Regulation of β-Adrenergic Receptors in the Heart: A Review on Emerging Therapeutic Strategies for Heart Failure
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Signal Transductions of β-ARs in the Regulation of Heart Functions
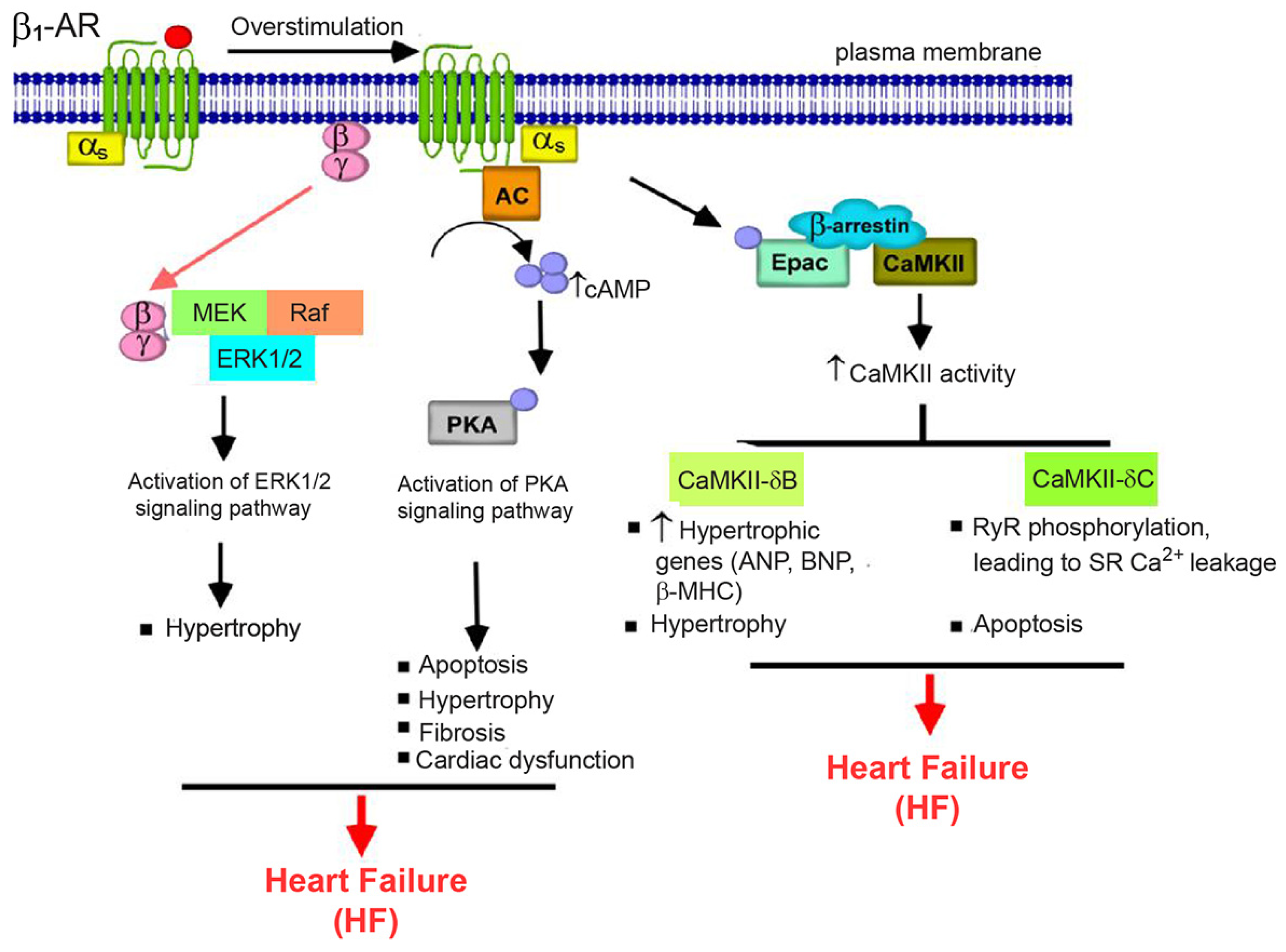
2.1. β1-AR Signaling
2.2. β2-AR Signaling
2.3. β3-AR Signaling
2.4. Biased Signaling of β-ARs
3. Role of β-ARs in Heart Failure (HF)
3.1. Changes in β-AR Expression and Signaling Network in Failing Hearts
3.2. Role of β-AR Genetic Polymorphism in HF
4. Role of G Protein and AC in HF
4.1. Gαs Protein
4.2. Gαi Protein
4.3. Adenylyl Cyclase (AC)
5. Role of G Protein-Coupled Receptor Kinases (GRKs) in HF
5.1. Introduction of GRKs
5.2. Pathophysiology of GRK in the Heart
5.3. Therapeutic Targets for HF: Focusing on GRK2
5.3.1. β-ARKct (or GRK2ct)
5.3.2. Small Molecule Inhibitors of GRKs
6. Roles of β-Arrestins in HF
6.1. Introduction of β-Arrestins
6.2. Cardioprotective Effects of β-Arrestins
6.3. Therapeutic Targets for HF: Focusing on β-Arrestins
7. Emerging Therapeutic Targets for HF Focusing on β-AR Regulation
7.1. Clinical Studies of β3-AR Agonist
7.2. Clinical Studies of GRK2 Inhibitor
7.3. Clinical Studies of CaMKII Inhibitors
8. Gene Therapy as a Potential Therapeutic Approach for HF
8.1. Clinical Studies of AC6 Gene Therapy
8.2. Clinical Studies of SERCA2a Gene Therapy
9. Limitations
10. Conclusions and Further Directions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- De Lucia, C.; Eguchi, A.; Koch, W.J. New insights in cardiac β-adrenergic signaling during heart failure and aging. Front. Pharmacol. 2018, 9, 904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Greenstein, J.L.; Tanskanen, A.J.; Winslow, R.L. Modeling the actions of β-adrenergic signaling on excitation-contraction coupling processes. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2004, 1015, 16–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Mangmool, S.; Duangrat, R.; Parichatikanond, W.; Kurose, H. New therapeutics for heart failure: Focusing on cGMP signaling. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 12866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mika, D.; Bobin, P.; Lindner, M.; Boet, A.; Hodzic, A.; Lefebvre, F.; Lechène, P.; Sadoune, M.; Samuel, J.L.; Algalarrondo, V.; et al. Synergic PDE3 and PDE4 control intracellular cAMP and cardiac excitation-contraction coupling in a porcine model. J. Mol. Cell. Cardiol. 2019, 133, 57–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mancia, G.; Grassi, G.; Giannattasio, C.; Seravalle, G. Sympathetic activation in the pathogenesis of hypertension and progression of organ damage. Hypertension 1999, 34, 724–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Madamanchi, A. β-Adrenergic receptor signaling in cardiac function and heart failure. McGill J. Med. 2007, 10, 99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Michel, L.Y.; Farah, C.; Balligand, J.L. The β3 adrenergic receptor in healthy and pathological cardiovascular tissues. Cells 2020, 9, 2584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaumann, A.J.; Preitner, F.; Sarsero, D.; Molenaar, P.; Revelli, J.P.; Giacobino, J.P. (-)-CGP 12177 causes cardiostimulation and binds to cardiac putative β4-adrenoceptors in both wild-type and β3-adrenoceptor knockout mice. Mol. Pharmacol. 1998, 53, 670–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galitzky, J.; Langin, D.; Verwaerde, P.; Montastruc, J.L.; Lafontan, M.; Berlan, M. Lipolytic effects of conventional beta 3-adrenoceptor agonists and of CGP 12,177 in rat and human fat cells: Preliminary pharmacological evidence for a putative beta 4-adrenoceptor. Br. J. Pharmacol. 1997, 122, 1244–1250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Port, J.D.; Bristow, M.R. Altered beta-adrenergic receptor gene regulation and signaling in chronic heart failure. J. Mol. Cell. Cardiol. 2001, 33, 887–905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lymperopoulos, A.; Rengo, G.; Koch, W.J. Adrenergic nervous system in heart failure: Pathophysiology and therapy. Circ. Res. 2013, 113, 739–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, X.; Kaindl, J.; Clark, M.J.; Hübner, H.; Hirata, K.; Sunahara, R.K.; Gmeiner, P.; Kobilka, B.K.; Liu, X. Binding pathway determines norepinephrine selectivity for the human β1AR over β2AR. Cell Res. 2021, 31, 569–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rockman, H.A.; Koch, W.J.; Lefkowitz, R.J. Seven-transmembrane-spanning receptors and heart function. Nature 2002, 415, 206–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alig, J.; Marger, L.; Mesirca, P.; Ehmke, H.; Mangoni, M.E.; Isbrandt, D. Control of heart rate by cAMP sensitivity of HCN channels. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 12189–12194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van der Heyden, M.A.; Wijnhoven, T.J.; Opthof, T. Molecular aspects of adrenergic modulation of cardiac L-type Ca2+ channels. Cardiovasc. Res. 2005, 65, 28–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reiken, S.; Gaburjakova, M.; Guatimosim, S.; Gomez, A.M.; D’Armiento, J.; Burkhoff, D.; Wang, J.; Vassort, G.; Lederer, W.J.; Marks, A.R. Protein kinase A phosphorylation of the cardiac calcium release channel (ryanodine receptor) in normal and failing hearts: Role of phosphatases and response to isoproterenol. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 444–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noma, T.; Lemaire, A.; Prasad, S.V.N.; Barki-Harrington, L.; Tilley, D.G.; Chen, J.; Le Corvoisier, P.; Violin, J.D.; Wei, H.; Lefkowitz, R.J. β-arrestin–mediated β1-adrenergic receptor transactivation of the EGFR confers cardioprotection. J. Clin. Investig. 2007, 117, 2445–2458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, R.A.; Premont, R.T.; Chow, C.W.; Blitzer, J.T.; Pitcher, J.A.; Claing, A.; Stoffel, R.H.; Barak, L.S.; Shenolikar, S.; Weinman, E.J.; et al. The beta2-adrenergic receptor interacts with the Na+/H+-exchanger regulatory factor to control Na+/H+ exchange. Nature 1998, 392, 626–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasseldine, A.; Harper, E.; Black, J. Cardiac-specific overexpression of human β2 adrenoceptors in mice exposes coupling to both Gs and Gi proteins. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2003, 138, 1358–1366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chesley, A.; Lundberg, M.S.; Asai, T.; Xiao, R.-P.; Ohtani, S.; Lakatta, E.G.; Crow, M.T. The β2-adrenergic receptor delivers an antiapoptotic signal to cardiac myocytes through Gi-dependent coupling to phosphatidylinositol 3′-kinase. Circ. Res. 2000, 87, 1172–1179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watson, L.J.; Alexander, K.M.; Mohan, M.L.; Bowman, A.L.; Mangmool, S.; Xiao, K.; Prasad, S.V.N.; Rockman, H.A. Phosphorylation of Src by phosphoinositide 3-kinase regulates β-adrenergic receptor-mediated EGFR transactivation. Cell. Signal. 