchoalveolar lavage |
| CXCL | Chemokine (C-X-C motif) ligand |
| CRP | C-reactive protein |
| SP-C and -D | Surfactant protein-C and -D |
| KL-6 | Krebs von den Lungen-6 |
| TGF-β | Transforming growth factor β |
| TNF-α | Tumor necrosis factor α |
| MMP | Matrix metalloproteinase |
| mPAP | Mean pulmonary artery pressure |
| PMF | Progressive massive fibrosis |
| MP | Microscopic polyangiitis |
| RAGE | Receptor for advanced glycation end-products |
| IL-13 | Interleukin-13 |
| MHV-68 | Mouse gamma herpes virus 68 |
| ROS | Reactive oxygen species |
| PDGF | Platelet -derived growth factor |
| ADA | Adenosine deaminase |
| CPI | Composite physiologic index |
References
- Auerbach, O.; Garfinkel, L.; Hammond, E.C. Relation of smoking and age to findings in lung parenchyma: A microscopic study. Chest 1974, 65, 29–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tourniaire, A.; Tartulier, M.; Blum, J.; Deyrieux, F. Early detection of pulmonary circulatory sound in pure fibrosis and in fibrosis complicated by emphysema. Presse Med. (1893) 1966, 74, 2139–2144. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wells, A.U.; King, A.D.; Rubens, M.B.; Cramer, D.; du Bois, R.M.; Hansell, D.M. Lone cryptogenic fibrosing alveolitis: A functional-morphologic correlation based on extent of disease on thin-section computed tomography. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 1997, 155, 1367–1375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wiggins, J.; Strickland, B.; Turner-Warwick, M. Combined cryptogenic fibrosing alveolitis and emphysema: The value of high resolution computed tomography in assessment. Respir. Med. 1990, 84, 365–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cottin, V.; Nunes, H.; Brillet, P.Y.; Delaval, P.; Devouassoux, G.; Tillie-Leblond, I.; Israel-Biet, D.; Court-Fortune, I.; Valeyre, D.; Cordier, J.F.; et al. Combined pulmonary fibrosis and emphysema: A distinct underrecognised entity. Eur. Respir. J. 2005, 26, 586–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cottin, V.; Selman, M.; Inoue, Y.; Wong, A.W.; Corte, T.J.; Flaherty, K.R.; Han, M.K.; Jacob, J.; Johannson, K.A.; Kitaichi, M.; et al. Syndrome of Combined Pulmonary Fibrosis and Emphysema: An Official ATS/ERS/JRS/ALAT Research Statement. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2022, 206, e7–e41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.J.; Shin, S.H.; Park, J.W.; Kyung, S.Y.; Kang, S.M.; Lee, S.P.; Sung, Y.M.; Kim, Y.K.; Jeong, S.H. Annual Change in Pulmonary Function and Clinical Characteristics of Combined Pulmonary Fibrosis and Emphysema and Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis: Over a 3-Year Follow-up. Tuberc. Respir. Dis. 2014, 77, 18–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurashima, K.; Takayanagi, N.; Tsuchiya, N.; Kanauchi, T.; Ueda, M.; Hoshi, T.; Miyahara, Y.; Sugita, Y. The effect of emphysema on lung function and survival in patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Respirology 2010, 15, 843–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Zhang, C.; Dong, F.; Song, Q.; Chi, F.; Liu, L.; Wang, Y.; Che, C. Combined pulmonary fibrosis and emphysema: A retrospective analysis of clinical characteristics, treatment and prognosis. BMC Pulm. Med. 2016, 16, 137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, C.M.; Neder, J.A.; Verrastro, C.G.; Paula-Ribeiro, M.; Ramos, R.; Ferreira, E.M.; Nery, L.E.; O’Donnell, D.E.; Pereira, C.A.C.; Ota-Arakaki, J. Uncovering the mechanisms of exertional dyspnoea in combined pulmonary fibrosis and emphysema. Eur. Respir. J. 2020, 55, 1901319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mura, M.; Zompatori, M.; Pacilli, A.M.; Fasano, L.; Schiavina, M.; Fabbri, M. The presence of emphysema further impairs physiologic function in patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Respir. Care 2006, 51, 257–265. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zhang, M.; Peng, L.-L.; Ji, X.-L.; Yang, H.-B.; Zha, R.-S.; Gui, G.-P. Tumor necrosis factor gene polymorphisms are associated with silicosis: A systemic review and meta-analysis. Biosci. Rep. 2019, 39, bsr20181896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chae, K.J.; Jin, G.Y.; Han, Y.M.; Kim, Y.S.; Chon, S.B.; Lee, Y.S.; Kwon, K.S.; Choi, H.M.; Lynch, D. Prevalence and progression of combined pulmonary fibrosis and emphysema in asymptomatic smokers: A case-control study. Eur. Radiol. 2015, 25, 2326–2334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cottin, V.; Hansell, D.M.; Sverzellati, N.; Weycker, D.; Antoniou, K.M.; Atwood, M.; Oster, G.; Kirchgaessler, K.U.; Collard, H.R.; Wells, A.U. Effect of Emphysema Extent on Serial Lung Function in Patients with Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2017, 196, 1162–1171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacob, J.; Bartholmai, B.J.; Rajagopalan, S.; Kokosi, M.; Maher, T.M.; Nair, A.; Karwoski, R.; Renzoni, E.; Walsh, S.L.F.; Hansell, D.M.; et al. Functional and prognostic effects when emphysema complicates idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Eur. Respir. J. 2017, 50, 1700379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jankowich, M.D.; Rounds, S. Combined pulmonary fibrosis and emphysema alters physiology but has similar mortality to pulmonary fibrosis without emphysema. Lung 2010, 188, 365–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mejia, M.; Carrillo, G.; Rojas-Serrano, J.; Estrada, A.; Suarez, T.; Alonso, D.; Barrientos, E.; Gaxiola, M.; Navarro, C.; Selman, M. Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis and emphysema: Decreased survival associated with severe pulmonary arterial hypertension. Chest 2009, 136, 10–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryerson, C.J.; Hartman, T.; Elicker, B.M.; Ley, B.; Lee, J.S.; Abbritti, M.; Jones, K.D.; King, T.E., Jr.; Ryu, J.; Collard, H.R. Clinical features and outcomes in combined pulmonary fibrosis and emphysema in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Chest 2013, 144, 234–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sangani, R.; Ghio, A.; Culp, S.; Patel, Z.; Sharma, S. Combined Pulmonary Fibrosis Emphysema: Role of Cigarette Smoking and Pulmonary Hypertension in a Rural Cohort. Int. J. Chronic Obs. Pulmon. Dis. 2021, 16, 1873–1885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, S.L.; Nambiar, A.M.; Tayob, N.; Sundaram, B.; Han, M.K.; Gross, B.H.; Kazerooni, E.A.; Chughtai, A.R.; Lagstein, A.; Myers, J.L.; et al. Pulmonary function measures predict mortality differently in IPF versus combined pulmonary fibrosis and emphysema. Eur. Respir. J. 2011, 38, 176–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugino, K.; Ishida, F.; Kikuchi, N.; Hirota, N.; Sano, G.; Sato, K.; Isobe, K.; Sakamoto, S.; Takai, Y.; Homma, S. Comparison of clinical characteristics and prognostic factors of combined pulmonary fibrosis and emphysema versus idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis alone. Respirology 2014, 19, 239–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tasaka, S.; Mizoguchi, K.; Funatsu, Y.; Namkoong, H.; Yamasawa, W.; Ishii, M.; Hasegawa, N.; Betsuyaku, T. Cytokine profile of bronchoalveolar lavage fluid in patients with combined pulmonary fibrosis and emphysema. Respirology 2012, 17, 814–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoon, H.Y.; Kim, T.H.; Seo, J.B.; Lee, S.M.; Lim, S.; Lee, H.N.; Kim, N.; Han, M.; Kim, D.S.; Song, J.W. Effects of emphysema on physiological and prognostic characteristics of lung function in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Respirology 2019, 24, 55–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Antoniou, K.M.; Margaritopoulos, G.A.; Goh, N.S.; Karagiannis, K.; Desai, S.R.; Nicholson, A.G.; Siafakas, N.M.; Coghlan, J.G.; Denton, C.P.; Hansell, D.M.; et al. Combined Pulmonary Fibrosis and Emphysema in Scleroderma-Related Lung Disease Has a Major Confounding Effect on Lung Physiology and Screening for Pulmonary Hypertension. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2016, 68, 1004–1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ariani, A.; Silva, M.; Bravi, E.; Parisi, S.; Saracco, M.; De Gennaro, F.; Caimmi, C.; Girelli, F.; De Santis, M.; Volpe, A.; et al. Overall mortality in combined pulmonary fibrosis and emphysema related to systemic sclerosis. RMD Open 2019, 5, e000820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Champtiaux, N.; Cottin, V.; Chassagnon, G.; Chaigne, B.; Valeyre, D.; Nunes, H.; Hachulla, E.; Launay, D.; Crestani, B.; Cazalets, C.; et al. Combined pulmonary fibrosis and emphysema in systemic sclerosis: A syndrome associated with heavy morbidity and mortality. Semin. Arthritis Rheum. 2019, 49, 98–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cottin, V.; Nunes, H.; Mouthon, L.; Gamondes, D.; Lazor, R.; Hachulla, E.; Revel, D.; Valeyre, D.; Cordier, J.F.; Groupe d’Etudes et de Recherche sur les Maladies “Orphelines” Pulmonaires. Combined pulmonary fibrosis and emphysema syndrome in connective tissue disease. Arthritis Rheum. 2011, 63, 295–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antoniou, K.M.; Walsh, S.L.; Hansell, D.M.; Rubens, M.R.; Marten, K.; Tennant, R.; Hansel, T.; Desai, S.R.; Siafakas, N.M.; du Bois, R.M.; et al. Smoking-related emphysema is associated with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis and rheumatoid lung. Respirology 2013, 18, 1191–1196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwartz, D.A.; Merchant, R.K.; Helmers, R.A.; Gilbert, S.R.; Dayton, C.S.; Hunninghake, G.W. The influence of cigarette smoking on lung function in patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Am. Rev. Respir. Dis. 1991, 144, 504–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akagi, T.; Matsumoto, T.; Harada, T.; Tanaka, M.; Kuraki, T.; Fujita, M.; Watanabe, K. Coexistent emphysema delays the decrease of vital capacity in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Respir. Med. 2009, 103, 1209–1215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alsumrain, M.; De Giacomi, F.; Nasim, F.; Koo, C.W.; Bartholmai, B.J.; Levin, D.L.; Moua, T. Combined pulmonary fibrosis and emphysema as a clinicoradiologic entity: Characterization of presenting lung fibrosis and implications for survival. Respir. Med. 2019, 146, 106–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andriana, I.P.; Konstantinos, K.; Effrosyni, D.M.; Georgia, P.; Aneza, R.; Likurgos, K.; Raphaël, B.; Demosthenis, B.; Spyridon, A.P. Combined pulmonary fibrosis and emphysema: The many aspects of a cohabitation contract. Respir. Med. 2016, 117, 14–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, H.; Jiang, S. Combined pulmonary fibrosis and emphysema (CPFE): An entity different from emphysema or pulmonary fibrosis alone. J. Thorac. Dis. 2015, 7, 767–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitaguchi, Y.; Fujimoto, K.; Hayashi, R.; Hanaoka, M.; Honda, T.; Kubo, K. Annual changes in pulmonary function in combined pulmonary fibrosis and emphysema: Over a 5-year follow-up. Respir. Med. 2013, 107, 1986–1992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brillet, P.Y.; Cottin, V.; Letoumelin, P.; Landino, F.; Brauner, M.W.; Valeyre, D.; Cordier, J.F.; Nunes, H. Combined apical emphysema and basal fibrosis syndrome (emphysema/fibrosis syndrome): CT imaging features and pulmonary function tests. J. Radiol. 2009, 90, 43–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kinoshita, Y.; Watanabe, K.; Ishii, H.; Kushima, H.; Fujita, M.; Nabeshima, K. Distribution of emphysema and fibrosis in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis with coexisting emphysema. Histopathology 2019, 74, 1103–1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kitaguchi, Y.; Fujimoto, K.; Hanaoka, M.; Kawakami, S.; Honda, T.; Kubo, K. Clinical characteristics of combined pulmonary fibrosis and emphysema. Respirology 2010, 15, 265–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghanem, M.K.; Makhlouf, H.A.; Hassan, A.A.; Hamed, H.A. Combined pulmonary fibrosis and emphysema syndrome: Clinical, functional, and radiological assessment. Egypt. J. Bronchol. 2018, 12, 76–82. [Google Scholar]
- Todd, N.W.; Jeudy, J.; Lavania, S.; Franks, T.J.; Galvin, J.R.; Deepak, J.; Britt, E.J.; Atamas, S.P. Centrilobular emphysema combined with pulmonary fibrosis results in improved survival. Fibrogenes. Tissue Repair. 2011, 4, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugino, K.; Nakamura, Y.; Ito, T.; Isshiki, T.; Sakamoto, S.; Homma, S. Comparison of clinical characteristics and outcomes between combined pulmonary fibrosis and emphysema associated with usual interstitial pneumonia pattern and non-usual interstitial pneumonia. Sarcoidosis Vasc. Diffus. Lung Dis. Off. J. WASOG 2015, 32, 129–137. [Google Scholar]
- Oikonomou, A.; Mintzopoulou, P.; Tzouvelekis, A.; Zezos, P.; Zacharis, G.; Koutsopoulos, A.; Bouros, D.; Prassopoulos, P. Pulmonary fibrosis and emphysema: Is the emphysema type associated with the pattern of fibrosis? World J. Radiol. 2015, 7, 294–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Otani, H.; Tanaka, T.; Murata, K.; Fukuoka, J.; Nitta, N.; Nagatani, Y.; Sonoda, A.; Takahashi, M. Smoking-related interstitial fibrosis combined with pulmonary emphysema: Computed tomography-pathologic correlative study using lobectomy specimens. Int. J. Chronic Obs. Pulmon. Dis. 2016, 11, 1521–1532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inomata, M.; Ikushima, S.; Awano, N.; Kondoh, K.; Satake, K.; Masuo, M.; Kusunoki, Y.; Moriya, A.; Kamiya, H.; Ando, T.; et al. An autopsy study of combined pulmonary fibrosis and emphysema: Correlations among clinical, radiological, and pathological features. BMC Pulm. Med. 2014, 14, 104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cottin, V. Combined pulmonary fibrosis and emphysema: Bad and ugly all the same? Eur. Respir. J. 2017, 50, 1700846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sakai, F.; Tominaga, J.; Kaga, A.; Usui, Y.; Kanazawa, M.; Ogura, T.; Yanagawa, N.; Takemura, T. Imaging diagnosis of interstitial pneumonia with emphysema (combined pulmonary fibrosis and emphysema). Pulm. Med. 2012, 2012, 816541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, A.W.; Liang, J.; Cottin, V.; Ryerson, C.J. Diagnostic Features in Combined Pulmonary Fibrosis and Emphysema: A Systematic Review. Ann. Am. Thorac. Soc. 2020, 17, 1333–1336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jankowich, M.D.; Polsky, M.; Klein, M.; Rounds, S. Heterogeneity in combined pulmonary fibrosis and emphysema. Respiration 2008, 75, 411–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akira, M.; Inoue, Y.; Kitaichi, M.; Yamamoto, S.; Arai, T.; Toyokawa, K. Usual interstitial pneumonia and nonspecific interstitial pneumonia with and without concurrent emphysema: Thin-section CT findings. Radiology 2009, 251, 271–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, J.L.; Tazelaar, H.D.; Churg, A. Fibrosis with emphysema. Histopathology 2011, 58, 517–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snider, G.L.; Kleinerman, J.L.; Thurlbeck, W.M.; Bengali, Z.H. The Definition of Emphysema—Report of a National-Heart-Lung-and-Blood-Institute, Division of Lung-Diseases Workshop. Am. Rev. Respir. Dis. 1985, 132, 182–185. [Google Scholar]
