Psychiatric Comorbidities of Inflammatory Bowel Disease: It Is a Matter of Microglia’s Gut Feeling
Abstract
:1. Introduction
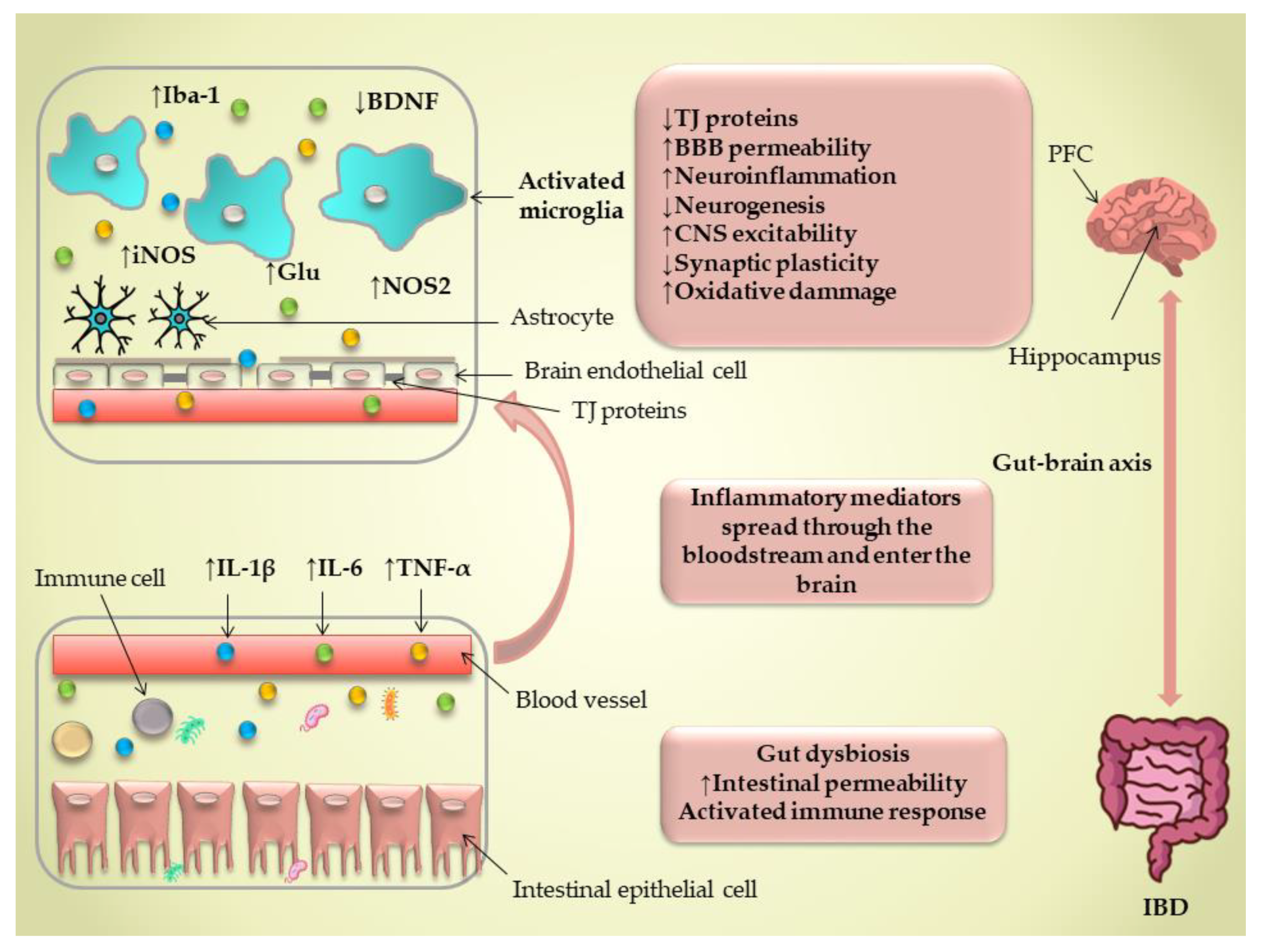
2. Gut Microbiota Abnormalities in IBD and Its Possible Connection to the Brain’s Innate Immune Response
3. Blood–Brain Barrier Integrity in IBD
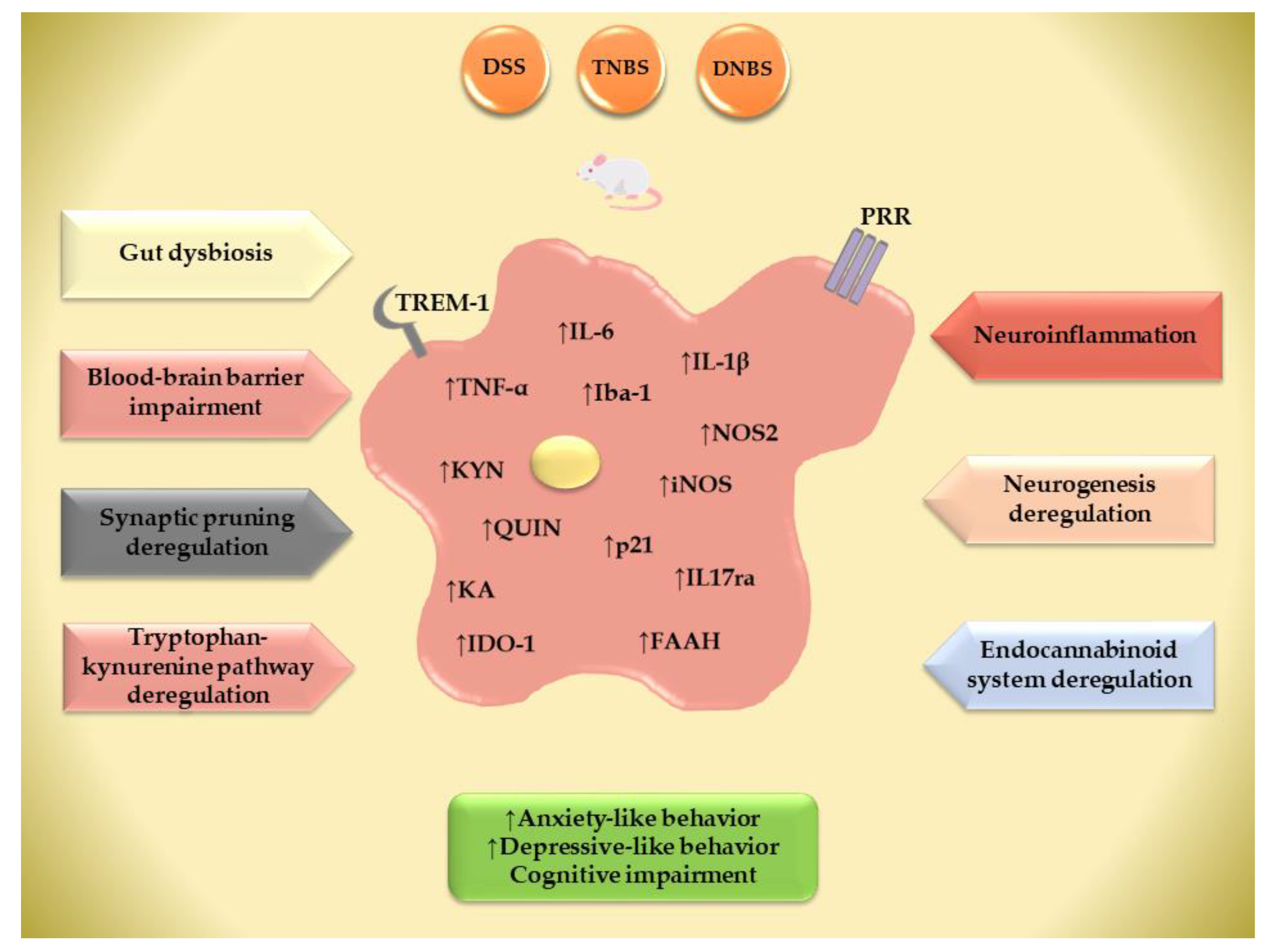
4. IBD-Associated Neuroinflammation—The Role of the Brain’s Innate Immune Response
5. Synaptic Pruning Deregulation in Behavioral Comorbidities in IBD
6. Neurogenesis Deregulation in Behavioral Comorbidities in IBD
7. Tryptophan–Kynurenine Pathway in Microglia and Its Possible Association with Behavioral Phenotypes in IBD
8. The Impact of Gut Inflammation on Central Endocannabinoid Function and the Development of Behavioral Comorbidities
9. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Guan, Q. A Comprehensive Review and Update on the Pathogenesis of Inflammatory Bowel Disease. J. Immunol. Res. 2019, 2019, 7247238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, J.T. Pathophysiology of Inflammatory Bowel Diseases. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 383, 2652–2664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ananthakrishnan, A.N.; Bernstein, C.N.; Iliopoulos, D.; Macpherson, A.; Neurath, M.F.; Ali, R.A.R.; Vavricka, S.R.; Fiocchi, C. Environmental Triggers in IBD: A Review of Progress and Evidence. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2018, 15, 39–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Byrne, G.; Rosenfeld, G.; Leung, Y.; Qian, H.; Raudzus, J.; Nunez, C.; Bressler, B. Prevalence of Anxiety and Depression in Patients with Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Can. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2017, 2017, 6496727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bernstein, C.N.; Hitchon, C.A.; Walld, R.; Bolton, J.M.; Sareen, J.; Walker, J.R.; Graff, L.A.; Patten, S.B.; Singer, A.; Lix, L.M.; et al. Increased Burden of Psychiatric Disorders in Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 2019, 25, 360–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barberio, B.; Zamani, M.; Black, C.J.; Savarino, E.V.; Ford, A.C. Prevalence of Symptoms of Anxiety and Depression in Patients with Inflammatory Bowel Disease: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Lancet Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2021, 6, 359–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gîlc-Blanariu, G.-E.; Ștefnescu, G.; Trifan, A.V.; Moscalu, M.; Dimofte, M.-G.; Ștefnescu, C.; Drug, V.L.; Afrsnie, V.-A.; Ciocoiu, M. Sleep Impairment and Psychological Distress among Patients with Inflammatory Bowel Disease—Beyond the Obvious. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 2304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hopkins, C.W.P.; Powell, N.; Norton, C.; Dumbrill, J.L.; Hayee, B.; Moulton, C.D. Cognitive Impairment in Adult Inflammatory Bowel Disease: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Acad. Consult. Psychiatry 2021, 62, 387–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikolova, V.L.; Pelton, L.; Moulton, C.D.; Zorzato, D.; Cleare, A.J.; Young, A.H.; Stone, J.M. The Prevalence and Incidence of Irritable Bowel Syndrome and Inflammatory Bowel Disease in Depression and Bipolar Disorder: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Psychosom. Med. 2022, 84, 313–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sung, K.; Zhang, B.; Wang, H.E.; Bai, Y.; Tsai, S.; Su, T.; Chen, T.; Hou, M.; Lu, C.; Wang, Y.; et al. Schizophrenia and Risk of New-onset Inflammatory Bowel Disease: A Nationwide Longitudinal Study. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2022, 55, 1192–1201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bisgaard, T.H.; Allin, K.H.; Keefer, L.; Ananthakrishnan, A.N.; Jess, T. Depression and Anxiety in Inflammatory Bowel Disease: Epidemiology, Mechanisms and Treatment. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2022, 19, 717–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fuller-Thomson, E.; Lateef, R.; Sulman, J. Robust Association Between Inflammatory Bowel Disease and Generalized Anxiety Disorder. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 2015, 21, 2341–2348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panara, A.J.; Yarur, A.J.; Rieders, B.; Proksell, S.; Deshpande, A.R.; Abreu, M.T.; Sussman, D.A. The Incidence and Risk Factors for Developing Depression after Being Diagnosed with Inflammatory Bowel Disease: A Cohort Study. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2014, 39, 802–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keefer, L.; Keshavarzian, A.; Mutlu, E. Reconsidering the Methodology of “Stress” Research in Inflammatory Bowel Disease. J. Crohn’s Colitis 2008, 2, 193–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eugenicos, M.P.; Ferreira, N.B. Psychological Factors Associated with Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Br. Med. Bull. 2021, 138, 16–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Black, J.; Sweeney, L.; Yuan, Y.; Singh, H.; Norton, C.; Czuber-Dochan, W. Systematic Review: The Role of Psychological Stress in Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2022, 56, 1235–1249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Armuzzi, A.; Liguori, G. Quality of Life in Patients with Moderate to Severe Ulcerative Colitis and the Impact of Treatment: A Narrative Review. Dig. Liver Dis. 2021, 53, 803–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, K.T.; Ehrlich, O.G.; Allen, J.I.; Meadows, P.; Szigethy, E.M.; Henrichsen, K.; Kim, S.C.; Lawton, R.C.; Murphy, S.M.; Regueiro, M.; et al. The Cost of Inflammatory Bowel Disease: An Initiative From the Crohn’s & Colitis Foundation. