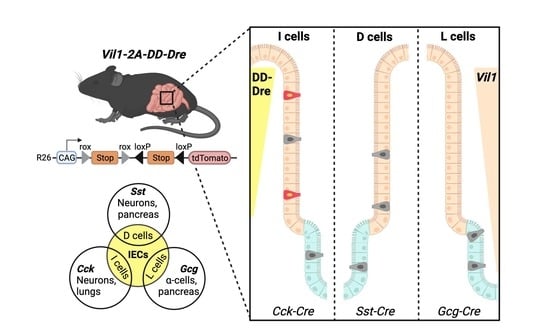
An Approach to Intersectionally Target Mature Enteroendocrine Cells in the Small Intestine of Mice
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Animal Care
2.2. Generation of Vil1-2A-DD-Dre Mice
2.3. In Vivo DD-Dre Recombination Activity Assessment
2.4. Analysis of Gene Expression
2.5. IEC Isolation and Ex Vivo Treatment
2.6. Crypt–Villus Fractionation
2.7. Immunohistochemistry
2.8. In Situ Hybridization (RNA Scope)
| Target Probes |
| Custom-Dre-C1 (442,641) |
| Cck-C1 (402,271) |
| Gcg-C1 (400,601) |
| Sst-C2/C3 (404,631) |
| Tac1-C1 (410,351) |
| Tdtomato-C2/C3 (317,041) |
| ZsGreen-C2 (461,251) |
| Vil1-C3 (463,301) |
2.9. Immunofluorescence
2.10. Image Acquisition and Analysis
2.11. Single-Cell RNA Sequencing of the Murine Intestinal Epithelium
2.12. Cell Culture Experiments
2.13. Flow Cytometry
2.14. Immunoblot Analysis and Quantification
2.15. Statistics
3. Results
3.1. Examination of TMP-Inducible DD-Dre System In Vitro
3.2. CRISPR/Cas9-Mediated Insertion of DD-Dre into IEC-Specific Vil1 Gene of C57BL/6N Mice
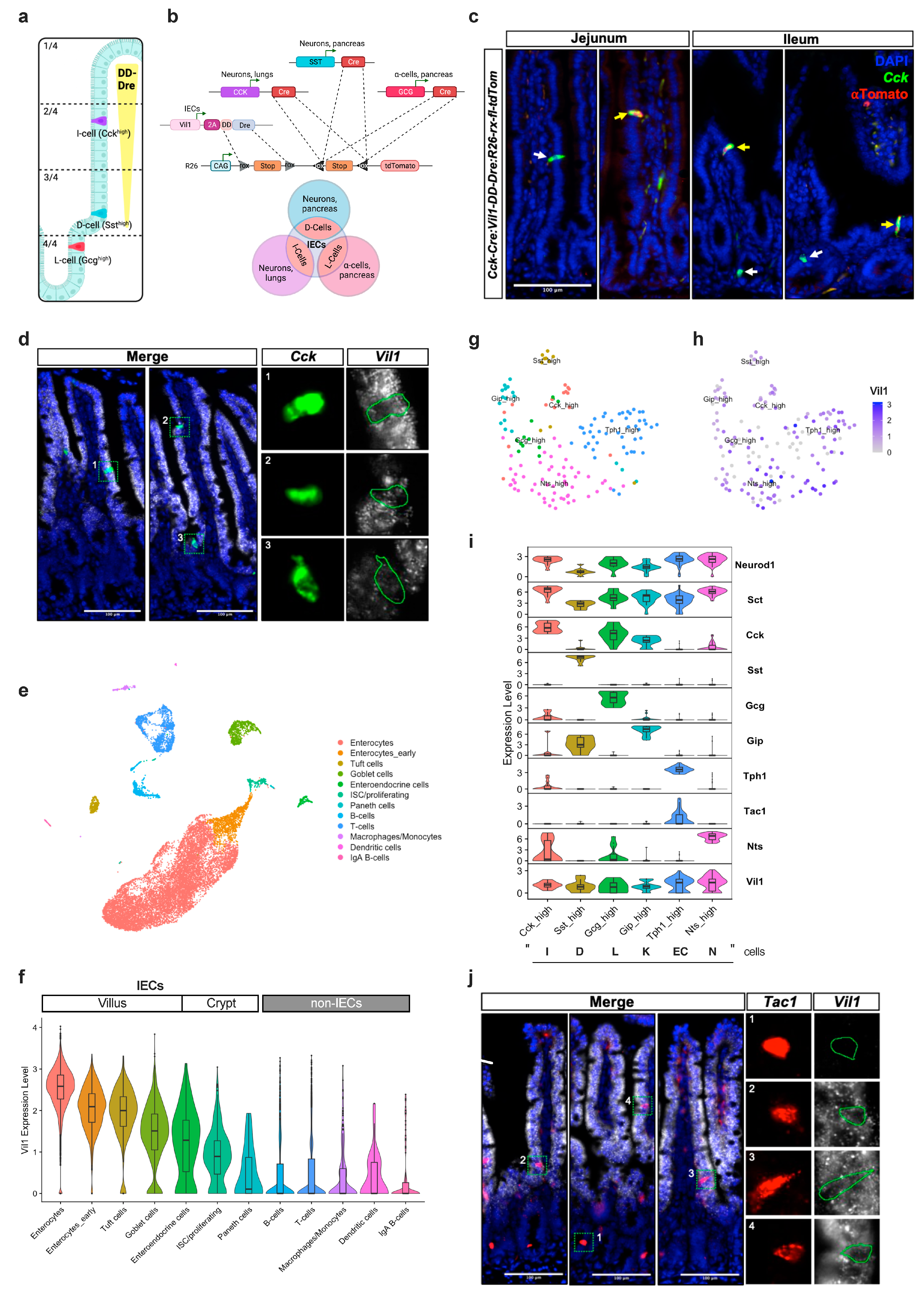
3.3. TMP-Independent Dre-Mediated Recombination in the Small Intestine of Vil1-2A-DD-Dre Mice
3.4. Intersectional Expression of tdTomato in Mature EECs
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Barker, N.; van Es, J.H.; Kuipers, J.; Kujala, P.; van den Born, M.; Cozijnsen, M.; Haegebarth, A.; Korving, J.; Begthel, H.; Peters, P.J.; et al. Identification of Stem Cells in Small Intestine and Colon by Marker Gene Lgr5. Nature 2007, 449, 1003–1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Darwich, A.S.; Aslam, U.; Ashcroft, D.M.; Rostami-Hodjegan, A. Meta-Analysis of the Turnover of Intestinal Epithelia in Preclinical Animal Species and Humans. Drug Metab. Dispos. 2014, 42, 2016–2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gehart, H.; Van Es, J.H.; Hamer, K.; Beumer, J.; Kretzschmar, K.; Dekkers, J.F.; Rios, A.; Clevers, H. Identification of Enteroendocrine Regulators by Real-Time Single-Cell Differentiation Mapping. Cell 2019, 176, 1158–1173.e16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Latorre, R.; Sternini, C.; De Giorgio, R.; Greenwood-Van Meerveld, B. Enteroendocrine Cells: A Review of Their Role in Brain–Gut Communication. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2016, 28, 620–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beumer, J.; Gehart, H.; Clevers, H. Enteroendocrine Dynamics—New Tools Reveal Hormonal Plasticity in the Gut. Endocr. Rev. 2020, 41, bnaa018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gribble, F.M.; Reimann, F. Function and Mechanisms of Enteroendocrine Cells and Gut Hormones in Metabolism. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2019, 15, 226–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, L.; Sivakumar, N.; Yu, S.; Mesgarzadeh, S.; Ding, T.; Ly, T.; Corpuz, T.V.; Grove, J.C.; Jarvie, B.C.; Knight, Z.A. Enteroendocrine Cell Types That Drive Food Reward and Aversion. eLife 2022, 11, e74964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Billing, L.J.; Larraufie, P.; Lewis, J.; Leiter, A.; Li, J.; Lam, B.; Yeo, G.S.; Goldspink, D.A.; Kay, R.G.; Gribble, F.M.; et al. Single Cell Transcriptomic Profiling of Large Intestinal Enteroendocrine Cells in Mice—Identification of Selective Stimuli for Insulin-like Peptide-5 and Glucagon-like Peptide-1 Co-Expressing Cells. Mol. Metab. 