Overexpression of Toxic Poly(Glycine-Alanine) Aggregates in Primary Neuronal Cultures Induces Time-Dependent Autophagic and Synaptic Alterations but Subtle Activity Impairments
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Primary Rat Cortical Neurons
2.2. Immunocytochemistry
2.3. Microscopy
2.4. Image Analysis
2.5. Western Blot
2.6. Antibody List
2.7. Multielectrode Array
2.8. Data and Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Poly(GA) Overexpression Induces Time-Dependent Autophagic Alterations Independent from C9orf72 Levels
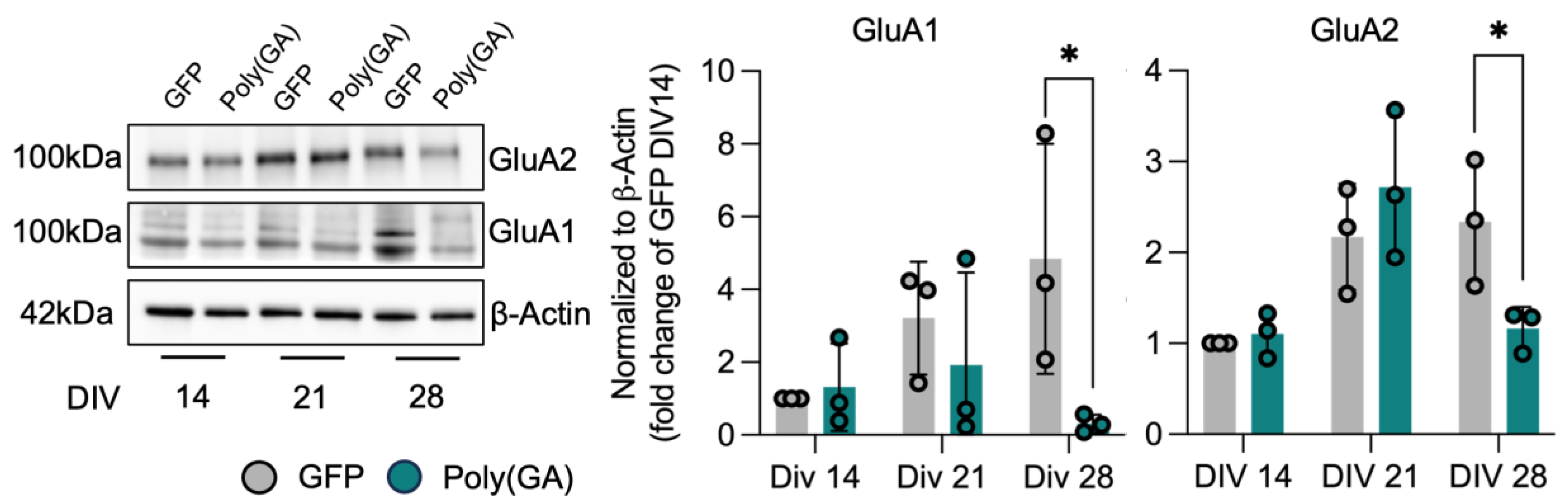
3.2. Loss of Synaptic Proteins Anticipates Autophagic Defects in Poly(GA)-Expressing Cultures
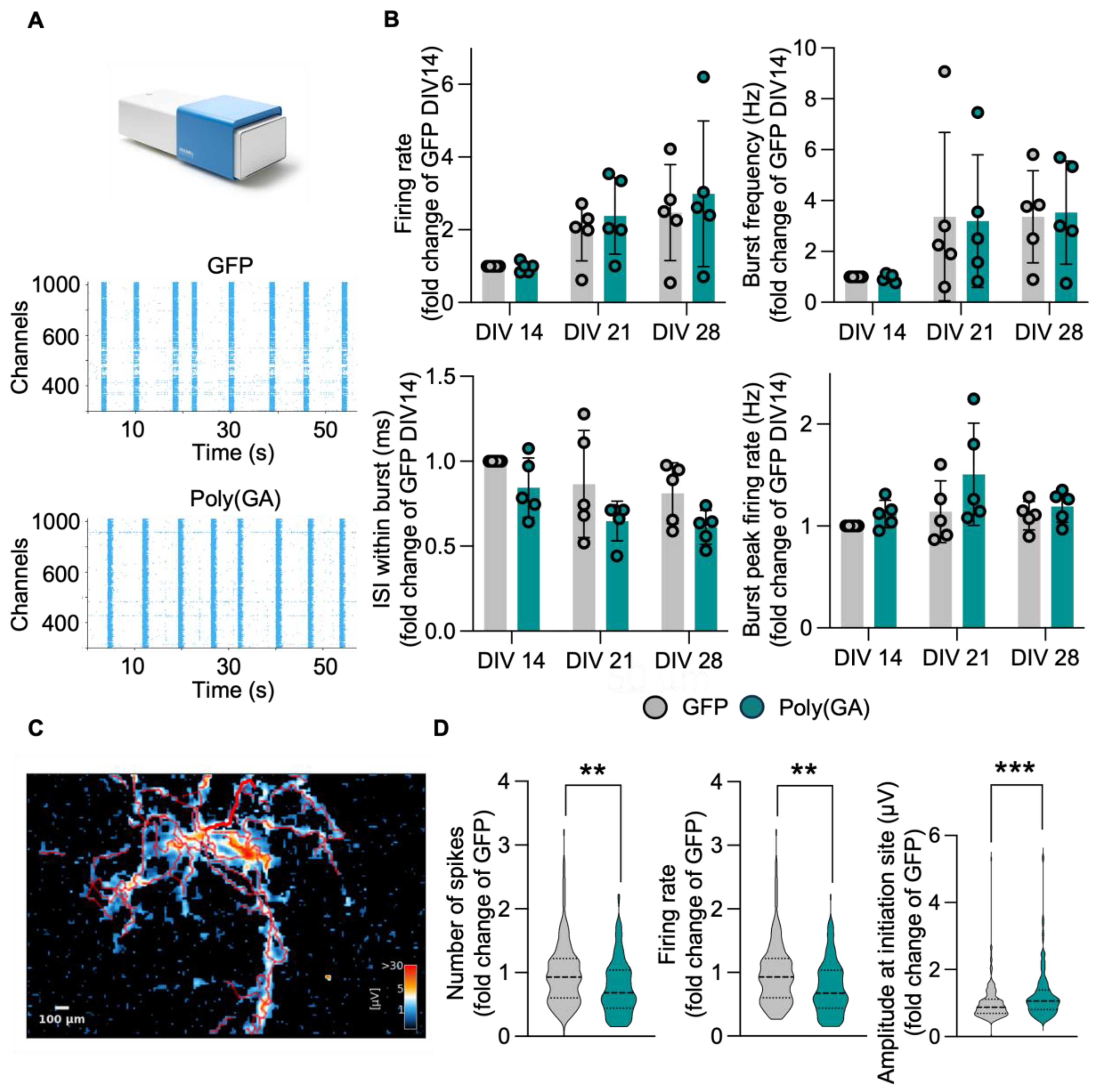
3.3. The Network Properties of Primary Cultures Are Minimally Affected by Poly(GA) Overexpression
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Levine, T.P.; Daniels, R.D.; Gatta, A.T.; Wong, L.H.; Hayes, M.J. The Product of C9orf72, a Gene Strongly Implicated in Neurodegeneration, Is Structurally Related to DENN Rab-GEFs. Bioinformatics 2013, 29, 499–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sellier, C.; Campanari, M.; Julie Corbier, C.; Gaucherot, A.; Kolb-Cheynel, I.; Oulad-Abdelghani, M.; Ruffenach, F.; Page, A.; Ciura, S.; Kabashi, E.; et al. Loss of C9ORF72 Impairs Autophagy and Synergizes with PolyQ Ataxin-2 to Induce Motor Neuron Dysfunction and Cell Death. EMBO J. 2016, 35, 1276–1297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marat, A.L.; Dokainish, H.; McPherson, P.S. DENN Domain Proteins: Regulators of Rab GTPases. J. Biol. Chem. 2011, 286, 13791–13800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bauer, C.S.; Cohen, R.N.; Sironi, F.; Livesey, M.R.; Gillingwater, T.H.; Highley, J.R.; Fillingham, D.J.; Coldicott, I.; Smith, E.F.; Gibson, Y.B.; et al. An Interaction between Synapsin and C9orf72 Regulates Excitatory Synapses and Is Impaired in ALS/FTD. Acta Neuropathol. 2022, 144, 437–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Majounie, E.; Renton, A.E.; Mok, K.; Dopper, E.G.P.; Waite, A.; Rollinson, S.; Chiò, A.; Restagno, G.; Nicolaou, N.; Simon-Sanchez, J.; et al. Frequency of the C9orf72Hexanucleotide Repeat Expansion in Patients with Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis and Frontotemporal Dementia: A Cross-Sectional Study. Lancet Neurol. 