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 2020, 26, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Günther, C.; Rothhammer, V.; Karow, M.; Neurath, M.; Winner, B. The Gut-Brain Axis in Inflammatory Bowel Disease-Current and Future Perspectives. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 8870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gracie, D.J.; Hamlin, P.J.; Ford, A.C. The Influence of the Brain–Gut Axis in Inflammatory Bowel Disease and Possible Implications for Treatment. Lancet Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2019, 4, 632–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Mello, C.; Riazi, K.; Le, T.; Stevens, K.M.; Wang, A.; McKay, D.M.; Pittman, Q.J.; Swain, M.G. P-Selectin-Mediated Monocyte-Cerebral Endothelium Adhesive Interactions Link Peripheral Organ Inflammation to Sickness Behaviors. J. Neurosci. 2013, 33, 14878–14888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, L.; Liu, S.; Li, S.; Yang, J.; Hu, G.; Xu, C.; Song, W. Psychological Stress in Inflammatory Bowel Disease: Psychoneuroimmunological Insights into Bidirectional Gut–Brain Communications. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 1016578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, X.; Cao, Q.; Cheng, Y.; Zhao, D.; Wang, Z.; Yang, H.; Wu, Q.; You, L.; Wang, Y.; Lin, Y.; et al. Chronic Stress Promotes Colitis by Disturbing the Gut Microbiota and Triggering Immune System Response. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, E2960–E2969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghia, J.-E.; Blennerhassett, P.; Collins, S.M. Impaired Parasympathetic Function Increases Susceptibility to Inflammatory Bowel Disease in a Mouse Model of Depression. J. Clin. Investig. 2008, 118, 2209–2218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghia, J.; Blennerhassett, P.; Deng, Y.; Verdu, E.F.; Khan, W.I.; Collins, S.M. Reactivation of Inflammatory Bowel Disease in a Mouse Model of Depression. Gastroenterology 2009, 136, 2280–2288.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riazi, K.; Galic, M.A.; Kuzmiski, J.B.; Ho, W.; Sharkey, K.A.; Pittman, Q.J. Microglial Activation and TNFα Production Mediate Altered CNS Excitability Following Peripheral Inflammation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 17151–17156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dunn, G.A.; Loftis, J.M.; Sullivan, E.L. Neuroinflammation in Psychiatric Disorders: An Introductory Primer. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 2020, 196, 172981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muzio, L.; Viotti, A.; Martino, G. Microglia in Neuroinflammation and Neurodegeneration: From Understanding to Therapy. Front. Neurosci. 2021, 15, 742065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shemer, A.; Erny, D.; Jung, S.; Prinz, M. Microglia Plasticity During Health and Disease: An Immunological Perspective. Trends Immunol. 2015, 36, 614–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maitra, M.; Mitsuhashi, H.; Rahimian, R.; Chawla, A.; Yang, J.; Fiori, L.M.; Davoli, M.A.; Perlman, K.; Aouabed, Z.; Mash, D.C.; et al. Cell Type Specific Transcriptomic Differences in Depression Show Similar Patterns between Males and Females but Implicate Distinct Cell Types and Genes. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 2912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahimian, R.; Béland, L.-C.; Kriz, J. Galectin-3: Mediator of Microglia Responses in Injured Brain. Drug Discov. Today 2018, 23, 375–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahimian, R.; Belliveau, C.; Chen, R.; Mechawar, N. Microglial Inflammatory-Metabolic Pathways and Their Potential Therapeutic Implication in Major Depressive Disorder. Front. Psychiatry 2022, 13, 871997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahimian, R.; Lalancette-Hébert, M.; Weng, Y.C.; Sato, S.; Kriz, J. Glucosamine-Mediated Immunomodulation after Stroke Is Sexually Dimorphic. Brain Behav. Immun. Health 2020, 3, 100041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahimian, R.; Béland, L.-C.; Sato, S.; Kriz, J. Microglia-Derived Galectin-3 in Neuroinflammation; a Bittersweet Ligand? Med. Res. Rev. 2021, 41, 2582–2589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahimian, R.; Perlman, K.; Canonne, C.; Mechawar, N. Targeting Microglia-Oligodendrocyte Crosstalk in Neurodegenerative and Psychiatric Disorders. Drug Discov. Today 2022, 27, 2562–2573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahimian, R.; Cordeau, P.; Kriz, J. Brain Response to Injuries: When Microglia Go Sexist. Neuroscience 2019, 405, 14–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahimian, R.; Wakid, M.; O’Leary, L.A.; Mechawar, N. The Emerging Tale of Microglia in Psychiatric Disorders. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2021, 131, 1–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres-Platas, S.G.; Cruceanu, C.; Chen, G.G.; Turecki, G.; Mechawar, N. Evidence for Increased Microglial Priming and Macrophage Recruitment in the Dorsal Anterior Cingulate White Matter of Depressed Suicides. Brain. Behav. Immun. 2014, 42, 50–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masanetz, R.K.; Winkler, J.; Winner, B.; Günther, C.; Süß, P. The Gut–Immune–Brain Axis: An Important Route for Neuropsychiatric Morbidity in Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 11111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Haq, R.; Schlachetzki, J.C.M.; Glass, C.K.; Mazmanian, S.K. Microbiome-Microglia Connections via the Gut-Brain Axis. J. Exp. Med. 2019, 216, 41–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishida, A.; Inoue, R.; Inatomi, O.; Bamba, S.; Naito, Y.; Andoh, A. Gut Microbiota in the Pathogenesis of Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Clin. J. Gastroenterol. 