A Focus on the Pathophysiology of Adrenomedullin Expression: Endothelitis and Organ Damage in Severe Viral and Bacterial Infections
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Physiology of Adrenomedullin
3. Adrenomedullin and Mid-Regional Pro-Adrenomedullin
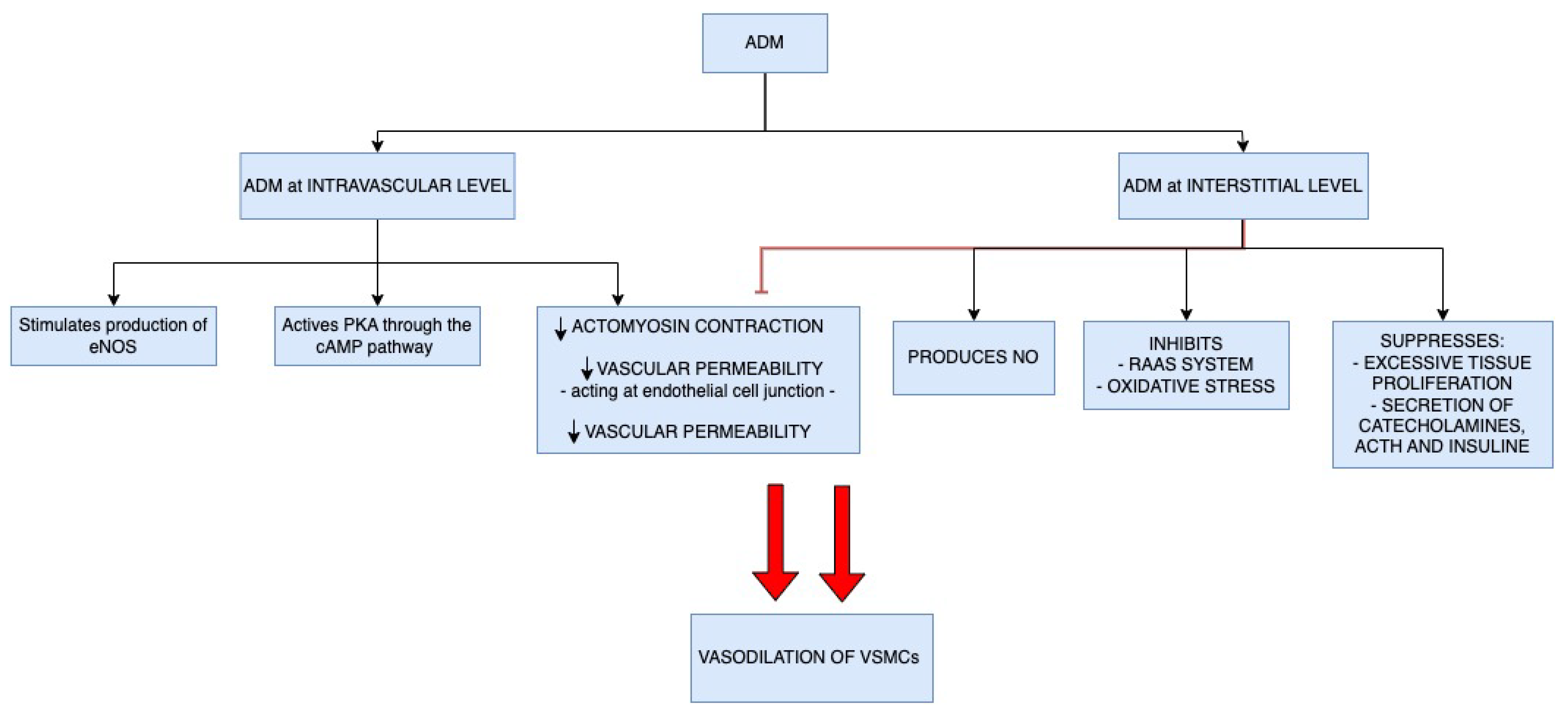
4. Adrenomedullin Physiologic Functions
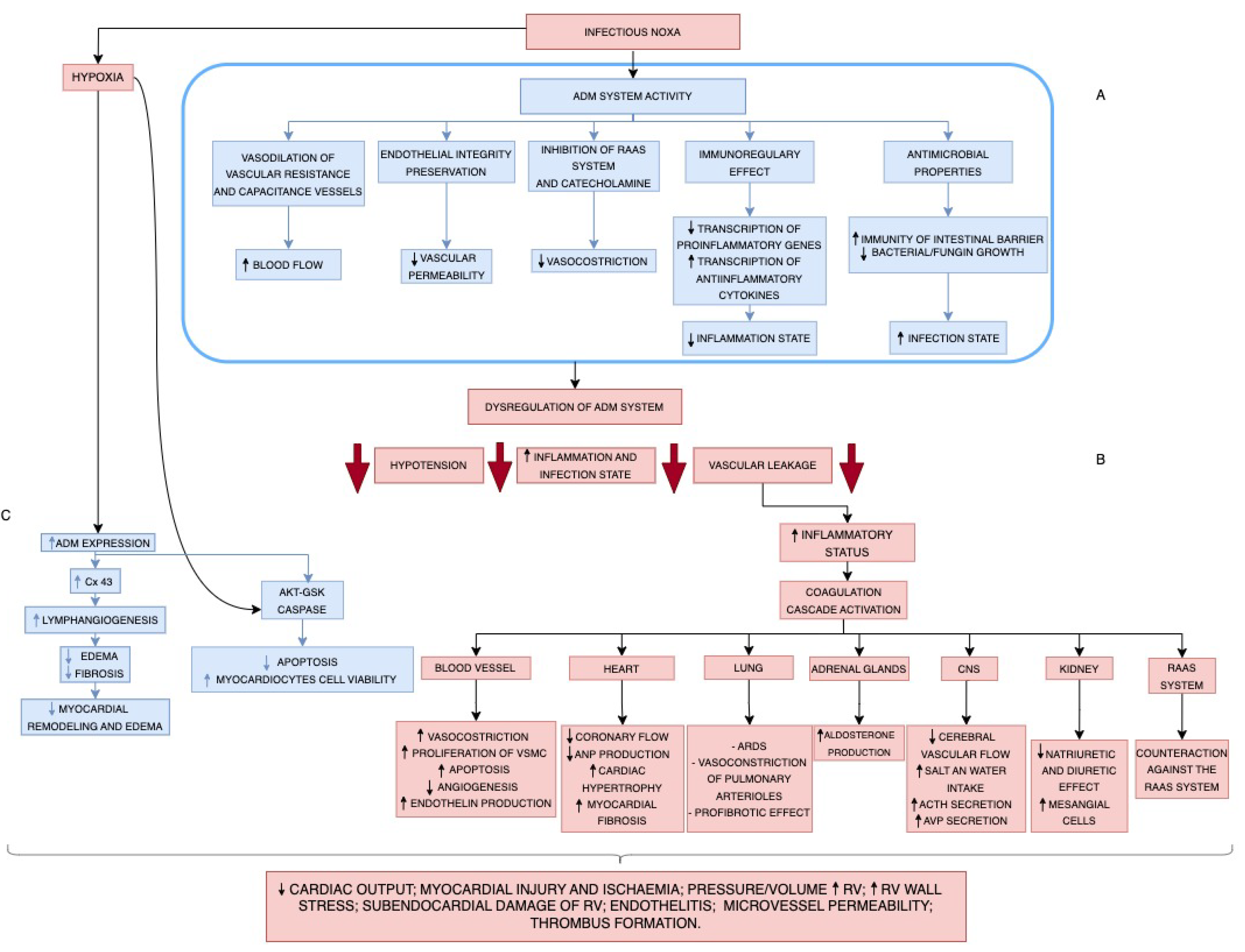
5. Pathophysiology of Endothelitis: Adrenomedullin Expression
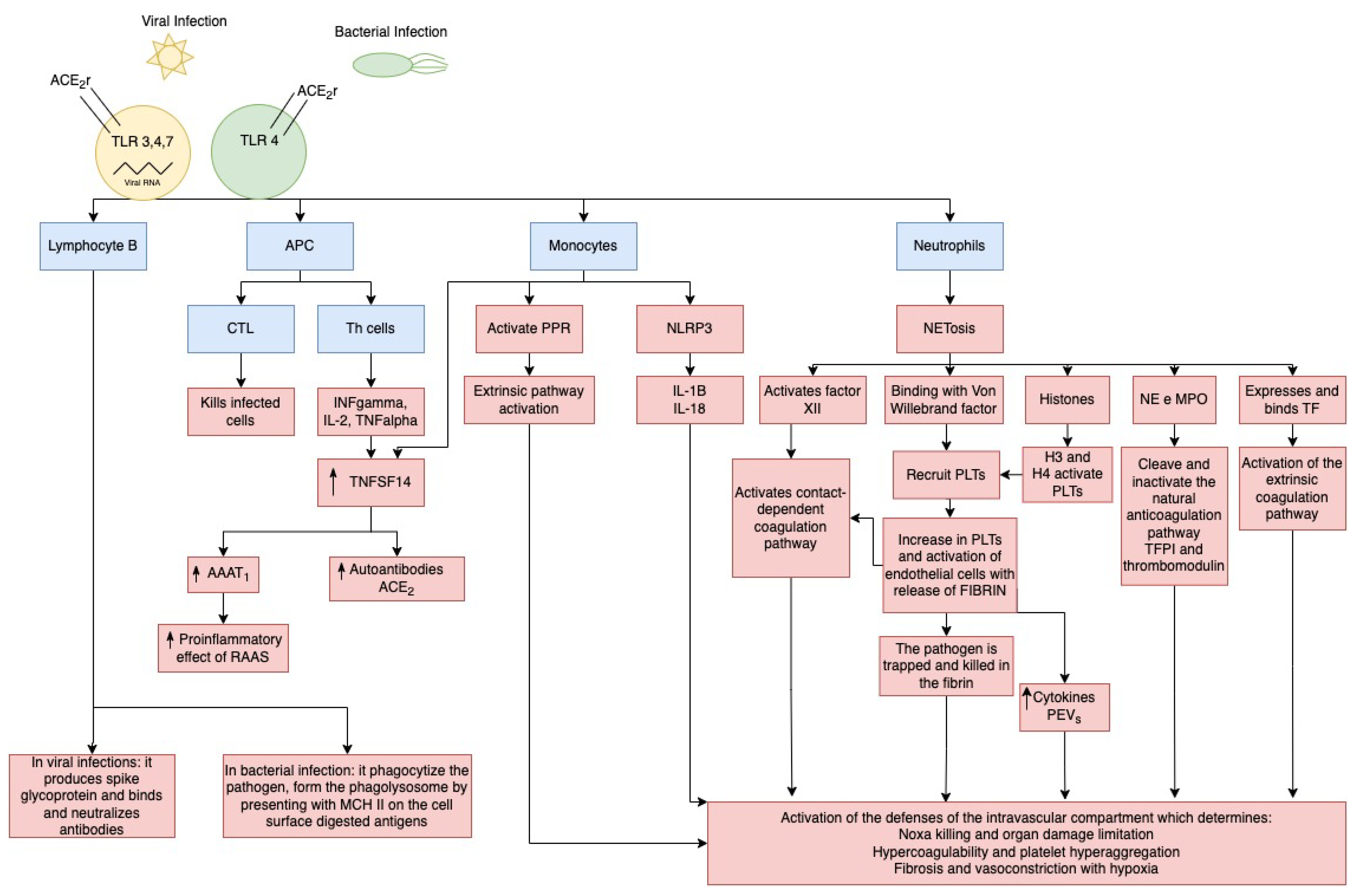
6. Pathophysiology of Severe Viral and Bacterial Infections and the Immune Modulation in the Intravascular Compartment
7. Pathophysiology of Severe Viral and Bacterial Infections on Endothelial Cells: Endothelitis and ADM Expression
8. Role of Adrenomedullin Expression in Severe Viral and Bacterial Pneumonia
9. Role of Adrenomedullin Expression in Infective Acute Cardiac Injury
10. Role of Adrenomedullin in Organ Damage and Patients’ Prognosis
11. Role of New Experimental Endothelial Barrier Stabilization Drugs Affecting ADM Expression
12. Concluding Remarks and Future Perspectives
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- Hellenthal, K.E.M.; Brabenec, L.; Wagner, N.-M. Regulation and Dysregulation of Endothelial Permeability during Systemic Inflammation. Cells 2022, 11, 1935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Czyzyk, T.A.; Ning, Y.; Hsu, M.-S.; Peng, B.; Mains, R.E.; Eipper, B.A.; Pintar, J.E. Deletion of Peptide Amidation Enzymatic Activity Leads to Edema and Embryonic Lethality in the Mouse. Dev. Biol. 2005, 287, 301–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Temmesfeld-Wollbrück, B.; Brell, B.; Dávid, I.; Dorenberg, M.; Adolphs, J.; Schmeck, B.; Suttorp, N.; Hippenstiel, S. Adrenomedullin Reduces Vascular Hyperpermeability and Improves Survival in Rat Septic Shock. Intensive Care Med. 2007, 33, 703–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Temmesfeld-Wollbrück, B.; Hocke, A.C.; Suttorp, N.; Hippenstiel, S. Adrenomedullin and Endothelial Barrier Function. Thromb. Haemost. 2007, 98, 944–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kita, T.; Kitamura, K. Translational Studies of Adrenomedullin and Related Peptides Regarding Cardiovascular Diseases. Hypertens. Res. 2022, 45, 389–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, P.; Shindo, T.; Iwata, H.; Ebihara, A.; Suematsu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Takeda, N.; Iimuro, S.; Hirata, Y.; Nagai, R. Accelerated Cardiac Hypertrophy and Renal Damage Induced by Angiotensin II in Adrenomedullin Knockout Mice. Hypertens. Res. 2003, 26, 731–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meens, M.J.; Kwak, B.R.; Duffy, H.S. Role of Connexins and Pannexins in Cardiovascular Physiology. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2015, 72, 2779–2792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montrucchio, G.; Sales, G.; Rumbolo, F.; Palmesino, F.; Fanelli, V.; Urbino, R.; Filippini, C.; Mengozzi, G.; Brazzi, L. Effectiveness of Mid-Regional pro-Adrenomedullin (MR-proADM) as Prognostic Marker in COVID-19 Critically Ill Patients: An Observational Prospective Study. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0246771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Voors, A.A.; Kremer, D.; Geven, C.; Ter Maaten, J.M.; Struck, J.; Bergmann, A.; Pickkers, P.; Metra, M.; Mebazaa, A.; Düngen, H.-D.; et al. Adrenomedullin in Heart Failure: Pathophysiology and Therapeutic Application. Eur. J. Heart Fail. 2019, 21, 163–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geven, C.; Kox, M.; Pickkers, P. Adrenomedullin and Adrenomedullin-Targeted Therapy As Treatment Strategies Relevant for Sepsis. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allaker, R.P.; Grosvenor, P.W.; McAnerney, D.C.; Sheehan, B.E.; Srikanta, B.H.; Pell, K.; Kapas, S. Mechanisms of Adrenomedullin Antimicrobial Action. Peptides 2006, 27, 661–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iring, A.; Jin, Y.-J.; Albarrán-Juárez, J.; Siragusa, M.; Wang, S.; Dancs, P.T.; Nakayama, A.; Tonack, S.; Chen, M.; Künne, C.; et al. Shear Stress-Induced Endothelial Adrenomedullin Signaling Regulates Vascular Tone and Blood Pressure. J. Clin. Investig. 2019, 129, 2775–2791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, P.; Shindo, T.; Iwata, H.; Iimuro, S.; Takeda, N.; Zhang, Y.; Ebihara, A.; Suematsu, Y.; Kangawa, K.; Hirata, Y.; et al. Protective Effects of Endogenous Adrenomedullin on Cardiac Hypertrophy, Fibrosis, and Renal Damage. Circulation 2004, 109, 1789–1794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spoto, S.; Agrò, F.E.; Sambuco, F.; Travaglino, F.; Valeriani, E.; Fogolari, M.; Mangiacapra, F.; Costantino, S.; Ciccozzi, M.; Angeletti, S. High Value of Mid-Regional Proadrenomedullin in COVID-19: A Marker of Widespread Endothelial Damage, Disease Severity, and Mortality. J. Med. Virol. 2021, 93, 2820–2827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheung, B.M.Y.; Tang, F. Adrenomedullin: Exciting New Horizons. Recent Pat. Endocr. Metab. Immune Drug Discov. 2012, 6, 4–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, F.A.; Spencer, F.A. Risk Factors for Venous Thromboembolism. Circulation 2003, 107, I9–I16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Porfidia, A.; Valeriani, E.; Pola, R.; Porreca, E.; Rutjes, A.W.S.; Di Nisio, M. Venous Thromboembolism in Patients with COVID-19: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Thromb. Res. 2020, 196, 67–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spoto, S.; Valeriani, E.; Caputo, D.; Cella, E.; Fogolari, M.; Pesce, E.; Mulè, M.T.; Cartillone, M.; Costantino, S.; Dicuonzo, G.; et al. The Role of Procalcitonin in the Diagnosis of Bacterial Infection after Major Abdominal Surgery: Advantage from Daily Measurement. Medicine 2018, 97, e9496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrés, C.; Andaluz-Ojeda, D.; Cicuendez, R.; Nogales, L.; Martín, S.; Martin-Fernandez, M.; Almansa, R.; Calvo, D.; Esteban-Velasco, M.C.; Vaquero-Roncero, L.M.; et al. MR- proADM to Detect Specific Types of Organ Failure in Infection. Eur. J. Clin. Investig. 