- Portillo, K.; Morera, J. Combined Pulmonary Fibrosis and Emphysema Syndrome: A New Phenotype within the Spectrum of Smoking-Related Interstitial Lung Disease. Pulm. Med. 2012, 2012, 867870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawabata, Y.; Hoshi, E.; Murai, K.; Ikeya, T.; Takahashi, N.; Saitou, Y.; Kurashima, K.; Ubukata, M.; Takayanagi, N.; Sugita, H.; et al. Smoking-related changes in the background lung of specimens resected for lung cancer: A semiquantitative study with correlation to postoperative course. Histopathology 2008, 53, 707–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rogliani, P.; Mura, M.; Mattia, P.; Ferlosio, A.; Farinelli, G.; Mariotta, S.; Graziano, P.; Pezzuto, G.; Ricci, A.; Saltini, C.; et al. HRCT and histopathological evaluation of fibrosis and tissue destruction in IPF associated with pulmonary emphysema. Respir. Med. 2008, 102, 1753–1761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katzenstein, A.L.; Mukhopadhyay, S.; Zanardi, C.; Dexter, E. Clinically occult interstitial fibrosis in smokers: Classification and significance of a surprisingly common finding in lobectomy specimens. Hum. Pathol. 2010, 41, 316–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yousem, S.A. Respiratory bronchiolitis-associated interstitial lung disease with fibrosis is a lesion distinct from fibrotic nonspecific interstitial pneumonia: A proposal. Mod. Pathol. 2006, 19, 1474–1479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fraig, M.; Shreesha, U.; Savici, D.; Katzenstein, A.-L.A. Respiratory Bronchiolitis: A Clinicopathologic Study in Current Smokers, Ex-Smokers, and Never-Smokers. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 2002, 26, 647–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardoso, W.V.; Sekhon, H.S.; Hyde, D.M.; Thurlbeck, W.M. Collagen and elastin in human pulmonary emphysema. Am. Rev. Respir. Dis. 1993, 147, 975–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lang, M.R.; Fiaux, G.W.; Gillooly, M.; Stewart, J.A.; Hulmes, D.J.; Lamb, D. Collagen content of alveolar wall tissue in emphysematous and non-emphysematous lungs. Thorax 1994, 49, 319–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hogg, J.C.; Nepszy, S.J.; Macklem, P.T.; Thurlbeck, W.M. Elastic properties of the centrilobular emphysematous space. J. Clin. Investig. 1969, 48, 1306–1312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niewoehner, D.E.; Kleinerman, J.; Rice, D.B. Pathologic changes in the peripheral airways of young cigarette smokers. N. Engl. J. Med. 1974, 291, 755–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awano, N.; Inomata, M.; Ikushima, S.; Yamada, D.; Hotta, M.; Tsukuda, S.; Kumasaka, T.; Takemura, T.; Eishi, Y. Histological analysis of vasculopathy associated with pulmonary hypertension in combined pulmonary fibrosis and emphysema: Comparison with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis or emphysema alone. Histopathology 2017, 70, 896–905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sato, T.; Tsujino, I.; Tanino, M.; Ohira, H.; Nishimura, M. Broad and heterogeneous vasculopathy in pulmonary fibrosis and emphysema with pulmonary hypertension. Respirol. Case Rep. 2013, 1, 10–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malli, F.; Papakosta, D.; Antoniou, K.; Dimadi, M.; Polychronopoulos, V.; Malagari, K.; Oikonomou, A.; Bouros, D.E.; Daniil, Z. Combined pulmonary fibrosis and emphysema characteristics in a Greek cohort. ERJ Open Res. 2019, 5, 00014–02018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cornwell, W.D.; Kim, C.; Lastra, A.C.; Dass, C.; Bolla, S.; Wang, H.; Zhao, H.; Ramsey, F.V.; Marchetti, N.; Rogers, T.J.; et al. Inflammatory signature in lung tissues in patients with combined pulmonary fibrosis and emphysema. Biomarkers 2019, 24, 232–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanino, M.; Betsuyaku, T.; Takeyabu, K.; Tanino, Y.; Yamaguchi, E.; Miyamoto, K.; Nishimura, M. Increased levels of interleukin-8 in BAL fluid from smokers susceptible to pulmonary emphysema. Thorax 2002, 57, 405–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, L.; Bian, W.; Gu, X.H.; Shen, C. Differing Expression of Cytokines and Tumor Markers in Combined Pulmonary Fibrosis and Emphysema Compared to Emphysema and Pulmonary Fibrosis. COPD J. Chronic Obrst. Pulm. Dis. 2017, 14, 245–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kokuho, N.; Ishii, T.; Kamio, K.; Hayashi, H.; Kurahara, M.; Hattori, K.; Motegi, T.; Azuma, A.; Gemma, A.; Kida, K. Diagnostic Values For Club Cell Secretory Protein (CC16) in Serum of Patients of Combined Pulmonary Fibrosis and Emphysema. COPD J. Chronic Obrst. Pulm. Dis. 2015, 12, 347–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiba, S.; Ohta, H.; Abe, K.; Hisata, S.; Ohkouchi, S.; Hoshikawa, Y.; Kondo, T.; Ebina, M. The Diagnostic Value of the Interstitial Biomarkers KL-6 and SP-D for the Degree of Fibrosis in Combined Pulmonary Fibrosis and Emphysema. Pulm. Med. 2012, 2012, 492960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caminati, A.; Lonati, C.; Cassandro, R.; Elia, D.; Pelosi, G.; Torre, O.; Zompatori, M.; Uslenghi, E.; Harari, S. Comorbidities in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: An underestimated issue. Eur. Respir. Rev. 2019, 28, 190044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gredic, M.; Blanco, I.; Kovacs, G.; Helyes, Z.; Ferdinandy, P.; Olschewski, H.; Barberà, J.A.; Weissmann, N. Pulmonary hypertension in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2021, 178, 132–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Humbert, M.; Kovacs, G.; Hoeper, M.M.; Badagliacca, R.; Berger, R.M.F.; Brida, M.; Carlsen, J.; Coats, A.J.S.; Escribano-Subias, P.; Ferrari, P.; et al. 2022 ESC/ERS Guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of pulmonary hypertension. Eur. Respir. J. 2023, 61, 2200879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grubstein, A.; Bendayan, D.; Schactman, I.; Cohen, M.; Shitrit, D.; Kramer, M.R. Concomitant upper-lobe bullous emphysema, lower-lobe interstitial fibrosis and pulmonary hypertension in heavy smokers: Report of eight cases and review of the literature. Respir. Med. 2005, 99, 948–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cottin, V.; Le Pavec, J.; Prevot, G.; Mal, H.; Humbert, M.; Simonneau, G.; Cordier, J.F.; Germ“O”P. Pulmonary hypertension in patients with combined pulmonary fibrosis and emphysema syndrome. Eur. Respir. J. 2010, 35, 105–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Liu, P.; Zhou, H.; Kong, H.; Xie, W. An increased risk of lung cancer in combined pulmonary fibrosis and emphysema patients with usual interstitial pneumonia compared with patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis alone: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Ther. Adv. Respir. Dis. 2021, 15, 17534666211017050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koo, H.J.; Do, K.H.; Lee, J.B.; Alblushi, S.; Lee, S.M. Lung Cancer in Combined Pulmonary Fibrosis and Emphysema: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0161437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Houston, K.A.; Henley, S.J.; Li, J.; White, M.C.; Richards, T.B. Patterns in lung cancer incidence rates and trends by histologic type in the United States, 2004–2009. Lung Cancer 2014, 86, 22–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pesch, B.; Kendzia, B.; Gustavsson, P.; Jöckel, K.H.; Johnen, G.; Pohlabeln, H.; Olsson, A.; Ahrens, W.; Gross, I.M.; Brüske, I.; et al. Cigarette smoking and lung cancer--relative risk estimates for the major histological types from a pooled analysis of case-control studies. Int. J. Cancer 2012, 131, 1210–1219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tzilas, V.; Bouros, D. Pathogenesis of combined pulmonary fibrosis and emphysema. Common pathogenetic pathways. Pneumon 2015, 28, 139–146. [Google Scholar]
