Targeted Inhibitors of EGFR: Structure, Biology, Biomarkers, and Clinical Applications
Abstract
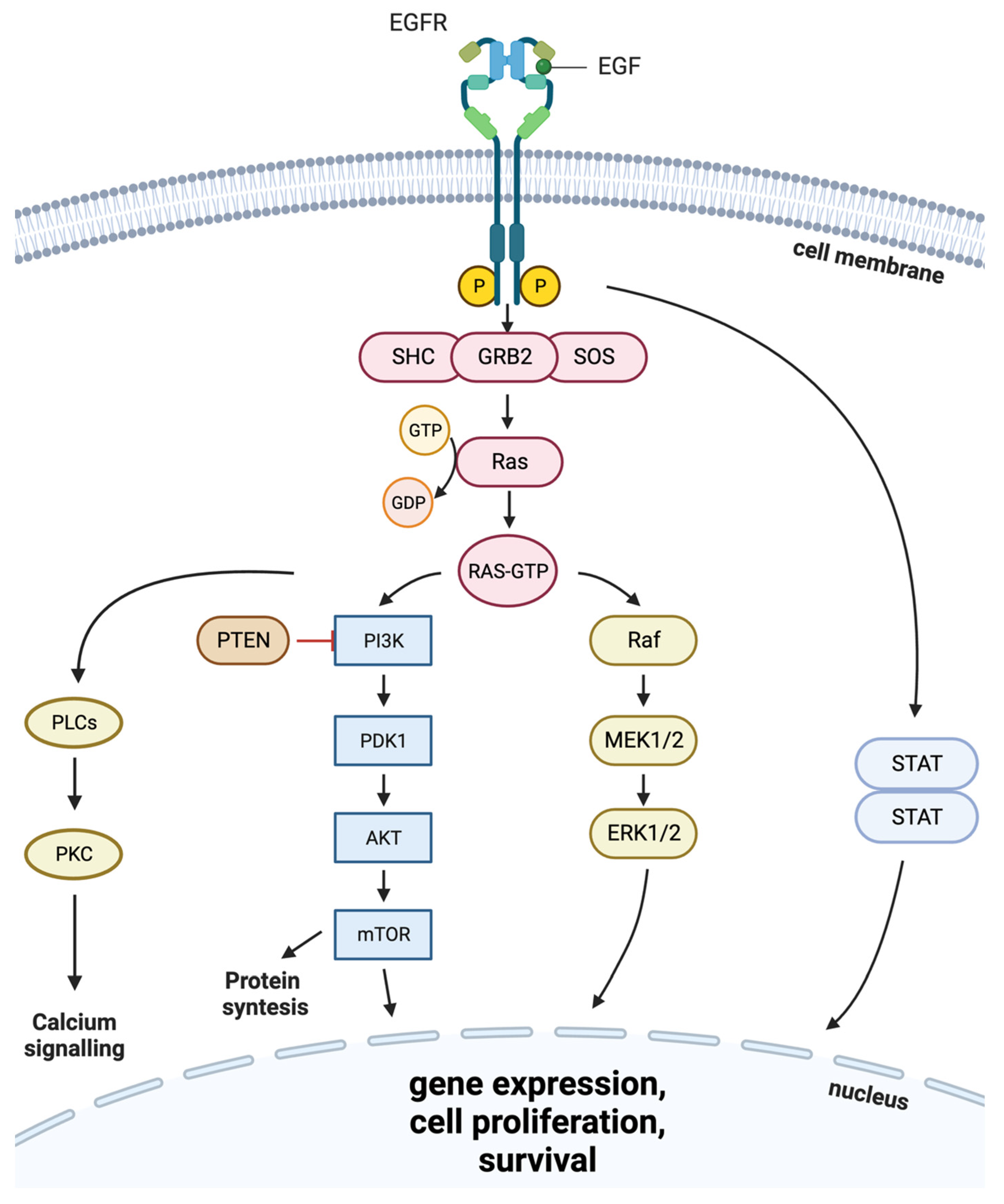
:1. EGF Receptor Protein Family
2. EGFR Role in Cancer
3. EGFR-Targeted Therapies
4. First Generation of EGFR-Targeted Drugs
5. Second Generation of EGFR-Targeted Drugs
6. Third Generation of EGFR-Targeted Drugs
7. Fourth Generation of EGFR-Targeted Drugs
8. EGFR-Specific Therapeutic Monoclonal Antibodies
9. Future Directions and Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mitsudomi, T.; Yatabe, Y. Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor in Relation to Tumor Development: EGFR Gene and Cancer: EGFR and Cancer. FEBS J. 2010, 277, 301–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holbro, T.; Hynes, N.E. ErbB Receptors: Directing Key Signaling Networks throughout Life. Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2004, 44, 195–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, S.; Geng, R.; Lin, E.; Zhao, P.; Chen, Y. ERBB1/2/3 Expression, Prognosis, and Immune Infiltration in Cutaneous Melanoma. Front. Genet. 2021, 12, 602160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arienti, C.; Pignatta, S.; Tesei, A. Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor Family and Its Role in Gastric Cancer. Front. Oncol. 2019, 9, 1308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roskoski, R. The ErbB/HER Family of Protein-Tyrosine Kinases and Cancer. Pharmacol. Res. 2014, 79, 34–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yarden, Y.; Sliwkowski, M.X. Untangling the ErbB Signalling Network. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2001, 2, 127–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wee, P.; Wang, Z. Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor Cell Proliferation Signaling Pathways. Cancers 2017, 9, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Byrne, P.O.; Hristova, K.; Leahy, D.J. EGFR Forms Ligand-Independent Oligomers That Are Distinct from the Active State. J. Biol. Chem. 2020, 295, 13353–13362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mudumbi, K.C.; Burns, E.A.; Schodt, D.J.; Petrova, Z.O.; Kiyatkin, A.; Kim, L.W.; Mangiacapre, E.M.; Ortiz-Caraveo, I.; Ortiz, H.R.; Hu, C.; et al. Distinct Interactions Stabilize EGFR Dimers and Higher-Order Oligomers in Cell Membranes. bioRxiv 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Needham, S.R.; Roberts, S.K.; Arkhipov, A.; Mysore, V.P.; Tynan, C.J.; Zanetti-Domingues, L.C.; Kim, E.T.; Losasso, V.; Korovesis, D.; Hirsch, M.; et al. EGFR Oligomerization Organizes Kinase-Active Dimers into Competent Signalling Platforms. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 13307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogiso, H.; Ishitani, R.; Nureki, O.; Fukai, S.; Yamanaka, M.; Kim, J.-H.; Saito, K.; Sakamoto, A.; Inoue, M.; Shirouzu, M.; et al. Crystal Structure of the Complex of Human Epidermal Growth Factor and Receptor Extracellular Domains. Cell 2002, 110, 775–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, B.; Coffey, R.J. From Wavy Hair to Naked Proteins: The Role of Transforming Growth Factor Alpha in Health and Disease. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 2014, 28, 12–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schneider, M.R.; Yarden, Y. Structure and Function of Epigen, the Last EGFR Ligand. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 2014, 28, 57–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berasain, C.; Avila, M.A. Amphiregulin. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 2014, 28, 31–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dunbar, A.J.; Goddard, C. Structure-Function and Biological Role of Betacellulin. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2000, 32, 805–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muraoka-Cook, R.S.; Sandahl, M.; Hunter, D.; Miraglia, L.; Earp, H.S. Prolactin and ErbB4/HER4 Signaling Interact via Janus Kinase 2 to Induce Mammary Epithelial Cell Gene Expression Differentiation. Mol. Endocrinol. 2008, 22, 2307–2321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sato, K.; Nakamura, T.; Mizuguchi, M.; Miura, K.; Tada, M.; Aizawa, T.; Gomi, T.; Miyamoto, K.; Kawano, K. Solution Structure of Epiregulin and the Effect of Its C-Terminal Domain for Receptor Binding Affinity. FEBS Lett. 2003, 553, 232–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozaki, M. Neuregulins and the Shaping of Synapses. Neuroscientist 2001, 7, 146–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Sliwkowski, M.X.; Mark, M.; Frantz, G.; Akita, R.; Sun, Y.; Hillan, K.; Crowley, C.; Brush, J.; Godowski, P.J. Neuregulin-3 (NRG3): A Novel Neural Tissue-Enriched Protein That Binds and Activates ErbB4. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1997, 94, 9562–9567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harari, D.; Tzahar, E.; Romano, J.; Shelly, M.; Pierce, J.H.; Andrews, G.C.; Yarden, Y. Neuregulin-4: A Novel Growth Factor That Acts through the ErbB-4 Receptor Tyrosine Kinase. Oncogene 1999, 18, 2681–2689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henriksen, L.; Grandal, M.V.; Knudsen, S.L.J.; van Deurs, B.; Grøvdal, L.M. Internalization Mechanisms of the Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor after Activation with Different Ligands. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e58148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leblanc, J.A.; Sugiyama, M.G.; Antonescu, C.N.; Brown, A.I. Quantitative Modeling of EGF Receptor Ligand Discrimination via Internalization Proofreading. Phys. Biol. 2023, 20, 056008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Landgraf, R. HER2 Therapy. HER2 (ERBB2): Functional Diversity from Structurally Conserved Building Blocks. Breast Cancer Res. 2007, 9, 202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tzahar, E.; Waterman, H.; Chen, X.; Levkowitz, G.; Karunagaran, D.; Lavi, S.; Ratzkin, B.J.; Yarden, Y. A Hierarchical Network of Interreceptor Interactions Determines Signal Transduction by Neu Differentiation Factor/Neuregulin and Epidermal Growth Factor. Mol. Cell. Biol. 1996, 16, 5276–5287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, R.B.; Gordus, A.; Krall, J.A.; MacBeath, G. A Quantitative Protein Interaction Network for the ErbB Receptors Using Protein Microarrays. Nature 2006, 439, 168–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jura, N.; Shan, Y.; Cao, X.; Shaw, D.E.; Kuriyan, J. Structural Analysis of the Catalytically Inactive Kinase Domain of the Human EGF Receptor 3. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 21608–21613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, F.; Telesco, S.E.; Liu, Y.; Radhakrishnan, R.; Lemmon, M.A. ErbB3/HER3 Intracellular Domain Is Competent to Bind ATP and Catalyze Autophosphorylation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 7692–7697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steinkamp, M.P.; Low-Nam, S.T.; Yang, S.; Lidke, K.A.; Lidke, D.S.; Wilson, B.S. erbB3 Is an Active Tyrosine Kinase Capable of Homo- and Heterointeractions. Mol. Cell Biol. 2014, 34, 965–977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, K.J.; Gilmore, J.L.; Foley, J.; Lemmon, M.A.; Riese, D.J. Functional Selectivity of EGF Family Peptide Growth Factors: Implications for Cancer. Pharmacol. Ther. 2009, 122, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gan, H.K.; Cvrljevic, A.N.; Johns, T.G. The Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor Variant III (EGFRvIII): Where Wild Things Are Altered. FEBS J. 2013, 280, 5350–5370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohgaki, H.; Kleihues, P. Genetic Alterations and Signaling Pathways in the Evolution of Gliomas. Cancer Sci. 2009, 100, 2235–2241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hinck, L.; Näthke, I. Changes in Cell and Tissue Organization in Cancer of the Breast and Colon. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 2014, 26, 87–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalyankrishna, S.; Grandis, J.R. Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor Biology in Head and Neck Cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2006, 24, 2666–2672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bethune, G.; Bethune, D.; Ridgway, N.; Xu, Z. Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor (EGFR) in Lung Cancer: An Overview and Update. J. Thorac. Dis. 2010, 2, 48–51. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Al-Kuraya, K.; Schraml, P.; Torhorst, J.; Tapia, C.; Zaharieva, B.; Novotny, H.; Spichtin, H.; Maurer, R.; Mirlacher, M.; Köchli, O.; et al. Prognostic Relevance of Gene Amplifications and Coamplifications in Breast Cancer. Cancer Res. 2004, 64, 8534–8540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oliveira-Cunha, M.; Newman, W.G.; Siriwardena, A.K. Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor in Pancreatic Cancer. Cancers 2011, 3, 1513–1526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pabla, B.; Bissonnette, M.; Konda, V.J. Colon Cancer and the Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor: Current Treatment Paradigms, the Importance of Diet, and the Role of Chemoprevention. World J. Clin. Oncol. 2015, 6, 133–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herbst, R.S. Review of Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor Biology. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2004, 59, 21–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pastwińska, J.; Karaś, K.; Karwaciak, I.; Ratajewski, M. Targeting EGFR in Melanoma—The Sea of Possibilities to Overcome Drug Resistance. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA)-Rev. Cancer 2022, 1877, 188754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gridelli, C.; Ciardiello, F.; Gallo, C.; Feld, R.; Butts, C.; Gebbia, V.; Maione, P.; Morgillo, F.; Genestreti, G.; Favaretto, A.; et al. First-Line Erlotinib Followed by Second-Line Cisplatin-Gemcitabine Chemotherapy in Advanced Non–Small-Cell Lung Cancer: The TORCH Randomized Trial. J. Clin. Oncol. 2012, 30, 3002–3011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Fu, S.; Shao, Q.; Zhou, Y.-B.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, X.; Xue, C.; Lin, J.-G.; Huang, L.-X.; Zhang, L.; et al. High EGFR Copy Number Predicts Benefits from Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor Treatment for Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Patients with Wild-Type EGFR. J. Transl. Med. 2013, 11, 90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Douillard, J.-Y.; Shepherd, F.A.; Hirsh, V.; Mok, T.; Socinski, M.A.; Gervais, R.; Liao, M.