2020, 50, e13246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valenzuela-Sánchez, F.; Valenzuela-Méndez, B.; Bohollo de Austria, R.; Rodríguez-Gutiérrez, J.F.; Estella-García, Á.; Fernández-Ruiz, L.; González-García, M.Á.; Rello, J. Plasma Levels of Mid-Regional pro-Adrenomedullin in Sepsis Are Associated with Risk of Death. Minerva Anestesiol. 2019, 85, 366–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montrucchio, G.; Balzani, E.; Lombardo, D.; Giaccone, A.; Vaninetti, A.; D’Antonio, G.; Rumbolo, F.; Mengozzi, G.; Brazzi, L. Proadrenomedullin in the Management of COVID-19 Critically Ill Patients in Intensive Care Unit: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Evidence and Uncertainties in Existing Literature. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 4543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sozio, E.; Tascini, C.; Fabris, M.; D’Aurizio, F.; De Carlo, C.; Graziano, E.; Bassi, F.; Sbrana, F.; Ripoli, A.; Pagotto, A.; et al. MR-proADM as Prognostic Factor of Outcome in COVID-19 Patients. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 5121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ince, C.; Mayeux, P.R.; Nguyen, T.; Gomez, H.; Kellum, J.A.; Ospina-Tascón, G.A.; Hernandez, G.; Murray, P.; De Backer, D.; ADQI XIV Workgroup. The Endothelium in Sepsis. Shock 2016, 45, 259–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Churpek, M.M.; Snyder, A.; Han, X.; Sokol, S.; Pettit, N.; Howell, M.D.; Edelson, D.P. Quick Sepsis-Related Organ Failure Assessment, Systemic Inflammatory Response Syndrome, and Early Warning Scores for Detecting Clinical Deterioration in Infected Patients Outside the Intensive Care Unit. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2017, 195, 906–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baldirà, J.; Ruiz-Rodríguez, J.C.; Wilson, D.C.; Ruiz-Sanmartin, A.; Cortes, A.; Chiscano, L.; Ferrer-Costa, R.; Comas, I.; Larrosa, N.; Fàbrega, A.; et al. Biomarkers and Clinical Scores to Aid the Identification of Disease Severity and Intensive Care Requirement Following Activation of an In-Hospital Sepsis Code. Ann. Intensive Care 2020, 10, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bell, D.; Campbell, M.; McAleer, S.F.; Ferguson, M.; Donaghy, L.; Harbinson, M.T. Endothelium-Derived Intermedin/Adrenomedullin-2 Protects Human Ventricular Cardiomyocytes from Ischaemia-Reoxygenation Injury Predominantly via the AM1 Receptor. Peptides 2016, 76, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kubo, A.; Minamino, N.; Isumi, Y.; Kangawa, K.; Dohi, K.; Matsuo, H. Adrenomedullin Production Is Correlated with Differentiation in Human Leukemia Cell Lines and Peripheral Blood Monocytes. FEBS Lett. 1998, 426, 233–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montrucchio, G.; Sales, G.; Balzani, E.; Lombardo, D.; Giaccone, A.; Cantù, G.; D’Antonio, G.; Rumbolo, F.; Corcione, S.; Simonetti, U.; et al. Effectiveness of Mid-Regional pro-Adrenomedullin, Compared to Other Biomarkers (Including Lymphocyte Subpopulations and Immunoglobulins), as a Prognostic Biomarker in COVID-19 Critically Ill Patients: New Evidence from a 15-Month Observational Prospective Study. Front. Med. 2023, 10, 1122367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Önal, U.; Valenzuela-Sánchez, F.; Vandana, K.E.; Rello, J. Mid-Regional Pro-Adrenomedullin (MR-proADM) as a Biomarker for Sepsis and Septic Shock: Narrative Review. Healthcare 2018, 6, 110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valenzuela Sanchez, F.; Valenzuela Mendez, B.; Rodríguez Gutierrez, J.; Bohollo de Austria, R.; Rubio Quiñones, J.; Puget Martínez, L.; Valiente Alemán, I.; Estella García, A. Initial Levels of Mr-Proadrenomedullin: A Predictor of Severity in Patients with Influenza a Virus Pneumonia. Intensive Care Med. Exp. 2015, 3, A832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valenzuela-Sánchez, F.; Valenzuela-Méndez, B.; Rodríguez-Gutiérrez, J.F.; Rello, J. Personalized Medicine in Severe Influenza. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2016, 35, 893–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guignant, C.; Voirin, N.; Venet, F.; Lepape, A.; Monneret, G. Persistent High Level of Circulating Midregional-Proadrenomedullin and Increased Risk of Nosocomial Infections after Septic Shock. J. Trauma Acute Care Surg. 2012, 72, 293–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Angeletti, S.; Spoto, S.; Fogolari, M.; Cortigiani, M.; Fioravanti, M.; De Florio, L.; Curcio, B.; Cavalieri, D.; Costantino, S.; Dicuonzo, G. Diagnostic and Prognostic Role of Procalcitonin (PCT) and MR-pro-Adrenomedullin (MR-proADM) in Bacterial Infections. APMIS 2015, 123, 740–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murray, C.J.L.; Ikuta, K.S.; Sharara, F.; Swetschinski, L.; Aguilar, G.R.; Gray, A.; Han, C.; Bisignano, C.; Rao, P.; Wool, E.; et al. Global Burden of Bacterial Antimicrobial Resistance in 2019: A Systematic Analysis. Lancet 2022, 399, 629–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morgenthaler, N.G.; Struck, J.; Alonso, C.; Bergmann, A. Measurement of Midregional Proadrenomedullin in Plasma with an Immunoluminometric Assay. Clin. Chem. 2005, 51, 1823–1829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thompson, W.W.; Weintraub, E.; Dhankhar, P.; Cheng, P.-Y.; Brammer, L.; Meltzer, M.I.; Bresee, J.S.; Shay, D.K. Estimates of US Influenza-Associated Deaths Made Using Four Different Methods. Influenza Other Respir. Viruses 2009, 3, 37–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nair, H.; Brooks, W.A.; Katz, M.; Roca, A.; Berkley, J.A.; Madhi, S.A.; Simmerman, J.M.; Gordon, A.; Sato, M.; Howie, S.; et al. Global Burden of Respiratory Infections Due to Seasonal Influenza in Young Children: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Lancet 2011, 378, 1917–1930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- COVID-19 Epidemiological Update—22 December 2023. Available online: https://www.who.int/publications/m/item/covid-19-epidemiological-update---22-december-2023 (accessed on 9 February 2024).