- Hiwatari, N.; Shimura, S.; Takishima, T. Pulmonary emphysema followed by pulmonary fibrosis of undetermined cause. Respiration 1993, 60, 354–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moon, S.W.; Park, M.S.; Kim, Y.S.; Jang, J.; Lee, J.H.; Lee, C.T.; Chung, J.H.; Shim, H.S.; Lee, K.W.; Kim, S.S.; et al. Combined pulmonary fibrosis and emphysema and idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis in non-small cell lung cancer: Impact on survival and acute exacerbation. BMC Pulm. Med. 2019, 19, 177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jankowich, M.D.; Rounds, S.I.S. Combined pulmonary fibrosis and emphysema syndrome: A review. Chest 2012, 141, 222–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baumgartner, K.B.; Samet, J.M.; Stidley, C.A.; Colby, T.V.; Waldron, J.A. Cigarette smoking: A risk factor for idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 1997, 155, 242–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, C.K.; Murray, L.A.; Molfino, N.A. Smoking and idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Pulm. Med. 2012, 2012, 808260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salvi, S.S.; Barnes, P.J. Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease in non-smokers. Lancet 2009, 374, 733–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marsh, S.; Aldington, S.; Shirtcliffe, P.; Weatherall, M.; Beasley, R. Smoking and COPD: What really are the risks? Eur. Respir. J. 2006, 28, 883–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Papiris, S.A.; Triantafillidou, C.; Manali, E.D.; Kolilekas, L.; Baou, K.; Kagouridis, K.; Bouros, D. Combined pulmonary fibrosis and emphysema. Expert. Rev. Respir. Med. 2013, 7, 19–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozbay, B.; Uzun, K.; Arslan, H.; Zehir, I. Functional and radiological impairment in women highly exposed to indoor biomass fuels. Respirology 2001, 6, 255–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daniil, Z.; Koutsokera, A.; Gourgoulianis, K. Combined pulmonary fibrosis and emphysema in patients exposed to agrochemical compounds. Eur. Respir. J. 2006, 27, 434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McConnochie, K.; Green, F.H.Y.; Vallyathan, V.; Wagner, J.C.; Seal, R.M.E.; Lyons, J.P. Interstitial Fibrosis in Coal Workers—Experience in Wales and West Virginia. Ann. Occup. Hyg. 1988, 32, 553–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blackley, D.J.; Reynolds, L.E.; Short, C.; Carson, R.; Storey, E.; Halldin, C.N.; Laney, A.S. Progressive Massive Fibrosis in Coal Miners from 3 Clinics in Virginia. JAMA 2018, 319, 500–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, R.A.; Patel, A.; Green, F.H. Lung disease caused by exposure to coal mine and silica dust. Semin. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2008, 29, 651–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leigh, J.; Driscoll, T.R.; Cole, B.D.; Beck, R.W.; Hull, B.P.; Yang, J. Quantitative relation between emphysema and lung mineral content in coalworkers. Occup. Environ. Med. 1994, 51, 400–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seixas, N.S.; Robins, T.G.; Attfield, M.D.; Moulton, L.H. Exposure-response relationships for coal mine dust and obstructive lung disease following enactment of the Federal Coal Mine Health and Safety Act of 1969. Am. J. Ind. Med. 1992, 21, 715–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petsonk, E.L.; Rose, C.; Cohen, R. Coal mine dust lung disease. New lessons from old exposure. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2013, 187, 1178–1185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cockcroft, A.; Seal, R.M.; Wagner, J.C.; Lyons, J.P.; Ryder, R.; Andersson, N. Post-mortem study of emphysema in coalworkers and non-coalworkers. Lancet 1982, 2, 600–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jelic, T.M.; Estalilla, O.C.; Sawyer-Kaplan, P.R.; Plata, M.J.; Powers, J.T.; Emmett, M.; Kuenstner, J.T. Coal Mine Dust Desquamative Chronic Interstitial Pneumonia: A Precursor of Dust-Related Diffuse Fibrosis and of Emphysema. Int. J. Occup. Environ. Med. 2017, 8, 153–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soumagne, T.; Chardon, M.L.; Dournes, G.; Laurent, L.; Degano, B.; Laurent, F.; Dalphin, J.C. Characterization of emphysema in active farmer’s lung disease. Eur. Respir. J. 2016, 48, PA1163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soumagne, T.; Pana-Katatali, H.; Degano, B.; Dalphin, J.C. Combined pulmonary fibrosis and emphysema in hypersensitivity pneumonitis. BMJ Case Rep. 2015, 2015, bcr2015211560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soumagne, T.; Chardon, M.L.; Dournes, G.; Laurent, L.; Degano, B.; Laurent, F.; Dalphin, J.C. Emphysema in active farmer’s lung disease. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0178263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Remy-Jardin, M.; Remy, J.; Wallaert, B.; Muller, N.L. Subacute and chronic bird breeder hypersensitivity pneumonitis: Sequential evaluation with CT and correlation with lung function tests and bronchoalveolar lavage. Radiology 1993, 189, 111–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karkhanis, V.S.; Joshi, J.M. Combined pulmonary fibrosis and emphysema in a tyre industry worker. Lung India 2012, 29, 273–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marchiori, E.; Lourenco, S.; Gasparetto, T.D.; Zanetti, G.; Mano, C.M.; Nobre, L.F. Pulmonary talcosis: Imaging findings. Lung 2010, 188, 165–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roshan, R.; Guptal, M.; Kulshrestha, R.; Menon, B.; Chhabra, S.K. Combined pulmonary fibrosis and emphysema in a welder. Monaldi Arch. Chest Dis. 2012, 77, 26–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Porru, S.; Placidi, D.; Quarta, C.; Sabbioni, E.; Pietra, R.; Fortaner, S. The potencial role of rare earths in the pathogenesis of interstitial lung disease: A case report of movie projectionist as investigated by neutron activation analysis. J. Trace Elem. Med. Biol. Organ Soc. Miner. Trace Elem. (GMS) 2001, 14, 232–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamakawa, H.; Takemura, T.; Iwasawa, T.; Yamanaka, Y.; Ikeda, S.; Sekine, A.; Kitamura, H.; Baba, T.; Iso, S.; Okudela, K.; et al. Emphysematous change with scleroderma-associated interstitial lung disease: The potential contribution of vasculopathy? BMC Pulm. Med. 2018, 18, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamakawa, H.; Hagiwara, E.; Kitamura, H.; Yamanaka, Y.; Ikeda, S.; Sekine, A.; Baba, T.; Iso, S.; Okudela, K.; Iwasawa, T.; et al. Clinical Features of Idiopathic Interstitial Pneumonia with Systemic Sclerosis-Related Autoantibody in Comparison with Interstitial Pneumonia with Systemic Sclerosis. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0161908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacob, J.; Song, J.W.; Yoon, H.Y.; Cross, G.; Barnett, J.; Woo, W.L.; Adams, F.; Kokosi, M.; Devaraj, A.; Renzoni, E.; et al. Prevalence and Effects of Emphysema in Never-Smokers with Rheumatoid Arthritis Interstitial Lung Disease. EBioMedicine 2018, 28, 303–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tzouvelekis, A.; Zacharis, G.; Oikonomou, A.; Mikroulis, D.; Margaritopoulos, G.; Koutsopoulos, A.; Antoniadis, A.; Koulelidis, A.; Steiropoulos, P.; Boglou, P.; et al. Increased incidence of autoimmune markers in patients with combined pulmonary fibrosis and emphysema. BMC Pulm. Med. 2013, 13, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tzouvelekis, A.; Zacharis, G.; Oikonomou, A.; Koulelidis, A.; Steiropoulos, P.; Froudarakis, M.; Kriki, P.; Vargemezis, V.; Bouros, D. Combined pulmonary fibrosis and emphysema associated with microscopic polyangiitis. Eur. Respr. J. 2012, 40, 505–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gocho, K.; Sugino, K.; Sato, K.; Hasegawa, C.; Uekusa, T.; Homma, S. Microscopic polyangiitis preceded by combined pulmonary fibrosis and emphysema. Respir. Med. Case Rep. 2015, 15, 128–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nemoto, M.; Noma, S.; Otsuki, A.; Nakashima, K.; Honma, K.; Johkoh, T.; Fukuoka, J.; Aoshima, M. Combined pulmonary fibrosis and emphysema with myeloperoxidase-antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibody positivity that resolved upon smoking cessation. Respir. Med. Case Rep. 2018, 25, 165–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cosio, M.G.; Saetta, M.; Agusti, A. Immunologic aspects of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2009, 360, 2445–2454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caramori, G.; Ruggeri, P.; Di Stefano, A.; Mumby, S.; Girbino, G.; Adcock, I.M.; Kirkham, P. Autoimmunity and COPD: Clinical Implications. Chest 2018, 153, 1424–1431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barnes, P.J. Inflammatory mechanisms in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2016, 138, 16–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alder, J.K.; Chen, J.J.