2019, 29, 158–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haber, A.L.; Biton, M.; Rogel, N.; Herbst, R.H.; Shekhar, K.; Smillie, C.; Burgin, G.; Delorey, T.M.; Howitt, M.R.; Katz, Y.; et al. A Single-Cell Survey of the Small Intestinal Epithelium. Nature 2017, 551, 333–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayashi, M.; Kaye, J.A.; Douglas, E.R.; Joshi, N.R.; Gribble, F.M.; Reimann, F.; Liberles, S.D. Enteroendocrine Cell Lineages That Differentially Control Feeding and Gut Motility. eLife 2023, 12, e78512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basak, O.; Beumer, J.; Wiebrands, K.; Seno, H.; Van Oudenaarden, A.; Clevers, H. Induced Quiescence of Lgr5+ Stem Cells in Intestinal Organoids Enables Differentiation of Hormone-Producing Enteroendocrine Cells. Cell Stem Cell 2017, 20, 177–190.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.J.; Kapoor, A.; Giel-Moloney, M.; Rindi, G.; Leiter, A.B. Notch Signaling Differentially Regulates the Cell Fate of Early Endocrine Precursor Cells and Their Maturing Descendants in the Mouse Pancreas and Intestine. Dev. Biol. 2012, 371, 156–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schonhoff, S.E.; Giel-Moloney, M.; Leiter, A.B. Neurogenin 3-Expressing Progenitor Cells in the Gastrointestinal Tract Differentiate into Both Endocrine and Non-Endocrine Cell Types. Dev. Biol. 2004, 270, 443–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biglari, N.; Gaziano, I.; Schumacher, J.; Radermacher, J.; Paeger, L.; Klemm, P.; Chen, W.; Corneliussen, S.; Wunderlich, C.M.; Sue, M.; et al. Functionally Distinct POMC-Expressing Neuron Subpopulations in Hypothalamus Revealed by Intersectional Targeting. Nat. Neurosci. 2021, 24, 913–929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borgmann, D.; Ciglieri, E.; Biglari, N.; Brandt, C.; Cremer, A.L.; Backes, H.; Tittgemeyer, M.; Wunderlich, F.T.; Brüning, J.C.; Fenselau, H. Gut-Brain Communication by Distinct Sensory Neurons Differently Controls Feeding and Glucose Metabolism. Cell Metab. 2021, 33, 1466–1482.e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beumer, J.; Artegiani, B.; Post, Y.; Reimann, F.; Gribble, F.; Nguyen, T.N.; Zeng, H.; Van Den Born, M.; Van Es, J.H.; Clevers, H. Enteroendocrine Cells Switch Hormone Expression along the Crypt-to-Villus BMP Signalling Gradient. Nat. Cell Biol. 2018, 20, 909–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sando, R.; Baumgaertel, K.; Pieraut, S.; Torabi-Rander, N.; Wandless, T.J.; Mayford, M.; Maximov, A. Inducible Control of Gene Expression with Destabilized Cre. Nat. Methods 2013, 10, 1085–1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pinson, K.I.; Dunbar, L.; Samuelson, L.; Gumucio, D.L. Targeted Disruption of the Mouse Villin Gene Does Not Impair the Morphogenesis of Microvilli. Dev. Dyn. 1998, 211, 109–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madisen, L.; Zwingman, T.A.; Sunkin, S.M.; Oh, S.W.; Zariwala, H.A.; Gu, H.; Ng, L.L.; Palmiter, R.D.; Hawrylycz, M.J.; Jones, A.R.; et al. A Robust and High-Throughput Cre Reporting and Characterization System for the Whole Mouse Brain. Nat. Neurosci. 