2018, 11, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manichanh, C.; Rigottier-Gois, L.; Bonnaud, E.; Gloux, K.; Pelletier, E.; Frangeul, L.; Nalin, R.; Jarrin, C.; Chardon, P.; Marteau, P.; et al. Reduced Diversity of Faecal Microbiota in Crohn’s Disease Revealed by a Metagenomic Approach. Gut 2006, 55, 205–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erny, D.; Hrabě de Angelis, A.L.; Jaitin, D.; Wieghofer, P.; Staszewski, O.; David, E.; Keren-Shaul, H.; Mahlakoiv, T.; Jakobshagen, K.; Buch, T.; et al. Host Microbiota Constantly Control Maturation and Function of Microglia in the CNS. Nat. Neurosci. 2015, 18, 965–977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eltokhi, A.; Janmaat, I.E.; Genedi, M.; Haarman, B.C.M.; Sommer, I.E.C. Dysregulation of Synaptic Pruning as a Possible Link between Intestinal Microbiota Dysbiosis and Neuropsychiatric Disorders. J. Neurosci. Res. 2020, 98, 1335–1369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, Q.; Xing, C.; Long, W.; Wang, H.Y.; Liu, Q.; Wang, R.-F. Impact of Microbiota on Central Nervous System and Neurological Diseases: The Gut-Brain Axis. J. Neuroinflamm. 2019, 16, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chu, C.; Murdock, M.H.; Jing, D.; Won, T.H.; Chung, H.; Kressel, A.M.; Tsaava, T.; Addorisio, M.E.; Putzel, G.G.; Zhou, L.; et al. The Microbiota Regulate Neuronal Function and Fear Extinction Learning. Nature 2019, 574, 543–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thion, M.S.; Low, D.; Silvin, A.; Chen, J.; Grisel, P.; Schulte-Schrepping, J.; Blecher, R.; Ulas, T.; Squarzoni, P.; Hoeffel, G.; et al. Microbiome Influences Prenatal and Adult Microglia in a Sex-Specific Manner. Cell 2018, 172, 500–516.e16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mossad, O.; Erny, D. The Microbiota-Microglia Axis in Central Nervous System Disorders. Brain Pathol. 2020, 30, 1159–1177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erny, D.; Dokalis, N.; Mezö, C.; Castoldi, A.; Mossad, O.; Staszewski, O.; Frosch, M.; Villa, M.; Fuchs, V.; Mayer, A.; et al. Microbiota-Derived Acetate Enables the Metabolic Fitness of the Brain Innate Immune System during Health and Disease. Cell Metab. 2021, 33, 2260–2276.e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furube, E.; Kawai, S.; Inagaki, H.; Takagi, S.; Miyata, S. Brain Region-Dependent Heterogeneity and Dose-Dependent Difference in Transient Microglia Population Increase during Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Inflammation. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 2203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janssens, Y.; Debunne, N.; De Spiegeleer, A.; Wynendaele, E.; Planas, M.; Feliu, L.; Quarta, A.; Claes, C.; Van Dam, D.; De Deyn, P.P.; et al. PapRIV, a BV-2 Microglial Cell Activating Quorum Sensing Peptide. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 10723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Forsythe, P.; Bienenstock, J.; Kunze, W.A. Vagal Pathways for Microbiome-Brain-Gut Axis Communication. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2014, 817, 115–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Çalışkan, G.; French, T.; Enrile Lacalle, S.; Del Angel, M.; Steffen, J.; Heimesaat, M.M.; Rita Dunay, I.; Stork, O. Antibiotic-Induced Gut Dysbiosis Leads to Activation of Microglia and Impairment of Cholinergic Gamma Oscillations in the Hippocampus. Brain. Behav. Immun. 2022, 99, 203–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guida, F.; Turco, F.; Iannotta, M.; De Gregorio, D.; Palumbo, I.; Sarnelli, G.; Furiano, A.; Napolitano, F.; Boccella, S.; Luongo, L.; et al. Antibiotic-Induced Microbiota Perturbation Causes Gut Endocannabinoidome Changes, Hippocampal Neuroglial Reorganization and Depression in Mice. Brain. Behav. Immun. 2018, 67, 230–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salvo, E.; Stokes, P.; Keogh, C.E.; Brust-Mascher, I.; Hennessey, C.; Knotts, T.A.; Sladek, J.A.; Rude, K.M.; Swedek, M.; Rabasa, G.; et al. A Murine Model of Pediatric Inflammatory Bowel Disease Causes Microbiota-Gut-Brain Axis Deficits in Adulthood. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2020, 319, G361–G374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vicentini, F.A.; Szamosi, J.C.; Rossi, L.; Griffin, L.; Nieves, K.; Bihan, D.; Lewis, I.A.; Pittman, Q.J.; Swain, M.G.; Surette, M.G.; et al. Colitis-Associated Microbiota Drives Changes in Behaviour in Male Mice in the Absence of Inflammation. Brain. Behav. Immun. 2022, 102, 266–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banks, W.A. Blood-Brain Barrier Transport of Cytokines: A Mechanism for Neuropathology. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2005, 11, 973–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, S.S.; Min, M.; Cummings, E.E.; Chen, X.; Sadowska, G.B.; Sharma, S.; Stonestreet, B.S. Effects of Interleukin-6 on the Expression of Tight Junction Proteins in Isolated Cerebral Microvessels from Yearling and Adult Sheep. Neuroimmunomodulation 2013, 20, 264–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, S.; Song, H.-L.; Zhou, Y.; Li, L.-X.; Cui, W.; Wang, W.; Liu, P. Tumour Necrosis Factor-Alpha Affects Blood-Brain Barrier Permeability and Tight Junction-Associated Occludin in Acute Liver Failure. Liver Int. 2010, 30, 1198–1210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rochfort, K.D.; Collins, L.E.; Murphy, R.P.; Cummins, P.M. Downregulation of Blood-Brain Barrier Phenotype by Proinflammatory Cytokines Involves NADPH Oxidase-Dependent ROS Generation: Consequences for Interendothelial Adherens and Tight Junctions. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e101815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Jin, S.; Sonobe, Y.; Cheng, Y.; Horiuchi, H.; Parajuli, B.; Kawanokuchi, J.; Mizuno, T.; Takeuchi, H.; Suzumura, A. Interleukin-1β Induces Blood–Brain Barrier Disruption by Downregulating Sonic Hedgehog in Astrocytes. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e110024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, R.; Chen, F.; Wen, S.; Teng, T.; Pan, Y.; Huang, H. Interleukin-10 Attenuates Impairment of the Blood-Brain Barrier in a Severe Acute Pancreatitis Rat Model. J. Inflamm. 2018, 15, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, Y.; Zhao, T.; Cheng, X.; Zhao, M.; Gong, S.-H.; Zhao, Y.-Q.; Wu, H.-T.; Fan, M.; Zhu, L.-L. Cortical Inflammation Is Increased in a DSS-Induced Colitis Mouse Model. Neurosci. Bull. 2018, 34, 1058–1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Natah, S.S.; Mouihate, A.; Pittman, Q.J.; Sharkey, K.A. Disruption of the Blood–Brain Barrier during TNBS Colitis. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2005, 17, 433–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devorak, J.; Torres-Platas, S.G.; Davoli, M.A.; Prud’homme, J.; Turecki, G.; Mechawar, N. Cellular and Molecular Inflammatory Profile of the Choroid Plexus in Depression and Suicide. Front. Psychiatry 2015, 6, 138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carloni, S.; Bertocchi, A.; Mancinelli, S.; Bellini, M.; Erreni, M.; Borreca, A.; Braga, D.; Giugliano, S.; Mozzarelli, A.M.; Manganaro, D.; et al. Identification of a Choroid Plexus Vascular Barrier Closing during Intestinal Inflammation. Science 2021, 374, 439–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menard, C.; Pfau, M.L.; Hodes, G.E.; Kana, V.; Wang, V.X.; Bouchard, S.; Takahashi, A.; Flanigan, M.E.; Aleyasin, H.; LeClair, K.B.; et al. Social Stress Induces Neurovascular Pathology Promoting Depression. Nat. Neurosci. 2017, 20, 1752–1760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morris, G.; Fernandes, B.S.; Puri, B.K.; Walker, A.J.; Carvalho, A.F.; Berk, M. Leaky Brain in Neurological and Psychiatric Disorders: Drivers and Consequences. Aust. N. Z. J. Psychiatry 2018, 52, 924–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Fonseca, A.C.C.; Matias, D.; Garcia, C.; Amaral, R.; Geraldo, L.H.; Freitas, C.; Lima, F.R.S. The Impact of Microglial Activation on Blood-Brain Barrier in Brain Diseases. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2014, 8, 362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haruwaka, K.; Ikegami, A.; Tachibana, Y.; Ohno, N.; Konishi, H.; Hashimoto, A.; Matsumoto, M.; Kato, D.; Ono, R.; Kiyama, H.; et al. Dual Microglia Effects on Blood Brain Barrier Permeability Induced by Systemic Inflammation. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 5816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bisht, K.; Okojie, K.A.; Sharma, K.; Lentferink, D.H.; Sun, Y.-Y.; Chen, H.-R.; Uweru, J.O.; Amancherla, S.; Calcuttawala, Z.; Campos-Salazar, A.B.; et al. Capillary-Associated Microglia Regulate Vascular Structure and Function through PANX1-P2RY12 Coupling in Mice. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 5289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liddelow, S.A.; Guttenplan, K.A.; Clarke, L.E.; Bennett, F.C.; Bohlen, C.J.; Schirmer, L.; Bennett, M.L.; Münch, A.E.; Chung, W.-S.; Peterson, T.C.; et al. Neurotoxic Reactive Astrocytes Are Induced by Activated Microglia. Nature 2017, 541, 481–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torres-Platas, S.G.; Hercher, C.; Davoli, M.A.; Maussion, G.; Labonté, B.; Turecki, G.; Mechawar, N. Astrocytic Hypertrophy in Anterior Cingulate White Matter of Depressed Suicides. Neuropsychopharmacology 2011, 36, 2650–2658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spampinato, S.F.; Bortolotto, V.; Canonico, P.L.; Sortino, M.A.; Grilli, M. Astrocyte-Derived Paracrine Signals: Relevance for Neurogenic Niche Regulation and Blood-Brain Barrier Integrity. Front. Pharmacol. 2019, 10, 1346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ishijima, T.; Nakajima, K. Inflammatory Cytokines TNFα, IL-1β, and IL-6 Are Induced in Endotoxin- Stimulated Microglia through Different Signaling Cascades. Sci. Prog. 2021, 104, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, J.; Yoon, D.; Nam, Y.; Seo, D.; Kim, J.-H.; Kim, M.S.; Lee, T.Y.; Kim, K.S.; Ko, P.-W.; Lee, H.-W.; et al. Lipopolysaccharide Administration for a Mouse Model of Cerebellar Ataxia with Neuroinflammation. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 13337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sudo, K.; Takezawa, Y.; Kohsaka, S.; Nakajima, K. Involvement of Nitric Oxide in the Induction of Interleukin-1 Beta in Microglia. Brain Res. 2015, 1625, 121–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nyuyki, K.D.; Pittman, Q.J. Toward a Better Understanding of the Central Consequences of Intestinal Inflammation. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2015, 1351, 149–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riazi, K.; Galic, M.A.; Kentner, A.C.; Reid, A.Y.; Sharkey, K.A.; Pittman, Q.J. Microglia-Dependent Alteration of Glutamatergic Synaptic Transmission and Plasticity in the Hippocampus during Peripheral Inflammation. J. Neurosci. 2015, 35, 4942–4952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, S.M.; Kallarackal, A.J.; Kvarta, M.D.; Van Dyke, A.M.; LeGates, T.A.; Cai, X. An Excitatory Synapse Hypothesis of Depression. Trends Neurosci. 2015, 38, 279–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnes, S.E.; Zera, K.A.; Ivison, G.T.; Buckwalter, M.S.; Engleman, E.G. Brain Profiling in Murine Colitis and Human Epilepsy Reveals Neutrophils and TNFα as Mediators of Neuronal Hyperexcitability. J. Neuroinflamm. 2021, 18, 199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riazi, K.; Honar, H.; Homayoun, H.; Demehri, S.; Bahadori, M.; Dehpour, A.R. Intestinal Inflammation Alters the Susceptibility to Pentylenetetrazole-Induced Seizure in Mice. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2004, 19, 270–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lasselin, J. Back to the Future of Psychoneuroimmunology: Studying Inflammation-Induced Sickness Behavior. Brain Behav. Immun. Health 2021, 18, 100379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cluny, N.L.; Nyuyki, K.D.; Almishri, W.; Griffin, L.; Lee, B.H.; Hirota, S.A.; Pittman, Q.J.; Swain, M.G.; Sharkey, K.A. Recruitment of A4β7 Monocytes and Neutrophils to the Brain in Experimental Colitis Is Associated with Elevated Cytokines and Anxiety-like Behavior. J. Neuroinflamm. 2022, 19, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anderson, G.; Berk, M.; Dean, O.; Moylan, S.; Maes, M. Role of Immune-Inflammatory and Oxidative and Nitrosative Stress Pathways in the Etiology of Depression: Therapeutic Implications. CNS Drugs 2014, 28, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heydarpour, P.; Rahimian, R.; Fakhfouri, G.; Khoshkish, S.; Fakhraei, N.; Salehi-Sadaghiani, M.; Wang, H.; Abbasi, A.; Dehpour, A.R.; Ghia, J.-E. Behavioral Despair Associated with a Mouse Model of Crohn’s Disease: Role of Nitric Oxide Pathway. Prog. Neuropsychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 2016, 64, 131–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gharedaghi, M.H.; Rahimian, R.; Dehpour, A.R.; Yousefzadeh-Fard, Y.; Mohammadi-Farani, A. Dinitrobenzene Sulphonic Acid-Induced Colitis Impairs Spatial Recognition Memory in Mice: Roles of N-Methyl D-Aspartate Receptors and Nitric Oxide. Psychopharmacology 2015, 232, 3081–3090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.-F.; Li, L.-L.; Xian, W.-B.; Li, M.-Y.; Zhang, L.-Y.; Xu, J.-H.; Pei, Z.; Zheng, H.-Q.; Hu, X.-Q. Chronic Colitis Exacerbates NLRP3-Dependent Neuroinflammation and Cognitive Impairment in Middle-Aged Brain. J. Neuroinflamm. 2021, 18, 153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, K.A.; Thomsen, C. The Role of the Innate Immune System in Psychiatric Disorders. Mol. Cell. Neurosci. 2013, 53, 52–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mondelli, V.; Vernon, A.C.; Turkheimer, F.; Dazzan, P.; Pariante, C.M. Brain Microglia in Psychiatric Disorders. Lancet Psychiatry 2017, 4, 563–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stein, D.J.; Vasconcelos, M.F.; Albrechet-Souza, L.; Ceresér, K.M.M.; de Almeida, R.M.M. Microglial Over-Activation by Social Defeat Stress Contributes to Anxiety- and Depressive-Like Behaviors. Front. Behav. Neurosci. 2017, 11, 207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Munshi, S.; Loh, M.K.; Ferrara, N.; DeJoseph, M.R.; Ritger, A.; Padival, M.; Record, M.J.; Urban, J.H.; Rosenkranz, J.A. Repeated Stress Induces a Pro-Inflammatory State, Increases Amygdala Neuronal and Microglial Activation, and Causes Anxiety in Adult Male Rats. Brain. Behav. Immun. 2020, 84, 180–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yirmiya, R.; Rimmerman, N.; Reshef, R. Depression as a Microglial Disease. Trends Neurosci. 2015, 38, 637–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Sousa, J.F.M.; Paghdar, S.; Khan, T.M.; Patel, N.P.; Chandrasekaran, S.; Tsouklidis, N. Stress and Inflammatory Bowel Disease: Clear Mind, Happy Colon. Cureus 2022, 14, e25006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sroor, H.M.; Hassan, A.M.; Zenz, G.; Valadez-Cosmes, P.; Farzi, A.; Holzer, P.; El-Sharif, A.; Gomaa, F.A.-Z.M.; Kargl, J.; Reichmann, F. Experimental Colitis Reduces Microglial Cell Activation in the Mouse Brain without Affecting Microglial Cell Numbers. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 20217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matisz, C.E.; Gruber, A.J. Neuroinflammatory Remodeling of the Anterior Cingulate Cortex as a Key Driver of Mood Disorders in Gastrointestinal Disease and Disorders. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2022, 133, 104497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, K.; Liu, Y.; Shao, S.; Song, W.; Chen, X.; Dong, Y.; Zhang, Y. The Microglial Innate Immune Receptors TREM-1 and TREM-2 in the Anterior Cingulate Cortex (ACC) Drive Visceral Hypersensitivity and Depressive-like Behaviors Following DSS-Induced Colitis. Brain. Behav. Immun. 2023, 112, 96–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talley, S.; Valiauga, R.; Anderson, L.; Cannon, A.R.; Choudhry, M.A.; Campbell, E.M. DSS-Induced Inflammation in the Colon Drives a Proinflammatory Signature in the Brain That Is Ameliorated by Prophylactic Treatment with the S100A9 Inhibitor Paquinimod. J. Neuroinflamm. 2021, 18, 263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basilico, B.; Ferrucci, L.; Khan, A.; Di Angelantonio, S.; Ragozzino, D.; Reverte, I. What Microglia Depletion Approaches Tell Us about the Role of Microglia on Synaptic Function and Behavior. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2022, 16, 1022431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cunningham, C.L.; Martínez-Cerdeño, V.; Noctor, S.C. Microglia Regulate the Number of Neural Precursor Cells in the Developing Cerebral Cortex. J. Neurosci. 2013, 33, 4216–4233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamoto, M.; Kim, M.; Imai, H.; Itakura, Y.; Ohtsuki, G. Microglia-Triggered Plasticity of Intrinsic Excitability Modulates Psychomotor Behaviors in Acute Cerebellar Inflammation. Cell Rep. 2019, 28, 2923–2938.e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dwyer, Z.; Rudyk, C.; Situt, D.; Beauchamp, S.; Abdali, J.; Dinesh, A.; Legancher, N.; Sun, H.; Schlossmacher, M.; Hayley, S. Microglia Depletion Prior to Lipopolysaccharide and Paraquat Treatment Differentially Modulates Behavioral and Neuronal Outcomes in Wild Type and G2019S LRRK2 Knock-in Mice. Brain Behav. Immun. Health 2020, 5, 100079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Ishima, T.; Wan, X.; Wei, Y.; Chang, L.; Zhang, J.; Qu, Y.; Hashimoto, K. Microglial Depletion and Abnormalities in Gut Microbiota Composition and Short-Chain Fatty Acids in Mice after Repeated Administration of Colony Stimulating Factor 1 Receptor Inhibitor PLX5622. Eur. Arch. Psychiatry Clin. Neurosci. 