-L.; Bischoff, H.; Reck, M.; Sellers, M.V.; et al. Molecular Predictors of Outcome with Gefitinib and Docetaxel in Previously Treated Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer: Data from the Randomized Phase III INTEREST Trial. J. Clin. Oncol. 2010, 28, 744–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lynch, T.J.; Bell, D.W.; Sordella, R.; Gurubhagavatula, S.; Okimoto, R.A.; Brannigan, B.W.; Harris, P.L.; Haserlat, S.M.; Supko, J.G.; Haluska, F.G.; et al. Activating Mutations in the Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor Underlying Responsiveness of Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer to Gefitinib. N. Engl. J. Med. 2004, 350, 2129–2139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Graham, R.P.; Treece, A.L.; Lindeman, N.I.; Vasalos, P.; Shan, M.; Jennings, L.J.; Rimm, D.L. Worldwide Frequency of Commonly Detected EGFR Mutations. Arch. Pathol. Lab. Med. 2018, 142, 163–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castañeda-González, J.P.; Chaves, J.J.; Parra-Medina, R. Multiple Mutations in the EGFR Gene in Lung Cancer: A Systematic Review. Transl. Lung Cancer Res. 2022, 11, 2148–2163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, Y.W.; Jeon, S.Y.; Jeong, G.S.; Lee, H.W.; Jeong, S.H.; Kang, S.Y.; Park, J.S.; Choi, J.-H.; Koh, Y.W.; Han, J.H.; et al. EGFR Exon 19 Deletion Is Associated with Favorable Overall Survival After First-Line Gefitinib Therapy in Advanced Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Patients. Am. J. Clin. Oncol. 2018, 41, 385–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yermekova, S.; Orazgaliyeva, M.; Goncharova, T.; Rakhimbekova, F.; Dushimova, Z.; Vasilieva, T. Mutational Damages in Malignant Lung Tumors. Asian Pac. J. Cancer Prev. 2023, 24, 709–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oxnard, G.R.; Lo, P.C.; Nishino, M.; Dahlberg, S.E.; Lindeman, N.I.; Butaney, M.; Jackman, D.M.; Johnson, B.E.; Jänne, P.A. Natural History and Molecular Characteristics of Lung Cancers Harboring EGFR Exon 20 Insertions. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2013, 8, 179–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burnett, H.; Emich, H.; Carroll, C.; Stapleton, N.; Mahadevia, P.; Li, T. Epidemiological and Clinical Burden of EGFR Exon 20 Insertion in Advanced Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: A Systematic Literature Review. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0247620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Li, C.; Wu, Q.; Lu, H. EGFR Exon 20 Insertion Mutations in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Transl. Cancer Res. 2020, 9, 2982–2991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vyse, S.; Huang, P.H. Targeting EGFR Exon 20 Insertion Mutations in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2019, 4, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rutkowska, A.; Stoczyńska-Fidelus, E.; Janik, K.; Włodarczyk, A.; Rieske, P. EGFRvIII: An Oncogene with Ambiguous Role. J. Oncol. 2019, 2019, 1092587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brennan, C.W.; Verhaak, R.G.W.; McKenna, A.; Campos, B.; Noushmehr, H.; Salama, S.R.; Zheng, S.; Chakravarty, D.; Sanborn, J.Z.; Berman, S.H.; et al. The Somatic Genomic Landscape of Glioblastoma. Cell 2013, 155, 462–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, Q.; Han, L.; Dong, Y.; Tian, J.; Huang, W.; Liu, Z.; Jia, X.; Jiang, T.; Zhang, J.; Li, X.; et al. JAK2/STAT3 Targeted Therapy Suppresses Tumor Invasion via Disruption of the EGFRvIII/JAK2/STAT3 Axis and Associated Focal Adhesion in EGFRvIII-Expressing Glioblastoma. Neuro-Oncology 2014, 16, 1229–1243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, S.V.; Bell, D.W.; Settleman, J.; Haber, D.A. Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor Mutations in Lung Cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2007, 7, 169–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsigelny, I.F.; Wheler, J.J.; Greenberg, J.P.; Kouznetsova, V.L.; Stewart, D.J.; Bazhenova, L.; Kurzrock, R. Molecular Determinants of Drug-Specific Sensitivity for Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor (EGFR) Exon 19 and 20 Mutants in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 6029–6039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu, W.; Lu, Z.; Shi, S.; Ma, J.; Lu, G.; Deng, W.; Ding, R.; Bu, F. Molecular Characteristics of EGFR Exon 19 Deletion Subtypes in NSCLC Patients. J. Clin. Oncol. 2021, 39, 8530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yun, C.-H.; Boggon, T.J.; Li, Y.; Woo, M.S.; Greulich, H.; Meyerson, M.; Eck, M.J. Structures of Lung Cancer-Derived EGFR Mutants and Inhibitor Complexes: Mechanism of Activation and Insights into Differential Inhibitor Sensitivity. Cancer Cell 2007, 11, 217–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garima, G.; Thanvi, S.; Singh, A.; Verma, V. Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor Variant III Mutation, an Emerging Molecular Marker in Glioblastoma Multiforme Patients: A Single Institution Study on the Indian Population. Cureus 2022, 14, e26412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhang, H.-B.; Chen, X.; Yang, X.; Ye, Y.; Bekaii-Saab, T.; Zheng, Y.; Zhang, Y. A Rare EGFR-SEPT14 Fusion in a Patient with Colorectal Adenocarcinoma Responding to Erlotinib. Oncologist 2020, 25, 203–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.; Wang, W.X.; Chen, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Liu, Y.; Wang, H.; Zhuang, W.; Chen, X.; Huang, Y.; Lai, J.; et al. Prevalence of EGFR Gene Fusions in a Large Cohort of Chinese Patients with Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer (NSCLC). J. Clin. Oncol. 2018, 36, e13538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konduri, K.; Gallant, J.-N.; Chae, Y.K.; Giles, F.J.; Gitlitz, B.J.; Gowen, K.; Ichihara, E.; Owonikoko, T.K.; Peddareddigari, V.; Ramalingam, S.S.; et al. EGFR Fusions as Novel Therapeutic Targets in Lung Cancer. Cancer Discov. 2016, 6, 601–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Shao, C. KIF5B-EGFR Fusion: A Novel EGFR Mutation in Lung Adenocarcinoma. Onco Targets Ther. 2020, 13, 8317–8321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cox, A.D.; Fesik, S.W.; Kimmelman, A.C.; Luo, J.; Der, C.J. Drugging the Undruggable RAS: Mission Possible? Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2014, 13, 828–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molina, J.R.; Adjei, A.A. The Ras/Raf/MAPK Pathway. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2006, 1, 7–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linardou, H.; Dahabreh, I.J.; Kanaloupiti, D.; Siannis, F.; Bafaloukos, D.; Kosmidis, P.; Papadimitriou, C.A.; Murray, S. Assessment of Somatic K-RAS Mutations as a Mechanism Associated with Resistance to EGFR-Targeted Agents: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Studies in Advanced Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer and Metastatic Colorectal Cancer. Lancet Oncol. 2008, 9, 962–972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gharwan, H.; Groninger, H. Kinase Inhibitors and Monoclonal Antibodies in Oncology: Clinical Implications. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2016, 13, 209–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roskoski, R. Small Molecule Inhibitors Targeting the EGFR/ErbB Family of Protein-Tyrosine Kinases in Human Cancers. Pharmacol. Res. 2019, 139, 395–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roskoski, R. Classification of Small Molecule Protein Kinase Inhibitors Based upon the Structures of Their Drug-Enzyme Complexes. Pharmacol. Res. 2016, 103, 26–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, Y.; Pond, M.P.; Roux, B. Tyrosine Kinase Activation and Conformational Flexibility: Lessons from Src-Family Tyrosine Kinases. Acc. Chem. Res. 2017, 50, 1193–1201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fry, D.W.; Kraker, A.J.; McMichael, A.; Ambroso, L.A.; Nelson, J.M.; Leopold, W.R.; Connors, R.W.; Bridges, A.J. A Specific Inhibitor of the Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor Tyrosine Kinase. Science 1994, 265, 1093–1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wakeling, A.E.; Barker, A.J.; Davies, D.H.; Brown, D.S.; Green, L.R.; Cartlidge, S.A.; Woodburn, J.R. Specific Inhibition of Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor Tyrosine Kinase by 4-Anilinoquinazolines. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 1996, 38, 67–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amelia, T.; Kartasasmita, R.E.; Ohwada, T.; Tjahjono, D.H. Structural Insight and Development of EGFR Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors. Molecules 2022, 27, 819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baselga, J.; Averbuch, S.D. ZD1839 (‘Iressa’) as an Anticancer Agent. Drugs 2000, 60 (Suppl. S1), 33–40; discussion 41–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moasser, M.M.; Basso, A.; Averbuch, S.D.; Rosen, N. The Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor ZD1839 (“Iressa”) Inhibits HER2-Driven Signaling and Suppresses the Growth of HER2-Overexpressing Tumor Cells. Cancer Res. 2001, 61, 7184–7188. [Google Scholar]