2016, 28, 1580–1592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, W.; Smrcka, A.V. Internalized β2-adrenergic receptors oppose PLC-dependent hypertrophic signaling. Circ. Res. 2024, 135, e24–e38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daaka, Y.; Luttrell, L.M.; Lefkowitz, R.J. Switching of the coupling of the β2-adrenergic receptor to different G proteins by protein kinase A. Nature 1997, 390, 88–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Communal, C.; Colucci, W.S.; Singh, K. p38 Mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway protects adult rat ventricular myocytes against β-adrenergic receptor-stimulated apoptosis. Evidence for Gi-dependent activation. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 19395–19400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, W.-Z.; Zheng, M.; Koch, W.J.; Lefkowitz, R.J.; Kobilka, B.K.; Xiao, R.-P. Dual modulation of cell survival and cell death by β2-adrenergic signaling in adult mouse cardiac myocytes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2001, 98, 1607–1612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, D.; Farrar, J.D. Adrenergic regulation of immune cell function and inflammation. Semin. Immunopathol. 2020, 42, 709–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grailer, J.J.; Haggadone, M.D.; Sarma, J.V.; Zetoune, F.S.; Ward, P.A. Induction of M2 regulatory macrophages through the β2-adrenergic receptor with protection during endotoxemia and acute lung injury. J. Innate Immun. 2014, 6, 607–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Donnelly, L.E.; Tudhope, S.J.; Fenwick, P.S.; Barnes, P.J. Effects of formoterol and salmeterol on cytokine release from monocyte-derived macrophages. Eur. Respir. J. 2010, 36, 178–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurose, H.; Mangmool, S. Myofibroblasts and inflammatory cells as players of cardiac fibrosis. Arch. Pharm. Res. 2016, 39, 1100–1113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van der Horst, J.; Rognant, S.; Hellsten, Y.; Aalkjær, C.; Jepps, T.A. Dynein coordinates β2-adrenoceptor-mediated relaxation in normotensive and hypertensive rat mesenteric arteries. Hypertension 2022, 79, 2214–2227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ehlers, T.S.; van der Horst, J.; Møller, S.; Piil, P.K.; Gliemann, L.; Aalkjaer, C.; Jepps, T.A.; Hellsten, Y. Colchicine enhances β adrenoceptor-mediated vasodilation in men with essential hypertension. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2023, 89, 2179–2189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, T.; Liu, G.; Yu, B. Colchicine for coronary artery disease: A review. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2022, 9, 892588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skeberdis, V.A.; Gendvilienė, V.; Zablockaitė, D.; Treinys, R.; Mačianskienė, R.; Bogdelis, A.; Jurevičius, J.; Fischmeister, R. β3-adrenergic receptor activation increases human atrial tissue contractility and stimulates the L-type Ca2+ current. J. Clin. Investig. 2008, 118, 3219–3227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Treinys, R.; Zablockaitė, D.; Gendvilienė, V.; Jurevičius, J.; Skeberdis, V.A. β3-Adrenergic regulation of L-type Ca2+ current and force of contraction in human ventricle. J. Membr. Biol. 2014, 247, 309–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moniotte, S.; Kobzik, L.; Feron, O.; Trochu, J.-N.; Gauthier, C.; Balligand, J.-L. Upregulation of β3-adrenoceptors and altered contractile response to inotropic amines in human failing myocardium. Circulation 2001, 103, 1649–1655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balligand, J.L. Beta3-adrenoreceptors in cardiovasular diseases: New roles for an “old” receptor. Curr. Drug Deliv. 2013, 10, 64–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gauthier, C.; Tavernier, G.; Charpentier, F.; Langin, D.; Le Marec, H. Functional beta3-adrenoceptor in the human heart. J. Clin. Investig. 1996, 98, 556–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gauthier, C.; Leblais, V.; Kobzik, L.; Trochu, J.-N.; Khandoudi, N.; Bril, A.; Balligand, J.-L.; Le Marec, H. The negative inotropic effect of β3-adrenoceptor stimulation is mediated by activation of a nitric oxide synthase pathway in human ventricle. J. Clin. Investig. 1998, 102, 1377–1384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belge, C.; Hammond, J.; Dubois-Deruy, E.; Manoury, B.; Hamelet, J.; Beauloye, C.; Markl, A.; Pouleur, A.-C.; Bertrand, L.; Esfahani, H. Enhanced expression of β3-adrenoceptors in cardiac myocytes attenuates neurohormone-induced hypertrophic remodeling through nitric oxide synthase. Circulation 2014, 129, 451–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bundgaard, H.; Liu, C.-C.; Garcia, A.; Hamilton, E.J.; Huang, Y.; Chia, K.K.; Hunyor, S.N.; Figtree, G.A.; Rasmussen, H.H. β3 adrenergic stimulation of the cardiac Na+-K+ pump by reversal of an inhibitory oxidative modification. Circulation 2010, 122, 2699–2708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ippolito, M.; Benovic, J.L. Biased agonism at β-adrenergic receptors. Cell. Signal. 2021, 80, 109905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Myagmar, B.E.; Flynn, J.M.; Cowley, P.M.; Swigart, P.M.; Montgomery, M.D.; Thai, K.; Nair, D.; Gupta, R.; Deng, D.X.; Hosoda, C.; et al. Adrenergic receptors in individual ventricular myocytes: The beta-1 and alpha-1B are in all cells, the alpha-1A is in a subpopulation, and the beta-2 and beta-3 are mostly absent. Circ. Res. 2017, 120, 1103–1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Hanada, K.; Staus, D.P.; Makara, M.A.; Dahal, G.R.; Chen, Q.; Ahles, A.; Engelhardt, S.; Rockman, H.A. Gαi is required for carvedilol-induced β1 adrenergic receptor β-arrestin biased signaling. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 1706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Pani, B.; Gokhan, I.; Xiong, X.; Kahsai, A.W.; Jiang, H.; Ahn, S.; Lefkowitz, R.J.; Rockman, H.A. β-Arrestin-biased allosteric modulator potentiates carvedilol-stimulated β adrenergic receptor cardioprotection. Mol. Pharmacol. 2021, 100, 568–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wisler, J.W.; DeWire, S.M.; Whalen, E.J.; Violin, J.D.; Drake, M.T.; Ahn, S.; Shenoy, S.K.; Lefkowitz, R.J. A unique mechanism of β-blocker action: Carvedilol stimulates β-arrestin signaling. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 16657–16662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Triposkiadis, F.; Karayannis, G.; Giamouzis, G.; Skoularigis, J.; Louridas, G.; Butler, J. The sympathetic nervous system in heart failure: Physiology, pathophysiology, and clinical implications. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2009, 54, 1747–1762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keys, J.; Koch, W. The adrenergic pathway and heart failure. Recent Prog. Horm. Res. 2004, 59, 13–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ungerer, M.; Böhm, M.; Elce, J.S.; Erdmann, E.; Lohse, M.J. Altered expression of beta-adrenergic receptor kinase and beta 1-adrenergic receptors in the failing human heart. Circulation 1993, 87, 454–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iwase, M.; Bishop, S.P.; Uechi, M.; Vatner, D.E.; Shannon, R.P.; Kudej, R.K.; Wight, D.C.; Wagner, T.E.; Ishikawa, Y.; Homcy, C.J. Adverse effects of chronic endogenous sympathetic drive induced by cardiac Gsα overexpression. Circ. Res. 1996, 78, 517–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bos, J.L. Epac proteins: Multi-purpose cAMP targets. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2006, 31, 680–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grimm, M.; Brown, J.H. β-Adrenergic receptor signaling in the heart: Role of CaMKII. J. Mol. Cell. Cardiol. 2010, 48, 322–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mangmool, S.; Shukla, A.K.; Rockman, H.A. β-Arrestin–dependent activation of Ca2+/calmodulin kinase II after β1–adrenergic receptor stimulation. J. Cell Biol. 2010, 189, 573–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, T.; Brown, J.H. Role of Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II in cardiac hypertrophy and heart failure. Cardiovasc. Res. 2004, 63, 476–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vidal, M.; Wieland, T.; Lohse, M.J.; Lorenz, K. β-Adrenergic receptor stimulation causes cardiac hypertrophy via a Gβγ/Erk-dependent pathway. Cardiovasc. Res. 2012, 96, 255–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, B.; Li, M.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, M.; Morotti, S.; Shi, Q.; Wang, Q.; Barbagallo, F.; Teoh, J.P.; Reddy, G.R.; et al. GRK5 controls SAP97-dependent cardiotoxic β1 adrenergic receptor-CaMKII signaling in heart failure. Circ. Res. 2020, 127, 796–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Métrich, M.; Laurent, A.C.; Breckler, M.; Duquesnes, N.; Hmitou, I.; Courillau, D.; Blondeau, J.P.; Crozatier, B.; Lezoualc’h, F.; Morel, E. Epac activation induces histone deacetylase nuclear export via a Ras-dependent signalling pathway. Cell. Signal. 2010, 22, 1459–1468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Métrich, M.; Lucas, A.; Gastineau, M.; Samuel, J.L.; Heymes, C.; Morel, E.; Lezoualc’h, F. Epac mediates beta-adrenergic receptor-induced cardiomyocyte hypertrophy. Circ. Res. 2008, 102, 959–965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laudette, M.; Coluccia, A.; Sainte-Marie, Y.; Solari, A.; Fazal, L.; Sicard, P.; Silvestri, R.; Mialet-Perez, J.; Pons, S.; Ghaleh, B.; et al. Identification of a pharmacological inhibitor of Epac1 that protects the heart against acute and chronic models of cardiac stress. Cardiovasc. Res. 2019, 115, 1766–1777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berthouze-Duquesnes, M.; Lucas, A.; Saulière, A.; Sin, Y.Y.; Laurent, A.C.; Galés, C.; Baillie, G.; Lezoualc’h, F. Specific interactions between Epac1, β-arrestin2 and PDE4D5 regulate β-adrenergic receptor subtype differential effects on cardiac hypertrophic signaling. Cell. Signal. 2013, 25, 970–980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engelhardt, S.; Hein, L.; Wiesmann, F.; Lohse, M.J. Progressive hypertrophy and heart failure in β1-adrenergic receptor transgenic mice. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1999, 96, 7059–7064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bisognano, J.D.; Weinberger, H.D.; Bohlmeyer, T.J.; Pende, A.; Raynolds, M.V.; Sastravaha, A.; Roden, R.; Asano, K.; Blaxall, B.C.; Wu, S.C. Myocardial-directed overexpression of the human β1-adrenergic receptor in transgenic mice. J. Mol. Cell. Cardiol. 2000, 32, 817–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Engelhardt, S.; Grimmer, Y.; Fan, G.H.; Lohse, M.J. Constitutive activity of the human β1-adrenergic receptor in β1-receptor transgenic mice. Mol. Pharmacol. 2001, 60, 712–717. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Iwase, M.; Uechi, M.; Vatner, D.E.; Asai, K.; Shannon, R.P.; Kudej, R.K.; Wagner, T.E.; Wight, D.C.; Patrick, T.A.; Ishikawa, Y. Cardiomyopathy induced by cardiac Gs alpha overexpression. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 1997, 272, H585–H589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liggett, S.B.; Tepe, N.M.; Lorenz, J.N.; Canning, A.M.; Jantz, T.D.; Mitarai, S.; Yatani, A.; Dorn, G.W. Early and delayed consequences of β2-adrenergic receptor overexpression in mouse hearts: Critical role for expression level. Circulation 2000, 101, 1707–1714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Witteles, R.M.; Fowler, M.B. Insulin-resistant cardiomyopathy: Clinical evidence, mechanisms, and treatment options. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2008, 51, 93–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belke, D.D.; Larsen, T.S.; Gibbs, E.M.; Severson, D.L. Altered metabolism causes cardiac dysfunction in perfused hearts from diabetic (db/db) mice. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2000, 279, E1104–E1113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mazumder, P.K.; O’Neill, B.T.; Roberts, M.W.; Buchanan, J.; Yun, U.J.; Cooksey, R.C.; Boudina, S.; Abel, E.D. Impaired cardiac efficiency and increased fatty acid oxidation in insulin-resistant ob/ob mouse hearts. Diabetes 2004, 53, 2366–2374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mangmool, S.; Denkaew, T.; Parichatikanond, W.; Kurose, H. β-Adrenergic receptor and insulin resistance in the heart. Biomol. Ther. 2017, 25, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mangmool, S.; Denkaew, T.; Phosri, S.; Pinthong, D.; Parichatikanond, W.; Shimauchi, T.; Nishida, M. Sustained βAR stimulation mediates cardiac insulin resistance in a PKA-dependent manner. Mol. Endocrinol. 2016, 30, 118–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parichatikanond, W.; Nishimura, A.; Nishida, M.; Mangmool, S. Prolonged stimulation of β2-adrenergic receptor with β2-agonists impairs insulin actions in H9c2 cells. J. Pharmacol. Sci. 2018, 138, 184–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohout, T.A.; Takaoka, H.; McDonald, P.H.; Perry, S.J.; Mao, L.; Lefkowitz, R.J.; Rockman, H.A. Augmentation of cardiac contractility mediated by the human β3-adrenergic receptor overexpressed in the hearts of transgenic mice. Circulation 2001, 104, 2485–2491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aragón, J.P.; Condit, M.E.; Bhushan, S.; Predmore, B.L.; Patel, S.S.; Grinsfelder, D.B.; Gundewar, S.; Jha, S.; Calvert, J.W.; Barouch, L.A. β3-adrenoreceptor stimulation ameliorates myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury via endothelial nitric oxide synthase and neuronal nitric oxide synthase activation. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2011, 58, 2683–2691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bundgaard, H.; Axelsson Raja, A.; Iversen, K.; Valeur, N.; Tønder, N.; Schou, M.; Christensen, A.H.; Bruun, N.E.; Søholm, H.; Ghanizada, M. Hemodynamic effects of cyclic guanosine monophosphate-dependent signaling through β3 adrenoceptor stimulation in patients with advanced heart failure: A randomized invasive clinical trial. Circ. Heart Fail. 2022, 15, e009120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bristow, M.R.; Ginsburg, R.; Umans, V.; Fowler, M.; Minobe, W.; Rasmussen, R.; Zera, P.; Menlove, R.; Shah, P.; Jamieson, S. Beta 1-and beta 2-adrenergic-receptor subpopulations in nonfailing and failing human ventricular myocardium: Coupling of both receptor subtypes to muscle contraction and selective β1-receptor down-regulation in heart failure. Circ. Res. 1986, 59, 297–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brodde, O.E. β-adrenoceptors in cardiac disease. Pharmacol. Ther. 1993, 60, 405–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lang, D.; Holzem, K.; Kang, C.; Xiao, M.; Hwang, H.J.; Ewald, G.A.; Yamada, K.A.; Efimov, I.R. Arrhythmogenic remodeling of β2 versus β1 adrenergic signaling in the human failing heart. Circ. Arrhythm. Electrophysiol. 2015, 8, 409–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Yuan, J.; Qian, Z.; Zhang, X.; Chen, Y.; Hou, X.; Zou, J. β2 adrenergic receptor activation governs cardiac repolarization and arrhythmogenesis in a guinea pig model of heart failure. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 7681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bristow, M.R. β-Adrenergic receptor blockade in chronic heart failure. Circulation 2000, 101, 558–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tatman, P.D.; Kao, D.P.; Chatfield, K.C.; Carroll, I.A.; Wagner, J.A.; Jonas, E.R.; Sucharov, C.C.; Port, J.D.; Lowes, B.D.; Minobe, W.A.; et al. An extensive β1-adrenergic receptor gene signaling network regulates molecular remodeling in dilated cardiomyopathies. J. Clin. Investig. Insight 2023, 8, e169720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.N.; Fu, K.L.; Gao, H.Y.; Shang, Y.Y.; Wang, Z.H.; Jiang, G.H.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, W.; Zhong, M. β1 adrenergic receptor polymorphisms and heart failure: A meta-analysis on susceptibility, response to β-blocker therapy and prognosis. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e37659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorn, G.W.; Liggett, S.B. Mechanisms of pharmacogenomic effects of genetic variation within the cardiac adrenergic network in heart failure. Mol. Pharmacol. 2009, 76, 466–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iwai, C.; Akita, H.; Kanazawa, K.; Shiga, N.; Terashima, M.; Matsuda, Y.; Takai, E.; Miyamoto, Y.; Shimizu, M.; Kajiya, T.; et al. Arg389Gly polymorphism of the human β1-adrenergic receptor in patients with nonfatal acute myocardial infarction. Am. Heart J. 2003, 146, 106–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagoner, L.E.; Craft, L.L.; Zengel, P.; McGuire, N.; Rathzb, D.A.; Dorn II, G.W.; Liggett, S.B. Polymorphisms of the β1-adrenergic receptor predict exercise capacity in heart failure. Am. Heart J. 2002, 144, 840–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perez, J.M.; Rathz, D.A.; Petrashevskaya, N.N.; Hahn, H.S.; Wagoner, L.E.; Schwartz, A.; Dorn, G.W.; Liggett, S.B. β1-adrenergic receptor polymorphisms confer differential function and predisposition to heart failure. Nat. Med. 2003, 9, 1300–1305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Terra, S.G.; Pauly, D.F.; Lee, C.R.; Patterson, J.H.; Adams, K.F., Jr.; Schofield, R.S.; Belgado, B.S.; Hamilton, K.K.; Aranda, J.M.; Hill, J.A. β-Adrenergic receptor polymorphisms and responses during titration of metoprolol controlled release/extended release in heart failure. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 2005, 77, 127–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rathz, D.A.; Brown, K.M.; Kramer, L.A.; Liggett, S.B. Amino acid 49 polymorphisms of the human β1-adrenergic receptor affect agonist-promoted trafficking. J. Cardiovasc. Pharmacol. 2002, 39, 155–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magnusson, Y.; Levin, M.C.; Eggertsen, R.; Nyström, E.; Mobini, R.; Schaufelberger, M.; Andersson, B. Ser49Gly of β1-adrenergic receptor is associated with effective β-blocker dose in dilated cardiomyopathy. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 2005, 78, 221–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vardeny, O.; Detry, M.A.; Moran, J.J.; Johnson, M.R.; Sweitzer, N.K. The β2 adrenergic receptor Gln27Glu polymorphism affects insulin resistance in patients with heart failure: Possible modulation by choice of beta-blocker. J. Cardiovasc. Pharmacol. 2008, 52, 500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Liggett, S.B.; Wagoner, L.E.; Craft, L.L.; Hornung, R.W.; Hoit, B.D.; McIntosh, T.C.; Walsh, R.A. The Ile164 β2-adrenergic receptor polymorphism adversely affects the outcome of congestive heart failure. J. Clin. Investig. 1998, 102, 1534–1539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Green, S.A.; Cole, G.; Jacinto, M.; Innis, M.; Liggett, S. A polymorphism of the human β2-adrenergic receptor within the fourth transmembrane domain alters ligand binding and functional properties of the receptor. J. Biol. Chem. 1993, 268, 23116–23121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feldman, A.M.; Ray, P.E.; Bristow, M.R. Expression of α-subunits of G proteins in failing human heart: A reappraisal utilizing quantitative polymerase chain reaction. J. Mol. Cell. Cardiol. 1991, 23, 1355–1358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feldman, D.S.; Zamah, A.M.; Pierce, K.L.; Miller, W.E.; Kelly, F.; Rapacciuolo, A.; Rockman, H.A.; Koch, W.J.; Luttrell, L.M. Selective inhibition of heterotrimeric Gs signaling. Targeting the receptor-G protein interface using a peptide minigene encoding the Gαs carboxyl terminus. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 28631–28640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Foerster, K.; Groner, F.; Matthes, J.; Koch, W.J.; Birnbaumer, L.; Herzig, S. Cardioprotection specific for the G protein Gi2 in chronic adrenergic signaling through β2-adrenoceptors. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 14475–14480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janssen, P.M.; Schillinger, W.; Donahue, J.K.; Zeitz, O.; Emami, S.; Lehnart, S.E.; Weil, J.; Eschenhagen, T.; Hasenfuss, G.; Prestle, J. Intracellular β-blockade: Overexpression of Gαi2 depresses the β-adrenergic response in intact myocardium. Cardiovasc. Res. 2002, 55, 300–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, R.P. β-Adrenergic signaling in the heart: Dual coupling of the β2-adrenergic receptor to Gs and Gi proteins. Sci. STKE 2001, 2001, re15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donahue, J.K.; Kikuchi, K.; Sasano, T. Gene therapy for cardiac arrhythmias. Trends Cardiovasc. Med. 2005, 15, 219–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Ostrom, K.F.; LaVigne, J.E.; Brust, T.F.; Seifert, R.; Dessauer, C.W.; Watts, V.J.; Ostrom, R.S. Physiological roles of mammalian transmembrane adenylyl cyclase isoforms. Physiol. Rev. 2022, 102, 815–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okumura, S.; Takagi, G.; Kawabe, J.; Yang, G.; Lee, M.C.; Hong, C.; Liu, J.; Vatner, D.E.; Sadoshima, J.; Vatner, S.F.; et al. Disruption of type 5 adenylyl cyclase gene preserves cardiac function against pressure overload. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 9986–9990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, L.; Vatner, S.F.; Vatner, D.E. Disruption of type 5 adenylyl cyclase prevents β-adrenergic receptor cardiomyopathy: A novel approach to β-adrenergic receptor blockade. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 2014, 307, H1521–H1528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Lai, N.C.; Tang, T.; Gao, M.H.; Saito, M.; Takahashi, T.; Roth, D.M.; Hammond, H.K. Activation of cardiac adenylyl cyclase expression increases function of the failing ischemic heart in mice. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2008, 51, 1490–1497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, T.; Tang, T.; Lai, N.C.; Roth, D.M.; Rebolledo, B.; Saito, M.; Lew, W.Y.; Clopton, P.; Hammond, H.K. Increased cardiac adenylyl cyclase expression is associated with increased survival after myocardial infarction. Circulation 2006, 114, 388–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roth, D.M.; Gao, M.H.; Lai, N.C.; Drumm, J.; Dalton, N.; Zhou, J.Y.; Zhu, J.; Entrikin, D.; Hammond, H.K. Cardiac-directed adenylyl cyclase expression improves heart function in murine cardiomyopathy. Circulation 1999, 99, 3099–3102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roth, D.M.; Bayat, H.; Drumm, J.D.; Gao, M.H.; Swaney, J.S.; Ander, A.; Hammond, H.K. Adenylyl cyclase increases survival in cardiomyopathy. Circulation 2002, 105, 1989–1994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lai, N.C.; Roth, D.M.; Gao, M.H.; Fine, S.; Head, B.P.; Zhu, J.; McKirnan, M.D.; Kwong, C.; Dalton, N.; Urasawa, K.; et al. Intracoronary delivery of adenovirus encoding adenylyl cyclase VI increases left ventricular function and cAMP-generating capacity. Circulation 2000, 102, 2396–2401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferguson, S.S. Evolving concepts in G protein-coupled receptor endocytosis: The role in receptor desensitization and signaling. Pharmacol. Rev. 2001, 53, 1–24. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, H.; Galtes, D.; Wang, J.; Rockman, H.A. G protein-coupled receptor signaling: Transducers and effectors. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 2022, 323, C731–C748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribas, C.; Penela, P.; Murga, C.; Salcedo, A.; García-Hoz, C.; Jurado-Pueyo, M.; Aymerich, I.; Mayor, F., Jr. The G protein-coupled receptor kinase (GRK) interactome: Role of GRKs in GPCR regulation and signaling. Biochim. Biophys. Acta–Biomembr. 2007, 1768, 913–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Penela, P.; Ribas, C.; Mayor, F., Jr. Mechanisms of regulation of the expression and function of G protein-coupled receptor kinases. Cell. Signal. 2003, 15, 973–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Penela, P.; Murga, C.; Ribas, C.; Tutor, A.S.; Peregrín, S.; Mayor, F., Jr. Mechanisms of regulation of G protein-coupled receptor kinases (GRKs) and cardiovascular disease. Cardiovasc. Res. 2006, 69, 46–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinge, L.E.; Øie, E.; Andersson, Y.; Grøgaard, H.K.; Andersen, G.Ø.; Attramadal, H. Myocardial distribution and regulation of GRK and β-arrestin isoforms in congestive heart failure in rats. Am. J. Physiol Heart Circ. Physiol. 2001, 281, H2490–H2499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Ungerer, M.; Kessebohm, K.; Kronsbein, K.; Lohse, M.J.; Richardt, G. Activation of β-adrenergic receptor kinase during myocardial ischemia. Circulation Res. 1996, 79, 455–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gros, R.; Benovic, J.L.; Tan, C.M.; Feldman, R.D. G-protein-coupled receptor kinase activity is increased in hypertension. J. Clin. Investig. 1997, 99, 2087–2093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, X.P.; Gerdes, A.M.; Li, F. Myocyte redistribution of GRK2 and GRK5 in hypertensive, heart-failure-prone rats. Hypertension 2002, 39, 1058–1063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dzimiri, N.; Muiya, P.; Andres, E.; Al-Halees, Z. Differential functional expression of human myocardial G protein receptor kinases in left ventricular cardiac diseases. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2004, 489, 167–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koch, W.J.; Rockman, H.A.; Samama, P.; Hamilton, R.A.; Bond, R.A.; Milano, C.A.; Lefkowitz, R.J. Cardiac function in mice overexpressing the β-adrenergic receptor kinase or a beta ARK inhibitor. Science 1995, 268, 1350–1353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takagi, C.; Urasawa, K.; Yoshida, I.; Takagi, Y.; Kaneta, S.; Nakano, N.; Onozuka, H.; Kitabatake, A. Enhanced GRK5 expression in the hearts of cardiomyopathic hamsters, J2N-k. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1999, 262, 206–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ping, P.; Anzai, T.; Gao, M.; Hammond, H.K. Adenylyl cyclase and G protein receptor kinase expression during development of heart failure. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 1997, 273, H707–H717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrofski, J.A.; Koch, W.J. The β-adrenergic receptor kinase in heart failure. J. Mol. Cell. Cardiol. 2003, 35, 1167–1174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrero, K.M.; Koch, W.J. GRK2 in cardiovascular disease and its potential as a therapeutic target. J. Mol. Cell. Cardiol. 