2010, 13, 133–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madison, B.B.; Dunbar, L.; Qiao, X.T.; Braunstein, K.; Braunstein, E.; Gumucio, D.L. Cis Elements of the Villin Gene Control Expression in Restricted Domains of the Vertical (Crypt) and Horizontal (Duodenum, Cecum) Axes of the Intestine. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 33275–33283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ostermann, A.L.; Wunderlich, C.M.; Schneiders, L.; Vogt, M.C.; Woeste, M.A.; Belgardt, B.F.; Niessen, C.M.; Martiny, B.; Schauss, A.C.; Frommolt, P.; et al. Intestinal Insulin/IGF1 Signalling through FoxO1 Regulates Epithelial Integrity and Susceptibility to Colon Cancer. Nat. Metab. 2019, 1, 371–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Madisen, L.; Garner, A.R.; Shimaoka, D.; Chuong, A.S.; Klapoetke, N.C.; Li, L.; van der Bourg, A.; Niino, Y.; Egolf, L.; Monetti, C.; et al. Transgenic Mice for Intersectional Targeting of Neural Sensors and Effectors with High Specificity and Performance. Neuron 2015, 85, 942–958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El Marjou, F.; Janssen, K.; Hung-Junn Chang, B.; Li, M.; Hindie, V.; Chan, L.; Louvard, D.; Chambon, P.; Metzger, D.; Robine, S. Tissue-specific and Inducible Cre-mediated Recombination in the Gut Epithelium. Genesis 2004, 39, 186–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Vossen, C.; Schmidt, P.; Wunderlich, C.M.; Mittenbühler, M.J.; Tapken, C.; Wienand, P.; Mirabella, P.N.; Cabot, L.; Schumacher, A.-L.; Folz-Donahue, K.; et al. An Approach to Intersectionally Target Mature Enteroendocrine Cells in the Small Intestine of Mice. Cells 2024, 13, 102. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells13010102
Vossen C, Schmidt P, Wunderlich CM, Mittenbühler MJ, Tapken C, Wienand P, Mirabella PN, Cabot L, Schumacher A-L, Folz-Donahue K, et al. An Approach to Intersectionally Target Mature Enteroendocrine Cells in the Small Intestine of Mice. Cells. 2024; 13(1):102. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells13010102
Chicago/Turabian StyleVossen, Christian, Patricia Schmidt, Claudia Maria Wunderlich, Melanie Joyce Mittenbühler, Claas Tapken, Peter Wienand, Paul Nicolas Mirabella, Leonie Cabot, Anna-Lena Schumacher, Kat Folz-Donahue, and et al. 2024. "An Approach to Intersectionally Target Mature Enteroendocrine Cells in the Small Intestine of Mice" Cells 13, no. 1: 102. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells13010102
APA StyleVossen, C., Schmidt, P., Wunderlich, C. M., Mittenbühler, M. J., Tapken, C., Wienand, P., Mirabella, P. N., Cabot, L., Schumacher, A.-L., Folz-Donahue, K., Kukat, C., Voigt, I., Brüning, J. C., Fenselau, H., & Wunderlich, F. T. (2024). An Approach to Intersectionally Target Mature Enteroendocrine Cells in the Small Intestine of Mice. Cells, 13(1), 102. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells13010102