- Moulder, S.L.; Yakes, F.M.; Muthuswamy, S.K.; Bianco, R.; Simpson, J.F.; Arteaga, C.L. Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor (HER1) Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor ZD1839 (Iressa) Inhibits HER2/Neu (erbB2)-Overexpressing Breast Cancer Cells In Vitro and In Vivo. Cancer Res. 2001, 61, 8887–8895. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Q.; Shen, B.; Qin, X.; Liu, S.; Feng, J. Akt/mTOR and AMPK Signaling Pathways Are Responsible for Liver X Receptor Agonist GW3965-Enhanced Gefitinib Sensitivity in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Cell Lines. Transl. Cancer Res. 2019, 8, 66–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.-Q.; Yu, Z.-Y.; Li, J.; Ouyang, X.-N. Gefitinib Induces Lung Cancer Cell Autophagy and Apoptosis via Blockade of the PI3K/AKT/mTOR Pathway. Oncol. Lett. 2016, 12, 63–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suenaga, M.; Yamaguchi, A.; Soda, H.; Orihara, K.; Tokito, Y.; Sakaki, Y.; Umehara, M.; Terashi, K.; Kawamata, N.; Oka, M.; et al. Antiproliferative Effects of Gefitinib Are Associated with Suppression of E2F-1 Expression and Telomerase Activity. Anticancer Res. 2006, 26, 3387–3391. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, X.; Zheng, M.; Chen, F.; Zhu, Y.; Yong, W.; Lin, H.; Sun, Y.; Han, X. Gefitinib Inhibits the Proliferation of Pancreatic Cancer Cells via Cell Cycle Arrest. Anat. Rec. 2009, 292, 1122–1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, J.; Yu, J.; Yang, M.; Tang, L. Gefitinib Suppresses Cervical Cancer Progression by Inhibiting Cell Cycle Progression and Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition. Exp. Ther. Med. 2019, 18, 1823–1830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, M.H.; Williams, G.A.; Sridhara, R.; Chen, G.; Pazdur, R. FDA Drug Approval Summary: Gefitinib (ZD1839) (Iressa) Tablets. Oncologist 2003, 8, 303–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, A.R.; Chitale, D.; Riely, G.J.; Pao, W.; Miller, V.A.; Zakowski, M.F.; Rusch, V.; Kris, M.G.; Ladanyi, M. EGFR Mutations in Lung Adenocarcinomas: Clinical Testing Experience and Relationship to EGFR Gene Copy Number and Immunohistochemical Expression. J. Mol. Diagn. 2008, 10, 242–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazandjian, D.; Blumenthal, G.M.; Yuan, W.; He, K.; Keegan, P.; Pazdur, R. FDA Approval of Gefitinib for the Treatment of Patients with Metastatic EGFR Mutation-Positive Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2016, 22, 1307–1312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Lartigue, J. Approval Reinstates Gefitinib as a Therapy for Lung Cancer. J. Community Support. Oncol. 2015, 13, 385–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, M.H.; Johnson, J.R.; Chen, Y.-F.; Sridhara, R.; Pazdur, R. FDA Drug Approval Summary: Erlotinib (Tarceva) Tablets. Oncologist 2005, 10, 461–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.-K.; Noh, M.H.; Hong, S.-W.; Kim, S.-M.; Kim, S.H.; Kim, Y.S.; Broaddus, V.C.; Hur, D.Y. Erlotinib Activates Different Cell Death Pathways in EGFR-Mutant Lung Cancer Cells Grown in 3D Versus 2D Culture Systems. Anticancer Res. 2021, 41, 1261–1269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shan, F.; Shao, Z.; Jiang, S.; Cheng, Z. Erlotinib Induces the Human Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer Cells Apoptosis via Activating ROS-Dependent JNK Pathways. Cancer Med. 2016, 5, 3166–3175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suenaga, M.; Yamamoto, M.; Tabata, S.; Itakura, S.; Miyata, M.; Hamasaki, S.; Furukawa, T. Influence of Gefitinib and Erlotinib on Apoptosis and C-MYC Expression in H23 Lung Cancer Cells. Anticancer Res. 2013, 33, 1547–1554. [Google Scholar]
- Kamashev, D.; Shaban, N.; Lebedev, T.; Prassolov, V.; Suntsova, M.; Raevskiy, M.; Gaifullin, N.; Sekacheva, M.; Garazha, A.; Poddubskaya, E.; et al. Human Blood Serum Can Diminish EGFR-Targeted Inhibition of Squamous Carcinoma Cell Growth through Reactivation of MAPK and EGFR Pathways. Cells 2023, 12, 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schöttle, J.; Chatterjee, S.; Volz, C.; Siobal, M.; Florin, A.; Rokitta, D.; Hinze, Y.; Dietlein, F.; Plenker, D.; König, K.; et al. Intermittent High-Dose Treatment with Erlotinib Enhances Therapeutic Efficacy in EGFR-Mutant Lung Cancer. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 38458–38468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosell, R.; Carcereny, E.; Gervais, R.; Vergnenegre, A.; Massuti, B.; Felip, E.; Palmero, R.; Garcia-Gomez, R.; Pallares, C.; Sanchez, J.M.; et al. Erlotinib versus Standard Chemotherapy as First-Line Treatment for European Patients with Advanced EGFR Mutation-Positive Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer (EURTAC): A Multicentre, Open-Label, Randomised Phase 3 Trial. Lancet Oncol. 2012, 13, 239–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, C.; Wu, Y.L.; Chen, G.; Feng, J.; Liu, X.-Q.; Wang, C.; Zhang, S.; Wang, J.; Zhou, S.; Ren, S.; et al. Final Overall Survival Results from a Randomised, Phase III Study of Erlotinib versus Chemotherapy as First-Line Treatment of EGFR Mutation-Positive Advanced Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer (OPTIMAL, CTONG-0802). Ann. Oncol. 2015, 26, 1877–1883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.-L.; Zhou, C.; Liam, C.-K.; Wu, G.; Liu, X.; Zhong, Z.; Lu, S.; Cheng, Y.; Han, B.; Chen, L.; et al. First-Line Erlotinib versus Gemcitabine/Cisplatin in Patients with Advanced EGFR Mutation-Positive Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer: Analyses from the Phase III, Randomized, Open-Label, ENSURE Study. Ann. Oncol. 2015, 26, 1883–1889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cappuzzo, F.; Ciuleanu, T.; Stelmakh, L.; Cicenas, S.; Szczésna, A.; Juhász, E.; Esteban, E.; Molinier, O.; Brugger, W.; Melezínek, I.; et al. Erlotinib as Maintenance Treatment in Advanced Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer: A Multicentre, Randomised, Placebo-Controlled Phase 3 Study. Lancet Oncol. 2010, 11, 521–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelley, R.K.; Ko, A.H. Erlotinib in the Treatment of Advanced Pancreatic Cancer. Biologics 2008, 2, 83–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.; Zhang, Z.; Fang, W.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Hong, S.; Ma, Y.; Zhou, T.; Yang, Y.; Huang, Y.; et al. Efficacy and Tolerability of Erlotinib 100 Mg/d vs. Gefitinib 250 Mg/d in EGFR-Mutated Advanced Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer (E100VG250): An Open-Label, Randomized, Phase 2 Study. Front. Oncol. 2020, 10, 587849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jazieh, A.-R.; Al Sudairy, R.; Abu-Shraie, N.; Al Suwairi, W.; Ferwana, M.; Murad, M.H. Erlotinib in Wild Type Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: A Systematic Review. Ann. Thorac. Med. 2013, 8, 204–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pao, W.; Miller, V.A.; Politi, K.A.; Riely, G.J.; Somwar, R.; Zakowski, M.F.; Kris, M.G.; Varmus, H. Acquired Resistance of Lung Adenocarcinomas to Gefitinib or Erlotinib Is Associated with a Second Mutation in the EGFR Kinase Domain. PLoS Med. 2005, 2, e73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bean, J.; Brennan, C.; Shih, J.-Y.; Riely, G.; Viale, A.; Wang, L.; Chitale, D.; Motoi, N.; Szoke, J.; Broderick, S.; et al. MET Amplification Occurs with or without T790M Mutations in EGFR Mutant Lung Tumors with Acquired Resistance to Gefitinib or Erlotinib. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 20932–20937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wood, E.R.; Truesdale, A.T.; McDonald, O.B.; Yuan, D.; Hassell, A.; Dickerson, S.H.; Ellis, B.; Pennisi, C.; Horne, E.; Lackey, K.; et al. A Unique Structure for Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor Bound to GW572016 (Lapatinib): Relationships among Protein Conformation, Inhibitor off-Rate, and Receptor Activity in Tumor Cells. Cancer Res. 2004, 64, 6652–6659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ongko, J.; Setiawan, J.V.; Feronytha, A.G.; Juliana, A.; Effraim, A.; Wahjudi, M.; Antonius, Y. In-Silico Screening of Inhibitor on Protein Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor (EGFR). IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2022, 1041, 012075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tevaarwerk, A.J.; Kolesar, J.M. Lapatinib: A Small-Molecule Inhibitor of Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor and Human Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor-2 Tyrosine Kinases Used in the Treatment of Breast Cancer. Clin. Ther. 2009, 31 Pt 2, 2332–2348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rusnak, D.W.; Lackey, K.; Affleck, K.; Wood, E.R.; Alligood, K.J.; Rhodes, N.; Keith, B.R.; Murray, D.M.; Knight, W.B.; Mullin, R.J.; et al. The Effects of the Novel, Reversible Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor/ErbB-2 Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor, GW2016, on the Growth of Human Normal and Tumor-Derived Cell Lines In Vitro and In Vivo. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2001, 1, 85–94. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, L.; Zhong, L.; Zhao, Y.; Chen, M.; Yao, S.; Li, L.; Xiao, C.; Shan, Z.; Gan, L.; Xu, T.; et al. Effects of Lapatinib on Cell Proliferation and Apoptosis in NB4 Cells. Oncol. Lett. 2018, 15, 235–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.W.; Kim, H.-P.; Im, S.-A.; Kang, S.; Hur, H.S.; Yoon, Y.-K.; Oh, D.-Y.; Kim, J.H.; Lee, D.S.; Kim, T.-Y.; et al. The Growth Inhibitory Effect of Lapatinib, a Dual Inhibitor of EGFR and HER2 Tyrosine Kinase, in Gastric Cancer Cell Lines. Cancer Lett. 2008, 272, 296–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konecny, G.E.; Venkatesan, N.; Yang, G.; Dering, J.; Ginther, C.; Finn, R.; Rahmeh, M.; Fejzo, M.S.; Toft, D.; Jiang, S.-W.; et al. Activity of Lapatinib a Novel HER2 and EGFR Dual Kinase Inhibitor in Human Endometrial Cancer Cells. Br. J. Cancer 2008, 98, 1076–1084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, Y.; Yashiro, M.; Takakura, N. Heregulin Induces Resistance to Lapatinib-Mediated Growth Inhibition of HER2-Amplified Cancer Cells. Cancer Sci. 2013, 104, 1618–1625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gril, B.; Palmieri, D.; Bronder, J.L.; Herring, J.M.; Vega-Valle, E.; Feigenbaum, L.; Liewehr, D.J.; Steinberg, S.M.; Merino, M.J.; Rubin, S.D.; et al. Effect of Lapatinib on the Outgrowth of Metastatic Breast Cancer Cells to the Brain. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2008, 100, 1092–1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wainberg, Z.A.; Anghel, A.; Desai, A.J.; Ayala, R.; Luo, T.; Safran, B.; Fejzo, M.S.; Hecht, J.R.; Slamon, D.J.; Finn, R.S. Lapatinib, a Dual EGFR and HER2 Kinase Inhibitor, Selectively Inhibits HER2-Amplified Human Gastric Cancer Cells and Is Synergistic with Trastuzumab In Vitro and In Vivo. Clin. Cancer Res. 2010, 16, 1509–1519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cameron, D.; Casey, M.; Oliva, C.; Newstat, B.; Imwalle, B.; Geyer, C.E. Lapatinib plus Capecitabine in Women with HER-2-Positive Advanced Breast Cancer: Final Survival Analysis of a Phase III Randomized Trial. Oncologist 2010, 15, 924–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnston, S.; Pippen, J.; Pivot, X.; Lichinitser, M.; Sadeghi, S.; Dieras, V.; Gomez, H.L.; Romieu, G.; Manikhas, A.; Kennedy, M.J.; et al. Lapatinib Combined with Letrozole versus Letrozole and Placebo as First-Line Therapy for Postmenopausal Hormone Receptor-Positive Metastatic Breast Cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2009, 27, 5538–5546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Leo, A.; Gomez, H.L.; Aziz, Z.; Zvirbule, Z.; Bines, J.; Arbushites, M.C.; Guerrera, S.F.; Koehler, M.; Oliva, C.; Stein, S.H.; et al. Phase III, Double-Blind, Randomized Study Comparing Lapatinib plus Paclitaxel with Placebo plus Paclitaxel as First-Line Treatment for Metastatic Breast Cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2008, 26, 5544–5552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Westover, D.; Zugazagoitia, J.; Cho, B.C.; Lovly, C.M.; Paz-Ares, L. Mechanisms of Acquired Resistance to First- and Second-Generation EGFR Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors. Ann. Oncol. 