-L.; Lancaster, L.; Danoff, S.; Su, S.-c.; Cogan, J.D.; Vulto, I.; Xie, M.; Qi, X.; Tuder, R.M.; et al. Short telomeres are a risk factor for idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 13051–13056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Courtwright, A.M.; El-Chemaly, S. Telomeres in Interstitial Lung Disease: The Short and the Long of It. Ann. Am. Thorac. Soc. 2019, 16, 175–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armanios, M.Y.; Chen, J.J.; Cogan, J.D.; Alder, J.K.; Ingersoll, R.G.; Markin, C.; Lawson, W.E.; Xie, M.; Vulto, I.; Phillips, J.A., 3rd; et al. Telomerase mutations in families with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2007, 356, 1317–1326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duckworth, A.; Gibbons, M.A.; Allen, R.J.; Almond, H.; Beaumont, R.N.; Wood, A.R.; Lunnon, K.; Lindsay, M.A.; Wain, L.V.; Tyrrell, J.; et al. Telomere length and risk of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: A mendelian randomisation study. Lancet Respir. Med. 2021, 9, 285–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanley, S.E.; Merck, S.J.; Armanios, M. Telomerase and the Genetics of Emphysema Susceptibility. Implications for Pathogenesis Paradigms and Patient Care. Ann. Am. Thorac. Soc. 2016, 13 (Suppl. S5), S447–S451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armanios, M. Telomerase and idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Mutat. Res. 2012, 730, 52–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cordoba-Lanus, E.; Cazorla-Rivero, S.; Espinoza-Jimenez, A.; de-Torres, J.P.; Pajares, M.J.; Aguirre-Jaime, A.; Celli, B.; Casanova, C. Telomere shortening and accelerated aging in COPD: Findings from the BODE cohort. Respir. Res. 2017, 18, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stanley, S.E.; Chen, J.J.; Podlevsky, J.D.; Alder, J.K.; Hansel, N.N.; Mathias, R.A.; Qi, X.; Rafaels, N.M.; Wise, R.A.; Silverman, E.K.; et al. Telomerase mutations in smokers with severe emphysema. J. Clin. Investig. 2015, 125, 563–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alder, J.K.; Guo, N.; Kembou, F.; Parry, E.M.; Anderson, C.J.; Gorgy, A.I.; Walsh, M.F.; Sussan, T.; Biswal, S.; Mitzner, W.; et al. Telomere Length Is a Determinant of Emphysema Susceptibility. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2011, 184, 904–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nunes, H.; Monnet, I.; Kannengiesser, C.; Uzunhan, Y.; Valeyre, D.; Kambouchner, M.; Naccache, J.-M. Is Telomeropathy the Explanation for Combined Pulmonary Fibrosis and Emphysema Syndrome?: Report of a Family with TERT Mutation. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2014, 189, 753–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guzmán-Vargas, J.; Ambrocio-Ortiz, E.; Pérez-Rubio, G.; Ponce-Gallegos, M.A.; Hernández-Zenteno, R.d.J.; Mejía, M.; Ramírez-Venegas, A.; Buendia-Roldan, I.; Falfán-Valencia, R. Differential Genomic Profile in TERT, DSP, and FAM13A between COPD Patients with Emphysema, IPF, and CPFE Syndrome. Front. Med. 2021, 8, 725144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stanley, S.E.; Gable, D.L.; Wagner, C.L.; Carlile, T.M.; Hanumanthu, V.S.; Podlevsky, J.D.; Khalil, S.E.; DeZern, A.E.; Rojas-Duran, M.F.; Applegate, C.D.; et al. Loss-of-function mutations in the RNA biogenesis factor <i>NAF1</i> predispose to pulmonary fibrosis–emphysema. Sci. Transl. Med. 2016, 8, 351ra107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Meng, Y.; Wang, Y.; Li, J.; Lam, M.; Wang, L.; Di, L.J. Nuclear localization of Desmoplakin and its involvement in telomere maintenance. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2019, 15, 2350–2362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amin, R.S.; Wert, S.E.; Baughman, R.P.; Tomashefski, J.F., Jr.; Nogee, L.M.; Brody, A.S.; Hull, W.M.; Whitsett, J.A. Surfactant protein deficiency in familial interstitial lung disease. J. Pediatr. 2001, 139, 85–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cameron, H.S.; Somaschini, M.; Carrera, P.; Hamvas, A.; Whitsett, J.A.; Wert, S.E.; Deutsch, G.; Nogee, L.M. A common mutation in the surfactant protein C gene associated with lung disease. J. Pediatr. 2005, 146, 370–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, A.Q.; Lane, K.; Phillips, J., 3rd; Prince, M.; Markin, C.; Speer, M.; Schwartz, D.A.; Gaddipati, R.; Marney, A.; Johnson, J.; et al. Heterozygosity for a surfactant protein C gene mutation associated with usual interstitial pneumonitis and cellular nonspecific interstitial pneumonitis in one kindred. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2002, 165, 1322–1328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Moorsel, C.H.; van Oosterhout, M.F.; Barlo, N.P.; de Jong, P.A.; van der Vis, J.J.; Ruven, H.J.; van Es, H.W.; van den Bosch, J.M.; Grutters, J.C. Surfactant protein C mutations are the basis of a significant portion of adult familial pulmonary fibrosis in a dutch cohort. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2010, 182, 1419–1425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mechri, M.; Epaud, R.; Emond, S.; Coulomb, A.; Jaubert, F.; Tarrant, A.; Feldmann, D.; Flamein, F.; Clement, A.; de Blic, J.; et al. Surfactant protein C gene (SFTPC) mutation-associated lung disease: High-resolution computed tomography (HRCT) findings and its relation to histological analysis. Pediatr. Pulmonol. 2010, 45, 1021–1029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cottin, V.; Reix, P.; Khouatra, C.; Thivolet-Bejui, F.; Feldmann, D.; Cordier, J.F. Combined pulmonary fibrosis and emphysema syndrome associated with familial SFTPC mutation. Thorax 2011, 66, 918–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campo, I.; Zorzetto, M.; Mariani, F.; Kadija, Z.; Morbini, P.; Dore, R.; Kaltenborn, E.; Frixel, S.; Zarbock, R.; Liebisch, G.; et al. A large kindred of pulmonary fibrosis associated with a novel ABCA3 gene variant. Respir. Res. 2014, 15, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klay, D.; Platenburg, M.G.J.P.; van Rijswijk, R.H.N.A.J.; Grutters, J.C.; van Moorsel, C.H.M. ABCA3 mutations in adult pulmonary fibrosis patients: A case series and review of literature. Curr. Opin. Pulm. Med. 2020, 26, 293–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, J.-G.; Thakkar, D.; Buchanan, P.; Graf, N.; Wheatley, J. ABCA3 deficiency from birth to adulthood presenting as paediatric interstitial lung disease. Respirol. Case Rep. 2020, 8, e00633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Epaud, R.; Delestrain, C.; Louha, M.; Simon, S.; Fanen, P.; Tazi, A. Combined pulmonary fibrosis and emphysema syndrome associated with ABCA3 mutations. Eur. Respir. J. 2014, 43, 638–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ota, C.; Kimura, M.; Kure, S. ABCA3 mutations led to pulmonary fibrosis and emphysema with pulmonary hypertension in an 8-year-old girl. Pediatr. Pulmonol. 2016, 51, E21–E23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gauldie, J.; Kolb, M.; Ask, K.; Martin, G.; Bonniaud, P.; Warburton, D. Smad3 signaling involved in pulmonary fibrosis and emphysema. Proc. Am. Thorac. Soc. 2006, 3, 696–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.G.; Cho, S.J.; Kang, M.J.; Chapoval, S.P.; Lee, P.J.; Noble, P.W.; Yehualaeshet, T.; Lu, B.; Flavell, R.A.; Milbrandt, J.; et al. Early growth response gene 1-mediated apoptosis is essential for transforming growth factor beta1-induced pulmonary fibrosis. J. Exp. Med. 2004, 200, 377–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Sun, J.; Buckley, S.; Chen, C.; Warburton, D.; Wang, X.