2012, 11, 323–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DeJesus-Hernandez, M.; Mackenzie, I.R.; Boeve, B.F.; Boxer, A.L.; Baker, M.; Rutherford, N.J.; Nicholson, A.M.; Finch, N.A.; Flynn, H.; Adamson, J.; et al. Expanded GGGGCC Hexanucleotide Repeat in Noncoding Region of C9ORF72 Causes Chromosome 9p-Linked FTD and ALS. Neuron 2011, 72, 245–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Renton, A.E.; Majounie, E.; Waite, A.; Simón-Sánchez, J.; Rollinson, S.; Gibbs, J.R.; Schymick, J.C.; Laaksovirta, H.; van Swieten, J.C.; Myllykangas, L.; et al. A Hexanucleotide Repeat Expansion in C9ORF72 Is the Cause of Chromosome 9p21-Linked ALS-FTD. Neuron 2011, 72, 257–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mori, K.; Arzberger, T.; Grässer, F.A.; Gijselinck, I.; May, S.; Rentzsch, K.; Weng, S.-M.; Schludi, M.H.; van der Zee, J.; Cruts, M.; et al. Bidirectional Transcripts of the Expanded C9orf72 Hexanucleotide Repeat Are Translated into Aggregating Dipeptide Repeat Proteins. Acta Neuropathol. 2013, 126, 881–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gijselinck, I.; Van Mossevelde, S.; van der Zee, J.; Sieben, A.; Engelborghs, S.; De Bleecker, J.; Ivanoiu, A.; Deryck, O.; Edbauer, D.; Zhang, M.; et al. The C9orf72 Repeat Size Correlates with Onset Age of Disease, DNA Methylation and Transcriptional Downregulation of the Promoter. Mol. Psychiatry 2016, 21, 1112–1124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xi, Z.; Zhang, M.; Bruni, A.C.; Maletta, R.G.; Colao, R.; Fratta, P.; Polke, J.M.; Sweeney, M.G.; Mudanohwo, E.; Nacmias, B.; et al. The C9orf72 Repeat Expansion Itself Is Methylated in ALS and FTLD Patients. Acta Neuropathol. 2015, 129, 715–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cantara, S.; Simoncelli, G.; Ricci, C. Antisense Oligonucleotides (ASOs) in Motor Neuron Diseases: A Road to Cure in Light and Shade. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 4809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Catanese, A.; Garrido, D.; Walther, P.; Roselli, F.; Boeckers, T.M. Nutrient Limitation Affects Presynaptic Structures through Dissociable Bassoon Autophagic Degradation and Impaired Vesicle Release. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 2018, 38, 1924–1939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Catanese, A.; Rajkumar, S.; Sommer, D.; Freisem, D.; Wirth, A.; Aly, A.; Massa-López, D.; Olivieri, A.; Torelli, F.; Ioannidis, V.; et al. Synaptic Disruption and CREB-Regulated Transcription Are Restored by K+ Channel Blockers in ALS. EMBO Mol. Med. 2021, 13, e13131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Braems, E.; Swinnen, B.; Van Den Bosch, L. C9orf72 Loss-of-Function: A Trivial, Stand-Alone or Additive Mechanism in C9 ALS/FTD? Acta Neuropathol. 