2018, 29, i10–i19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, W.; Chen, X.; Guan, S.-X.; Ruan, H.-L.; Huang, Y.; Zhang, H.-Z.; Yang, Y.-P.; Fang, W.-F.; Zhao, H.-Y.; Zhuang, W.; et al. Rational Application of Gefitinib in NSCLC Patients with Sensitive EGFR Mutations Based on Pharmacokinetics and Metabolomics. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2022, 43, 1857–1864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Yao, W.; Min, X.; Gu, K.; Yu, G.; Zhang, Z.; Cui, J.; Miao, L.; Zhang, L.; Yuan, X.; et al. Apatinib Plus Gefitinib as First-Line Treatment in Advanced EGFR-Mutant NSCLC: The Phase III ACTIVE Study (CTONG1706). J. Thorac. Oncol. 2021, 16, 1533–1546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dungo, R.T.; Keating, G.M. Afatinib: First Global Approval. Drugs 2013, 73, 1503–1515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wind, S.; Schnell, D.; Ebner, T.; Freiwald, M.; Stopfer, P. Clinical Pharmacokinetics and Pharmacodynamics of Afatinib. Clin. Pharmacokinet. 2017, 56, 235–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duggirala, K.B.; Lee, Y.; Lee, K. Chronicles of EGFR Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors: Targeting EGFR C797S Containing Triple Mutations. Biomol. Ther. 2022, 30, 19–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Ambrogio, L.; Shimamura, T.; Kubo, S.; Takahashi, M.; Chirieac, L.R.; Padera, R.F.; Shapiro, G.I.; Baum, A.; Himmelsbach, F.; et al. BIBW2992, an Irreversible EGFR/HER2 Inhibitor Highly Effective in Preclinical Lung Cancer Models. Oncogene 2008, 27, 4702–4711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, N.R.; Soneru, C.; Liu, J.; Grushko, T.A.; Hardeman, A.; Olopade, O.I.; Baum, A.; Solca, F.; Cohen, E.E.W. Afatinib Efficacy against Squamous Cell Carcinoma of the Head and Neck Cell Lines In Vitro and In Vivo. Target. Oncol. 2015, 10, 501–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Xue, C.; Tian, Y.; Zhang, J.; Zhao, Y.; Zhan, J.; Fang, W. In Vitro and In Vivo Efficacy of Afatinib as a Single Agent or in Combination with Gemcitabine for The Treatment of Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma. Drug Des. Dev. Ther. 2016, 10, 1299–1306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banno, E.; Togashi, Y.; Kobayashi, Y.; Hayashi, H.; Mitsudomi, T.; Nishio, K. Afatinib Is Especially Effective against Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Carrying an EGFR Exon 19 Deletion. Anticancer Res. 2015, 35, 2005–2008. [Google Scholar]
- Schuler, M.; Wu, Y.-L.; Hirsh, V.; O’Byrne, K.; Yamamoto, N.; Mok, T.; Popat, S.; Sequist, L.V.; Massey, D.; Zazulina, V.; et al. First-Line Afatinib versus Chemotherapy in Patients with Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer and Common Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor Gene Mutations and Brain Metastases. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2016, 11, 380–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, K.; Tan, E.-H.; O’Byrne, K.; Zhang, L.; Boyer, M.; Mok, T.; Hirsh, V.; Yang, J.C.-H.; Lee, K.H.; Lu, S.; et al. Afatinib versus Gefitinib as First-Line Treatment of Patients with EGFR Mutation-Positive Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer (LUX-Lung 7): A Phase 2B, Open-Label, Randomised Controlled Trial. Lancet Oncol. 2016, 17, 577–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, N.U.; Winer, E.P.; Wheatley, D.; Carey, L.A.; Houston, S.; Mendelson, D.; Munster, P.; Frakes, L.; Kelly, S.; Garcia, A.A.; et al. A Phase II Study of Afatinib (BIBW 2992), an Irreversible ErbB Family Blocker, in Patients with HER2-Positive Metastatic Breast Cancer Progressing after Trastuzumab. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2012, 133, 1057–1065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awada, A.; Dirix, L.; Manso Sanchez, L.; Xu, B.; Luu, T.; Diéras, V.; Hershman, D.L.; Agrapart, V.; Ananthakrishnan, R.; Staroslawska, E. Safety and Efficacy of Neratinib (HKI-272) plus Vinorelbine in the Treatment of Patients with ErbB2-Positive Metastatic Breast Cancer Pretreated with Anti-HER2 Therapy. Ann. Oncol. 2013, 24, 109–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabindran, S.K.; Discafani, C.M.; Rosfjord, E.C.; Baxter, M.; Floyd, M.B.; Golas, J.; Hallett, W.A.; Johnson, B.D.; Nilakantan, R.; Overbeek, E.; et al. Antitumor Activity of HKI-272, an Orally Active, Irreversible Inhibitor of the HER-2 Tyrosine Kinase. Cancer Res. 2004, 64, 3958–3965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wissner, A.; Mansour, T.S. The Development of HKI-272 and Related Compounds for the Treatment of Cancer. Arch. Pharm. 2008, 341, 465–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conlon, N.T.; Kooijman, J.J.; van Gerwen, S.J.C.; Mulder, W.R.; Zaman, G.J.R.; Diala, I.; Eli, L.D.; Lalani, A.S.; Crown, J.; Collins, D.M. Comparative Analysis of Drug Response and Gene Profiling of HER2-Targeted Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors. Br. J. Cancer 2021, 124, 1249–1259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mullooly, M.; Conklin, D.; McGowan, P.M.; O’Brien, N.A.; O’Donovan, N.; Slamon, D.J.; Crown, J.; Finn, R.S.; Duffy, M.J. Neratinib to Inhibit the Growth of Triple-Negative Breast Cancer Cells. J. Clin. Oncol. 2015, 33, 1099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, H.; Liu, Y.; Miao, Z.; Cheng, S.; Zhu, Y.; Wu, Y.; Fan, X.; Yang, J.; Li, X.; Guo, L. Neratinib Inhibits Proliferation and Promotes Apoptosis of Acute Myeloid Leukemia Cells by Activating Autophagy-Dependent Ferroptosis. Drug Dev. Res. 2022, 83, 1641–1653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canonici, A.; Gijsen, M.; Mullooly, M.; Bennett, R.; Bouguern, N.; Pedersen, K.; O’Brien, N.A.; Roxanis, I.; Li, J.-L.; Bridge, E.; et al. Neratinib Overcomes Trastuzumab Resistance in HER2 Amplified Breast Cancer. Oncotarget 2013, 4, 1592–1605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burstein, H.J.; Sun, Y.; Dirix, L.Y.; Jiang, Z.; Paridaens, R.; Tan, A.R.; Awada, A.; Ranade, A.; Jiao, S.; Schwartz, G.; et al. Neratinib, an Irreversible ErbB Receptor Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor, in Patients with Advanced ErbB2-Positive Breast Cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2010, 28, 1301–1307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saura, C.; Garcia-Saenz, J.A.; Xu, B.; Harb, W.; Moroose, R.; Pluard, T.; Cortés, J.; Kiger, C.; Germa, C.; Wang, K.; et al. Safety and Efficacy of Neratinib in Combination with Capecitabine in Patients with Metastatic Human Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor 2-Positive Breast Cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2014, 32, 3626–3633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, H.; Walker, A.J.; Amiri-Kordestani, L.; Cheng, J.; Tang, S.; Balcazar, P.; Barnett-Ringgold, K.; Palmby, T.R.; Cao, X.; Zheng, N.; et al. U.S. Food and Drug Administration Approval: Neratinib for the Extended Adjuvant Treatment of Early-Stage HER2-Positive Breast Cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2018, 24, 3486–3491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holmes, F.A.; Moy, B.; Delaloge, S.; Chia, S.K.L.; Ejlertsen, B.; Mansi, J.; Iwata, H.; Gnant, M.; Buyse, M.; Barrios, C.H.; et al. Overall Survival with Neratinib after Trastuzumab-Based Adjuvant Therapy in HER2-Positive Breast Cancer (ExteNET): A Randomised, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled, Phase 3 Trial. Eur. J. Cancer 2023, 184, 48–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saura, C.; Oliveira, M.; Feng, Y.-H.; Dai, M.-S.; Chen, S.-W.; Hurvitz, S.A.; Kim, S.-B.; Moy, B.; Delaloge, S.; Gradishar, W.; et al. Neratinib Plus Capecitabine Versus Lapatinib Plus Capecitabine in HER2-Positive Metastatic Breast Cancer Previously Treated with ≥2 HER2-Directed Regimens: Phase III NALA Trial. J. Clin. Oncol. 2020, 38, 3138–3149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asami, K.; Atagi, S. Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors for Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. World J. Clin. Oncol. 2014, 5, 646–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagano, T.; Tachihara, M.; Nishimura, Y. Dacomitinib, a Second-Generation Irreversible Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor (EGFR-TKI) to Treat Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Drugs Today 2019, 55, 231–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garuti, L.; Roberti, M.; Bottegoni, G. Irreversible Protein Kinase Inhibitors. Curr. Med. Chem. 2011, 18, 2981–2994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engelman, J.A.; Zejnullahu, K.; Gale, C.-M.; Lifshits, E.; Gonzales, A.J.; Shimamura, T.; Zhao, F.; Vincent, P.W.; Naumov, G.N.; Bradner, J.E.; et al. PF00299804, an Irreversible Pan-ERBB Inhibitor, Is Effective in Lung Cancer Models with EGFR and ERBB2 Mutations That Are Resistant to Gefitinib. Cancer Res. 2007, 67, 11924–11932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzales, A.J.; Hook, K.E.; Althaus, I.W.; Ellis, P.A.; Trachet, E.; Delaney, A.M.; Harvey, P.J.; Ellis, T.A.; Amato, D.M.; Nelson, J.M.; et al. Antitumor Activity and Pharmacokinetic Properties of PF-00299804, a Second-Generation Irreversible Pan-erbB Receptor Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2008, 7, 1880–1889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, J.P.; Kim, I.; Ito, E.; Shi, W.; Yue, S.; Siu, L.L.; Waldron, J.; O’Sullivan, B.; Yip, K.W.; Liu, F.-F. Pre-Clinical Characterization of Dacomitinib (PF-00299804), an Irreversible Pan-ErbB Inhibitor, Combined with Ionizing Radiation for Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e98557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grivas, P.D.; Day, K.C.; Karatsinides, A.; Paul, A.; Shakir, N.; Owainati, I.; Liebert, M.; Kunju, L.P.; Thomas, D.; Hussain, M.; et al. Evaluation of the Antitumor Activity of Dacomitinib in Models of Human Bladder Cancer. Mol. Med. 2013, 19, 367–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.-L.; Cheng, Y.; Zhou, X.; Lee, K.H.; Nakagawa, K.; Niho, S.; Tsuji, F.; Linke, R.; Rosell, R.; Corral, J.; et al. Dacomitinib versus Gefitinib as First-Line Treatment for Patients with EGFR-Mutation-Positive Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer (ARCHER 1050): A Randomised, Open-Label, Phase 3 Trial. Lancet Oncol. 