2022, 172, 14–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mangmool, S.; Parichatikanond, W.; Kurose, H. Therapeutic targets for treatment of heart failure: Focus on GRKs and β-arrestins affecting βAR signaling. Front. Pharmacol. 2018, 9, 1336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rockman, H.A.; Chien, K.R.; Choi, D.J.; Iaccarino, G.; Hunter, J.J.; Ross, J., Jr.; Lefkowitz, R.J.; Koch, W.J. Expression of a β-adrenergic receptor kinase 1 inhibitor prevents the development of myocardial failure in gene-targeted mice. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1998, 95, 7000–7005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harding, V.B.; Jones, L.R.; Lefkowitz, R.J.; Koch, W.J.; Rockman, H.A. Cardiac βARK1 inhibition prolongs survival and augments β blocker therapy in a mouse model of severe heart failure. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2001, 98, 5809–5814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raake, P.W.; Vinge, L.E.; Gao, E.; Boucher, M.; Rengo, G.; Chen, X.; DeGeorge, B.R., Jr.; Matkovich, S.; Houser, S.R.; Most, P. G protein-coupled receptor kinase 2 ablation in cardiac myocytes before or after myocardial infarction prevents heart failure. Circ. Res. 2008, 103, 413–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williams, M.L.; Koch, W.J. Viral-based myocardial gene therapy approaches to alter cardiac function. Ann. Rev. Physiol. 2004, 66, 49–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thal, D.M.; Yeow, R.Y.; Schoenau, C.; Huber, J.; Tesmer, J.J. Molecular mechanism of selectivity among G protein-coupled receptor kinase 2 inhibitors. Mol. Pharmacol. 2011, 80, 294–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pilgrim, T.; Vollenbroich, R.; Deckarm, S.; Gräni, C.; Dobner, S.; Stark, A.W.; Erne, S.A.; Babongo Bosombo, F.; Fischer, K.; Stortecky, S.; et al. Effect of paroxetine-mediated G-protein receptor kinase 2 inhibition vs placebo in patients with anterior myocardial infarction: A randomized clinical trial. JAMA Cardiol. 2021, 6, 1171–1176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pilgrim, T.; Bernhard, B.; Fürholz, M.; Vollenbroich, R.; Babongo Bosombo, F.; Losdat, S.; Reusser, N.; Windecker, S.; Stortecky, S.; Siontis, G.C.M.; et al. Paroxetine-mediated G-protein receptor kinase 2 inhibition in patients with acute anterior myocardial infarction: Final 1-year outcomes of the randomized CARE-AMI trial. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2022, 11, e026362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Traynham, C.J.; Hullmann, J.; Koch, W.J. Canonical and non-canonical actions of GRK5 in the heart. J. Mol. Cell. Cardiol. 2016, 92, 196–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, C.A.; Milano, S.K.; Benovic, J.L. Regulation of receptor trafficking by GRKs and arrestins. Ann. Rev. Physiol. 2007, 69, 451–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shenoy, S.K.; Drake, M.T.; Nelson, C.D.; Houtz, D.A.; Xiao, K.; Madabushi, S.; Reiter, E.; Premont, R.T.; Lichtarge, O.; Lefkowitz, R.J. β-Arrestin-dependent, G protein-independent ERK1/2 activation by the β2 adrenergic receptor. J. Biol. Chem. 2006, 281, 1261–1273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azzi, M.; Charest, P.G.; Angers, S.; Rousseau, G.; Kohout, T.; Bouvier, M.; Piñeyro, G. β-Arrestin-mediated activation of MAPK by inverse agonists reveals distinct active conformations for G protein-coupled receptors. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 11406–11411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watari, K.; Nakaya, M.; Nishida, M.; Kim, K.M.; Kurose, H. β-arrestin2 in infiltrated macrophages inhibits excessive inflammation after myocardial infarction. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e68351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahn, S.; Kim, J.; Hara, M.R.; Ren, X.R.; Lefkowitz, R.J. β-Arrestin-2 mediates anti-apoptotic signaling through regulation of BAD phosphorylation. J. Biol. Chem. 2009, 284, 8855–8865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Zhou, G.; Ren, T.; Li, H.; Zhang, Y.; Yin, D.; Qian, H.; Li, Q. β-Arrestin prevents cell apoptosis through pro-apoptotic ERK1/2 and p38 MAPKs and anti-apoptotic Akt pathways. Apoptosis 2012, 17, 1019–1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, M.; Cao, N.; Gu, H.; Xu, J.; Xu, W.; Zhang, D.; Wei, T.W.; Wang, K.; Guo, R.; Cui, H.; et al. AMPK attenuation of β-adrenergic receptor-induced cardiac injury via phosphorylation of β-arrestin-1-ser330. Circ. Res. 2024, 135, 651–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Violin, J.D.; Lefkowitz, R.J. β-Arrestin-biased ligands at seven-transmembrane receptors. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2007, 28, 416–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, I.M.; Tilley, D.G.; Chen, J.; Salazar, N.C.; Whalen, E.J.; Violin, J.D.; Rockman, H.A. Beta-blockers alprenolol and carvedilol stimulate β-arrestin-mediated EGFR transactivation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 14555–14560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tzingounis, A.V.; Von Zastrow, M.; Yudowski, G.A. β-Blocker drugs mediate calcium signaling in native central nervous system neurons by β–arrestin–biased agonism. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 21028–21033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakaya, M.; Chikura, S.; Watari, K.; Mizuno, N.; Mochinaga, K.; Mangmool, S.; Koyanagi, S.; Ohdo, S.; Sato, Y.; Ide, T. Induction of cardiac fibrosis by β-blocker in G protein-independent and G protein-coupled receptor kinase 5/β-arrestin2-dependent signaling pathways. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 35669–35677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erickson, C.E.; Gul, R.; Blessing, C.P.; Nguyen, J.; Liu, T.; Pulakat, L.; Bastepe, M.; Jackson, E.K.; Andresen, B.T. The β-blocker nebivolol is a GRK/β-arrestin biased agonist. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e71980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schena, G.; Caplan, M.J. Everything you always wanted to know about β3-AR* (* but were afraid to ask). Cells 2019, 8, 357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balligand, J.L.; Brito, D.; Brosteanu, O.; Casadei, B.; Depoix, C.; Edelmann, F.; Ferreira, V.; Filippatos, G.; Gerber, B.; Gruson, D.; et al. Repurposing the β3-adrenergic receptor agonist mirabegron in patients with structural cardiac disease: The beta3-LVH phase 2b randomized clinical trial. JAMA Cardiol. 