2022, 272, 483–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frick, L.R.; Williams, K.; Pittenger, C. Microglial Dysregulation in Psychiatric Disease. Clin. Dev. Immunol. 2013, 2013, 608654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paolicelli, R.C.; Bolasco, G.; Pagani, F.; Maggi, L.; Scianni, M.; Panzanelli, P.; Giustetto, M.; Ferreira, T.A.; Guiducci, E.; Dumas, L.; et al. Synaptic Pruning by Microglia Is Necessary for Normal Brain Development. Science 2011, 333, 1456–1458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guedes, J.R.; Ferreira, P.A.; Costa, J.M.; Cardoso, A.L.; Peça, J. Microglia-Dependent Remodeling of Neuronal Circuits. J. Neurochem. 2022, 163, 74–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stevens, B.; Allen, N.J.; Vazquez, L.E.; Howell, G.R.; Christopherson, K.S.; Nouri, N.; Micheva, K.D.; Mehalow, A.K.; Huberman, A.D.; Stafford, B.; et al. The Classical Complement Cascade Mediates CNS Synapse Elimination. Cell 2007, 131, 1164–1178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schafer, D.P.; Lehrman, E.K.; Kautzman, A.G.; Koyama, R.; Mardinly, A.R.; Yamasaki, R.; Ransohoff, R.M.; Greenberg, M.E.; Barres, B.A.; Stevens, B. Microglia Sculpt Postnatal Neural Circuits in an Activity and Complement-Dependent Manner. Neuron 2012, 74, 691–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Chen, H.-S.; Li, H.-H.; Wang, H.-J.; Zou, R.-S.; Lu, X.-J.; Wang, J.; Nie, B.-B.; Wu, J.-F.; Li, S.; et al. Microglia-Dependent Excessive Synaptic Pruning Leads to Cortical Underconnectivity and Behavioral Abnormality Following Chronic Social Defeat Stress in Mice. Brain. Behav. Immun. 2023, 109, 23–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunner, G.; Cheadle, L.; Johnson, K.M.; Ayata, P.; Badimon, A.; Mondo, E.; Nagy, M.A.; Liu, L.; Bemiller, S.M.; Kim, K.-W.; et al. Sensory Lesioning Induces Microglial Synapse Elimination via ADAM10 and Fractalkine Signaling. Nat. Neurosci. 2019, 22, 1075–1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filipello, F.; Morini, R.; Corradini, I.; Zerbi, V.; Canzi, A.; Michalski, B.; Erreni, M.; Markicevic, M.; Starvaggi-Cucuzza, C.; Otero, K.; et al. The Microglial Innate Immune Receptor TREM2 Is Required for Synapse Elimination and Normal Brain Connectivity. Immunity 2018, 48, 979–991.e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scott-Hewitt, N.; Perrucci, F.; Morini, R.; Erreni, M.; Mahoney, M.; Witkowska, A.; Carey, A.; Faggiani, E.; Schuetz, L.T.; Mason, S.; et al. Local Externalization of Phosphatidylserine Mediates Developmental Synaptic Pruning by Microglia. EMBO J. 2020, 39, e105380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Izuo, N.; Nitta, A. New Insights Regarding Diagnosis and Medication for Schizophrenia Based on Neuronal Synapse-Microglia Interaction. J. Pers. Med. 2021, 11, 371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sellgren, C.M.; Gracias, J.; Watmuff, B.; Biag, J.D.; Thanos, J.M.; Whittredge, P.B.; Fu, T.; Worringer, K.; Brown, H.E.; Wang, J.; et al. Increased Synapse Elimination by Microglia in Schizophrenia Patient-Derived Models of Synaptic Pruning. Nat. Neurosci. 2019, 22, 374–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, M.-M.; Guo, M.-X.; Zhang, Q.-P.; Chen, X.-Q.; Li, N.-Z.; Liu, Q.; Cheng, J.; Wang, S.-L.; Xu, G.-H.; Li, C.-F.; et al. IL-1R/C3aR Signaling Regulates Synaptic Pruning in the Prefrontal Cortex of Depression. Cell Biosci. 2022, 12, 90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lieberman, O.J.; McGuirt, A.F.; Tang, G.; Sulzer, D. Roles for Neuronal and Glial Autophagy in Synaptic Pruning during Development. Neurobiol. Dis. 2019, 122, 49–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.-J.; Cho, M.-H.; Shim, W.H.; Kim, J.K.; Jeon, E.-Y.; Kim, D.-H.; Yoon, S.-Y. Deficient Autophagy in Microglia Impairs Synaptic Pruning and Causes Social Behavioral Defects. Mol. Psychiatry 2017, 22, 1576–1584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fracas, E.; Costantino, A.; Vecchi, M.; Buoli, M. Depressive and Anxiety Disorders in Patients with Inflammatory Bowel Diseases: Are There Any Gender Differences? Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2023, 20, 6255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Huang, G.; Cong, Y.; Yu, Y.; Li, Y. Sex-Related Differences in Inflammatory Bowel Diseases: The Potential Role of Sex Hormones. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 2022, 28, 1766–1775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villa, A.; Vegeto, E.; Poletti, A.; Maggi, A. Estrogens, Neuroinflammation, and Neurodegeneration. Endocr. Rev. 2016, 37, 372–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krolick, K.N.; Zhu, Q.; Shi, H. Effects of Estrogens on Central Nervous System Neurotransmission: Implications for Sex Differences in Mental Disorders. Prog. Mol. Biol. Transl. Sci. 2018, 160, 105–171. [Google Scholar]