2017, 18, 1454–1466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mok, T.S.; Cheng, Y.; Zhou, X.; Lee, K.H.; Nakagawa, K.; Niho, S.; Chawla, A.; Rosell, R.; Corral, J.; Migliorino, M.R.; et al. Updated Overall Survival in a Randomized Study Comparing Dacomitinib with Gefitinib as First-Line Treatment in Patients with Advanced Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer and EGFR-Activating Mutations. Drugs 2021, 81, 257–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, H.; Sakamoto, H.; Akita, T.; Ohyanagi, F.; Kawashima, Y.; Tambo, Y.; Tanimoto, A.; Horiike, A.; Miyauchi, E.; Tsuchiya-Kawano, Y.; et al. Clinical Efficacy of Dacomitinib in Rechallenge Setting for Patients with Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor Mutant Non–Small Cell Lung Cancer: A Multicenter Retrospective Analysis ( TOPGAN2020-02). Thorac. Cancer 2022, 13, 1471–1478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Shi, C.; Gao, Z.; Zhong, H.; Xiong, L.; Gu, A.; Wang, W.; Chu, T.; Zhang, W.; Wang, H.; et al. Rationale and Design of a Phase II Trial of Dacomitinib in Advanced Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Patients with Uncommon Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor Mutations: A Prospective and Single Arm Study (DANCE Study). BMC Cancer 2022, 22, 294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chau, N.G.; Haddad, R.I. Vandetanib for the Treatment of Medullary Thyroid Cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2013, 19, 524–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CAPRELSA® (Vandetanib) Tablets, for Oral Use Abϕ—∏oиck b Google. Available online: https://www.google.com/search?q=CAPRELSA%C2%AE+%28vandetanib%29+tablets%2C+for+oral+use+%D0%B0%D0%B2%D1%84&newwindow=1&client=safari&sca_esv=585026838&rls=en&ei=YYJgZYT7ONOXjgb3hrmgCw&ved=0ahUKEwjEr-vrvdyCAxXTi8MKHXdDDrQQ4dUDCA8&uact=5&oq=CAPRELSA%C2%AE+%28vandetanib%29+tablets%2C+for+oral+use+%D0%B0%D0%B2%D1%84&gs_lp=Egxnd3Mtd2l6LXNlcnAiNENBUFJFTFNBwq4gKHZhbmRldGFuaWIpIHRhYmxldHMsIGZvciBvcmFsIHVzZSDQsNCy0YQyCBAAGIAEGKIEMggQABiABBiiBEizDFArWLYLcAF4AZABAJgBkAGgAaIDqgEDMi4yuAEDyAEA-AEBwgIKEAAYRxjWBBiwA-IDBBgAIEGIBgGQBgU&sclient=gws-wiz-serp (accessed on 24 November 2023).
- Kitamura, S.; Maeda, T.; Yanagi, T. Vandetanib Inhibits Cell Growth in EGFR-Expressing Cutaneous Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2020, 531, 396–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ichihara, E.; Ohashi, K.; Takigawa, N.; Osawa, M.; Ogino, A.; Tanimoto, M.; Kiura, K. Effects of Vandetanib on Lung Adenocarcinoma Cells Harboring Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor T790M Mutation In Vivo. Cancer Res. 2009, 69, 5091–5098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.S.; Hirsh, V.; Park, K.; Qin, S.; Blajman, C.R.; Perng, R.-P.; Chen, Y.-M.; Emerson, L.; Langmuir, P.; Manegold, C. Vandetanib Versus Placebo in Patients with Advanced Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer after Prior Therapy with an Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor: A Randomized, Double-Blind Phase III Trial (ZEPHYR). J. Clin. Oncol. 2012, 30, 1114–1121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, R.; Arshad, J.; Palacio, S.; Mudad, R. Brigatinib for ALK-Positive Metastatic Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer: Design, Development and Place in Therapy. Drug Des. Dev. Ther. 2019, 13, 569–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Food and Drug Administration. FDA Approves Brigatinib for ALK-Positive Metastatic NSCLC; FDA: Silver Spring, MD, USA, 2021.
- Uchibori, K.; Inase, N.; Araki, M.; Kamada, M.; Sato, S.; Okuno, Y.; Fujita, N.; Katayama, R. Brigatinib Combined with Anti-EGFR Antibody Overcomes Osimertinib Resistance in EGFR-Mutated Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 14768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gettinger, S.N.; Bazhenova, L.A.; Langer, C.J.; Salgia, R.; Gold, K.A.; Rosell, R.; Shaw, A.T.; Weiss, G.J.; Tugnait, M.; Narasimhan, N.I.; et al. Activity and Safety of Brigatinib in ALK-Rearranged Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer and Other Malignancies: A Single-Arm, Open-Label, Phase 1/2 Trial. Lancet Oncol. 2016, 17, 1683–1696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arcila, M.E.; Oxnard, G.R.; Nafa, K.; Riely, G.J.; Solomon, S.B.; Zakowski, M.F.; Kris, M.G.; Pao, W.; Miller, V.A.; Ladanyi, M. Rebiopsy of Lung Cancer Patients with Acquired Resistance to EGFR Inhibitors and Enhanced Detection of the T790M Mutation Using a Locked Nucleic Acid-Based Assay. Clin. Cancer Res. 2011, 17, 1169–1180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cross, D.A.E.; Ashton, S.E.; Ghiorghiu, S.; Eberlein, C.; Nebhan, C.A.; Spitzler, P.J.; Orme, J.P.; Finlay, M.R.V.; Ward, R.A.; Mellor, M.J.; et al. AZD9291, an Irreversible EGFR TKI, Overcomes T790M-Mediated Resistance to EGFR Inhibitors in Lung Cancer. Cancer Discov. 2014, 4, 1046–1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leonetti, A.; Sharma, S.; Minari, R.; Perego, P.; Giovannetti, E.; Tiseo, M. Resistance Mechanisms to Osimertinib in EGFR-Mutated Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Br. J. Cancer 2019, 121, 725–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soria, J.-C.; Ohe, Y.; Vansteenkiste, J.; Reungwetwattana, T.; Chewaskulyong, B.; Lee, K.H.; Dechaphunkul, A.; Imamura, F.; Nogami, N.; Kurata, T.; et al. Osimertinib in Untreated EGFR-Mutated Advanced Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 378, 113–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mok, T.S.; Wu, Y.-L.; Ahn, M.-J.; Garassino, M.C.; Kim, H.R.; Ramalingam, S.S.; Shepherd, F.A.; He, Y.; Akamatsu, H.; Theelen, W.S.M.E.; et al. Osimertinib or Platinum–Pemetrexed in EGFR T790M–Positive Lung Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 376, 629–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Remon, J.; Steuer, C.E.; Ramalingam, S.S.; Felip, E. Osimertinib and Other Third-Generation EGFR TKI in EGFR-Mutant NSCLC Patients. Ann. Oncol. 2018, 29, i20–i27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, H.; Nair, S.K.; Murray, B.W. Recent Progress on Third Generation Covalent EGFR Inhibitors. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2016, 26, 1861–1868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.C.-H.; Camidge, D.R.; Yang, C.-T.; Zhou, J.; Guo, R.; Chiu, C.-H.; Chang, G.-C.; Shiah, H.-S.; Chen, Y.; Wang, C.-C.; et al. Safety, Efficacy, and Pharmacokinetics of Almonertinib (HS-10296) in Pretreated Patients with EGFR-Mutated Advanced NSCLC: A Multicenter, Open-Label, Phase 1 Trial. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2020, 15, 1907–1918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, X.; Zhang, Y.; Huang, F.; Wu, Y.; Pang, J.; Li, X.; Fan, F.; Liu, H.; Li, S. EGFR Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor Almonertinib Induces Apoptosis and Autophagy Mediated by Reactive Oxygen Species in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Cells. Hum. Exp. Toxicol. 2021, 40, S49–S62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, S.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, G.; Dong, X.; Yang, C.; Song, Y.; Chang, G.; Lu, Y.; Pan, H.; Chiu, C.; et al. OA02.03 The Third Generation EGFR Inhibitor (EGFR-TKI) HS-10296 in Advanced NSCLC Patients with Resistance to First Generation EGFR-TKI. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2019, 14, S208–S209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, S.; Dong, X.; Jian, H.; Chen, J.; Chen, G.; Sun, Y.; Ji, Y.; Wang, Z.; Shi, J.; Lu, J.; et al. AENEAS: A Randomized Phase III Trial of Aumolertinib Versus Gefitinib as First-Line Therapy for Locally Advanced or MetastaticNon-Small-Cell Lung Cancer with EGFR Exon 19 Deletion or L858R Mutations. J. Clin. Oncol. 2022, 40, 3162–3171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yun, J.; Hong, M.H.; Kim, S.-Y.; Park, C.-W.; Kim, S.; Yun, M.R.; Kang, H.N.; Pyo, K.-H.; Lee, S.S.; Koh, J.S.; et al. YH25448, an Irreversible EGFR-TKI with Potent Intracranial Activity in EGFR Mutant Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2019, 25, 2575–2587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koga, T.; Suda, K.; Mitsudomi, T. Utility of the Ba/F3 Cell System for Exploring on-Target Mechanisms of Resistance to Targeted Therapies for Lung Cancer. Cancer Sci. 2022, 113, 815–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, M.-J.; Han, J.-Y.; Lee, K.H.; Kim, S.-W.; Kim, D.-W.; Lee, Y.-G.; Cho, E.K.; Kim, J.-H.; Lee, G.-W.; Lee, J.-S.; et al. Lazertinib in Patients with EGFR Mutation-Positive Advanced Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer: Results from the Dose Escalation and Dose Expansion Parts of a First-in-Human, Open-Label, Multicentre, Phase 1–2 Study. Lancet Oncol. 2019, 20, 1681–1690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhillon, S. Lazertinib: First Approval. Drugs 2021, 81, 1107–1113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.S.; Ou, S.-H.I. Spotlight on Furmonertinib (Alflutinib, AST2818). The Swiss Army Knife (Del19, L858R, T790M, Exon 20 Insertions, “Uncommon-G719X, S768I, L861Q”) Among the Third-Generation EGFR TKIs? Lung Cancer 2022, 13, 67–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.-Y.; Guo, Z.-T.; Chen, Z.-D.; Zhang, Y.-F.; Zhou, J.-L.; Jiang, Y.; Zhao, Q.-Y.; Diao, X.-X.; Zhong, D.-F. Alflutinib (AST2818), Primarily Metabolized by CYP3A4, Is a Potent CYP3A4 Inducer. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2020, 41, 1366–1376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Zhang, S.; Hu, X.; Feng, J.; Ma, Z.; Zhou, J.; Yang, N.; Wu, L.; Liao, W.; Zhong, D.; et al. Safety, Clinical Activity, and Pharmacokinetics of Alflutinib (AST2818) in Patients with Advanced NSCLC with EGFR T790M Mutation. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2020, 15, 1015–1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Chen, G.; Wang, X.; Liu, Y.; Wu, L.; Hao, Y.; Liu, C.; Zhu, S.; Zhang, X.; Li, Y.; et al. Furmonertinib (AST2818) versus Gefitinib as First-Line Therapy for Chinese Patients with Locally Advanced or Metastatic EGFR Mutation-Positive Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer (FURLONG): A Multicentre, Double-Blind, Randomised Phase 3 Study. Lancet Respir. Med. 2022, 10, 1019–1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ArriVent BioPharma, Inc. Study to Compare Furmonertinib to Platinum-Based Chemotherapy for Patients with Locally Advanced or Metastatic Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer (NSCLC) With Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor (EGFR) Exon 20 Insertion Mutations (FURVENT)—Clinicaltrials.gov. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT05607550 (accessed on 17 November 2023).