- Fleischmann, C.; Scherag, A.; Adhikari, N.K.J.; Hartog, C.S.; Tsaganos, T.; Schlattmann, P.; Angus, D.C.; Reinhart, K.; International Forum of Acute Care Trialists. Assessment of Global Incidence and Mortality of Hospital-Treated Sepsis. Current Estimates and Limitations. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2016, 193, 259–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kallen, A.J.; Brunkard, J.; Moore, Z.; Budge, P.; Arnold, K.E.; Fosheim, G.; Finelli, L.; Beekmann, S.E.; Polgreen, P.M.; Gorwitz, R.; et al. Staphylococcus Aureus Community-Acquired Pneumonia during the 2006 to 2007 Influenza Season. Ann. Emerg. Med. 2009, 53, 358–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitamura, K.; Kangawa, K.; Kawamoto, M.; Ichiki, Y.; Nakamura, S.; Matsuo, H.; Eto, T. Adrenomedullin: A Novel Hypotensive Peptide Isolated from Human Pheochromocytoma. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1993, 192, 553–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jougasaki, M.; Burnett, J.C. Adrenomedullin: Potential in Physiology and Pathophysiology. Life Sci. 2000, 66, 855–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sugo, S.; Minamino, N.; Kangawa, K.; Miyamoto, K.; Kitamura, K.; Sakata, J.; Eto, T.; Matsuo, H. Endothelial Cells Actively Synthesize and Secrete Adrenomedullin. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1994, 201, 1160–1166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sugo, S.; Minamino, N.; Shoji, H.; Kangawa, K.; Kitamura, K.; Eto, T.; Matsuo, H. Production and Secretion of Adrenomedullin from Vascular Smooth Muscle Cells: Augmented Production by Tumor Necrosis Factor-Alpha. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1994, 203, 719–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pierrakos, C.; Vincent, J.-L. Sepsis Biomarkers: A Review. Crit. Care 2010, 14, R15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- LaRosa, S.P.; Opal, S.M. Biomarkers: The Future. Crit. Care Clin. 2011, 27, 407–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kitamura, K.; Sakata, J.; Kangawa, K.; Kojima, M.; Matsuo, H.; Eto, T. Cloning and Characterization of cDNA Encoding a Precursor for Human Adrenomedullin. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1993, 194, 720–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ishimitsu, T.; Kojima, M.; Kangawa, K.; Hino, J.; Matsuoka, H.; Kitamura, K.; Eto, T.; Matsuo, H. Genomic Structure of Human Adrenomedullin Gene. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1994, 203, 631–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brell, B.; Temmesfeld-Wollbrück, B.; Altzschner, I.; Frisch, E.; Schmeck, B.; Hocke, A.C.; Suttorp, N.; Hippenstiel, S. Adrenomedullin Reduces Staphylococcus Aureus Alpha-Toxin-Induced Rat Ileum Microcirculatory Damage. Crit. Care Med. 2005, 33, 819–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allaker, R.P.; Zihni, C.; Kapas, S. An Investigation into the Antimicrobial Effects of Adrenomedullin on Members of the Skin, Oral, Respiratory Tract and Gut Microflora. FEMS Immunol. Med. Microbiol. 1999, 23, 289–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez, A.; Garayoa, M.; Pío, R.; Miller, M.J.; Cuttitta, F. Adrenomedullin: A new peptide with many clinical implications. An. Sist. Sanit. Navar. 1999, 22, 307–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pugin, J. Adrenomedullin: A Vasodilator to Treat Sepsis? Crit. Care 2014, 18, 152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lacquaniti, A.; Ceresa, F.; Campo, S.; Barbera, G.; Caruso, D.; Palazzo, E.; Patanè, F.; Monardo, P. Acute Kidney Injury and Sepsis after Cardiac Surgery: The Roles of Tissue Inhibitor Metalloproteinase-2, Insulin-like Growth Factor Binding Protein-7, and Mid-Regional Pro-Adrenomedullin. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 5193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, W.; Jiang, W.; Yao, J.; Nicholson, C.J.; Li, R.H.; Sigurslid, H.H.; Wooster, L.; Rotter, J.I.; Guo, X.; Malhotra, R. Predictors of Mortality in Hospitalized COVID-19 Patients: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Med. Virol. 2020, 92, 1875–1883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- García de Guadiana-Romualdo, L.; Martínez Martínez, M.; Rodríguez Mulero, M.D.; Esteban-Torrella, P.; Hernández Olivo, M.; Alcaraz García, M.J.; Campos-Rodríguez, V.; Sancho-Rodríguez, N.; Galindo Martínez, M.; Alcaraz, A.; et al. Circulating MR-proADM Levels, as an Indicator of Endothelial Dysfunction, for Early Risk Stratification of Mid-Term Mortality in COVID-19 Patients. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2021, 111, 211–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spoto, S.; Nobile, E.; Carnà, E.P.R.; Fogolari, M.; Caputo, D.; De Florio, L.; Valeriani, E.; Benvenuto, D.; Costantino, S.; Ciccozzi, M.; et al. Best Diagnostic Accuracy of Sepsis Combining SIRS Criteria or qSOFA Score with Procalcitonin and Mid-Regional pro-Adrenomedullin Outside ICU. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 16605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Linscheid, P.; Seboek, D.; Zulewski, H.; Keller, U.; Müller, B. Autocrine/Paracrine Role of Inflammation-Mediated Calcitonin Gene-Related Peptide and Adrenomedullin Expression in Human Adipose Tissue. Endocrinology 2005, 146, 2699–2708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hinson, J.P.; Kapas, S.; Smith, D.M. Adrenomedullin, a Multifunctional Regulatory Peptide. Endocr. Rev. 2000, 21, 138–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kubo, A.; Minamino, N.; Isumi, Y.; Katafuchi, T.; Kangawa, K.; Dohi, K.; Matsuo, H. Production of Adrenomedullin in Macrophage Cell Line and Peritoneal Macrophage. J. Biol. Chem. 1998, 273, 16730–16738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sugo, S.; Minamino, N.; Shoji, H.; Kangawa, K.; Kitamura, K.; Eto, T.; Matsuo, H. Interleukin-1, Tumor Necrosis Factor and Lipopolysaccharide Additively Stimulate Production of Adrenomedullin in Vascular Smooth Muscle Cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1995, 207, 25–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coppock, H.A.; Owji, A.A.; Bloom, S.R.; Smith, D.M. A Rat Skeletal Muscle Cell Line (L6) Expresses Specific Adrenomedullin Binding Sites but Activates Adenylate Cyclase via Calcitonin Gene-Related Peptide Receptors. Biochem. J. 1996, 318 Pt 1, 241–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Owji, A.A.; Smith, D.M.; Coppock, H.A.; Morgan, D.G.; Bhogal, R.; Ghatei, M.A.; Bloom, S.R. An Abundant and Specific Binding Site for the Novel Vasodilator Adrenomedullin in the Rat. Endocrinology 1995, 136, 2127–2134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, H.; Minami, S.; Yamamoto, R.; Masumoto, K.; Yanagita, T.; Uezono, Y.; Tsuchiya, K.; Mohri, M.; Kitamura, K.; Eto, T.; et al. Adrenomedullin Receptors in Rat Cerebral Microvessels. Brain Res. Mol. Brain Res. 2000, 81, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, H.; Shiraishi, S.; Minami, S.; Yokoo, H.; Yanagita, T.; Saitoh, T.; Mohri, M.; Wada, A. Adrenomedullin Receptors in Rat Choroid Plexus. Neurosci. Lett. 2001, 297, 167–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Passaglia, P.; Gonzaga, N.A.; Tirapelli, D.P.C.; Tirapelli, L.F.; Tirapelli, C.R. Pharmacological Characterisation of the Mechanisms Underlying the Relaxant Effect of Adrenomedullin in the Rat Carotid Artery. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2014, 66, 1734–1746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamauchi, A.; Sakurai, T.; Kamiyoshi, A.; Ichikawa-Shindo, Y.; Kawate, H.; Igarashi, K.; Toriyama, Y.; Tanaka, M.; Liu, T.; Xian, X.; et al. Functional Differentiation of RAMP2 and RAMP3 in Their Regulation of the Vascular System. J. Mol. Cell. Cardiol. 2014, 77, 73–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, D.M.; Coppock, H.A.; Withers, D.J.; Owji, A.A.; Hay, D.L.; Choksi, T.P.; Chakravarty, P.; Legon, S.; Poyner, D.R. Adrenomedullin: Receptor and Signal Transduction. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 2002, 30, 432–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuwasako, K.; Kitamura, K.; Nagata, S.; Hikosaka, T.; Takei, Y.; Kato, J. Shared and Separate Functions of the RAMP-Based Adrenomedullin Receptors. Peptides 2011, 32, 1540–1550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishimatsu, H.; Suzuki, E.; Nagata, D.; Moriyama, N.; Satonaka, H.; Walsh, K.; Sata, M.; Kangawa, K.; Matsuo, H.; Goto, A.; et al. Adrenomedullin Induces Endothelium-Dependent Vasorelaxation via the Phosphatidylinositol 3-Kinase/Akt–Dependent Pathway in Rat Aorta. Circ. Res. 2001, 89, 63–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshimoto, R.; Mitsui-Saito, M.; Ozaki, H.; Karaki, H. Effects of Adrenomedullin and Calcitonin Gene-Related Peptide on Contractions of the Rat Aorta and Porcine Coronary Artery. Br. J. Pharmacol. 1998, 123, 1645–1654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eguchi, S.; Hirata, Y.; Iwasaki, H.; Sato, K.; Watanabe, T.X.; Inui, T.; Nakajima, K.; Sakakibara, S.; Marumo, F. Structure-Activity Relationship of Adrenomedullin, a Novel Vasodilatory Peptide, in Cultured Rat Vascular Smooth Muscle Cells. Endocrinology 1994, 135, 2454–2458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamura, K.; Toda, H.; Terasako, K.; Kakuyama, M.; Hatano, Y.; Mori, K.; Kangawa, K. Vasodilative Effect of Adrenomedullin in Isolated Arteries of the Dog. Jpn. J. Pharmacol. 1995, 67, 259–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimosawa, T.; Shibagaki, Y.; Ishibashi, K.; Kitamura, K.; Kangawa, K.; Kato, S.; Ando, K.; Fujita, T. Adrenomedullin, an Endogenous Peptide, Counteracts Cardiovascular Damage. Circulation 2002, 105, 106–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spoto, S.; Fogolari, M.; De Florio, L.; Minieri, M.; Vicino, G.; Legramante, J.; Lia, M.S.; Terrinoni, A.; Caputo, D.; Costantino, S.; et al. Procalcitonin and MR-proAdrenomedullin Combination in the Etiological Diagnosis and Prognosis of Sepsis and Septic Shock. Microb. Pathog. 2019, 137, 103763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hirata, Y.; Mitaka, C.; Sato, K.; Nagura, T.; Tsunoda, Y.; Amaha, K.; Marumo, F. Increased Circulating Adrenomedullin, a Novel Vasodilatory Peptide, in Sepsis. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 1996, 81, 1449–1453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsuruda, T.; Kato, J.; Kitamura, K.; Kawamoto, M.; Kuwasako, K.; Imamura, T.; Koiwaya, Y.; Tsuji, T.; Kangawa, K.; Eto, T. An Autocrine or a Paracrine Role of Adrenomedullin in Modulating Cardiac Fibroblast Growth. Cardiovasc. Res. 1999, 43, 958–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsuruda, T.; Kato, J.; Kitamura, K.; Kuwasako, K.; Imamura, T.; Koiwaya, Y.; Tsuji, T.; Kangawa, K.; Eto, T. Adrenomedullin: A Possible Autocrine or Paracrine Inhibitor of Hypertrophy of Cardiomyocytes. Hypertension 1998, 31, 505–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsuruda, T.; Kato, J.; Kuwasako, K.; Kitamura, K. Adrenomedullin: Continuing to Explore Cardioprotection. Peptides 2019, 111, 47–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nishikimi, T.; Yoshihara, F.; Mori, Y.; Kangawa, K.; Matsuoka, H. Cardioprotective Effect of Adrenomedullin in Heart Failure. Hypertens. Res. 2003, 26, S121–S127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikeda, U.; Kanbe, T.; Kawahara, Y.; Yokoyama, M.; Shimada, K. Adrenomedullin Augments Inducible Nitric Oxide Synthase Expression in Cytokine-Stimulated Cardiac Myocytes. Circulation 1996, 94, 2560–2565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horio, T.; Nishikimi, T.; Yoshihara, F.; Matsuo, H.; Takishita, S.; Kangawa, K. Effects of Adrenomedullin on Cultured Rat Cardiac Myocytes and Fibroblasts. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 1999, 382, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bell, D.; Campbell, M.; Wang, X.; Earle, J.A.P.; Cosby, S.L.; McDermott, B.J. Adrenomedullin Gene Delivery Is Cardio-Protective in a Model of Chronic Nitric Oxide Deficiency Combining Pressure Overload, Oxidative Stress and Cardiomyocyte Hypertrophy. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2010, 26, 383–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caron, K.M.; Smithies, O. Extreme Hydrops Fetalis and Cardiovascular Abnormalities in Mice Lacking a Functional Adrenomedullin Gene. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2001, 98, 615–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dackor, R.T.; Fritz-Six, K.; Dunworth, W.P.; Gibbons, C.L.; Smithies, O.; Caron, K.M. Hydrops Fetalis, Cardiovascular Defects, and Embryonic Lethality in Mice Lacking the Calcitonin Receptor-like Receptor Gene. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2006, 26, 2511–2518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ter Maaten, J.M.; Kremer, D.; Demissei, B.G.; Struck, J.; Bergmann, A.; Anker, S.D.; Ng, L.L.; Dickstein, K.; Metra, M.; Samani, N.J.; et al. Bio-Adrenomedullin as a Marker of Congestion in Patients with New-Onset and Worsening Heart Failure. Eur. J. Heart Fail. 2019, 21, 732–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arrigo, M.; Parenica, J.; Ganovska, E.; Pavlusova, M.; Mebazaa, A. Plasma Bio-Adrenomedullin Is a Marker of Acute Heart Failure Severity in Patients with Acute Coronary Syndrome. Int. J. Cardiol. Heart Vasc. 2019, 22, 174–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fink, M.P.; Warren, H.S. Strategies to Improve Drug Development for Sepsis. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2014, 13, 741–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shindo, T.; Kurihara, Y.; Nishimatsu, H.; Moriyama, N.; Kakoki, M.; Wang, Y.; Imai, Y.; Ebihara, A.; Kuwaki, T.; Ju, K.H.; et al. Vascular Abnormalities and Elevated Blood Pressure in Mice Lacking Adrenomedullin Gene. Circulation 2001, 104, 1964–1971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ichikawa-Shindo, Y.; Sakurai, T.; Kamiyoshi, A.; Kawate, H.; Iinuma, N.; Yoshizawa, T.; Koyama, T.; Fukuchi, J.; Iimuro, S.; Moriyama, N.; et al. The GPCR Modulator Protein RAMP2 Is Essential for Angiogenesis and Vascular Integrity. J. Clin. Investig. 2008, 118, 29–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fritz-Six, K.L.; Dunworth, W.P.; Li, M.; Caron, K.M. Adrenomedullin Signaling Is Necessary for Murine Lymphatic Vascular Development. J. Clin. Investig. 2008, 118, 40–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klein, K.R.; Caron, K.M. Adrenomedullin in Lymphangiogenesis: From Development to Disease. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2015, 72, 3115–3126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morbach, C.; Marx, A.; Kaspar, M.; Güder, G.; Brenner, S.; Feldmann, C.; Störk, S.; Vollert, J.O.; Ertl, G.; Angermann, C.E.; et al. Prognostic Potential of Midregional Pro-Adrenomedullin Following Decompensation for Systolic Heart Failure: Comparison with Cardiac Natriuretic Peptides. Eur. J. Heart Fail. 2017, 19, 1166–1175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Welsh, P.; Kou, L.; Yu, C.; Anand, I.; van Veldhuisen, D.J.; Maggioni, A.P.; Desai, A.S.; Solomon, S.D.; Pfeffer, M.A.; Cheng, S.; et al. Prognostic Importance of Emerging Cardiac, Inflammatory, and Renal Biomarkers in Chronic Heart Failure Patients with Reduced Ejection Fraction and Anaemia: RED-HF Study. Eur. J. Heart Fail. 2018, 20, 268–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walsh, T.J.; Martinez, A.; Peter, J.; Unsworth, E.; Cuttitta, F. Antimicrobial Activity of Adrenomedullin and Its Gene-Related Peptides. Clin. Infect. Dis. 1996, 23, 96. [Google Scholar]
- Trincot, C.E.; Xu, W.; Zhang, H.; Kulikauskas, M.R.; Caranasos, T.G.; Jensen, B.C.; Sabine, A.; Petrova, T.V.; Caron, K.M. Adrenomedullin Induces Cardiac Lymphangiogenesis after Myocardial Infarction and Regulates Cardiac Edema Via Connexin 43. Circ. Res. 2019, 124, 101–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- García Ponce, A.; Citalán Madrid, A.F.; Vargas Robles, H.; Chánez Paredes, S.; Nava, P.; Betanzos, A.; Zarbock, A.; Rottner, K.; Vestweber, D.; Schnoor, M. Loss of Cortactin Causes Endothelial Barrier Dysfunction via Disturbed Adrenomedullin Secretion and Actomyosin Contractility. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 29003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schnoor, M.; Lai, F.P.L.; Zarbock, A.; Kläver, R.; Polaschegg, C.; Schulte, D.; Weich, H.A.; Oelkers, J.M.; Rottner, K.; Vestweber, D. Cortactin Deficiency Is Associated with Reduced Neutrophil Recruitment but Increased Vascular Permeability In Vivo. J. Exp. Med. 2011, 208, 1721–1735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farmer, P.J.; Bernier, S.G.; Lepage, A.; Guillemette, G.; Regoli, D.; Sirois, P. Permeability of Endothelial Monolayers to Albumin Is Increased by Bradykinin and Inhibited by Prostaglandins. Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell. Mol. Physiol. 2001, 280, L732–L738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langeler, E.G.; van Hinsbergh, V.W. Norepinephrine and Iloprost Improve Barrier Function of Human Endothelial Cell Monolayers: Role of cAMP. Am. J. Physiol. 1991, 260, C1052–C1059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stelzner, T.J.; Weil, J.V.; O’Brien, R.F. Role of Cyclic Adenosine Monophosphate in the Induction of Endothelial Barrier Properties. J. Cell. Physiol. 1989, 139, 157–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sassone-Corsi, P. The Cyclic AMP Pathway. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2012, 4, a011148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cullere, X.; Shaw, S.K.; Andersson, L.; Hirahashi, J.; Luscinskas, F.W.; Mayadas, T.N. Regulation of Vascular Endothelial Barrier Function by Epac, a cAMP-Activated Exchange Factor for Rap GTPase. Blood 2005, 105, 1950–1955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park-Windhol, C.; D’Amore, P.A. Disorders of Vascular Permeability. Annu. Rev. Pathol. 2016, 11, 251–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Kreuk, B.-J.; Gingras, A.R.; Knight, J.D.; Liu, J.J.; Gingras, A.-C.; Ginsberg, M.H. Heart of Glass Anchors Rasip1 at Endothelial Cell-Cell Junctions to Support Vascular Integrity. eLife 2016, 5, e11394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ando, K.; Fukuhara, S.; Moriya, T.; Obara, Y.; Nakahata, N.; Mochizuki, N. Rap1 Potentiates Endothelial Cell Junctions by Spatially Controlling Myosin II Activity and Actin Organization. J. Cell. Biol. 2013, 202, 901–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marutsuka, K.; Nawa, Y.; Asada, Y.; Hara, S.; Kitamura, K.; Eto, T.; Sumiyoshi, A. Adrenomedullin and Proadrenomudullin N-Terminal 20 Peptide (PAMP) Are Present in Human Colonic Epithelia and Exert an Antimicrobial Effect. Exp. Physiol. 2001, 86, 543–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martínez, A.; Pío, R.; Zipfel, P.F.; Cuttitta, F. Mapping of the Adrenomedullin-Binding Domains in Human Complement Factor H. Hypertens. Res. 2003, 26, S55–S59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Julián-Jiménez, A.; Candel-González, F.J.; González Del Castillo, J. [Usefulness of inflammation and infection biomarkers in the Emergency Department]. Enferm. Infecc. Microbiol. Clin. 2014, 32, 177–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sekine, N.; Takano, K.; Kimata-Hayashi, N.; Kadowaki, T.; Fujita, T. Adrenomedullin Inhibits Insulin Exocytosis via Pertussis Toxin-Sensitive G Protein-Coupled Mechanism. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2006, 291, E9–E14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Langen, U.H.; Ayloo, S.; Gu, C. Development and Cell Biology of the Blood-Brain Barrier. Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol. 2019, 35, 591–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Claesson-Welsh, L.; Dejana, E.; McDonald, D.M. Permeability of the Endothelial Barrier: Identifying and Reconciling Controversies. Trends Mol. Med. 2021, 27, 314–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aird, W.C. The Role of the Endothelium in Severe Sepsis and Multiple Organ Dysfunction Syndrome. Blood 2003, 101, 3765–3777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Henneke, P.; Golenbock, D.T. Innate Immune Recognition of Lipopolysaccharide by Endothelial Cells. Crit. Care Med. 2002, 30, S207–S213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malbrain, M.L.N.G.; Marik, P.E.; Witters, I.; Cordemans, C.; Kirkpatrick, A.W.; Roberts, D.J.; Van Regenmortel, N. Fluid Overload, de-Resuscitation, and Outcomes in Critically Ill or Injured Patients: A Systematic Review with Suggestions for Clinical Practice. Anaesthesiol. Intensive Ther. 2014, 46, 361–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thygesen, K.; Alpert, J.S.; Jaffe, A.S.; Chaitman, B.R.; Bax, J.J.; Morrow, D.A.; White, H.D.; Executive Group on behalf of the Joint European Society of Cardiology (ESC)/American College of Cardiology (ACC)/American Heart Association (AHA)/World Heart Federation (WHF) Task Force for the Universal Definition of Myocardial Infarction. Fourth Universal Definition of Myocardial Infarction (2018). Circulation 2018, 138, e618–e651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seymour, C.W.; Kennedy, J.N.; Wang, S.; Chang, C.-C.H.; Elliott, C.F.; Xu, Z.; Berry, S.; Clermont, G.; Cooper, G.; Gomez, H.; et al. Derivation, Validation, and Potential Treatment Implications of Novel Clinical Phenotypes for Sepsis. JAMA 2019, 321, 2003–2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guan, W.-J.; Ni, Z.-Y.; Hu, Y.; Liang, W.-H.; Ou, C.-Q.; He, J.-X.; Liu, L.; Shan, H.; Lei, C.-L.; Hui, D.S.C.; et al. Clinical Characteristics of Coronavirus Disease 2019 in China. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 382, 1708–1720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Z.; McGoogan, J.M. Characteristics of and Important Lessons from the Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) Outbreak in China: Summary of a Report of 72 314 Cases from the Chinese Center for Disease Control and Prevention. JAMA 2020, 323, 1239–1242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, H.; Chao, L.; Chao, J. Adrenomedullin Protects Against Myocardial Apoptosis After Ischemia/Reperfusion through Activation of Akt-GSK Signaling. Hypertension 2004, 43, 109–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spoto, S.; Basili, S.; Cangemi, R.; D’Avanzo, G.; Lupoi, D.M.; Romiti, G.F.; Argemi, J.; Yuste, J.R.; Lucena, F.; Locorriere, L.; et al. Mid-Regional Pro-Adrenomedullin Can Predict Organ Failure and Prognosis in Sepsis? Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 17429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Z.; Chen, W.-S.; Yin, Y.; Chan, E.C.; Terai, K.; Long, L.M.; Myers, T.G.; Dudek, A.Z.; Druey, K.M. Adrenomedullin Surges Are Linked to Acute Episodes of the Systemic Capillary Leak Syndrome (Clarkson Disease). J. Leukoc. Biol. 2018, 103, 749–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vigué, B.; Leblanc, P.-E.; Moati, F.; Pussard, E.; Foufa, H.; Rodrigues, A.; Figueiredo, S.; Harrois, A.; Mazoit, J.-X.; Rafi, H.; et al. Mid-Regional pro-Adrenomedullin (MR-proADM), a Marker of Positive Fluid Balance in Critically Ill Patients: Results of the ENVOL Study. Crit. Care 2016, 20, 363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kirkpatrick, C.J.; Bittinger, F.; Klein, C.L.; Hauptmann, S.; Klosterhalfen, B. The Role of the Microcirculation in Multiple Organ Dysfunction Syndrome (MODS): A Review and Perspective. Virchows Arch. 1996, 427, 461–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schuetz, P.; Hausfater, P.; Amin, D.; Amin, A.; Haubitz, S.; Faessler, L.; Kutz, A.; Conca, A.; Reutlinger, B.; Canavaggio, P.; et al. Biomarkers from Distinct Biological Pathways Improve Early Risk Stratification in Medical Emergency Patients: The Multinational, Prospective, Observational TRIAGE Study. Crit. Care 2015, 19, 377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mirijello, A.; Tosoni, A.; on behalf of the Internal Medicine Sepsis Study Group. New Strategies for Treatment of Sepsis. Medicina 2020, 56, 527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mirijello, A.; Tosoni, A. Sepsis: New Challenges and Future Perspectives for an Evolving Disease—Precision Medicine Is the Way! Medicina 2021, 57, 1109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mazzone, A.; Dentali, F.; La Regina, M.; Foglia, E.; Gambacorta, M.; Garagiola, E.; Bonardi, G.; Clerici, P.; Concia, E.; Colombo, F.; et al. Clinical Features, Short-Term Mortality, and Prognostic Risk Factors of Septic Patients Admitted to Internal Medicine Units: Results of an Italian Multicenter Prospective Study. Medicine 2016, 95, e2124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mirijello, A.; Fontana, A.; Greco, A.P.; Tosoni, A.; D’Agruma, A.; Labonia, M.; Copetti, M.; Piscitelli, P.; De Cosmo, S. Identifying Predictors Associated with Risk of Death or Admission to Intensive Care Unit in Internal Medicine Patients with Sepsis: A Comparison of Statistical Models and Machine Learning Algorithms. Antibiotics 2023, 12, 925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andaluz-Ojeda, D.; Nguyen, H.B.; Meunier-Beillard, N.; Cicuéndez, R.; Quenot, J.-P.; Calvo, D.; Dargent, A.; Zarca, E.; Andrés, C.; Nogales, L.; et al. Superior Accuracy of Mid-Regional Proadrenomedullin for Mortality Prediction in Sepsis with Varying Levels of Illness Severity. Ann. Intensive Care 2017, 7, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Samavati, L.; Uhal, B.D. ACE2, Much More than Just a Receptor for SARS-COV-2. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2020, 10, 317. [Google Scholar]
- Wan, T.-T.; Li, Y.; Li, J.-X.; Xiao, X.; Liu, L.; Li, H.-H.; Guo, S.-B. ACE2 Activation Alleviates Sepsis-Induced Cardiomyopathy by Promoting MasR-Sirt1-Mediated Mitochondrial Biogenesis. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2024, 752, 109855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonaventura, A.; Vecchié, A.; Dagna, L.; Martinod, K.; Dixon, D.L.; Van Tassell, B.W.; Dentali, F.; Montecucco, F.; Massberg, S.; Levi, M.; et al. Endothelial Dysfunction and Immunothrombosis as Key Pathogenic Mechanisms in COVID-19. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2021, 21, 319–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harding, C.V.; Ramachandra, L.; Wick, M.J. Interaction of Bacteria with Antigen Presenting Cells: Influences on Antigen Presentation and Antibacterial Immunity. Curr. Opin. Immunol. 2003, 15, 112–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poland, G.A.; Ovsyannikova, I.G.; Kennedy, R.B. SARS-CoV-2 Immunity: Review and Applications to Phase 3 Vaccine Candidates. Lancet 2020, 396, 1595–1606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santos, R.A.S.; Sampaio, W.O.; Alzamora, A.C.; Motta-Santos, D.; Alenina, N.; Bader, M.; Campagnole-Santos, M.J. The ACE2/Angiotensin-(1–7)/MAS Axis of the Renin-Angiotensin System: Focus on Angiotensin-(1–7). Physiol. Rev. 2018, 98, 505–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Y.; Xu, D.; Deng, F.; Yan, Y.; Li, J.; Zhang, C.; Chu, J. Angiotensin (1-7) Attenuates Sepsis-Induced Acute Kidney Injury by Regulating the NF-κB Pathway. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 601909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zambelli, V.; Bellani, G.; Borsa, R.; Pozzi, F.; Grassi, A.; Scanziani, M.; Castiglioni, V.; Masson, S.; Decio, A.; Laffey, J.G.; et al. Angiotensin-(1-7) Improves Oxygenation, While Reducing Cellular Infiltrate and Fibrosis in Experimental Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome. Intensive Care Med. Exp. 2015, 3, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsu, C.-Y.; Tseng, W.-K.; Wu, Y.-W.; Lin, T.-H.; Yeh, H.-I.; Chang, K.-C.; Wang, J.-H.; Chou, R.-H.; Huang, C.-Y.; Huang, P.-H.; et al. Circulating TNFSF14 (Tumor Necrosis Factor Superfamily 14) Predicts Clinical Outcome in Patients with Stable Coronary Artery Disease. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2019, 39, 1240–1252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ashizuka, S.; Kita, T.; Inatsu, H.; Kitamura, K. Adrenomedullin: A Novel Therapeutic for the Treatment of Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Biomedicines 2021, 9, 1068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilson, D.C.; Schefold, J.C.; Baldirà, J.; Spinetti, T.; Saeed, K.; Elke, G. Adrenomedullin in COVID-19 Induced Endotheliitis. Crit. Care 2020, 24, 411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hofbauer, K.H.; Jensen, B.L.; Kurtz, A.; Sandner, P. Tissue Hypoxygenation Activates the Adrenomedullin System In Vivo. Am. J. Physiol. Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 2000, 278, R513–R519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shoji, H.; Minamino, N.; Kangawa, K.; Matsuo, H. Endotoxin Markedly Elevates Plasma Concentration and Gene Transcription of Adrenomedullin in Rat. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1995, 215, 531–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garayoa, M.; Martínez, A.; Lee, S.; Pío, R.; An, W.G.; Neckers, L.; Trepel, J.; Montuenga, L.M.; Ryan, H.; Johnson, R.; et al. Hypoxia-Inducible Factor-1 (HIF-1) up-Regulates Adrenomedullin Expression in Human Tumor Cell Lines during Oxygen Deprivation: A Possible Promotion Mechanism of Carcinogenesis. Mol. Endocrinol. 2000, 14, 848–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugo, S.; Minamino, N.; Shoji, H.; Kangawa, K.; Matsuo, H. Effects of Vasoactive Substances and cAMP Related Compounds on Adrenomedullin Production in Cultured Vascular Smooth Muscle Cells. FEBS Lett. 1995, 369, 311–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ueda, S.; Nishio, K.; Minamino, N.; Kubo, A.; Akai, Y.; Kangawa, K.; Matsuo, H.; Fujimura, Y.; Yoshioka, A.; Masui, K.; et al. Increased Plasma Levels of Adrenomedullin in Patients with Systemic Inflammatory Response Syndrome. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 1999, 160, 132–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shindo, T.; Kurihara, H.; Maemura, K.; Kurihara, Y.; Kuwaki, T.; Izumida, T.; Minamino, N.; Ju, K.H.; Morita, H.; Oh-hashi, Y.; et al. Hypotension and Resistance to Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Shock in Transgenic Mice Overexpressing Adrenomedullin in Their Vasculature. Circulation 2000, 101, 2309–2316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helan, M.; Malaska, J.; Tomandl, J.; Jarkovsky, J.; Helanova, K.; Benesova, K.; Sitina, M.; Dastych, M.; Ondrus, T.; Pavkova Goldbergova, M.; et al. Kinetics of Biomarkers of Oxidative Stress in Septic Shock: A Pilot Study. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsushita, K.; Morrell, C.N.; Cambien, B.; Yang, S.-X.; Yamakuchi, M.; Bao, C.; Hara, M.R.; Quick, R.A.; Cao, W.; O’Rourke, B.; et al. Nitric Oxide Regulates Exocytosis by S-Nitrosylation of N-Ethylmaleimide-Sensitive Factor. Cell 2003, 115, 139–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Isumi, Y.; Shoji, H.; Sugo, S.; Tochimoto, T.; Yoshioka, M.; Kangawa, K.; Matsuo, H.; Minamino, N. Regulation of Adrenomedullin Production in Rat Endothelial Cells. Endocrinology 1998, 139, 838–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pietrasanta, C.; Pugni, L.; Ronchi, A.; Bottino, I.; Ghirardi, B.; Sanchez-Schmitz, G.; Borriello, F.; Mosca, F.; Levy, O. Vascular Endothelium in Neonatal Sepsis: Basic Mechanisms and Translational Opportunities. Front. Pediatr. 2019, 7, 340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wrenger, S.; Kähne, T.; Bohuon, C.; Weglöhner, W.; Ansorge, S.; Reinhold, D. Amino-Terminal Truncation of Procalcitonin, a Marker for Systemic Bacterial Infections, by Dipeptidyl Peptidase IV (DP IV). FEBS Lett. 2000, 466, 155–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korhonen, E.A.; Lampinen, A.; Giri, H.; Anisimov, A.; Kim, M.; Allen, B.; Fang, S.; D’Amico, G.; Sipilä, T.J.; Lohela, M.; et al. Tie1 Controls Angiopoietin Function in Vascular Remodeling and Inflammation. J. Clin. Investig. 2016, 126, 3495–3510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fiedler, U.; Scharpfenecker, M.; Koidl, S.; Hegen, A.; Grunow, V.; Schmidt, J.M.; Kriz, W.; Thurston, G.; Augustin, H.G. The Tie-2 Ligand Angiopoietin-2 Is Stored in and Rapidly Released upon Stimulation from Endothelial Cell Weibel-Palade Bodies. Blood 2004, 103, 4150–4156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kümpers, P.; van Meurs, M.; David, S.; Molema, G.; Bijzet, J.; Lukasz, A.; Biertz, F.; Haller, H.; Zijlstra, J.G. Time Course of Angiopoietin-2 Release during Experimental Human Endotoxemia and Sepsis. Crit. Care 2009, 13, R64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davis, J.S.; Yeo, T.W.; Piera, K.A.; Woodberry, T.; Celermajer, D.S.; Stephens, D.P.; Anstey, N.M. Angiopoietin-2 Is Increased in Sepsis and Inversely Associated with Nitric Oxide-Dependent Microvascular Reactivity. Crit. Care 2010, 14, R89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geven, C.; Peters, E.; Schroedter, M.; Struck, J.; Bergmann, A.; McCook, O.; Radermacher, P.; Kox, M.; Pickkers, P. Effects of the Humanized Anti-Adrenomedullin Antibody Adrecizumab (HAM8101) on Vascular Barrier Function and Survival in Rodent Models of Systemic Inflammation and Sepsis. Shock 2018, 50, 648–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valenzuela-Méndez, B.; Valenzuela-Sánchez, F.; Rodríguez-Gutiérrez, J.F.; Bohollo-de-Austria, R.; Estella, Á.; Martínez-García, P.; González-García, M.Á.; Rello, J. Plasma Levels of Mid-Regional Proadrenomedullin Accurately Identify H1N1pdm09 Influenza Virus Patients with Risk of Intensive Care Admission and Mortality in the Emergency Department. J. Pers. Med. 2022, 12, 84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valero Cifuentes, S.; García Villalba, E.; Alcaraz García, A.; Alcaraz García, M.J.; Muñoz Pérez, Á.; Piñera Salmerón, P.; Bernal Morell, E. Prognostic Value of Pro-Adrenomedullin and NT-proBNP in Patients Referred from the Emergency Department with Influenza Syndrome. Emergencias 2019, 31, 180–184. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Spoto, S.; Valeriani, E.; Locorriere, L.; Anguissola, G.B.; Pantano, A.L.; Terracciani, F.; Riva, E.; Ciccozzi, M.; Costantino, S.; Angeletti, S. Influenza B Virus Infection Complicated by Life-Threatening Pericarditis: A Unique Case-Report and Literature Review. BMC Infect. Dis. 2019, 19, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Oers, J.A.H.; Kluiters, Y.; Bons, J.A.P.; de Jongh, M.; Pouwels, S.; Ramnarain, D.; de Lange, D.W.; de Grooth, H.-J.; Girbes, A.R.J. Endothelium-Associated Biomarkers Mid-Regional Proadrenomedullin and C-Terminal Proendothelin-1 Have Good Ability to Predict 28-Day Mortality in Critically Ill Patients with SARS-CoV-2 Pneumonia: A Prospective Cohort Study. J. Crit. Care 2021, 66, 173–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García de Guadiana-Romualdo, L.; Calvo Nieves, M.D.; Rodríguez Mulero, M.D.; Calcerrada Alises, I.; Hernández Olivo, M.; Trapiello Fernández, W.; González Morales, M.; Bolado Jiménez, C.; Albaladejo-Otón, M.D.; Fernández Ovalle, H.; et al. MR-proADM as Marker of Endotheliitis Predicts COVID-19 Severity. Eur. J. Clin. Investig. 2021, 51, e13511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karakas, M.; Jarczak, D.; Becker, M.; Roedl, K.; Addo, M.M.; Hein, F.; Bergmann, A.; Zimmermann, J.; Simon, T.-P.; Marx, G.; et al. Targeting Endothelial Dysfunction in Eight Extreme-Critically Ill Patients with COVID-19 Using the Anti-Adrenomedullin Antibody Adrecizumab (HAM8101). Biomolecules 2020, 10, 1171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Potere, N.; Valeriani, E.; Candeloro, M.; Tana, M.; Porreca, E.; Abbate, A.; Spoto, S.; Rutjes, A.W.S.; Di Nisio, M. Acute Complications and Mortality in Hospitalized Patients with Coronavirus Disease 2019: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Crit. Care 2020, 24, 389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spoto, S.; Legramante, J.M.; Minieri, M.; Fogolari, M.; Terrinoni, A.; Valeriani, E.; Sebastiano, C.; Bernardini, S.; Ciccozzi, M.; Angeletti, P.S. How Biomarkers Can Improve Pneumonia Diagnosis and Prognosis: Procalcitonin and Mid-Regional-pro-Adrenomedullin. Biomark. Med. 2020, 14, 549–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Christ-Crain, M.; Morgenthaler, N.G.; Stolz, D.; Müller, C.; Bingisser, R.; Harbarth, S.; Tamm, M.; Struck, J.; Bergmann, A.; Müller, B. Pro-Adrenomedullin to Predict Severity and Outcome in Community-Acquired Pneumonia [ISRCTN04176397]. Crit. Care 2006, 10, R96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, M.P.; Cau, A.; Lee, T.C.; Brodie, D.; Slutsky, A.; Marshall, J.; Murthy, S.; Lee, T.; Singer, J.; Demir, K.K.; et al. Acute Cardiac Injury in Coronavirus Disease 2019 and Other Viral Infections-A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Crit. Care Med. 2021, 49, 1558–1566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pellegrini, D.; Kawakami, R.; Guagliumi, G.; Sakamoto, A.; Kawai, K.; Gianatti, A.; Nasr, A.; Kutys, R.; Guo, L.; Cornelissen, A.; et al. Microthrombi as a Major Cause of Cardiac Injury in COVID-19: A Pathologic Study. Circulation 2021, 143, 1031–1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roshdy, A.; Zaher, S.; Fayed, H.; Coghlan, J.G. COVID-19 and the Heart: A Systematic Review of Cardiac Autopsies. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2020, 7, 626975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, C.C.E.; Ali, K.; Connell, D.; Mordi, I.R.; George, J.; Lang, E.M.; Lang, C.C. COVID-19-Associated Cardiovascular Complications. Diseases 2021, 9, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gheblawi, M.; Wang, K.; Viveiros, A.; Nguyen, Q.; Zhong, J.-C.; Turner, A.J.; Raizada, M.K.; Grant, M.B.; Oudit, G.Y. Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme 2: SARS-CoV-2 Receptor and Regulator of the Renin-Angiotensin System: Celebrating the 20th Anniversary of the Discovery of ACE2. Circ. Res. 2020, 126, 1456–1474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diaz, J.H. Hypothesis: Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme Inhibitors and Angiotensin Receptor Blockers May Increase the Risk of Severe COVID-19. J. Travel Med. 2020, 27, taaa041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ison, M.G.; Campbell, V.; Rembold, C.; Dent, J.; Hayden, F.G. Cardiac Findings during Uncomplicated Acute Influenza in Ambulatory Adults. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2005, 40, 415–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mamas, M.A.; Fraser, D.; Neyses, L. Cardiovascular Manifestations Associated with Influenza Virus Infection. Int. J. Cardiol. 2008, 130, 304–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watanabe, M.; Panetta, G.L.; Piccirillo, F.; Spoto, S.; Myers, J.; Serino, F.M.; Costantino, S.; Di Sciascio, G. Acute Epstein-Barr Related Myocarditis: An Unusual but Life-Threatening Disease in an Immunocompetent Patient. J. Cardiol. Cases 2020, 21, 137–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakahara, T.; Iwabuchi, Y.; Miyazawa, R.; Tonda, K.; Shiga, T.; Strauss, H.W.; Antoniades, C.; Narula, J.; Jinzaki, M. Assessment of Myocardial 18F-FDG Uptake at PET/CT in Asymptomatic SARS-CoV-2-Vaccinated and Nonvaccinated Patients. Radiology 2023, 308, e230743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, T.; Fan, Y.; Chen, M.; Wu, X.; Zhang, L.; He, T.; Wang, H.; Wan, J.; Wang, X.; Lu, Z. Cardiovascular Implications of Fatal Outcomes of Patients with Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19). JAMA Cardiol. 2020, 5, 811–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Demir, O.M.; Ryan, M.; Cirillo, C.; Desai, N.; Pericao, A.; Sinclair, H.; Stylianidis, V.; Victor, K.; Alaour, B.; Jones, A.; et al. Impact and Determinants of High-Sensitivity Cardiac Troponin-T Concentration in Patients with COVID-19 Admitted to Critical Care. Am. J. Cardiol. 2021, 147, 129–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kurz, D.J.; Eberli, F.R. Cardiovascular Aspects of COVID-19. Swiss Med. Wkly. 2020, 150, w20417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lala, A.; Johnson, K.W.; Januzzi, J.L.; Russak, A.J.; Paranjpe, I.; Richter, F.; Zhao, S.; Somani, S.; Van Vleck, T.; Vaid, A.; et al. Prevalence and Impact of Myocardial Injury in Patients Hospitalized with COVID-19 Infection. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2020, 76, 533–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, P.P.; Blet, A.; Smyth, D.; Li, H. The Science Underlying COVID-19: Implications for the Cardiovascular System. Circulation 2020, 142, 68–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, S.; Qin, M.; Shen, B.; Cai, Y.; Liu, T.; Yang, F.; Gong, W.; Liu, X.; Liang, J.; Zhao, Q.; et al. Association of Cardiac Injury with Mortality in Hospitalized Patients with COVID-19 in Wuhan, China. JAMA Cardiol. 