2020, 140, 625–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, X.; Tan, W.; Westergard, T.; Krishnamurthy, K.; Markandaiah, S.S.; Shi, Y.; Lin, S.; Shneider, N.A.; Monaghan, J.; Pandey, U.B.; et al. Antisense Proline-Arginine RAN Dipeptides Linked to C9ORF72-ALS/FTD Form Toxic Nuclear Aggregates That Initiate In Vitro and In Vivo Neuronal Death. Neuron 2014, 84, 1213–1225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, Y.-B.; Baskaran, P.; Gomez-Deza, J.; Chen, H.-J.; Nishimura, A.L.; Smith, B.N.; Troakes, C.; Adachi, Y.; Stepto, A.; Petrucelli, L.; et al. C9orf72 Poly GA RAN-Translated Protein Plays a Key Role in Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis via Aggregation and Toxicity. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2017, 26, 4765–4777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butti, Z.; Pan, Y.E.; Giacomotto, J.; Patten, S.A. Reduced C9orf72 Function Leads to Defective Synaptic Vesicle Release and Neuromuscular Dysfunction in Zebrafish. Commun. Biol. 2021, 4, 792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lall, D.; Lorenzini, I.; Mota, T.A.; Bell, S.; Mahan, T.E.; Ulrich, J.D.; Davtyan, H.; Rexach, J.E.; Muhammad, A.K.M.G.; Shelest, O.; et al. C9orf72 Deficiency Promotes Microglial-Mediated Synaptic Loss in Aging and Amyloid Accumulation. Neuron 2021, 109, 2275–2291.e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boivin, M.; Pfister, V.; Gaucherot, A.; Ruffenach, F.; Negroni, L.; Sellier, C.; Charlet-Berguerand, N. Reduced Autophagy upon C9ORF72 Loss Synergizes with Dipeptide Repeat Protein Toxicity in G4C2 Repeat Expansion Disorders. EMBO J. 2020, 39, e100574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beckers, J.; Tharkeshwar, A.K.; Fumagalli, L.; Contardo, M.; Van Schoor, E.; Fazal, R.; Thal, D.R.; Chandran, S.; Mancuso, R.; Van Den Bosch, L.; et al. A Toxic Gain-of-Function Mechanism in C9orf72 ALS Impairs the Autophagy-Lysosome Pathway in Neurons. Acta Neuropathol. Commun. 2023, 11, 151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Lin, S.; Staats, K.A.; Li, Y.; Chang, W.-H.; Hung, S.-T.; Hendricks, E.; Linares, G.R.; Wang, Y.; Son, E.Y.; et al. Haploinsufficiency Leads to Neurodegeneration in C9ORF72 ALS/FTD Human Induced Motor Neurons. Nat. Med. 2018, 24, 313–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seidel, M.; Rajkumar, S.; Steffke, C.; Noeth, V.; Agarwal, S.; Roger, K.; Lipecka, J.; Ludolph, A.; Guerrera, C.I.; Boeckers, T.; et al. Propranolol Reduces the Accumulation of Cytotoxic Aggregates in C9orf72-ALS/FTD in Vitro Models. Curr. Res. Neurobiol. 