- Brann, D.W.; Dhandapani, K.; Wakade, C.; Mahesh, V.B.; Khan, M.M. Neurotrophic and Neuroprotective Actions of Estrogen: Basic Mechanisms and Clinical Implications. Steroids 2007, 72, 381–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zonis, S.; Pechnick, R.N.; Ljubimov, V.A.; Mahgerefteh, M.; Wawrowsky, K.; Michelsen, K.S.; Chesnokova, V. Chronic Intestinal Inflammation Alters Hippocampal Neurogenesis. J. Neuroinflamm. 2015, 12, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gampierakis, I.-A.; Koutmani, Y.; Semitekolou, M.; Morianos, I.; Polissidis, A.; Katsouda, A.; Charalampopoulos, I.; Xanthou, G.; Gravanis, A.; Karalis, K.P. Hippocampal Neural Stem Cells and Microglia Response to Experimental Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD). Mol. Psychiatry 2021, 26, 1248–1263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Myint, A.-M.; Halaris, A. Imbalances in Kynurenines as Potential Biomarkers in the Diagnosis and Treatment of Psychiatric Disorders. Front. Psychiatry 2022, 13, 913303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujigaki, H.; Yamamoto, Y.; Saito, K. L-Tryptophan-Kynurenine Pathway Enzymes Are Therapeutic Target for Neuropsychiatric Diseases: Focus on Cell Type Differences. Neuropharmacology 2017, 112, 264–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suzuki, H.; Ohgidani, M.; Kuwano, N.; Chrétien, F.; Lorin de la Grandmaison, G.; Onaya, M.; Tominaga, I.; Setoyama, D.; Kang, D.; Mimura, M.; et al. Suicide and Microglia: Recent Findings and Future Perspectives Based on Human Studies. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2019, 13, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steiner, J.; Walter, M.; Gos, T.; Guillemin, G.J.; Bernstein, H.-G.; Sarnyai, Z.; Mawrin, C.; Brisch, R.; Bielau, H.; Meyer zu Schwabedissen, L.; et al. Severe Depression Is Associated with Increased Microglial Quinolinic Acid in Subregions of the Anterior Cingulate Gyrus: Evidence for an Immune-Modulated Glutamatergic Neurotransmission? J. Neuroinflamm. 2011, 8, 94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Busse, M.; Busse, S.; Myint, A.M.; Gos, T.; Dobrowolny, H.; Müller, U.J.; Bogerts, B.; Bernstein, H.-G.; Steiner, J. Decreased Quinolinic Acid in the Hippocampus of Depressive Patients: Evidence for Local Anti-Inflammatory and Neuroprotective Responses? Eur. Arch. Psychiatry Clin. Neurosci. 2015, 265, 321–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, S.M.; Pocivavsek, A.; Nicholson, J.D.; Notarangelo, F.M.; Langenberg, P.; McMahon, R.P.; Kleinman, J.E.; Hyde, T.M.; Stiller, J.; Postolache, T.T.; et al. Reduced Kynurenine Pathway Metabolism and Cytokine Expression in the Prefrontal Cortex of Depressed Individuals. J. Psychiatry Neurosci. 2016, 41, 386–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erhardt, S.; Lim, C.K.; Linderholm, K.R.; Janelidze, S.; Lindqvist, D.; Samuelsson, M.; Lundberg, K.; Postolache, T.T.; Träskman-Bendz, L.; Guillemin, G.J.; et al. Connecting Inflammation with Glutamate Agonism in Suicidality. Neuropsychopharmacology 2013, 38, 743–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bay-Richter, C.; Linderholm, K.R.; Lim, C.K.; Samuelsson, M.; Träskman-Bendz, L.; Guillemin, G.J.; Erhardt, S.; Brundin, L. A Role for Inflammatory Metabolites as Modulators of the Glutamate N-Methyl-D-Aspartate Receptor in Depression and Suicidality. Brain. Behav. Immun. 2015, 43, 110–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Y.; Drevets, W.; Turecki, G.; Li, Q.S. The Relationship between Plasma Serotonin and Kynurenine Pathway Metabolite Levels and the Treatment Response to Escitalopram and Desvenlafaxine. Brain. Behav. Immun. 2020, 87, 404–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Platten, M.; Nollen, E.A.A.; Röhrig, U.F.; Fallarino, F.; Opitz, C.A. Tryptophan Metabolism as a Common Therapeutic Target in Cancer, Neurodegeneration and Beyond. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2019, 18, 379–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.-M.; Bao, C.-H.; Wu, Y.; Liang, S.-H.; Wang, D.; Wu, L.-Y.; Huang, Y.; Liu, H.-R.; Wu, H.-G. Tryptophan-Kynurenine Metabolism: A Link between the Gut and Brain for Depression in Inflammatory Bowel Disease. J. Neuroinflamm. 2021, 18, 135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.-P.; Wu, J.; Quan, W.; Zhou, Y.; Hong, H.; Niu, G.-Y.; Li, T.; Huang, S.-B.; Qiao, C.-M.; Zhao, W.-J.; et al. DSS-Induced Colitis Activates the Kynurenine Pathway in Serum and Brain by Affecting IDO-1 and Gut Microbiota. Front. Immunol. 2023, 13, 1089200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Więdłocha, M.; Marcinowicz, P.; Janoska-Jaździk, M.; Szulc, A. Gut Microbiota, Kynurenine Pathway and Mental Disorders—Review. Prog. Neuropsychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 2021, 106, 110145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, Y.; Zhou, M.; Wang, J.; Yao, J.; Yu, J.; Liu, W.; Wu, L.; Wang, J.; Gao, R. Involvement of the Microbiota-Gut-Brain Axis in Chronic Restraint Stress: Disturbances of the Kynurenine Metabolic Pathway in Both the Gut and Brain. Gut Microbes 2021, 13, 1869501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, H.J.; Kim, S.A.; Kang, W.S.; Kim, J.W. Early-Life Stress Modulates Gut Microbiota and Peripheral and Central Inflammation in a Sex-Dependent Manner. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 1899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morena, M.; Patel, S.; Bains, J.S.; Hill, M.N. Neurobiological Interactions Between Stress and the Endocannabinoid System. Neuropsychopharmacology 2016, 41, 80–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, S.; Hill, M.N.; Cheer, J.F.; Wotjak, C.T.; Holmes, A. The Endocannabinoid System as a Target for Novel Anxiolytic Drugs. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2017, 76, 56–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharkey, K.A.; Wiley, J.W. The Role of the Endocannabinoid System in the Brain-Gut Axis. Gastroenterology 2016, 151, 252–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vecchiarelli, H.A.; Morena, M.; Keenan, C.M.; Chiang, V.; Tan, K.; Qiao, M.; Leitl, K.; Santori, A.; Pittman, Q.J.; Sharkey, K.A.; et al. Comorbid Anxiety-like Behavior in a Rat Model of Colitis Is Mediated by an Upregulation of Corticolimbic Fatty Acid Amide Hydrolase. Neuropsychopharmacology 2021, 46, 992–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Navarrete, M.; Araque, A. Endocannabinoids Potentiate Synaptic Transmission through Stimulation of Astrocytes. Neuron 2010, 68, 113–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mecha, M.; Carrillo-Salinas, F.J.; Feliú, A.; Mestre, L.; Guaza, C. Microglia Activation States and Cannabinoid System: Therapeutic Implications. Pharmacol. Ther. 2016, 166, 40–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reusch, N.; Ravichandran, K.A.; Olabiyi, B.F.; Komorowska-Müller, J.A.; Hansen, J.N.; Ulas, T.; Beyer, M.; Zimmer, A.; Schmöle, A.