- Vasconcelos, P.E.N.S.; Kobayashi, I.S.; Kobayashi, S.S.; Costa, D.B. Preclinical Characterization of Mobocertinib Highlights the Putative Therapeutic Window of This Novel EGFR Inhibitor to EGFR Exon 20 Insertion Mutations. JTO Clin. Res. Rep. 2021, 2, 100105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnold, A.; Ganti, A.K. Clinical Utility of Mobocertinib in the Treatment of NSCLC—Patient Selection and Reported Outcomes. OncoTargets Ther. 2023, 16, 559–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalvez, F.; Zhu, X.; Huang, W.-S.; Baker, T.E.; Ning, Y.; Wardwell, S.D.; Nadworny, S.; Zhang, S.; Das, B.; Gong, Y.; et al. Abstract 2644: AP32788, a Potent, Selective Inhibitor of EGFR and HER2 Oncogenic Mutants, Including Exon 20 Insertions, in Preclinical Models. Cancer Res. 2016, 76, 2644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, C.; Ramalingam, S.S.; Kim, T.M.; Kim, S.-W.; Yang, J.C.-H.; Riely, G.J.; Mekhail, T.; Nguyen, D.; Garcia Campelo, M.R.; Felip, E.; et al. Treatment Outcomes and Safety of Mobocertinib in Platinum-Pretreated Patients with EGFR Exon 20 Insertion-Positive Metastatic Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: A Phase 1/2 Open-Label Nonrandomized Clinical Trial. JAMA Oncol. 2021, 7, e214761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kagawa, Y.; Hayashida, T.; Liu, J.; Mori, S.; Izumi, H.; Kumagai, S.; Udagawa, H.; Hattori, N.; Goto, K.; Kobayashi, S.S. The EGFR C797S Mutation Confers Resistance to a Novel EGFR Inhibitor CLN-081 to EGFR Exon 20 Insertion Mutations. JTO Clin. Res. Rep. 2023, 4, 100462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.S.; Zhu, V.W. Spotlight on Mobocertinib (TAK-788) in NSCLC with EGFR Exon 20 Insertion Mutations. Lung Cancer 2021, 12, 61–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FDA and Takeda to Withdraw Mobocertinib for EGFR Exon20+ NSCLC. Available online: https://www.targetedonc.com/view/fda-and-takeda-to-withdraw-mobocertinib-for-egfr-exon20-nsclc (accessed on 16 November 2023).
- Chen, M.; Yu, H. Lactobacillus Metabolites Relieves the Rash and Diarrhea Induced by Egfr Tki: Two Case Reports and Literature Review. Clin. Nutr. ESPEN 2023, 54, 593–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kunimasa, K.; Kamada, R.; Oka, T.; Oboshi, M.; Kimura, M.; Inoue, T.; Tamiya, M.; Nishikawa, T.; Yasui, T.; Shioyama, W.; et al. Cardiac Adverse Events in EGFR-Mutated Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Treated with Osimertinib. Cardio Oncol. 2020, 2, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Meng, L.; Yang, B.; Sun, S.; Luo, Z.; Chen, H. Safety Profile of Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors: A Disproportionality Analysis of FDA Adverse Event Reporting System. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 4803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shyam Sunder, S.; Sharma, U.C.; Pokharel, S. Adverse Effects of Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors in Cancer Therapy: Pathophysiology, Mechanisms and Clinical Management. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2023, 8, 262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; Ke, L.; Zhang, Z.; Yu, J.; Meng, X. Development of EGFR TKIs and Options to Manage Resistance of Third-Generation EGFR TKI Osimertinib: Conventional Ways and Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors. Front. Oncol. 2020, 10, 602762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papadimitrakopoulou, V.A.; Wu, Y.-L.; Han, J.-Y.; Ahn, M.-J.; Ramalingam, S.S.; John, T.; Okamoto, I.; Yang, J.C.-H.; Bulusu, K.C.; Laus, G.; et al. Analysis of Resistance Mechanisms to Osimertinib in Patients with EGFR T790M Advanced NSCLC from the AURA3 Study. Ann. Oncol. 2018, 29, viii741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oxnard, G.R.; Hu, Y.; Mileham, K.F.; Husain, H.; Costa, D.B.; Tracy, P.; Feeney, N.; Sholl, L.M.; Dahlberg, S.E.; Redig, A.J.; et al. Assessment of Resistance Mechanisms and Clinical Implications in Patients with EGFR T790M-Positive Lung Cancer and Acquired Resistance to Osimertinib. JAMA Oncol. 2018, 4, 1527–1534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papini, F.; Sundaresan, J.; Leonetti, A.; Tiseo, M.; Rolfo, C.; Peters, G.J.; Giovannetti, E. Hype or Hope—Can Combination Therapies with Third-Generation EGFR-TKIs Help Overcome Acquired Resistance and Improve Outcomes in EGFR-Mutant Advanced/Metastatic NSCLC? Crit. Rev. Oncol. Hematol. 2021, 166, 103454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, P.; Yao, M.-Y.; Zhu, S.-J.; Chen, J.-Y.; Yun, C.-H. Crystal Structure of EGFR T790M/C797S/V948R in Complex with EAI045. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2018, 502, 332–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, Y.; Yun, C.-H.; Park, E.; Ercan, D.; Manuia, M.; Juarez, J.; Xu, C.; Rhee, K.; Chen, T.; Zhang, H.; et al. Overcoming EGFR(T790M) and EGFR(C797S) Resistance with Mutant-Selective Allosteric Inhibitors. Nature 2016, 534, 129–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- To, C.; Jang, J.; Chen, T.; Park, E.; Mushajiang, M.; De Clercq, D.J.H.; Xu, M.; Wang, S.; Cameron, M.D.; Heppner, D.E.; et al. Single and Dual Targeting of Mutant EGFR with an Allosteric Inhibitor. Cancer Discov. 2019, 9, 926–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kashima, K.; Kawauchi, H.; Tanimura, H.; Tachibana, Y.; Chiba, T.; Torizawa, T.; Sakamoto, H. CH7233163 Overcomes Osimertinib-Resistant EGFR-Del19/T790M/C797S Mutation. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2020, 19, 2288–2297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eno, M.S.; Brubaker, J.D.; Campbell, J.E.; De Savi, C.; Guzi, T.J.; Williams, B.D.; Wilson, D.; Wilson, K.; Brooijmans, N.; Kim, J.; et al. Discovery of BLU-945, a Reversible, Potent, and Wild-Type-Sparing Next-Generation EGFR Mutant Inhibitor for Treatment-Resistant Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer. J. Med. Chem. 2022, 65, 9662–9677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shum, E.; Elamin, Y.Y.; Piotrowska, Z.; Spigel, D.R.; Reckamp, K.L.; Rotow, J.K.; Tan, D.S.-W.; Lim, S.M.; Kim, T.M.; Lin, C.-C.; et al. A Phase 1/2 Study of BLU-945 in Patients with Common Activating EGFR-Mutant Non–Small Cell Lung Cancer (NSCLC): SYMPHONY Trial in Progress. J. Clin. Oncol. 2022, 40, TPS9156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elamin, Y.Y.; Nagasaka, M.; Shum, E.; Bazhenova, L.; Camidge, D.R.; Cho, B.C.; Felip, E.; Goto, K.; Lin, C.-C.; Piotrowska, Z.; et al. BLU-945 Monotherapy and in Combination with Osimertinib (OSI) in Previously Treated Patients with Advanced EGFR-Mutant (EGFRm) NSCLC in the Phase 1/2 SYMPHONY Study. J. Clin. Oncol. 2023, 41, 9011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conti, C.; Campbell, J.; Woessner, R.; Guo, J.; Timsit, Y.; Iliou, M.; Wardwell, S.; Davis, A.; Chicklas, S.; Hsieh, J.; et al. Abstract 1262: BLU-701 Is a Highly Potent, Brain-Penetrant and WT-Sparing next-Generation EGFR TKI for the Treatment of Sensitizing (Ex19del, L858R) and C797S Resistance Mutations in Metastatic NSCLC. Cancer Res. 2021, 81, 1262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tavera, L.; Schalm, S.; Campbell, J.; Guo, J.; Medendorp, C.; Chen, M.; Albayya, F.; Dineen, T.; Zhang, Z.; Iliou, M.; et al. Abstract 3328: Antitumor Activity of BLU-945 and BLU-701 as Single Agents and in Combination in EGFR L858R-Driven Models of NSCLC. Cancer Res. 2022, 82, 3328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spira, A.I.; Spigel, D.R.; Camidge, D.R.; De Langen, A.; Kim, T.M.; Goto, K.; Elamin, Y.Y.; Shum, E.; Reckamp, K.L.; Rotow, J.K.; et al. A Phase 1/2 Study of the Highly Selective EGFR Inhibitor, BLU-701, in Patients with EGFR-Mutant Non–Small Cell Lung Cancer (NSCLC). J. Clin. Oncol. 2022, 40, TPS9142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yun, M.R.; Yu, M.R.; Duggirala, K.B.; Lee, K.; Jo, A.; Seah, E.; Kim, C.; Cho, B.C. MA07.08 JIN-A02, a Highly Effective 4th Generation EGFR-TKI, Targeting EGFR C797S Triple Mutation in NSCLC. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2022, 17, S69–S70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, S.M.; Fujino, T.; Kim, C.; Lee, G.; Lee, Y.