-F.; Shi, W. Abnormal mouse lung alveolarization caused by Smad3 deficiency is a developmental antecedent of centrilobular emphysema. Am. J. Physiol. Cell. Mol. Physiol. 2005, 288, L683–L691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, L.; Bian, W.; Gu, X.-H.; Shen, C. Genetic polymorphism in matrix metalloproteinase-9 and transforming growth factor-β1 and susceptibility to combined pulmonary fibrosis and emphysema in a Chinese population. Kaohsiung J. Med. Sci. 2017, 33, 124–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kinjo, T.; Kitaguchi, Y.; Droma, Y.; Yasuo, M.; Wada, Y.; Ueno, F.; Ota, M.; Hanaoka, M. The Gly82Ser mutation in AGER contributes to pathogenesis of pulmonary fibrosis in combined pulmonary fibrosis and emphysema (CPFE) in Japanese patients. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 12811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cottin, V.; Nasser, M.; Traclet, J.; Chalabreysse, L.; Lebre, A.S.; Si-Mohamed, S.; Philit, F.; Thivolet-Bejui, F. Prolidase deficiency: A new genetic cause of combined pulmonary fibrosis and emphysema syndrome in the adult. Eur. Respir. J. 2020, 55, 1901952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lundblad, L.K.; Thompson-Figueroa, J.; Leclair, T.; Sullivan, M.J.; Poynter, M.E.; Irvin, C.G.; Bates, J.H. Tumor necrosis factor-alpha overexpression in lung disease: A single cause behind a complex phenotype. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2005, 171, 1363–1370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Küçükaycan, M.; Van Krugten, M.; Pennings, H.J.; Huizinga, T.W.; Buurman, W.A.; Dentener, M.A.; Wouters, E.F. Tumor necrosis factor-alpha +489G/A gene polymorphism is associated with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Respir. Res. 2002, 3, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, Z.; Wang, Y.; Liu, F.; Shu, H.; Huang, P. Association Between TNF-α-308, +489, −238 Polymorphism, and COPD Susceptibility: An Updated Meta-Analysis and Trial Sequential Analysis. Front. Genet. 2022, 12, 772032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, P.; Wang, J.; Wei, S.Z.; Qian, Q.; Qiu, L.X.; Yu, L.K.; Song, Y. TNF-308 gene polymorphism is associated with COPD risk among Asians: Meta-analysis of data for 6,118 subjects. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2011, 38, 219–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riha, R.L.; Yang, I.A.; Rabnott, G.C.; Tunnicliffe, A.M.; Fong, K.M.; Zimmerman, P.V. Cytokine gene polymorphisms in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Intern. Med. J. 2004, 34, 126–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, N.; Zhao, H.; Chen, M.L.; Xie, Z.F. Association of the IL-13 polymorphisms rs1800925 and rs20541 with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease risk: An updated meta-analysis. Medicine 2017, 96, e8556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, M.; Sheng, H.; Shen, W.; Zhen, J.; Xi, L.; Zeng, J.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, D.; Deng, L. Association of the SNP rs1800925(C/T) in the interleukin-13 gene promoter with pulmonary function in Chinese Han patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Cell Biochem. Biophys. 2013, 67, 905–909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sung-Moo, L.; Young-Jun, S.; Ryeo-Eun, G.; Seon-Hee, B.; Cho-Won, K.; Soochong, K.; Min-Seok, K.; Kyung-Chul, C. Inhalation exposure by cigarette smoke: Effects on the progression of bleomycin- and lipopolysaccharide-induced lung injuries in rat models. Toxicology 2021, 451, 152695. [Google Scholar]
- Li-Ling, Z.; Meng, W.; Fei, L.; Yu-Zhi, L.; Lin-Jie, S.; Liang, X.; Fei, X.; Xin-Liang, H.; Shi-Yuan, S.; Jian-Bao, X.; et al. Cigarette smoking aggravates bleomycin-induced experimental pulmonary fibrosis. Toxicol. Lett. 2019, 303, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Takada, K.; Takahashi, K.; Sato, S.; Yasui, S. Cigarette smoke modifies bleomycin-induced lung injury to produce lung emphysema. Tohoku J. Exp. Med. 1987, 153, 137–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cass, S.P.; Mekhael, O.; Thayaparan, D.; McGrath, J.J.C.; Revill, S.D.; Fantauzzi, M.F.; Wang, P.; Reihani, A.; Hayat, A.I.; Stevenson, C.S.; et al. Increased Monocyte-Derived CD11b+ Macrophage Subpopulations Following Cigarette Smoke Exposure Are Associated with Impaired Bleomycin-Induced Tissue Remodelling. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 740330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kulshrestha, R.; Singh, H.; Pandey, A.; Soundarya, D.; Jaggi, A.S.; Ravi, K. Differential expression of caveolin-1 during pathogenesis of combined pulmonary fibrosis and emphysema: Effect of phosphodiesterase-5 inhibitor. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA)-Mol. Basis Dis. 2020, 1866, 165802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wan-Guang, Z.; Si-Si, W.; Li, H.; Qun, Y.; Yi-Kuan, F.; Yue-Tao, C.; Guo-Hua, Z.; Yong-Jian, X.; Zhen-Xiang, Z.; Jian-Ping, Z.; et al. Comparative study of two models of combined pulmonary fibrosis and emphysema in mice. Acta Histochem. 2017, 119, 244–251. [Google Scholar]
- Hoyle, G.W.; Li, J.; Finkelstein, J.B.; Eisenberg, T.; Liu, J.Y.; Lasky, J.A.; Athas, G.; Morris, G.F.; Brody, A.R. Emphysematous lesions, inflammation, and fibrosis in the lungs of transgenic mice overexpressing platelet-derived growth factor. Am. J. Pathol. 1999, 154, 1763–1775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fulkerson, P.C.; Fischetti, C.A.; Hassman, L.M.; Nikolaidis, N.M.; Rothenberg, M.E. Persistent effects induced by IL-13 in the lung. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2006, 35, 337–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glasser, S.W.; Detmer, E.A.; Ikegami, M.; Na, C.L.; Stahlman, M.T.; Whitsett, J.A. Pneumonitis and emphysema in sp-C gene targeted mice. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 14291–14298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collum, S.D.; Molina, J.G.; Hanmandlu, A.; Bi, W.; Pedroza, M.; Mertens, T.C.J.; Wareing, N.; Wei, W.; Wilson, C.; Sun, W.; et al. Adenosine and hyaluronan promote lung fibrosis and pulmonary hypertension in combined pulmonary fibrosis and emphysema. Dis. Model Mech. 2019, 12, dmm038711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frasca, J.M.; Auerbach, O.; Parks, V.R.; Jamieson, J.D. Electron microscopic observations on pulmonary fibrosis and emphysema in smoking dogs. Exp. Mol. Pathol. 1971, 15, 108–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Picavet, T.; Muylle, E.; Verschooten, F.; Maenhout, T.; Deprez, P.; Sustronck, B. Interstitial lung fibrosis and emphysema in a standardbred horse: A case report. J. Equine Vet. Sci. 1990, 10, 429–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaup, F.J.; Drommer, W.; Damsch, S.; Deegen, E. Ultrastructural findings in horses with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). II: Pathomorphological changes of the terminal airways and the alveolar region. Equine Vet. J. 1990, 22, 349–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wright, J.L.; Cosio, M.; Churg, A. Animal models of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell. Mol. Physiol. 2008, 295, L1–L15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seimetz, M.; Sommer, N.; Bednorz, M.; Pak, O.; Veith, C.; Hadzic, S.; Gredic, M.; Parajuli, N.; Kojonazarov, B.; Kraut, S.; et al. NADPH oxidase subunit NOXO1 is a target for emphysema treatment in COPD. Nat. Metab. 