2023, 8, 1031–1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bundgaard, H.; Axelsson, A.; Hartvig Thomsen, J.; Sørgaard, M.; Kofoed, K.F.; Hasselbalch, R.; Fry, N.A.; Valeur, N.; Boesgaard, S.; Gustafsson, F.; et al. The first-in-man randomized trial of a β3 adrenoceptor agonist in chronic heart failure: The BEAT-HF trial. Eur. J. Heart Fail. 2017, 19, 566–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- García-Álvarez, A.; Blanco, I.; García-Lunar, I.; Jordà, P.; Rodriguez-Arias, J.J.; Fernández-Friera, L.; Zegri, I.; Nuche, J.; Gomez-Bueno, M.; Prat, S.; et al. β3 adrenergic agonist treatment in chronic pulmonary hypertension associated with heart failure (SPHERE-HF): A double blind, placebo-controlled, randomized clinical trial. Eur. J. Heart Fail. 2023, 25, 373–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, X.; Wang, Q.; Guo, R.; Xu, L.; Chen, Q.M.; Hou, Y. Effects of paroxetine-mediated inhibition of GRK2 expression on depression and cardiovascular function in patients with myocardial infarction. Neuropsychiatr. Dis. Treat. 2016, 12, 2333–2341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunasekara, N.S.; Noble, S.; Benfield, P. Paroxetine. An update of its pharmacology and therapeutic use in depression and a review of its use in other disorders. Drugs 1998, 55, 85–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thal, D.M.; Homan, K.T.; Chen, J.; Wu, E.K.; Hinkle, P.M.; Huang, Z.M.; Chuprun, J.K.; Song, J.; Gao, E.; Cheung, J.Y.; et al. Paroxetine is a direct inhibitor of g protein-coupled receptor kinase 2 and increases myocardial contractility. ACS Chem. Biol. 2012, 7, 1830–1839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Meng, L.; Long, H.; Shi, Y.; Liu, Y.; Wang, L.; Liu, D. Paroxetine and Mortality in Heart Failure: A Retrospective Cohort Study. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2021, 8, 794584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Wang, L.; Wu, L.; Zhang, M.; Hu, S.; Wang, R.; Han, Y.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, L.; Wang, X.; et al. Paroxetine alleviates T lymphocyte activation and infiltration to joints of collagen-induced arthritis. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 45364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabiri, M.; Hemmatpour, A.; Zare, F.; Hadinedoushan, H.; Karimollah, A. Paroxetine modulates immune responses by activating a JAK2/STAT3 signaling pathway. J. Biochem. Mol. Toxicol. 2020, 34, e22464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Visseren, F.L.J.; Mach, F.; Smulders, Y.M.; Carballo, D.; Koskinas, K.C.; Bäck, M.; Benetos, A.; Biffi, A.; Boavida, J.M.; Capodanno, D.; et al. 2021 ESC Guidelines on cardiovascular disease prevention in clinical practice. Eur. Heart J. 2021, 42, 3227–3337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reyes Gaido, O.E.; Nkashama, L.J.; Schole, K.L.; Wang, Q.; Umapathi, P.; Mesubi, O.O.; Konstantinidis, K.; Luczak, E.D.; Anderson, M.E. CaMKII as a therapeutic target in cardiovascular disease. Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2023, 63, 249–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nassal, D.; Gratz, D.; Hund, T.J. Challenges and opportunities for therapeutic targeting of calmodulin kinase II in heart. Front. Pharmacol. 2020, 11, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Liang, R.; Wang, K.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, M.; Jin, L.; Xie, P.; Zheng, W.; Shang, H.; Hu, Q.; et al. Novel CaMKII-δ inhibitor hesperadin exerts dual functions to ameliorate cardiac ischemia/reperfusion injur and inhibit tumor growth. Circulation 2022, 145, 1154–1168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beauverger, P.; Ozoux, M.; Bégis, G.; Glénat, V.; Briand, V.; Philippo, M.; Caveu, C.; Tavares, G.; Roy, S.; Corbier, A.; et al. Reversion of cardiac dysfunction by a novel orally available calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II inhibitor, RA306, in a genetic model of dilated cardiomyopathy. Cardiovasc. Res. 2020, 116, 329–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyle, A.J.; Schultz, C.; Selvanayagam, J.B.; Moir, S.; Kovacs, R.; Dib, N.; Zlotnick, D.; Al-Omary, M.; Sugito, S.; Selvarajah, A.; et al. Calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II delta inhibition and ventricular remodeling after myocardial infarction A randomized clinical trial. JAMA Cardiol. 2021, 6, 762–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kieserman, J.M.; Myers, V.D.; Dubey, P.; Cheung, J.Y.; Feldman, A.M. Current landscape of heart failure gene therapy. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2019, 8, e012239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammond, H.K.; Penny, W.F.; Traverse, J.H.; Henry, T.D.; Watkins, M.W.; Yancy, C.W.; Sweis, R.N.; Adler, E.D.; Patel, A.N.; Murray, D.R.; et al. Intracoronary gene transfer of adenylyl cyclase 6 in patients with heart failure: A randomized clinical trial. JAMA Cardiol. 2016, 1, 163–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Penny, W.F.; Henry, T.D.; Watkins, M.W.; Patel, A.N.; Hammond, H.K. Design of a Phase 3 trial of intracoronary administration of human adenovirus 5 encoding human adenylyl cyclase type 6 (RT-100) gene transfer in patients with heart failure with reduced left ventricular ejection fraction: The FLOURISH Clinical Trial. Am. Heart, J. 2018, 201, 111–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Ni, J.; Li, L.; Michael, S.; Guo, R.; Bian, X.; Liu, X.; Fan, G. SERCA2a: A key protein in the Ca2+ cycle of the heart failure. Heart Fail. Rev. 2020, 25, 523–535. [Google Scholar]
- Jessup, M.; Greenberg, B.; Mancini, D.; Cappola, T.; Pauly, D.F.; Jaski, B.; Yaroshinsky, A.; Zsebo, K.M.; Dittrich, H.; Hajjar, R.J. Calcium upregulation by percutaneous administration of gene therapy in cardiac disease (CUPID): A phase 2 trial of intracoronary gene therapy of sarcoplasmic reticulum Ca2+-ATPase in patients with advanced heart failure. Circulation 2011, 124, 304–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Greenberg, B.; Butler, J.; Felker, G.M.; Ponikowski, P.; Voors, A.A.; Desai, A.S.; Barnard, D.; Bouchard, A.; Jaski, B.; Lyon, A.R.; et al. Calcium upregulation by percutaneous administration of gene therapy in patients with cardiac disease (CUPID 2): A randomised, multinational, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 2b trial. Lancet 2016, 387, 1178–1186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hulot, J.S.; Salem, J.E.; Redheuil, A.; Collet, J.P.; Varnous, S.; Jourdain, P.; Logeart, D.; Gandjbakhch, E.; Bernard, C.; Hatem, S.N.; et al. Effect of intracoronary administration of AAV1/SERCA2a on ventricular remodelling in patients with advanced systolic heart failure: Results from the AGENT-HF randomized phase 2 trial. Eur. J Heart Fail. 2017, 19, 1534–1541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lyon, A.R.; Babalis, D.; Morley-Smith, A.C.; Hedger, M.; Suarez Barrientos, A.; Foldes, G.; Couch, L.S.; Chowdhury, R.A.; Tzortzis, K.N.; Peters, N.S.; et al. Investigation of the safety and feasibility of AAV1/SERCA2a gene transfer in patients with chronic heart failure supported with a left ventricular assist device–the SERCA-LVAD TRIAL. Gene Ther. 2020, 27, 579–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riehle, C.; Bauersachs, J. Small animal models of heart failure. Cardiovasc. Res. 2019, 115, 1838–1849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Houser, S.R.; Margulies, K.B.; Murphy, A.M.; Spinale, F.G.; Francis, G.S.; Prabhu, S.D.; Rockman, H.A.; Kass, D.A.; Molkentin, J.D.; Sussman, M.A.; et al. Animal models of heart failure: A scientific statement from the American Heart Association. Circ. Res. 2012, 111, 131–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frangogiannis, N.G. Why animal model studies are lost in translation. J. Cardiovasc. Aging 2022, 2, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| β-AR Alleles | Main Findings | Ref. |