2023, 5, 100105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ho, W.Y.; Tai, Y.K.; Chang, J.-C.; Liang, J.; Tyan, S.-H.; Chen, S.; Guan, J.-L.; Zhou, H.; Shen, H.-M.; Koo, E.; et al. The ALS-FTD-Linked Gene Product, C9orf72, Regulates Neuronal Morphogenesis via Autophagy. Autophagy 2019, 15, 827–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Liang, Z.; Gu, Z.; Qin, Z. Molecular Mechanism and Regulation of Autophagy. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2005, 26, 1421–1434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farg, M.A.; Sundaramoorthy, V.; Sultana, J.M.; Yang, S.; Atkinson, R.A.K.; Levina, V.; Halloran, M.A.; Gleeson, P.A.; Blair, I.P.; Soo, K.Y.; et al. C9ORF72, Implicated in Amytrophic Lateral Sclerosis and Frontotemporal Dementia, Regulates Endosomal Trafficking. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2014, 23, 3579–3595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aly, A.; Laszlo, Z.I.; Rajkumar, S.; Demir, T.; Hindley, N.; Lamont, D.J.; Lehmann, J.; Seidel, M.; Sommer, D.; Franz-Wachtel, M.; et al. Integrative Proteomics Highlight Presynaptic Alterations and C-Jun Misactivation as Convergent Pathomechanisms in ALS. Acta Neuropathol. 2023, 146, 451–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Steffke, C.; Agarwal, S.; Kabashi, E.; Catanese, A. Overexpression of Toxic Poly(Glycine-Alanine) Aggregates in Primary Neuronal Cultures Induces Time-Dependent Autophagic and Synaptic Alterations but Subtle Activity Impairments. Cells 2024, 13, 1300. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells13151300
Steffke C, Agarwal S, Kabashi E, Catanese A. Overexpression of Toxic Poly(Glycine-Alanine) Aggregates in Primary Neuronal Cultures Induces Time-Dependent Autophagic and Synaptic Alterations but Subtle Activity Impairments. Cells. 2024; 13(15):1300. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells13151300
Chicago/Turabian StyleSteffke, Christina, Shreya Agarwal, Edor Kabashi, and Alberto Catanese. 2024. "Overexpression of Toxic Poly(Glycine-Alanine) Aggregates in Primary Neuronal Cultures Induces Time-Dependent Autophagic and Synaptic Alterations but Subtle Activity Impairments" Cells 13, no. 15: 1300. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells13151300
APA StyleSteffke, C., Agarwal, S., Kabashi, E., & Catanese, A. (2024). Overexpression of Toxic Poly(Glycine-Alanine) Aggregates in Primary Neuronal Cultures Induces Time-Dependent Autophagic and Synaptic Alterations but Subtle Activity Impairments. Cells, 13(15), 1300. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells13151300