-C. Cannabinoid Receptor 2 Is Necessary to Induce Toll-like Receptor-Mediated Microglial Activation. Glia 2022, 70, 71–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mecha, M.; Feliú, A.; Carrillo-Salinas, F.J.; Rueda-Zubiaurre, A.; Ortega-Gutiérrez, S.; de Sola, R.G.; Guaza, C. Endocannabinoids Drive the Acquisition of an Alternative Phenotype in Microglia. Brain. Behav. Immun. 2015, 49, 233–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, Y.; Li, L.; Jiang, B.; Feng, Z.; Yang, L.; Tang, J.; Chen, Q.; Zhang, J.; Tan, Q.; Feng, H.; et al. Cannabinoid Receptor-2 Stimulation Suppresses Neuroinflammation by Regulating Microglial M1/M2 Polarization through the CAMP/PKA Pathway in an Experimental GMH Rat Model. Brain. Behav. Immun. 2016, 58, 118–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Liang, P.; Liu, J.; Jiang, H.; Fan, X.; Chen, G.; Zhou, C. Elevation of Arachidonoylethanolamide Levels by Activation of the Endocannabinoid System Protects against Colitis and Ameliorates Remote Organ Lesions in Mice. Exp. Ther. Med. 2017, 14, 5664–5670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domschke, K.; Dannlowski, U.; Ohrmann, P.; Lawford, B.; Bauer, J.; Kugel, H.; Heindel, W.; Young, R.; Morris, P.; Arolt, V.; et al. Cannabinoid Receptor 1 (CNR1) Gene: Impact on Antidepressant Treatment Response and Emotion Processing in Major Depression. Eur. Neuropsychopharmacol. 2008, 18, 751–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onaivi, E.S.; Ishiguro, H.; Gong, J.-P.; Patel, S.; Meozzi, P.A.; Myers, L.; Perchuk, A.; Mora, Z.; Tagliaferro, P.A.; Gardner, E.; et al. Functional Expression of Brain Neuronal CB2 Cannabinoid Receptors Are Involved in the Effects of Drugs of Abuse and in Depression. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2008, 1139, 434–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, X.; Miao, Q.; Lu, X.; Zhang, Z.; Chen, M.; Zhang, J.; Zhai, J. The Association of Endocannabinoid Receptor Genes (CNR1 and CNR2) Polymorphisms with Depression: A Meta-Analysis. Medicine 2019, 98, e17403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hill, M.N.; Miller, G.E.; Carrier, E.J.; Gorzalka, B.B.; Hillard, C.J. Circulating Endocannabinoids and N-Acyl Ethanolamines Are Differentially Regulated in Major Depression and Following Exposure to Social Stress. Psychoneuroendocrinology 2009, 34, 1257–1262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hungund, B.L.; Vinod, K.Y.; Kassir, S.A.; Basavarajappa, B.S.; Yalamanchili, R.; Cooper, T.B.; Mann, J.J.; Arango, V. Upregulation of CB1 Receptors and Agonist-Stimulated [35S]GTPgammaS Binding in the Prefrontal Cortex of Depressed Suicide Victims. Mol. Psychiatry 2004, 9, 184–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lisboa, S.F.; Niraula, A.; Resstel, L.B.; Guimaraes, F.S.; Godbout, J.P.; Sheridan, J.F. Repeated Social Defeat-Induced Neuroinflammation, Anxiety-like Behavior and Resistance to Fear Extinction Were Attenuated by the Cannabinoid Receptor Agonist WIN55,212-2. Neuropsychopharmacology 2018, 43, 1924–1933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zoppi, S.; Pérez Nievas, B.G.; Madrigal, J.L.M.; Manzanares, J.; Leza, J.C.; García-Bueno, B. Regulatory Role of Cannabinoid Receptor 1 in Stress-Induced Excitotoxicity and Neuroinflammation. Neuropsychopharmacology 2011, 36, 805–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beins, E.C.; Beiert, T.; Jenniches, I.; Hansen, J.N.; Leidmaa, E.; Schrickel, J.W.; Zimmer, A. Cannabinoid Receptor 1 Signalling Modulates Stress Susceptibility and Microglial Responses to Chronic Social Defeat Stress. Transl. Psychiatry 2021, 11, 164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nadjar, A. Nanoparticles: The New Promise for Region-Specific Targeting of Microglia. Matter 2022, 5, 2529–2530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boutej, H.; Rahimian, R.; Thammisetty, S.S.; Béland, L.-C.; Lalancette-Hébert, M.; Kriz, J. Diverging MRNA and Protein Networks in Activated Microglia Reveal SRSF3 Suppresses Translation of Highly Upregulated Innate Immune Transcripts. Cell Rep. 2017, 21, 3220–3233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maes, M.E.; Colombo, G.; Schulz, R.; Siegert, S. Targeting Microglia with Lentivirus and AAV: Recent Advances and Remaining Challenges. Neurosci. Lett. 2019, 707, 134310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fakhfouri, G.; Mijailović, N.R.; Rahimian, R. Psychiatric Comorbidities of Inflammatory Bowel Disease: It Is a Matter of Microglia’s Gut Feeling. Cells 2024, 13, 177. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells13020177
Fakhfouri G, Mijailović NR, Rahimian R. Psychiatric Comorbidities of Inflammatory Bowel Disease: It Is a Matter of Microglia’s Gut Feeling. Cells. 2024; 13(2):177. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells13020177
Chicago/Turabian StyleFakhfouri, Gohar, Nataša R. Mijailović, and Reza Rahimian. 2024. "Psychiatric Comorbidities of Inflammatory Bowel Disease: It Is a Matter of Microglia’s Gut Feeling" Cells 13, no. 2: 177. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells13020177
APA StyleFakhfouri, G., Mijailović, N. R., & Rahimian, R. (2024). Psychiatric Comorbidities of Inflammatory Bowel Disease: It Is a Matter of Microglia’s Gut Feeling. Cells, 13(2), 177. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells13020177