2020, 2, 532–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kosanovic, D.; Luitel, H.; Dahal, B.K.; Cornitescu, T.; Janssen, W.; Danser, A.H.; Garrelds, I.M.; De Mey, J.G.; Fazzi, G.; Schiffers, P.; et al. Chymase: A multifunctional player in pulmonary hypertension associated with lung fibrosis. Eur. Respir. J. 2015, 46, 1084–1094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gredic, M.; Wu, C.Y.; Hadzic, S.; Pak, O.; Savai, R.; Kojonazarov, B.; Doswada, S.; Weiss, A.; Weigert, A.; Guenther, A.; et al. Myeloid-cell-specific deletion of inducible nitric oxide synthase protects against smoke-induced pulmonary hypertension in mice. Eur. Respir. J. 2022, 59, 2101153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leberl, M.; Kratzer, A.; Taraseviciene-Stewart, L. Tobacco smoke induced COPD/emphysema in the animal model—Are we all on the same page? Front. Physiol. 2013, 4, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyazaki, Y.; Araki, K.; Vesin, C.; Garcia, I.; Kapanci, Y.; Whitsett, J.A.; Piguet, P.F.; Vassalli, P. Expression of a tumor necrosis factor-alpha transgene in murine lung causes lymphocytic and fibrosing alveolitis. A mouse model of progressive pulmonary fibrosis. J. Clin. Investig. 1995, 96, 250–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujita, M.; Shannon, J.M.; Irvin, C.G.; Fagan, K.A.; Cool, C.; Augustin, A.; Mason, R.J. Overexpression of tumor necrosis factor-alpha produces an increase in lung volumes and pulmonary hypertension. Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell. Mol. Physiol. 2001, 280, L39–L49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujita, M.; Shannon, J.M.; Morikawa, O.; Gauldie, J.; Hara, N.; Mason, R.J. Overexpression of Tumor Necrosis Factor-α Diminishes Pulmonary Fibrosis Induced by Bleomycin or Transforming Growth Factor-β. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2003, 29, 669–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Errol, M.T.; Andrew, W.; Carole, L.Y.; Renaud, V. Overexpression of Tumor Necrosis Factor-α in the Lungs Alters Immune Response, Matrix Remodeling, and Repair and Maintenance Pathways. Am. J. Pathol. 2012, 180, 1413–1430. [Google Scholar]
- Duerr, J.; Leitz, D.H.W.; Szczygiel, M.; Dvornikov, D.; Fraumann, S.G.; Kreutz, C.; Zadora, P.K.; Seyhan Agircan, A.; Konietzke, P.; Engelmann, T.A.; et al. Conditional deletion of Nedd4-2 in lung epithelial cells causes progressive pulmonary fibrosis in adult mice. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karmouty-Quintana, H.; Weng, T.; Garcia-Morales, L.J.; Chen, N.-Y.; Pedroza, M.; Zhong, H.; Molina, J.G.; Bunge, R.; Bruckner, B.A.; Xia, Y.; et al. Adenosine A2B Receptor and Hyaluronan Modulate Pulmonary Hypertension Associated with Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2013, 49, 1038–1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chunn, J.L.; Molina, J.G.; Mi, T.; Xia, Y.; Kellems, R.E.; Blackburn, M.R. Adenosine-Dependent Pulmonary Fibrosis in Adenosine Deaminase-Deficient Mice1. J. Immunol. 2005, 175, 1937–1946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Auerbach, O.; Hammond, E.C.; Kirman, D.; Garfinkel, L. Emphysema Produced in Dogs by Cigarette Smoking. JAMA 1967, 199, 241–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Celli, B.; Fabbri, L.; Criner, G.; Martinez, F.J.; Mannino, D.; Vogelmeier, C.; Montes de Oca, M.; Papi, A.; Sin, D.D.; Han, M.K.; et al. Definition and Nomenclature of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease: Time for Its Revision. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2022, 206, 1317–1325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nemoto, M.; Koo, C.W.; Ryu, J.H. Diagnosis and Treatment of Combined Pulmonary Fibrosis and Emphysema in 2022. JAMA 2022, 328, 69–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomioka, H.; Mamesaya, N.; Yamashita, S.; Kida, Y.; Kaneko, M.; Sakai, H. Combined pulmonary fibrosis and emphysema: Effect of pulmonary rehabilitation in comparison with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. BMJ Open Respir. Res. 2016, 3, e000099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cottin, V.; Azuma, A.; Raghu, G.; Stansen, W.; Stowasser, S.; Schlenker-Herceg, R.; Kolb, M. Therapeutic effects of nintedanib are not influenced by emphysema in the INPULSIS trials. Eur. Respir. J. 2019, 53, 1801655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, F.; Zhang, Y.; Chi, F.; Song, Q.; Zhang, L.; Wang, Y.; Che, C. Clinical efficacy and safety of ICS/LABA in patients with combined idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis and emphysema. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Med. 2015, 8, 8617–8625. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Tathagat, N.; Archer, K.M.; Abuzar, A.A.; Ashley, V.F.; Zhuo, L.; David, B.E.; Francisco, A.; Mathew, T. Outcomes of Lung Transplantation in Patients With Combined Pulmonary Fibrosis and Emphysema: A Single-Center Experience. Transplant. Proc. 2023, 55, 449–455. [Google Scholar]
- Takahashi, T.; Terada, Y.; Pasque, M.K.; Liu, J.; Byers, D.E.; Witt, C.A.; Nava, R.G.; Puri, V.; Kozower, B.D.; Meyers, B.F.; et al. Clinical Features and Outcomes of Combined Pulmonary Fibrosis and Emphysema After Lung Transplantation. Chest 2021, 160, 1743–1750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Humbert, M.; Kovacs, G.; Hoeper, M.M.; Badagliacca, R.; Berger, R.M.F.; Brida, M.; Carlsen, J.; Coats, A.J.S.; Escribano-Subias, P.; Ferrari, P.; et al. 2022 ESC/ERS Guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of pulmonary hypertension: Developed by the task force for the diagnosis and treatment of pulmonary hypertension of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC) and the European Respiratory Society (ERS). Endorsed by the International Society for Heart and Lung Transplantation (ISHLT) and the European Reference Network on rare respiratory diseases (ERN-LUNG). Eur. Heart J. 2022, 43, 3618–3731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chebib, N.; Mornex, J.-F.; Traclet, J.; Philit, F.; Khouatra, C.; Zeghmar, S.; Turquier, S.; Cottin, V. Pulmonary hypertension in chronic lung diseases: Comparison to other pulmonary hypertension groups. Pulm. Circ. 2018, 8, 2045894018775056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nathan, S.D.; Cottin, V.; Behr, J.; Hoeper, M.M.; Martinez, F.J.; Corte, T.J.; Keogh, A.M.; Leuchte, H.; Mogulkoc, N.; Ulrich, S.; et al. Impact of lung morphology on clinical outcomes with riociguat in patients with pulmonary hypertension and idiopathic interstitial pneumonia: A post hoc subgroup analysis of the RISE-IIP study. J. Heart Lung Transplant. Off. Publ. Int. Soc. Heart Transplant. 2021, 40, 494–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nathan, S.D.; Tapson, V.F.; Elwing, J.; Rischard, F.; Mehta, J.; Shapiro, S.; Shen, E.; Deng, C.; Smith, P.; Waxman, A. Efficacy of Inhaled Treprostinil on Multiple Disease Progression Events in Patients with Pulmonary Hypertension due to Parenchymal Lung Disease in the INCREASE Trial. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2022, 205, 198–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanabe, N.; Taniguchi, H.; Tsujino, I.; Sakamaki, F.; Emoto, N.; Kimura, H.; Takamura, K.; Hanaoka, M.; Nishimura, M.; Tatsumi, K.; et al. Multi-institutional retrospective cohort study of patients with severe pulmonary hypertension associated with respiratory diseases. Respirology 2015, 20, 805–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kusaka, K.; Morio, Y.; Kimura, Y.; Takeda, K.; Kawashima, M.; Masuda, K.; Matsui, H. Improvement of pulmonary arterial compliance by pulmonary vasodilator in pulmonary hypertension from combined pulmonary fibrosis and emphysema. Respir. Med. Case Rep. 2019, 28, 100940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roccia, F.; Campolo, B.; Gallelli, L.; Spaccarotella, C.; Mongiardo, A.; Falcone, D.; Savino, R.; Pelaia, G.; Indolfi, C.; Maselli, R. Effects of ambrisentan in a patient affected by combined pulmonary fibrosis and emphysema and by severe pulmonary hypertension: Clinical, functional, and biomolecular findings. Clin. Drug Investig. 