2020, 5, 802–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, F.; Quan, Y.; Lei, M.; Liu, R.; Qin, S.; Zeng, J.; Zhao, Z.; Yu, N.; Yang, L.; Cao, J. Clinical Features and Risk Factors for ICU Admission in COVID-19 Patients with Cardiovascular Diseases. Aging Dis. 2020, 11, 763–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cremer, S.; Jakob, C.; Berkowitsch, A.; Borgmann, S.; Pilgram, L.; Tometten, L.; Classen, A.; Wille, K.; Weidlich, S.; Gruener, B.; et al. Elevated Markers of Thrombo-Inflammatory Activation Predict Outcome in Patients with Cardiovascular Comorbidities and COVID-19 Disease: Insights from the LEOSS Registry. Clin. Res. Cardiol. 2021, 110, 1029–1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhatraju, P.K.; Ghassemieh, B.J.; Nichols, M.; Kim, R.; Jerome, K.R.; Nalla, A.K.; Greninger, A.L.; Pipavath, S.; Wurfel, M.M.; Evans, L.; et al. COVID-19 in Critically Ill Patients in the Seattle Region—Case Series. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 382, 2012–2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szekely, Y.; Lichter, Y.; Taieb, P.; Banai, A.; Hochstadt, A.; Merdler, I.; Gal Oz, A.; Rothschild, E.; Baruch, G.; Peri, Y.; et al. Spectrum of Cardiac Manifestations in COVID-19: A Systematic Echocardiographic Study. Circulation 2020, 142, 342–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basso, C.; Leone, O.; Rizzo, S.; De Gaspari, M.; van der Wal, A.C.; Aubry, M.-C.; Bois, M.C.; Lin, P.T.; Maleszewski, J.J.; Stone, J.R. Pathological Features of COVID-19-Associated Myocardial Injury: A Multicentre Cardiovascular Pathology Study. Eur. Heart J. 2020, 41, 3827–3835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spoto, S.; Mangiacapra, F.; D’Avanzo, G.; Lemme, D.; Bustos Guillén, C.; Abbate, A.; Markley, J.D.; Sambuco, F.; Markley, R.; Fogolari, M.; et al. Synergistic Effect of Myocardial Injury and Mid-Regional proAdrenomedullin Elevation in Determining Clinical Outcomes of SARS-CoV-2 Patients. Front. Med. 2022, 9, 929408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spoto, S.; Argemi, J.; Di Costanzo, R.; Gavira Gomez, J.J.; Salterain Gonzales, N.; Basili, S.; Cangemi, R.; Abbate, A.; Locorriere, L.; Masini, F.; et al. Mid-Regional Pro-Adrenomedullin and N-Terminal Pro-B-Type Natriuretic Peptide Measurement: A Multimarker Approach to Diagnosis and Prognosis in Acute Heart Failure. J. Pers. Med. 2023, 13, 1155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- García de Guadiana-Romualdo, L.; Andaluz Ojeda, D. Editorial: Inflammation and Organic Damage in COVID-19: What Have We Learned 2 Years into the Pandemic? Front. Med. 2023, 10, 1238804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Romiti, G.F.; Cangemi, R.; Toriello, F.; Ruscio, E.; Sciomer, S.; Moscucci, F.; Vincenti, M.; Crescioli, C.; Proietti, M.; Basili, S.; et al. Sex-Specific Cut-Offs for High-Sensitivity Cardiac Troponin: Is Less More? Cardiovasc. Ther. 2019, 2019, 9546931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naghavi, M.; Barlas, Z.; Siadaty, S.; Naguib, S.; Madjid, M.; Casscells, W. Association of Influenza Vaccination and Reduced Risk of Recurrent Myocardial Infarction. Circulation 2000, 102, 3039–3045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zampino, R.; Iossa, D.; Ursi, M.P.; Bertolino, L.; Andini, R.; Molaro, R.; Fabrazzo, O.; Leonardi, S.; Atripaldi, L.; Durante-Mangoni, E. Prognostic Value of Pro-Adrenomedullin and Copeptin in Acute Infective Endocarditis. BMC Infect. Dis. 2021, 21, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vieillard-Baron, A.; Caille, V.; Charron, C.; Belliard, G.; Page, B.; Jardin, F. Actual Incidence of Global Left Ventricular Hypokinesia in Adult Septic Shock. Crit. Care Med. 2008, 36, 1701–1706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pulido, J.N.; Afessa, B.; Masaki, M.; Yuasa, T.; Gillespie, S.; Herasevich, V.; Brown, D.R.; Oh, J.K. Clinical Spectrum, Frequency, and Significance of Myocardial Dysfunction in Severe Sepsis and Septic Shock. Mayo Clin. Proc. 2012, 87, 620–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vieillard-Baron, A. Septic Cardiomyopathy. Ann. Intensive Care 2011, 1, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Liu, D. Sepsis-Related Cardiomyopathy: Not an Easy Task for ICU Physicians. J. Intensive Med. 2022, 2, 257–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valenzuela-Sánchez, F.; Valenzuela-Méndez, B.; Rodríguez-Gutiérrez, J.F.; Estella-García, Á.; González-García, M.Á. New Role of Biomarkers: Mid-Regional pro-Adrenomedullin, the Biomarker of Organ Failure. Ann. Transl. Med. 2016, 4, 329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paul Glezen, W.; Schmier, J.K.; Kuehn, C.M.; Ryan, K.J.; Oxford, J. The Burden of Influenza B: A Structured Literature Review. Am. J. Public Health 2013, 103, e43–e51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zapata-Arriaza, E.; Mancha, F.; Bustamante, A.; Moniche, F.; Pardo-Galiana, B.; Serrano-Gotarredona, P.; Navarro-Herrero, S.; Pallisa, E.; Faura, J.; Vega-Salvatierra, Á.; et al. Biomarkers Predictive Value for Early Diagnosis of Stroke-Associated Pneumonia. Ann. Clin. Transl. Neurol. 2019, 6, 1882–1887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Öner, Ö.; Deveci, F.; Telo, S.; Kuluöztürk, M.; Balin, M. MR-proADM and MR-proANP Levels in Patients with Acute Pulmonary Embolism. J. Med. Biochem. 2020, 39, 328–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graziadio, S.; O’Leary, R.A.; Stocken, D.D.; Power, M.; Allen, A.J.; Simpson, A.J.; Price, D.A. Can Mid-Regional pro-Adrenomedullin (MR-proADM) Increase the Prognostic Accuracy of NEWS in Predicting Deterioration in Patients Admitted to Hospital with Mild to Moderately Severe Illness? A Prospective Single-Centre Observational Study. BMJ Open 2019, 8, e020337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramasco Rueda, F.; Planas Roca, A.; Méndez Hernández, R.; Figuerola Tejerina, A.; Tamayo Gómez, E.; Garcia Bernedo, C.; Maseda Garrido, E.; Pascual Gómez, N.F.; de la Varga-Martínez, O. Usefulness of Preoperative Determination of Serum MR-ProAdrenomedullin Levels to Predict the Need for Postoperative Organ Support in Abdominal Oncological Surgery. J. Pers. Med. 2023, 13, 1151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Golubović, M.; Janković, R.; Sokolović, D.; Ćosić, V.; Maravić-Stojkovic, V.; Kostić, T.; Perišić, Z.; Lađević, N. Preoperative Midregional Pro-Adrenomedullin and High-Sensitivity Troponin T Predict Perioperative Cardiovascular Events in Noncardiac Surgery. Med. Princ. Pract. 2018, 27, 278–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zelniker, T.A.; Schwall, D.; Hamidi, F.; Steinbach, S.; Scheller, P.; Spaich, S.; Michels, G.; Giannitsis, E.; Katus, H.A.; Frey, N.; et al. Mid-Regional pro-Adrenomedullin and Lactate Levels for Risk Stratification in Patients with out-of-Hospital Cardiac Arrest. Eur. Heart J. Acute Cardiovasc. Care 2023, 12, 364–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Domizi, R.; Damiani, E.; Scorcella, C.; Carsetti, A.; Giaccaglia, P.; Casarotta, E.; Montomoli, J.; Gabbanelli, V.; Brugia, M.; Moretti, M.; et al. Mid-Regional Proadrenomedullin (MR-proADM) and Microcirculation in Monitoring Organ Dysfunction of Critical Care Patients with Infection: A Prospective Observational Pilot Study. Front. Med. 2021, 8, 680244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davidson, L.T.; Schilling, U.M.; Arnqvist, H.J.; Nystrom, F.H.; Chisalita, S.I. Association of Physiological Stress Markers at the Emergency Department to Readmission and Death within 90 Days: A Prospective Observational Study. Ups. J. Med. Sci. 2023, 128, e9300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bernal-Morell, E.; García-Villalba, E.; Vera, M.D.C.; Medina, B.; Martinez, M.; Callejo, V.; Valero, S.; Cinesi, C.; Piñera, P.; Alcaraz, A.; et al. Usefulness of Midregional Pro-Adrenomedullin as a Marker of Organ Damage and Predictor of Mortality in Patients with Sepsis. J. Infect. 2018, 76, 249–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baldirà, J.; Ruiz-Rodríguez, J.C.; Ruiz-Sanmartin, A.; Chiscano, L.; Cortes, A.; Sistac, D.Á.; Ferrer-Costa, R.; Comas, I.; Villena, Y.; Larrosa, M.N.; et al. Use of Biomarkers to Improve 28-Day Mortality Stratification in Patients with Sepsis and SOFA ≤ 6. Biomedicines 2023, 11, 2149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haag, E.; Gregoriano, C.; Molitor, A.; Kloter, M.; Kutz, A.; Mueller, B.; Schuetz, P. Does Mid-Regional pro-Adrenomedullin (MR-proADM) Improve the Sequential Organ Failure Assessment-Score (SOFA Score) for Mortality-Prediction in Patients with Acute Infections? Results of a Prospective Observational Study. Clin. Chem. Lab Med. 2021, 59, 1165–1176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viaggi, B.; Poole, D.; Tujjar, O.; Marchiani, S.; Ognibene, A.; Finazzi, S. Mid Regional Pro-Adrenomedullin for the Prediction of Organ Failure in Infection. Results from a Single Centre Study. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0201491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eckart, A.; Hauser, S.I.; Kutz, A.; Haubitz, S.; Hausfater, P.; Amin, D.; Amin, A.; Huber, A.; Mueller, B.; Schuetz, P. Combination of the National Early Warning Score (NEWS) and Inflammatory Biomarkers for Early Risk Stratification in Emergency Department Patients: Results of a Multinational, Observational Study. BMJ Open 2019, 9, e024636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gar, C.; Thorand, B.; Herder, C.; Sujana, C.; Heier, M.; Meisinger, C.; Peters, A.; Koenig, W.; Rathmann, W.; Roden, M.; et al. Association of Circulating MR-proADM with All-Cause and Cardiovascular Mortality in the General Population: Results from the KORA F4 Cohort Study. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0262330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kita, T.; Kitamura, K. Adrenomedullin Therapy in Moderate to Severe COVID-19. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Lier, D.; Picod, A.; Marx, G.; Laterre, P.-F.; Hartmann, O.; Knothe, C.; Azibani, F.; Struck, J.; Santos, K.; Zimmerman, J.; et al. Effects of Enrichment Strategies on Outcome of Adrecizumab Treatment in Septic Shock: Post-Hoc Analyses of the Phase II Adrenomedullin and Outcome in Septic Shock 2 Trial. Front. Med. 2022, 9, 1058235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maisel, A.; Mueller, C.; Nowak, R.; Peacock, W.F.; Landsberg, J.W.; Ponikowski, P.; Mockel, M.; Hogan, C.; Wu, A.H.B.; Richards, M.; et al. Mid-Region pro-Hormone Markers for Diagnosis and Prognosis in Acute Dyspnea: Results from the BACH (Biomarkers in Acute Heart Failure) Trial. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2010, 55, 2062–2076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitamura, K.; Kangawa, K.; Eto, T. Adrenomedullin and PAMP: Discovery, Structures, and Cardiovascular Functions. Microsc. Res. Tech. 2002, 57, 3–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kröller-Schön, S.; Knorr, M.; Hausding, M.; Oelze, M.; Schuff, A.; Schell, R.; Sudowe, S.; Scholz, A.; Daub, S.; Karbach, S.; et al. Glucose-Independent Improvement of Vascular Dysfunction in Experimental Sepsis by Dipeptidyl-Peptidase 4 Inhibition. Cardiovasc. Res. 2012, 96, 140–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheung, K.C.P.; Fanti, S.; Mauro, C.; Wang, G.; Nair, A.S.; Fu, H.; Angeletti, S.; Spoto, S.; Fogolari, M.; Romano, F.; et al. Preservation of Microvascular Barrier Function Requires CD31 Receptor-Induced Metabolic Reprogramming. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 3595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laterre, P.-F.; Pickkers, P.; Marx, G.; Wittebole, X.; Meziani, F.; Dugernier, T.; Huberlant, V.; Schuerholz, T.; François, B.; Lascarrou, J.-B.; et al. Safety and Tolerability of Non-Neutralizing Adrenomedullin Antibody Adrecizumab (HAM8101) in Septic Shock Patients: The AdrenOSS-2 Phase 2a Biomarker-Guided Trial. Intensive Care Med. 2021, 47, 1284–1294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mebazaa, A.; Geven, C.; Hollinger, A.; Wittebole, X.; Chousterman, B.G.; Blet, A.; Gayat, E.; Hartmann, O.; Scigalla, P.; Struck, J.; et al. Circulating Adrenomedullin Estimates Survival and Reversibility of Organ Failure in Sepsis: The Prospective Observational Multinational Adrenomedullin and Outcome in Sepsis and Septic Shock-1 (AdrenOSS-1) Study. Crit. Care 2018, 22, 354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steven, S.; Hausding, M.; Kröller-Schön, S.; Mader, M.; Mikhed, Y.; Stamm, P.; Zinßius, E.; Pfeffer, A.; Welschof, P.; Agdauletova, S.; et al. Gliptin and GLP-1 Analog Treatment Improves Survival and Vascular Inflammation/Dysfunction in Animals with Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Endotoxemia. Basic Res. Cardiol. 2015, 110, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tavares, E.; Maldonado, R.; Miñano, F.J. Immunoneutralization of Endogenous Aminoprocalcitonin Attenuates Sepsis-Induced Acute Lung Injury and Mortality in Rats. Am. J. Pathol. 2014, 184, 3069–3083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brabenec, L.; Müller, M.; Hellenthal, K.E.M.; Karsten, O.S.; Pryvalov, H.; Otto, M.; Holthenrich, A.; Matos, A.L.L.; Weiss, R.; Kintrup, S.; et al. Targeting Procalcitonin Protects Vascular Barrier Integrity. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2022, 206, 488–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Struck, J.; Strebelow, M.; Tietz, S.; Alonso, C.; Morgenthaler, N.G.; van der Hoeven, J.G.; Pickkers, P.; Bergmann, A. Method for the Selective Measurement of Amino-Terminal Variants of Procalcitonin. Clin. Chem. 2009, 55, 1672–1679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weglöhner, W.; Struck, J.; Fischer-Schulz, C.; Morgenthaler, N.G.; Otto, A.; Bohuon, C.; Bergmann, A. Isolation and Characterization of Serum Procalcitonin from Patients with Sepsis. Peptides 2001, 22, 2099–2103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baranowsky, A.; Appelt, J.; Kleber, C.; Lange, T.; Ludewig, P.; Jahn, D.; Pandey, P.; Keller, D.; Rose, T.; Schetler, D.; et al. Procalcitonin Exerts a Mediator Role in Septic Shock Through the Calcitonin Gene-Related Peptide Receptor. Crit. Care Med. 2021, 49, e41–e52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sexton, P.M.; Christopoulos, G.; Christopoulos, A.; Nylen, E.S.; Snider, R.H.; Becker, K.L. Procalcitonin Has Bioactivity at Calcitonin Receptor Family Complexes: Potential Mediator Implications in Sepsis. Crit. Care Med. 2008, 36, 1637–1640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Minami, E.; Ito, S.; Sugiura, T.; Fujita, Y.; Sasano, H.; Sobue, K. Markedly Elevated Procalcitonin in Early Postoperative Period in Pediatric Open Heart Surgery: A Prospective Cohort Study. J. Intensive Care 2014, 2, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klingele, M.; Bomberg, H.; Schuster, S.; Schäfers, H.-J.; Groesdonk, H.V. Prognostic Value of Procalcitonin in Patients after Elective Cardiac Surgery: A Prospective Cohort Study. Ann. Intensive Care 2016, 6, 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spoto, S.; Daniel Markley, J.; Valeriani, E.; Abbate, A.; Argemi, J.; Markley, R.; Fogolari, M.; Locorriere, L.; Anguissola, G.B.; Battifoglia, G.; et al. Active Surveillance Cultures and Procalcitonin in Combination with Clinical Data to Guide Empirical Antimicrobial Therapy in Hospitalized Medical Patients with Sepsis. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 797932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bálint, L.; Nelson-Maney, N.P.; Tian, Y.; Serafin, S.D.; Caron, K.M. Clinical Potential of Adrenomedullin Signaling in the Cardiovascular System. Circ. Res. 2023, 132, 1185–1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.-Y.; Ning, B.-T. Signaling Pathways and Intervention Therapies in Sepsis. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2021, 6, 407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buchtele, N.; Schwameis, M.; Schoergenhofer, C.; Derhaschnig, U.; Firbas, C.; Karch, R.; Nix, D.; Schenk, R.; Jilma, B. Safety, Tolerability, Pharmacokinetics and Pharmacodynamics of Parenterally Administered Dutogliptin: A Prospective Dose-escalating Trial. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2020, 86, 979–990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deacon, C.F. A Review of Dipeptidyl Peptidase-4 Inhibitors. Hot Topics from Randomized Controlled Trials. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2018, 20 (Suppl. S1), 34–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williams-Herman, D.; Engel, S.S.; Round, E.; Johnson, J.; Golm, G.T.; Guo, H.; Musser, B.J.; Davies, M.J.; Kaufman, K.D.; Goldstein, B.J. Safety and Tolerability of Sitagliptin in Clinical Studies: A Pooled Analysis of Data from 10,246 Patients with Type 2 Diabetes. BMC Endocr. Disord. 2010, 10, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bergman, A.; Ebel, D.; Liu, F.; Stone, J.; Wang, A.; Zeng, W.; Chen, L.; Dilzer, S.; Lasseter, K.; Herman, G.; et al. Absolute Bioavailability of Sitagliptin, an Oral Dipeptidyl Peptidase-4 Inhibitor, in Healthy Volunteers. Biopharm. Drug Dispos. 2007, 28, 315–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, S.; Lee, S.-J.; Kim, K.E.; Lee, H.S.; Oh, N.; Park, I.; Ko, E.; Oh, S.J.; Lee, Y.-S.; Kim, D.; et al. Amelioration of Sepsis by TIE2 Activation-Induced Vascular Protection. Sci. Transl. Med. 2016, 8, 335ra55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garcia, B.; Su, F.; Manicone, F.; Dewachter, L.; Favory, R.; Khaldi, A.; Moiroux-Sahroui, A.; Moreau, A.; Herpain, A.; Vincent, J.-L.; et al. Angiotensin 1–7 in an Experimental Septic Shock Model. Crit. Care 2023, 27, 106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Osterholm, M.T.; Kelley, N.S.; Sommer, A.; Belongia, E.A. Efficacy and Effectiveness of Influenza Vaccines: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2012, 12, 36–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, W.; Gui, M.; Wang, X.; Xiang, Y. Cryo-EM Structure of the SARS Coronavirus Spike Glycoprotein in Complex with Its Host Cell Receptor ACE2. PLoS Pathog. 2018, 14, e1007236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamous, Y.F.; Alhomoud, D.A. The Safety and Effectiveness of mRNA Vaccines Against SARS-CoV-2. Cureus 2023, 15, e45602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, J.B.; June, C.H. Cytokine Release Syndrome in Severe COVID-19. Science 2020, 368, 473–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Spoto, S.; Basili, S.; Cangemi, R.; Yuste, J.R.; Lucena, F.; Romiti, G.F.; Raparelli, V.; Argemi, J.; D’Avanzo, G.; Locorriere, L.; et al. A Focus on the Pathophysiology of Adrenomedullin Expression: Endothelitis and Organ Damage in Severe Viral and Bacterial Infections. Cells 2024, 13, 892. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells13110892
Spoto S, Basili S, Cangemi R, Yuste JR, Lucena F, Romiti GF, Raparelli V, Argemi J, D’Avanzo G, Locorriere L, et al. A Focus on the Pathophysiology of Adrenomedullin Expression: Endothelitis and Organ Damage in Severe Viral and Bacterial Infections. Cells. 2024; 13(11):892. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells13110892
Chicago/Turabian StyleSpoto, Silvia, Stefania Basili, Roberto Cangemi, José Ramón Yuste, Felipe Lucena, Giulio Francesco Romiti, Valeria Raparelli, Josepmaria Argemi, Giorgio D’Avanzo, Luciana Locorriere, and et al. 2024. "A Focus on the Pathophysiology of Adrenomedullin Expression: Endothelitis and Organ Damage in Severe Viral and Bacterial Infections" Cells 13, no. 11: 892. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells13110892
APA StyleSpoto, S., Basili, S., Cangemi, R., Yuste, J. R., Lucena, F., Romiti, G. F., Raparelli, V., Argemi, J., D’Avanzo, G., Locorriere, L., Masini, F., Calarco, R., Testorio, G., Spiezia, S., Ciccozzi, M., & Angeletti, S. (2024). A Focus on the Pathophysiology of Adrenomedullin Expression: Endothelitis and Organ Damage in Severe Viral and Bacterial Infections. Cells, 13(11), 892. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells13110892