-H.; Kim, D.-W.; Ahn, J.S.; Mitsudomi, T.; Jin, T.; Lee, S.-Y. BBT-176, a Novel Fourth-Generation Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor for Osimertinib-Resistant EGFR Mutations in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2023, 29, 3004–3016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mansour, M.A.; AboulMagd, A.M.; Abbas, S.H.; Abdel-Rahman, H.M.; Abdel-Aziz, M. Insights into Fourth Generation Selective Inhibitors of (C797S) EGFR Mutation Combating Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Resistance: A Critical Review. RSC Adv. 2023, 13, 18825–18853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawamoto, T.; Sato, J.D.; Le, A.; Polikoff, J.; Sato, G.H.; Mendelsohn, J. Growth Stimulation of A431 Cells by Epidermal Growth Factor: Identification of High-Affinity Receptors for Epidermal Growth Factor by an Anti-Receptor Monoclonal Antibody. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1983, 80, 1337–1341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zahavi, D.; Weiner, L. Monoclonal Antibodies in Cancer Therapy. Antibodies 2020, 9, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferris, R.L.; Lenz, H.-J.; Trotta, A.M.; García-Foncillas, J.; Schulten, J.; Audhuy, F.; Merlano, M.; Milano, G. Rationale for Combination of Therapeutic Antibodies Targeting Tumor Cells and Immune Checkpoint Receptors: Harnessing Innate and Adaptive Immunity through IgG1 Isotype Immune Effector Stimulation. Cancer Treat. Rev. 2018, 63, 48–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arnould, L.; Gelly, M.; Penault-Llorca, F.; Benoit, L.; Bonnetain, F.; Migeon, C.; Cabaret, V.; Fermeaux, V.; Bertheau, P.; Garnier, J.; et al. Trastuzumab-Based Treatment of HER2-Positive Breast Cancer: An Antibody-Dependent Cellular Cytotoxicity Mechanism? Br. J. Cancer 2006, 94, 259–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kimura, H.; Sakai, K.; Arao, T.; Shimoyama, T.; Tamura, T.; Nishio, K. Antibody-Dependent Cellular Cytotoxicity of Cetuximab against Tumor Cells with Wild-Type or Mutant Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor. Cancer Sci. 2007, 98, 1275–1280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galizia, G.; Lieto, E.; De Vita, F.; Orditura, M.; Castellano, P.; Troiani, T.; Imperatore, V.; Ciardiello, F. Cetuximab, a Chimeric Human Mouse Anti-Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor Monoclonal Antibody, in the Treatment of Human Colorectal Cancer. Oncogene 2007, 26, 3654–3660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldstein, N.I.; Prewett, M.; Zuklys, K.; Rockwell, P.; Mendelsohn, J. Biological Efficacy of a Chimeric Antibody to the Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor in a Human Tumor Xenograft Model. Clin. Cancer Res. 1995, 1, 1311–1318. [Google Scholar]
- Li, S.; Schmitz, K.R.; Jeffrey, P.D.; Wiltzius, J.J.W.; Kussie, P.; Ferguson, K.M. Structural Basis for Inhibition of the Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor by Cetuximab. Cancer Cell 2005, 7, 301–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waksal, H.W. Role of an Anti-Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor in Treating Cancer. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 1999, 18, 427–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mukohara, T.; Engelman, J.A.; Hanna, N.H.; Yeap, B.Y.; Kobayashi, S.; Lindeman, N.; Halmos, B.; Pearlberg, J.; Tsuchihashi, Z.; Cantley, L.C.; et al. Differential Effects of Gefitinib and Cetuximab on Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancers Bearing Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor Mutations. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2005, 97, 1185–1194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hotz, B.; Keilholz, U.; Fusi, A.; Buhr, H.J.; Hotz, H.G. In Vitro and In Vivo Antitumor Activity of Cetuximab in Human Gastric Cancer Cell Lines in Relation to Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor (EGFR) Expression and Mutational Phenotype. Gastric Cancer 2012, 15, 252–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balin-Gauthier, D.; Delord, J.-P.; Rochaix, P.; Mallard, V.; Thomas, F.; Hennebelle, I.; Bugat, R.; Canal, P.; Allal, C. In Vivo and In Vitro Antitumor Activity of Oxaliplatin in Combination with Cetuximab in Human Colorectal Tumor Cell Lines Expressing Different Level of EGFR. Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol. 2006, 57, 709–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kiyota, A.; Shintani, S.; Mihara, M.; Nakahara, Y.; Ueyama, Y.; Matsumura, T.; Tachikawa, T.; Wong, D.T.W. Anti-Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor Monoclonal Antibody 225 Upregulates P27KIP1 and P15INK4B and Induces G1 Arrest in Oral Squamous Carcinoma Cell Lines. Oncology 2002, 63, 92–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okuyama, K.; Suzuki, K.; Naruse, T.; Tsuchihashi, H.; Yanamoto, S.; Kaida, A.; Miura, M.; Umeda, M.; Yamashita, S. Prolonged Cetuximab Treatment Promotes p27Kip1-Mediated G1 Arrest and Autophagy in Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 5259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ozkan, A.; Erdogan, A.; Ozkan, O.; Manguoglu, E.; Kiraz, N. Enhanced Anticancer Effect of Cetuximab Combined with Stabilized Silver Ion Solution in EGFR-Positive Lung Cancer Cells. Turk. J. Biochem. 2019, 44, 426–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamashev, D.; Sorokin, M.; Kochergina, I.; Drobyshev, A.; Vladimirova, U.; Zolotovskaia, M.; Vorotnikov, I.; Shaban, N.; Raevskiy, M.; Kuzmin, D.; et al. Human Blood Serum Can Donor-Specifically Antagonize Effects of EGFR-Targeted Drugs on Squamous Carcinoma Cell Growth. Heliyon 2021, 7, e06394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamashev, D.; Shaban, N.; Suntsova, M.; Raevskiy, M.; Efimov, V.; Moisseev, A.; Sorokin, M.; Buzdin, A. Human Blood Serum Inhibits Ductal Carcinoma Cells BT474 Growth and Modulates Effect of HER2 Inhibition. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 1914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saltz, L.B.; Meropol, N.J.; Loehrer, P.J.; Needle, M.N.; Kopit, J.; Mayer, R.J. Phase II Trial of Cetuximab in Patients with Refractory Colorectal Cancer That Expresses the Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor. J. Clin. Oncol. 2004, 22, 1201–1208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sobrero, A.F.; Maurel, J.; Fehrenbacher, L.; Scheithauer, W.; Abubakr, Y.A.; Lutz, M.P.; Vega-Villegas, M.E.; Eng, C.; Steinhauer, E.U.; Prausova, J.; et al. EPIC: Phase III Trial of Cetuximab plus Irinotecan after Fluoropyrimidine and Oxaliplatin Failure in Patients with Metastatic Colorectal Cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2008, 26, 2311–2319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, S.; Li, J.; Wang, L.; Xu, J.; Cheng, Y.; Bai, Y.; Li, W.; Xu, N.; Lin, L.-Z.; Wu, Q.; et al. Efficacy and Tolerability of First-Line Cetuximab Plus Leucovorin, Fluorouracil, and Oxaliplatin (FOLFOX-4) Versus FOLFOX-4 in Patients with RAS Wild-Type Metastatic Colorectal Cancer: The Open-Label, Randomized, Phase III TAILOR Trial. J. Clin. Oncol. 2018, 36, 3031–3039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, Y.; Luo, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Huang, X.; Li, Z.; Shen, L.; Feng, J.; Sun, Y.; Yang, K.; Ge, M.; et al. First-Line Treatment with Chemotherapy plus Cetuximab in Chinese Patients with Recurrent and/or Metastatic Squamous Cell Carcinoma of the Head and Neck: Efficacy and Safety Results of the Randomised, Phase III CHANGE-2 Trial. Eur. J. Cancer 2021, 156, 35–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonner, J.A.; Harari, P.M.; Giralt, J.; Azarnia, N.; Shin, D.M.; Cohen, R.B.; Jones, C.U.; Sur, R.; Raben, D.; Jassem, J.; et al. Radiotherapy plus Cetuximab for Squamous-Cell Carcinoma of the Head and Neck. N. Engl. J. Med. 2006, 354, 567–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Information on Cetuximab (Marketed as Erbitux)|FDA. Available online: https://www.fda.gov/drugs/postmarket-drug-safety-information-patients-and-providers/information-cetuximab-marketed-erbitux (accessed on 17 November 2023).