2013, 33, 451–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nasim, F.; Moua, T. Lung cancer in combined pulmonary fibrosis and emphysema: A large retrospective cohort analysis. ERJ Open Res. 2020, 6, 00521–02020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.H.; Kim, H.J.; Park, C.M.; Lim, K.Y.; Lee, J.Y.; Kim, D.J.; Yeon, J.H.; Hwang, S.S.; Kim, D.K.; Lee, S.M.; et al. The impact of combined pulmonary fibrosis and emphysema on mortality. Int. J. Tuberc. Lung Dis. Off. J. Int. Union Against Tuberc. Lung Dis. 2011, 15, 1111–1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, C.G.; Fu, Q.; Zheng, C.M. Prognosis of combined pulmonary fibrosis and emphysema: Comparison with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis alone. Ther. Adv. Respir. Dis. 2019, 13, 1753466619888119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, A.; Gudmundsson, E.; Mogulkoc, N.; Jones, M.G.; van Moorsel, C.; Corte, T.J.; Romei, C.; Savas, R.; Brereton, C.J.; van Es, H.W.; et al. Mortality in combined pulmonary fibrosis and emphysema patients is determined by the sum of pulmonary fibrosis and emphysema. ERJ Open Res. 2021, 7, 00316–02021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oh, J.Y.; Lee, Y.S.; Min, K.H.; Hur, G.Y.; Lee, S.Y.; Kang, K.H.; Shim, J.J. Impact and prognosis of lung cancer in patients with combined pulmonary fibrosis and emphysema. Sarcoidosis Vasc. Diffus. Lung Dis. Off. J. WASOG 2020, 37, e2020020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wells, A.U.; Desai, S.R.; Rubens, M.B.; Goh, N.S.; Cramer, D.; Nicholson, A.G.; Colby, T.V.; du Bois, R.M.; Hansell, D.M. Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: A composite physiologic index derived from disease extent observed by computed tomography. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2003, 167, 962–969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Combined Cigarette Smoke Exposure and Bleomycin Injury in Rodents | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Study | Animal Species | Smoke Exposure | Bleomycin Injury | Emphysema Pathology | Fibrosis Pathology |
| Sung-Moo et al. [152] | Rats | Nose-only exposure to 100, 200 or 300 μg total particulate matter/L, 4 h/day for 28 days | Single intratracheal dose of 2.5 mg/kg bleomycin | None | Stronger than in the bleomycin-only group, with more prominent neutrophilic infiltration and BALF cytokine concentrations |
| Li-Ling et al. [153] | Mice | Exposure to sidestream smoke from 12 cigarettes for 1 h/day, 5 days/week for 40 days | 5 intraperitoneal injections of 40 mg/kg bleomycin at days 1, 5, 8, 11 and 15 | None | Stronger than in the bleomycin-only group |
| Takada et al. [154] | Hamsters | 3 sets of 4 cigarettes/5 min (separated by 5 min room air flow), twice per day, 5 days/week, for 2 months | Single intratracheal dose of 5 mg/kg bleomycin, 25 days after the start of smoke exposure | Histologically evident, more prominent than in the smoke-only group. Lack of changes in lung function | None reported, but lack of lung function changes might indicate the coexistence of obstructive and restrictive pattern |
| Cass et al. [155] | M = Mice | 2 sets of 12 cigarettes (3R4F without filters), 5 days/week for 15 weeks | Single intratracheal dose of 0.05 U/mouse at the beginning of the 12th week | Changes in lung elastance, atelectasis and inspiratory capacity | Prevented by smoke, no significant changes in the percentage of myofibroblasts and in collagen staining |
| Kulshrestha et al. [156] | Rats | Sidestream smoke from 4 cigarettes for 1 h/day, 5 days/week for 12 weeks | Single intratracheal dose of 7 U/kg at the beginning of the 7th week | Histologically evident, same as in smoke-only group | Histologically evident, alternating with emphysematous areas. Pulmonary vascular remodeling is also present |
| Wan-Guang et al. [157] | Mice | Sidestream smoke from 10 cigarettes (at a concentration of 1000 mg/mm3), for 1 h/twice a day for 13 months, 5 days/week | Single intratracheal dose of 2 mg/kg bleomycin, 28 days before sacrifice | Histologically evident, same as in smoke-only group | Histologically evident |
| Combined cigarette smoke exposure and mouse gamma herpes virus (MHV)—68 infections | |||||
| Study | Animal species | Smoke exposure | MHV infection | Emphysema pathology | Fibrosis pathology |
| Wan-Guang et al. [157] | Mice | Sidestream smoke from 10 cigarettes (at a concentration of 1000 mg/mm3), for 1 h/twice a day for 13 months, 5 days/week | Single intratracheal dose of 1 × 105 plaque-forming units of MHV-68, 28 days prior to sacrifice | Histologically evident, same as in smoke-only group | Histologically evident, albeit milder than in the bleomycin group |
| Transgenic mouse models | |||||
| Study | Animal species | Genetic modification | Emphysema pathology | Fibrosis pathology | |
| Lundblad et al. [145] | Aged mice | TNF-α overexpression under the control of SP-C promotor | Complex lung function changes and increased lung volumes; reduction of the number of small airspaces on histology | Septal wall thickening, increased collagen | |
| Hoyle et al. [158] | Aged mice | PDGF-B overexpression under the control of SP-C promotor | Existing throughout the lung, likely the consequence of congenital abnormalities | Confined to focal areas, inflammation present | |
| Fulkerson et al. [159] | Mice | Inducible IL-13 overexpression under the control of CC10 promotor | Histologically confirmed | Peribronchial and peribronchiolar collagen deposition, inflammation also present | |
| Glasser et al. [160] | Aged mice | SPC knockout | Histologically confirmed | Increased collagen deposition and α-smooth muscle actin staining, monocytic infiltration | |
| Collum et al. [161] | Mice | ADA knockout mice supplemented with polyethylene glycol (PEG)-modified ADA until week 24, after which PEG-ADA was gradually reduced over 9 weeks. Physiological readouts were performed in week 38 | Histologically confirmed | Histologically confirmed. Macrophage accumulation and pulmonary vascular remodeling are present | |
| Other animal species | |||||
| Study | Animal species | Experimental intervention | Emphysema pathology | Fibrosis pathology | |
| Frasca et al. [162] | Dogs | Long-term smoke exposure through a tracheostomy tube, various concentrations and durations (715–1156 days) | Histologically confirmed | Fibrous thickening of alveolar walls | |
| Picavet et al. [163], Kaup et al. [164] | Horses | None | Histologically confirmed | Extensive peribronchial and peribronchiolar fibrosis, desquamative changes, patchy fibrotic changes with a pronounced increase in collagen fibers and honeycombing | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gredic, M.; Karnati, S.; Ruppert, C.; Guenther, A.; Avdeev, S.N.; Kosanovic, D. Combined Pulmonary Fibrosis and Emphysema: When Scylla and Charybdis Ally. Cells 2023, 12, 1278. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells12091278
Gredic M, Karnati S, Ruppert C, Guenther A, Avdeev SN, Kosanovic D. Combined Pulmonary Fibrosis and Emphysema: When Scylla and Charybdis Ally. Cells. 2023; 12(9):1278. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells12091278
Chicago/Turabian StyleGredic, Marija, Srikanth Karnati, Clemens Ruppert, Andreas Guenther, Sergey N. Avdeev, and Djuro Kosanovic. 2023. "Combined Pulmonary Fibrosis and Emphysema: When Scylla and Charybdis Ally" Cells 12, no. 9: 1278. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells12091278
APA StyleGredic, M., Karnati, S., Ruppert, C., Guenther, A., Avdeev, S. N., & Kosanovic, D. (2023). Combined Pulmonary Fibrosis and Emphysema: When Scylla and Charybdis Ally. Cells, 12(9), 1278. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells12091278