|---|---|---|
| β1-AR Polymorphisms | ||
| β1-AR-Arg389 | Provided a better response to β-blocker therapy in both HF patients and animals compared to β1-AR-Gly389 | [80,84,85] |
| Impaired cardiac functions and led to failing heart in transgenic mice with β1-AR-Arg389 | [84] | |
| β1-AR-Gly389 | Expressed a high risk of HF in the East Asian population | [80] |
| β1-AR-Gly49 | Had higher level of agonist-induced β1-AR downregulation | [86] |
| β1-AR-Gly49 | No relationship between the prognosis and risk of HF | [80] |
| β1-AR-Ser49 | Required a higher dose of β-blockers in the management of HF compared to β1-AR-Gly49 | [87] |
| β2-AR Polymorphisms | ||
| β2-AR-Glu27 | Increased risk of insulin resistance in HF patients | [88] |
| β2-AR-Ile164 | Reduced efficiency of β2-AR signaling and responses in HF patients | [89] |
| Study Models | Main Findings | Ref. |
|---|---|---|
| Cardiac-specific β-ARKct overexpression in HF mice |
| [121] |
| Cardiac-specific β-ARKct overexpression in HF mice |
| [115] |
| Cardiac-specific β-ARKct overexpression in HF mice |
| [122] |
| GRK2 ablation in MI mice |
| [123] |
| β-Arrestin-Biased Ligands | Study Models | Main Findings | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|
| Alprenolol Carvedilol | HEK-293 cells and mice |
| [137] |
| Carvedilol Propranolol | Rat hippocampal neurons |
| [138] |
| Carvedilol | β2-AR-expressing HEK-293 cells |
| [45] |
| Metoprolol | Cardiac myocytes and GRK5/β-arrestin2-knock out mice |
| [139] |
| Nebivolol | Mouse embryonic fibroblasts and cardiac myocytes |
| [140] |
| Drugs | Phase | Participants | Treatment | Main Findings | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mirabegron (Beta3-LVH trial) | II | Patients who had LV hypertrophy with or without HF symptoms (NYHA I-II) (N = 296) | Mirabegron 50 mg/day or placebo Duration: 12 months |
| [142] |
| Mirabegron (BEAT-HF trial) | II | HFrEF patients with LVEF < 40% and NYHA II-III (N = 70) | Mirabegron 300 mg/day or placebo Duration: 6 months |
| [143] |
| Mirabegron (BEAT-HF-II trial) | II/III | HFrEF patients with NYHA III–IV, LVEF < 35%, and increased NT-proBNP levels (N = 22) | Mirabegron 300 mg/day or placebo Duration: 1 week |
| [73] |
| Mirabegron (SPHERE-HF trial) | II | Patients with combined pre- and post-capillary pulmonary hypertension (CpcPH) associated with symptomatic HF (N = 80) | Mirabegron 200 mg/day or placebo Duration: 16 weeks |
| [144] |
| Drug | Phase | Participants | Treatment | Main Findings | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Paroxetine (CARE-AMI trial) | II | Patients with acute anterior MI with LVEF ≤ 45% (N = 50) | Paroxetine 20 mg/day or placebo Duration: 3 months |
| [126] |
| II | Patients with acute anterior MI with LVEF ≤ 45% (N = 50) | Paroxetine 20 mg/day or placebo Duration: 1 year |
| [127] | |
| Paroxetine and fluoxetine | II | Acute MI patients with depression (N = 67) | Paroxetine 20 mg/day or fluoxetine 20 mg/day Duration: 2 months | Paroxetine:
| [145] |
| Drug | Phase | Participants | Treatment | Main Findings | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NP2O2 | II | Patients after PCI for anterior STEMI with LVEF ≤ 45% (N = 147) | NP2O2 at 1000 mg/day or placebo Duration: 3 months |
| [156] |
| Drug | Phase | Participants | Treatment | Main Findings | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ad5.hAC6 | II | Patients with symptomatic HF and LVEF ≤ 40% (N = 56) | Ad5.hAC6 (3.2 × 109 to 1012 particles) or placebo, Intracoronary Duration: 1 year |
| [158] |
| Ad5.hAC6 (or RT-100) (FLOURISH trial) | III | HFrEF patients with LVEF 10–35% (N = 536) | Ad5.hAC6 (1012 particles) or placebo, Intracoronary Duration: 1 year |
| [159] |
| Drug | Phase | Participants | Treatment | Main Findings | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AAV1/ SERCA2a (CUPID trial) | II | Patients with advanced HF (NYHA class III-IV; LVEF ≤ 30%) (N = 39) | AAV1/SERCA2a (1 × 1013 particles) or placebo, Intracoronary Duration: 1 year |
| [161] |
| AAV1/ SERCA2a (CUPID2 trial) | II | Patients with HF (NYHA class II-IV; LVEF ≤ 35%) (N = 250) | AAV1/SERCA2a (1 × 1013 particles) or placebo, Intracoronary Duration: 1 year |
| [162] |
| AAV1/ SERCA2a (AGENT-HF trial) | II | Patients with advanced HF (NYHA class II-IV; LVEF ≤ 35%) (N = 9) | AAV1/SERCA2a (1 × 1013 particles) or placebo, Intracoronary Duration: 6 months |
| [163] |
| AAV1/ SERCA2a (SERCA-LVAD trial) | II | Patients with chronic HF and implanted with an LV assist device (N = 5) | AAV1/SERCA2a (1 × 1013 particles) or placebo, Intracoronary Duration: 3 years |
| [164] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Parichatikanond, W.; Duangrat, R.; Kurose, H.; Mangmool, S. Regulation of β-Adrenergic Receptors in the Heart: A Review on Emerging Therapeutic Strategies for Heart Failure. Cells 2024, 13, 1674. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells13201674
Parichatikanond W, Duangrat R, Kurose H, Mangmool S. Regulation of β-Adrenergic Receptors in the Heart: A Review on Emerging Therapeutic Strategies for Heart Failure. Cells. 2024; 13(20):1674. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells13201674
Chicago/Turabian StyleParichatikanond, Warisara, Ratchanee Duangrat, Hitoshi Kurose, and Supachoke Mangmool. 2024. "Regulation of β-Adrenergic Receptors in the Heart: A Review on Emerging Therapeutic Strategies for Heart Failure" Cells 13, no. 20: 1674. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells13201674
APA StyleParichatikanond, W., Duangrat, R., Kurose, H., & Mangmool, S. (2024). Regulation of β-Adrenergic Receptors in the Heart: A Review on Emerging Therapeutic Strategies for Heart Failure. Cells, 13(20), 1674. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells13201674