- Blick, S.K.A.; Scott, L.J. Cetuximab: A Review of Its Use in Squamous Cell Carcinoma of the Head and Neck and Metastatic Colorectal Cancer. Drugs 2007, 67, 2585–2607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karapetis, C.S.; Khambata-Ford, S.; Jonker, D.J.; O’Callaghan, C.J.; Tu, D.; Tebbutt, N.C.; Simes, R.J.; Chalchal, H.; Shapiro, J.D.; Robitaille, S.; et al. K-Ras Mutations and Benefit from Cetuximab in Advanced Colorectal Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2008, 359, 1757–1765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jimeno, A.; Messersmith, W.A.; Hirsch, F.R.; Franklin, W.A.; Eckhardt, S.G. KRAS Mutations and Susceptibility to Cetuximab and Panitumumab in Colorectal Cancer. Cancer J. 2009, 15, 110–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voigt, M.; Braig, F.; Göthel, M.; Schulte, A.; Lamszus, K.; Bokemeyer, C.; Binder, M. Functional Dissection of the Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor Epitopes Targeted by Panitumumab and Cetuximab. Neoplasia 2012, 14, 1023–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, G.P.; Grothey, A. Targeting Colorectal Cancer with Human Anti-EGFR Monoclonocal Antibodies: Focus on Panitumumab. Biologics 2008, 2, 223–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.D.; Jia, X.C.; Corvalan, J.R.; Wang, P.; Davis, C.G.; Jakobovits, A. Eradication of Established Tumors by a Fully Human Monoclonal Antibody to the Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor without Concomitant Chemotherapy. Cancer Res. 1999, 59, 1236–1243. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, X.D.; Jia, X.C.; Corvalan, J.R.; Wang, P.; Davis, C.G. Development of ABX-EGF, a Fully Human Anti-EGF Receptor Monoclonal Antibody, for Cancer Therapy. Crit. Rev. Oncol. Hematol. 2001, 38, 17–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Cutsem, E.; Peeters, M.; Siena, S.; Humblet, Y.; Hendlisz, A.; Neyns, B.; Canon, J.-L.; Van Laethem, J.-L.; Maurel, J.; Richardson, G.; et al. Open-Label Phase III Trial of Panitumumab plus Best Supportive Care Compared with Best Supportive Care Alone in Patients with Chemotherapy-Refractory Metastatic Colorectal Cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2007, 25, 1658–1664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Douillard, J.-Y.; Siena, S.; Cassidy, J.; Tabernero, J.; Burkes, R.; Barugel, M.; Humblet, Y.; Bodoky, G.; Cunningham, D.; Jassem, J.; et al. Randomized, Phase III Trial of Panitumumab with Infusional Fluorouracil, Leucovorin, and Oxaliplatin (FOLFOX4) versus FOLFOX4 Alone as First-Line Treatment in Patients with Previously Untreated Metastatic Colorectal Cancer: The PRIME Study. J. Clin. Oncol. 2010, 28, 4697–4705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Battaglin, F.; Puccini, A.; Ahcene Djaballah, S.; Lenz, H.-J. The Impact of Panitumumab Treatment on Survival and Quality of Life in Patients with RAS Wild-Type Metastatic Colorectal Cancer. Cancer Manag. Res. 2019, 11, 5911–5924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fala, L. Portrazza (Necitumumab), an IgG1 Monoclonal Antibody, FDA Approved for Advanced Squamous Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer. Am. Health Drug Benefits 2016, 9, 119–122. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lu, D.; Zhang, H.; Koo, H.; Tonra, J.; Balderes, P.; Prewett, M.; Corcoran, E.; Mangalampalli, V.; Bassi, R.; Anselma, D.; et al. A Fully Human Recombinant IgG-like Bispecific Antibody to Both the Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor and the Insulin-like Growth Factor Receptor for Enhanced Antitumor Activity. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 19665–19672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuenen, B.; Witteveen, P.O.; Ruijter, R.; Giaccone, G.; Dontabhaktuni, A.; Fox, F.; Katz, T.; Youssoufian, H.; Zhu, J.; Rowinsky, E.K.; et al. A Phase I Pharmacologic Study of Necitumumab (IMC-11F8), a Fully Human IgG1 Monoclonal Antibody Directed Against EGFR in Patients with Advanced Solid Malignancies. Clin. Cancer Res. 2010, 16, 1915–1923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Samakoglu, S.; Deevi, D.S.; Li, H.; Wang, S.; Murphy, M.; Bao, C.; Bassi, R.; Prewett, M.; Tonra, J.R. Preclinical Rationale for Combining an EGFR Antibody with Cisplatin/Gemcitabine for the Treatment of NSCLC. Cancer Genom. Proteom. 2012, 9, 77–92. [Google Scholar]
- Thatcher, N.; Hirsch, F.R.; Luft, A.V.; Szczesna, A.; Ciuleanu, T.E.; Dediu, M.; Ramlau, R.; Galiulin, R.K.; Bálint, B.; Losonczy, G.; et al. Necitumumab plus Gemcitabine and Cisplatin versus Gemcitabine and Cisplatin Alone as First-Line Therapy in Patients with Stage IV Squamous Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer (SQUIRE): An Open-Label, Randomised, Controlled Phase 3 Trial. Lancet Oncol. 2015, 16, 763–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- di Noia, V.; D’Argento, E.; Pilotto, S.; Grizzi, G.; Caccese, M.; Iacovelli, R.; Tortora, G.; Bria, E. Necitumumab in the Treatment of Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer: Clinical Controversies. Expert. Opin. Biol. Ther. 2018, 18, 937–945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pirker, R. Third-Generation Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors in Advanced Nonsmall Cell Lung Cancer. Curr. Opin. Oncol. 2016, 28, 115–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niederst, M.J.; Hu, H.; Mulvey, H.E.; Lockerman, E.L.; Garcia, A.R.; Piotrowska, Z.; Sequist, L.V.; Engelman, J.A. The Allelic Context of the C797S Mutation Acquired upon Treatment with Third-Generation EGFR Inhibitors Impacts Sensitivity to Subsequent Treatment Strategies. Clin. Cancer Res. 2015, 21, 3924–3933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Mashock, M.; Tong, Z.; Mu, X.; Chen, H.; Zhou, X.; Zhang, H.; Zhao, G.; Liu, B.; Li, X. Changing Technologies of RNA Sequencing and Their Applications in Clinical Oncology. Front. Oncol. 2020, 10, 447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tkachev, V.; Sorokin, M.; Garazha, A.; Borisov, N.; Buzdin, A. Oncobox Method for Scoring Efficiencies of Anticancer Drugs Based on Gene Expression Data. Methods Mol. Biol. 2020, 2063, 235–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sorokin, M.; Zolotovskaia, M.; Nikitin, D.; Suntsova, M.; Poddubskaya, E.; Glusker, A.; Garazha, A.; Moisseev, A.; Li, X.; Sekacheva, M.; et al. Personalized Targeted Therapy Prescription in Colorectal Cancer Using Algorithmic Analysis of RNA Sequencing Data. BMC Cancer 2022, 22, 1113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Q.; Izumchenko, E.; Aliper, A.M.; Makarev, E.; Paz, K.; Buzdin, A.A.; Zhavoronkov, A.A.; Sidransky, D. Pathway Activation Strength Is a Novel Independent Prognostic Biomarker for Cetuximab Sensitivity in Colorectal Cancer Patients. Hum. Genome Var. 2015, 2, 15009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Drug | Tumor Type | Therapeutic Indication | Molecular Target | Inhibitor Type | Molecular Markers of Efficiency |
| First Generation | |||||
| Gefitinib | Advanced or metastatic NSCLC | First-line therapy for NSCLC carrying EGFR-activating mutations | EGFR: ATP-binding site | I | Activating mutations of EGFR: Exon 19 deletions; L858R |
| Erlotinib | Advanced or metastatic NSCLC, pancreatic cancer | First-line therapy for NSCLC carrying EGFR-activating mutations With gemcitabine: first-line treatment option for patients with locally advanced and metastatic pancreatic carcinoma | EGFR: ATP-binding site | I | Activating mutations of EGFR: Exon 19 deletions; L858R |
| Lapatinib | Metastatic breast cancer | With capecitabine: the treatment of HER2-positive MBC in patients who have previously received therapy (anthracycline, a taxane, trastuzumab) With letrozole: the treatment of postmenopausal women with hormone receptor positive MBC that overexpresses the HER2 receptor for whom hormonal therapy is indicated | ATP-binding site of EGFR and HER2 | I½ | HER2-positive status of tumor |
| Second Generation | |||||
| Afatinib | Metastatic NSCLC | First-line therapy for metastatic NSCLC carrying EGFR-activating mutations | ATP-binding site of EGFR, HER2, and HER4 | IV | Activating mutations of EGFR: Exon 19 deletions; L858R |
| Neratinib | Breast cancer | Extended adjuvant treatment of patients with early stage HER2-positive breast cancer, to follow adjuvant trastuzumab based therapy With capecitabine: the treatment of patients with advanced or metastatic HER2-positive BC who have received two or more prior anti-HER2 based regimens in the metastatic setting | ATP-binding site of EGFR, HER2, and HER4 | IV | HER2-positive status of tumor |
| Dacomitinib | Metastatic NSCLC | First-line therapy for metastatic NSCLC carrying EGFR-activating mutations | ATP-binding site of EGFR, HER2, and HER4 | IV | Activating mutations of EGFR: Exon 19 deletions; L858R |
| Third Generation | |||||
| Osimertinib | Advanced or metastatic NSCLC | Adjuvant and first-line therapy for metastatic NSCLC carrying EGFR-activating mutations The treatment of adult patients with metastatic EGFR T790M mutation-positive NSCLC, whose disease has progressed on or after EGFR TKI therapy | ATP-binding site of the EGFR | IV | Activating mutations of EGFR: Exon 19 deletions; L858R The secondary T790M resistance mutation |
| Almonertinib | Advanced NSCLC | Adjuvant therapy for advanced NSCLC patients with T790M-mutant EGFR who had developed resistance to first- and second-generation EGFR TKIs like gefitinib and afatinib | ATP-binding site of the EGFR | IV | Activating mutations of EGFR: Exon 19 deletions; L858R The secondary T790M resistance mutation |
| Lazertinib | Advanced NSCLC | Treatment of locally advanced or metastatic NSCLC carrying EGFR T790M mutation | ATP-binding site of the EGFR | IV | Activating mutations of EGFR: Exon 19 deletions; L858R The secondary T790M resistance mutation |
| Furmonertinib | Locally advanced or metastatic NSCLC | Treatment of locally advanced or metastatic EGFR T790M+ NSCLC that developed after progression on treatment with first-generation EGFR TKIs | ATP-binding site of the EGFR | The secondary T790M resistance mutation | |
| Monoclonal Antibodies | |||||
| Drug | Tumor Type | Therapeutic Indication | Molecular Target | Molecular Markers of Efficiency | |
| Cetuximab | Advanced or metastatic SCCHN, metastatic CRC | With radiation therapy: treatment of locally or regionally advanced SCCHN With platinum-based therapy with fluorouracil: metastatic SCCHN Metastatic SCCHN progressing after platinum-based therapy With FOLFIRI: first-line treatment of KRASwt EGFR-overexpressing mCRC With irinotecan in patients who are refractory to irinotecan-based chemotherapy: treatment of KRASwt EGFR-overexpressing mCRC; as a single-agent in patients who have failed oxaliplatin-and irinotecan-based chemotherapy or who are intolerant to irinotecan | The binding site in domain III of EGFR | KRAS wild-type status of EGFR-overexpressing tumor | |
| Panitumumab | Metastatic CRC | Single agent treatment of metastatic CRC with disease progression on or following fluoropyrimidine, oxaliplatin, and irinotecan chemotherapy regimens | The binding site in domain III of EGFR | RAS wild-type status of EGFR-overexpressing tumor | |
| Necitumumab | Metastatic NSCLC | With gemcitabine and cisplatin: first-line treatment of patients with metastatic NSCLC | The binding site in domain III of EGFR | EGFR-overexpressing status of tumor | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shaban, N.; Kamashev, D.; Emelianova, A.; Buzdin, A. Targeted Inhibitors of EGFR: Structure, Biology, Biomarkers, and Clinical Applications. Cells 2024, 13, 47. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells13010047
Shaban N, Kamashev D, Emelianova A, Buzdin A. Targeted Inhibitors of EGFR: Structure, Biology, Biomarkers, and Clinical Applications. Cells. 2024; 13(1):47. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells13010047
Chicago/Turabian StyleShaban, Nina, Dmitri Kamashev, Aleksandra Emelianova, and Anton Buzdin. 2024. "Targeted Inhibitors of EGFR: Structure, Biology, Biomarkers, and Clinical Applications" Cells 13, no. 1: 47. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells13010047
APA StyleShaban, N., Kamashev, D., Emelianova, A., & Buzdin, A. (2024). Targeted Inhibitors of EGFR: Structure, Biology, Biomarkers, and Clinical Applications. Cells, 13(1), 47. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells13010047







